MCB Lec 16 - REVISED
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i hate glycolysis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UBudWWUqAmc this helps
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Glycolysis
- 1 glucose —> 2 pyruvate
- nets 2 ATP
- catabolic and anaerobic
Glycolysis overall reaction
Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi → 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O
Stage 1 glycolysis
Energy Investment Stage
traps glucose in the cell and modifies it so that it can be cleaved into a pair of phosphorylated 3-C compounds
2 ATP are “invested” to couple unfavorable reactions (steps 1 and 3 - the irreversible reactions)
Stage 2 Glycolysis
Energy Harvesting Stage
oxidizes the 3-carbon compounds to pyruvate while generating a NET of 2 ATP
Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions using
acid-base, covalent, and metal ion catalysis.
Which coenzymes pick up electrons from compounds being oxidized?
NAD+, FAD, and ubiquinone
Larger negative change in free energy of a reaction can be coupled with
an unfavorable reaction
Breaking a phosphoanhydride bond in ATP requires….
lots of energy
First Stage of Glycolysis steps
Hexokinase - transferase
Phosphoglucose isomerase - isomerase
Phosphofructokinase - transferase
Aldose - lyase
Triose Phosphate Isomerase - isomerase
1. Hexokinase
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: transferase
transfer the phosphate group
Reaction:
glucose + ATP → glucose-6-phosphate + ADP
● IRREVERSIBLE
What is does: Substrate binding induced fit is used to minimize hydrolysis of ATP
Important: Requires a cofactor of Mn2+ or Mg2+
2. Phosphoglucose isomerase
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: isomerase (Aldose to ketose)
reaction:
Glucose-6-phosphate —> Fructose-6-phosphate
Crucial reaction because G6P is not readily cleaved into two 3-C fragments, while F6P is
main goal of energy investment stage is to get a pair of 3-C compounds
3. Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: Transferase
Reaction:
Fructose-6- phosphate —> Fructose-1,6- bisphosphate
● IRREVERSIBLE
Traps the carbohydrate in the fructose form by the addition of a second phosphate group
RATE DETERMINING STEP - slow step
Allosteric enzyme through induced fit
Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate is the main activator of PFK in mammals
KEY REGULATOR OF GLYCOLYSIS
4. Aldose
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: Lyase
Reaction:
Fructose1,6-bisphosphate —> Glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate + DHAP
5. Triose Phosphate
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: Isomerase
Reaction:
DHAP —> Glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate
DHAP must be converted to G3P to enter stage 2
Important
Catalytically perfect enzyme - catalysis occurs every time the substrate and enzyme meet
Acid-base catalysis
Try and replicate the first stage of glycolysis
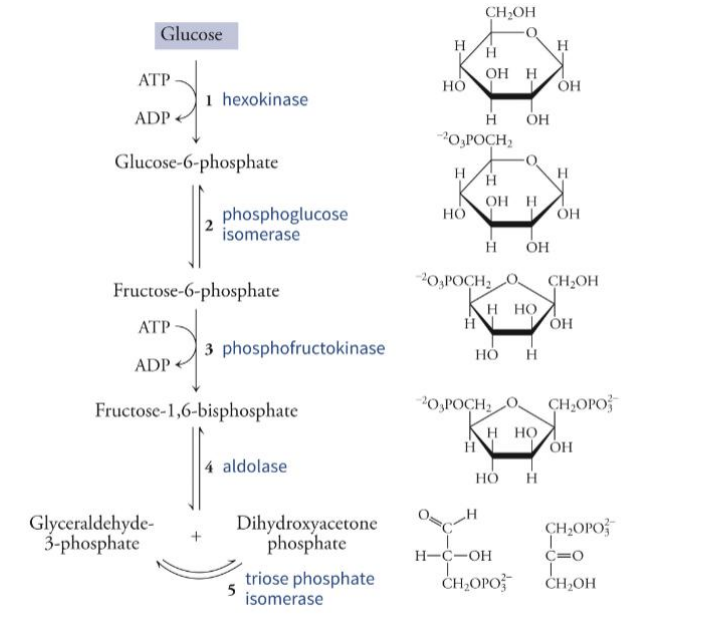
Second Stage of Glycolysis:
oxidizes the 3-carbon compounds to pyruvate whole generating two molecules of ATP
Second Stage of Glycolysis steps
6. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase - redox
7. Phosphoglycerate Kinase - Transferase
8. Phosphoglycerate Mutase - Isomerase
