Chapter 9 + in class notes
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
What is the only artery that doesn’t carry oxygenated blood?
pulmonary artery
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
Atria
Ventricles
Lowe chambers of the heart
How many chambers in the heart?
4
Do the atrium and ventricles contract at the same time?
Yes
Describe blood flow through heart to lungs
superior vena cava to right atrium, right atrioventricular valve opens, right ventricle, out of pulmonary arteries to lungs
Why do we need less pressure lower when going to the lungs.
Why is the left ventricular wall thicker than the right?
This is where pressure is generated and at its highest
What happens if there’s an occlusion? What happens to the pulmonary artery
pulmonary artery develops more pressure to compensate.
What are the two type of cardiac cells?
Cardiumyocytes (majority) and ___ (minority)
What dictates strength of contraction?
gradient of calcium
Coronaries
Blood flow to the heart. Happens in diastolic when heart relaxes
What are the three important ion movements of pacemaker potential?
In Na, In Ca, Out K
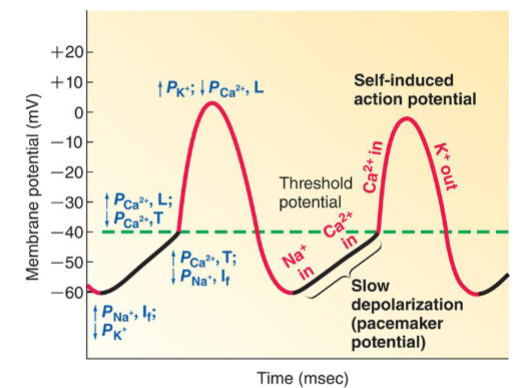
How to increase strength in heart
Membrane and calcium clock
What is the membrane clock
changes in the permeability of the surface membrane ion channels
Does permeability to calcium change
Yes
Action potential in cardiac cells
Has resting membrane potential of -90 to match K. Threshold potential at -70
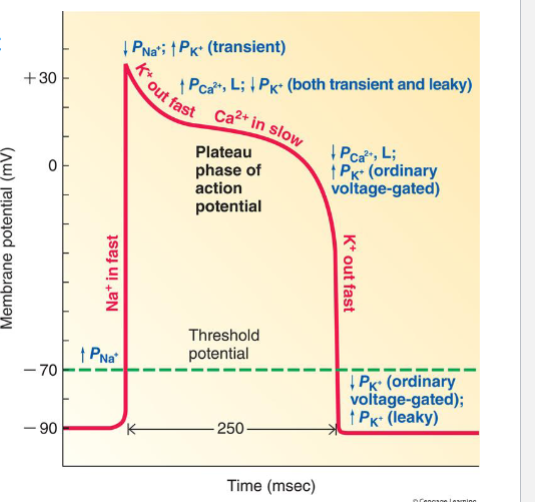
What causes the peak in cardiac AP
Opening of Na Pumps and Na into the cell
Why do we want calcium to slowly come in during plateau
Uniform contraction, prevent tetanus of the heart
What ion controls majorly the plateu phase of AP
calcium
How do you start the contraction in contractile cells (starting AP)
Na (sodium)
How do the L-type channels differ from the other channels in autorhythmic vs contractile cells
Compare L-type and T-type channels
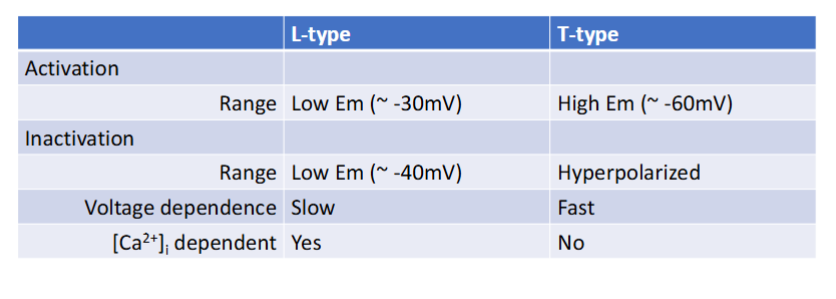
Why does the heart not have summation/shorter refractory period
Do not want risk of tetanus. Peak tension of heart has a little bit of a delay. Shortening of the refractory period is bad.
