ALL OF IT
1/880
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
881 Terms
Definition of Exposure?
Amount of charge - of one sign - liberated per mass of air (C/kg)
Definition of TERMA? Equation (coefficient relation)?
Total Energy Released in MAtter
T = Ψ(μ/ρ)… related to mass attenuation coefficient, μ
Definition of KERMA? Equation (coefficient relation)?
Kinetic Energy Released per unit MAss to charged particles
K = Ψ(μtr/ρ)… related to mass energy transfer coefficient, μtr
What are 2 contributions to KERMA?
Kcoll and Krad
What is Kcoll? Equation (coefficient relation)?
Energy released in collision type interaction by charged particles
Kcoll = Ψ(μen/ρ)…related to mass energy absorption coefficient, μen
What is Krad? Equation?
Energy released in radiation interactions.
→ the particles that get this kinetic energy can radiate Bremsstrahlung… Krad accounts for Brem and positron annihilation photons
Krad = Kcoll(g/1-g) … g: fraction of energy lost to radiative processes
KERMA > TERMA. T/F?
False. TERMA > KERMA
Why is TERMA > KERMA?
TERMA includes ALL energy losses, KERMA only include KE transfer to electrons
not all energy is transferred to charged particles (e-) from photons entering medium → some carried away in Compton scattering and photonuclear interactions
Definition of Dose (D)?
Energy absorbed per unit mass (J/kg)
What is Charged-Particle Equilibrium?
when the number of charged particles entering a volume = the number leaving (of the same energy and type)
If CPE exists, what can we say about dose as it relates to Kerma?
Dose in volume = collision Kerma
Dmed = Kcoll
Do we see true CPE in practice? why/why not?
No, because scattering & attenuation
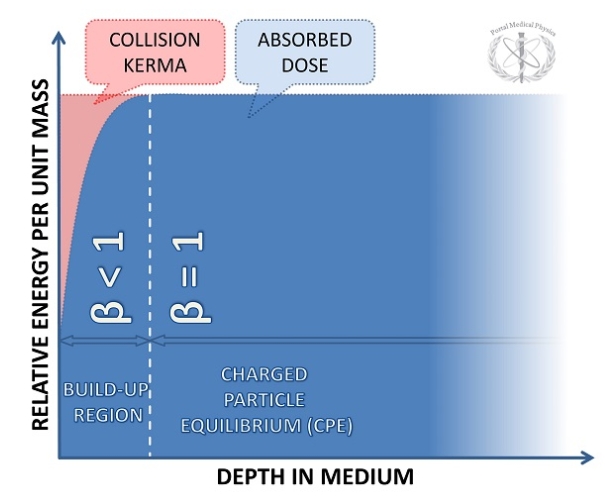
What type of CPE do we see in practice?
Transient CPE
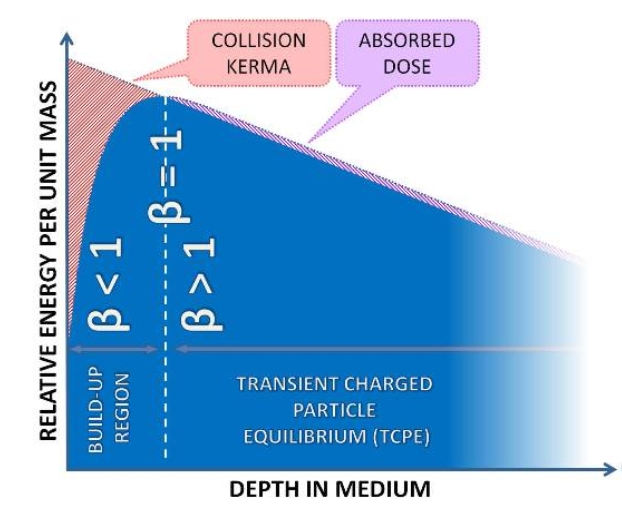
Transient CPE gives what relation to Dose and Kerma?
D = Kcoll * β
β is proportionality between Kerma and Dose
Bremsstrahlung deposits dose in a cavity. T/F, and what relation does this give?
False. Bremsstrahlung generally escape the volume.
Thus, Krad = 0
What relationship do ion chambers provide between Kerma and exposure?
(Kcoll)air = X * Wair/e
What is Wair/e? What does it mean?