9. Enolase - Lyase
10. Pyruvate Kinase - Transferase
6. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: REDOX
Reaction
G3P + NAD+ (oxidant) + Pi —> 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate + NADH (reductant) + H+
Oxidation of aldehyde to a carboxylic acid using NAD+
Joining the carboxylic acid and orthophosphate to form the acyl-phosphate product
Important
1,3-BPG has higher phosphoryl transfer potential than ATP - can be used to synthesize ATP
7. Phosphoglycerate Kinase
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: Transferase
Reaction:
1,3-BPG + ADP —> 3-Phosphoglycerate + ATP
Substrate level phosphorylation
Happens twice, meets the ATP investment
8. Phosphoglycerate Mutase
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: isomerase
Reaction:
3- Phosphoglycerate —> 2- phosphoglycerate
Enzyme is both kinase & phosphatase in route to the OVERALL isomerization
Important
Phospho-Histidine used to transfer the phosphate group from the 3 position to the 2 position
9. Enolase
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: Lyase
Reaction:
2- Phosphoglycerate —> Phosphoenolpyruvate, H2O
Phosphoenolpyruvate has high phosphoryl-transfer potential (can create ATP)
Presence of the phosphate traps compound in an unstable enol tautomer (readily reactive)
10. Pyruvate Kinase
Type, Reaction, Reversibility, What it does, important
Type of reaction: Transferase
Reaction:
Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP —> Pyruvate + ATP
● IRREVERSIBLE
Enol to ketone conversion drives the reaction
Second of two substrate level phosphorylation steps in glycolysis
ADP is substrate
Fates of Pyruvate
- Oxidation of glucose to pyruvate requires NAD+
- NAD+ is regenerated by further oxidation of pyruvate to CO2 (presence of oxygen) or in fermentation of ethanol of lactate (no oxygen)
Fermentation
anaerobic ATP-generating pathways in which electrons are removed from one organic molecule and passed to another
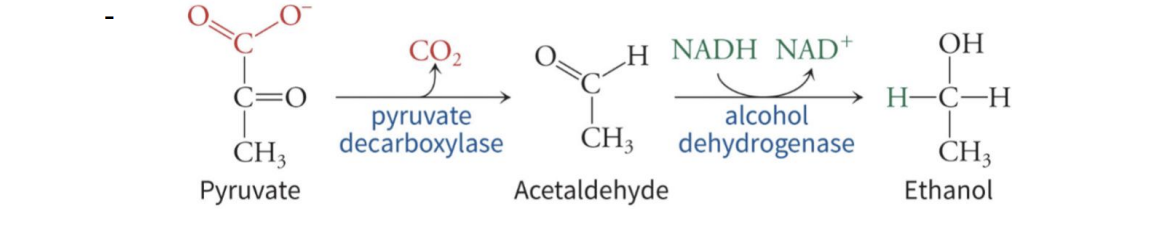
Alcohol Fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation
Alcohol Fermentation
glucose to ethanol
Pyruvate carboxylase catalyzes the decarboxylation of pyruvate - Alcohol dehydrogenase reduces the acetaldehyde to ethanol, regenerating NAD+
Enzymes:
pyruvate decarboxylase
alcohol dehydrogenase
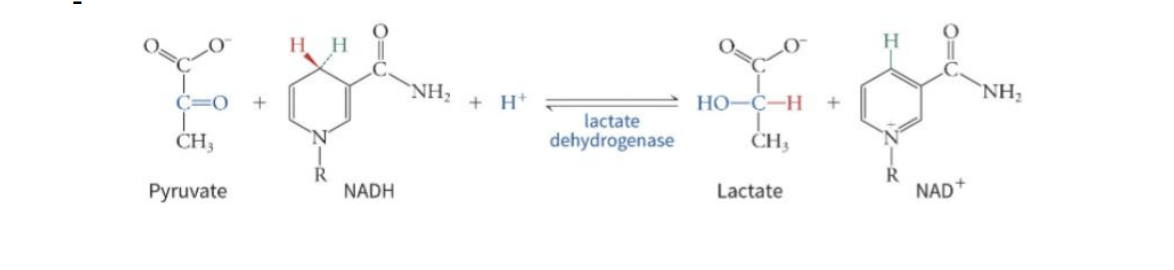
Lactic Acid Fermentation:
- Conversion of glucose into two molecules of lactate
Enzyme: Lactate dehydrogenase
● REVERSIBLE
● Liver uses NAD+ to regenerate pyruvate from lactate
Entry of fructose in glycolysis
Fructose
Fructose 1-phosphate pathway (liver)
Phosphorylated into hexokinase (adipose tissue)
The creation of GAP and DHAP through the fructose 1- phosphate pathway allows it to enter into the glycolysis pathway in the liver
Fructose in adipose tissue can enter glycolysis at Fructose-6P step
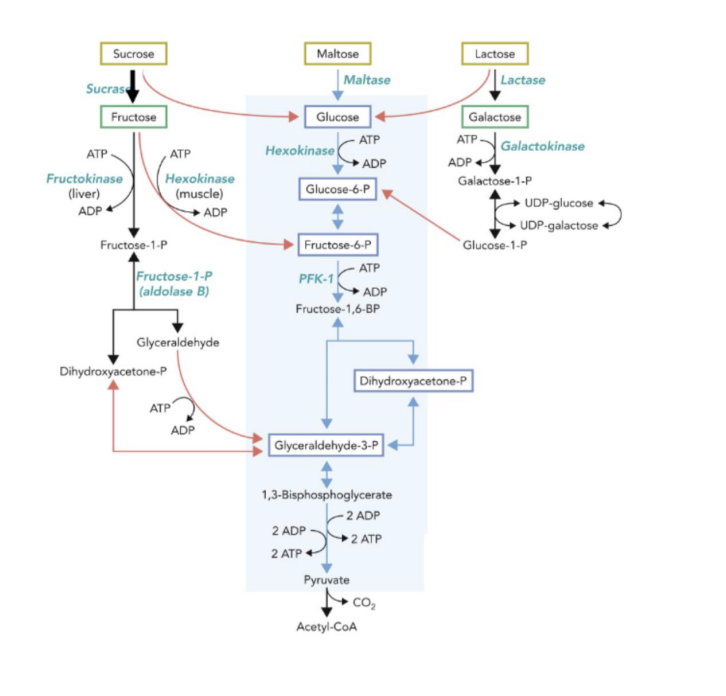
Entry of galactose in glycolysis
Galactose
Converted to 6-phosphate by the galactose-glucose interconversion pathway
Galactose is phosphorylated by galactokinase
G1P is converted into glucose 6-phosphate by phosphoglucomutase
Glucose 1-phosphate is generated using UDPglucose, a transferase, and an epimerase
Galactose 1-phosphate uridyl transferase is mostly mutated in galactosemia