Overview of Human Physiology and Immune System Concepts
1/648
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
649 Terms
Anatomy
Study of the structure of the human body.
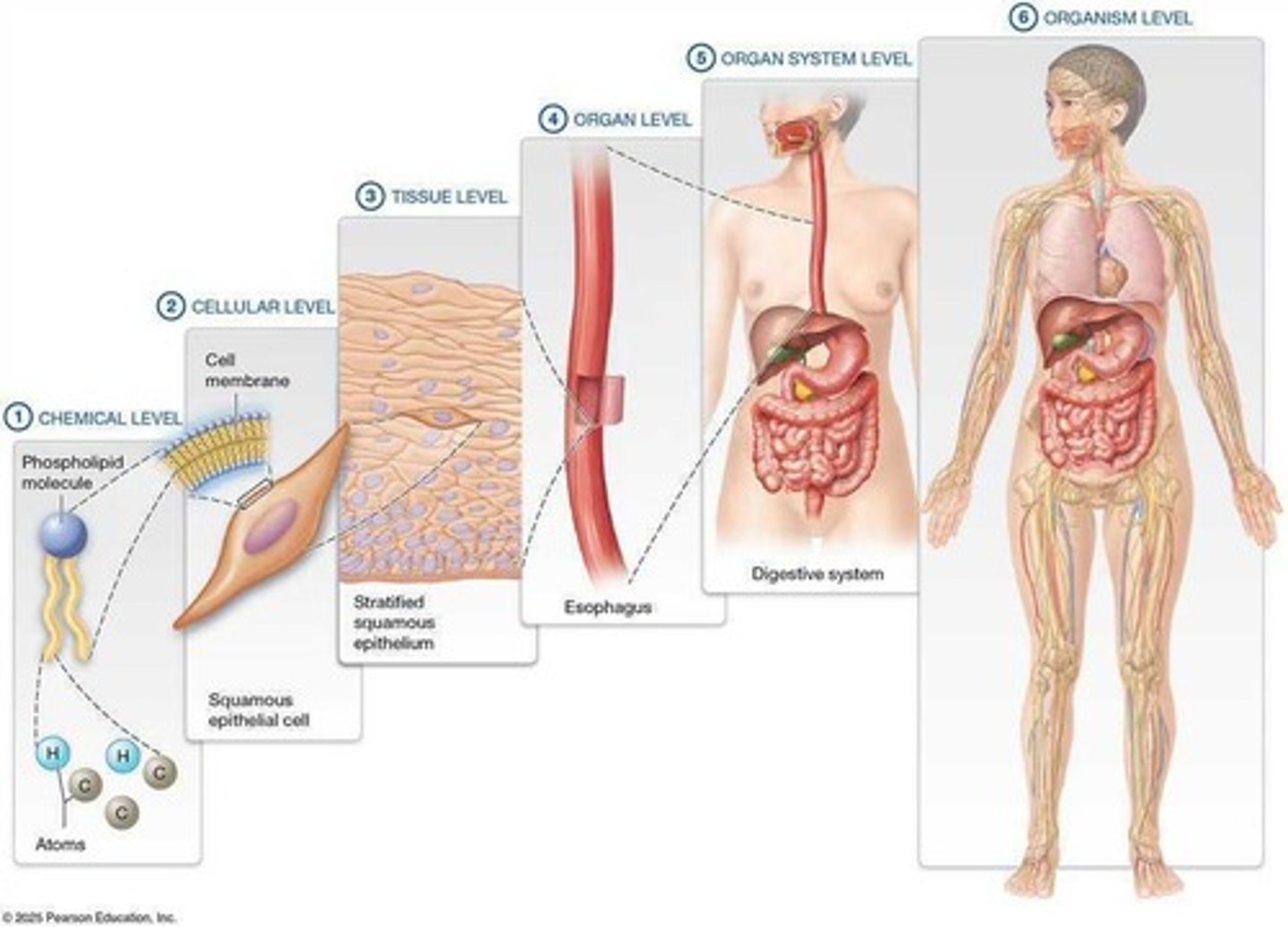
Physiology
Study of body functions related to structure.
Cells
Basic building blocks of all living organisms.
Tissues
Groups of similar cells performing specific functions.
Organs
Structures formed from multiple tissue types.
