Neuropathic pain+ Fibromyalgia- Dart
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1 hr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
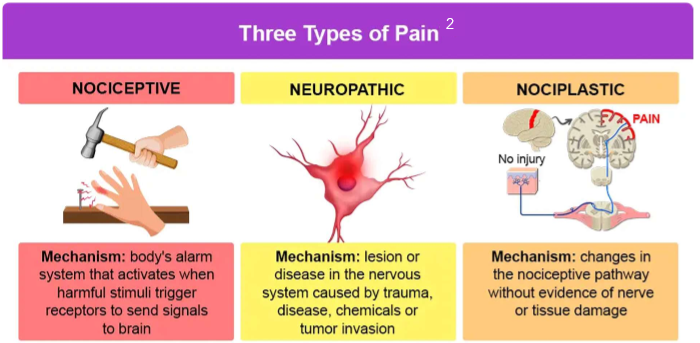
Describe the difference types of pain:
nociceptive
neuropathic
nociplastic
mixed
nociceptive
most common type of pain
pain due to actual or threatened damage to non-neural tissue activating nociceptors
adaptive
2 subtypes (somatic, visceral)
neuropathic
pain due to lesion or disease affecting the somatosensory system
damage to peripheral or central nerves
often chronic
maladaptive
nociplastic
idiopathic pain that has no clear evidence of tissue damage or damage to the somatosensory system
fibromyalgia
IBS
mixed
overlap of nociceptive and neuropathic sx
ex: cancer, OA
What NTs are associated with neuropathic pain?
GABA—> primary inhibitory NT, decreasing release of glutamate, aspartate, and sub P
NE
Serotonin
What are the 4 neuropathic types?
motor—> damage to nerve cells controlling muscles= loss of control/coordination
sensory—> damage to sensory nerves= loss of pain/touch
autonomic nerve—> damage to nerve cells controlling unconscious bodily functions
combo
What are the 6 different neuropathic sensations a pt. can experience?
paresthesias- abnormal skin sensation (tingle, prick)
dysesthesias- abnormal painful sensation
allodynia- non-painful stimulus can elicit pain like light or cold temp
hyperalgesia- increased sensitivity to mild pain stimulus
hyperpathia- exaggerated response to stimuli often delayed or prolonged
hyperesthesia- increased sensitivity to both non-painful and painful stimulus
How is neuropathic pain diagnosed?
combo of a lot of things: physical, pain interview, PMH, blood tests, DM, electrodiagnostic tests, quantitative sensory testing
List examples of neuropathic syndromes:
do not memorize, just an overview
painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN)- most common
postherpetic neuralgia
chemotherapy induced neuropathy
guillain-barre syndrome
chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
trigeminal neuralgia
phantom limb pain
spinal cord injury pain
WHAT ARE THE FIRST LINE AND ALTERNATIVES TX FOR PDN?
1st line: PREGABALIN or DULOXETINE
alt 1st line: gabapentin, TCAs
last line: opioids
nonpharm: glucose control
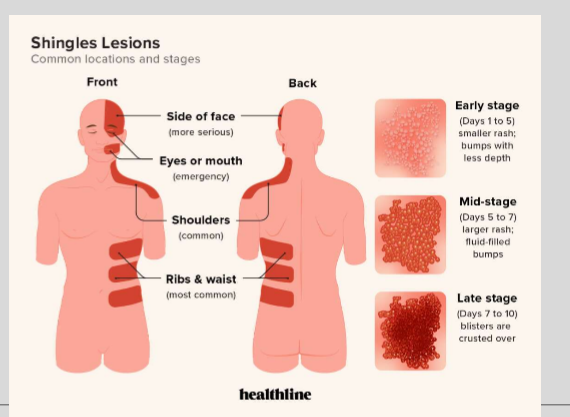
postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a pain syndrome after nerves have been damaged due to WHAT INFECTION?
varicella zoster virus infection aka SHINGLES
Shingles follows what to produce a rash and pain on that area of the body? What are they?
DERMATOMES—> aka areas/pathways on the body that rely on a specific spinal nerve for fxn
What is 97% effective at preventing the formation of shingles and technically PHN?
Herpes Zoster vaccination—> SHINGRIX
Indication for Shingrix?
recommended for pts. 50+ with a history of shingles, previously vaccinated with Zostavax, or who previously received the varicella vaccine
What are the topical and systemic tx options for PHN?
which is 1st line?
topical: Lidocaine 5% patch (1st line), capsaicin cream
systemic:
APAP, NSAIDs
GABA Analogs
TCAs
opioids—> last line
What are the names of the GABA Analogs? MOA?
names: Gabapentin, Pregabalin
MOA: mimic the action of the GABA a-2-d subunit decreasing the release of NTs
Which GABA analog is a controlled med? which isn’t?
