CVS Pathology Image-Based Learning
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
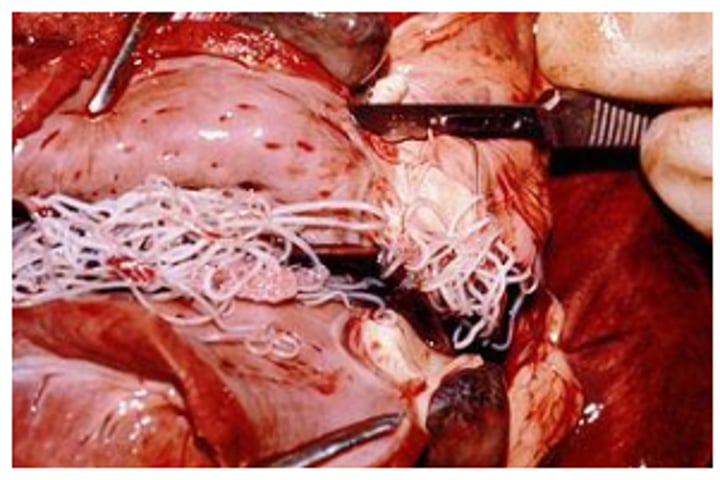
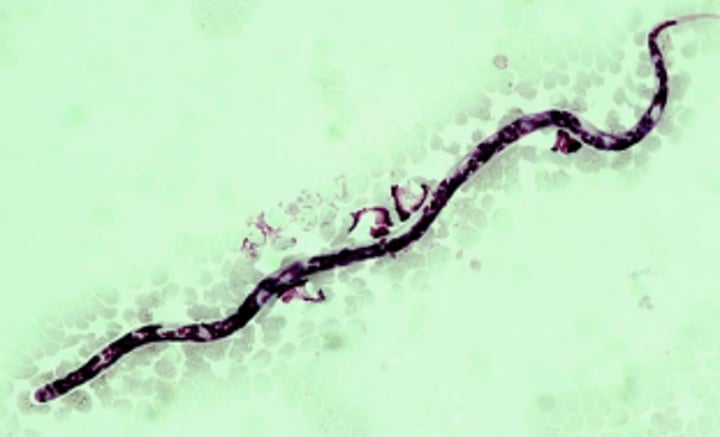
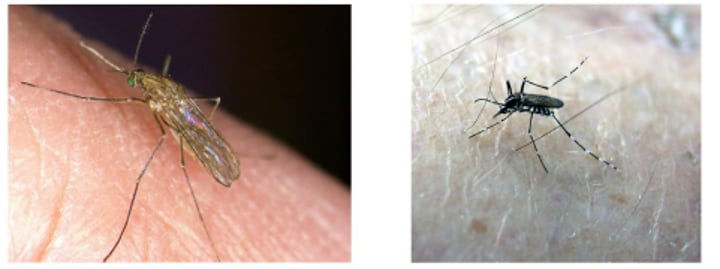
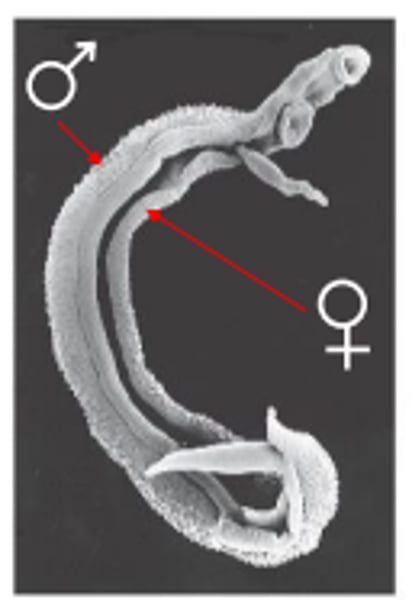
Heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis)
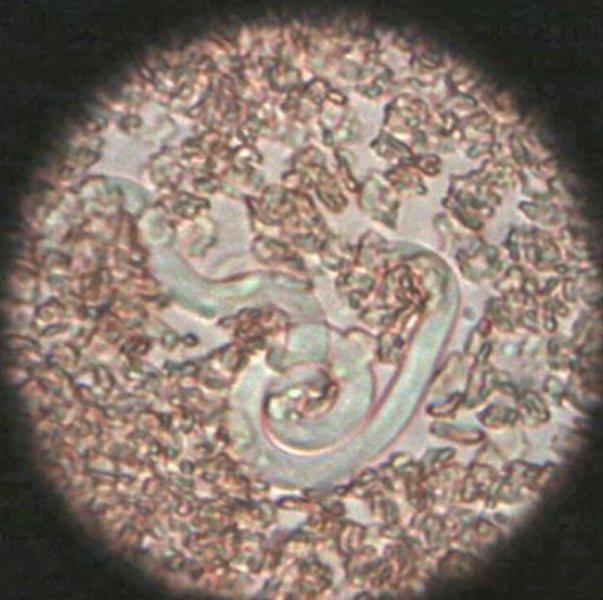
Heartworm microfilaria from canine blood
Mosquitos (culex pipiens pipiens and stegomyia)
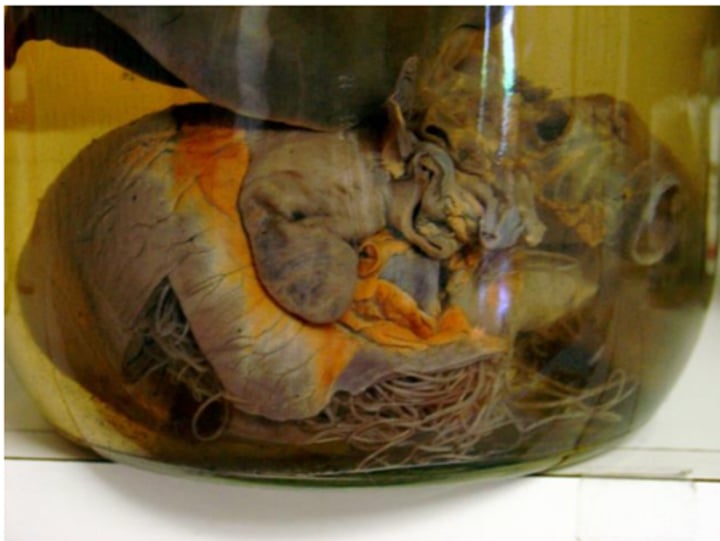
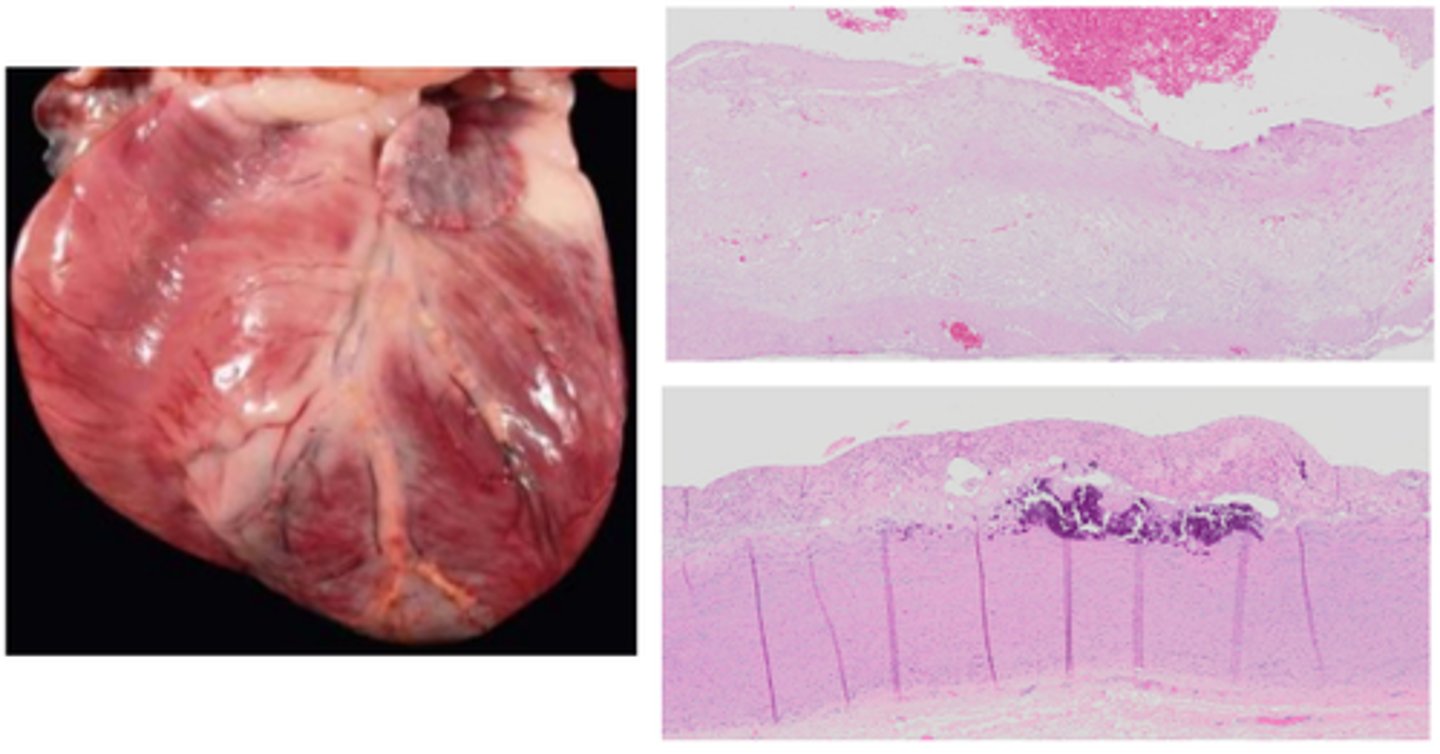
Heartworm - Dirofilaria immitis "Vena Cava Syndrome"
Worms in the RHS of the heart and vena cava leading to tricuspid valve problems and blood flow obstruction

Heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis)
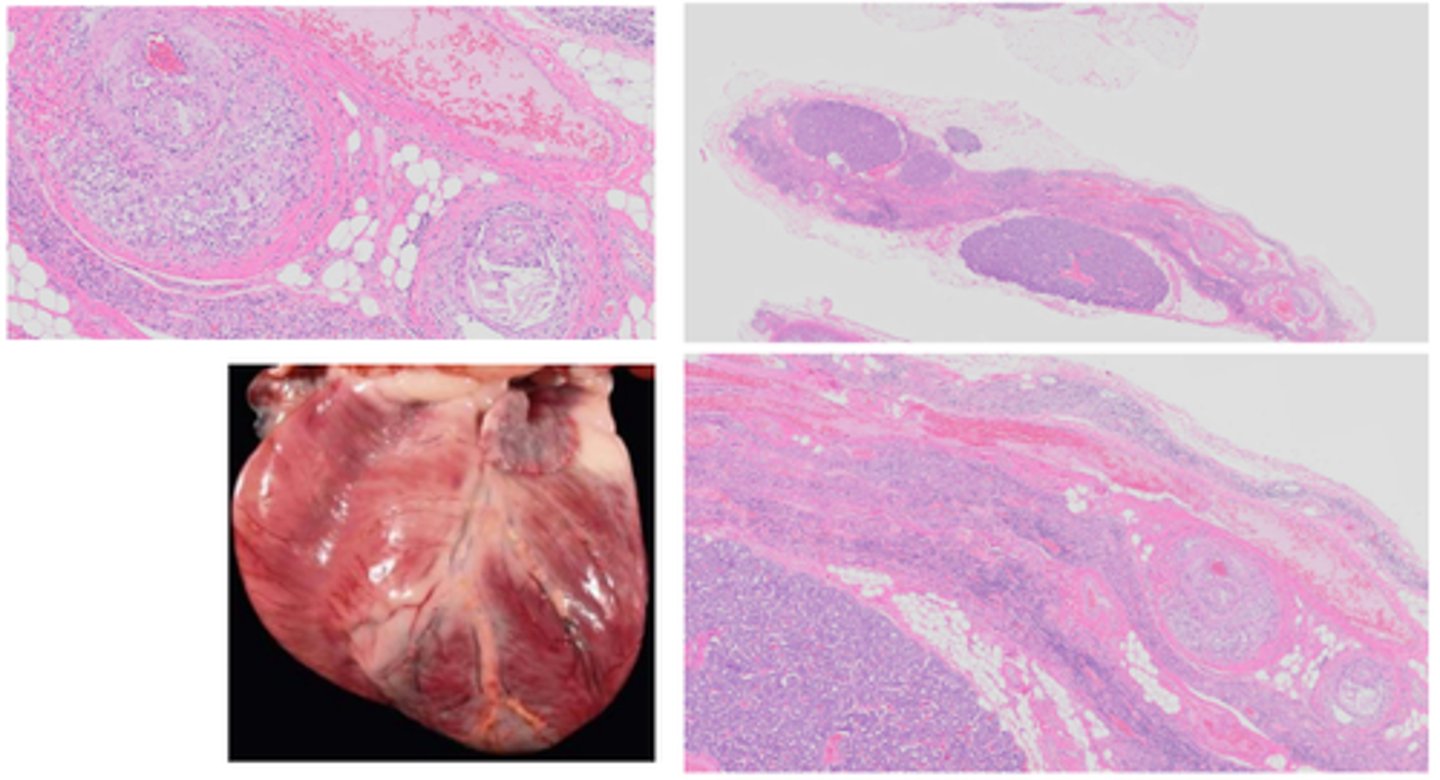
Schistosoma (blood fluke)
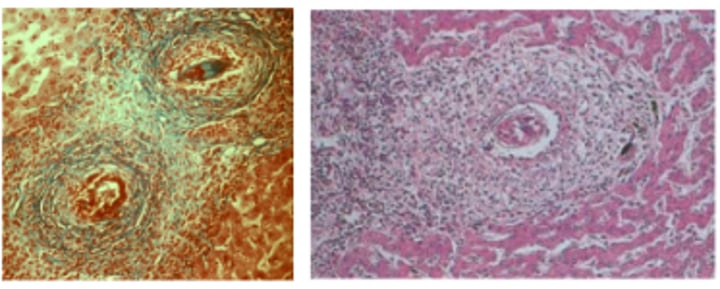
Granuloma formation with calcification and fibrosis due to schistoma egg accumulation in tissues
Dilation
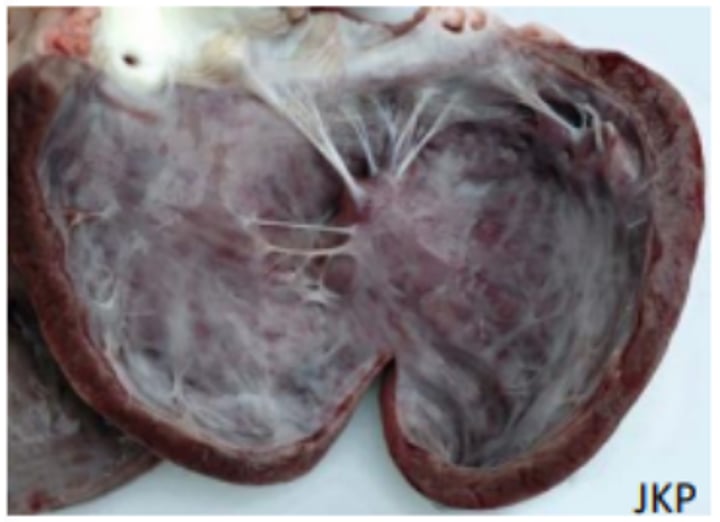
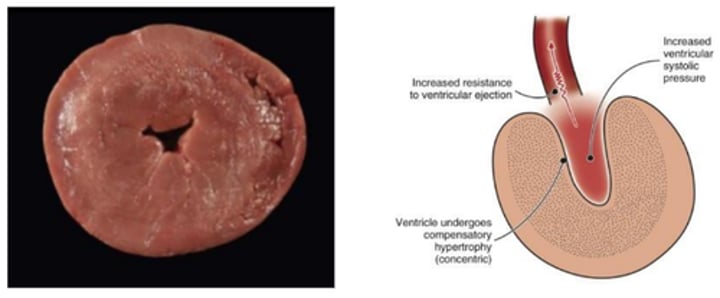
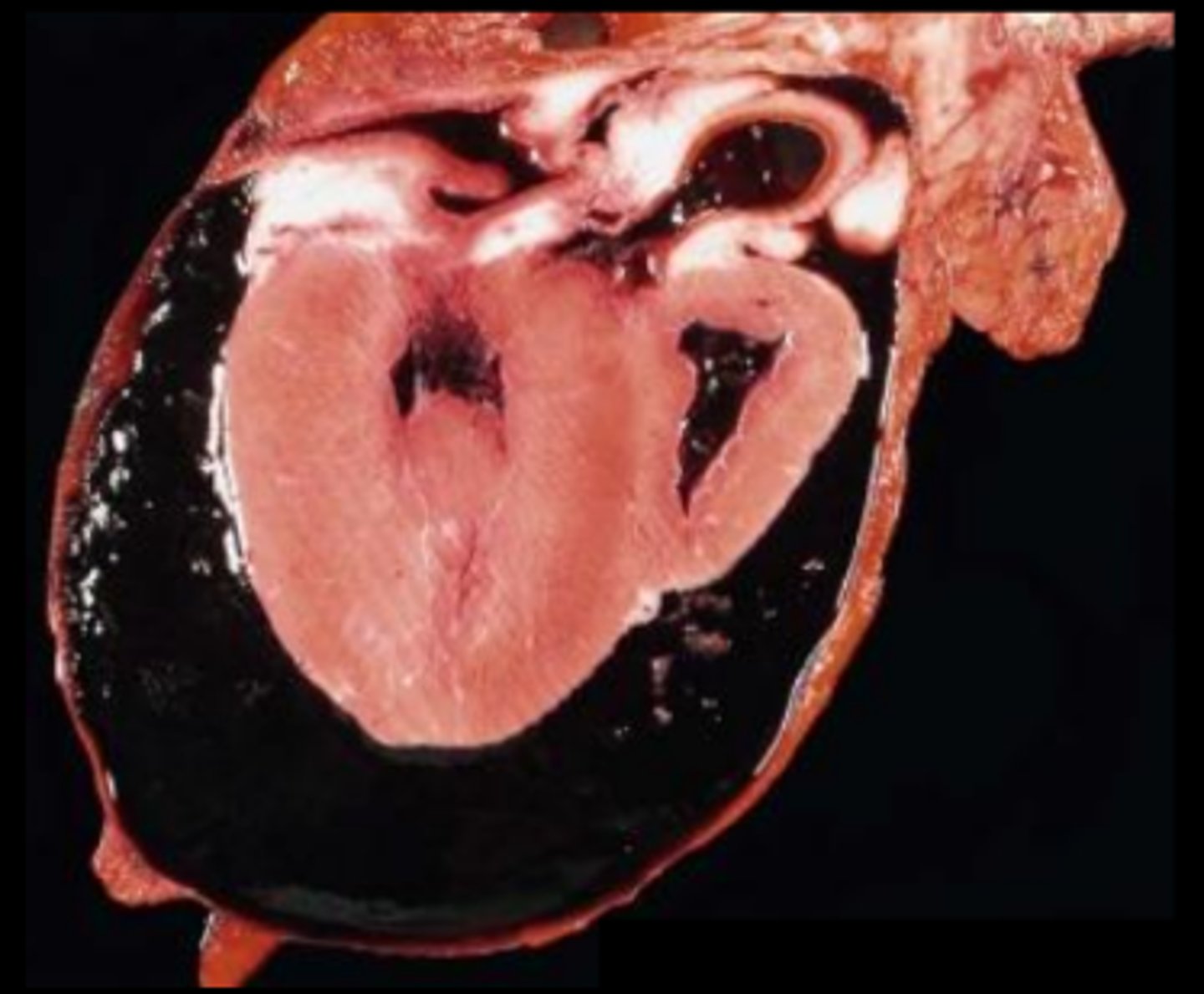
Concentric hypertrophy of the heart
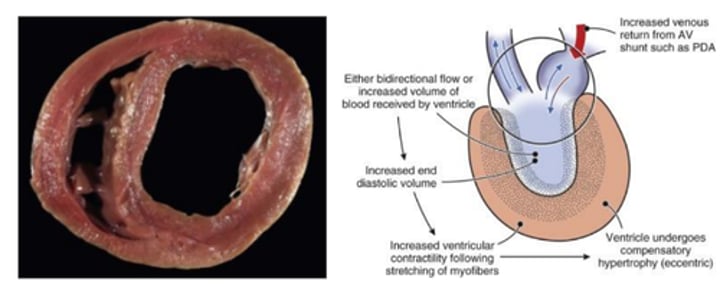
Eccentric hypertrophy of the heart
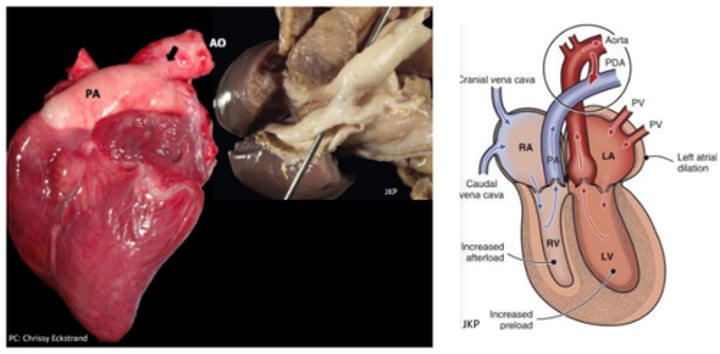
Patent ductus arteriosus
Atrial septal defect - Systemic to pulmonary shunting (left to right)
Continuous washing machine murmur, basil
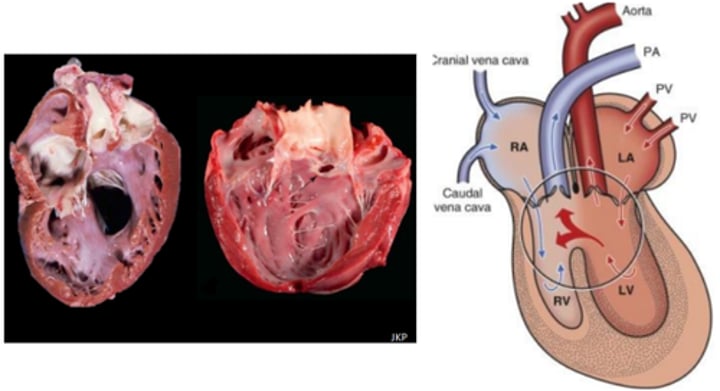
Ventricular septal defect
Systemic to pulmonary shunting (left to right)
Right apical to basilar systolic, the smaller the defect, the louder the murmur
Pulmonic stenosis
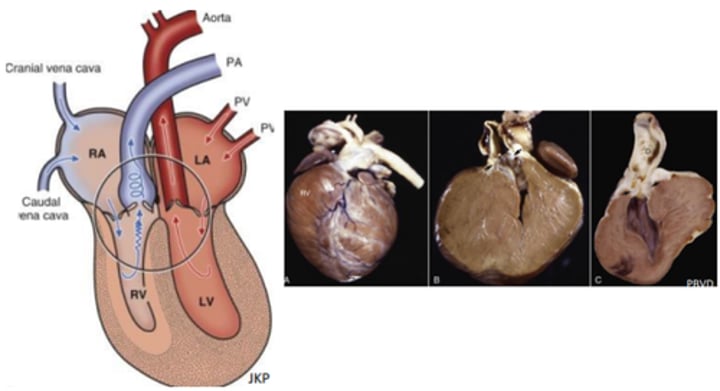
Pulmonic stenosis
Post stenotic dilation
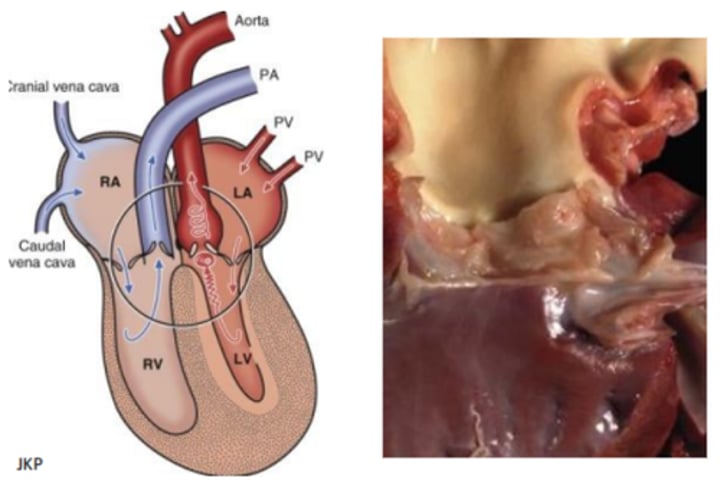
Aortic and subaortic stenosis (SAS)
Pressure overload in LV → concentric hypertrophy
