AST101 Midterm #1
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Mercury
Closest to sun (62.052 million km)
No atmosphere
No moons
Rocky exterior with iron core
Hot&cold temp,
Venus
2nd to Sun (107.52 million km)
Similar size to Earth
Thick CO2 atmosphere
No moons
Rotates backwards & slowly (days = long)
Earth
3rd to Sun (150.22 million km 1 light year), Similar size to Venus, O2 & N2 atmosphere, 23.4-degree rotational tilt.
Mars
4th to Sun (234.12 million km), No sign of life, Thin CO2 atmosphere, 2 small moons, Ice caps
Terrestrial Planets Summary
Closer to the Sun, Small, Rocky, Thin/no atmosphere, Heavier elements, Few moons, Faster orbits around the Sun

Jupiter
5th to the Sun (773.69 million km)
Largest planet in solar system
Thick gaseous atmosphere
Non-visible rings
Many moons
Saturn
6th to Sun (1.4282 billion km)
2nd largest planet
Structure similar to Jupiter
Visible rings
Many moons
Uranus
7th to Sun (2.9173 billion km)
Coldest planet
Small rocky core
Thick H2 & HE atmosphere
Axial tilt 98 degrees
Thin rings
Lots of moons
Neptune
8th to Sun (4.4706 billion km)
Furthest planet from the Sun,
Structure similar to Uranus,
Axial tilt 28 degrees,
Has surface features,
Strongest winds
Jovian Planets Summary
Gas & Liquids
Many moons
Mainly light elements
Slower orbit around the Sun.
The Moon’s Orbit
Tipped about 5 degrees in comparison to the Ecliptic Plane.
This is what causes Eclipses to not be monthly.
Orbits in the same direction as the planets.
Dwarf Planets
Pluto, Ceres, Haumea, Quoar, Makemake, Gonggong, & Eris
there could be hundreds more that are unidentified
Asteroid Belt
Surrounding the Terrestrial Planets (between Mars and Jupiter)
A ring where most of the asteroids in our Solar System are found orbiting the Sun
Total mass is around 3% of the Moon’s.
Kuiper Belt
Surrounds the Jovian & Terrestrial planets (beyond Neptune)
A ring of asteroids, comets, and other icy bodies that orbit the sun beyond Neptune
Includes several of the Dwarf Planets
Comets
Smaller icy bodies from the outer solar system, cosmic snowballs of frozen gases, rock, and dust that orbit the Sun
Earth’s Axial Tilt
Tipped in relation to the orbital plane 23.4 degrees
The reason for the Seasons
Sun’s Rays
Impacted due to Earth’s axial tilt, the seasons are affected based on the directness of the sun’s rays. Steep angle = more direct & hotter, Shallow angle = less direct & colder
Ecliptic Plane
The imaginary plane containing the Earth’s orbit around the Sun
The Celestial Sphere
A model for the two-dimensional direction to the stars, sun and moon as viewed from a particular place on earth
Points on Celestial Sphere
Zenith (directly above an observer on Earth), Celestial Poles, Celestial Equator, Ecliptic
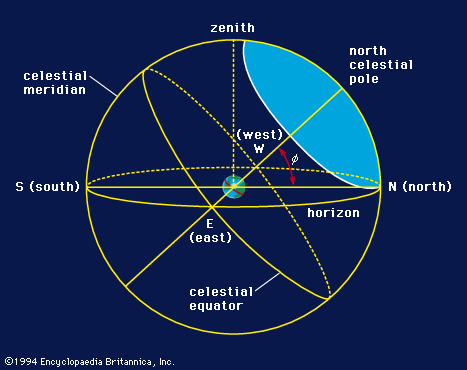
The Ecliptic
The apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of the year
Constellations
People mapped constellations (patterns) onto the stars, representing different things. They differ as the seasons change because the light changes (Ex: on Dec. 21, Sagittarius is the most visible constellation).
Moon Phases
Determined by which part of the Moon is illuminated from the Earth. The phase we see is dependent on where the Moon is compared to the Sun.
Phases are best seen in the middle sections of their rising&setting times
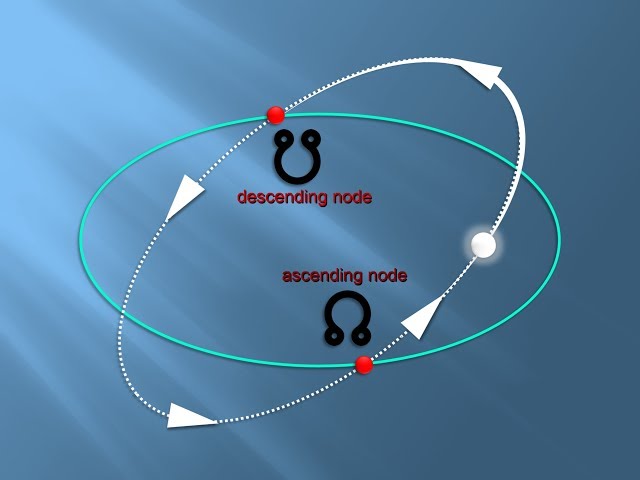
Nodes
When the Moon passes the Ecliptic Plane at the right time, causing Eclipses. This happens about every six months.