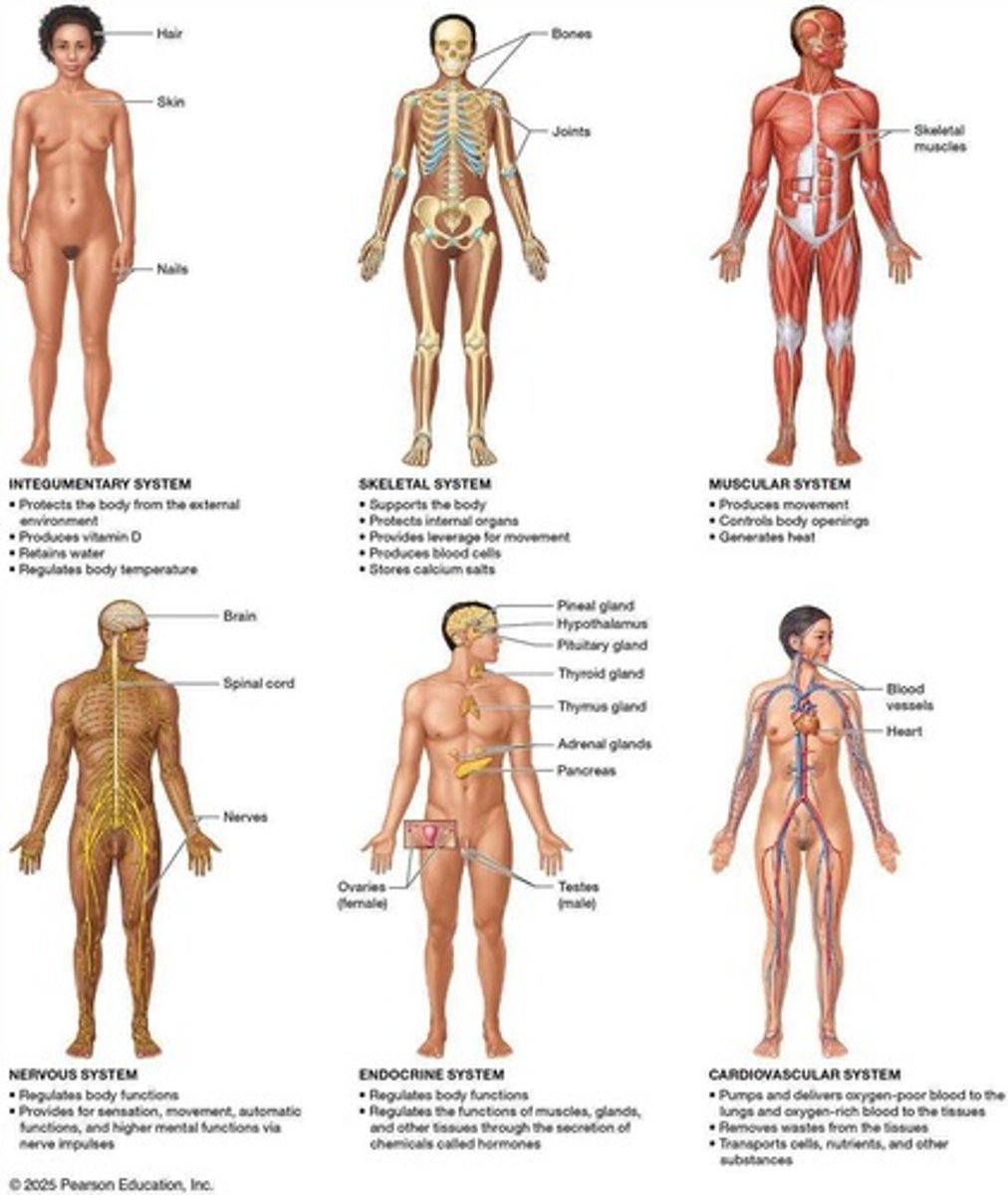
Organ Systems
Groups of organs working together for functions.
Homeostasis
Stable internal environment maintained by the body.
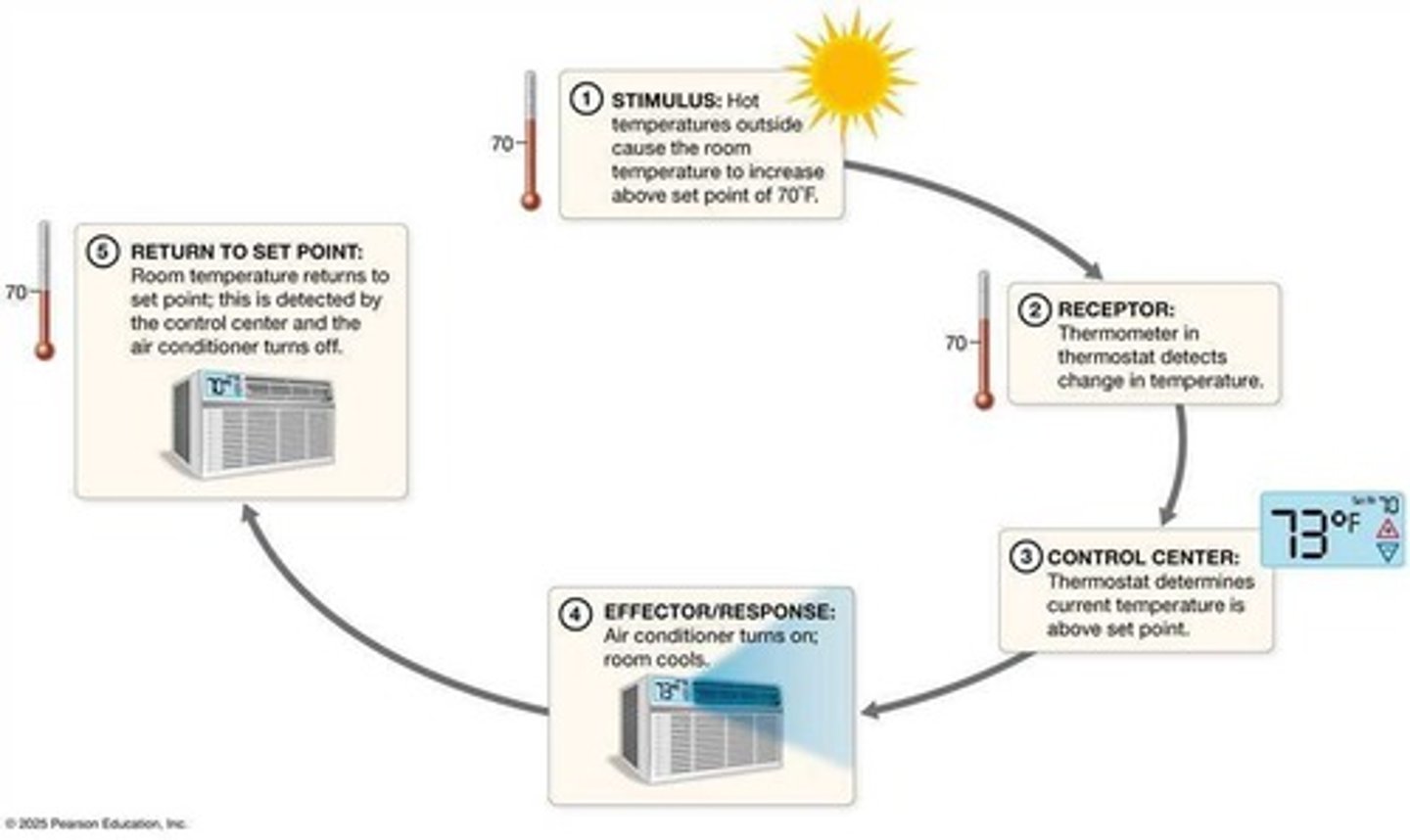
Feedback Loops
Mechanisms regulating homeostasis through responses.
Gradients
Differences in concentration or electrical charge.
Cell-Cell Communication
Interaction between cells for coordination.
Extracellular Matrix
Material outside cells providing structural support.
Chemical Gradients
Concentration differences of substances across membranes.
