Animal Behavior
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Which behavior is innate and is molded by natural selection in order to increase fitness?
behavior inherited through genes
(Note: behavior can also be learned)
What is the study of behavior that seeks to explain how specific behaviors increase fitness?
behavioral ecology
Which reflexes are automatic and involve two nerves: afferent and efferent nerves?
simple reflexes
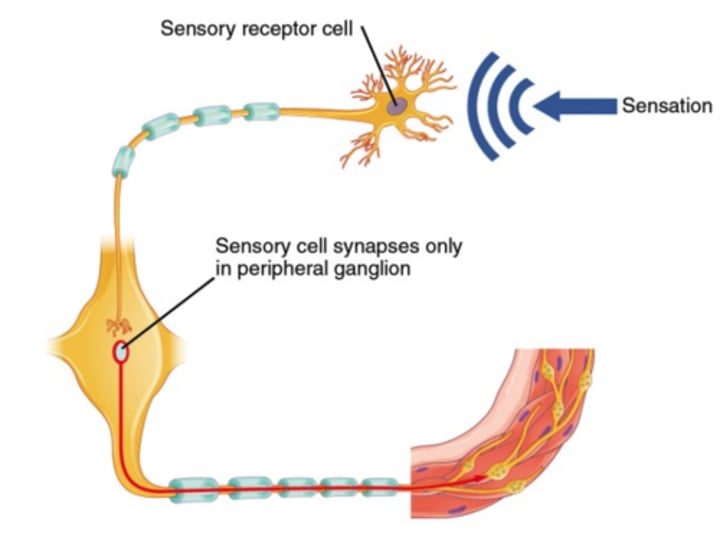
In simple reflexes, where in the body is the response to the stimulus controlled?
spinal cord
Which reflexes are automatic responses to significant stimuli?
complex reflexes
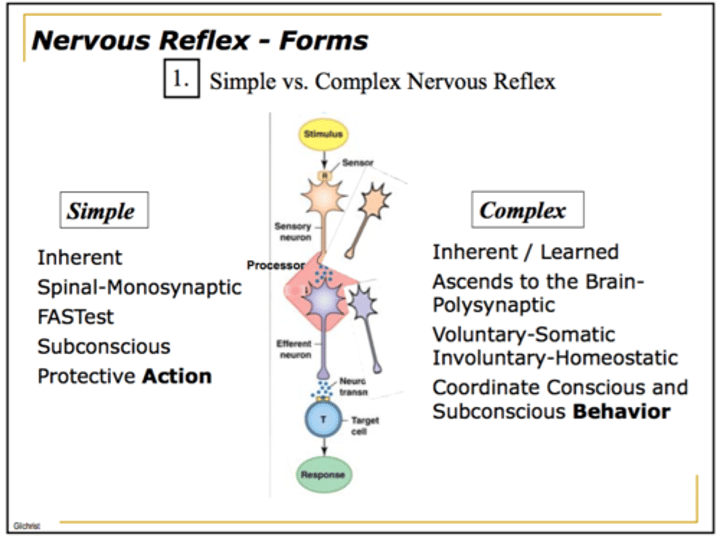
Why are complex reflexes slower than simple reflexes?