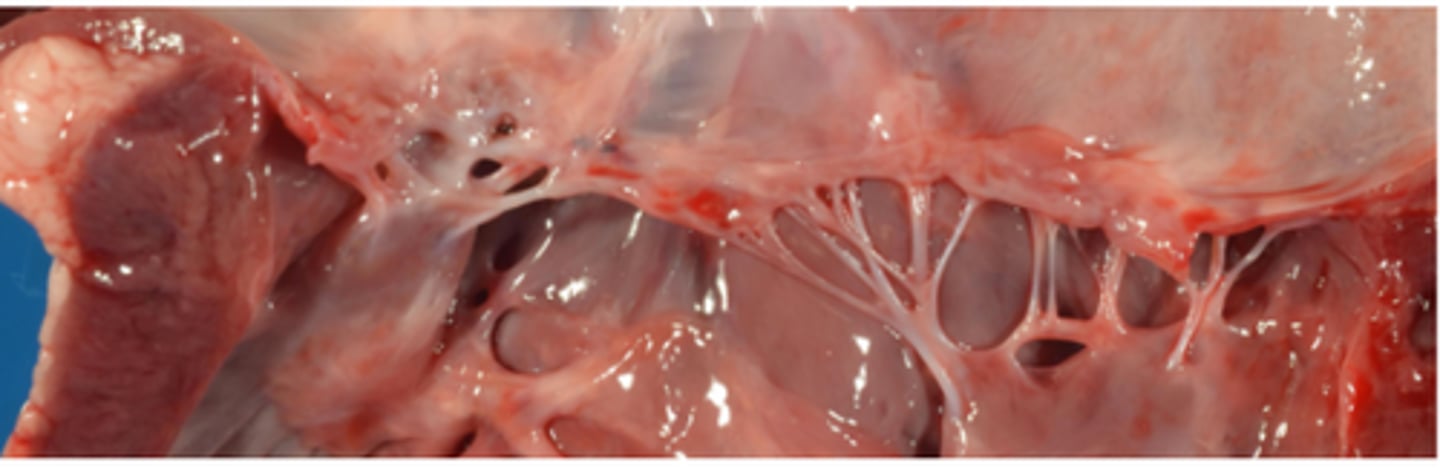
AV valve dysplasia
Shortening, rolling and thickening of leaflets
Incomplete separation of valve components from ventricular wall
Elongation, shortening, fusion, thickening of chordae tendineae
Direct insertion of the vale edges into papillary muscle
Atrophy, fusion, mal-position of papillary muscles and chordae tendineae
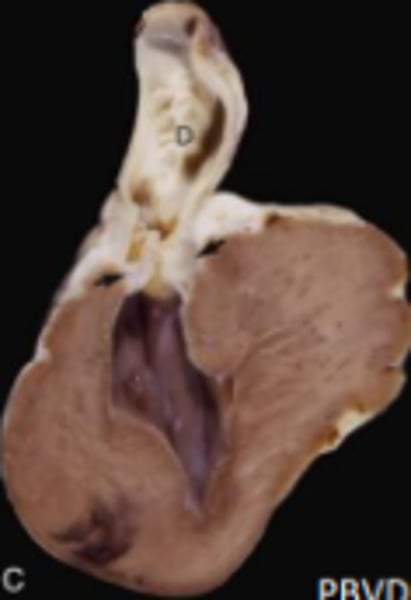
Tetralogy of Fallot (Partial Transposition)
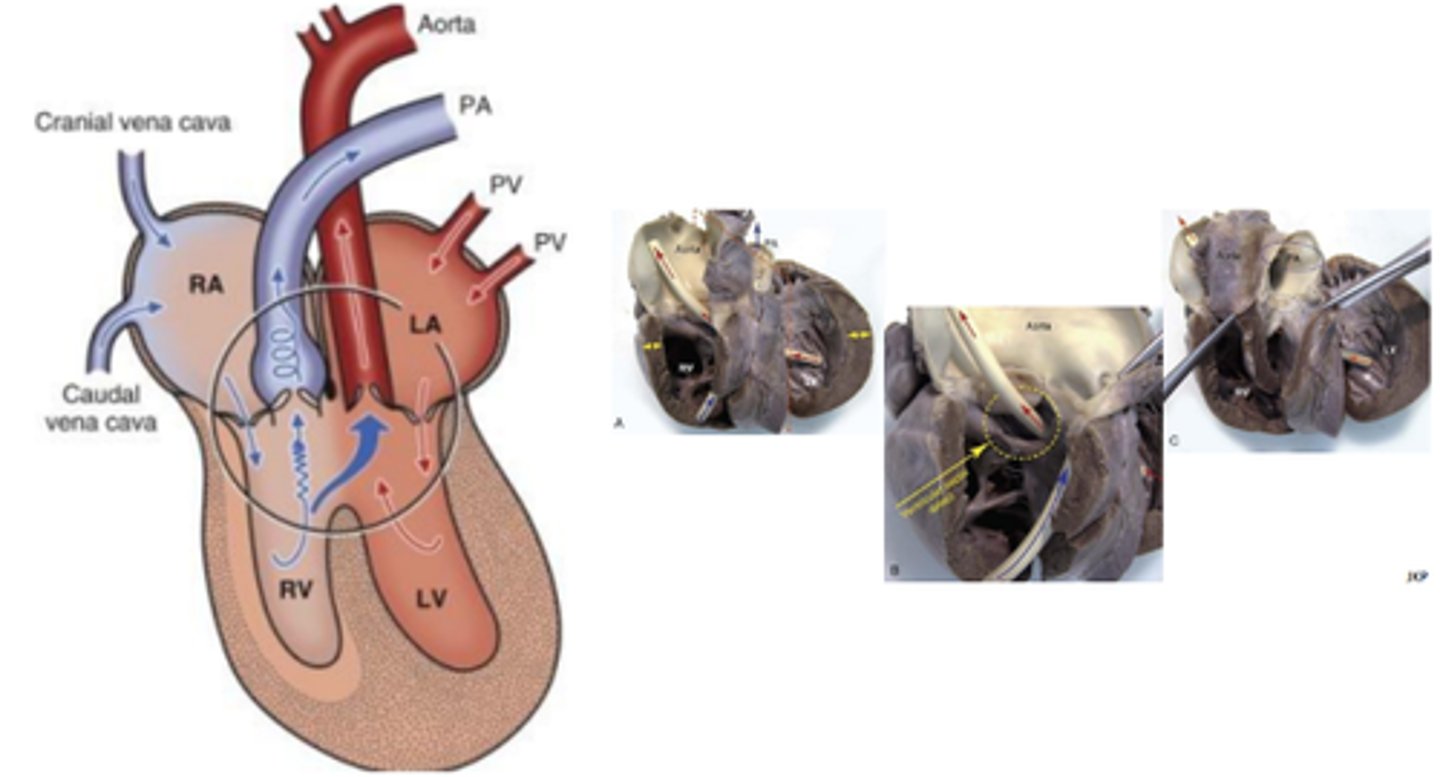
Persistent right aortic arch where the aorta forms from right 4th aortic arch instead of left
Megaoesophagus (E)
Aspiration pneumonia
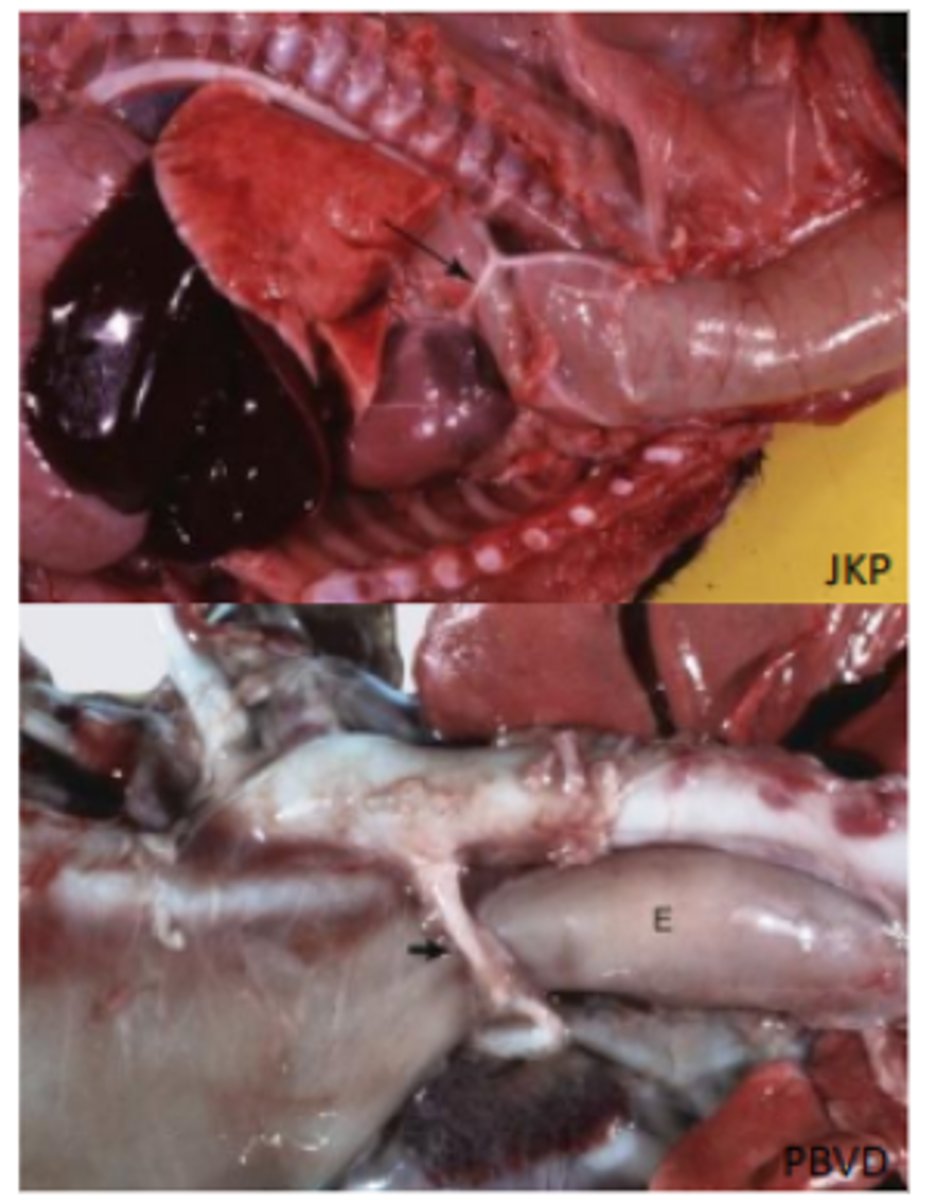
Peritoneal pericardium diaphragmatic hernia
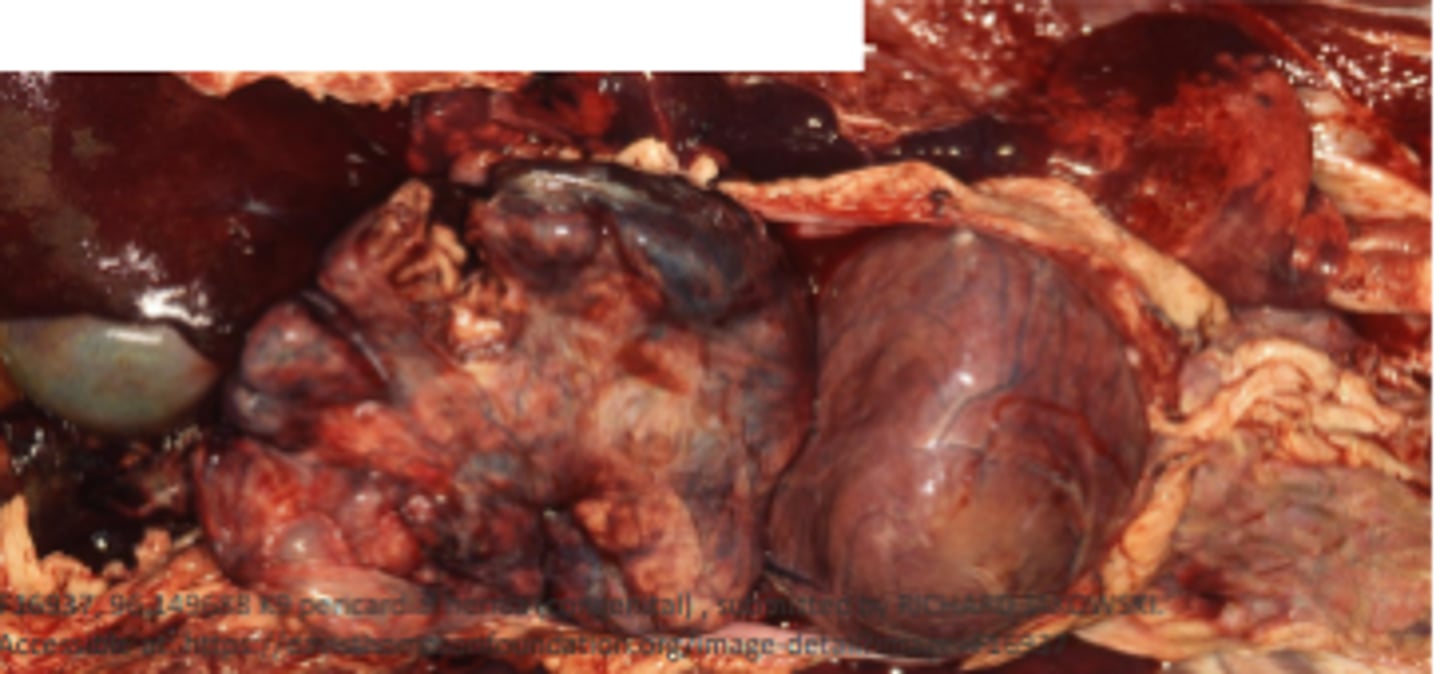
Left - lymphocyst of the heart
Right - haemocyst of the heart
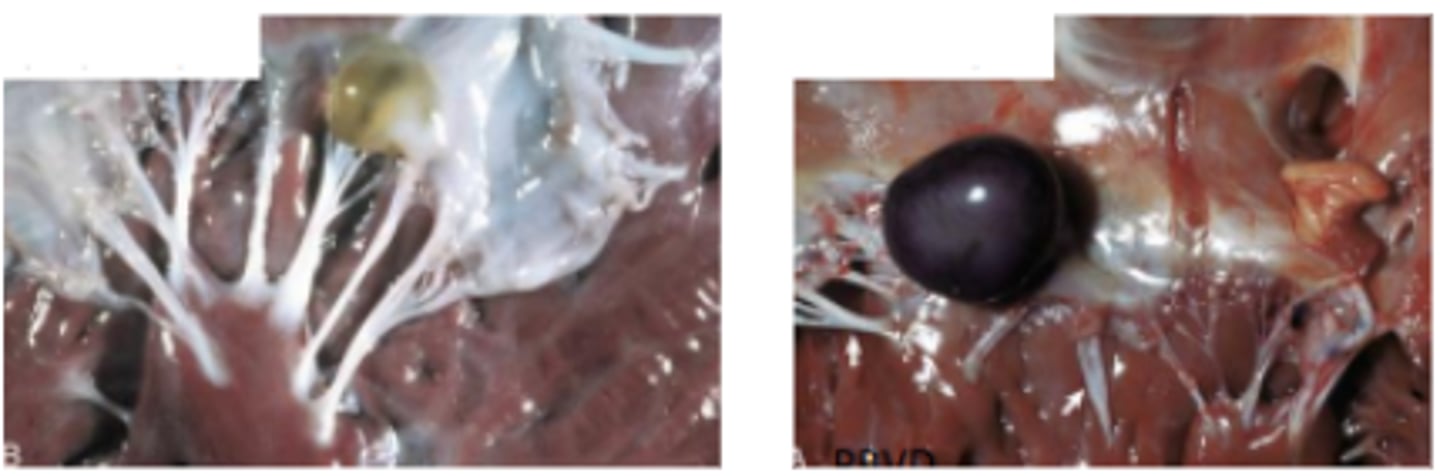
Ectopia cordis
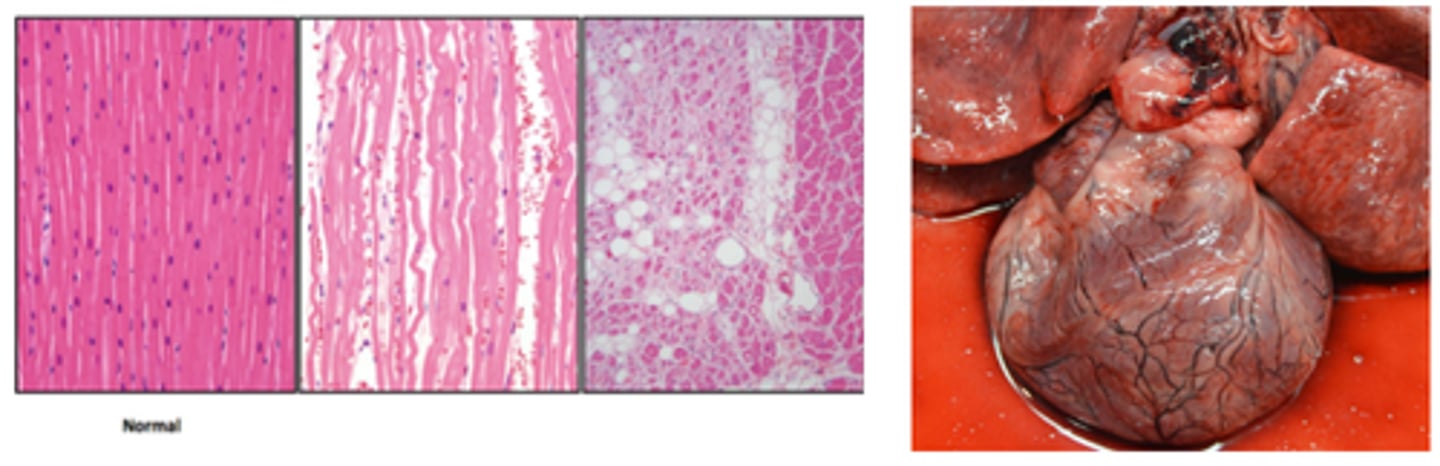
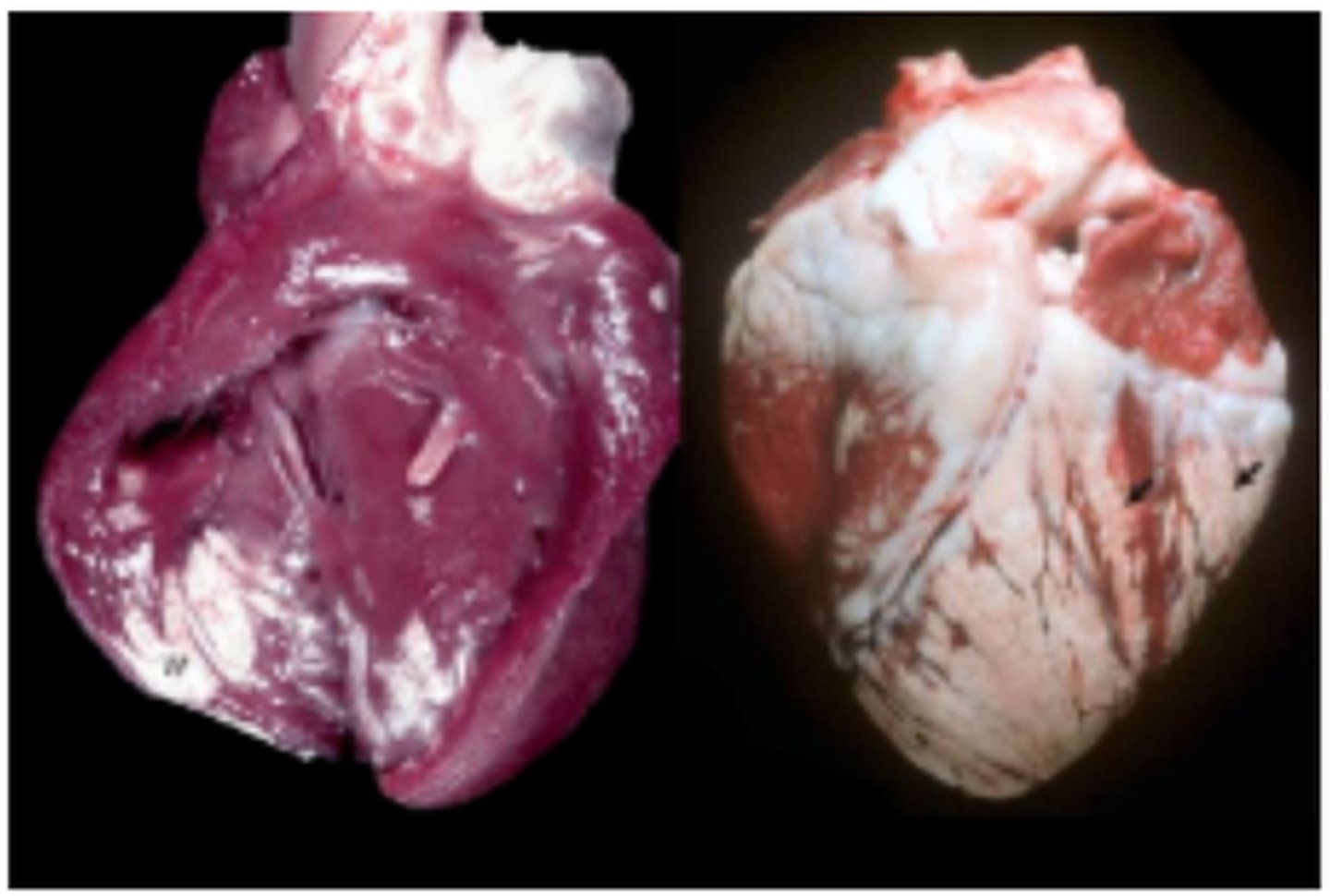
Dilated (DCM) Primary Cardiomyopathy
Dilation of atria and ventricles, increased annulus circumference, eccentric hypertrophy of ventricles, papillary muscles often flattened/ atrophic
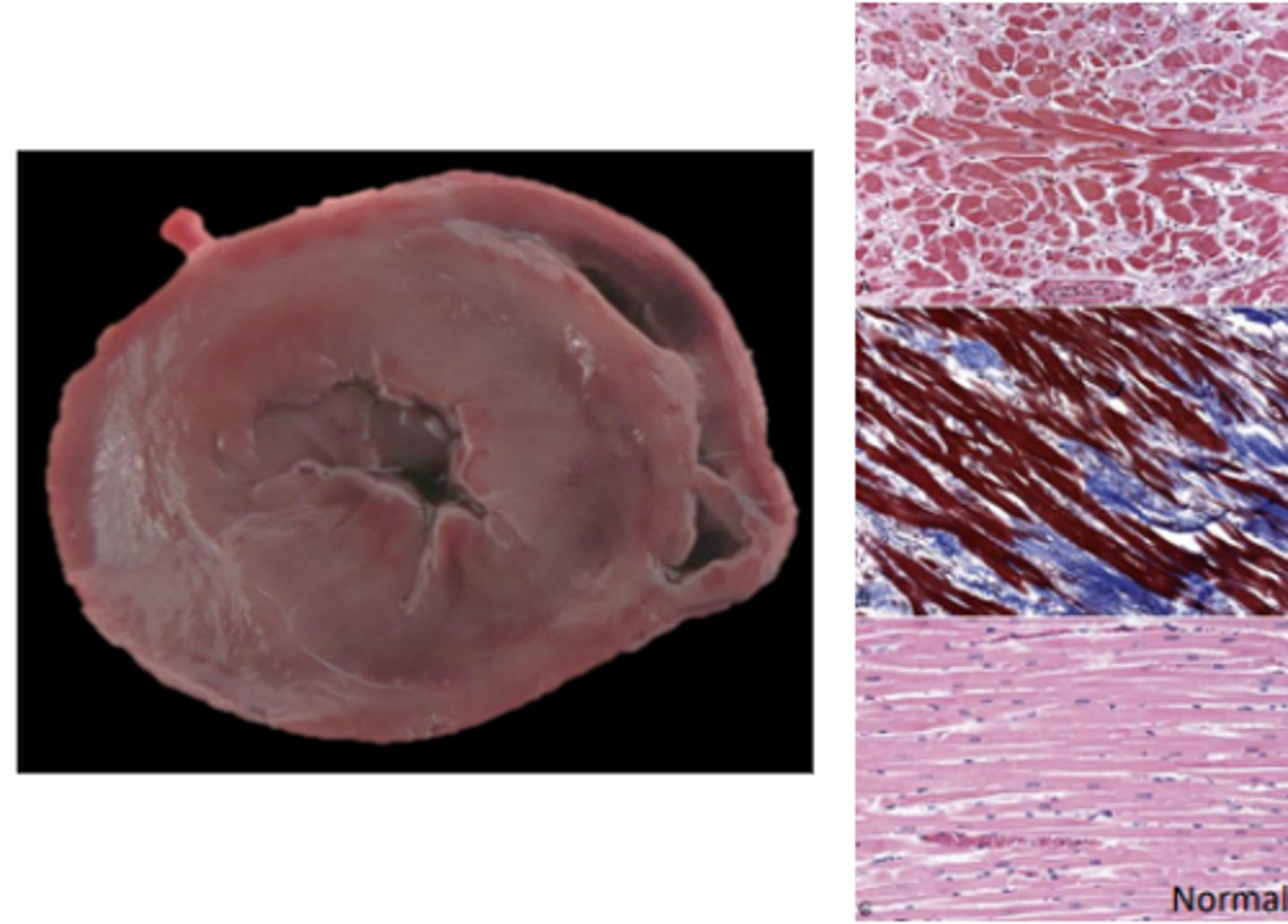
Hypertrophic (HCM) Primary Cardiomyopathy
Asymmetrical septal hypertrophy to symmetrical hypertrophy of the LV, replacement fibrosis
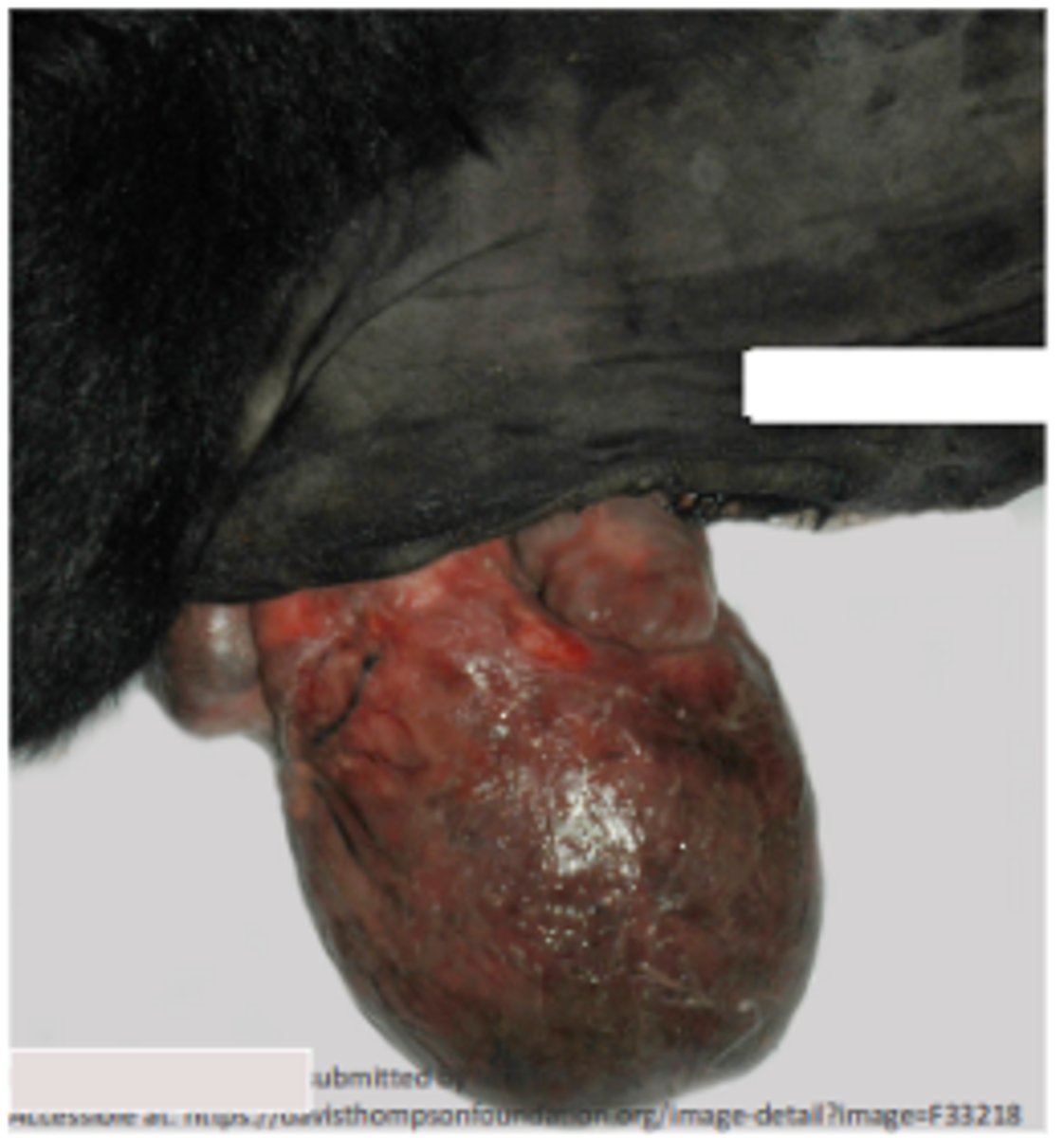
Saddle thrombus at the aortic trifurcation (cat)
Restrictive Primary Cardiomyopathy
Endomyocardial fibrosis → heart unable to expand, excessive moderator bands of fibrosis in cats, dilated atria with normal ventricular size
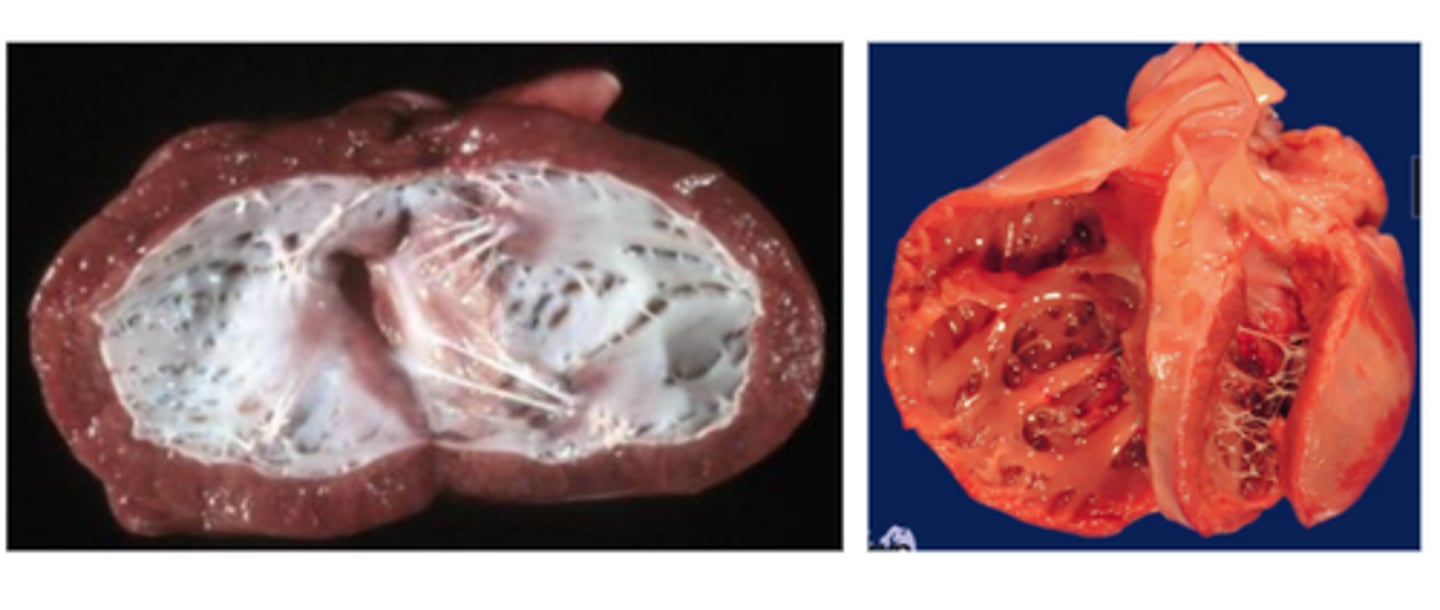
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (Primary)
+/- RV hypertrophy, RA dilation, fibro-fatty replacement of cardiomyocytes
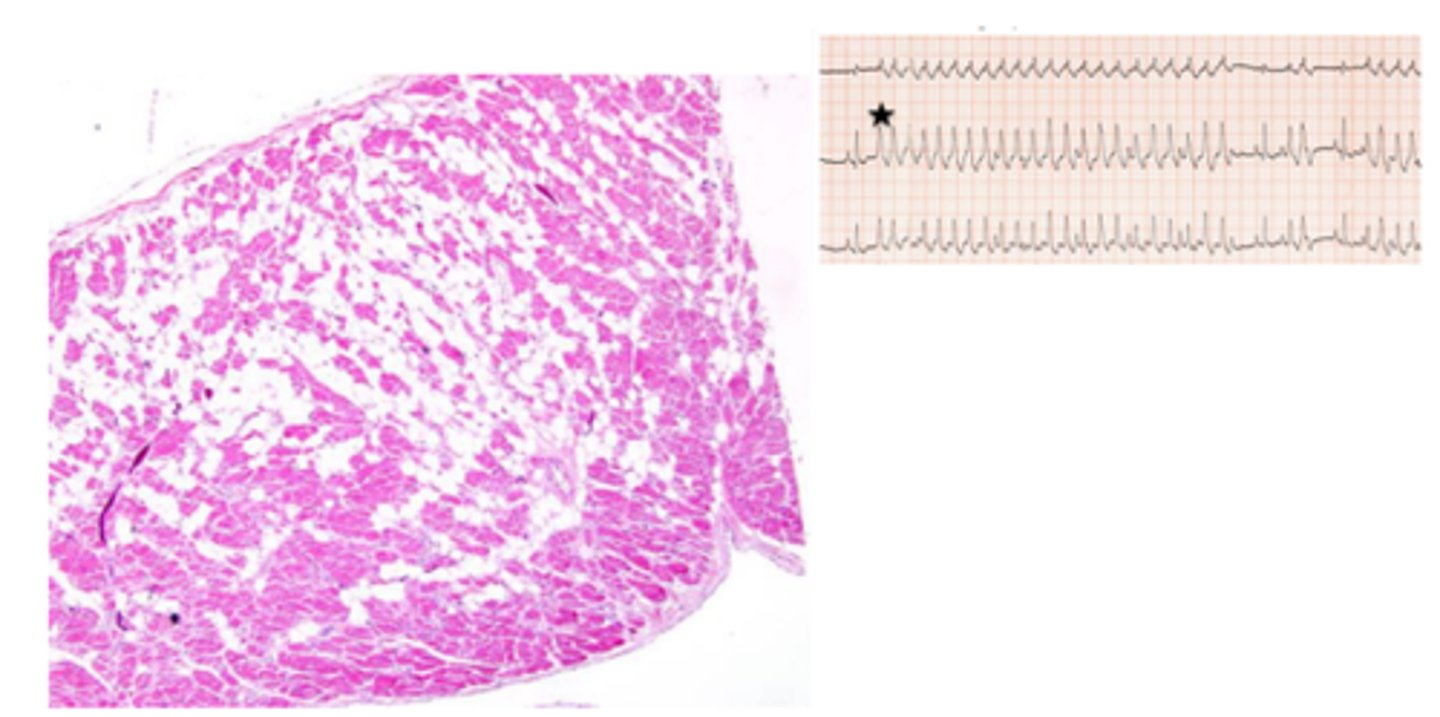
