Vertebrate Zoology Exam 2 - Organism Clades
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Rhyncocephlians
Tuatara
Sister to Squamata (lizards, snakes, and more lizards)

2 Ecomorphs for Limbless Lizards
Surface-dwelling: long tails, devolved legs as they would get in the way of moving through dense grass or shrubbery
Fossorial (burrowing): short tails
Amphisbaenians
“Weird” burrowing lizards
Legless (or only front legs, as in genus Bipes)
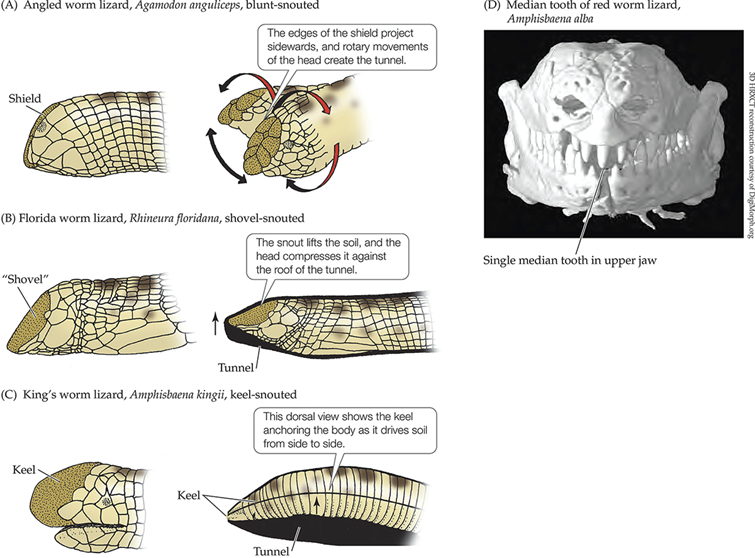
Use heads to tunnel, with head shape corresponding to burrowing type
Distinctive skin: annuli (rings), skin is detached from body to facilitate locomotion

Amphisbaenian Burrowing Methods
3 methods of burowing:
Blunt-snouted
Shovel-snouted (flat like a shovel)
Keel-snouting
AND
Single median tooth in the upper jaw, a synapomorphy for Amphisbaenians
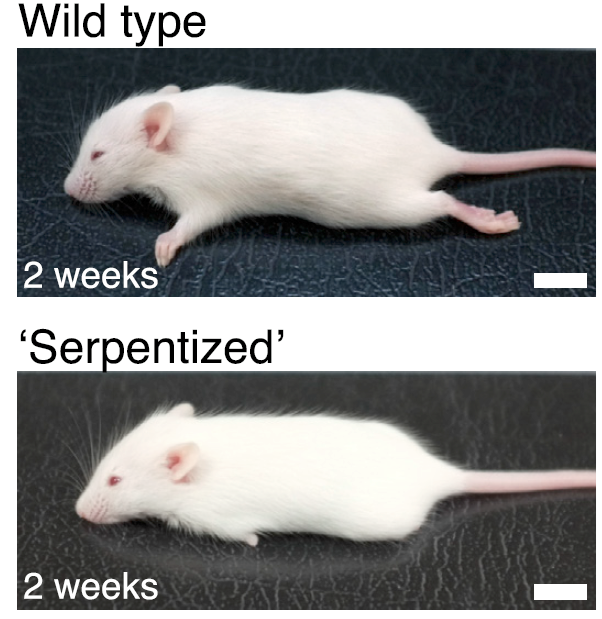
How does the regulatory protein ZRS affect snakes’ body shape?
ZRS controls the Sonic hedgehog (Shh) gene, which stimulates limb formation
ZRS gene is mutated in snakes, reducing ZRS activity and expression of Shh, therefore reducing limbs

What are the main types of snake locomotion?
Lateral undulation - swerving side to side, all snakes
Rectilinear locomotion - crawl along using abdominal muscle, usually heavy-bodied snakes or for moving through tunnels
Concertina locomotion - crumple themselves up, anchor, then pull forward, good for use in narrow tunnels
Sidewinding - sideways movement, unique to desert-dwelling snakes
What is special about snakes’ lungs?
Their lungs are very long, makking them naturally buoyant
What are the main differences between Pythonidae and Boidae?
Pythons - Old World
Boas - New World
However, they are sister taxa.
Why do predators constrict their prey?
Needs to immobilize prey and wait for it to die for consumption
Duvernoy’s Gland
Venom gland found in upper jaw of many extant colubrids, homologous to viperids’ and elapids’ venom glands
3 Categories of Venomous Snakes
Opisthoglyphous - rear-fanged, smaller teeth in front (e.x. Boomslang)
Proteroglyphous - fangs in front of maxillae (e.x. elapids such as cobras, sea snakes)
Solenoglyphous - hollow fangs, only teeth on the maxillae (e.x. true vipers, New World pit vipers)