Electrical Gradients
Charge differences across cell membranes influencing activity.
Organism
A living entity made of multiple organ systems.
Building Blocks
Progressively larger structures forming the body.
Organ Formation
Combination of tissues creating recognizable organ shapes.
Disease
Disturbances in homeostasis leading to health issues.
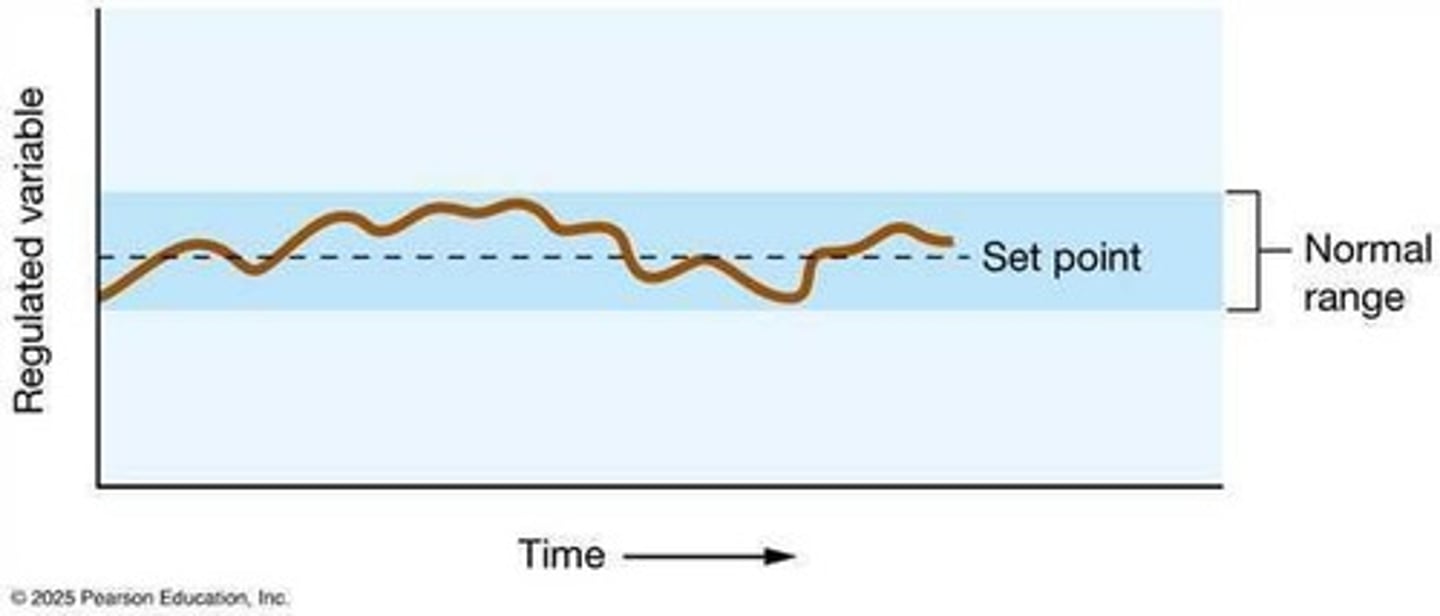
Regulated Variables
Factors manipulated to maintain homeostasis.
Stable Environment
Condition where internal variables remain constant.