Myocardial Necrosis (Brain-heart syndrome)
Multifocal myocardial necrosis associated with neurological disease of diverse origin; cardiomyocyte mineralisation, fragmentation and loss of cross striations
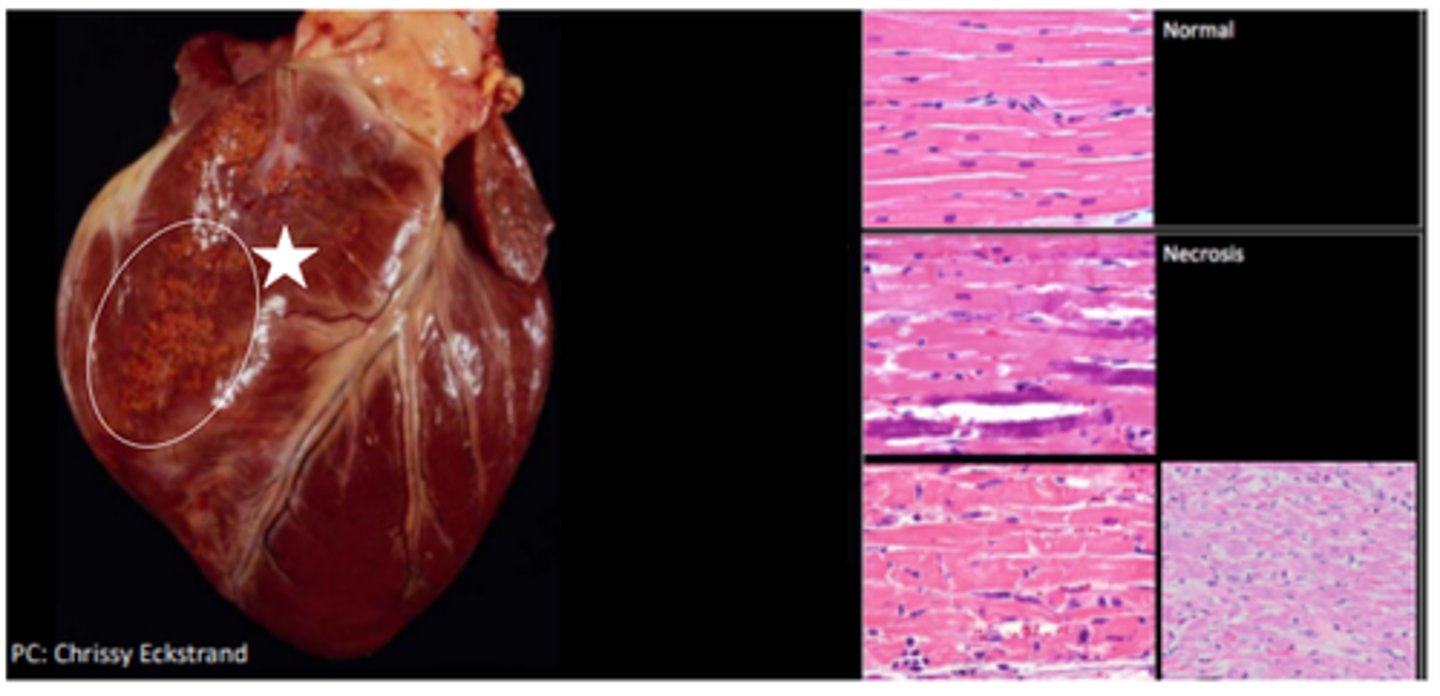
White muscle disease (Vitamin E/ selenium deficiency)
Myocyte necrosis and mineralisation (white muscle) → death via ventricular arrhythmia
Mulberry heart disease (Vitamin E/ selenium deficiency)
Myocyte necrosis and mineralisation (white muscle) → death via ventricular arrhythmia
Multifocal necrosis with widespread epicardial and myocardial haemorrhage, fibrinoid arteriolar necrosis, hepatosis dietetica
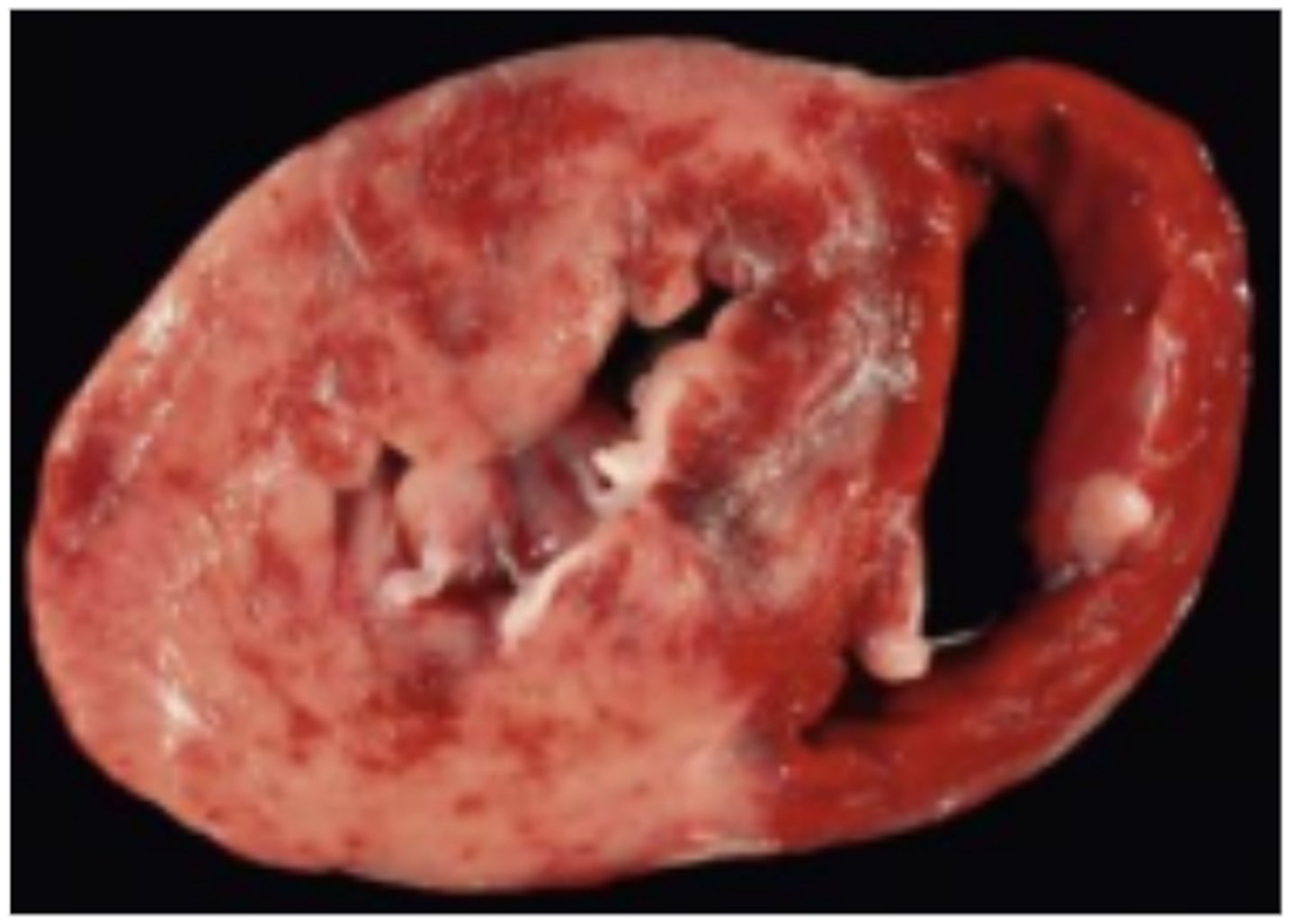
Hydropericardium
Secondary myocardial disease (taurine deficiency)
Dilated Cardiomyopathy-like phenotype
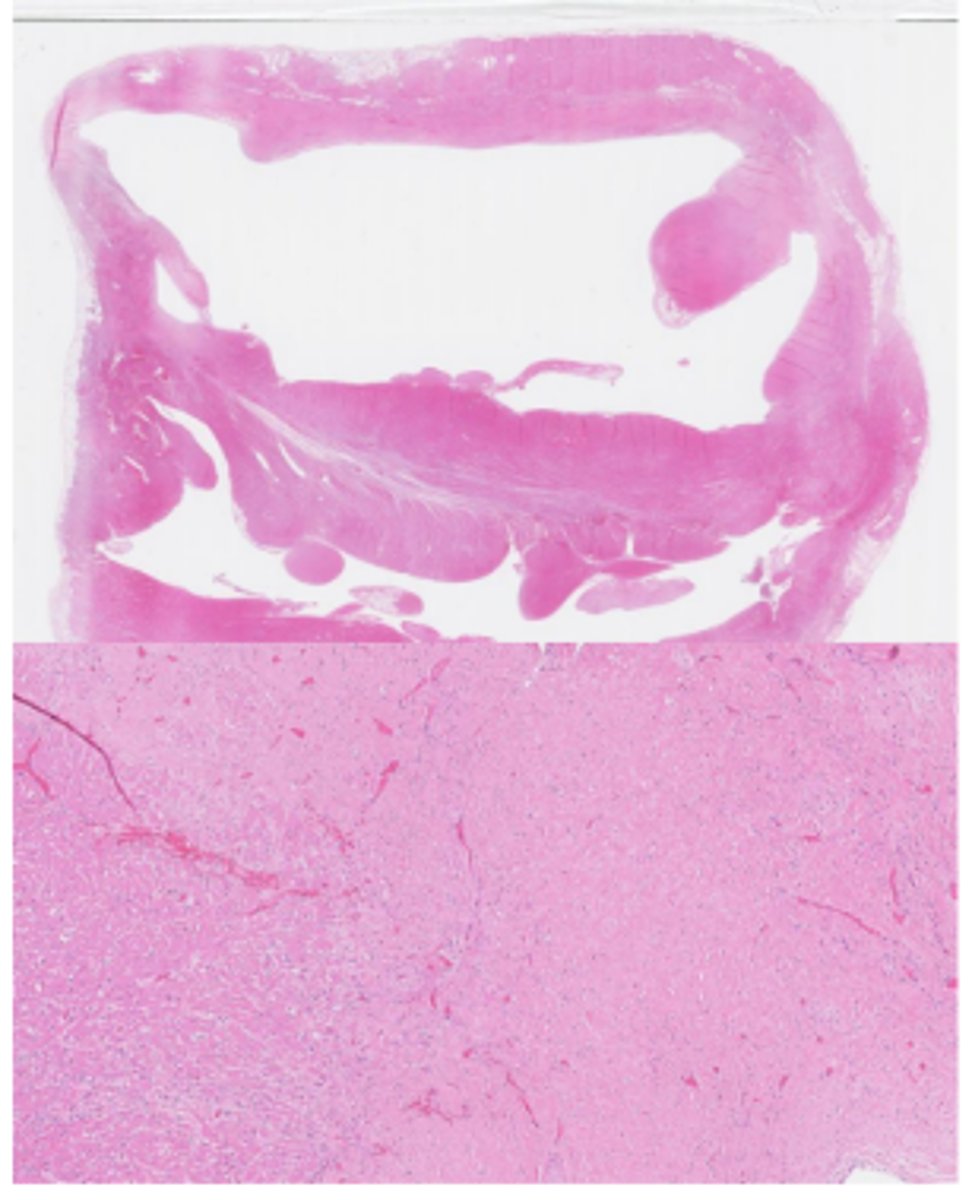
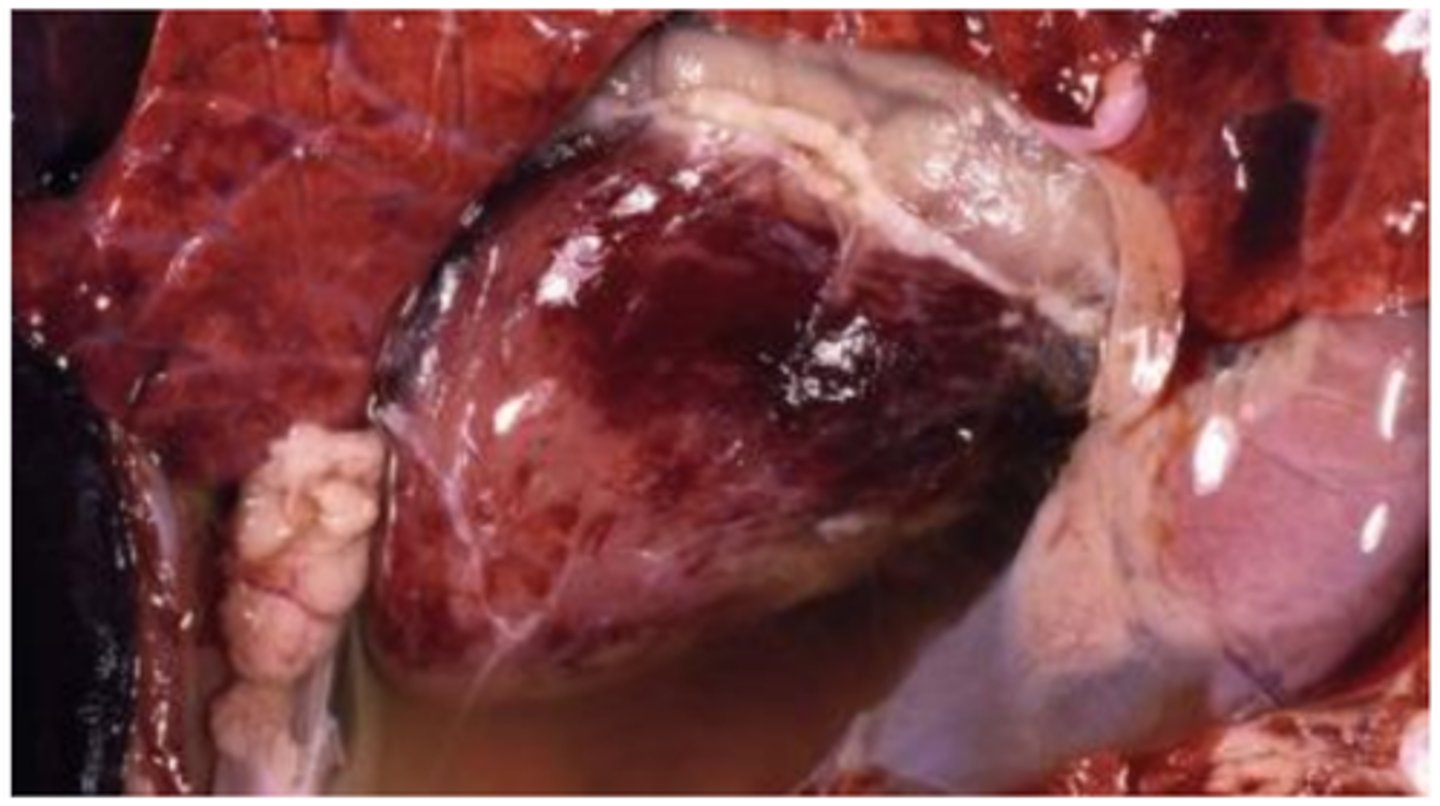
Secondary myocardial disease (taurine deficiency)
Masson’s Trichrome stain - Dilated Cardiomyopathy-like phenotype
(pink = myocytes, blue = collagen)
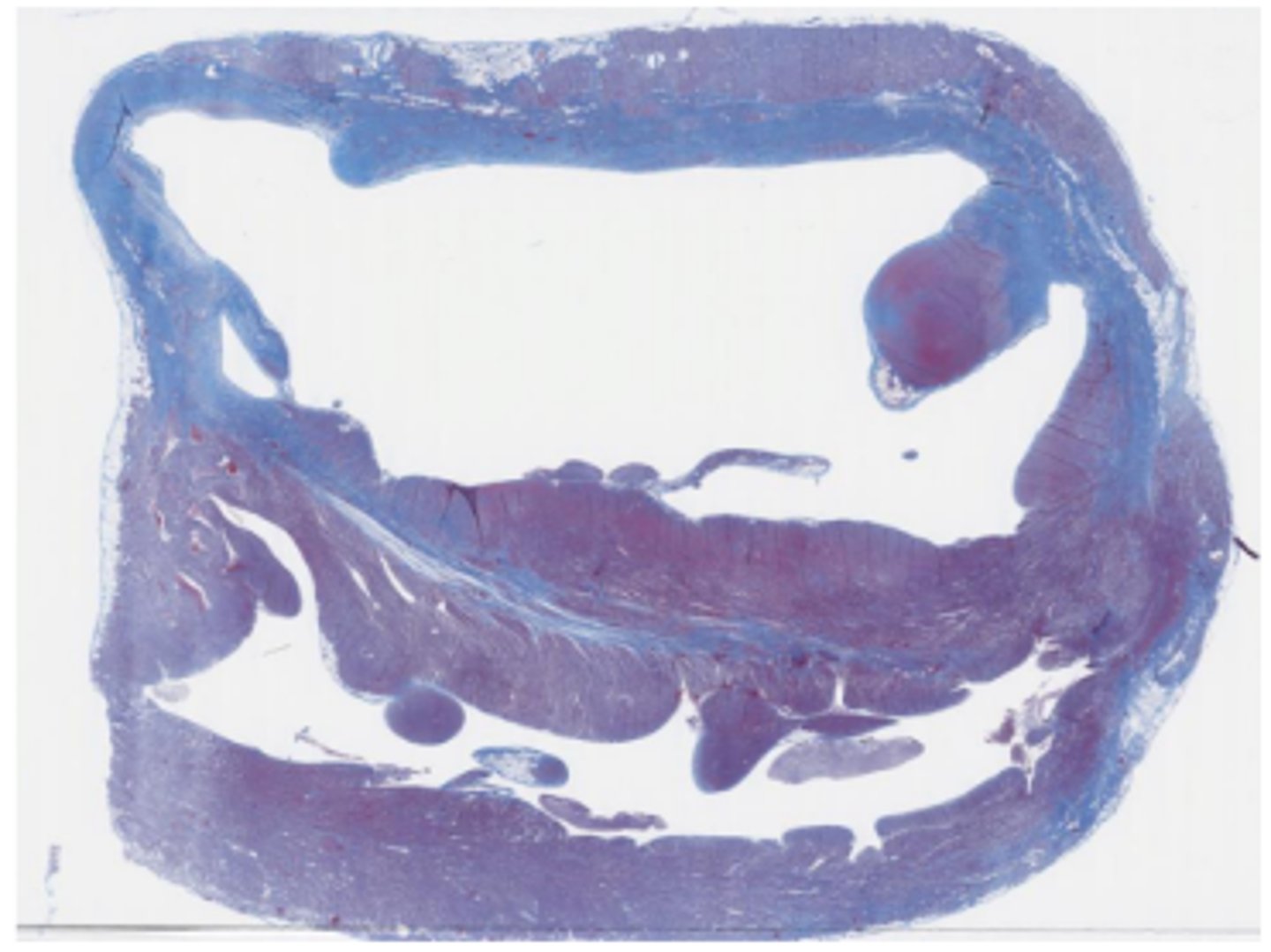
Cardiomyocyte loss, replacement fibrosis, compensatory hypertrophy
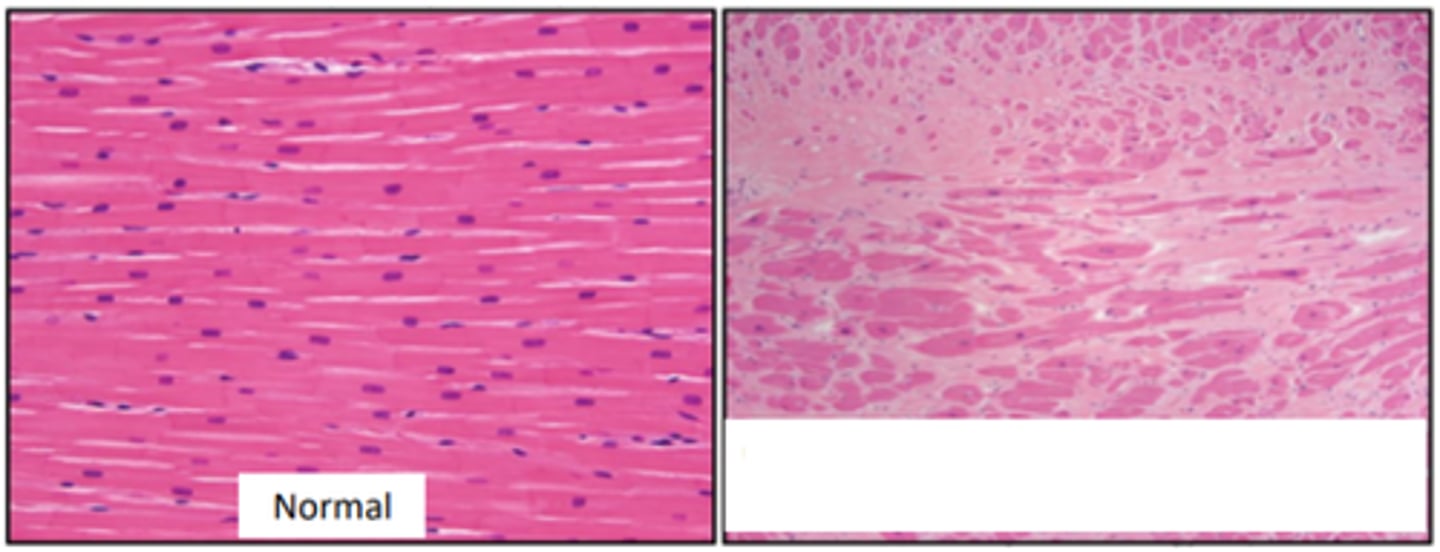
Endocardial mineralisation
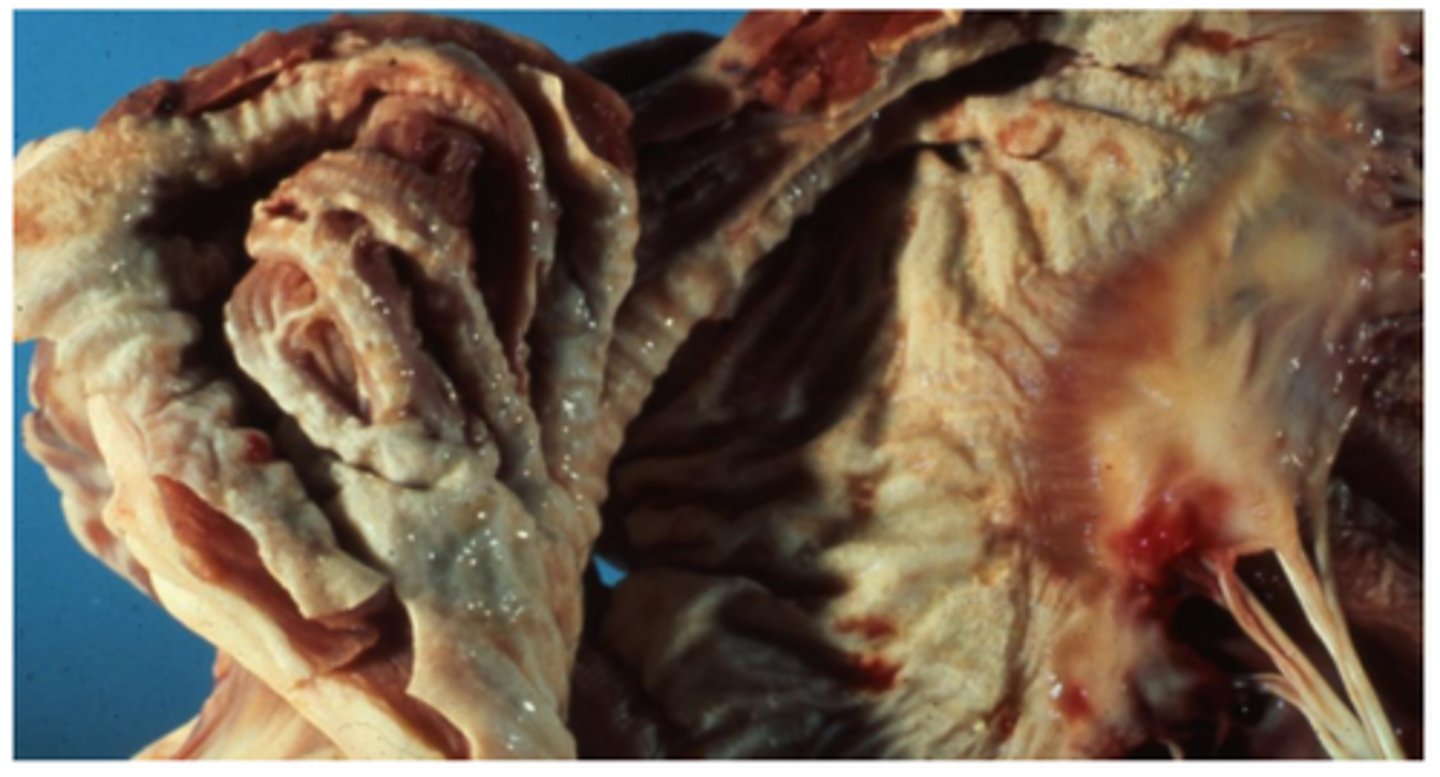
Myxomatous valve degeneration (MVD)/ Endocardiosis
Thickened (nodular) and shortened valves with smooth endocardial surface, ‘Jet lesions’ / endocardial fibrosis in the left atrium, myofibroblastic proliferation, deposition of acid mucopolysaccharides within valvular stroma
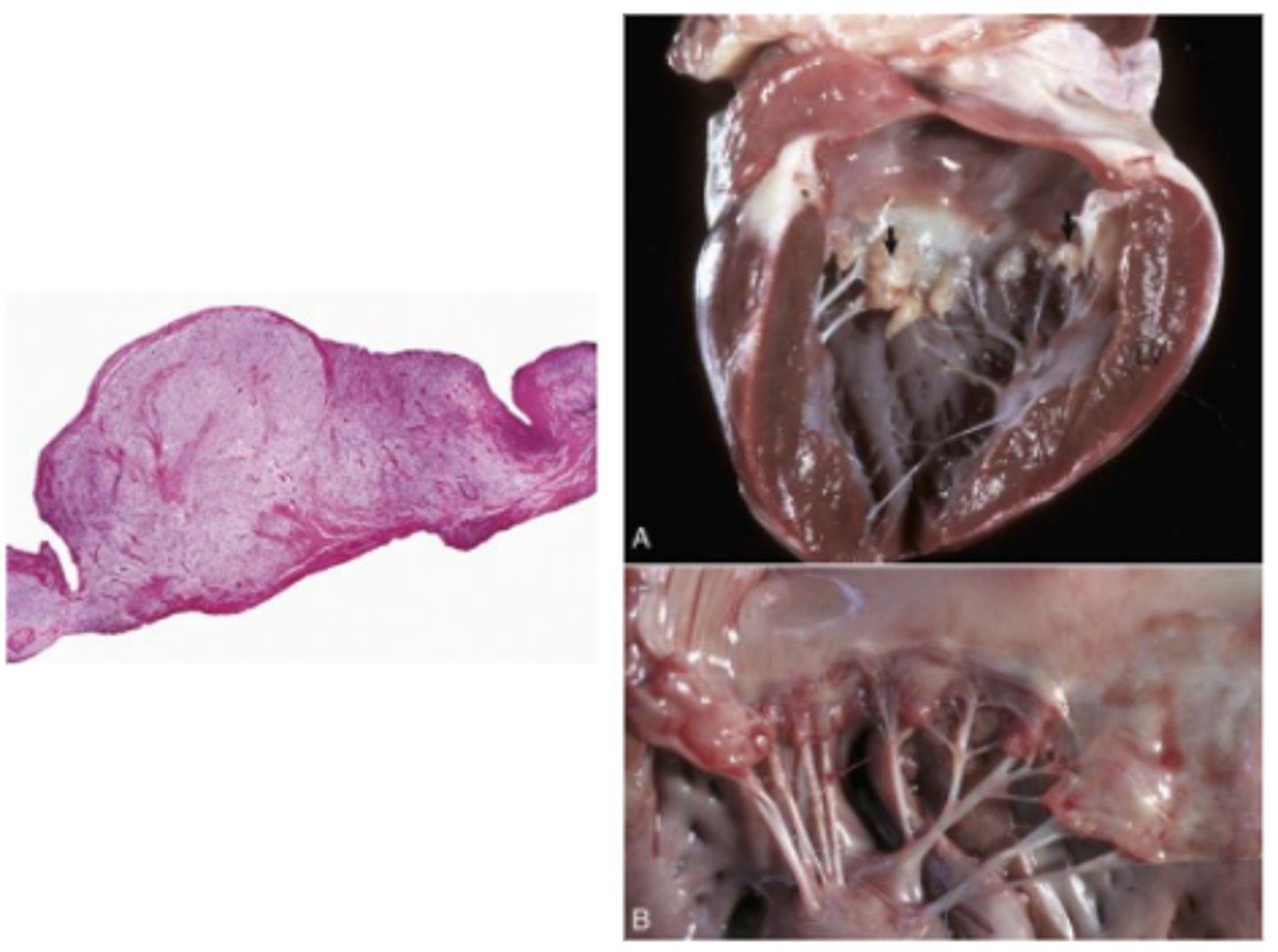
Valvular insufficiency (regurgitation)
Endocardial (endothelial) injury == “jet lesions”
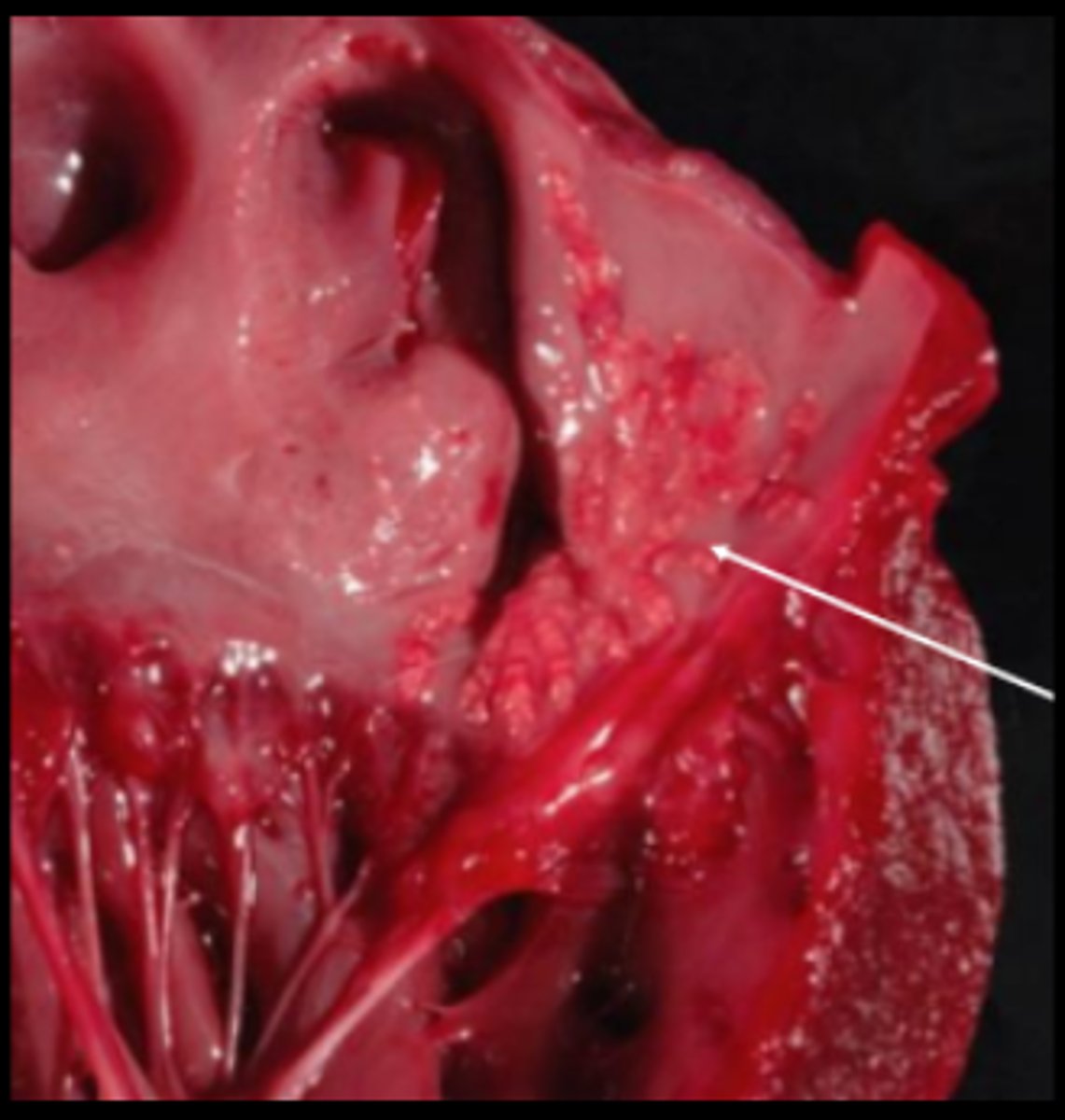
Bacterial vegetative valvular endocarditis (Truperella pyogenes)