New Moon
When the Moon is lined up in front of the Sun/in the direction of the Sun
Unlit side faces the Earth
When Solar Eclipses can happen
Rises 6AM and sets at 6PM

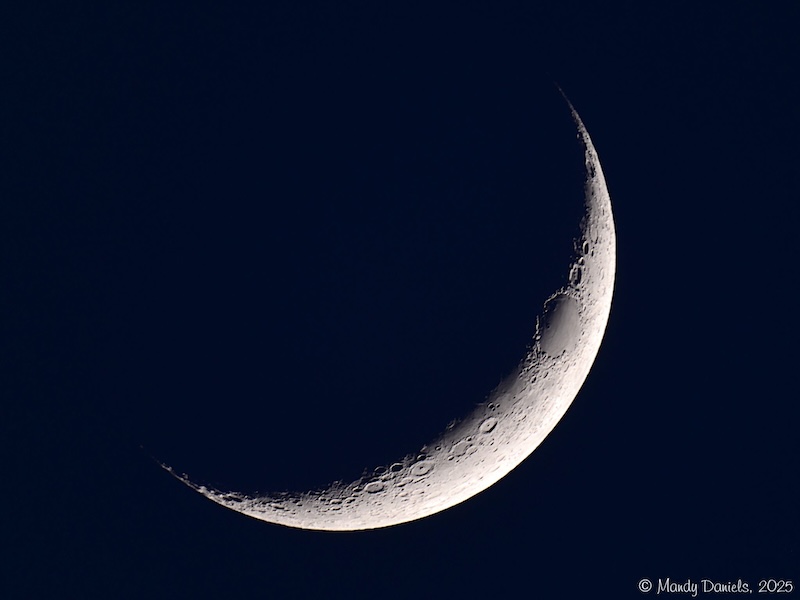
Waxing Crescent Moon
Seeing mostly the dark side of the Moon
Rises 9 AM, sets 9 PM

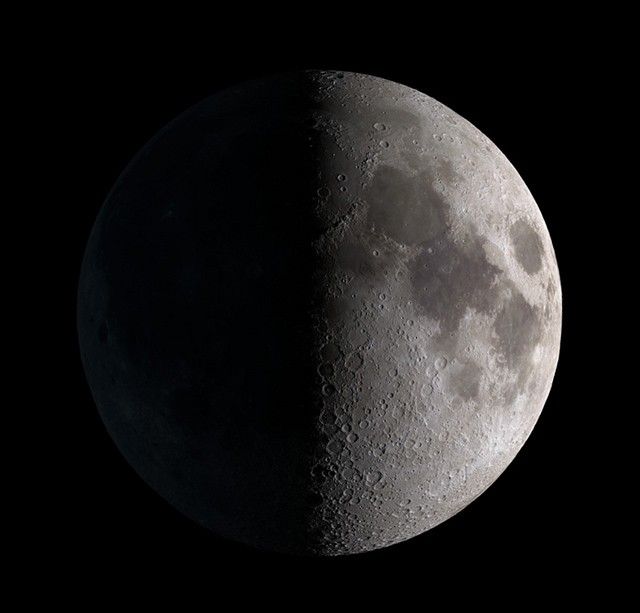
First Quarter / Waxing Quarter Moon
A quarter of the way around it’s orbit
Half Moon
Rises 12 PM, sets 12 AM

Waxing Gibbous Moon
Starting to get behind the Earth, so we are seeing more of the Moon
Rises 3 PM, sets 3 AM
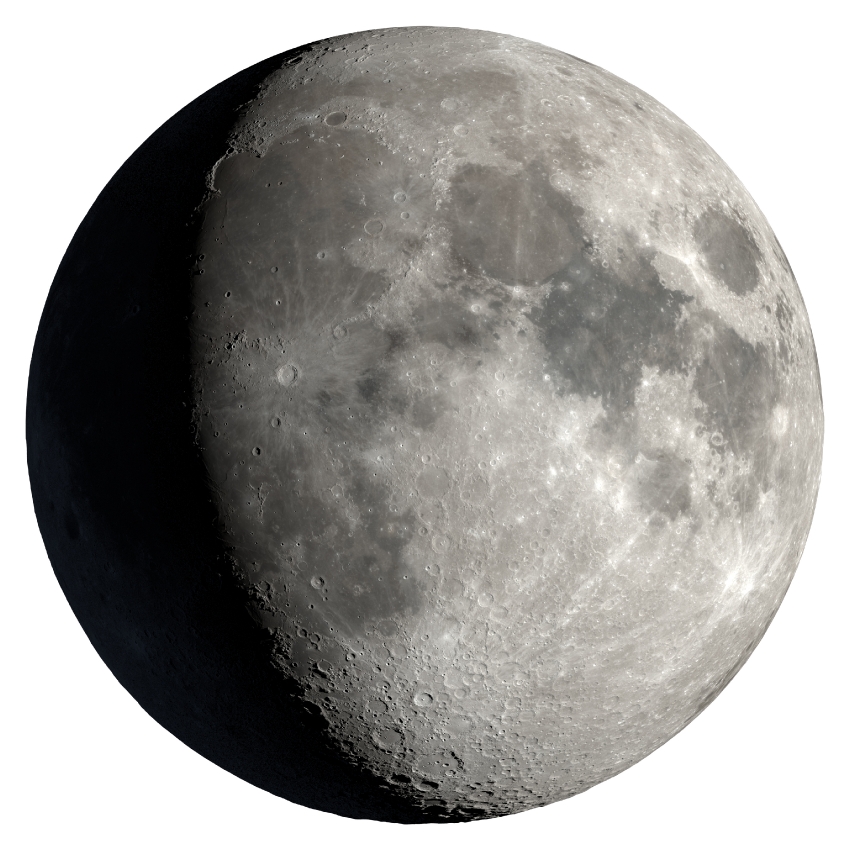

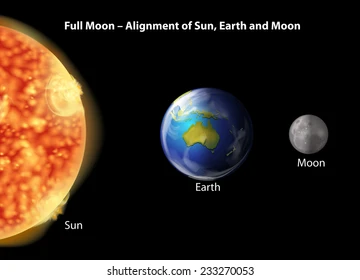
Full Moon
Lunar Eclipse is possible
Moon is behind the Earth, below the Ecliptic