Pregabalin—> CV
Gabapentin—> not a CS, but some states elected it as one
GABA Analog ADRs:
idk how imp
both: CNS/respiratory depression, dizzy, somnolence, dry mouth
gabapentin: n, ataxia, fatigue, neuropsych effects
pregabalin: blurred vision, weight gain, peri edema, difficulty concentrating
Pregabalin ER not recommended if CrCl <___ ml.min
30
What are the names of the TCAs? MOA?
names: desipramine, nortriptyline, amitriptyline, impramine
MOA: block Na+ channels, impact NE and 5-HT
When should TCAs be avoided and used in caution?
avoid:
pts. with 2’ or 3’ heart block
arrhythmias
QT prolongation
recent MI
severe liver disease
caution:
closed-angle glaucoma
BPH
CV disease
urinary retention
constipation
liver dysfunction
TCA ADRs:
idk how imp
constipation
dry mouth
blurred vision
urinary hesistency
tachycardia
mental status changes
orthostatic hypotension
sedation
weight gain
falls
Duloxetine belongs to what class of drugs?
SNRI (selective serotonin and NE reuptake inhibitor)
BBW of Duloxetine
Suicidality
C/I of Duloxetine
with concurrent or recent MAOI use or closed-angle glaucoma
ADRs of Duloxetine:
idk how imp
n
dizzy
HA
somnolence
constipation
dry mouth
hyperhidrosis
Precautions of Duloxetine
serotonin syndrome
may increase HR or BP
may increase glucose
bleeding risk
hepatotoxicity
should be tapered off
What is the place of Tramadol in therapy of neuropathy?
for acute pain management until neuro agents reach effect
ADRs of Tramadol:
idk how imp
addiction risk
CNS depression
constipation
serotonin syndrome
For lidocaine transdermal patches how many patches can you wear at once? for how long?
can the patches be cut?
1-3 patches for up to 12 hours daily
patches CAN be cut
What is the name of the irritant derived from hot chili peppers and used topically for PHN, arthritis pain, and post-op pain?
capsaicin
Is Capsaicin a good option for immediate relief?
no! takes 2-4 weeks for onset and 4-6 weeks till max effects
What antiepileptics can be used for PHN?
idk how imp
carbamazepine
lamotrigine
oxcarbazepine
phenytoin
topiramate
valproic acid
zonisamide
What is fibromyalgia? cure?
musculoskeletal connective tissue disorder with chronic widespread pain and fatigue which can be difficult to localize
no cure
What is the pathophys behind fibromyalgia?
exact mechanism not known—> thought to deal with serotonin and NE imbalances
Symptoms of fibromyalgia:
most common—> widespread pain in joints with fatigue and sleep problems
generally hurts all over
other sx:
numb, tingle, burning sensations
memory problems “fibro fog”
depression/anxiety
HA
digestion problems
urinary issues
pelvic pain
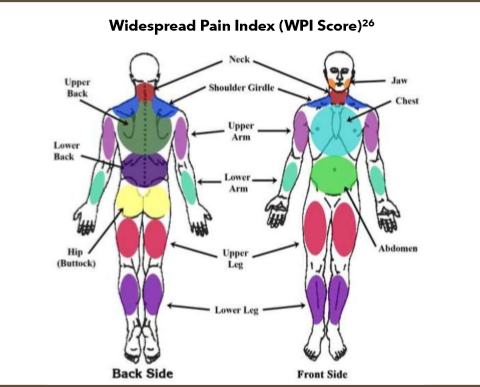
How is fibromyalgia diagnosed?
not one formal diagnostic test
look for:
presence of pain in 6+ body sites with other common fts.
identify common comorbidities like IBS, chronic HA, or depression
ACR criteria—> assigns a widespread pain index (WPI) score
SS score
clinical diagnosis from WPI or SS score
Nonpharm for fibromyalgia:
lifestyle: exercise, stress management, sleep hygiene
alt therapies: acupuncture, massages, and other bs like that
What is the pharm tx for fibromyalgia?
analgesics—> APAP
anticonvulsants—> pregabalin, gabapentin
muscle relaxers—> cyclobenzaprine
opioids—> strongly discouraged, but maybe tramadol
SNRIs—> duloxetine, milnacipran
TCAs—> amitrptyline
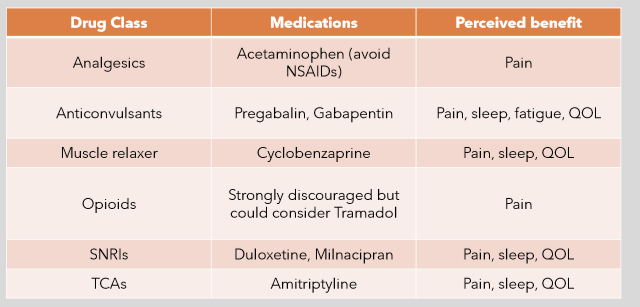
What is the only class of drugs for fibromyalgia helps with pain, sleep, fatigue, and QOL?
anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin)
What selective SNRI is only currently approved for fibromyalgia pain in adults?
What’s the boxed warning?
Milnacipran—> BBW for suicide