Mammary gland; mitral valve. Necrosuppurative mastitis and chronic endocarditis with endocardial plaques, pus
Heart; inflammation of the valve
Bacterial vegetative valvular endocarditis
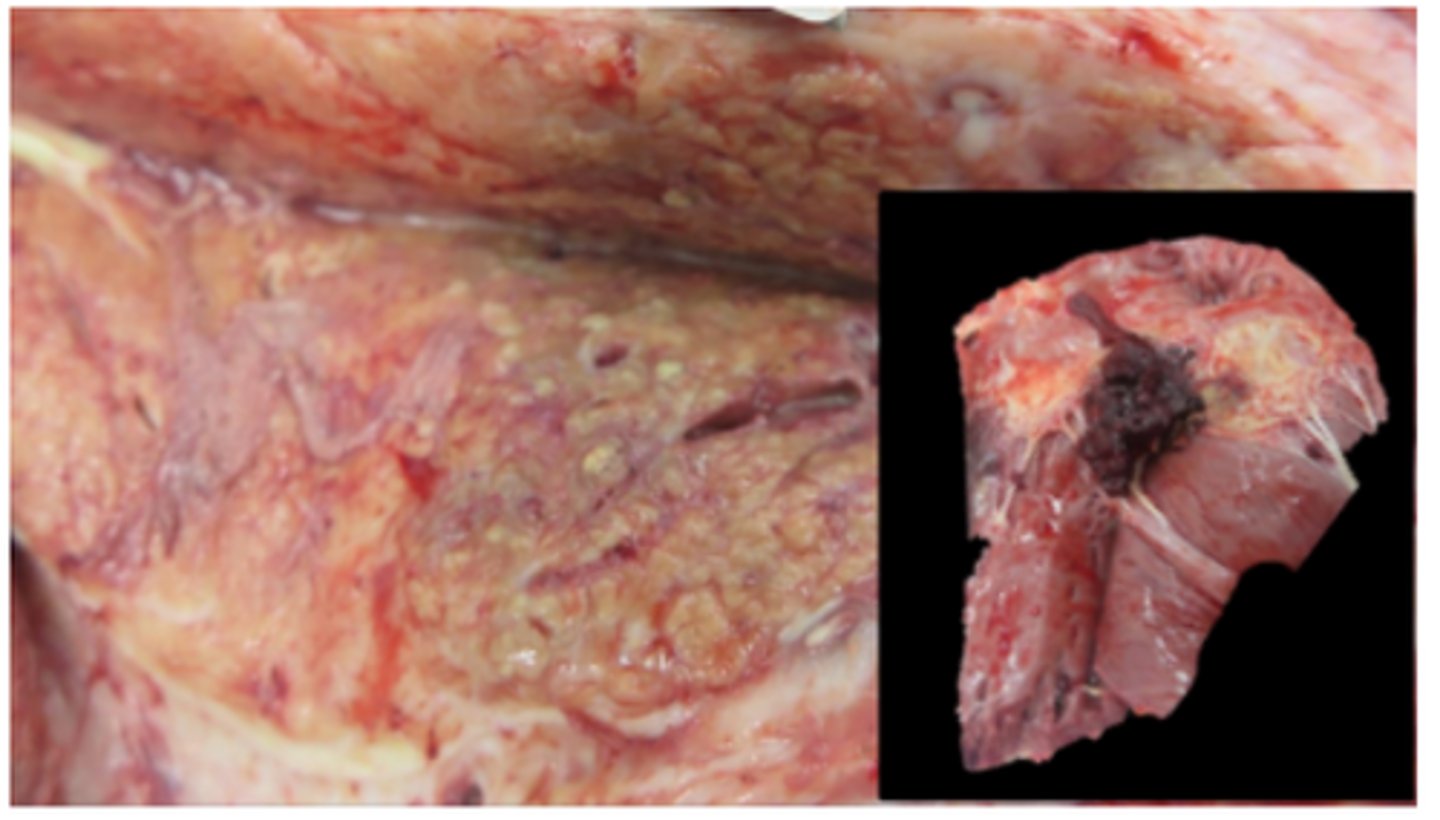
Ox, tricuspid valve endocarditis
Friable, yellow-to-grey-to-red masses of fibrin (vegetations), fibrotic with chronicity
Bacterial vegetative valvular endocarditis
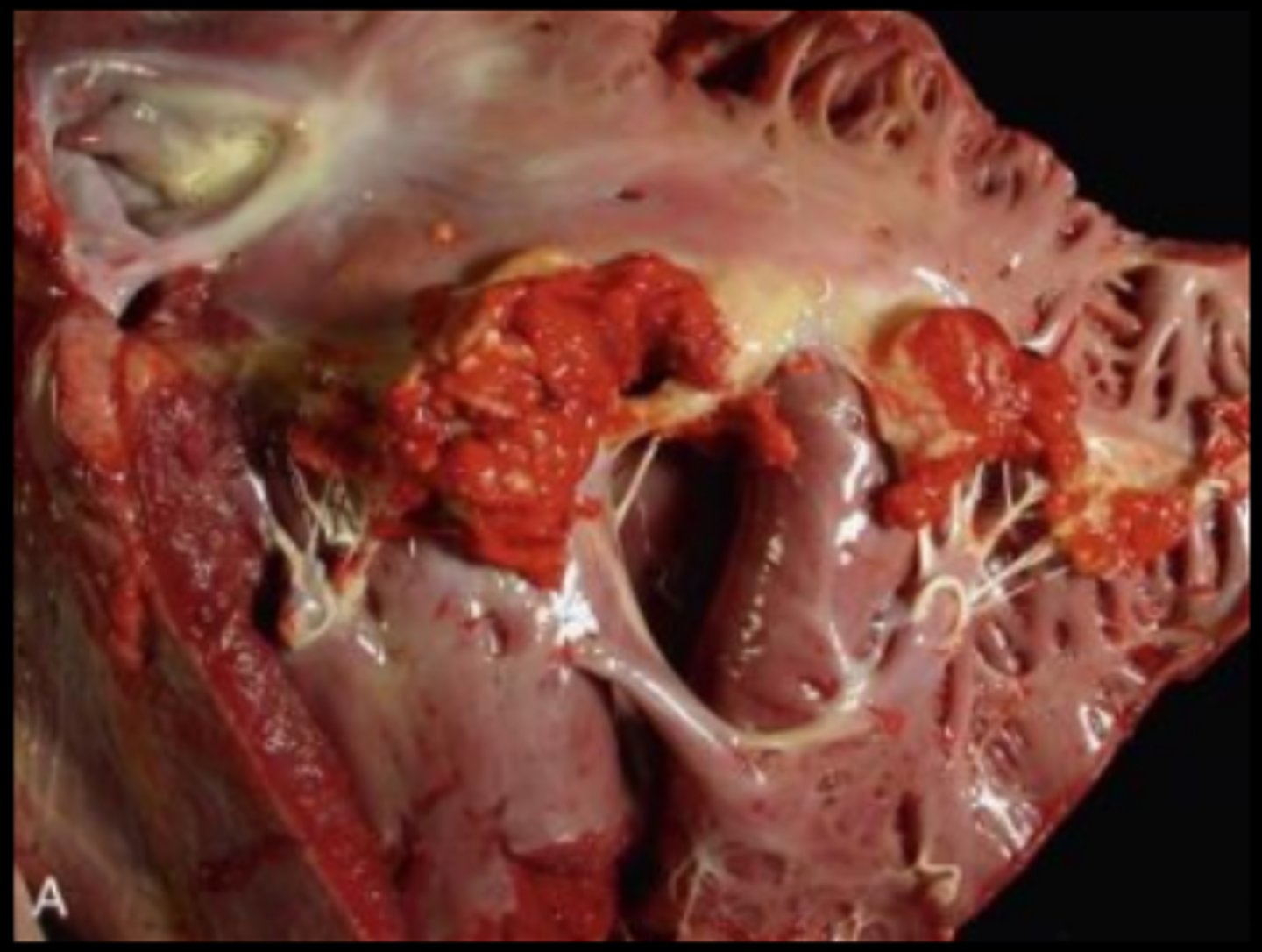
Horse, aortic valve. Chronic aortic valve endocarditis with endocardial plaques; friable, yellow-to-grey-to-red masses of fibrin (vegetations), fibrotic with chronicity
Bacterial vegetative valvular endocarditis
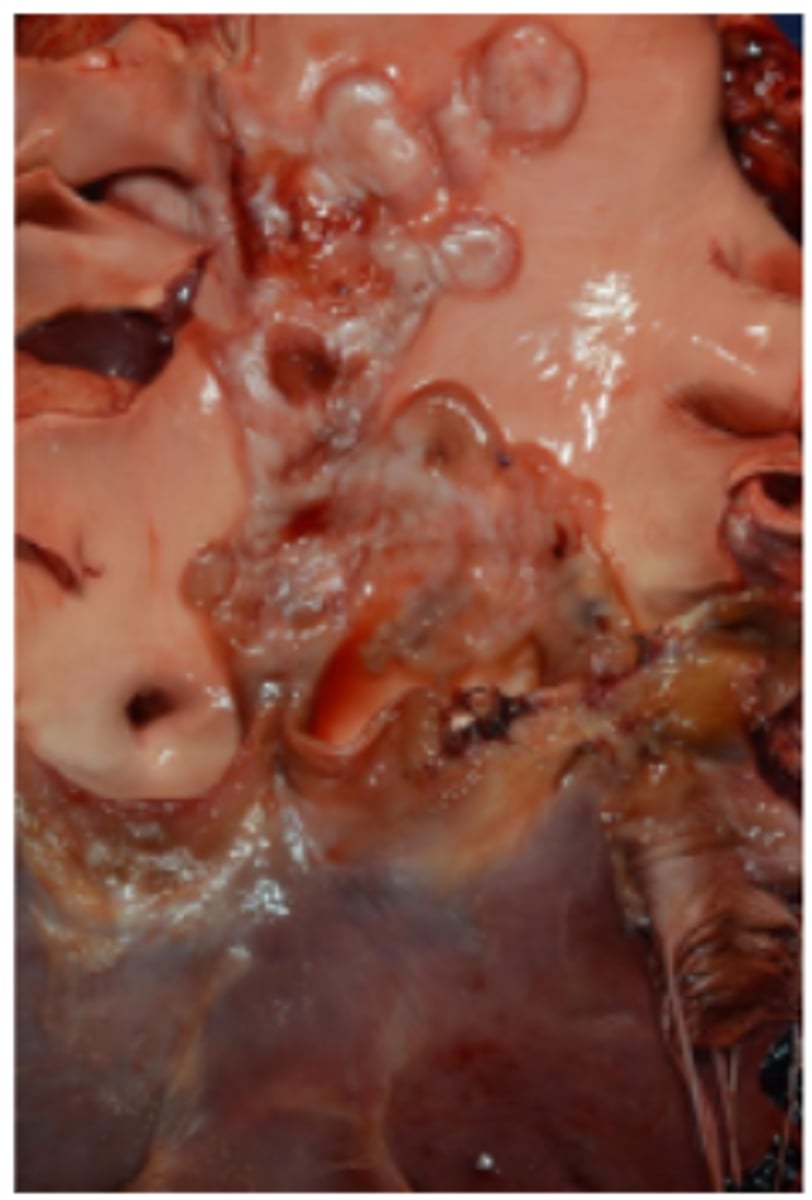
Mitral valve. Chronic bacterial endocarditis
Lamellar fibrin, mixed leukocytes, granulation tissue (chronic), +/- bacterial colonies
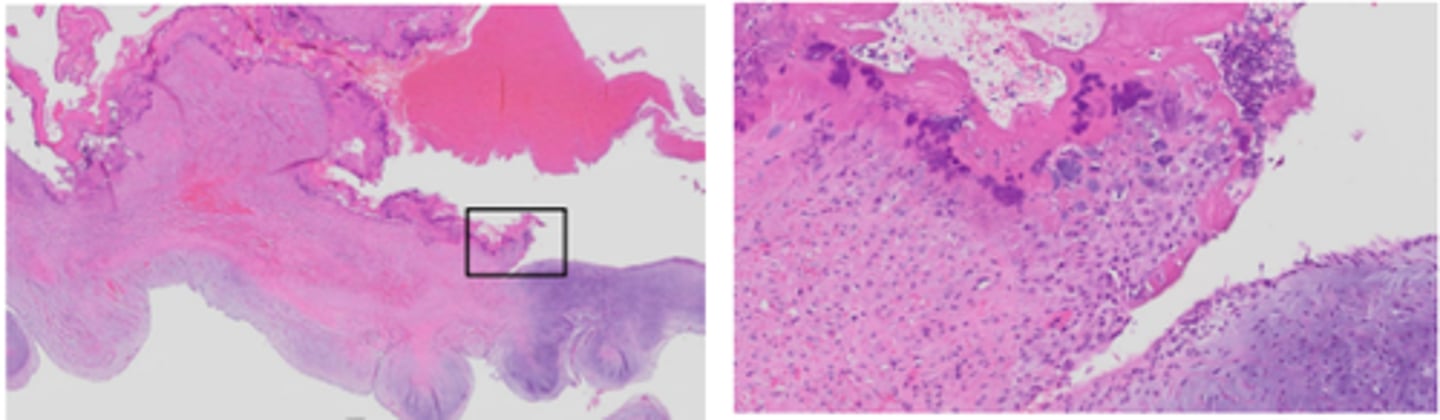
Endocardiosis
Smooth in appearance
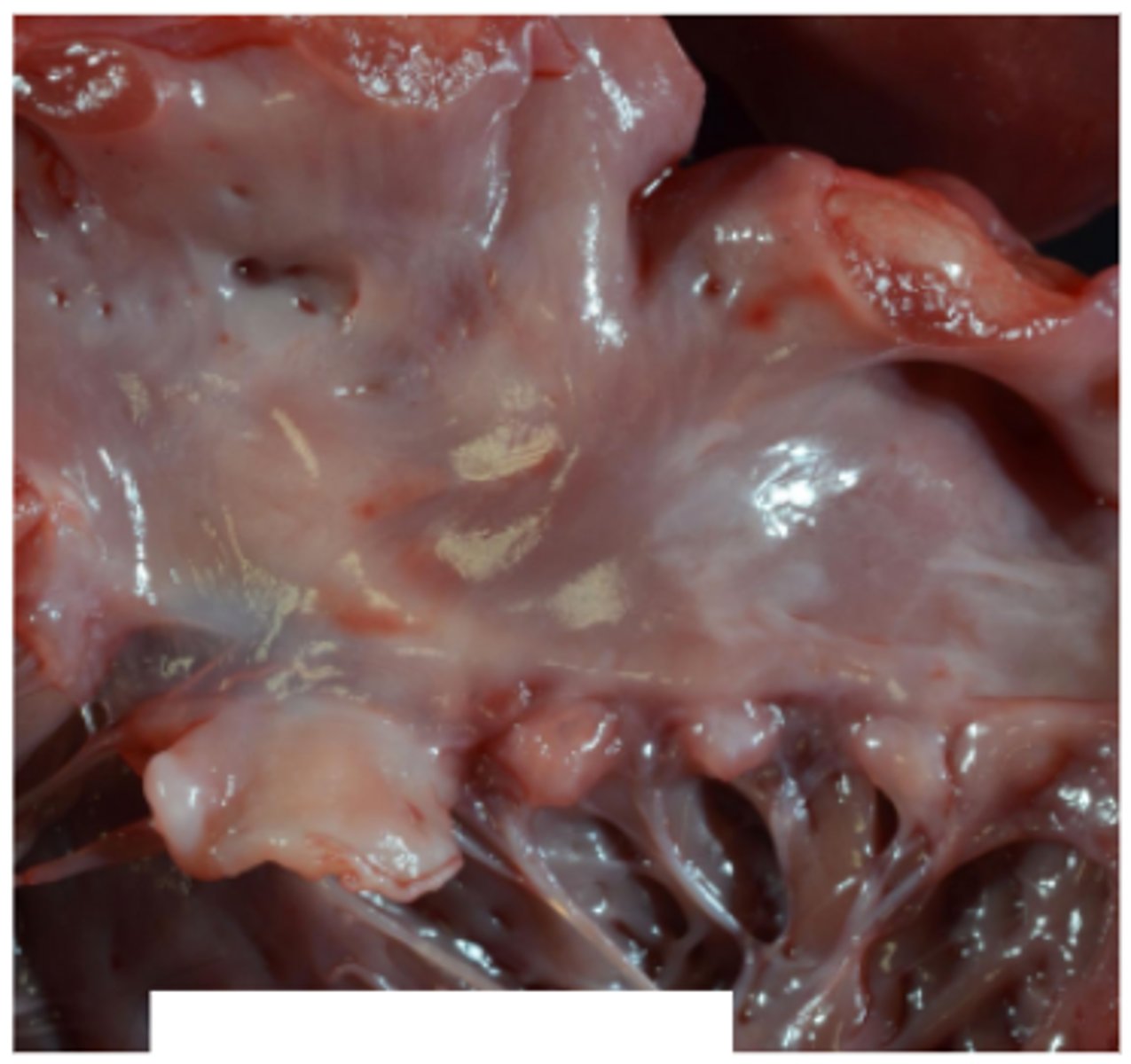
Endocarditis
Rough in appearance
Areas of haemorrhage, fibrosis, bacteria
Hydropericardium
Goat kid, hydropericardium. Secondary to CHF. Tricavitary effusion present.
Excess clear fluid within the pericardial cavity
Haemopericardium
Secondary to ruptured RA hemangiosarcoma
Pure blood in the pericardial cavity
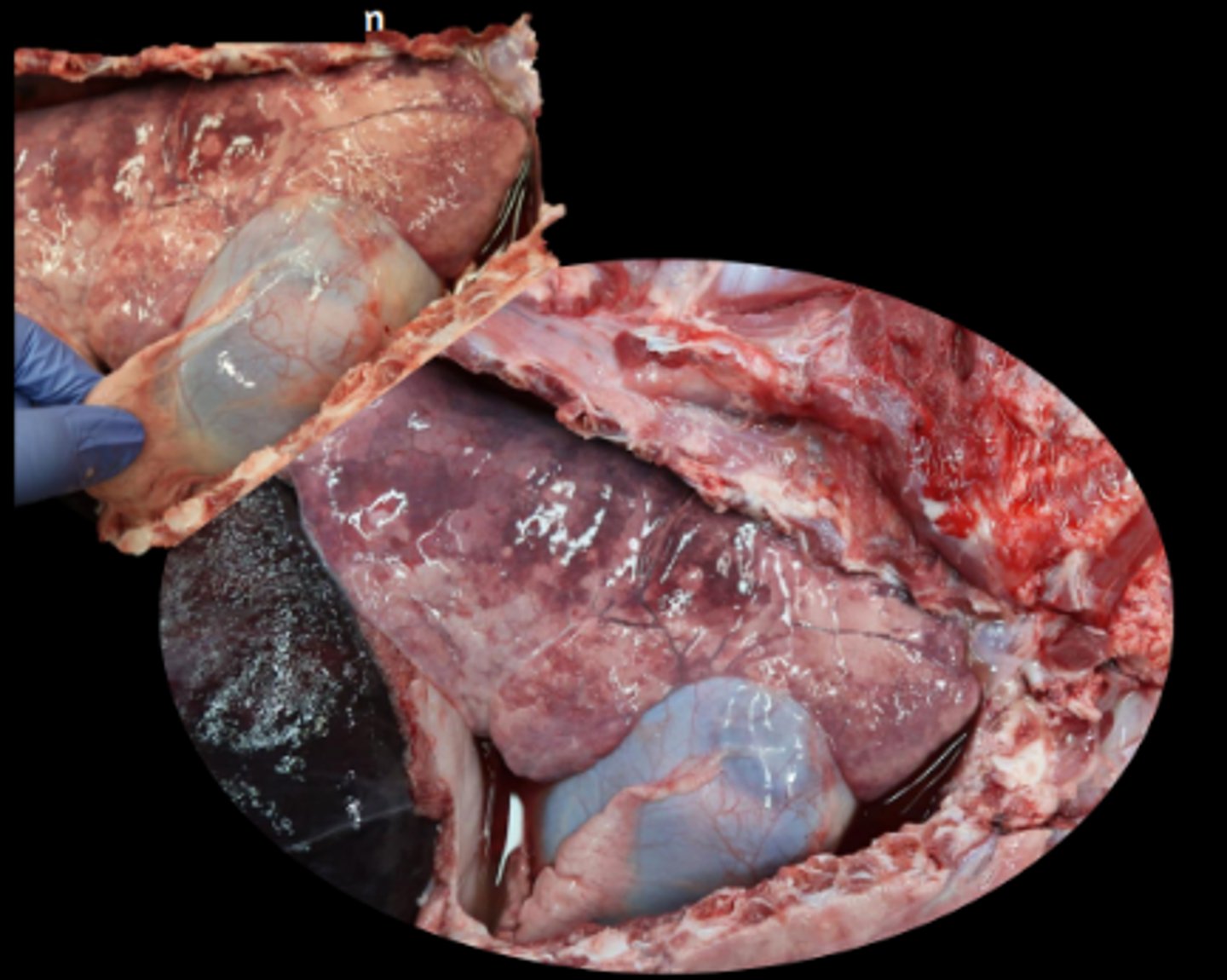
Serous atrophy of fat (SAF)
Lipid replaced by proteinaceous fluid - gelatinous and translucent
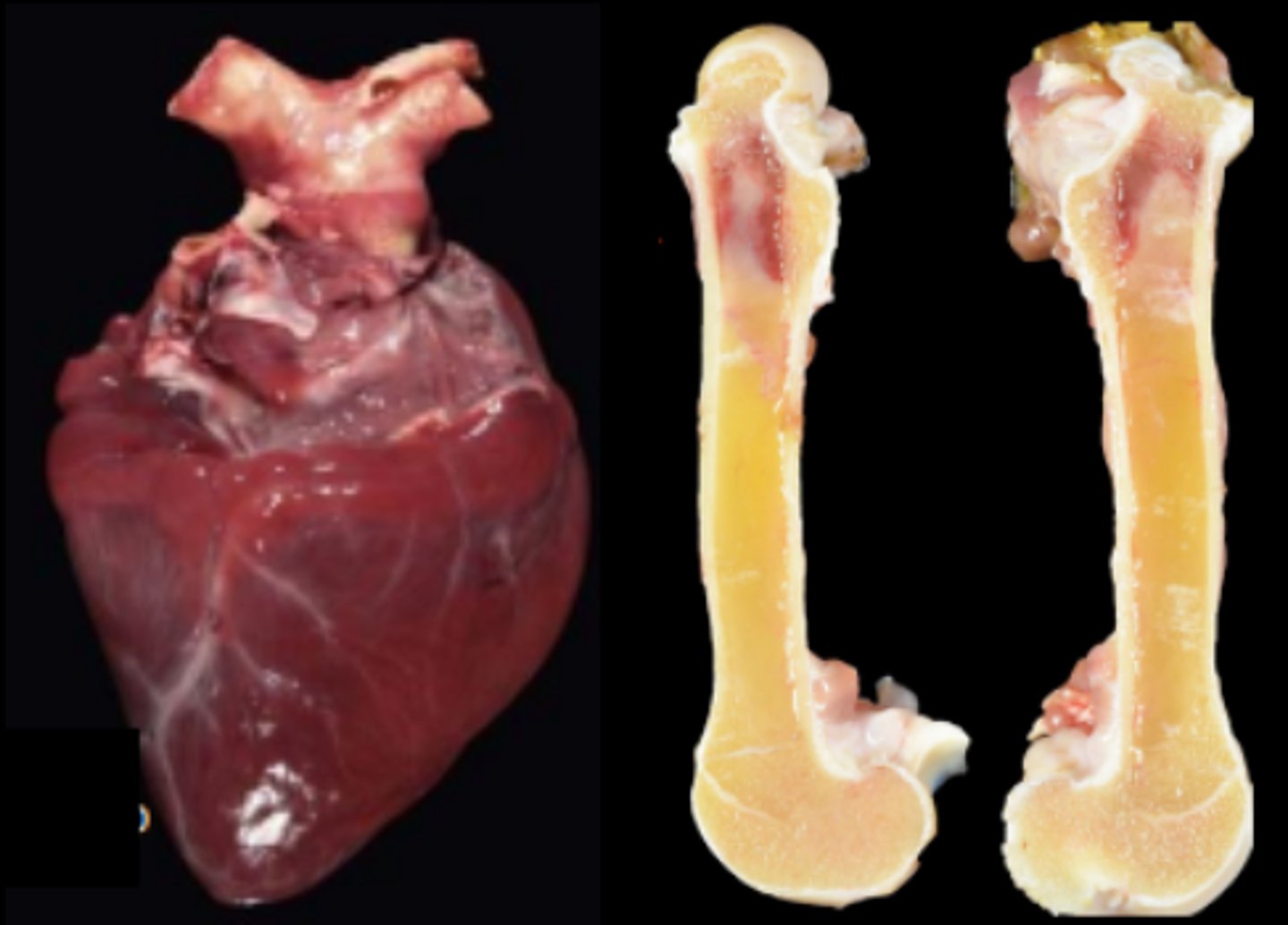
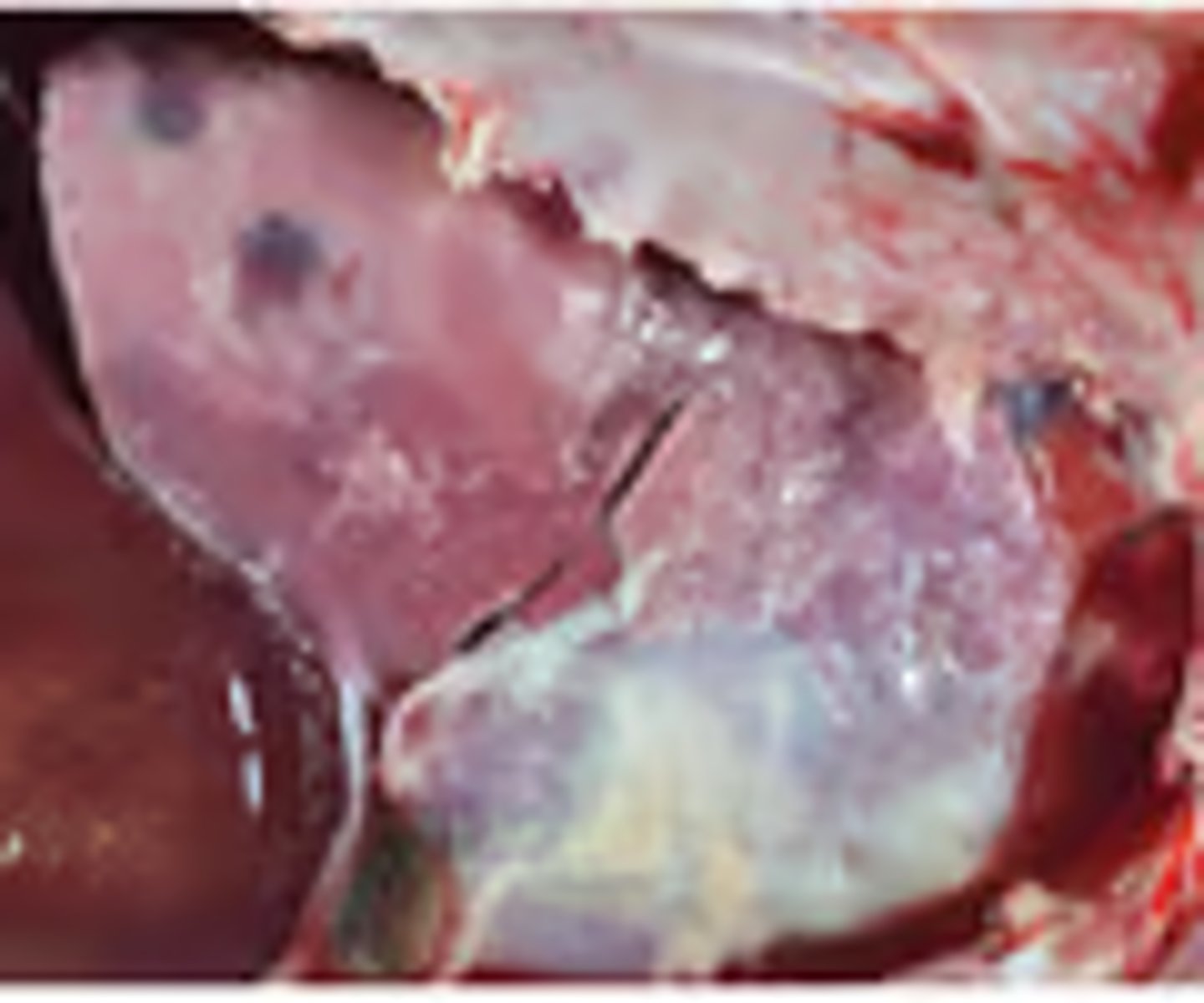
Goat, fibrinous pleuropneumonia and pericarditis. Mannheimia haemolytica
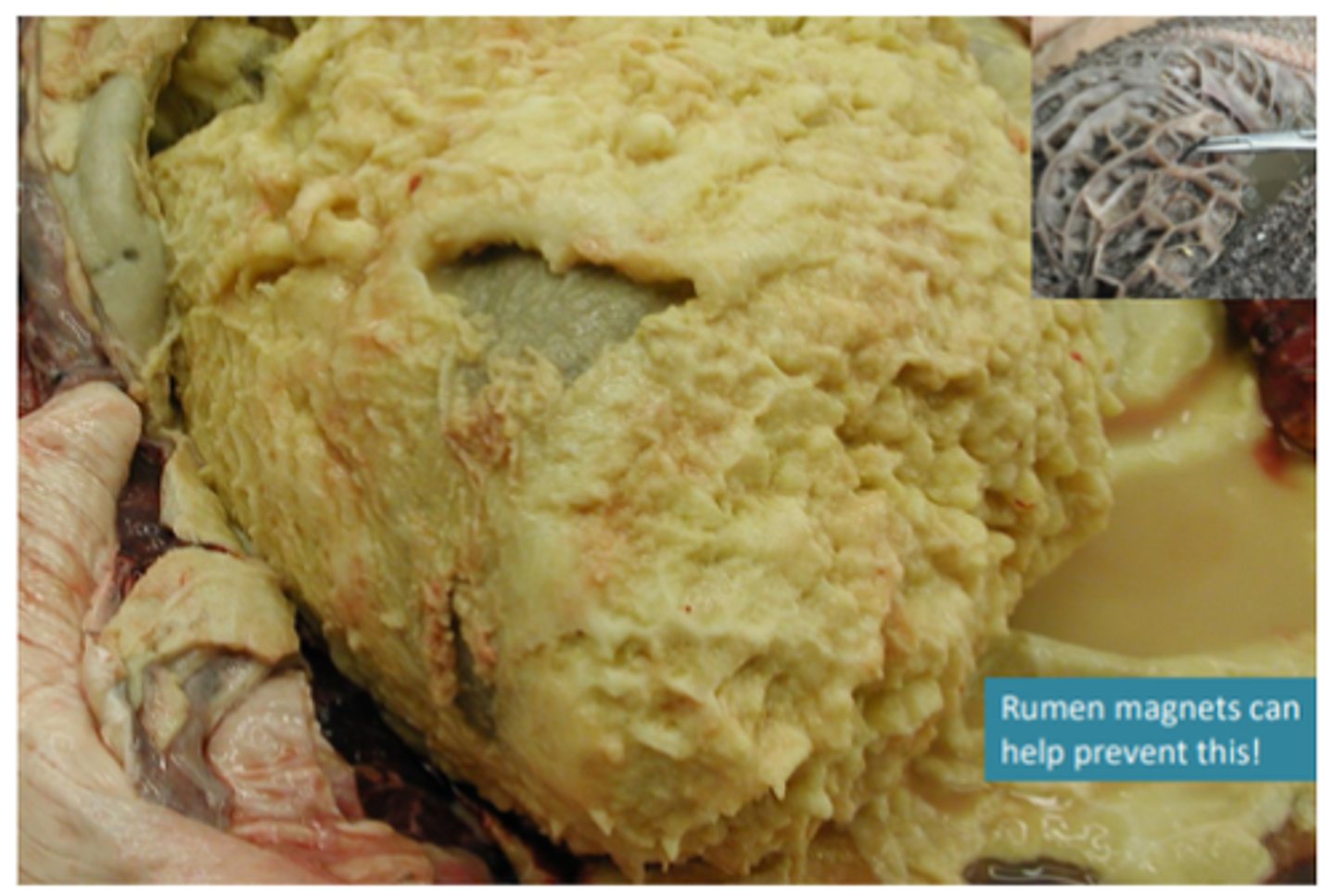
Traumatic reticulopericarditis (TRP)/ Hardware disease
Wire penetration through the reticulum wall, diaphragm, pericardium
Seeding of bacteria in the pericardium (bacterial pericarditis); fibrosis - leading to constrictive pericarditis, right sided heart failure
