Basic Economic Concepts
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Scarcity
A situation in which unlimited wants exceed the limited resources available to fulfill those wants.

Economics
study of how people and societies use limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants.
Goods
Objects, such as food, clothing, and furniture that can be bought.

Services
Actions or activities that one person performs for another.

Consumer
A person who buys and uses goods and services.
Producer
a maker of goods or a provider of services.
Resources
the inputs used by a society to produce outputs.

Factors of Production
Land, labor, capital and entrepreneurship; the four groups of resources that are used to make all goods and services
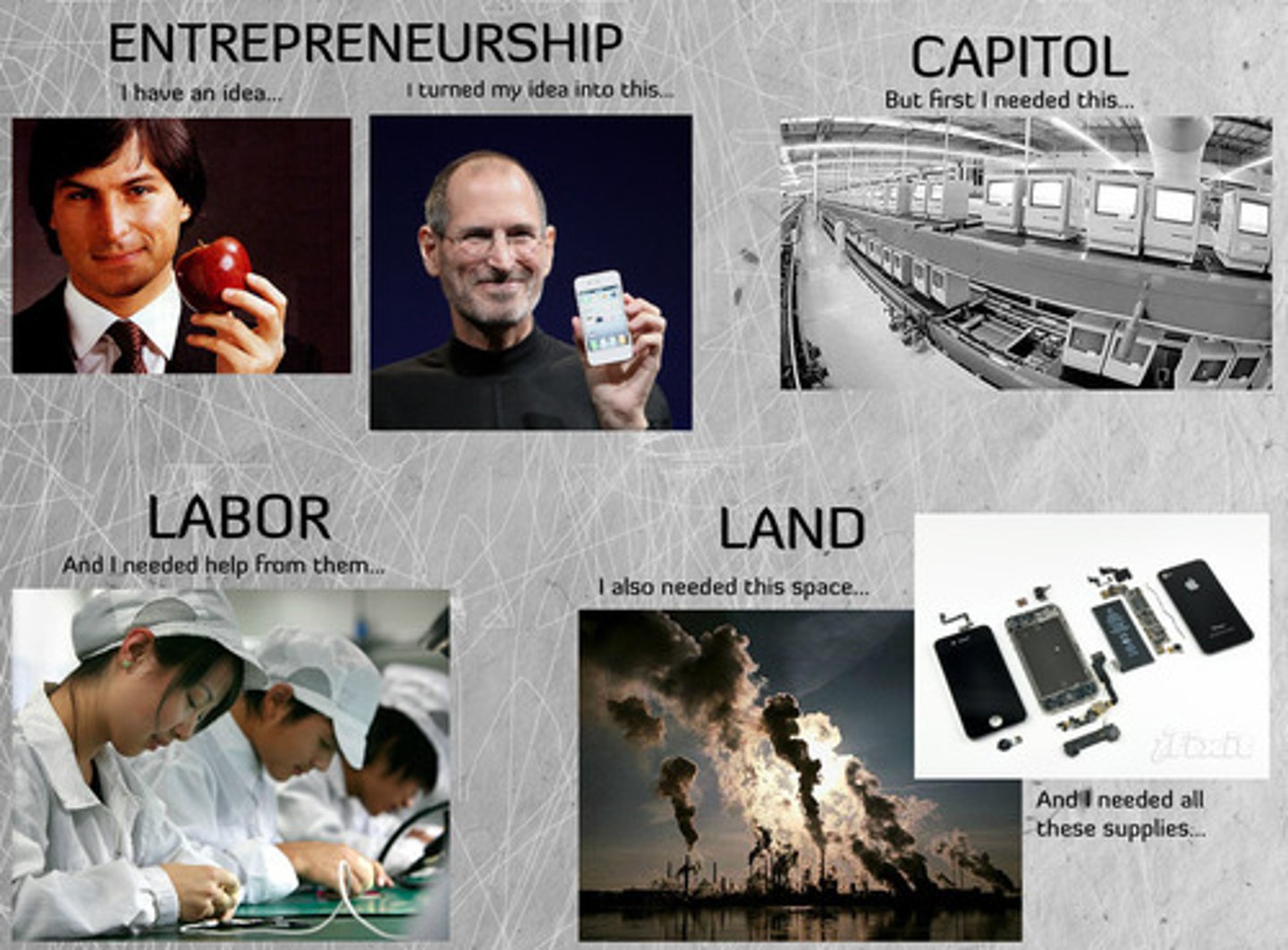
Land
Any natural resource provided by nature and used in the production process

