Ionic bonding (3.1.3.1) + Metallic bonding (3.1.3.3)
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What is an ionic bond in terms of atoms and electrostatic forces of attraction?
Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal
They have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between cations and anions
What are the properties of ionic compounds?
Melting and boiling point
High MP and BP as they have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between cations and anions that require a lot of energy to overcome
Conductivity
Don’t conduct electricity when solid as the ions that carry charge are held in a fixed position. However, when the compounds are molton they become mobile so it can conduct electricity.
Brittality
Ionic compounds are often brittle as when the layers of alternating charge are distorted, like charges repel, breaking apart the lattice into fragments
How do you represent the bonding in ionic compounds?
Dot and cross diagrams
What is metallic bonding in terms of electrostatic forces?
Electrostatic forces of attraction between metal cations and a sea of delocalised electrons
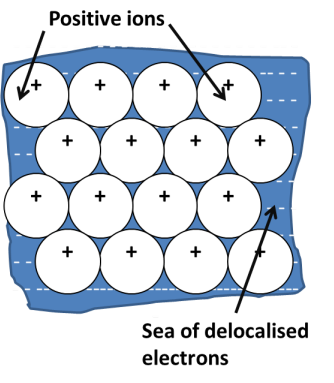
What affects the attractive forces of metallically bonded atoms?
The larger the charge on the cation, the stronger the attraction as more electrons are released into the ‘sea’ - this causes the boiling point to be higher
Ions that are larger produce weaker attraction due to their greater atomic radius
What are the properties of metallically bonded atoms?
Melting and boiling point
They have low MP and BP because of the repulsive forces between the negative electrons which need little energy to break
Conductivity
They can conduct electricity because of the sea of delocalised electrons which can move through the structure and carry charge
Malleability
They are malleable as the layers of cations are able to slide over each other