phys ed studies ATAR 12 - biomechanics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
force
an interaction between two objects
external: gravity, friction, air or water resistance
internal: actions of tendons and muscles
newtons 1st law
a body will continue in its state of rest or motion unless acted upon by a force
law of inertia
inertia: the amount of resistance to change an objects state of motion
newtons 2nd law
the rate of change of acceleration to a body is proportional to the mass of the object
the greater the force applied the faster the acceleration
law of acceleration
newtons 3rd law
every action has an equal and opposite reaction
momentum
the amount of motion passed by a moving body
p=mv
an object can only have momentum if its moving
conservation of linear momentum
the total momentum of two objects before and after are both equal
imperfect elastic collision
not all momentum is conserved, some is lost
most applicable to sport
perfect elastic collision
all or most momentum is lost
no energy is lost to sound or frictions
the momentum of one object is transferred to another with no change in momentum
impulse
the application of force over time to change momentum
force x time
impulse-momentum relationship graphs
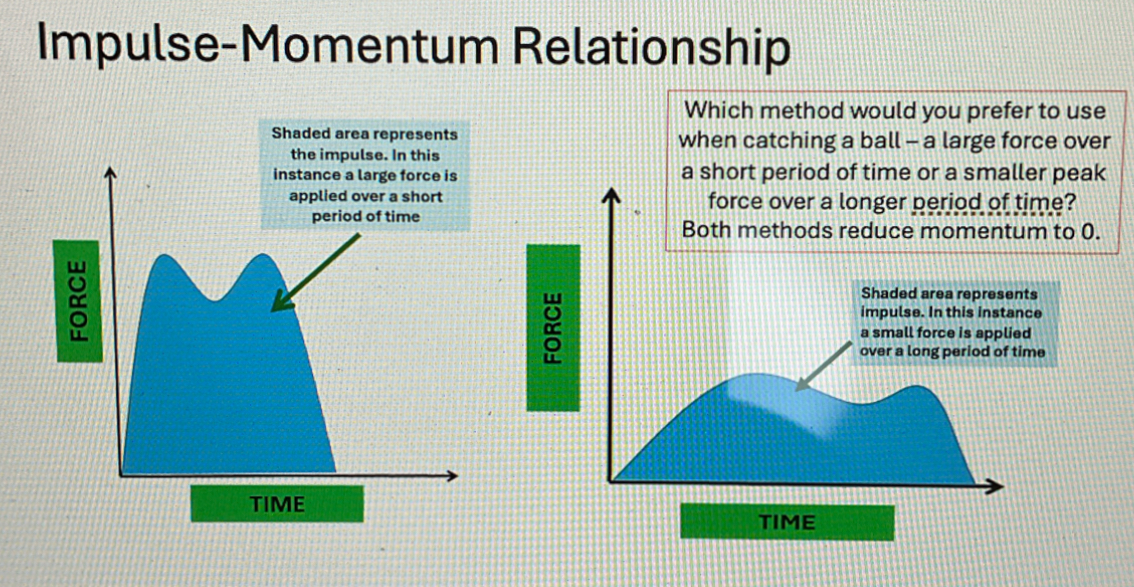
coefficient of restitution (COR)
the amount of energy that remains after an elastic collision
compares height of bounce and the original drop height (0-1)
COR equation - square root of height bounced over height dropped
an object loses energy through noise and friction
COR ratings
1 - represents a perfect elastic collision (rebounds to the same height)
0 - represents a perfect inelastic collision (stops when it hits the surface)
elastic
the property of an object to regains its original shape after impact
3 main factors that affects COR
temperature: as the temperature of the ball increases so does the COR
velocity of collision: when velocity increases the COR reduces because there is a greater compression of the ball - more energy is lost to the collision
equipment and surfaces: condition of the ball - new vs old
material of the ball - rubber is better than a netball
different surfaces - the harder the surface the higher the bounce
material of striking implement - wood causes a lower COR than aluminium
angular motion
all body parts turn on rotation around an axis
full or part circle
how to create angular motion
torque - the amount of eccentric/off centre force (increased force = increase turn)
distance from the centre
torque
a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate
force x perpendicular distance
moment of inertia
the resistance of rotating an objet to change its state of motion
mass x radius of rotation
factors that contribute to moment of inertia
mass
moment arm - distance from mass to axis of rotation
examples of moment of inertia
normal hammer: the mass is distributed away from the axis of rotation (wrist) makes L higher and makes the hammer harder to rotate but produces more force
upside down hammer: the mass is closer to the axis of rotation which lowers L making it easier to rotate
angular velocity
the rate of rotation - how fast an object rotates (W)
factors that affect velocity
moment of inertia: depends on the mass distribution and axis of rotation
applied torque: increased toque increases the change in angular velocity
mass distribution: mass is distributed in relation to the axis of rotation - when mass is closer to the W it increases
initial angular velocity: starting velocity will influence its subsequent W when no additional forces are applied
angular momentum (L)
the measure of the amount of rotation an object possesses
relation to newton: a body will rotate on an axis unless acted upon by external forces
factors that relate to angular momentum
W - angular velocity - increases for angular momentum
L - moment of inertia - decrease for constant angular momentum
they are interchangeable