Monopolistic competition
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
What are the assumption of monopolistic competition?
Many small buyers and sellers
Low barriers to enter or leave
Differentiated goods (similar but slightly different)
What does low barriers to enter or leave mean?
no economies of scale, few patents, low sunk costs
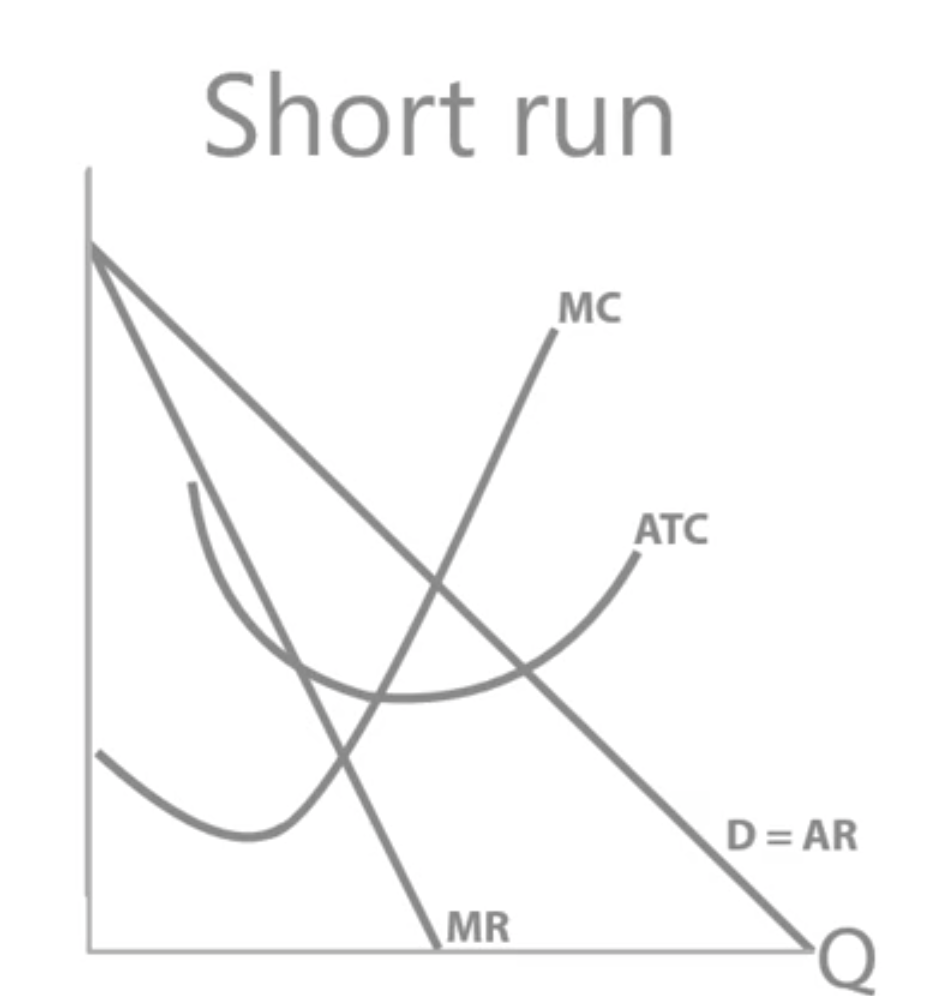
If a firm is making supernormal profit, new entrants will be incentivised to enter the industry.
These new entrants will steal potential customers, what are the effect of this on the costs/ revenue diagram?
AR and MR decrease
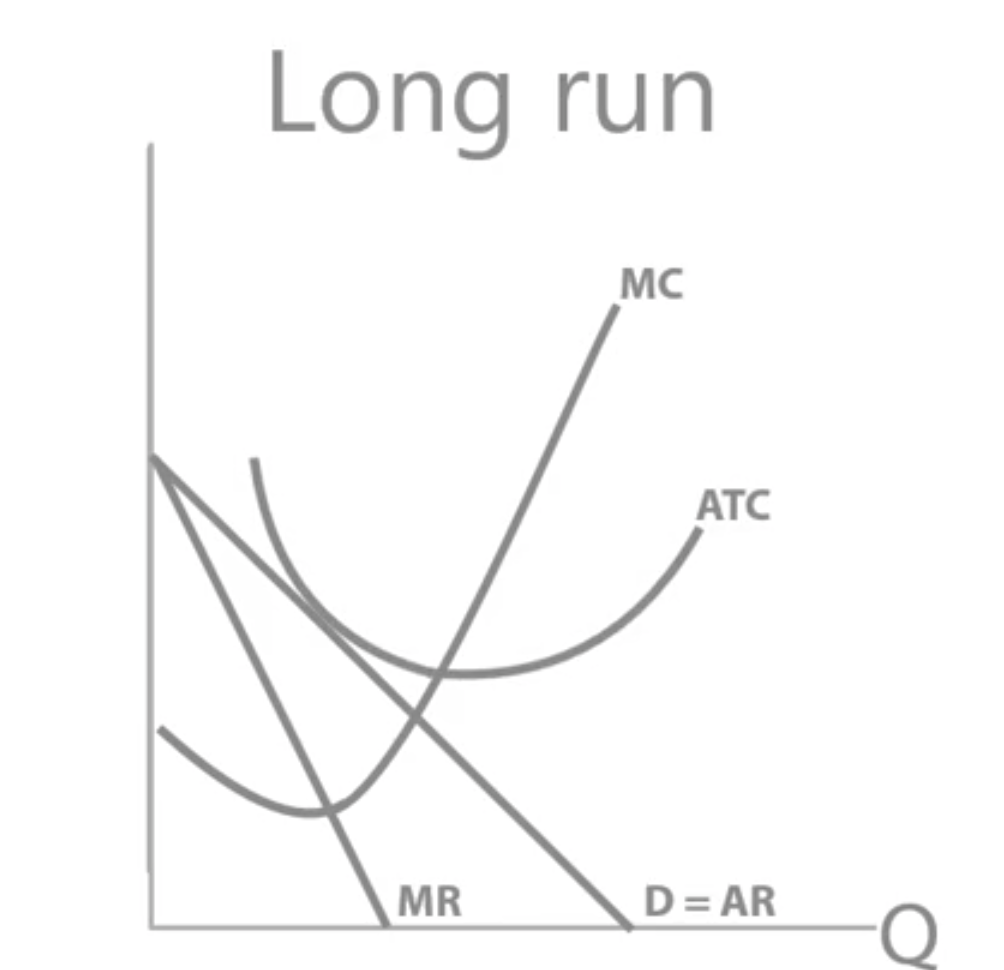
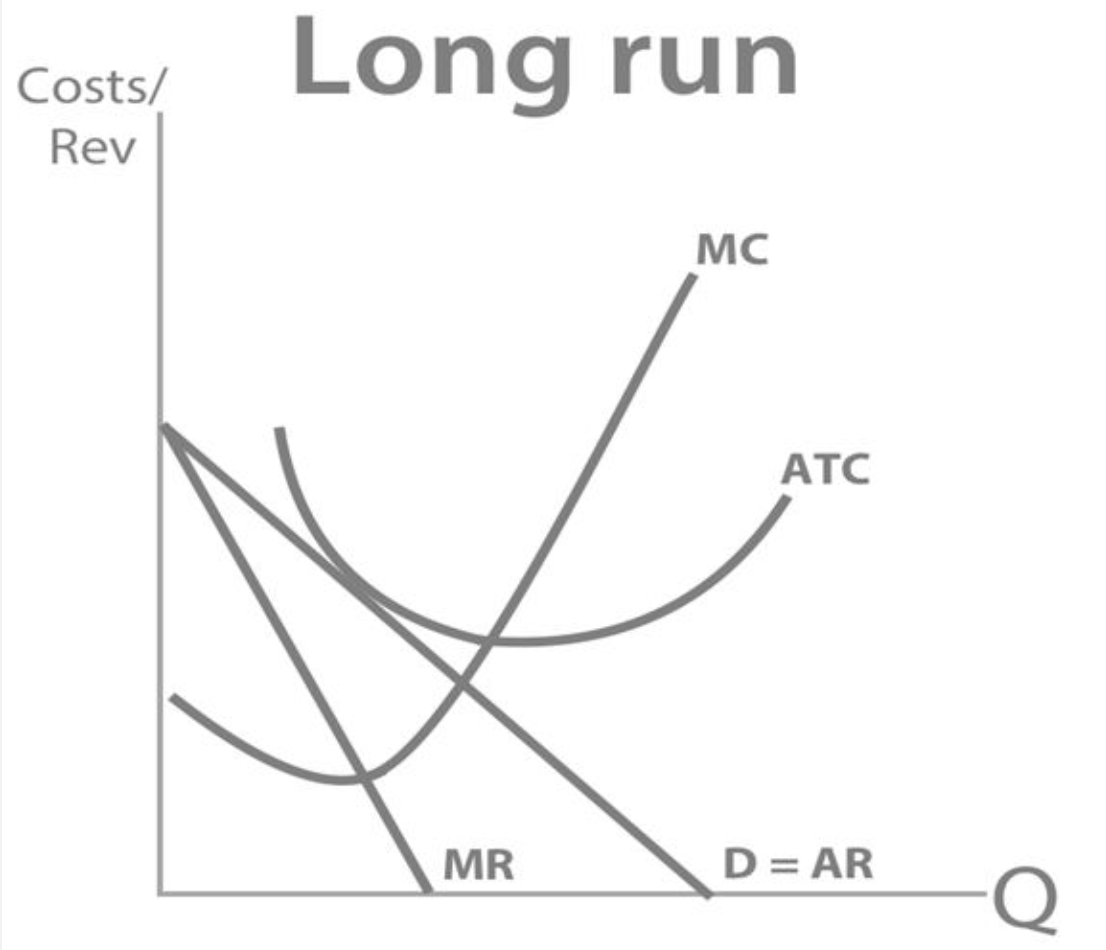
What profit is a firm making?
In the long run, perfectly competitive firms will only be able to make normal profit.
Explain what happens as a monopolistically competitive market moves to its long run equilibrium. (4 marks)
In the short run, if a monopolistically competitive firm is making supernormal profit, it will incentivise new firms to enter the market.
There are low barriers to entry, so new firms will enter the market, stealing customers from existing (or incumbent) firms.
This will decrease their demand (or AR), shifting AR and MR down, until AR just touches the firm’s AC curve - so only normal profit will be left and all the supernormal profit is gone,.
Potential suppliers outside the market will no longer enter the market because they can no longer make supernormal profit, so we have reached the long run equilibrium.