The Sun, Earth, and Moon are lined up
Rises 6 PM, sets 6 AM
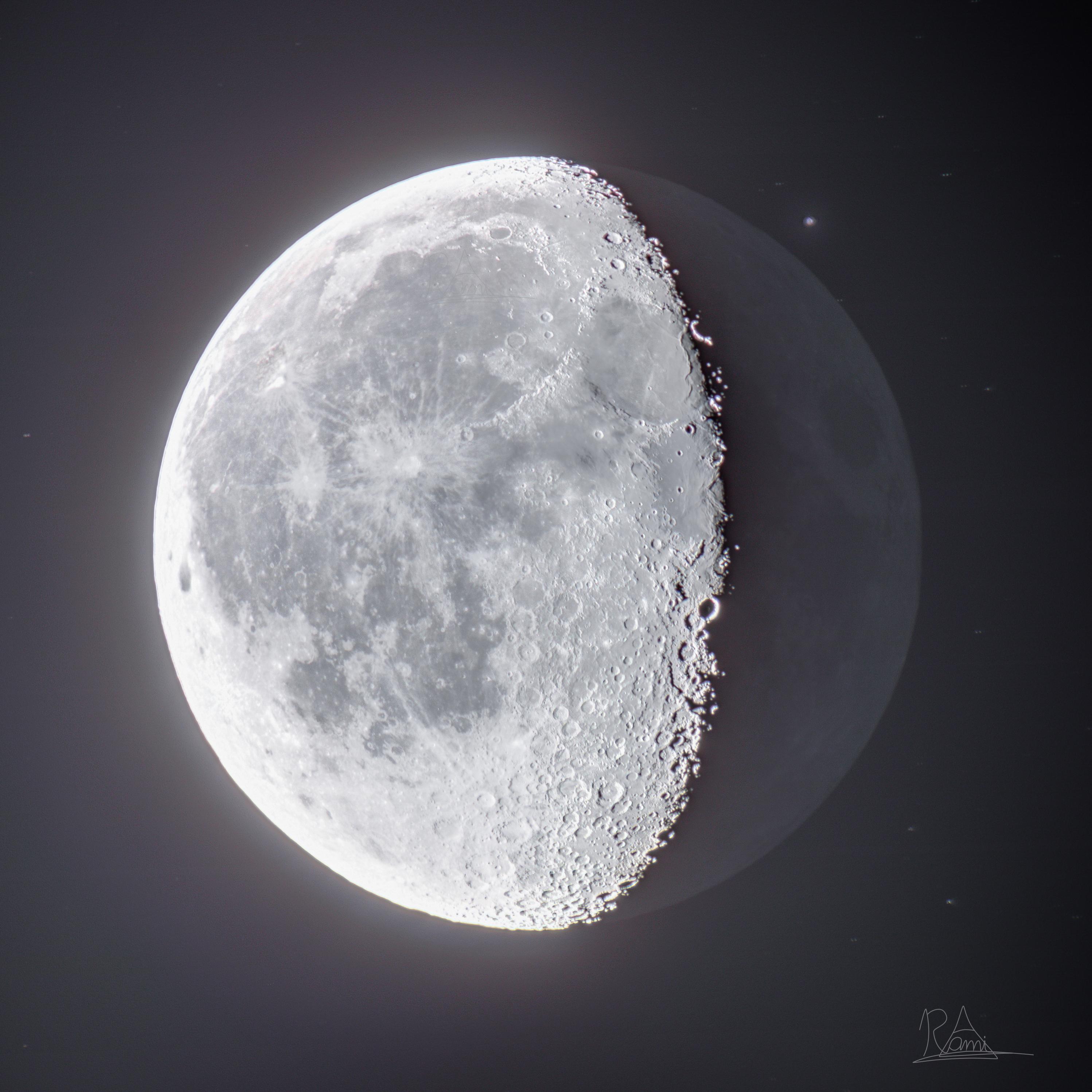
Waning Gibbous Moon
Coming around the Earth now
“Midnight” or “Late-night” Moon
Rises 9 PM, sets 9 AM

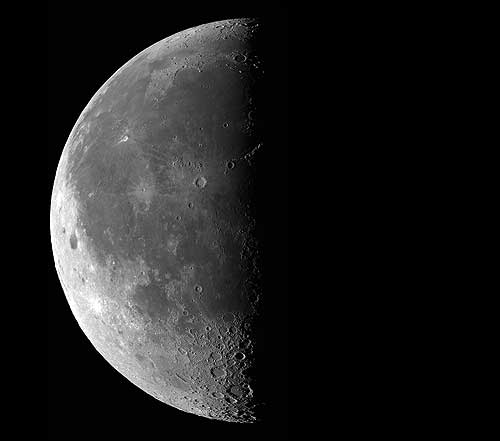
3rd / Waning Quarter Moon
Half Moon
3/4s around it’s orbit
Rises 12 AM, sets 12 PM

Waning Crescent Moon
Rare to see
Rises 3 AM, sets 3 PM
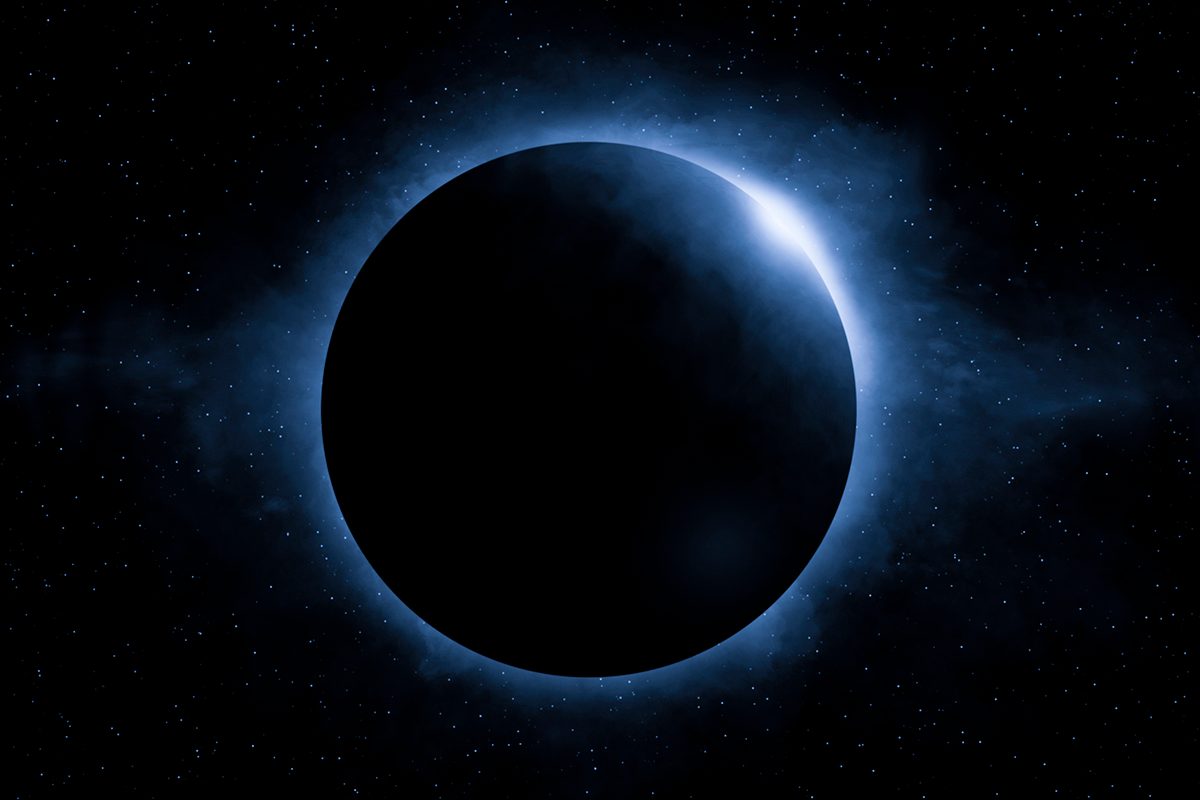
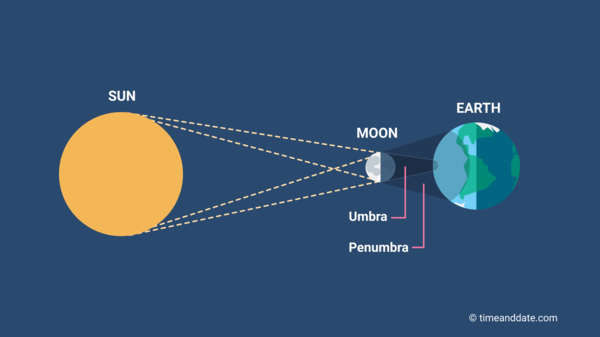
Solar Eclipse
Happens during a New Moon
When the Moon blocks the light from the Sun
Earth, Moon, Sun
Happens only when the New Moon crosses the Ecliptic Plane (Node)
Casts a shadow on a small part of the Earth (only a specific area/region will experience a full Solar Eclipse/full shadow)
