Introduction to Substitution Elimination Reactions
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
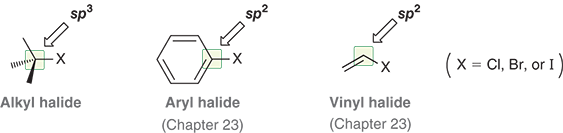
What are alkyl halides?
Compounds where a halogen is bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon
Which halogens are common in alkyl halides?
Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), and Iodine (I)
What kind of carbon is a halogen attached to in an alkyl halide?
An sp3 hybridized carbon ( a carbon with four single bonds)
What are aryl halides and vinyl halides?
There are compounds where the halogen is attached to an sp2 hybridized carbon
benzene ring (aryl)
double bond (vinyl)
Example of alkyl, aryl, and vinyl halide
What are the two main types of reactions alkyl halides can undergo?
Substitution and elimination reactions
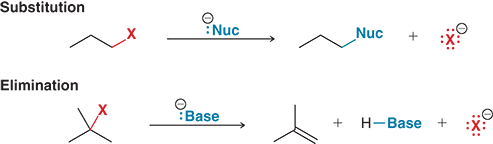
What happens in a substitution reaction?
A nucleophile replaces the halogen with a carbon atom
What reagent causes a substitution reaction?
A nucleophile
What happens in an elimination reaction?
A base removes a hydrogen (H) from a nearby carbon, and the halogen leaves, forming a π (pi bond)
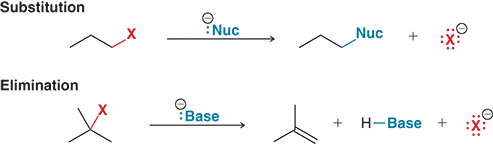
What is formed during an elimination reaction?
An alkene, which is a carbon-carbon double bond (π bond)
What reagent causes an elimination reaction?
A base
How can you tell if an alkyl halide will do substitution or elimination?
Nucleophile → substitution reaction
Base → elimination reaction
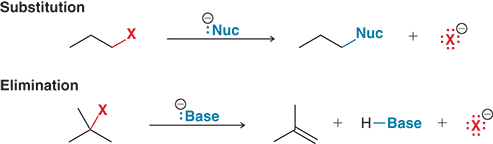
Why can substitution and elimination reactions compete with each other?
Because many reagents, like hydroxide (HO-), can act as either a nucleophile or a base, allowing both reaction types to occur
When a reagent acts as a nucleophile, what type of reaction occcurs?
A substitution reaction, where the nucleophile replaces the halogen
When a reagent acts as a base, what type of reaction occurs?
An elimination reaction, where the base removes a hydrogen, forming a double bond
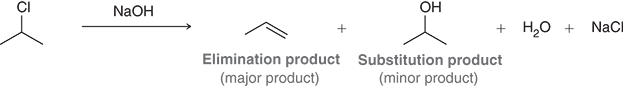
What does the following picture demonstrate?
NaOH can act as both a base and a nucleophile, so both elimination and substitution occur.
But because conditions favor the base behavior, the elimination product (alkene) forms in larger amounts.
What is the substrate in substitution and elimination reactions?
The alkyl halide- the molecule containing the halogen
What two critical roles does the halogen play in an alkyl halide?
It pulls electron density away, making the carbon electrophilic
It can leave as a stable anion or neutral molecules ( a leaving group)
Why does the halogen make the carbon electrophilic?
Because it withdraws electron density through its inductive effect, leaving the carbon electron-poor
What makes a good leaving group?
A weak base or a stable anion when it leaves
Why is iodine (I-) a good leaving group?
Because it is a conjugate base of a strong acid (HI), making it a very weak base and therefore a good leaving group
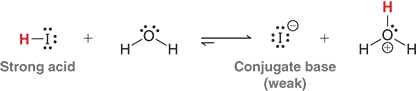
Explain the image
The image shows a strong acid donating a proton to water, forming a weak conjugate base and H3O+
This demonstrates that strong acids have weak conjugate bases which are good leaving groups in reactions
Are bromide (Br-) and chloride (Cl-) good leaving groups?
Yes- like iodide, they are weak bases and stable, so they are good leaving groupd
Why is hydroxide (OH-) a poor leaving group?
Because it is a strong base and unstable when it leaves- it does not make a good leaving group
What is the relationship between base strength and leaving group ability?
The weaker the base, the better the leaving group
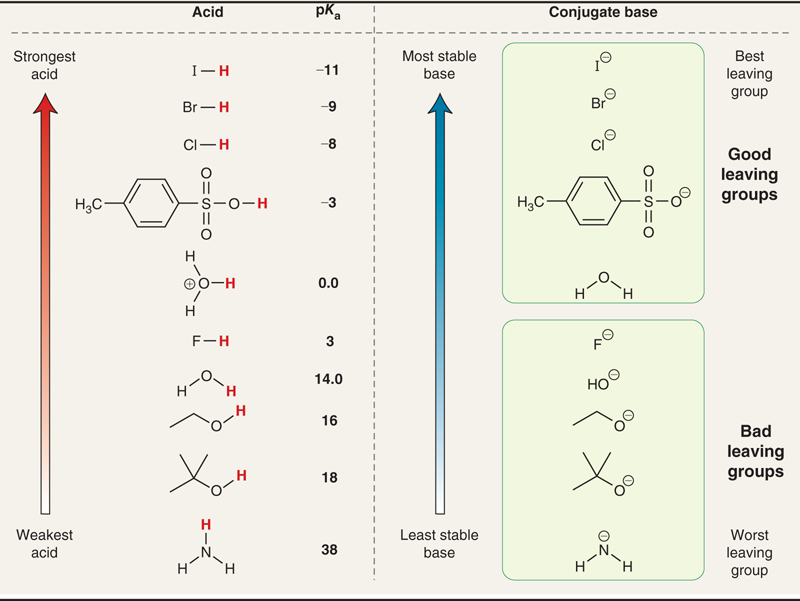
Explain the chart
The chart shows the relationship between acid strength (pKa), base stability, and leaving group ability
Good leaving groups come from strong acids (low pKa) → weak conjugate bases → stable when they leave.
What makes a good leaving group?
A weak base that is the conjugate base of a strong acid (pKa <0)
Among halides, which is the best leaving group?
Iodide (I-)- it is the weakest base and most stable when it leaves
Why is fluoride (F-) a poor leaving group?
Because HF has a high pKa, so F- is a strong base and unstable when it leaves
What are the most common types of leaving groups?
Halides (I-, Br-, Cl-) and sulfonate ions (RSO3-)
What is the rule of thumb for predicting good leaving groups?
If the conjugate acid has a pKa less than 0, its conjugate base is a good leaving group