Epicardium covered in a thick mat of fibrin
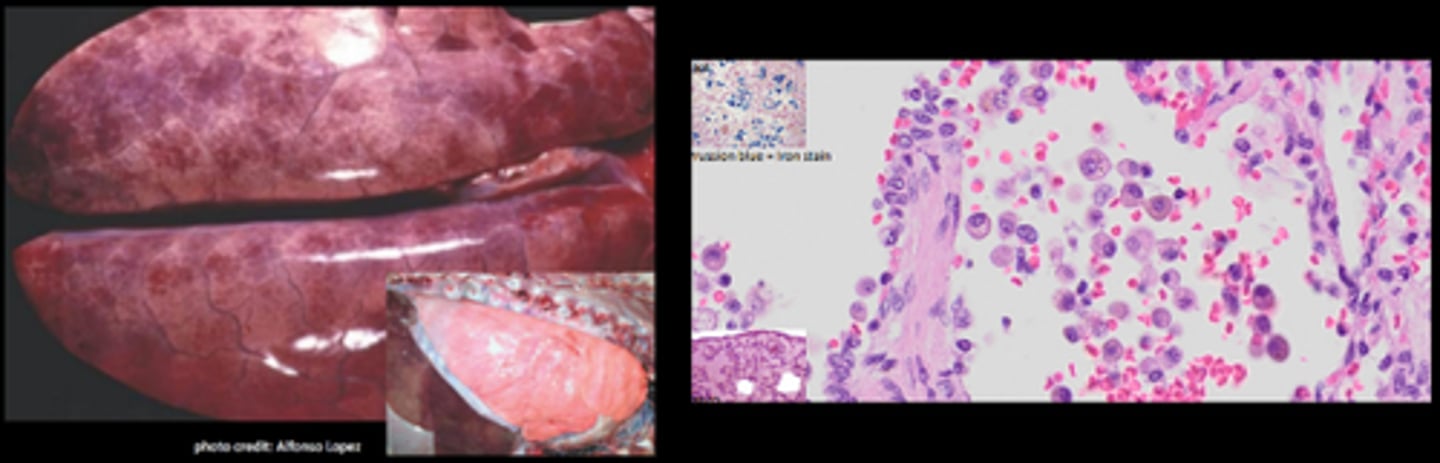
Left sided congestive heart failure - pulmonary congestion and oedema
Diffusely wet and heavy lungs which feel rubbery, ooze fluid on cut surface
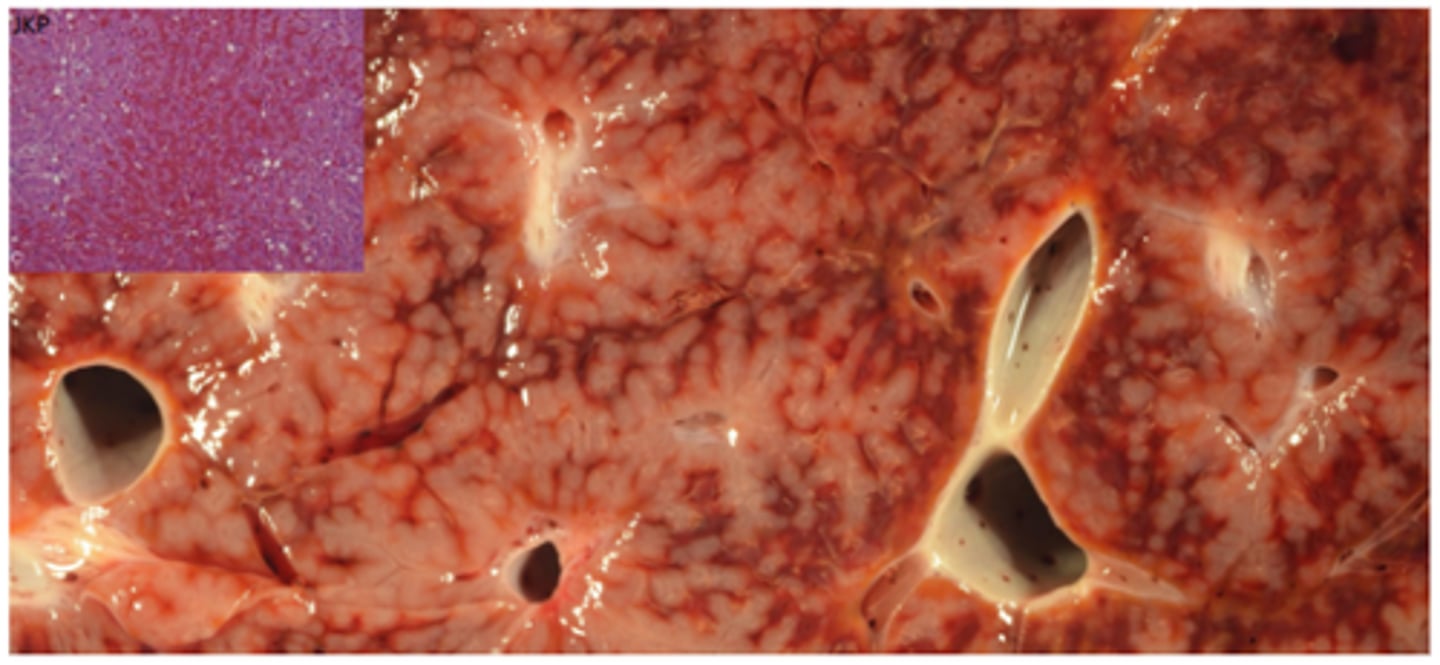
Right sided congestive heart failure - Liver
Chronically congested and enlarged nutmeg liver, central veins congested first, atrophy of zone 3 sinusoids (central vein area) → fibrosis and loss of hepatocytes
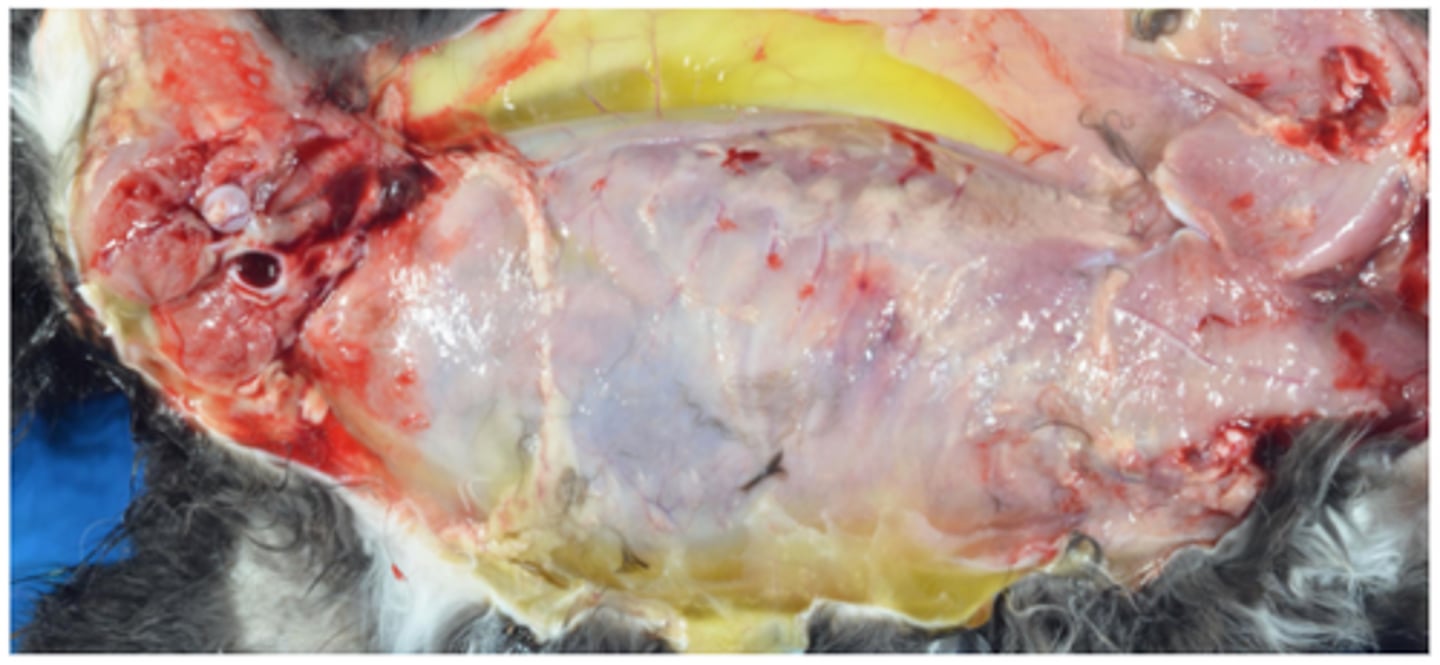
Right sided congestive heart failure - subcutaneous oedema
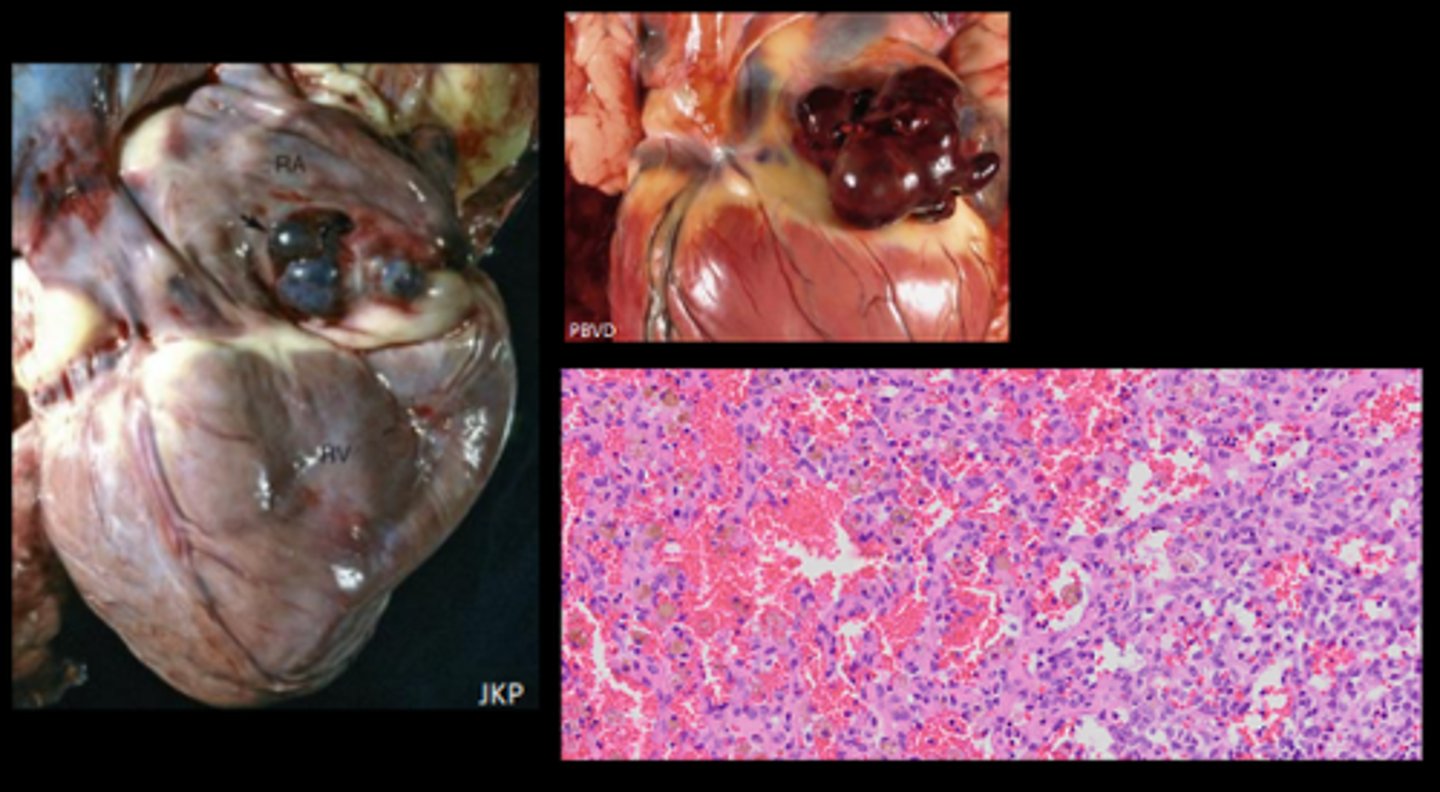
Haemangiosarcoma
Endothelial cells, right atrium and auricle
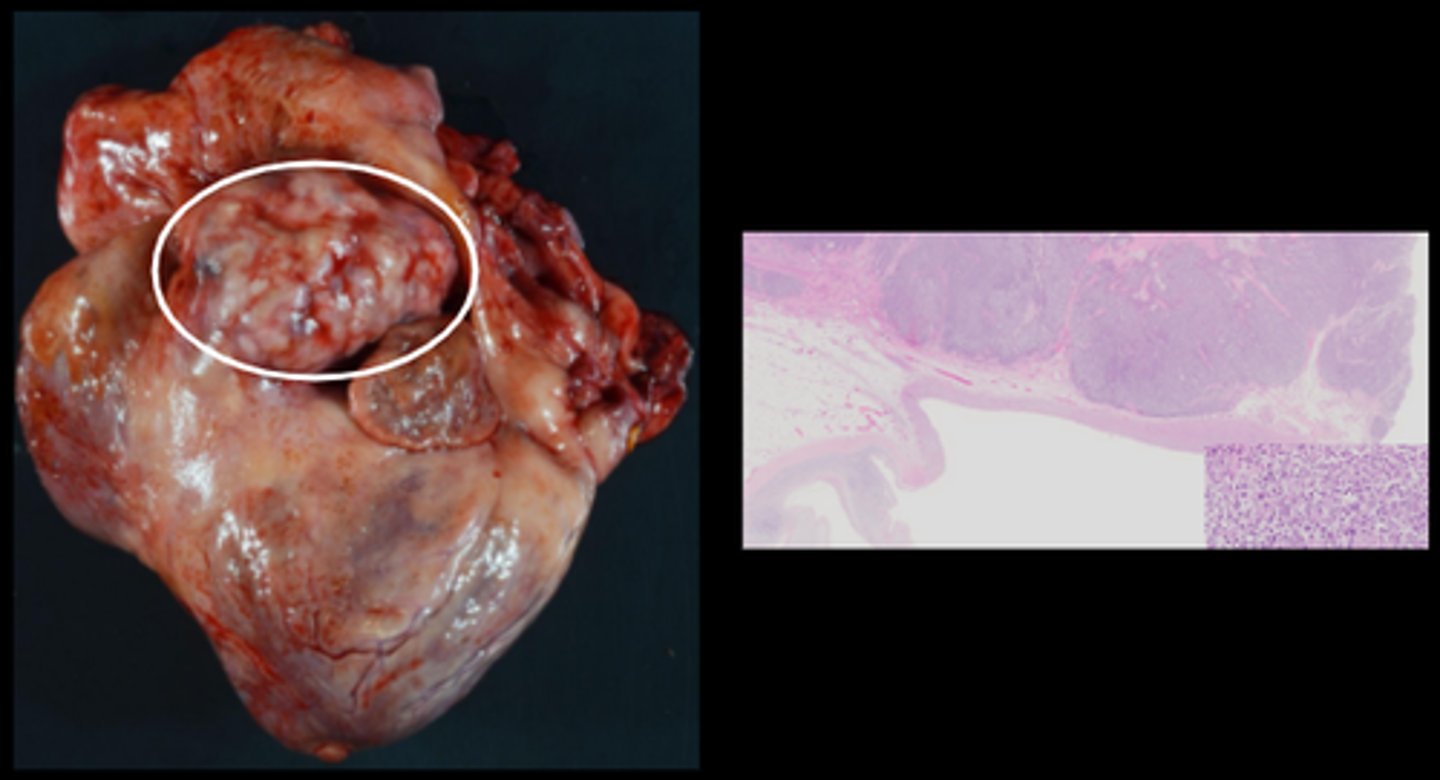
Paraganglioma (chemodectoma)/ aortic body tumour
Concentric hypertrophy
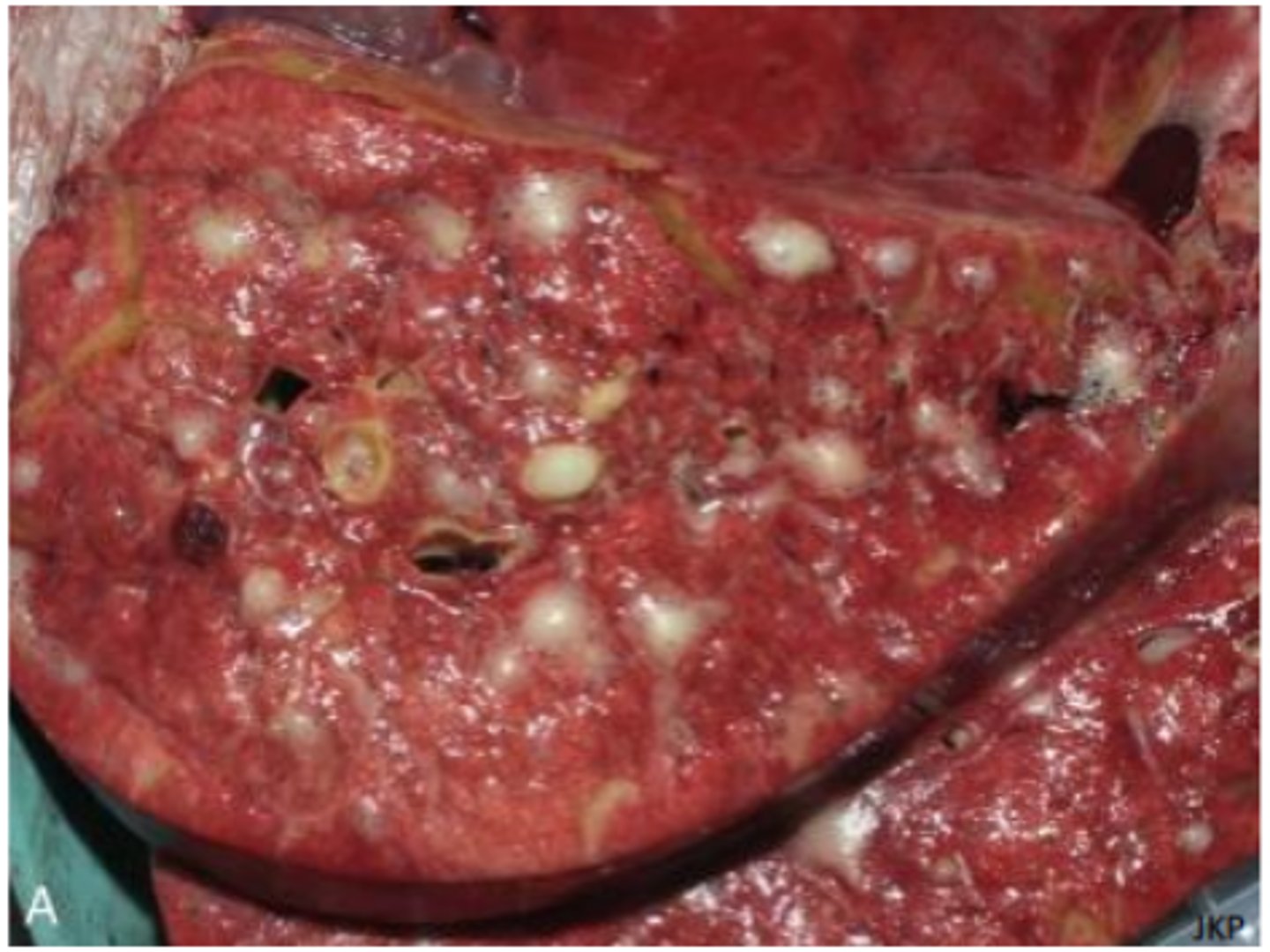
Lymphoma
Gross: Multifocal to coalescing pale tan to white nodules, varied demarcation
Histological: Sheets of neoplastic cells with disruption of the surrounding myocardium
Histiocytic sarcoma
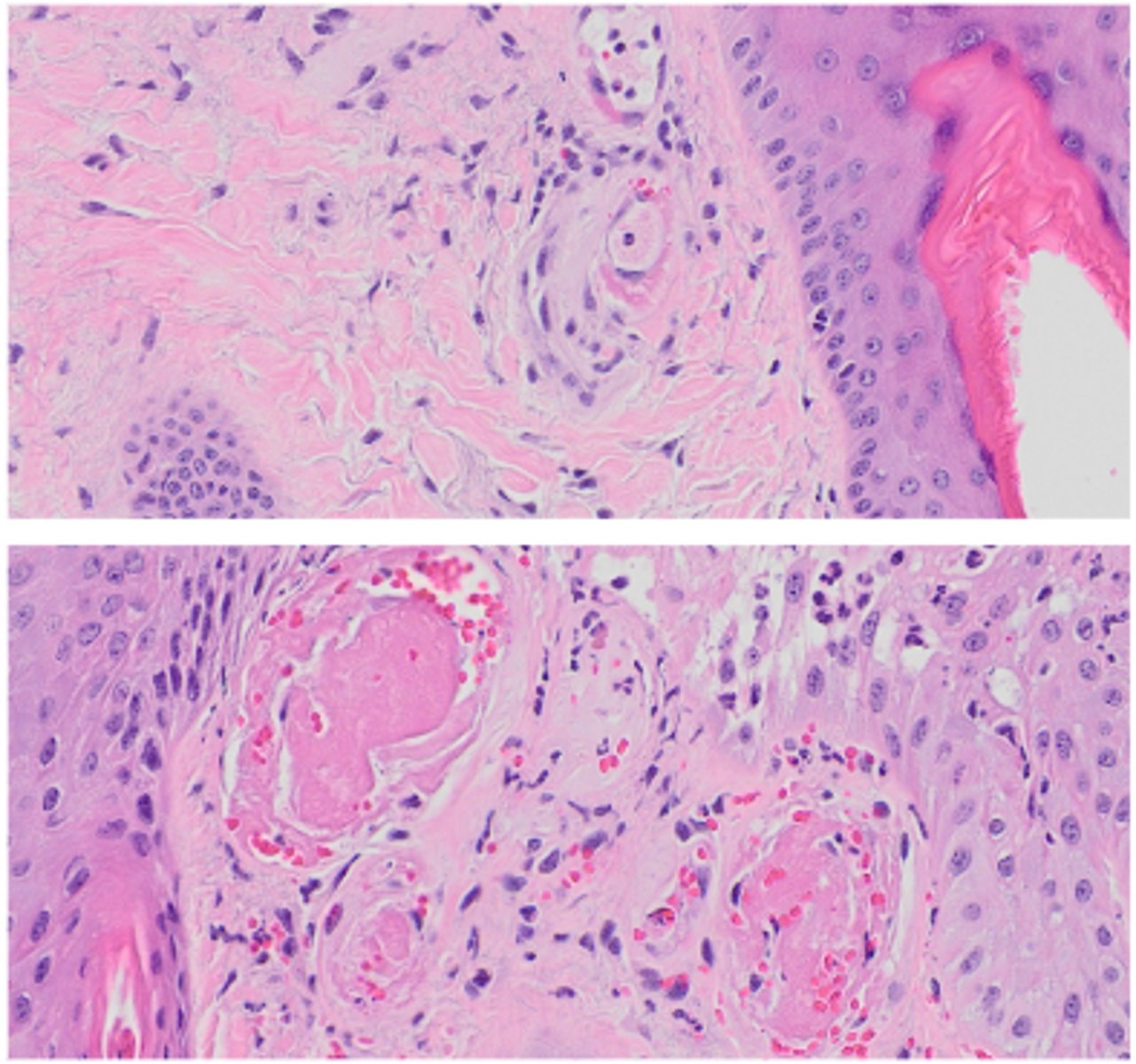
Fibrinoid vascular necrosis
Endothelial damage characterised by accumulation of serum proteins and polymerised fibrin within the vessel wall
Homogenous eosinophilic material within the vessel wall which obscures cellular detail
Arteriosclerosis of vessels
Hardening of the arteries and loss of elasticity, mineralisation of the tunica media, arterial wall thickening and luminal narrowing
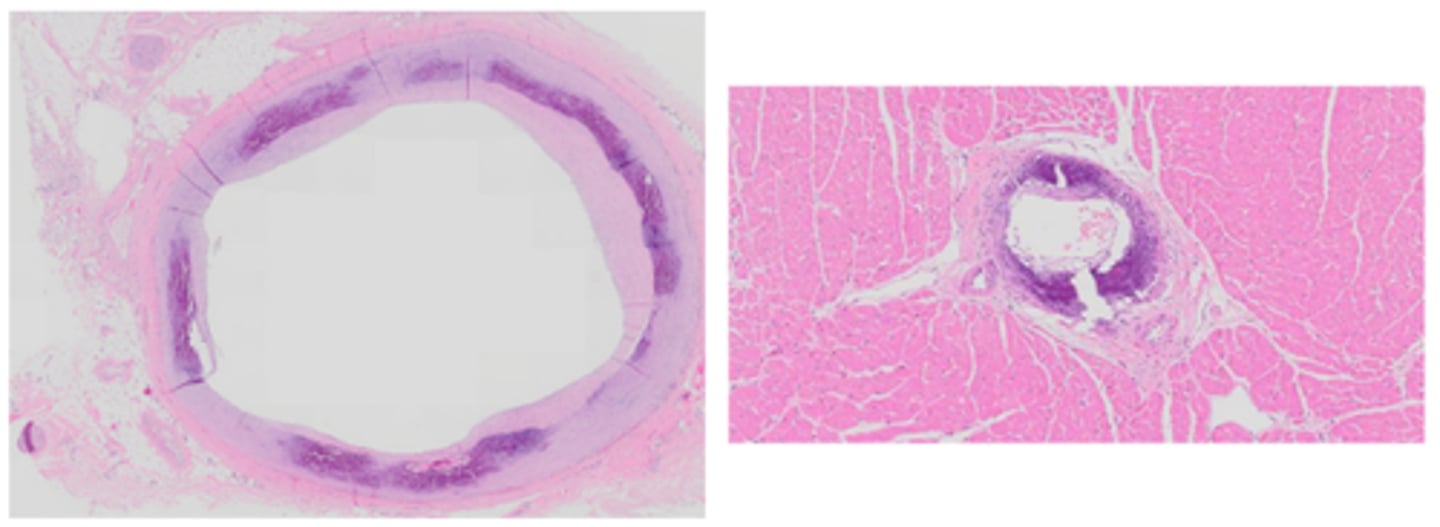
Atherosclerosis
Prominent pale tan vessels, fibrofatty plaque, arterial wall thickening and luminal narrowing
Atherosclerosis of vessels
Atheromas (fibrofatty plaque), arterial wall thickening and luminal narrowing
Medial hypertrophy and hyperplasia of vessels