Labor
the mental and physical efforts of human beings in the production process

Capital
Man made creations that are used to make goods or services. Tools, equipment, factories

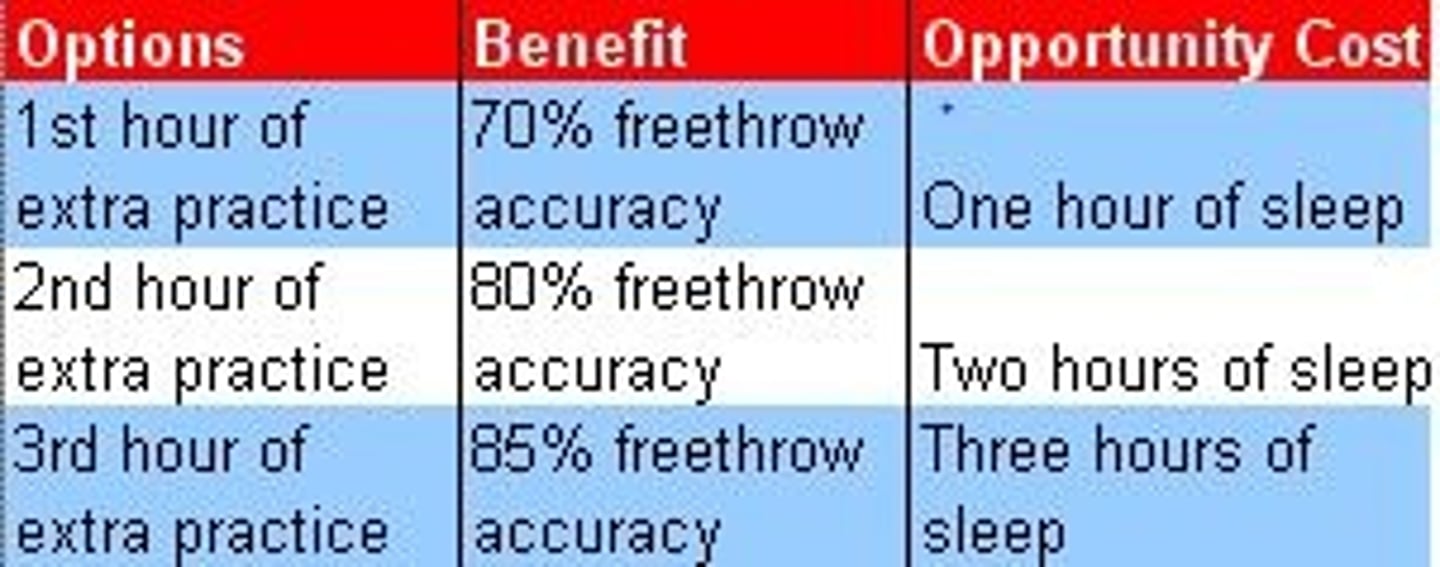
Opportunity Cost
Cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or resources when one choice is made rather than another

TINSTAAFL
Acronym for THERE IS NO SUCH THING AS A FREE LUNCH; means that there is always a cost for a product, even if it is not evident.