What causes the refractory period in cardiac?
The period of inactivation of sodium channels accounts for this duration. So, it doesnt fire another AP again before one is done
Where in the heart does the first AP occur
Sinoatrial node
Where does the sinoatrial node send the impulse to?
Interarterial pathway and internodal pathway
Where does the internodal pathway lead?
atrioventricular node
Where does AV node lead
down the bundle of His to the Purkinje fibers
Where is the blood filled first
atrium
Explain the timing of impulse through the heart
SA node fires AP, AV node delays, bundle of His + P-fibers are same speed as SA node to AV node
Why fo the P-fibers conduct faster?
they are bigger, and bigger fibers conduct impulse faster
What happens if the SA node fails?
AV node takes over, doesn’t fire as fast, contraction of atria is not as good b/c of the interatrial pathway
What does the AV node connect?
impulse between atria and ventricles
What is the AV node responsible for?
contraction of ventricle so blood can go out of heart to the body
What do ECGs record?
overall speed of electrical activity through the heart
What can NOT be seen from ECG + parts of the ECG
initiation of SA node impulse or AP, amplitude of atrial contraction, repolarization of atria
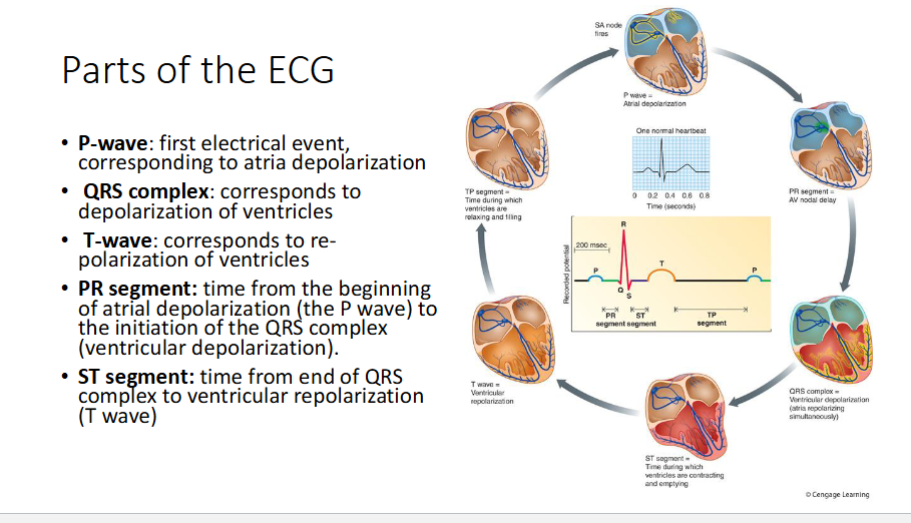
What features of electrical conduction are evident on ECG
depolarization of ventricles
During normal cardiac cycle, which is the point where left ventricular ejection fraction LVEF is determines?
LVEF defined as stroke volume divided by end-diastolic volume
What is cardiac output?
L/min of blood being pumped
Venous Return
rate of bloodflow back to heart
Preload
Afterload
Systole
contraction phase (1/3)
Diastole
relaxation (2/3)
Does parasympathetic or sympathetic impact ventricular contraction
sympathetic
What is intrinsic control in stroke volume
the extent of venous return
what is extrinsic control in stroke volume
extent of sympathetic stimulation of the heart
Cardiac Output =
Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
Will increasing blood volume increase cardiac muscle contractions?
Yes
Which nerve is para sympathetic stimulation
Vegas Nerve
How does increase in heart rate occur after sympathetic stimulation
increased rush of Na and Ca in pacemaker cells, AV node delay is shortened, Everything is sped up. relax faster too via circa pump
When would cardiac output increase?