Disturbances
Changes that disrupt homeostasis and can cause harm.
Physiological Processes
Activities or rates that maintain body functions.
Chemical Communication
Molecular signals exchanged between cells for function.
Homeostasis
Stable internal environment maintained by regulatory mechanisms.
Regulated Variable
Variable controlled to stay near a set point.
Negative Feedback Loop
Process that counteracts changes to maintain stability.
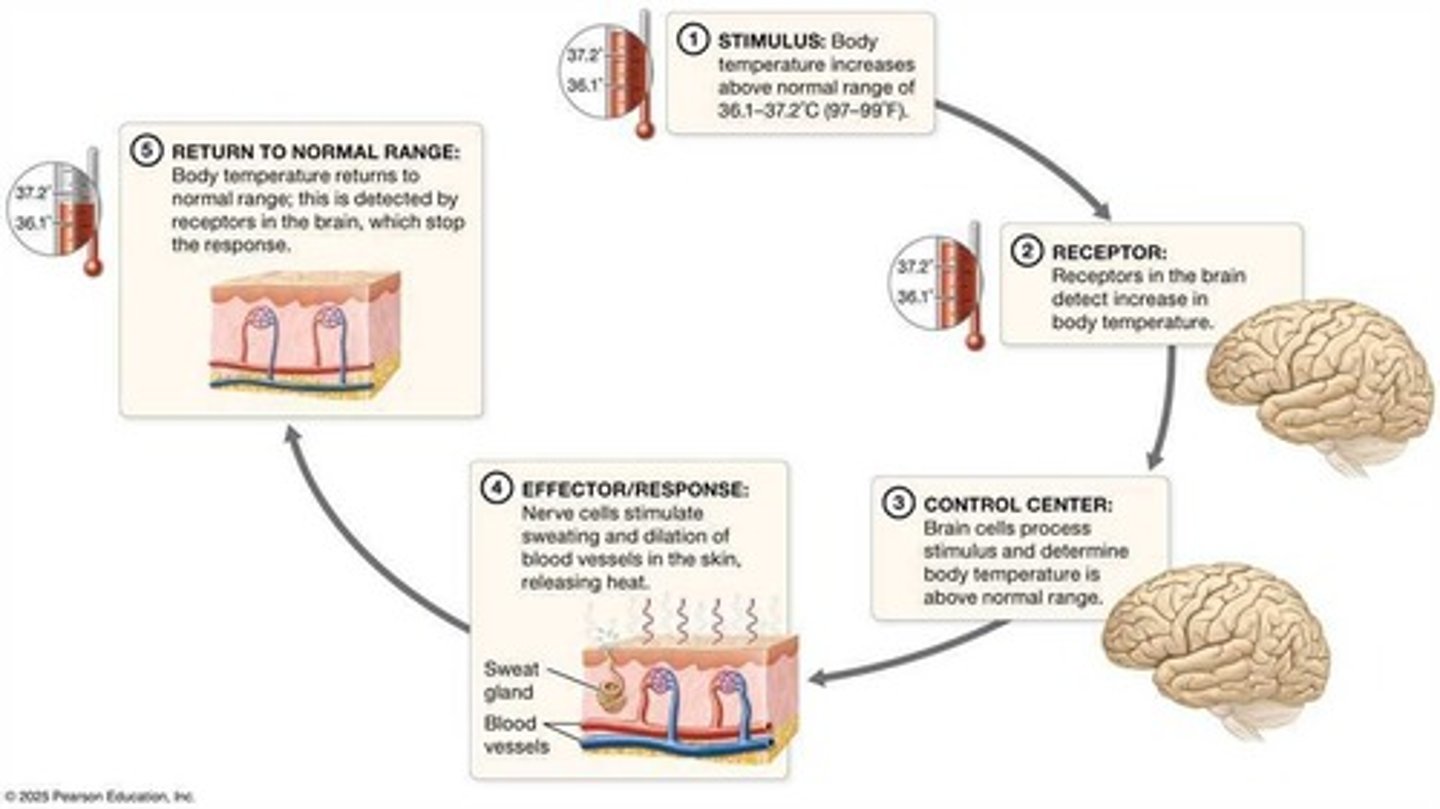
Stimulus
Change that disrupts homeostasis in a variable.
Control Center
Brain or gland that processes stimulus information.
Effector
Organ or cell that responds to restore balance.