Trade-off
alternatives that must be given up when one is chosen over another

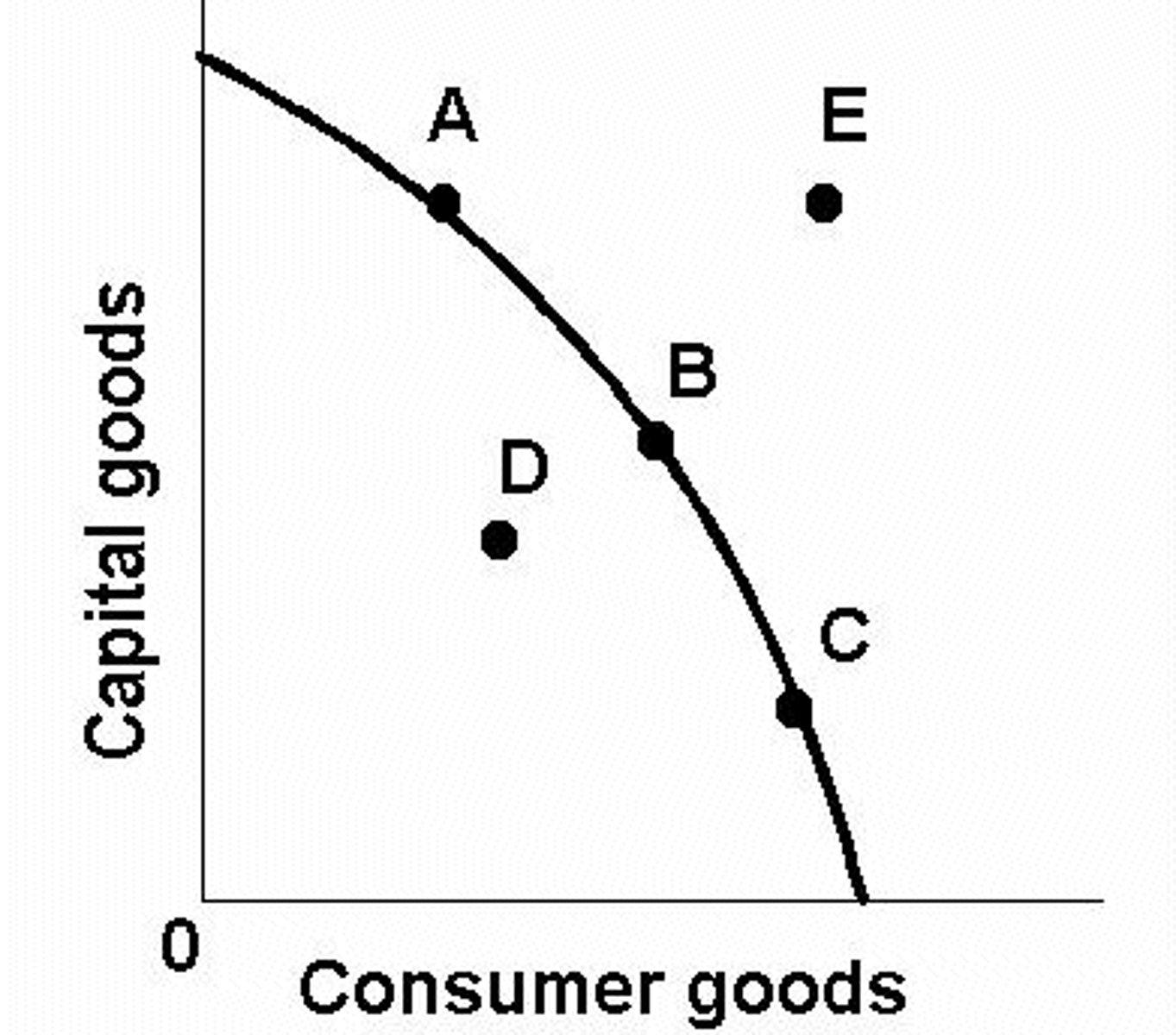
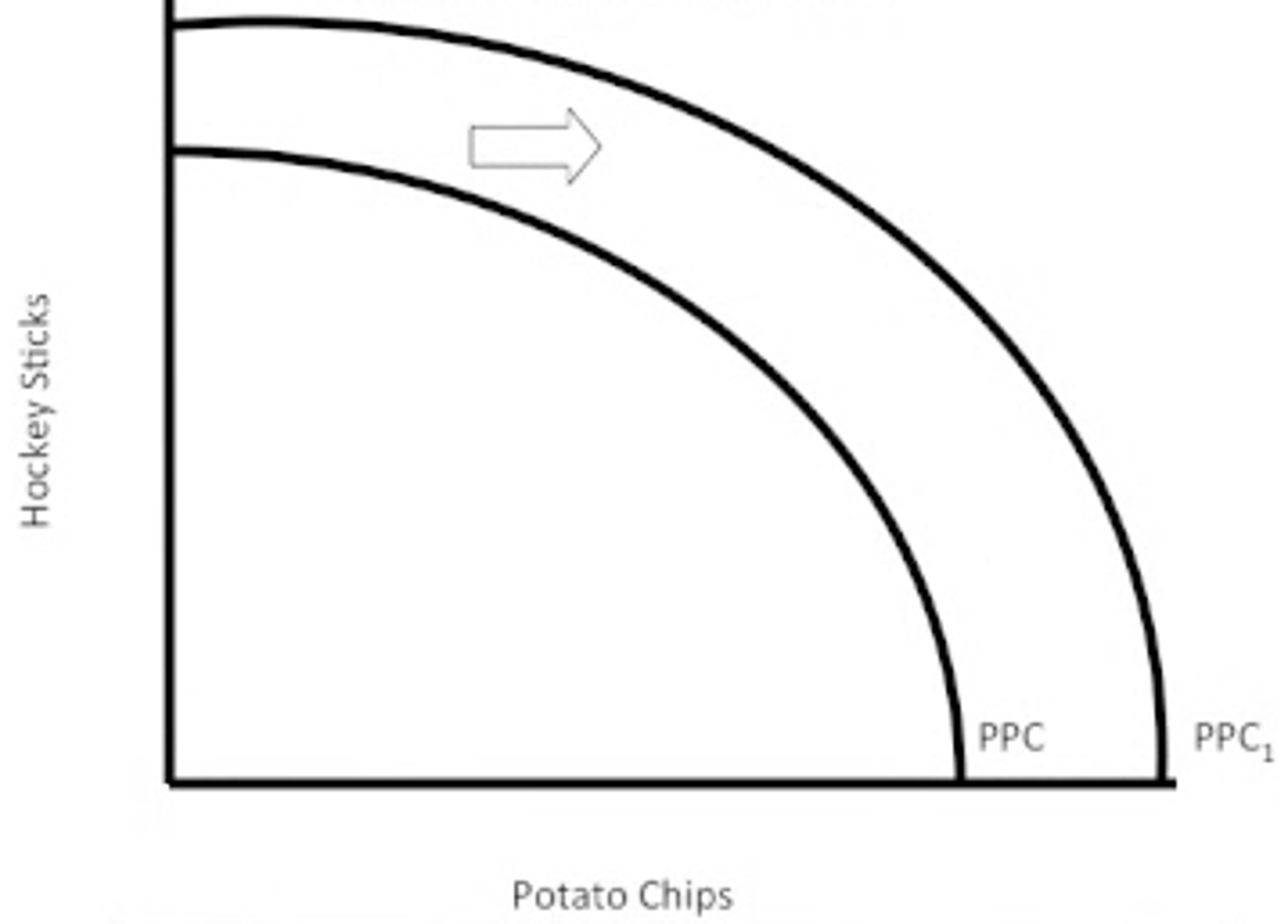
Production Possibility Curve
graph showing the maximum combinations of goods and services that can be produced from a fixed amount of resources in a given period of time
Three Basic Economic Questions
What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce?