Work function for dry air, 33.97 J/C
Amount of energy required to form 1 ion pair in air
Is Brem included in dose calculations? Equation of Dose?
Generally no, because brem escapes the cavity volume…
D ≈ X (Wair/e)
Equations for Dose in medium for photons? Electrons?
photons → Dmed=Ψ(μen/ρ)
electrons → Dmed=φ(S/P)…
φ is partial fluence (# electrons).. S/P is mass collisional spring stopping power
Why we need cavity theory?
to relate dose to air in the chamber to dose in medium of interest
3 main types of cavities?
Bragg-Gray. Spencer-Attix. Burlin
Equation associated with BG cavity theory?
Dmed/Dgas = (S/ρ)med/(S/ρ)gas
(S/ρ) is mass collisional stopping power
What causes ionization in BG cavity?
electrons from outside cavity… requires CPE/TCPE
How does BG cavity presence affect secondary electron spectrum? What does this mean for the size of a BG cavity?
it doesn’t → implies small cavity
T/F, delta rays contribute more dose to the opposite wall of a BG cavity.
False. BG cavity theory IGNORES delta rays
Equation for Spencer-Attix Cavity theory?
Dmed/Dgas = (Lbar/ρ)med/(Lbar/ρ)gas
Restricted stopping power ratio
How are secondary electrons impacted in SA theory?
2 groups defined by cutoff energy, Δ.. E ∝ Δ required for electron to just cross cavity
1. E < Δ (Slow electron) deposit energy where created
2. E > Δ (fast. DELTA RAYS) deposit energy according to CSDA
Size of SA cavity?
Small. Because restricted Stopping powers ∝ Δ
Differences between BG and SA cavity theories?
BG → ignores delta rays. Uses normal mass collisional stopping powers
SA → Includes deltas. Uses Restricted mass collisional stopping powers
Size of Burlin Cavity?
Medium… bridges gap between small and large
Could be any, depending on d factor
CPE requirement for all 3 cavities?
BG → CPE or TCPE
SA → CPE or TCPE
Burlin → CPE in medium (wall), but not cavity
Equation of Burlin cavity theory?
Dmed/Dgas = d(ratio of restricted stopping powers) + (1-d)(ratio of mass attenuation coefficients over rho)
d is parameter related to size of cavity → d=1 if small. d=0 if large
Full equation for Dair? (with those 6 scaling parameters)
Dair = Dair,chamber∗Pfl∗Pgr∗Pwall∗Pcel∗Pion∗Ppol
Dair,chamber=X∗Work function
What is Pfl? two main issues?
Chamber fluence effects
In-scattering - more electrons scatter in than out of chamber, because electrons don’t scatter as readily by air as they do water
Presence of chamber INCREASES fluence, therefore readings
Obliquity - gas doesn’t scatter secondary electrons as much as phantom
electron travel straighter in chamber… reduces ionization and therefore DECREASES reading
Which chamber fluence effect is most pronounced in RT sized chambers?
In scattering
T/F, when using a plane parallel chamber, it is especially important to include chamber fluence corrections
False. Plane parallel chamebrs don’t need these corrections at all
What is Pgr? For what chambers?
Gradient effects, for cylindrical chambers…
cylindrical chamebrs behave like they read upstream of chamber’s center → if reading where fluence is changing, ERRORS (like descending portion of %DD curve)
Pion?
Recombination effects - accounts for ion pairs recombining before collection
Ppol? More severe in which species of beam?
Polarity effects - changes in reading when voltage is reversed on chamber
More severe for electron beams
2 types of polarity effects?
Compton current - secondary e- may be counted as ionized charge in cavity
Extracameral current - current collected outside of sensitive volume
Pwall?
Wall corrections - if chamber wall is different material than phantom → accounts for ionization events in wall
Pcel?
Central electrode corrections - materials of central electrode
What is full theoretical equation for Dose in medium?
Dair = Q∗Nx∗PTP∗Pfl∗Pgr∗Pwall∗Pcel∗Pion∗Ppol
Q∗Nx∗PTP is the dose in air equation from earlier, just written with NX correction for TG-21
What is the TG-51 Dose equation?
Dw,Q=Mraw∗(NCo-60/ND,w)∗KQ∗PTP∗Pelec∗Pion∗Ppol
Dw,Q is dose to water for beam quality Q
Mraw is raw chamber reading
N ratio is cal factor in a Co-60 beam in water
Pelec is cal factor for different electrometers
KQ relates chamebr response in C0-60 to your beam of quality Q (KQ has all the corrections from the theoretical equation)
Equation for KQ in TG-51 Dw,Q equation?