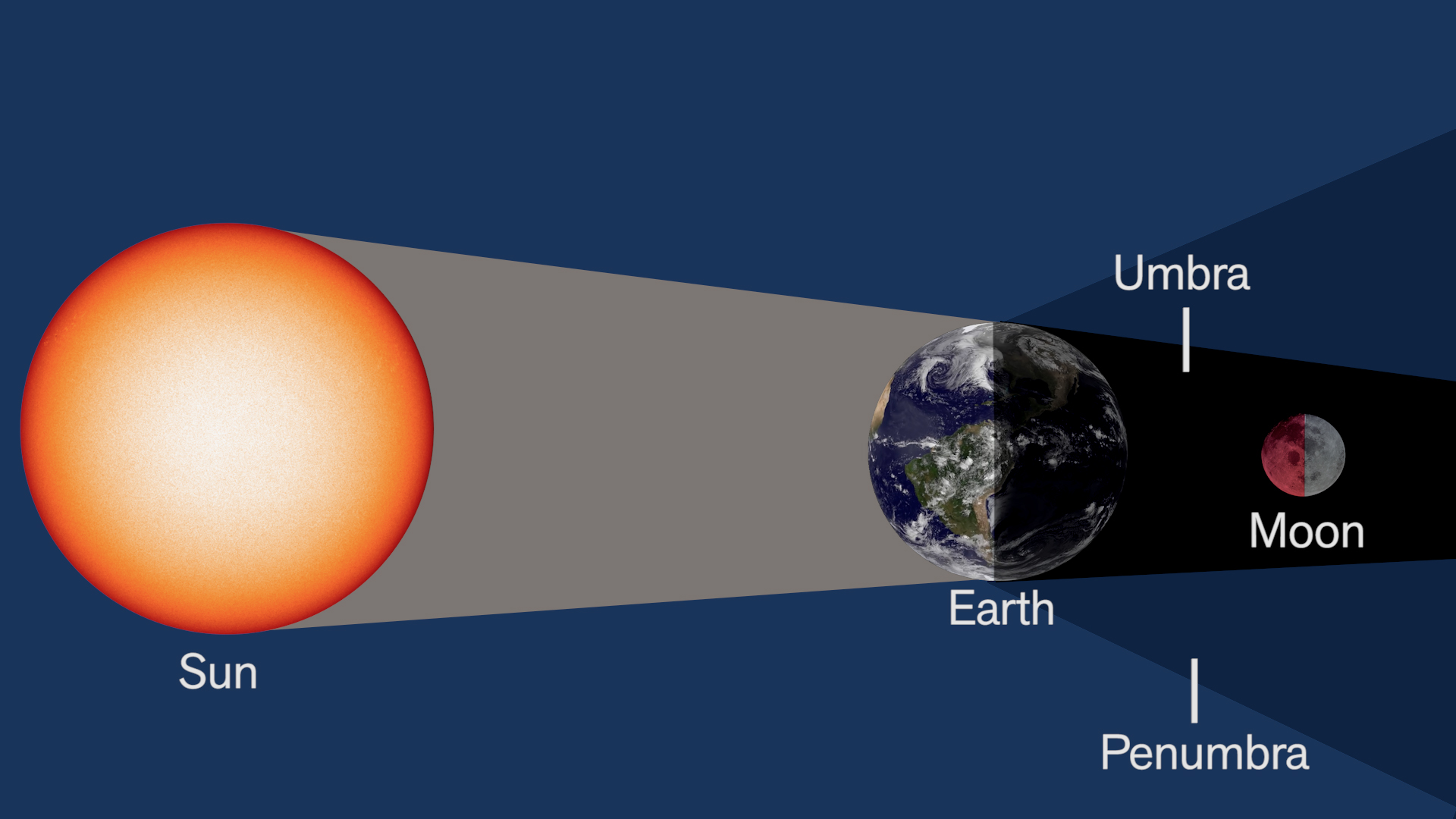
Lunar Eclipse
Happens during a Full Moon
Blood Moon
When the Moon enters the Earth’s Shadow
Moon, Earth, Sun
Happens only when a Full Moon crosses the Ecliptic Plane (Node)
You can see it from everywhere on Earth
More common than a Solar Eclipse
Pre-Copernicus
Earth was the center of the Universe
Everything revolves around the Earth in circles
Retrograde Motion
Copernicus
An illusion created when we observe other planets from the moving planet of Earth
Backwards motion
As Earth passes Mars, the position of Mars compared to the stars changes
Used to explain the motion of the planets in the sky