The nerves in a complex
reflex are separated by
an interneuron and do
not converge in the spinal cord
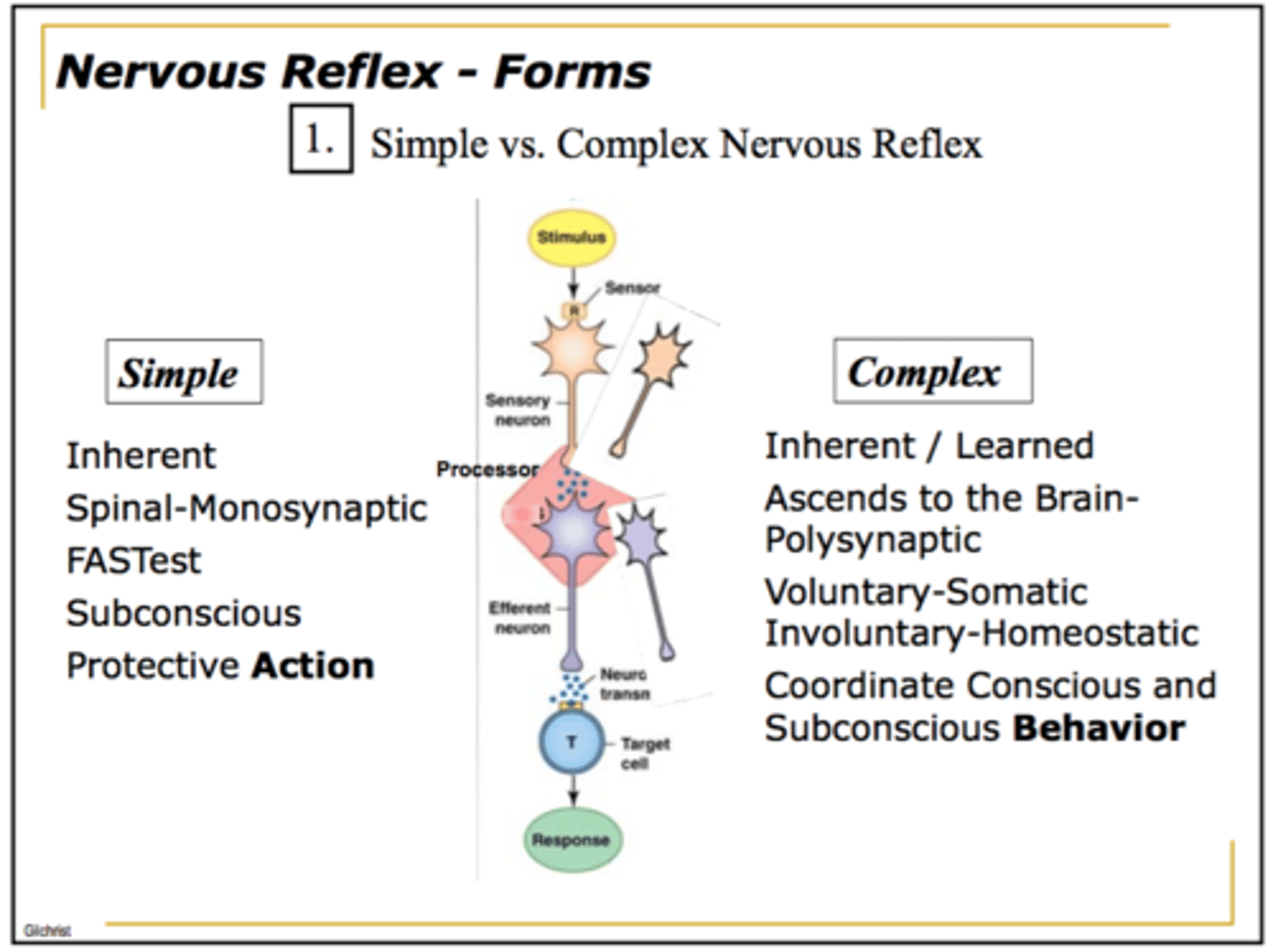
Where in the body are complex reflexes controlled?
brain stem or even cerebrum
(Ex: startle response)
What are behaviors that are innate, or inherited?
instincts
What are innate behaviors that follow a regular, unvarying pattern?
fixed action patterns (FAP)
What specific stimulus initiates fixed action patterns (FAP)?
sign stimuli
What is a sign stimulus called when it is between members of the same species?
releaser

In many FAPs, what will happen to the action if the original sign stimulus is removed?
the action will be completed
(Note: even if the original intent of the behavior cannot be fulfilled)
What is the innate program for acquiring specific behaviors during a critical/sensitive period?
imprinting

In imprinting, when is a trait irreversible?
once acquired
(Note: it can influence
sexual selection

What process occurs when an animal recognizes (learns) that events are connected?