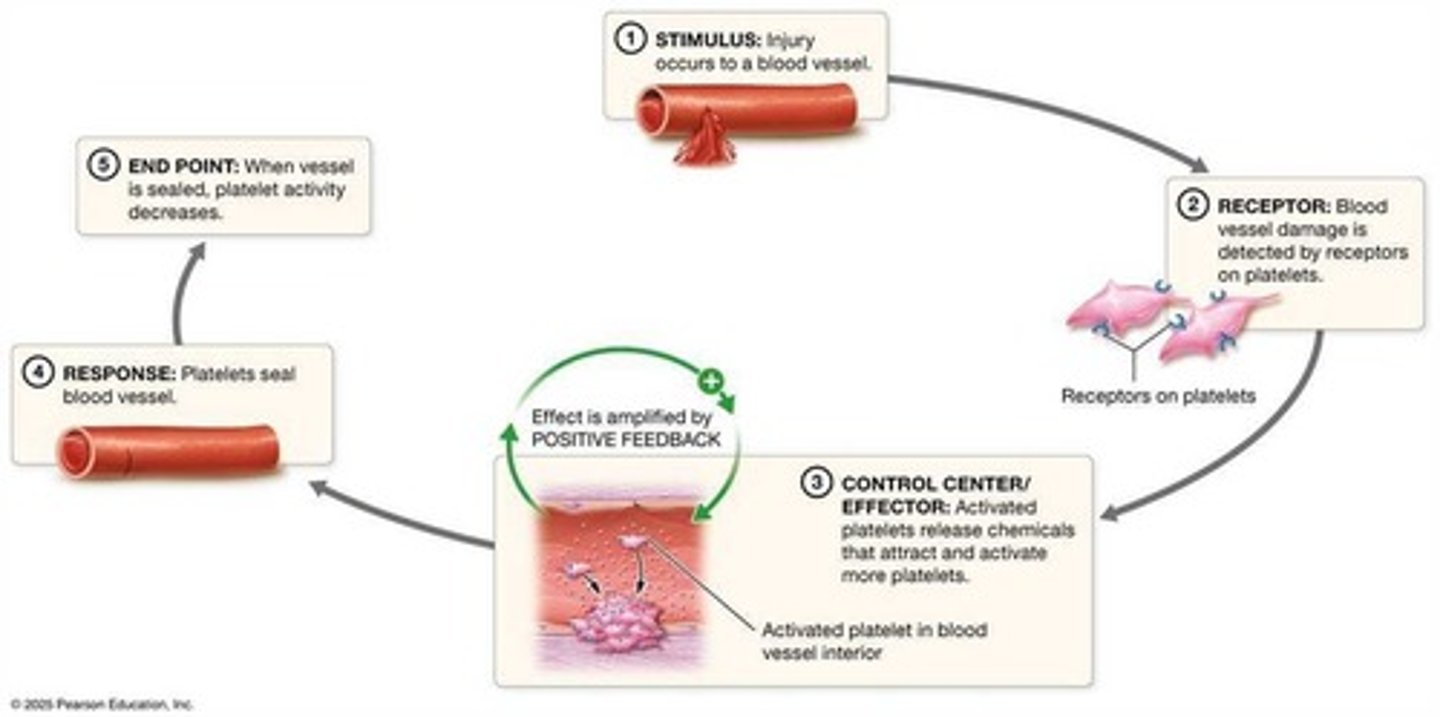
Positive Feedback Loop
Amplifies response to a stimulus until an endpoint.
Chemotaxis
Movement of cells towards a chemical stimulus.
Blood Clotting
Example of positive feedback in response to injury.
Childbirth
Labor initiated by positive feedback mechanisms.
Nervous System
Transmits stimulus information to the control center.
Endocrine System
Releases hormones to regulate body functions.
Set Point
Desired value for a regulated variable.
Cervix
Structure that stretches during childbirth.
Uterine Contractions
Muscle contractions triggered by hormonal feedback.
Oxytocin
Hormone that stimulates uterine contractions during labor.
Temperature Regulation
Example of homeostasis through negative feedback.
Vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels to cool the body.
Sweating
Cooling mechanism activated by increased body temperature.
Cellular Metabolism
Chemical reactions that sustain life in cells.
Cell Membrane
Barrier that controls entry and exit of substances.
Cytoplasm
Fluid inside the cell where organelles reside.
Nucleus
Cell structure housing DNA and controlling functions.
Nuclear Envelope
Double-membrane enclosing the nucleus.
Nucleoplasm
Gel-like substance within the nucleus.
Nucleolus
Site for RNA types and ribosome assembly.