When Earth passes Mars, which means it’s moving faster, it happens
Copernicus
New theory: Sun is the center of the Universe
Apparent Retrograde Motion
Earth orbits faster than Mars, making it look like Mars is orbiting in the opposite direction
Tycho Brahe
Precise measurements of Mars
Parallax
Measurement of distance to nearby stars
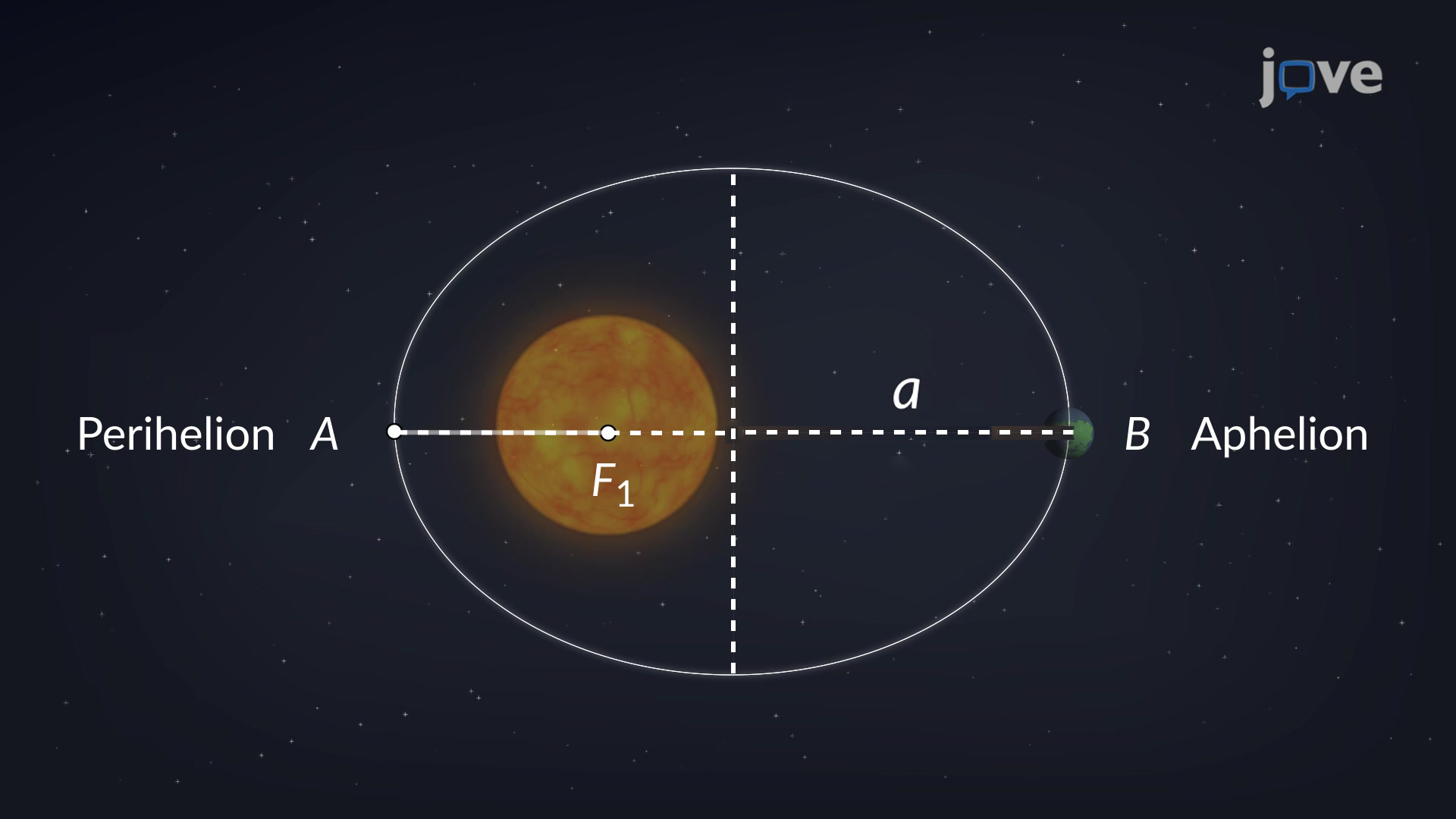
Kepler’s 1st Law
The orbit of each planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus
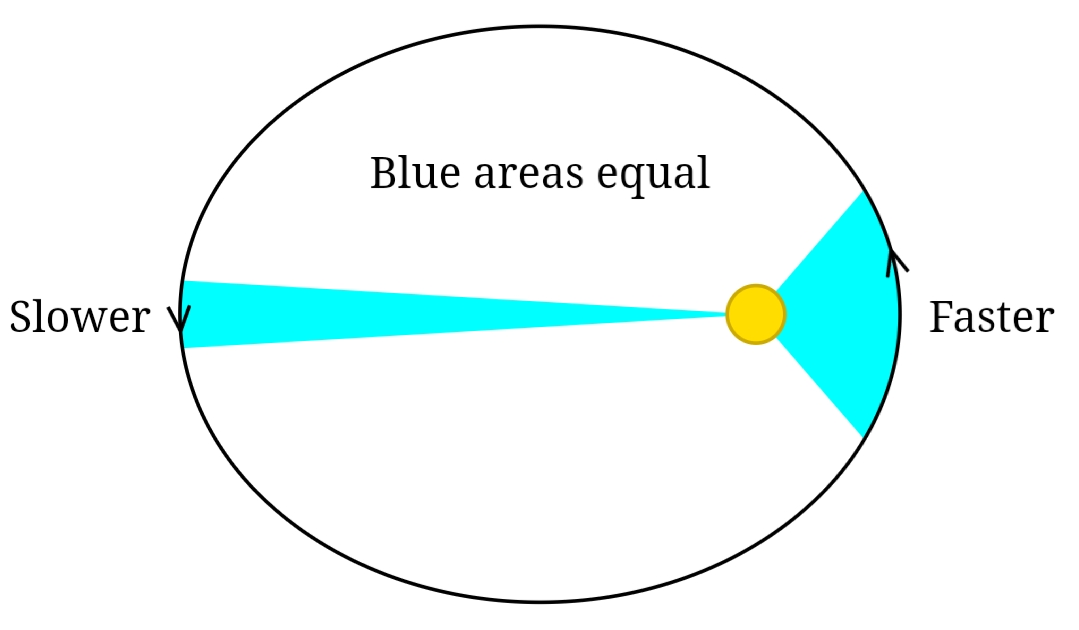
Kepler’s 2nd Law
A planet moves faster in the part of its orbit nearer to the Sun and slower when farther from the Sun, sweeping out equal areas in equal times.
Slower = further away from the Sun
Faster = closer to the Sun