KQ = (Ratio of L/ρ for water to air ∗Pfl∗Pgr∗Pwall∗Pcel∗Pion)Q divided by (Ratio of L/ρ for water to air ∗Pfl∗Pgr∗Pwall∗Pcel∗Pion)Co-60
Definition of Exposure?
Amount of charge - of one sign - liberated per mass of air (C/kg)
Definition of TERMA? Equation (coefficient relation)?
Total Energy Released in MAtter
T = Ψ(μ/ρ)… related to mass attenuation coefficient, μ
Definition of KERMA? Equation (coefficient relation)?
Kinetic Energy Released per unit MAss to charged particles
K = Ψ(μtr/ρ)… related to mass energy transfer coefficient, μtr
What are 2 contributions to KERMA?
Kcoll and Krad
What is Kcoll? Equation (coefficient relation)?
Energy released in collision type interaction by charged particles
Kcoll = Ψ(μen/ρ)…related to mass energy absorption coefficient, μen
What is Krad? Equation?
Energy released in radiation interactions.
→ the particles that get this kinetic energy can radiate Bremsstrahlung… Krad accounts for Brem and positron annihilation photons
Krad = Kcoll(g/1-g) … g: fraction of energy lost to radiative processes
KERMA > TERMA. T/F?
False. TERMA > KERMA
Why is TERMA > KERMA?
TERMA includes ALL energy losses, KERMA only include KE transfer to electrons
not all energy is transferred to charged particles (e-) from photons entering medium → some carried away in Compton scattering and photonuclear interactions
Definition of Dose (D)?
Energy absorbed per unit mass (J/kg)
What is Charged-Particle Equilibrium?
when the number of charged particles entering a volume = the number leaving (of the same energy and type)
If CPE exists, what can we say about dose as it relates to Kerma?
Dose in volume = collision Kerma
D = Kcoll
Do we see true CPE in practice? why/why not?
No, because scattering & attenuation

What type of CPE do we see in practice?
Transient CPE

Transient CPE gives what relation to Dose and Kerma?
D = Kcoll * β
β is proportionality between Kerma and Dose
Bremsstrahlung deposits dose in a cavity. T/F, and what relation does this give?
False. Bremsstrahlung generally escape the volume.
Thus, Krad = 0
What relationship do ion chambers provide between Kerma and exposure?
(Kcoll)air = X * Wair/e
What is Wair/e? What does it mean?
Work function for dry air, 33.97 J/C
Amount of energy required to form 1 ion pair in air
Sodium’s atomic number is 11, what is likely decay mode for Na21?
positron emission, β+… because Z = 11 and N = 10, extra proton removed, returns to Line of Stability
Nearly all emitted radiation from Tc-99m is characterized as what?
Gamma rays… Because Tc-99m is in an excited state, it will undergo Isomeric Transition, emitting a γ-ray
Activity of a radioactive material may be defined as dN/dt, where N is number of atoms, and t is time. T/F.
True
What is true regarding radioactive decay constant?
inversely proportional to half life
Equal to inverse of mean life
Defined as fractional decay in a given time
What is true regarding specific activity?
Defined as activity per unit mass
proportional to decay constant → because A=λN, Aspecific is proportional as well
Carbon has an atomic number of 6, what is likely decay mode for C14?
β-, because Z=6 and N=8, β- removes the extra neutron, returning it to line of stability
Pure Ra-226 (T1/2=1600 yr) is chemically isolated. Its direct progeny, Rn-222 has T1/2=3.8 days. Immediately after isolation, what equilibrium is present, if any?
NO equilibrium. Key word: IMMEDIATELY. Full equilibrium takes several half lives of daughter
Two isotopes in secular equilibrium both appear to decay with T1/2, parent. T/F
True! Since Progeny is being replaced at a rate equal to parent’s decay, it appears to decay at the same rate
Decay schemes…
yuh
Accompanying all positron emission decays there is also a…? (Neutrino, antineutrino, electron)
Neutrino
Nuclear fission most likely with light nuclei. T/F
False
Which would occur 2 months after placing Ra-226 in a sealed container with its progeny? (Transient, Secular, No equilibrium)
Secular… takes ~ a month
As Z increases, the ratio of Z:N does what?
decreases.