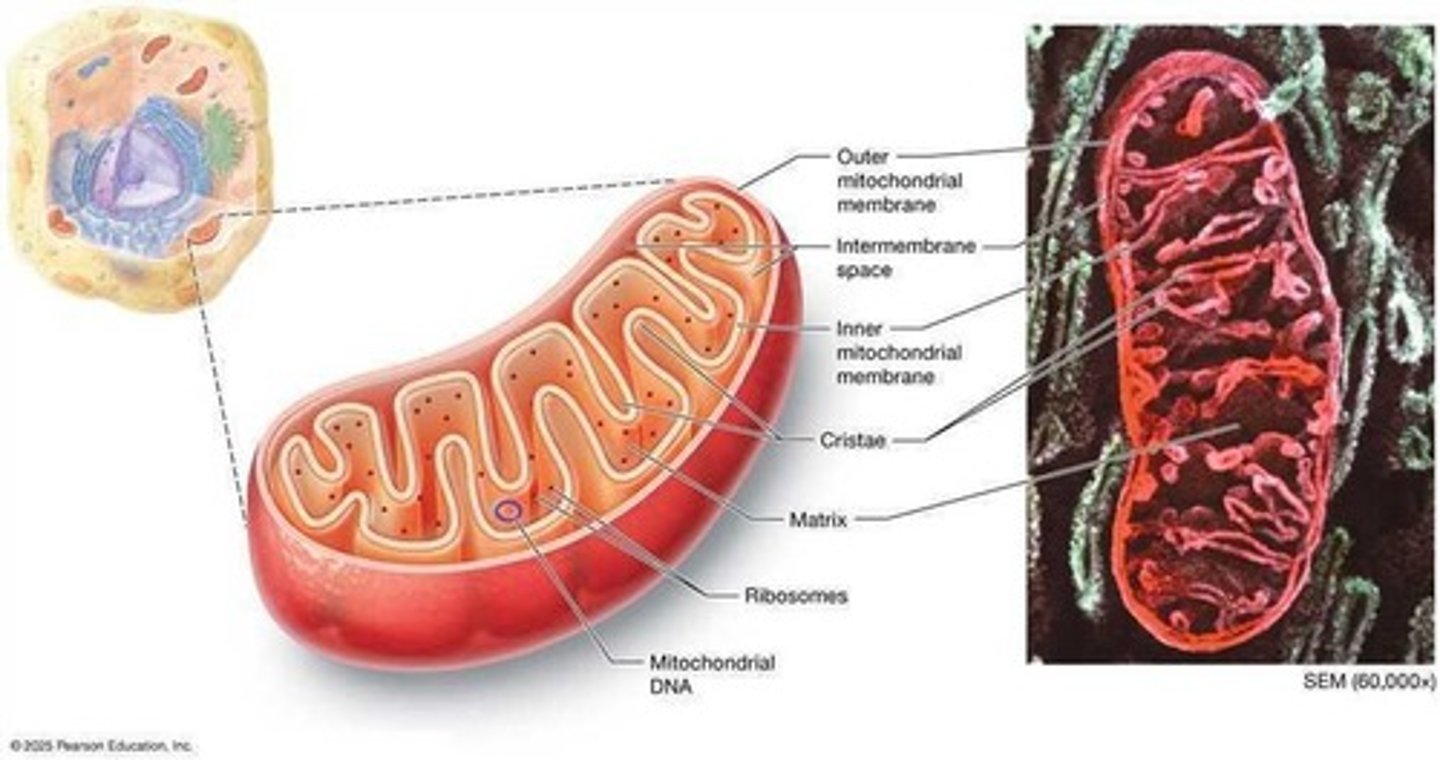
Mitochondria
ATP-producing organelles with double membranes.
Oxidative Catabolism
Process breaking down fuels to produce ATP.
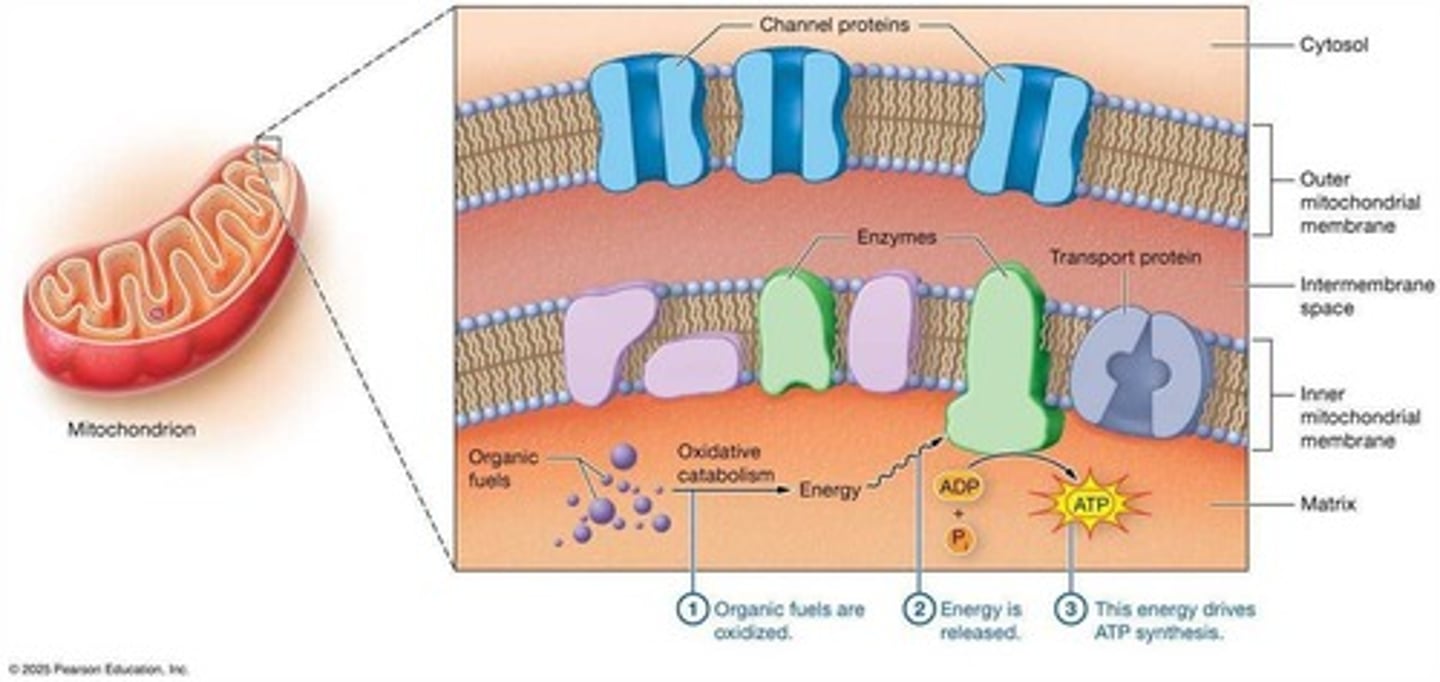
Outer Membrane (Mitochondria)
Contains channels for cytosol substance entry.
