
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
How to calculated (Disability-adjusted life years) DALYs?
DALY= YLL (years of life lost) + YLD (year of life disabled)
YLL= N (number of deaths) x L (standard life expectancy at age of death in years)
YLD= I (number of incident cases) X DW (disability weight) X L (average duration of the case until remission or death)
Substance use
Use of psychoactive substances that alter mood, perception, and level of consciousness.
Stimulants
Overstimulate the CNS, resulting in accelerated heart rate, high blood pressure, and other symptoms related to stimulation of the CNS
Examples of stimulants
Cocaine, amphetamines, methylphenidate, nicotine, methamphetamine, Ritalin, caffeine, and methedrine
Narcotics
relieve pain and can result in a state of euphoria and other mood changes
Examples of narcotics
Vicodin and OxyContin, opium, morphine, heroin, codeine, hydromorphone, meperidine, methadone, Darvon
Dissociative anesthetics
inhibits the body’s ability to perceive pain
Example of Dissociative anesthetics
PCP
Depressants
Depress the CNS, thus slowing down the brain and the body
Examples of depressants
Alcohol, barbiturates, and anti-anxiety tranquilizers (e.g., Valium, Librium, Xanax, Prozac, and Thorazine)
Inhalants
Come from a wide range of chemicals that are inhaled, producing mind-altering effects
Examples of Inhalants
Butyl nitrite, amyl nitrite gas used in some aerosol cans, gasoline and toluene vapors from correction fluid, glue, marking pens
Hallucinogens
Result in altered perception of reality
Examples of hallucinogens
PCP, LSD, mescaline, peyote, psilocybin, ecstasy, PCE, methamphetamine, and cannabis
Cannabis
Results in a feeling of euphoria and can include distorted perceptions and memory impairment, as well as difficulty thinking and solving problems
Examples of Cannabis
marijuana, tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC; hashish; hashish oil; and synthetics such as dronabinol
Components of substance use
helps determine the risk of adverse consequences
quantity of substance
frequent use
pattern of use
duration of use over lifetime
quality of substance
quantity of substance
the amount consumed (dose)
Frequency
how often the substance us consumed (daily, weekly, or monthly)
Pattern of use
whether the use is consistent or occurs in an episodic manner (binging)
Duration of use over a lifetime
how long over a lifetime the use has occured.
Quality of substance
manufacturing process of the substance consumers and whether the product might include toxins or other substances.
what are levels of continuum of substance use?
No use
Beneficial use: under medical supervisions
Non-problematic: use without any physical or mental health impacts
Problematic use: patterns and types if use that have a higher risk of physical and mental health impacts.
Potential harmful: episodic use that can and may be leading to harmful impacts
Substance use disorder
Substance Use Disorder
maladaptive pattern of substance use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress
Tolerance
an adaptation of the body to a drug that results in needing more drug to achieve a certain effect
Withdrawal
drug-specific physical or mental symptoms that occur on abrupt stop of drug use.
Physiologic dependence
evidence of tolerance to or withdrawal of a foreign substance.
Physical Dependence
unpleasant physical symptoms that occur when the drug is stopped or taken in smaller doses
What are some upstream approach for substance use disorder?
Reduce harm at the population level through prevention of substance use.
Reduction of harms associated with substance use.
Early treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs).
Decriminalization of substance use. ( rather than sending them to jail, they focus on treating the problems)
Broader policy initiatives.
Harm reduction model
Intervention focus ranges from safer use to abstinence
Intervention goals are to minimize physical, emotional, social and economic harm
Interventions address individual and population levels
Interventions are free of judgement and blame
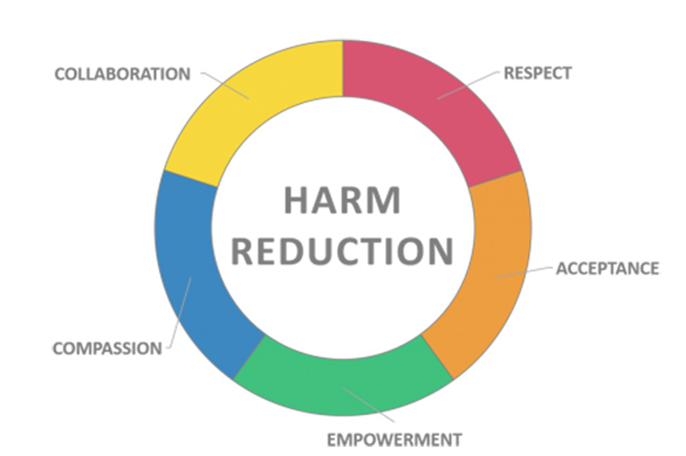
Nursing guidelines for harm reduction
Be culturally competent and nonjudgmental in providing services.
Be responsible for delivering interventions that reduce the impact of SDOH in the community.
Develop new strategies to address unsafe health practices in addition to traditional strategies.
Develop harm reduction strategies for those clients who are unable or unwilling to modify unsafe behaviors.
Don’t’ treat relapses and returns to unsafe health practices as failure of treatment.
Work in collaboration with other programs to provide comprehensive services.
Offer a range of treatments across a continuum of care for your clients.
Effects of alcohol
The direct effect of alcohol is determined by the blood
Excess alcohol that is not metabolized circulates in the blood and affects the central nervous system and the brain alcohol level.
The body processes alcohol dependent on several factors
Size and weight of the drinker
Sex (affects metabolism)
Carbonation (increases absorption)
Time elapsed during alcohol consumption
Food in the stomach
The drinker’s emotional state
Type of alcohol
What are the vulnerable population exposed to alcohol across the lifespan?
Pregnancy and Fetal Exposure
Children
Adolescents and early adulthood
Older Adults
What are the 5-As
Ask about nicotine use
Advise to quit using clear, personalized massages
Assess willingness to make a quit attempts
Assists in quit attempt
Arrange follow up and support
MPOWER
Policy interventions
Monitor tobacco use and prevention policies.
Protect people from tobacco smoke
Offer help to quit tobacco use
Warn about the dangers of tobacco
Enforce bans on tobacco advertising, promotion, and sponsorship
Raise taxes on tobacco
Physical Assessment Findings
VITAL SIGNS: Varies depending on the substance being used.
APPEARANCE: Individual can appear disheveled with an unsteady gait.
EYES: Pupils can appear dilated or pinpoint, red, and with poor eye contact.
SKIN: Can be diaphoretic, cool, and/or clammy. Needle track marks or spider angiomas can be visible.
NOSE: Can be runny, congested, red, and/or cauliflower‐shaped.
TREMORS: Fine or coarse tremors can be present.