Need more neutrons to overcome repulsion force of protons
Equilibrium between Mo-99 and Tc-99m?
Transient
I-125 is implanted and gives a total dose of 145 Gy. What is the implanted dose rate? (units given at cGy/hr)
2 ways…
T1/2 given on ABR sheet. Calculate Mean Life using Tmean=1.443*T1/2… follow through with units
Amean = Ao1.443T1/2, so Dmean = 1.443DoT1/2 as well
So 7 cGy/hr
In a sealed container, parent and progeny achieved secular equilibrium. What is true about decay of progeny? (decays as same rate as parent, reaches steady state value which remains stable)
Reaches steady state value which remains stable
Match decay types with their effect on Z…
Alpha - Z-2
gamma - Z
β- - Z+1
e- capture - Z-1
What is released during isomeric decay?
Gamma ray
Ir-192 has activity of 10 Ci. After how many half-lives will it be 2.5 Ci?
2
Which decay type emits characteristic x-ray? (isomeric, internal conversion, alpha)
internal conversion…
not uncommon after isomeric, as emitted gamma can undergo “photoelectric effect” type interaction
Qualities of EM radiation…
NO mass or charge → BUT HAS momentum
NOT deflected in B field
IS deflected by gravitational field
NOT always 3×108
Photons of 1.5 MeV interactions?
virtually ZERO probability of photoelectric and pair production
electron in water has Bragg peak similar to proton. T/F
True, all charged particles do. However, NOT seen in practice because random paths blur the Bragg Peak
Interaction type most associated with Auger electron?
Photoelectric
Energies where Pair Production dominates?
over 25 MeV
6 MV photons, is neutron activation appreciable?
NO. neutrons activated at 8 MV, appreciable at 10 MV
range of 0.8 MeV beta is 4mm, what is LET?
800 keV / 4000 um = 0.2 keV/um
Compton qualities. Max energy? CHaracteristic x-rays?
max energy transfer at 180 backscatter.
NO characteristic x-rays, because outer shell electrons for Compton interactions
interaction type with scattered photon of different direction & energy?
Compton
Interaction responsible for blue sky?
Coherent Scattering
Does muscle or bone receive higher neutron dose?
muscle, because higher hydrogen content (lower Z)
Bremsstrahlung efficiency in diagnostic tubes?
~1%
What is the average energy of Bremsstrahlung spectrum?
1/3 of max energy
What interaction(s) is/are Z INdependent?
ONLY Compton
Match graphs…
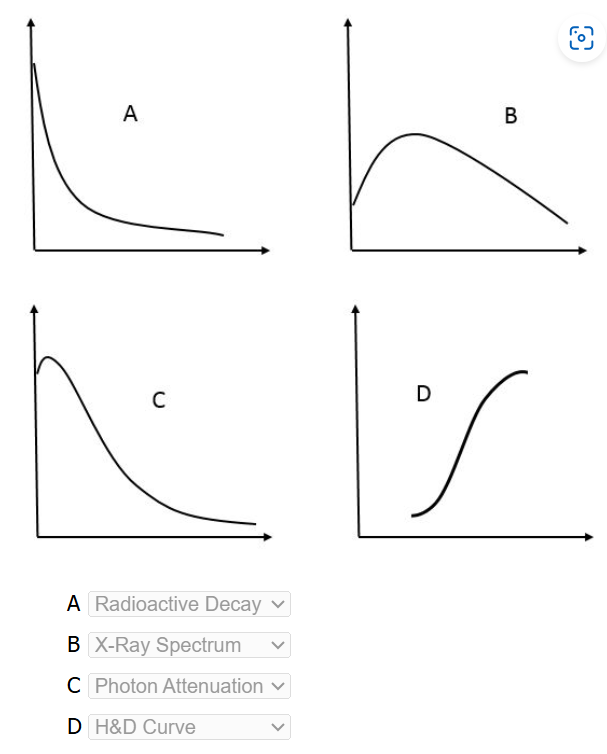
Match interactions and descriptions…
Rayleigh = attenuation w/o absorption
photoelectric = characteristic x-rays
compton = most scattered electrons
Pair production = min 1.022 MeV photon
photodisintegration = neutron production
What has a threshold of 8 MeV?
Photonuclear interactions… 8 MeV to overcome nucleon binding energy