Heavy exercise, fight or flight response
Increased end diastolic volume correlates to increased SV true or false
true
What is the advantage of length-tension relationship
both sides have equalized output
Why is force in left ventricle greater than right
left has to pump through higher resistance, and has thicker wall = more muscle, more force, more tension
Equation for ejection fraction =
SV/EDV (end diastolic volume)
What would happen if B_1 blocker given to heart
Slows down the effecti? idk needd to ask
What can cause high bp
afterload
Why does sodium increase bp
Name the layers of the artery
______ are major resistance vessels
arterioles - they change size and radius based on metabolic needs. ex: when exercising, they relax
What is the most potent vasodilating paracrine released by arteriolar endothelial cells
Nitric Oxide - is a paracrine because its produced by endothelial cells and is released in same area…also produced by other cells
What is a vasoconstrictor
Endothelin
When is acetylcholine released?
parasympathetic activity
What do our vessels do when it is cold?
vasocontrict
Are the arterials influenced by parasympathetic?
No. they only sense how much activity, not what activity
What is strength of constriction dependent on?
Ca, cold, angiotensin 2, oxygen, sympathetic stimulation, decreased tissue activity, CO2, H+
When does vasodilation occur?
increased tissue activity, decreased oxygen and decreased symp.
Local chemical changes act on the vascular endothelium with paracrines like
nitric oxide, endothelin, angiogenesis, ex: body can release nitric oxide to get past a blockage in the blood - dialates vessels
Look at reactive hyperemia chart
What does histamine do?
dialates arterioles
Why is histamine released?
when injured, or allergy. rushes blood to that area. take anti histamine tells body to stop reacting to that injury
when u have a wound, increase in blood flow to wound happens = increase in fluid in the area that cant return back to heart
too much can lead to a delay in recovery
What is myogenic response?
response of arteriole dilation
What happens during sympathetic
constriction everywhere but the blood
What are the receptors of arteriolar smooth muscle adrenergic?
alpha 1 and beta 1
NE acts on a1 to vasoconstrict
E acts on b2 to vasodilate
What does vasopressin do?
What does angiotensin 2 do?
water balance; salt balance
Capillaries have small water filled pores for?
small water soluble ions, glucose, AA can pass through
What is the difference in brain capillaries?
Blood brain barrier→ brain capillaries are joines by tight junctions. NO pores
Histamine increases ________ permeability
capillary
What is capillary blood flow based on?
gradients
Metarteriole
main channel from arteriole to venule
Review fig 10-20 pg 365
What quantifies passive diffusion?
Fick’s law - understand
Bulk Flow equation
ECF distribution
Ultrafiltration for ECF distribution
fluid moving out of capillary into interstitial space
pi_C
Plasma colloid osmotic (oncotic) pressure is based on protein concentration inside the capillary
Find reabsorption or the ultrafiltration: reabsorption will result in a negative
outward pressure - inward pressure????
How to increase flow out of capillary
decrease protein in the interstitial space, increase capillary pressure
Primary lymphatics
Open flaps + fenestrations allow for fluids and proteins to connect
Secondary lymphatic
have valves to help prevent backflow. Can contract on their own b/c made of smooth muscles. Both go against the gradient
What is lymph?
in lymphatics, protein fluids, nothing much, lower viscosity than blood in capillaries
When does edema occur
too much ISF is accumulating
how will the following impact hydrostatic and oncotic pressure
red. conc of plasma proteins, reduced oncotic pressure = LESS reabsorption = less fluids in ISF
Inc. permeability of capillary walls, caused by histamine, ultrafiltration increases
inc. venous pressure, causes edema, not enough reabsorption happening, Net exchange pressure wouldnt be negative
blockage/cant pump lymph vessels
What are venules
beginning of venous structure where reabsorption occurs w. very low resistance: kinda just pass the blood
Veins
hold majority of blood until body needs it
Veins vs Arteries
veins are lower pressure, arteries are higher pressure. veins also have valves and would be limited to that region
Why does skeletal muscle contraction not affect arteries but affect veins
arteries hvae thicker wall, skeletal muscles can collapse on the veins
______ activity causes vains to constrict
sympathetic - so when you stand up, need to get up and move
How do varicose veins occur
venous valves become incompetent/insufficient. not opening and closing properly