Incentives
A reward or penalty that encourages or discourages behavior.

Marginal Thinking
Requires decision-makers to evaluate whether the benefit of one more unit of something is greater than its cost
Market Economy
An economic system in which people choose freely what to buy and sell

Efficiency
A measure of how well or how productively resources are used to achieve a goal
Economic Growth
steady growth in the productive capacity of the economy (and so a growth of national income)
Marginal Benefit
the additional benefit to a consumer from consuming one more unit of a good or service
Competition
A situation that occurs when there are many buyers and sellers acting independently,
businesses attempt to gain consumers and sales.

The Invisible Hand
The combined forces of self-interest and competition working within the free market, guiding resources to where they do the most good for society.

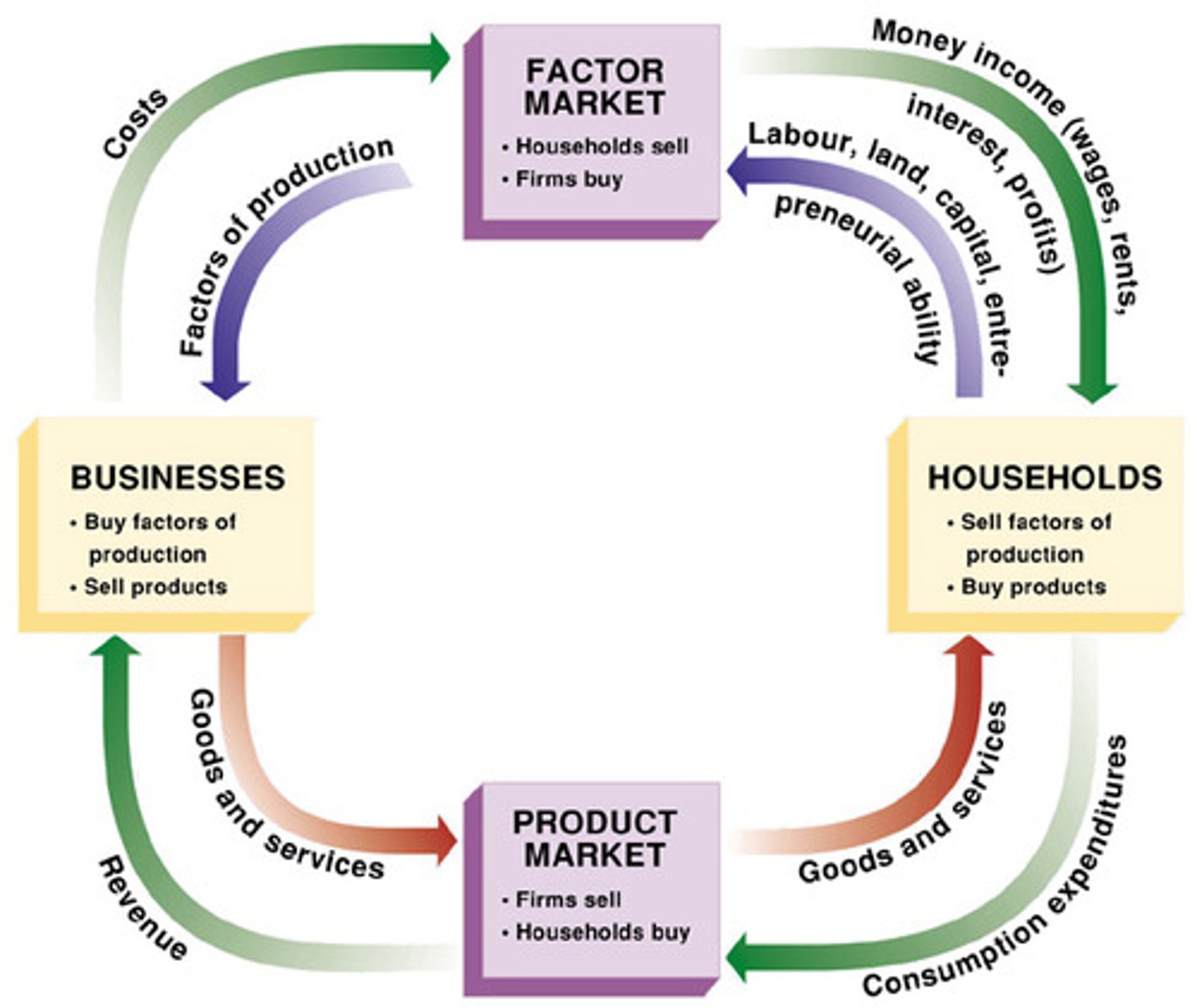
Circular Flow Model
a diagram that shows the circular movement of money, resources, and goods and services among households and producers in an economy
Market
The process of freely exchanging goods and services between buyers and sellers...can be in cyberspace, local, regional, national, or global