Inner Membrane (Mitochondria)
Selective membrane transporting specific substances.
Mitochondrial Matrix
Contains DNA, proteins, enzymes for ATP production.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Membrane with ribosomes, synthesizes proteins.
Polypeptide Folding
RER enzymes fold proteins into 3-D shapes.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrates, often exported from cells.
Transport Vesicle
Membrane-enclosed structure for protein transport.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Lacks ribosomes, involved in lipid synthesis.
Calcium Ion Storage
SER stores calcium ions for cellular use.
Detoxification
SER processes harmful substances in liver cells.
Lipid Synthesis
SER synthesizes cell membrane components and hormones.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis, composed of subunits.
Free Ribosomes
Ribosomes suspended in cytosol.
Bound Ribosomes
Ribosomes attached to organelle membranes.
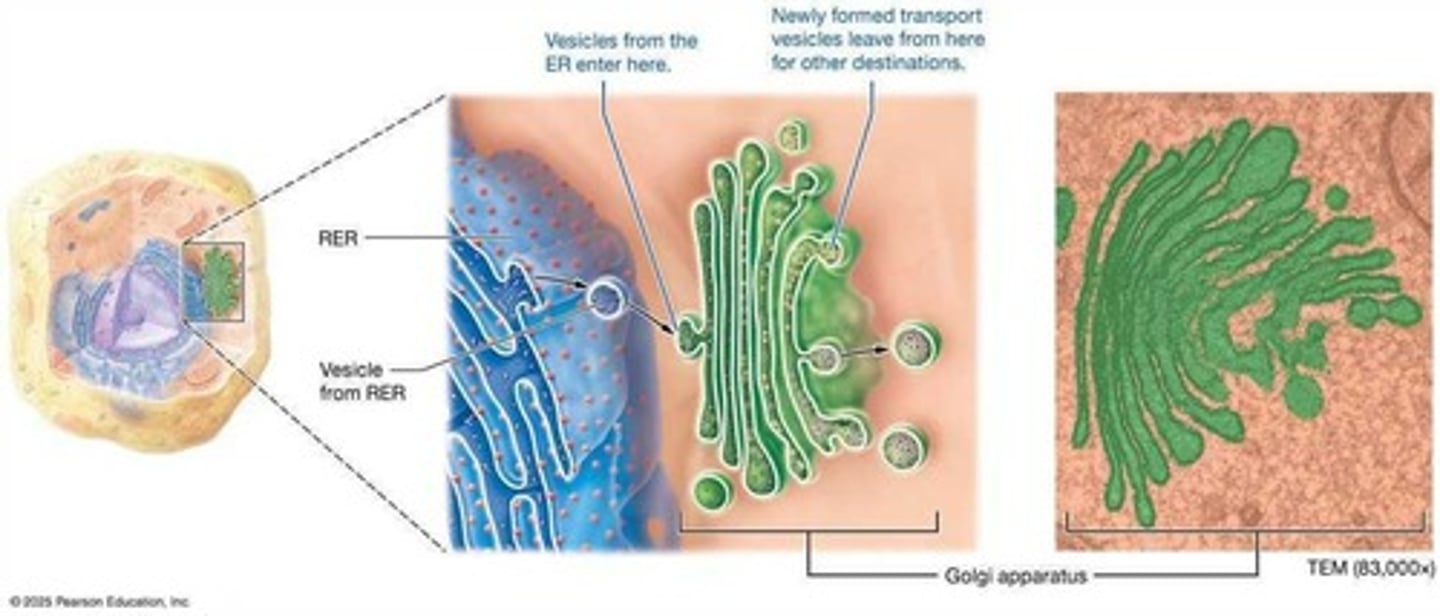
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids.
Secretory Vesicles
Transport proteins outside or within the cell.
Peroxisome
Membrane-bound vesicle containing oxidative enzymes.
Cristae
Folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Modifies and folds proteins; studded with ribosomes.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesizes lipids and detoxifies substances; no ribosomes.
Lysosome
Vesicle containing digestive enzymes for waste breakdown.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Main energy source for cellular processes.
ATP Synthesis
Formed from ADP and inorganic phosphate; energy-intensive.
Glycolysis
First step in glucose catabolism; occurs in cytosol.