associative learning
(Note: benefit from exposure
to unexpected repeated events)
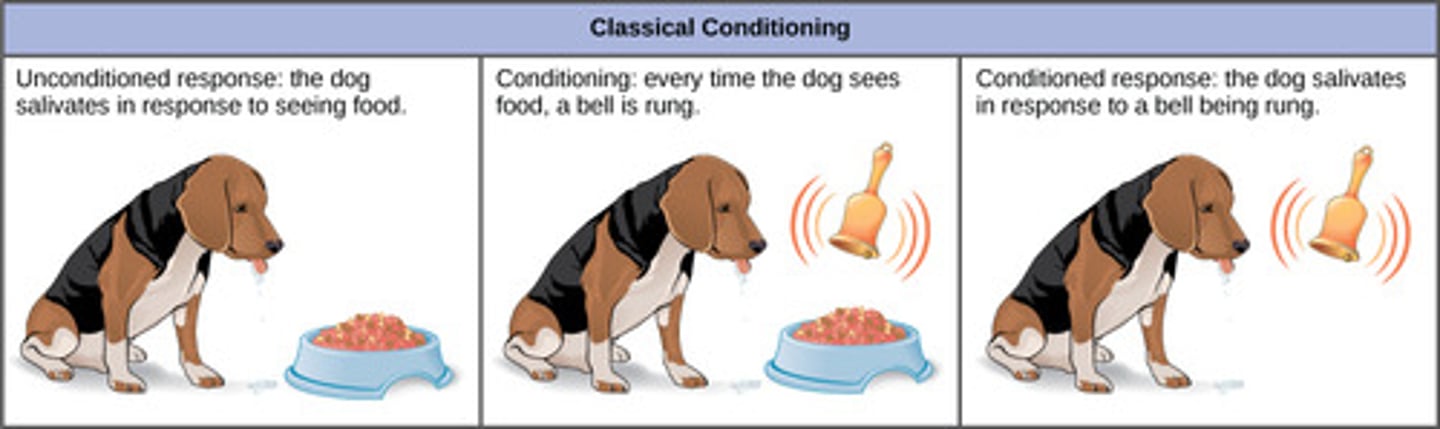
Which associative learning occurs when two stimuli are repeatedly paired?
classical conditioning
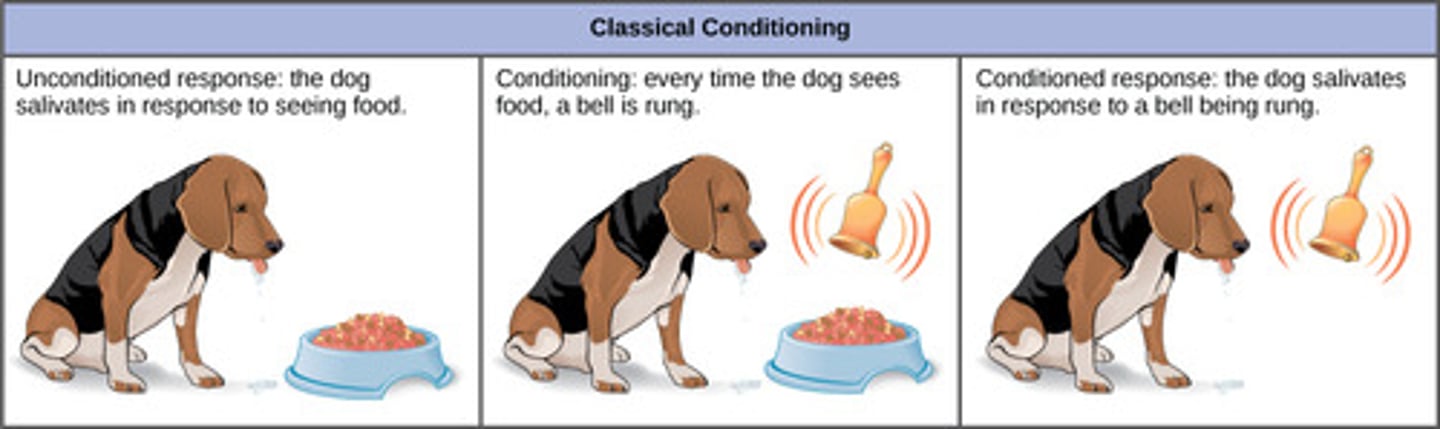
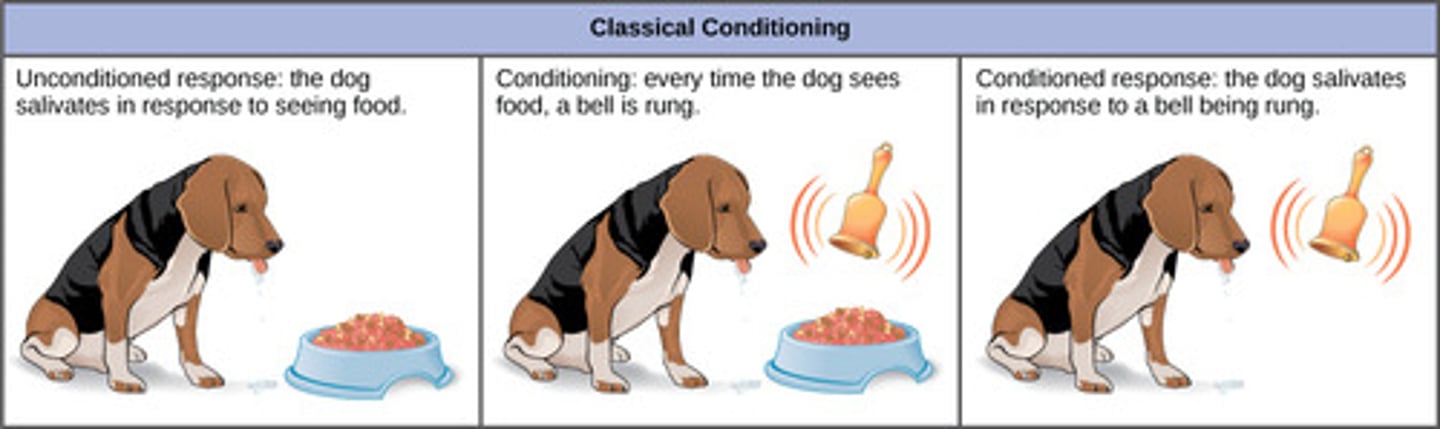