Kepler’s 3rd Law
More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower average speeds, obeying a precise mathematical relationship
An equation that helps us predict each planet’s orbit
Geocentric Model
Earth is the assumed center of the Universe
Heliocentric Model
The Sun is at the center of the Universe
Epicycles
Geocentric model
Spirograph
Circles within circles
Ellipses
Heliocentric model
The Sun’s center is always one focal point
Describing a planet’s orbit about the Sun
Makes it so that the planet’s distance to the Sun is constantly changing as the planet orbits around the Sun
Galileo Galilei
Pioneer in telescopes
Telescope → Moon has craters = Not everything in the heavens are perfect circles and spheres
Telescope → Jupiter has moons = Earth is not the center of the Universe
Telescope → Venus has phases = Venus is orbiting the Sun
Issac Newton
Unified Physics and Astronomy
Laws of Motion
Unified set of rules for both the Earth and the Heavens
Universal Law of Gravitation
Speed
The rate of change of position
e.g., The car is traveling 60km per hour
Velocity
Speed & Direction
e.g., The car is traveling 60km per hour
Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity, how quickly your velocity is changing
e.g., The car, traveling in a straight line, changes speed from 0km/hour to 100km/hour in 9s.
e.g., The car changes from going due north at 60km/hour to going due east at 60km/hour in 20s.
