Chapter 6- Ionic Bonding
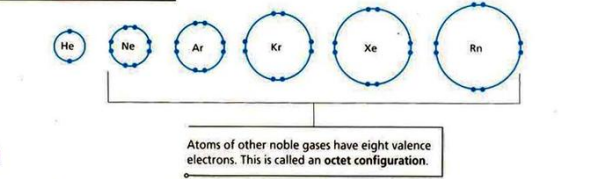
Noble gases have complete octets or duplets so they are stable (unreactive). In order for other atoms to gain stability, they either lose, gain, or share electrons to form ions.
Atoms lose or gain electrons to become either positive ions (cations) or negative ions (anions).
Ions are charged particles formed from atoms or the group of atoms by losing or gaining electrons.
Ions are either negative or positive.
Metals lose electrons to form cations and non-metals gain electrons to form anions.
A polyatomic ion is a group of atoms that carry a charge.
FORMATION OF IONIC BONDS
Formed between metals and non-metals.
Metal atoms lose electrons which are transferred to each of the non-metal atoms.
Positive metal ions and negative non-metal ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces of attraction.

To write the chemical formula of an ionic compound, balance the charges on each ion such that there is no net charge on the compound.
PROPERTIES OF IONIC COMPOUNDS
- Ionic compounds have regularly-arranged, giant lattice structures.
- They have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between ions.
- They are soluble in water but not in organic solvents such as ethanol and oil.
- They conduct electricity in molten and aqueous state due to free electrons and ions respectively. They do not conduct in solid state.