Pulmonary arteries; myofibroblast proliferation and hypertrophy within the tunica media as a result of hypertension and hyperperfusion - hypoxia
High Altitude disease: Medial hypertrophy and hyperplasia/ Brisket disease
Concentric hypertrophy of the RHS of the heart → right-sided heart failure and increased hydrostatic pressure
Aortic rupture
Equine viral arteritis virus
Gross: oedema, congestion, haemorrhage, abortion
Histopathology: fibrinoid vascular necrosis, lymphocytic vasculitis
Orbivirus infection
Cardiac and pulmonary presentations - alveolar oedema, widespread haemorrhages, massive pulmonary oedema with frothiness
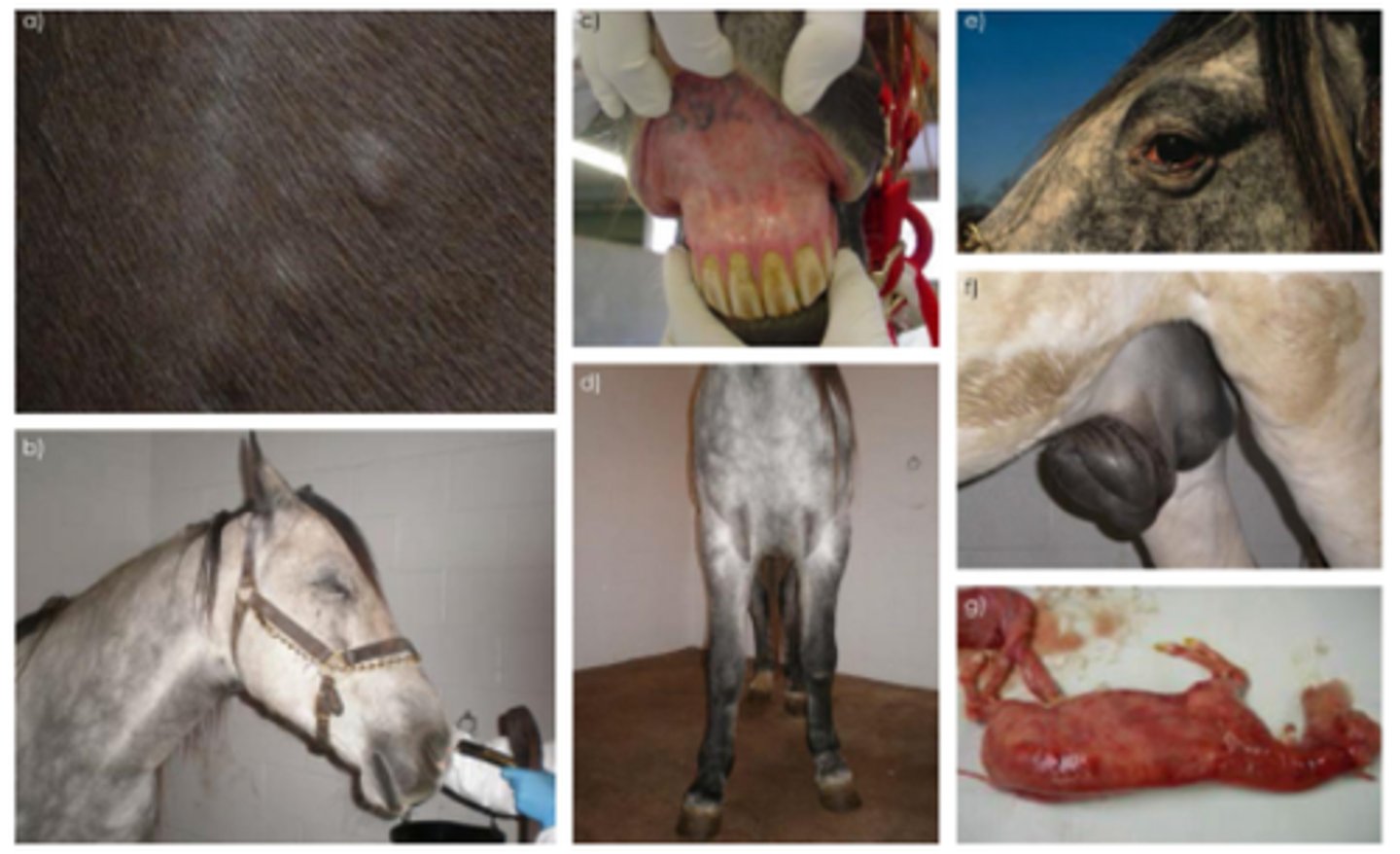
Bluetongue virus - Viral vasculitis
Oral oedema with blue tongue (cyanosis and hypoxia), coronary band alopecia and ulceration, oral peticiations, oro-nasal discharge (muco-purulent)
Fibrinoid necrotising arteriolitis (Swine haemorrhagic viruses)
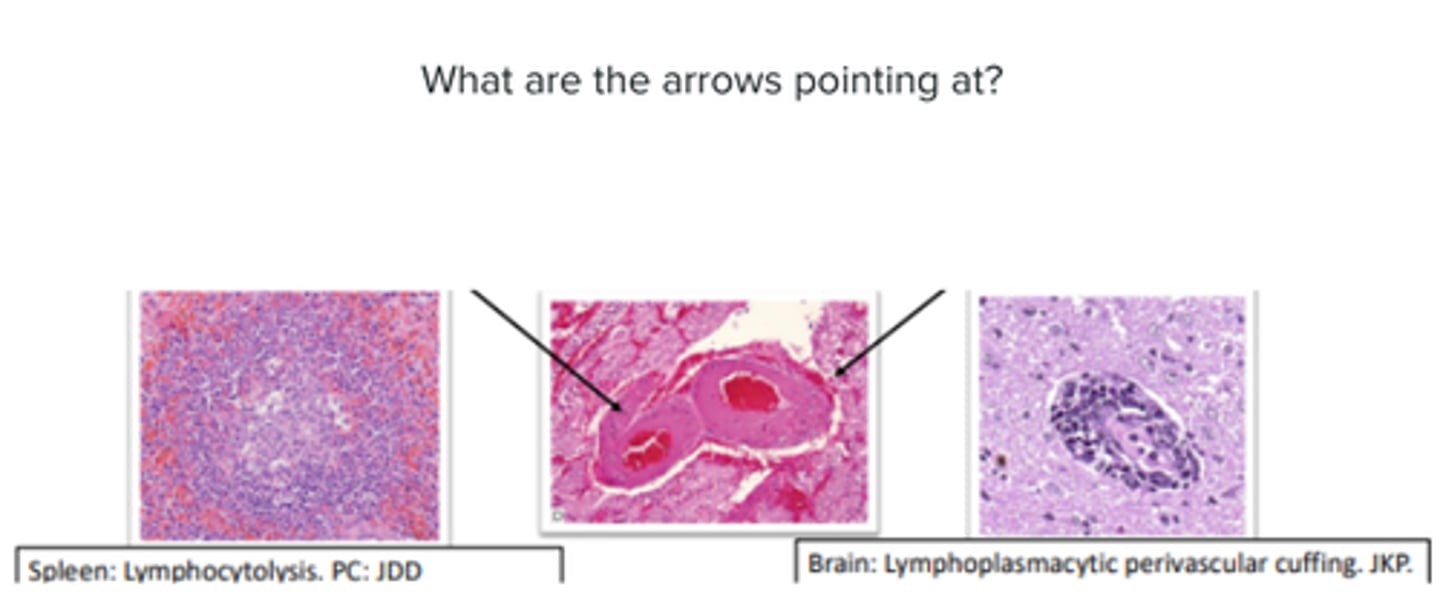
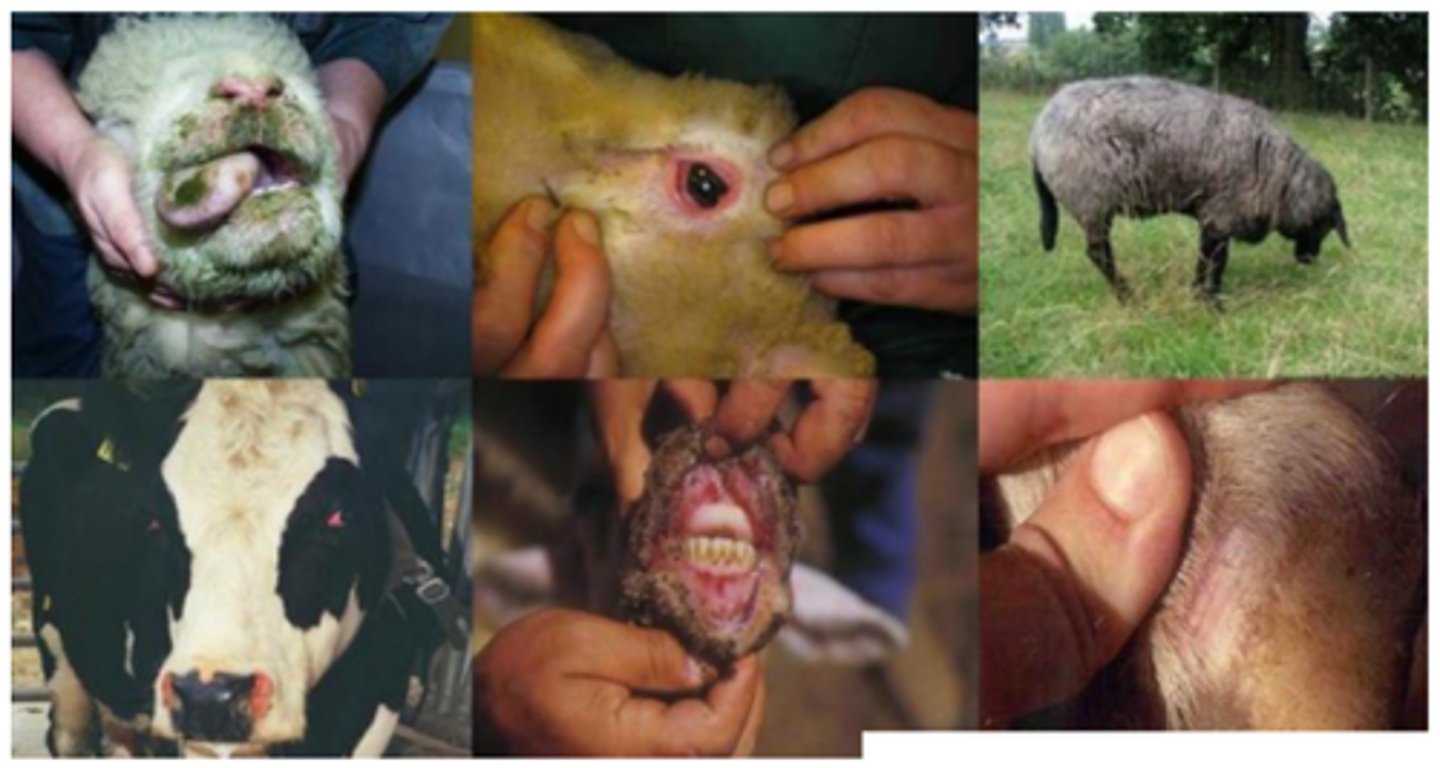
Rickettsia - Ehrlichia ruminantium (Heartwater/ cowdriosis)
Gross pathology: hydropericardium, hydrothorax, splenomegaly
Histopathology: small vessel degeneration +/- vasculitis, colonies of bacterial within endothelial cytoplasm
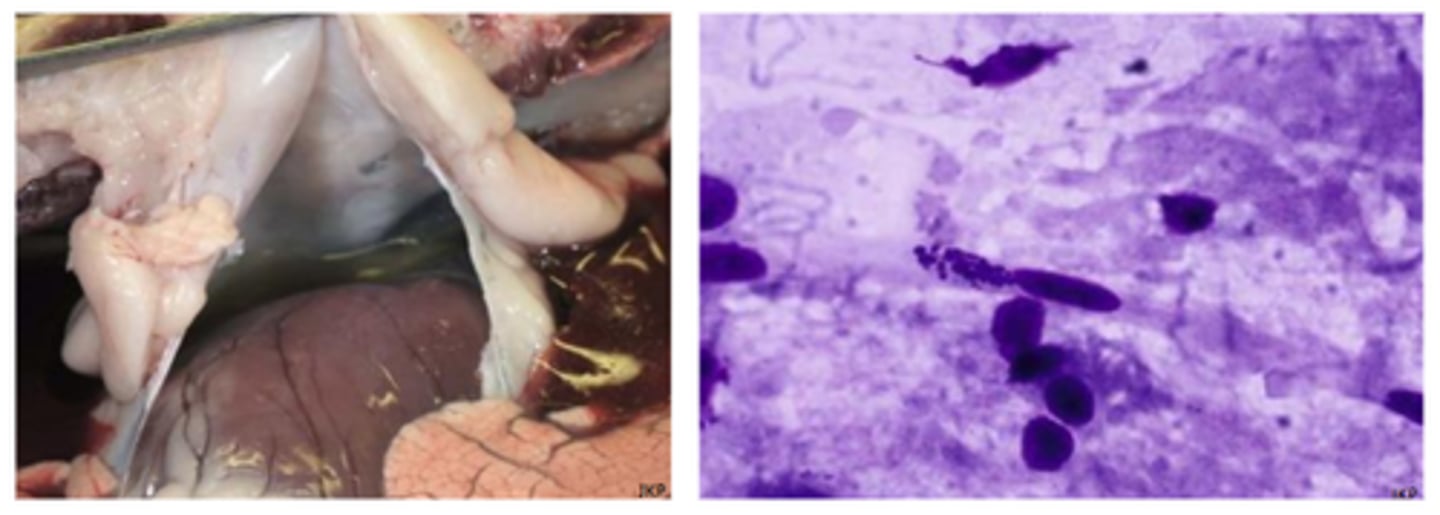
Rickettsia - Rocky mountain fever (Rickettsia rickettsiii)
Gross pathology: oedema of ears and muzzle, petechiation of mucous membranes and skin, lymphadenomegaly with haemorrhage, haemorrhagic colitis
Histopathology: necrotising vasculitis of small veins, capillaries and arterioles, perivascular mononuclear inflammation
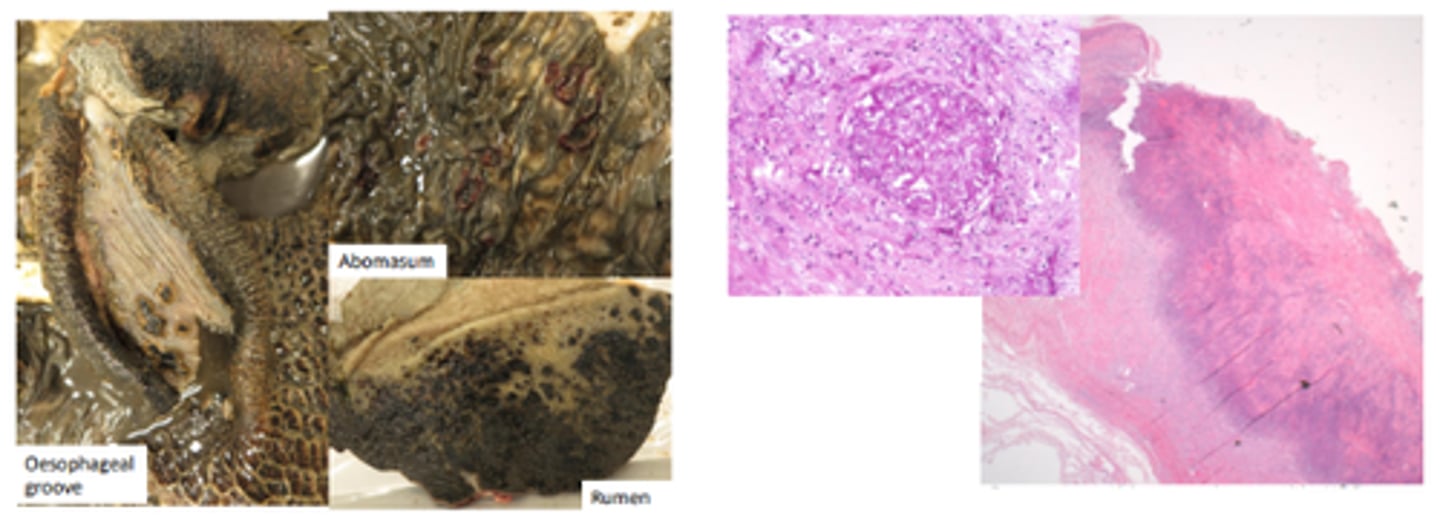
Mycotic abomastitis and rumenitis
Gross pathology: multifocal ulcers with necrosis which can be transmural and lead to peritonitis, can spread to the liver (multifocal necrotising hepatitis)