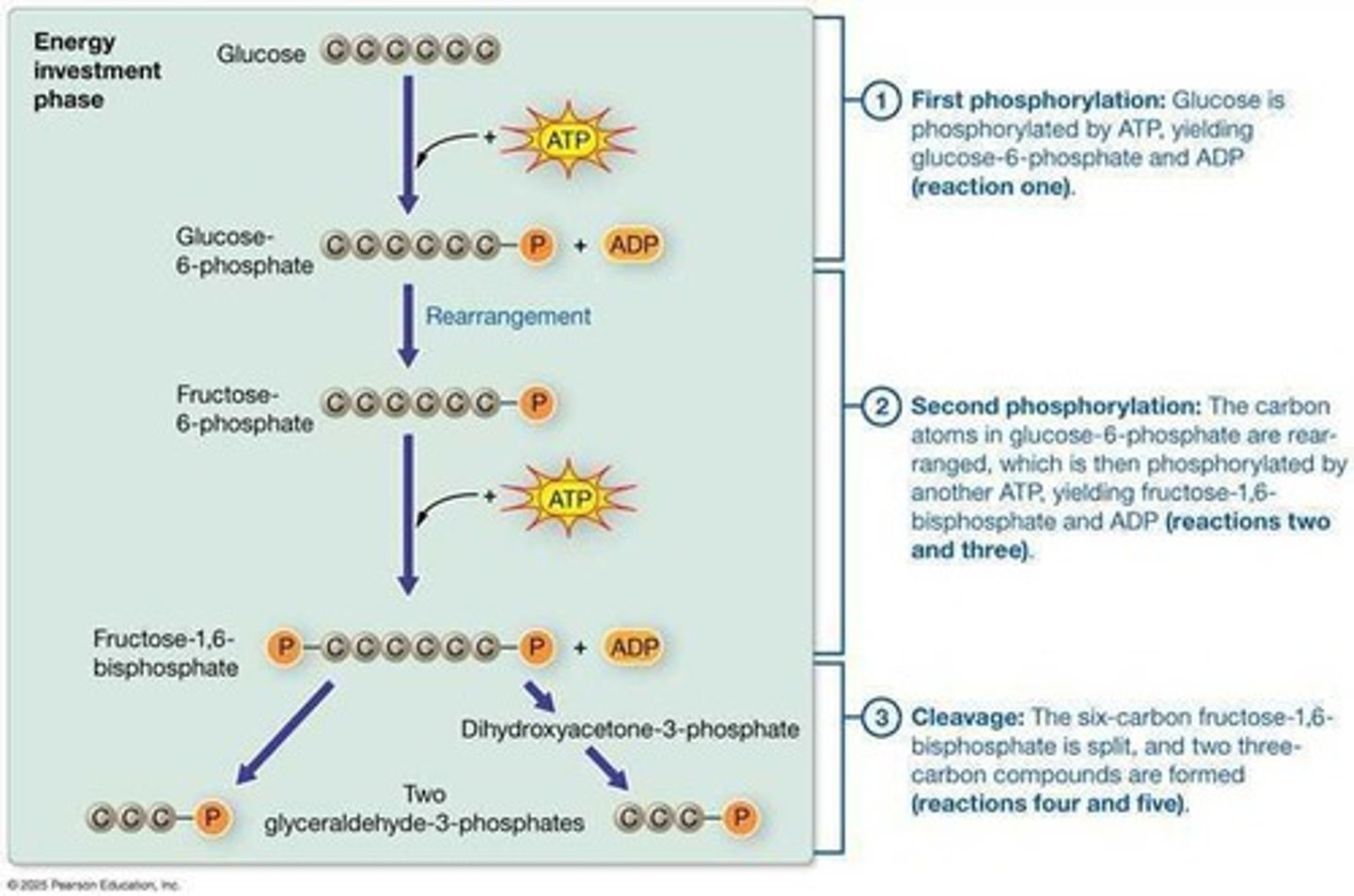
Pyruvate
End product of glycolysis; can convert to lactate.
Mitochondrion
Site of ATP production; involved in aerobic respiration.
Citric Acid Cycle
Series of reactions in mitochondrial matrix; produces ATP.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Transfers electrons to generate ATP via a proton gradient.
NADH
Electron carrier; produced during glycolysis and citric acid cycle.
FADH2
Another electron carrier; produced in the citric acid cycle.
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Direct ATP production during glycolysis and citric acid cycle.
Hydrogen Ion Gradient
Created by ETC; drives ATP synthesis.
Calcium Ion Storage
Function of smooth ER; regulates cellular calcium levels.
Detoxification
Process of neutralizing harmful substances; occurs in smooth ER.
Ribosomes
Molecular machines that synthesize proteins from amino acids.
Plasma Membrane Components
Proteins and lipids synthesized by the endoplasmic reticulum.
Energy Catabolism
Breakdown of glucose, amino acids, or fatty acids for ATP.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Final stage of ATP production; occurs in mitochondria.
ATP Replenishment
Cells continuously regenerate ATP; requires oxygen.
Membranous System
Network of membranes involved in cellular functions.
Saclike Membranes
Structure of rough ER; encloses the ER lumen.
Cyanide
Almond-scented poison affecting ATP production.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Process utilizing oxygen to produce ATP.
Cellular Hypoxia
Condition of insufficient oxygen in cells.
Metabolic Acidosis
Increased acidity in body fluids due to metabolism.
Antidotes for Cyanide
Hydroxocobalamin, sodium nitrite, sodium thiosulfate.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Two-layer structure forming cell membrane barrier.
Hydrophilic Regions
Polar phosphate heads interacting with water.
Hydrophobic Regions
Nonpolar fatty acid tails repelling water.
Intracellular Space
Fluid space within cells containing cytosol.