Newton’s First Law
An object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an outside force
If there was no force, it wouldn’t stop
Newton’s Second Law
Acceleration is proportional to Force and inversely proportional to Mass
Acceleration = Force divided by Mass
More force = more acceleration
More mass = less acceleration
You apply a force, then you change either the direction or speed (acceleration)
Newton’s Third Law
For every force, there is always an equal and opposite reaction force
Jumping off a boat
You apply force to the boat, its reaction force pushes you to land, while the action force pushes the boat backwards.
Momentum
Mass times Velocity (P = mV)
Mass in motion
Dependent on how much stuff is moving (mass) and how fast the stuff is moving (velocity)
Angular Momentum
Mass times Velocity times Distance
W = mVr
Ex. Figure skater pulling in arms tight as they spin
Causes them to move faster while keeping the same total momentum
Back to Kepler’s Laws — speed up when you’re closest, slow down when you’re farthest (Ellipses)
Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
There is a force between any two objects in the Universe
F = G x (M1M2/d2)
The force is proportional to the product of the masses of each object
If you double the mass of either object, you double the force
The force is dependent on the distance between the two objects
If you double the distance, the force decreases and vice versa
Freefall
No forces other than gravity are being applied
The force of gravity equals the force you need to go in a circle/orbit around the earth without falling
Tides
Movement in the ocean due to the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon & Sun
Happens twice a day
Earth’s Size/Shape Shift
It gets squished, so there are tides on both sides
Tides are deeper on the side away from the Moon and facing the Moon
Tidal Locking
No matter when the Moon is observed from Earth, the same hemisphere of the Moon is always seen
Tides have slowed the spinning of the Moon down overtime so it has completely stopped
Tidal Lagging
Due to friction with the rotating Earth
They don’t happen at the highest point
It then applies force to the Earth, causing its rotation to slow down over time
Spring Tide
When the Moon, Earth, and Sun are all lined up (Full or New Moons)
The forces of the Sun and Moon combine/work together, squishing the Earth x2
Creates the largest tides twice a month
Neap Tides
During Quarter moons
The Sun and Moon aren’t lined up, which means that their forces cancel each other/work against each other
The Moon wins
Smallest tides twice a month
Moonrises
6 AM — New
9 AM — Crescent
12 PM — Quarter
3 PM — Gibbous
6 PM — Full
9 PM — Gibbous
12 AM — Quarter
3 AM — Crescent
Blue Light
Atmosphere scatters it
Makes you see a blue sky and a white sun when the sun is high
Red Light
Makes it through the atmosphere unscattered
When the Sun is low in the sky, it looks red/orange
Parts of the Sun
The Core
The Radiative Zone
The Conective Zone
Photosphere
Corona
Nuclear Fusion
Mass is converted into energy
When two light atoms combine together
The remaining mass releases energy
Nuclear Fission
Mass is converted into energy
Splitting a heavy atom into two lighter atoms
The remaining mass is converted into energy
What the Sun is made up of
Hot gas
70% Hydrogen
28% Helium
What keeps the Sun burning
Nuclear Fusion
Fusing hydrogen atoms to make helium in its core
Ideal Gas Law
Pressure
Gas & plasma are made of particles that bounce around, applying pressure
faster & more of them = more pressure
Temperature
particles moving faster → higher pressure = Higher temperature
Density
The more particles there are → higher pressure = Higher density
Hydrostatic Equilibrium in the Sun
Density is above equilibrium
The rate of Fusion then increases
Leads to temperature increase
The pressure then increases
So, the Core expands
Making the density drop
Equilibrium is restored
The Core
Hottest part of the Sun (10 million C)
Over 100 times the density of water
Fusion takes place here
The Radiative Zone
Hot but calm
No Fusion
A few million C
Around the density of water
The Convection Zone
Hot plasma rises, bringing heat to the surface
Hundreds of thousands of C
Density of styrofoam
The Surface of the Sun
Bright regions = Hot plasma rises from below
Darker regions = Cooler plasma sinking
This is convection
Sunspots
Cooler spots on the surface of the sun
11 year activity cycle