Histopathology: necrotising vasculitis with venous thrombi, fungal hyphae within vessel walls
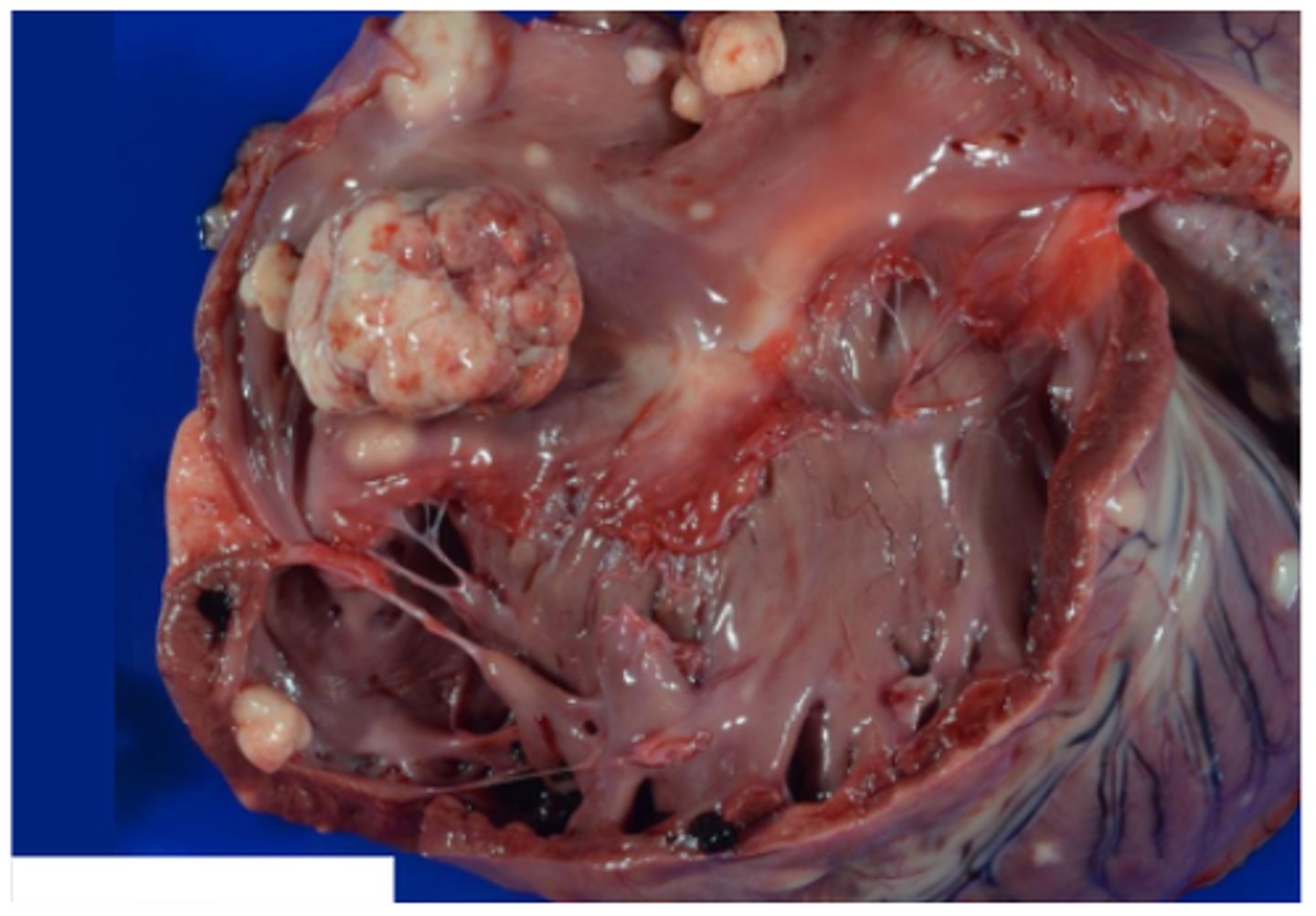
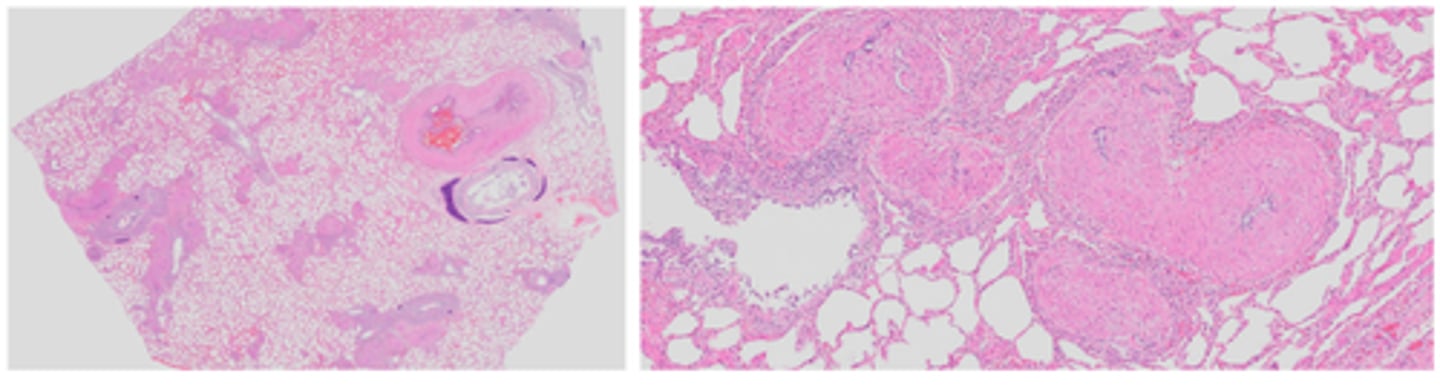
Parasitic (verminous) vasculitis
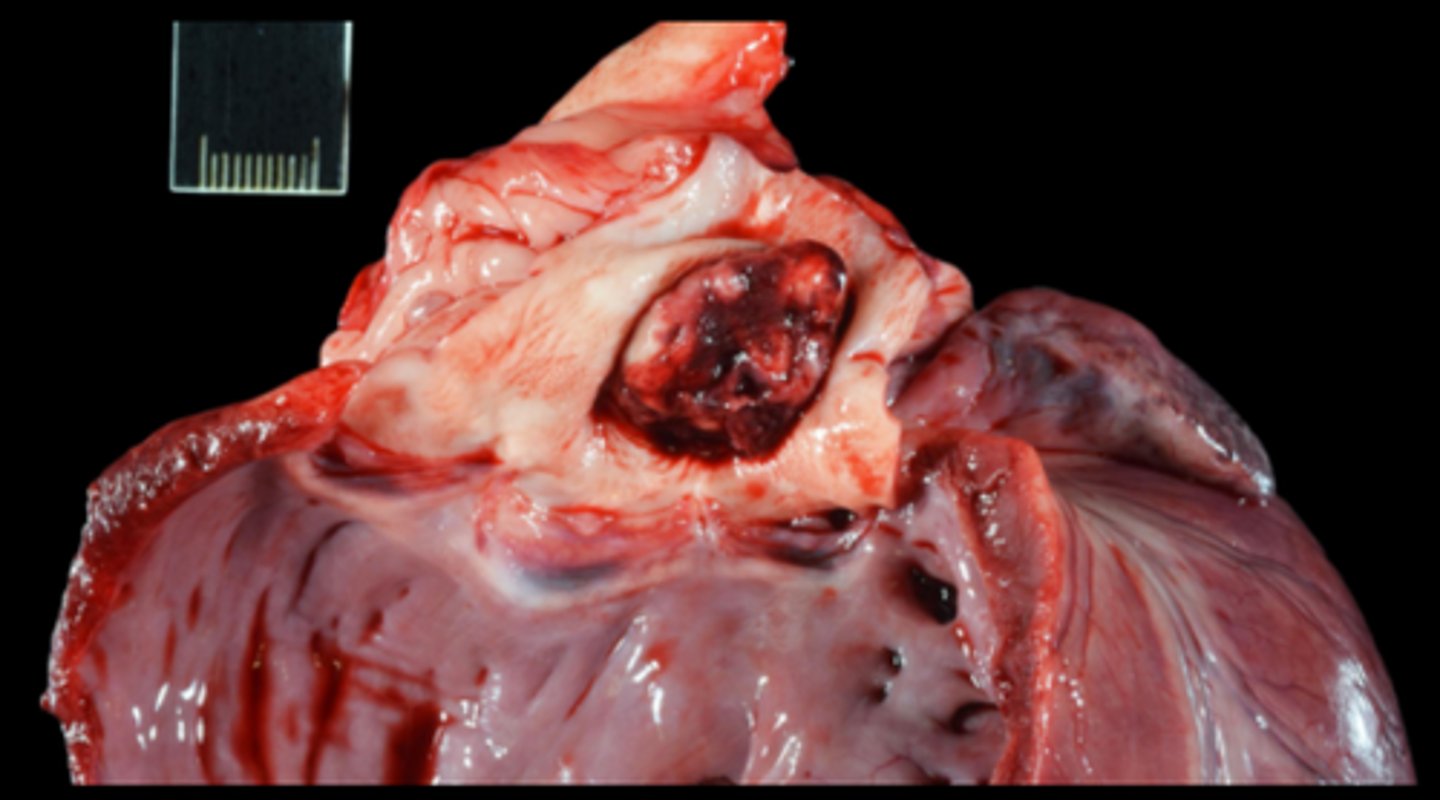
Gross pathology: adult nematodes in pulmonary arteries and right ventricle, right ventricle concentric hypertrophy
Histopathology: Pulmonary arteries and right ventricle endocardium: intimal proliferation, medial hypertrophy and arteritis/ endocarditis (lymphoplasmacytic or eosinophilic), circulating microfilariae seen within alveoli of lungs
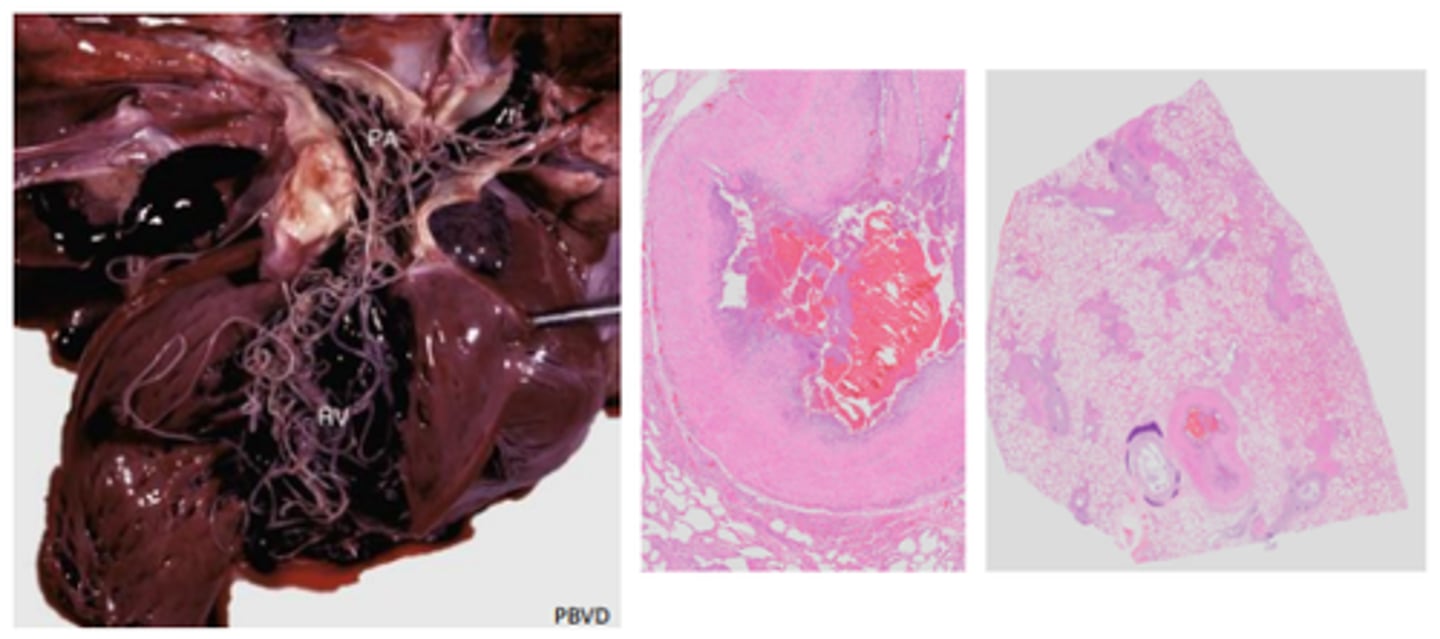
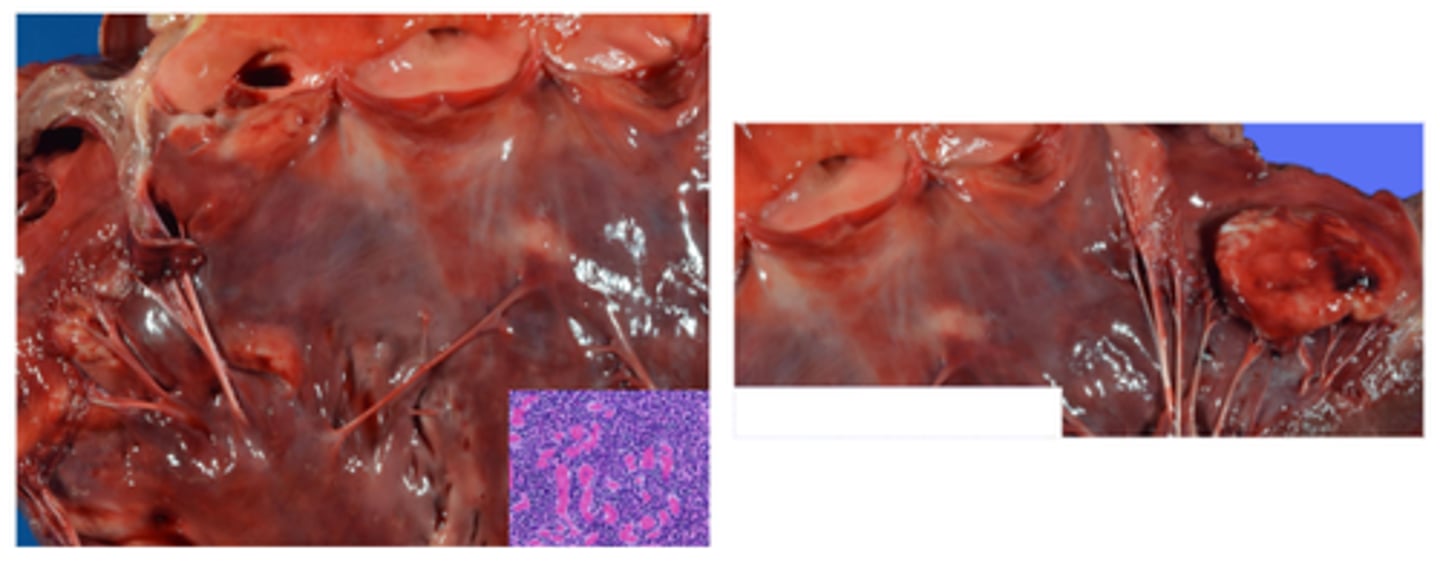
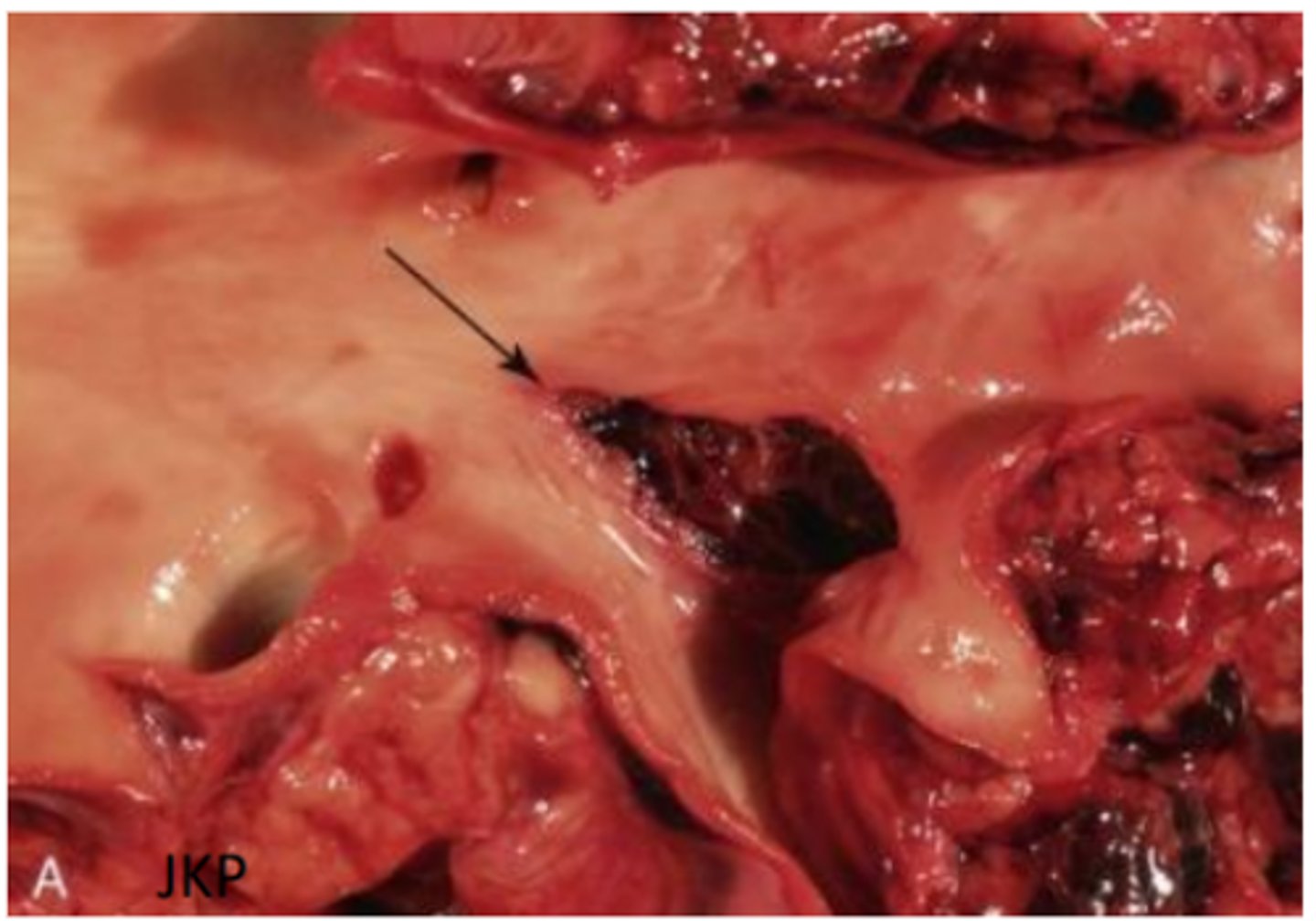
Verminous vascultiits
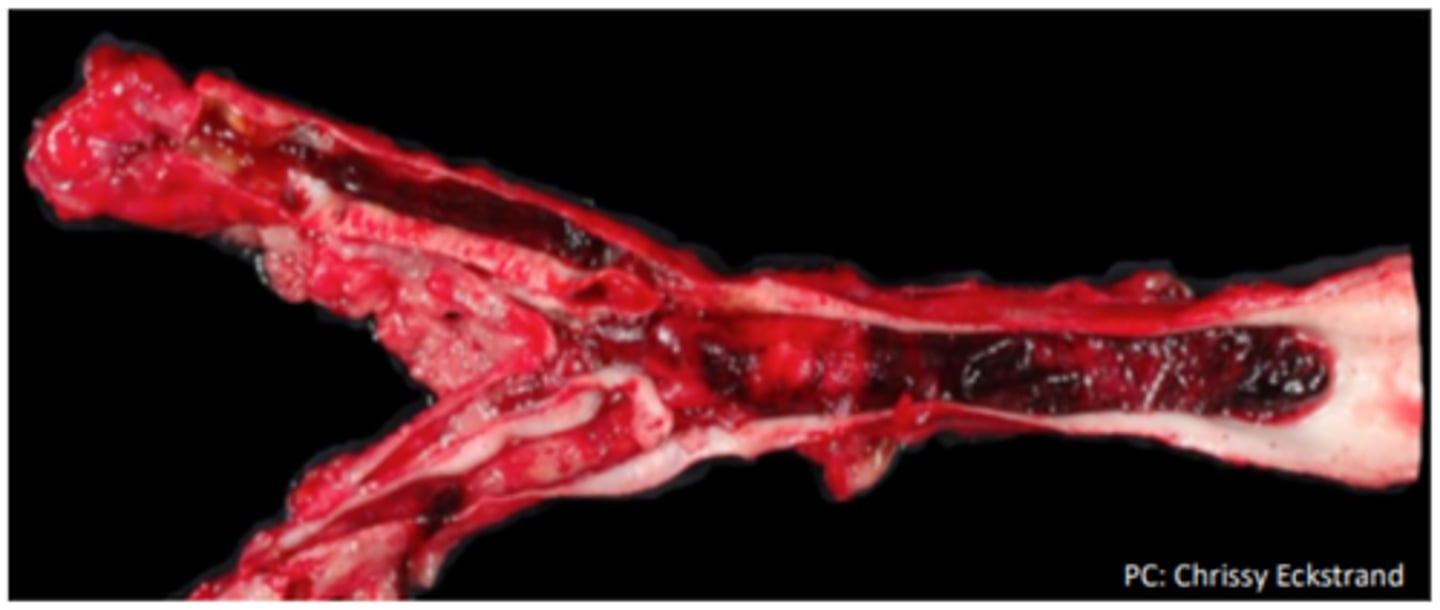
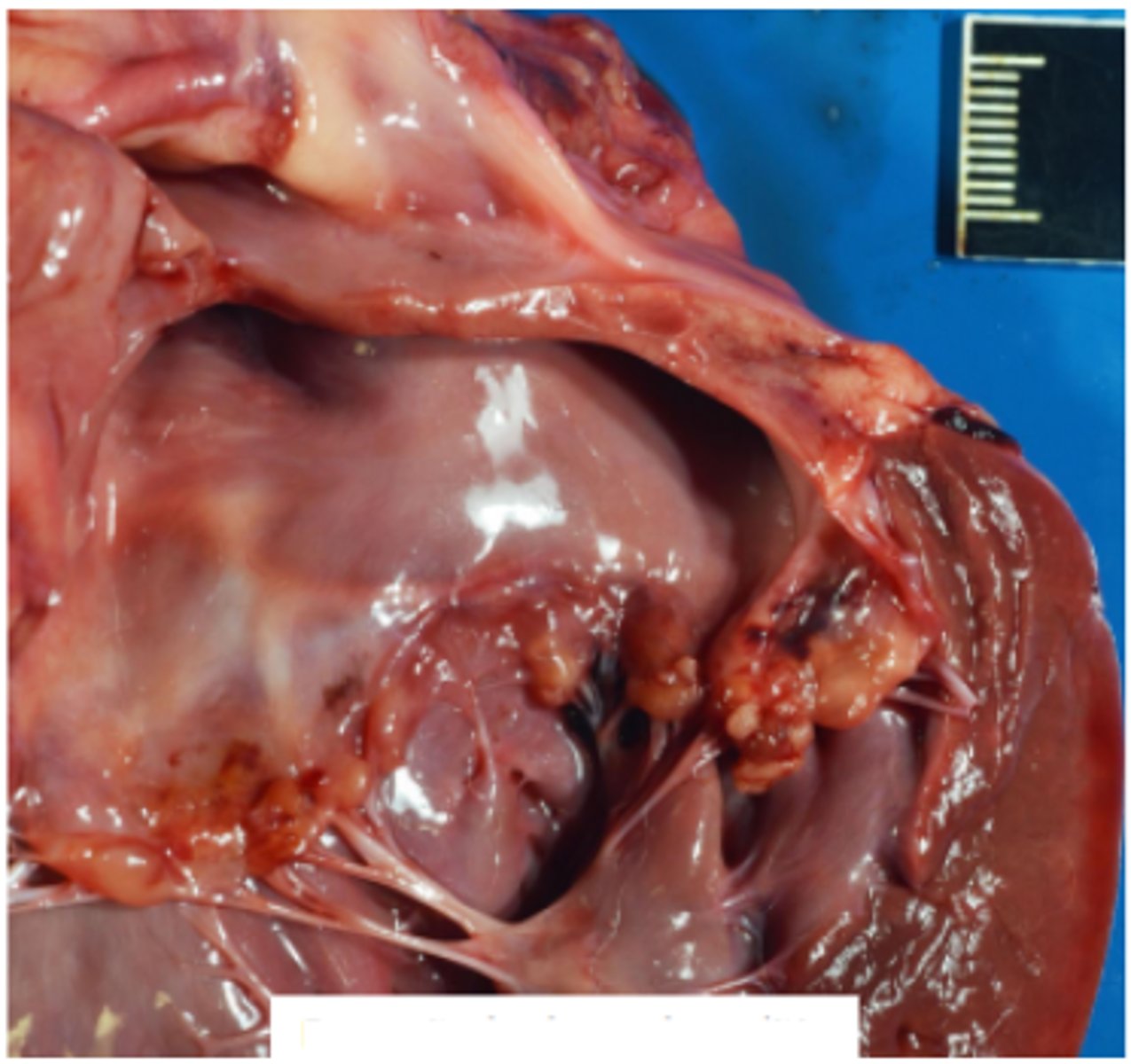
Dog heart, pulmonary artery thrombus, infarction, multiple pulmonary embolisms
Treated for heartworm 3 years prior - right sided heart failure
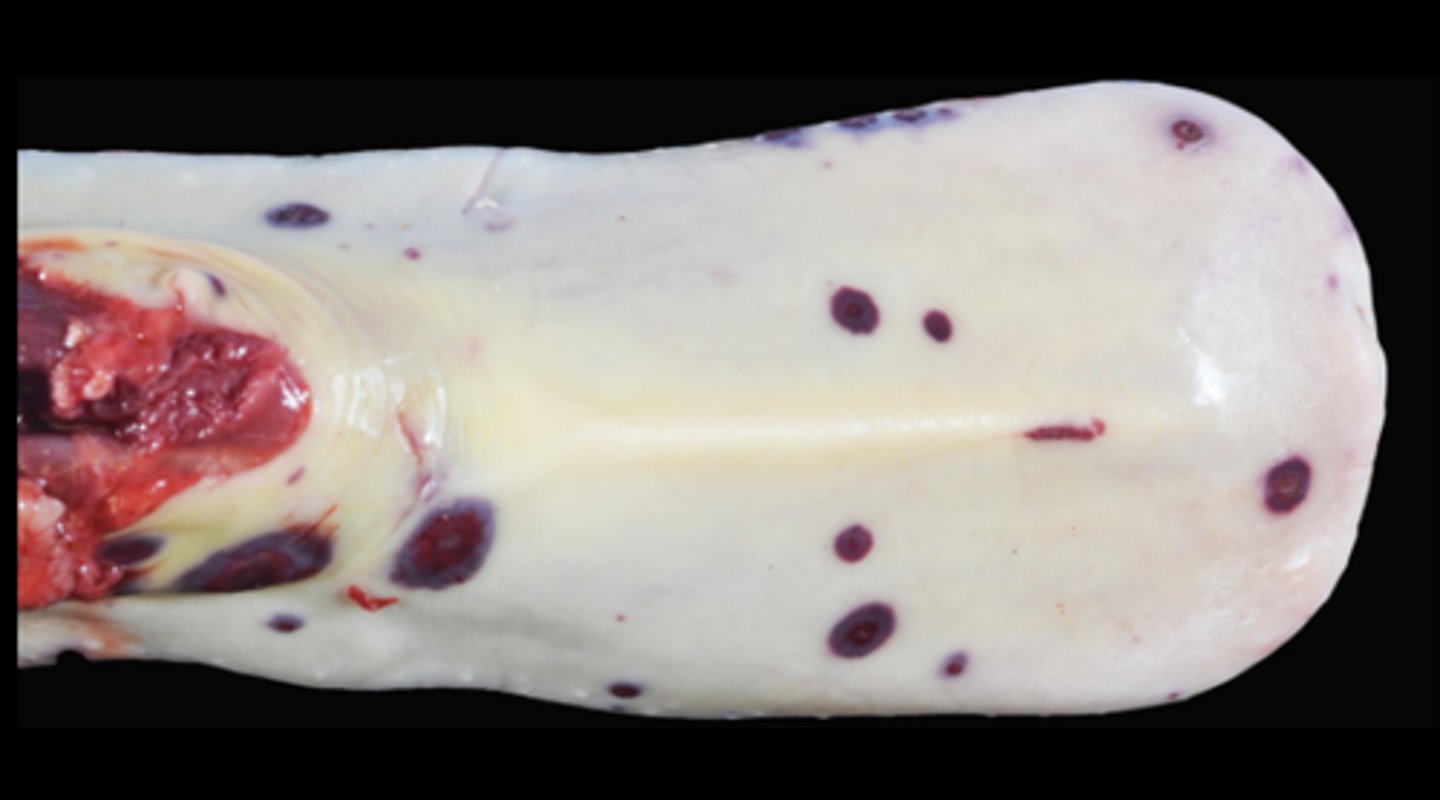
Ecchymosis, haemorrhage, infarction of the tongue, vasculitis
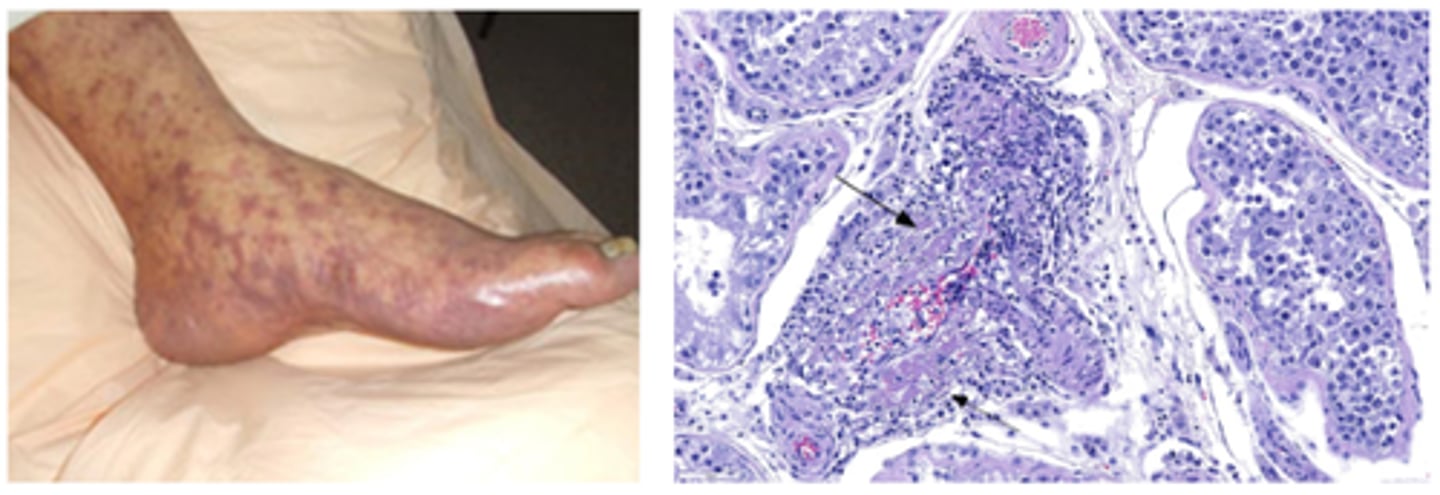
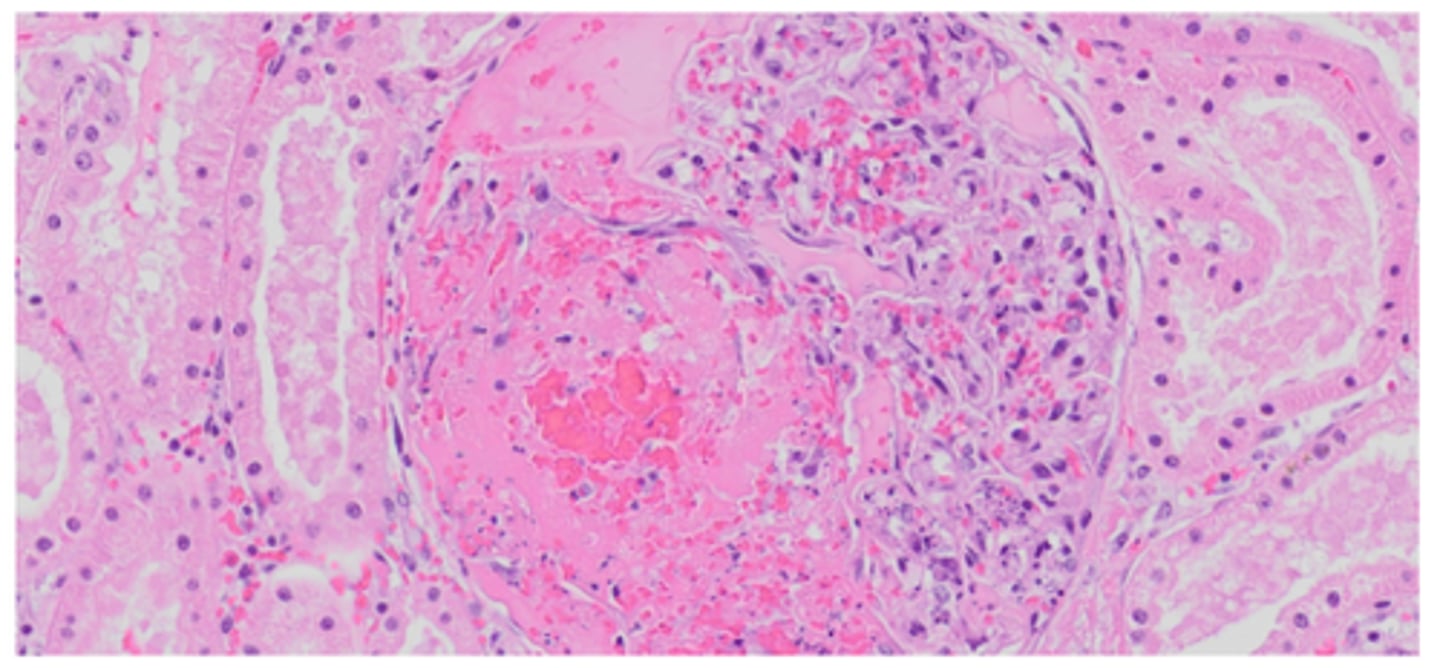
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Glomerular; basophilic stippling
Feline infectious peritonitis - Coronavirus
Phlebitis
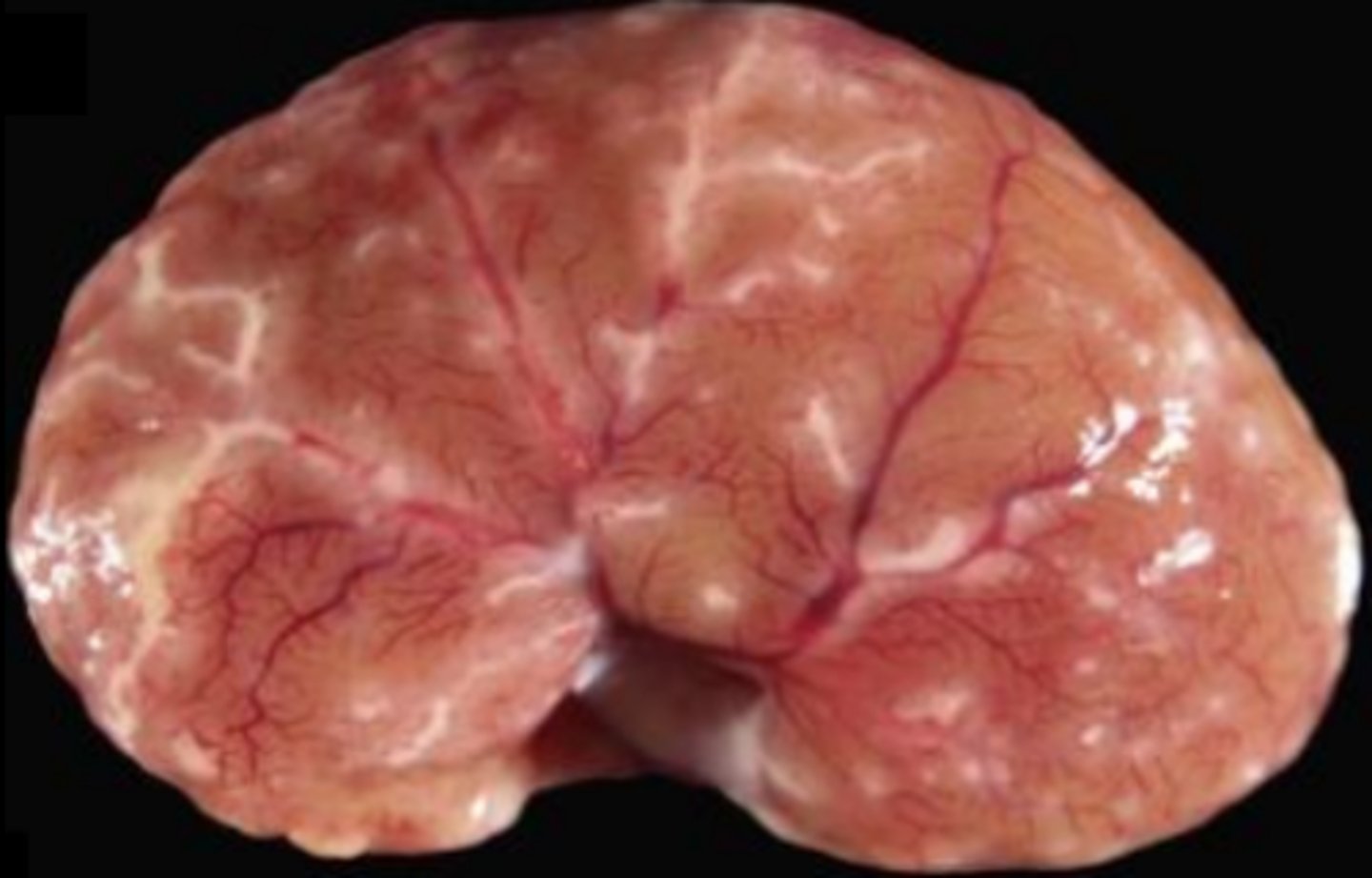
Feline infectious peritonitis
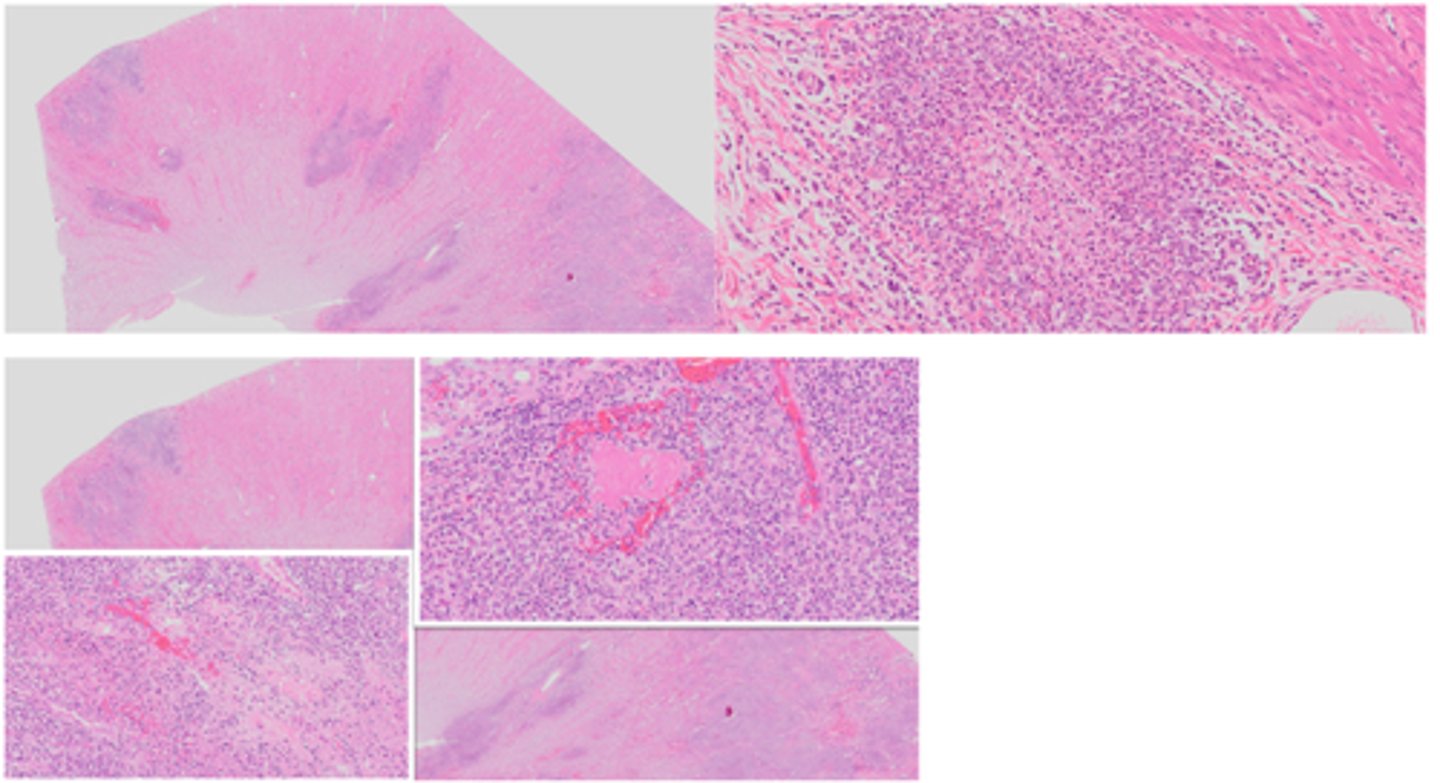
Lymphoedema
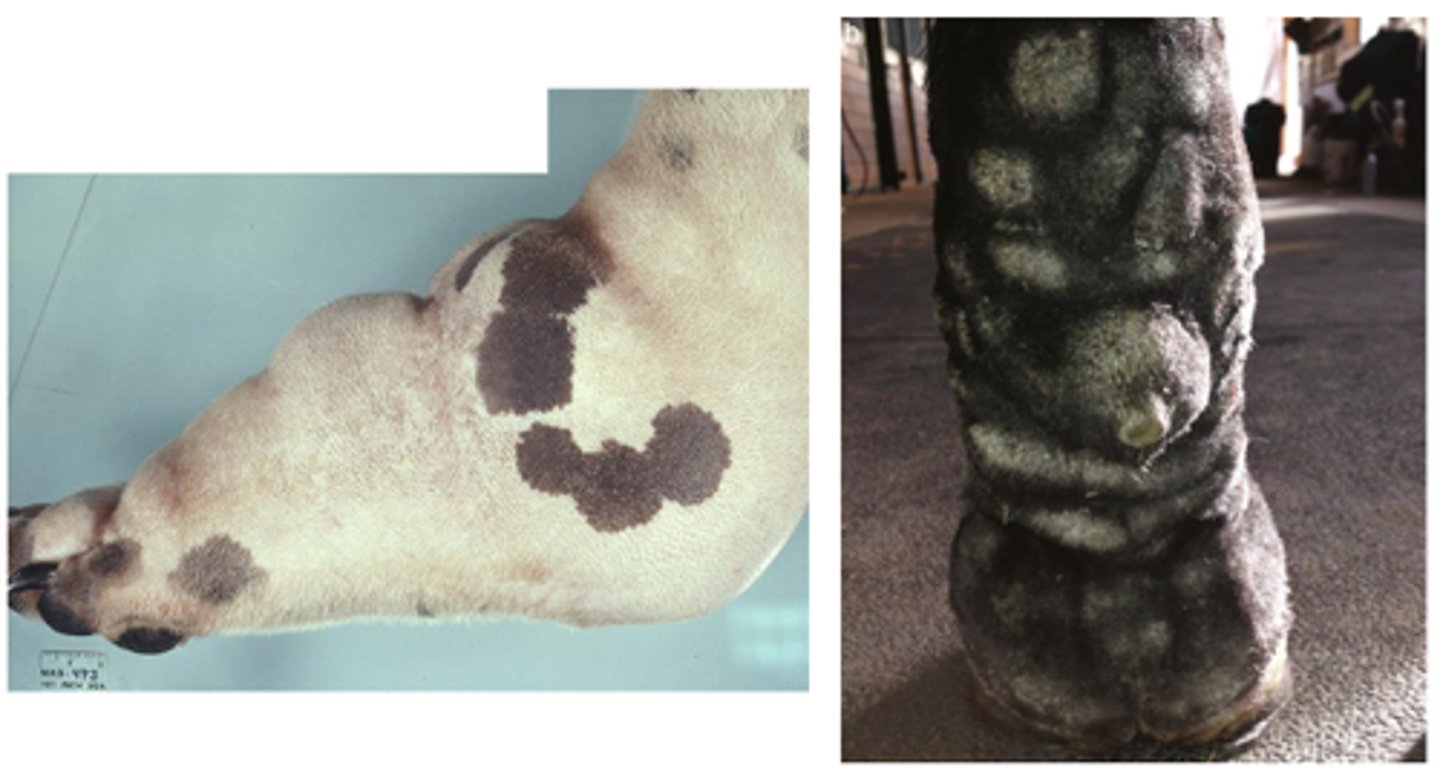
Intestinal Lymphangiectasia
A. Intestinal villi are expanded by ectasia of the lymphatic vessels (raised white areas). Lymphangiectasia can be a congenital developmental disorder of the lymphatic vessels, or it can be acquired secondary to lymph vessel obstruction caused by granulomatous or neoplastic diseases.
B. Lacteals are dilated (asterisks), thus resulting in diminished lymph absorption by lacteals in the lamina propria and subsequent loss of protein (hypoproteinemia) and other nutrients into the intestinal lumen. H&E stain. PBVD
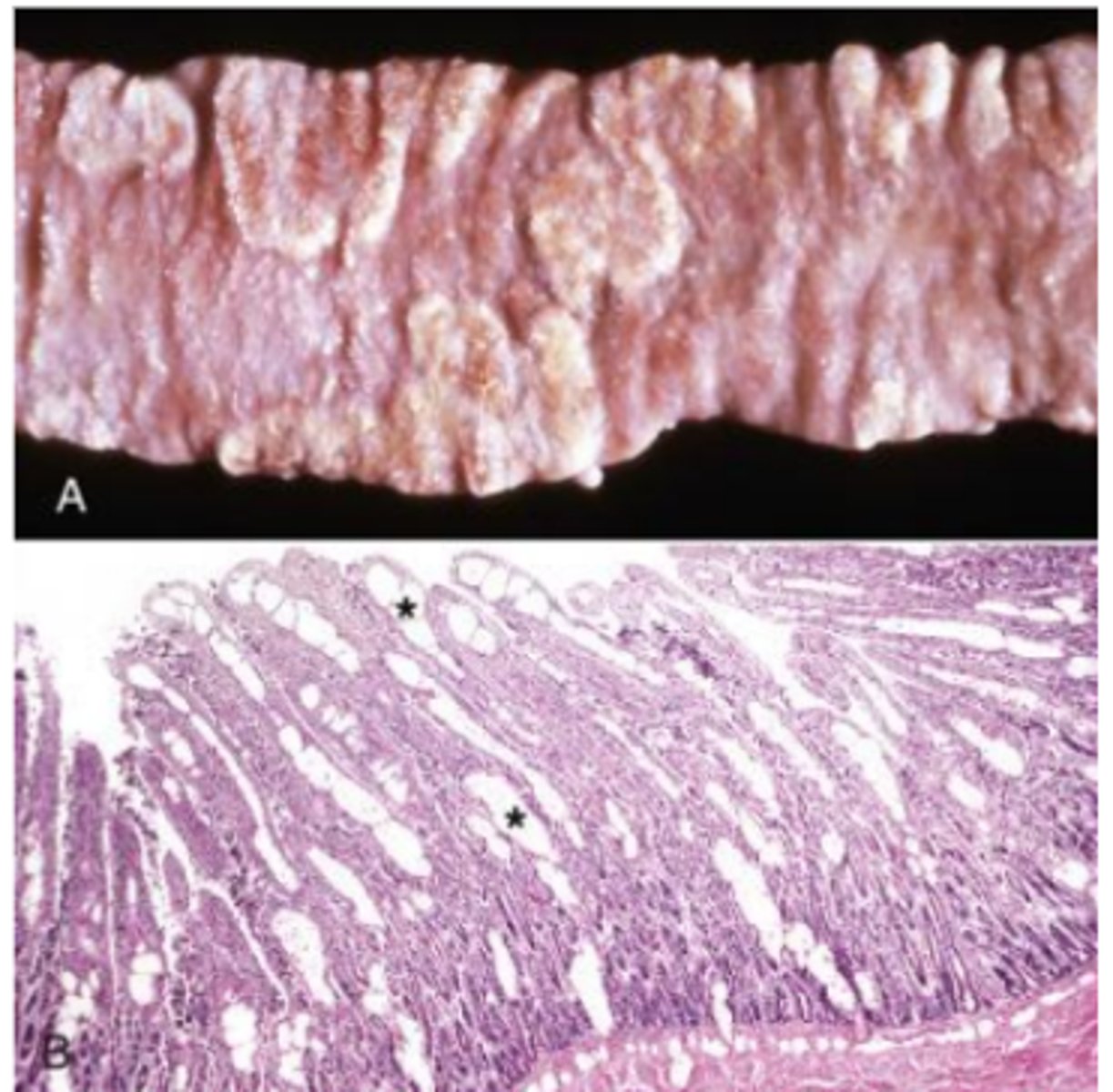
Lymphangiectasia
Granulomatous inflammation
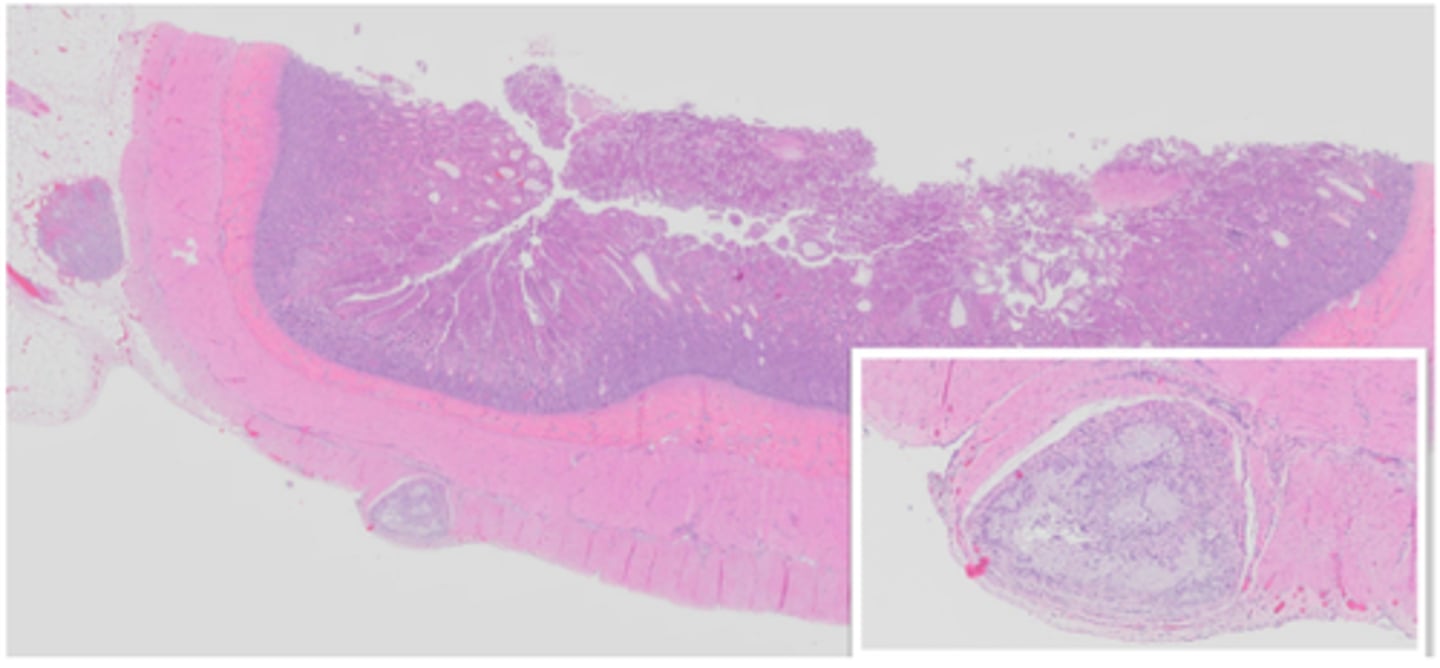
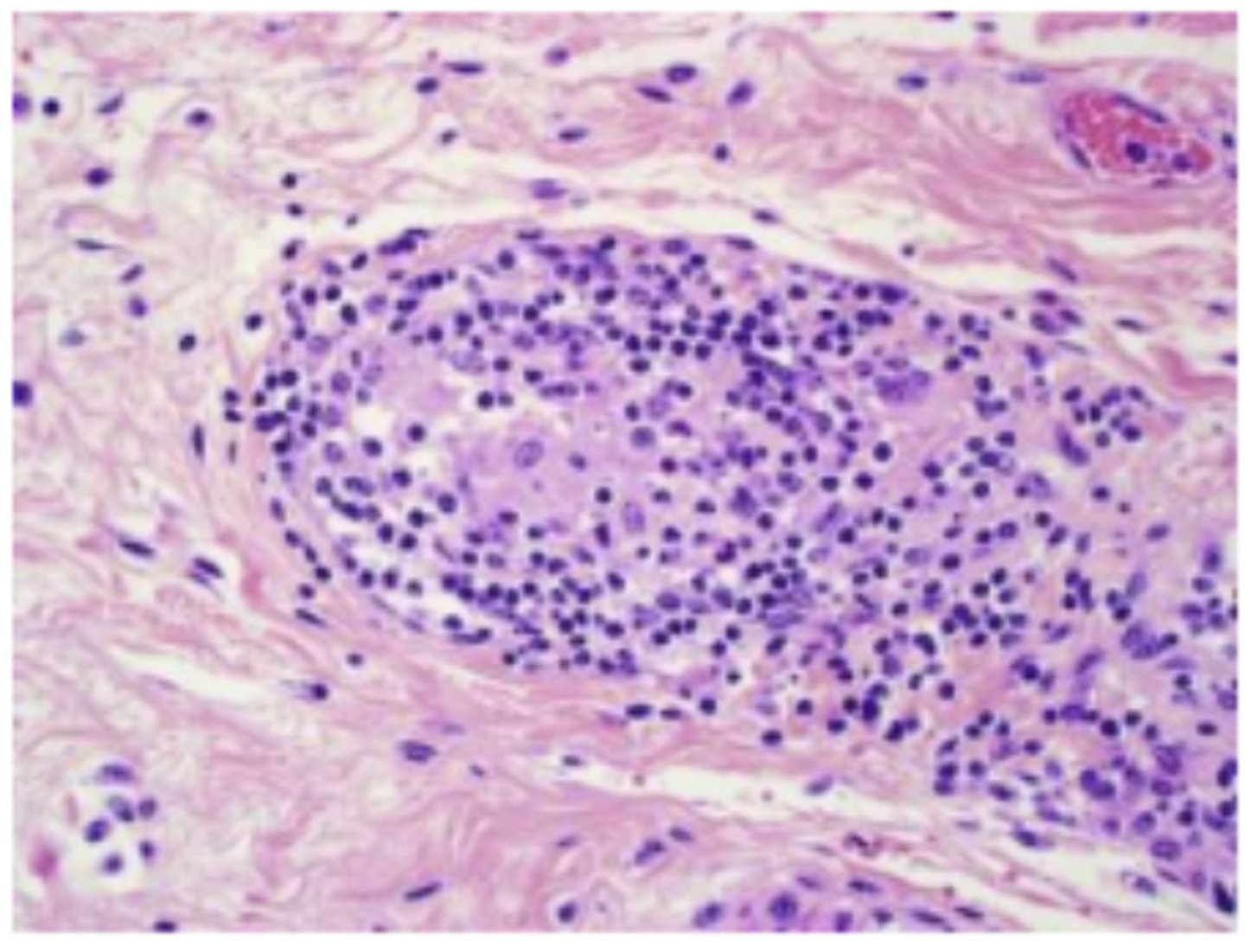
Lymphangitis
Granulomatous lymphangitis in Johne's disease in a cow
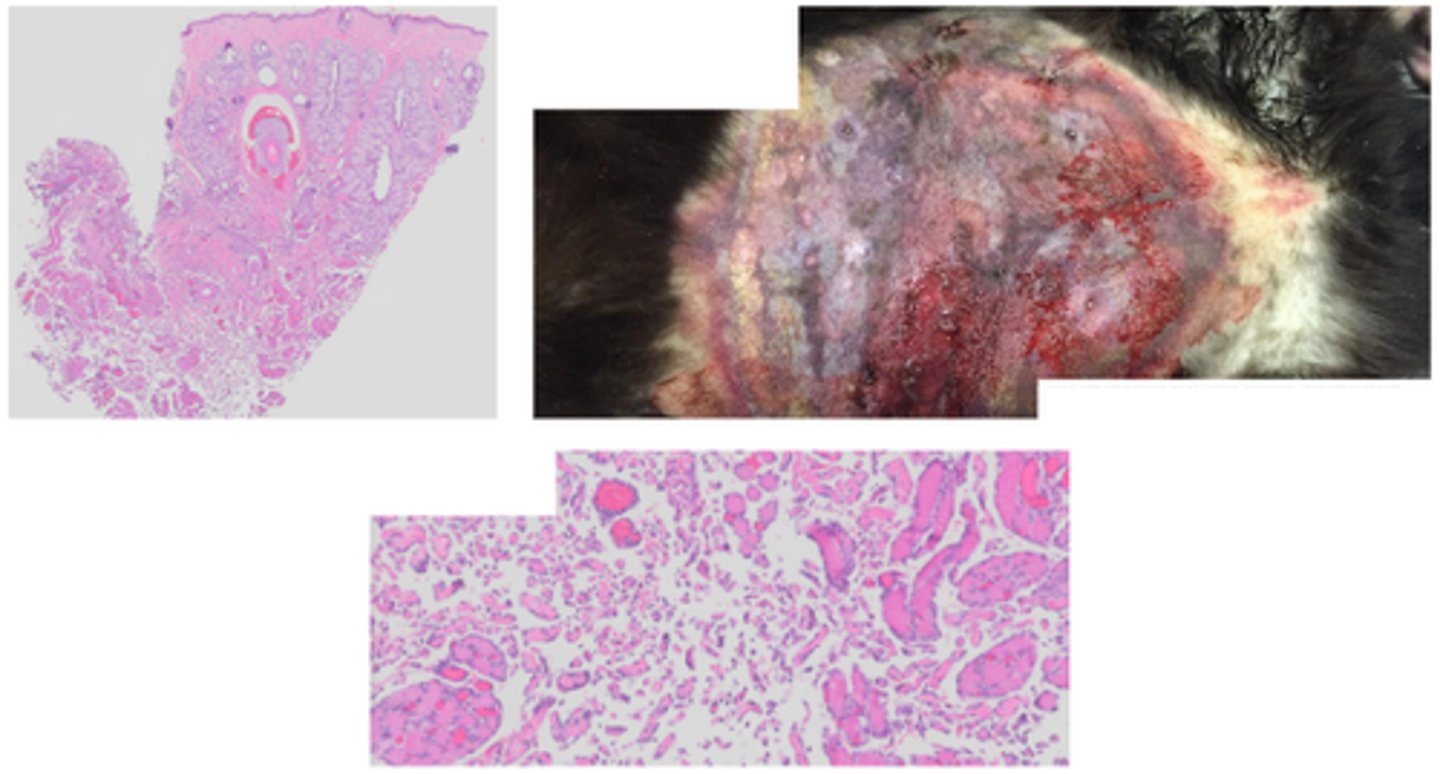
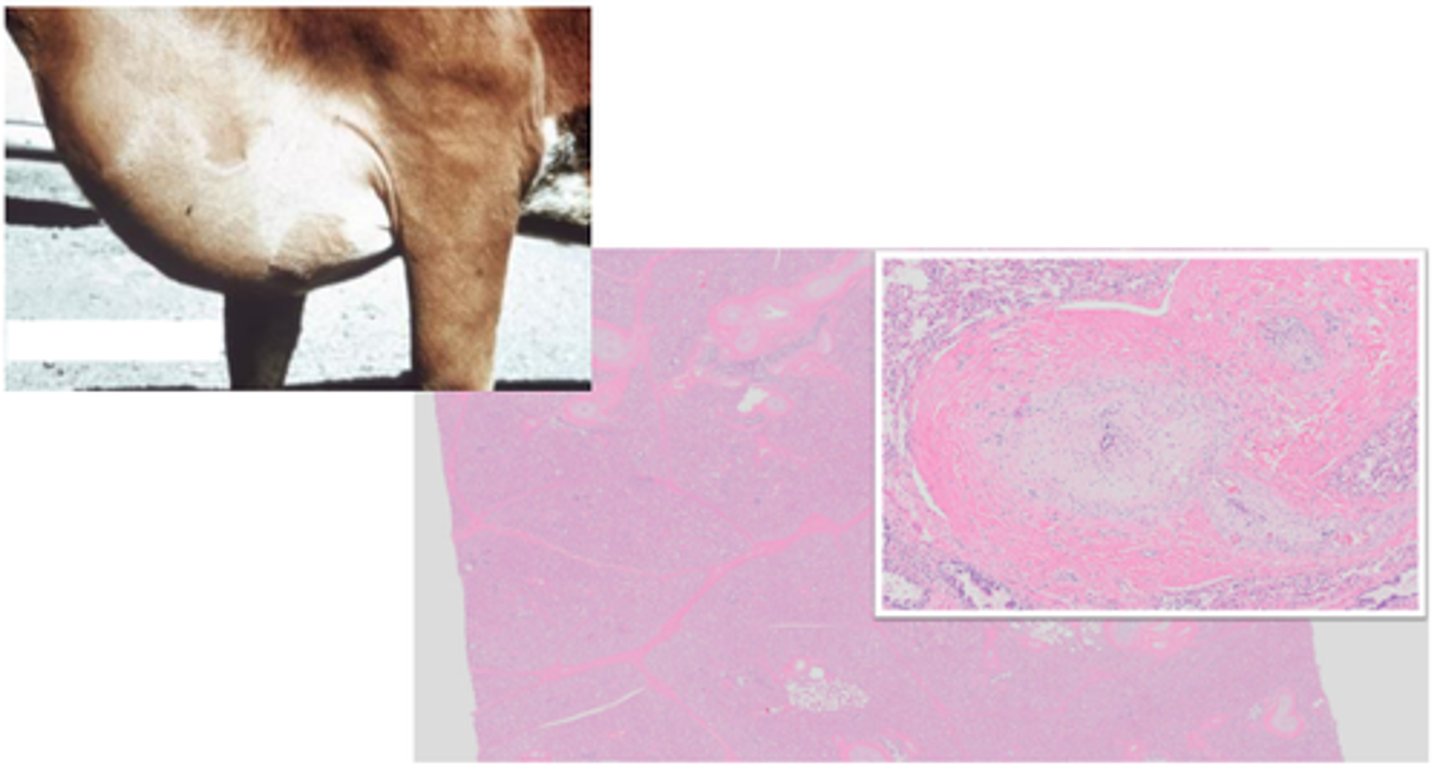
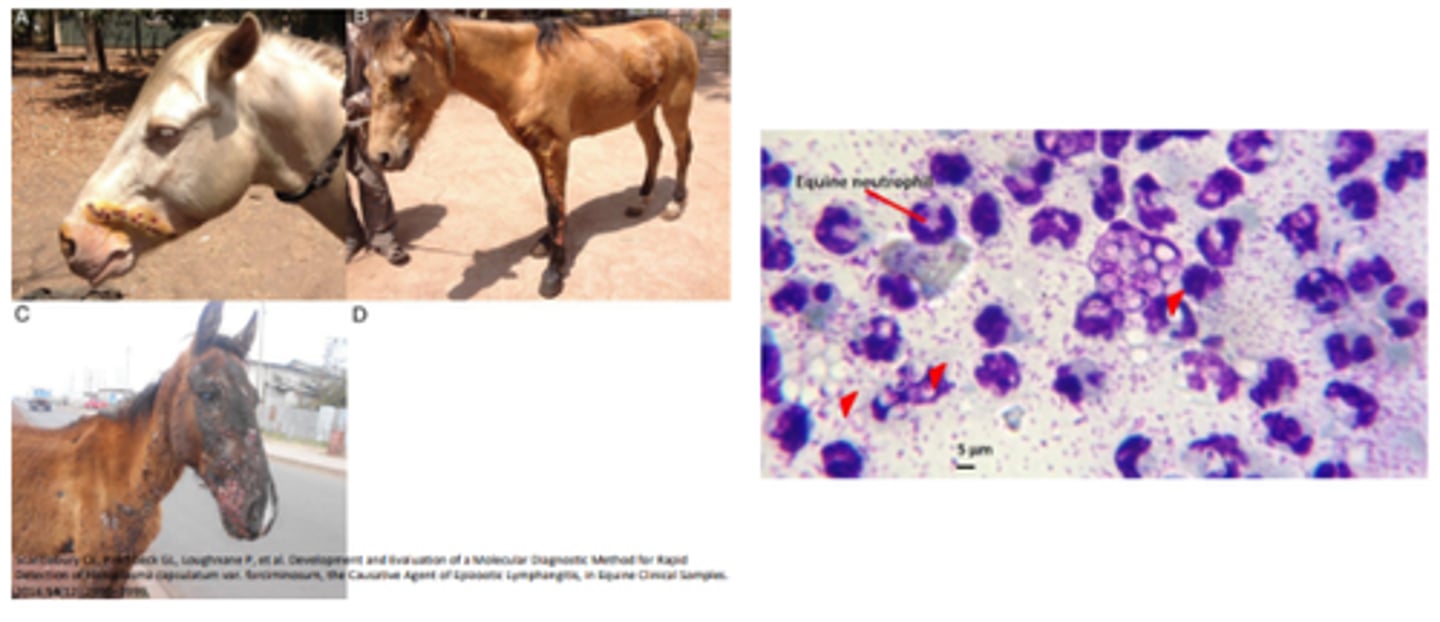
Epizootic lymphangitis (horses and mules)
Histoplasma capsulatum vs histoplasma farcinonosum (HCF)
Pyogranulomatous ulcerative dermatitis and lymphangitis
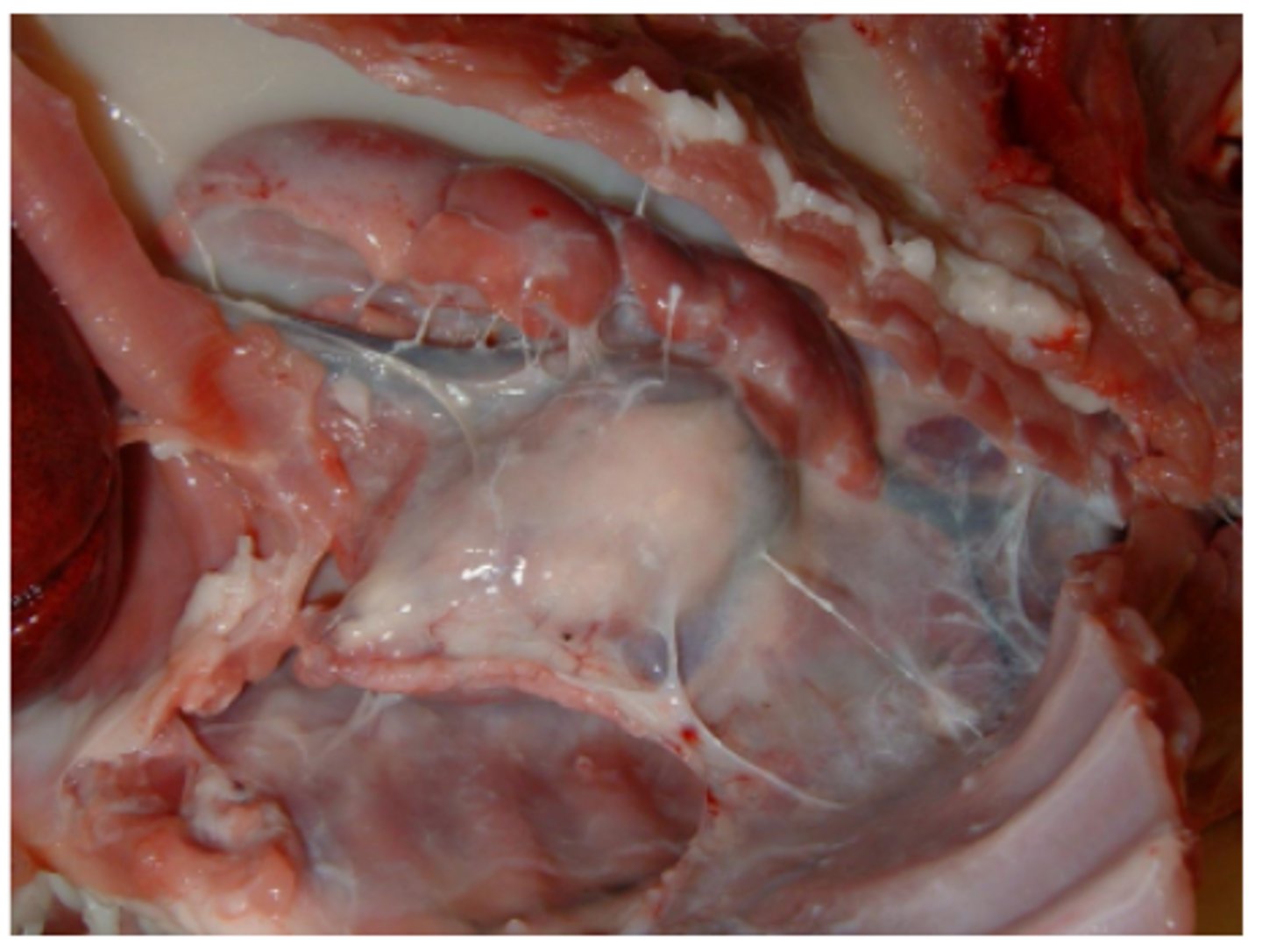
Chylothorax
Chyle leakage or rupture into the thorax
Gross: opaque, thin, white fluid with lipid droplets filling thorax
Lymphangiosarcoma - ventral abdomen
Gross: ill defined area of soft, gelantinous skin with bruised appearance
Histopathology: channels contain few, if any blood cells (VERY similar to haemangiosarcoma)