In dogs, their innate reflex to salivate when presented food is called what?
unconditioned response
(Note: classical conditioning)
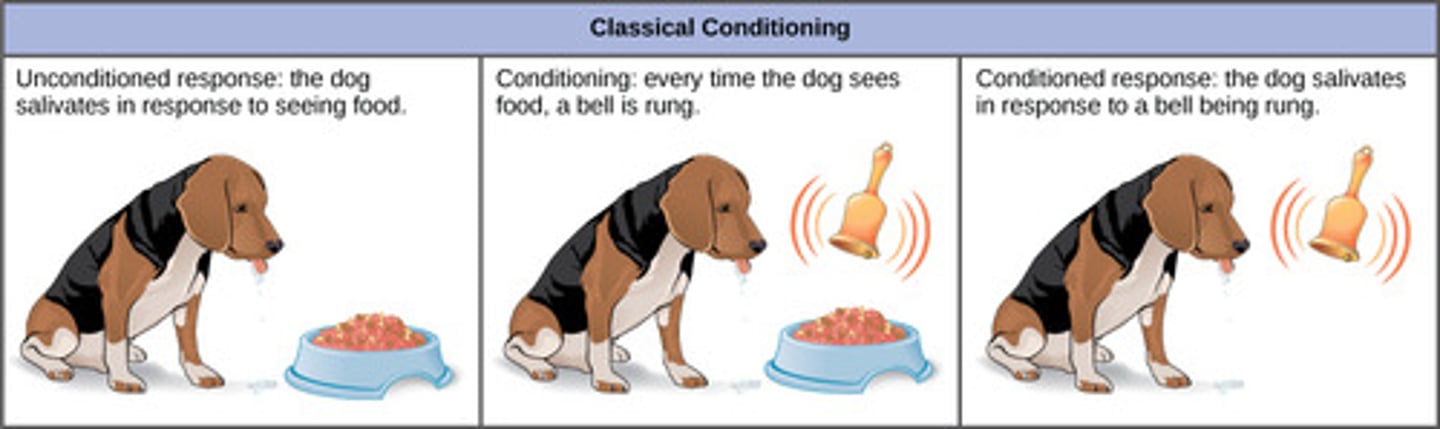
The presentation of food to dogs causing then to salivate is called what?
unconditioned stimulus
(Note: classical conditioning)
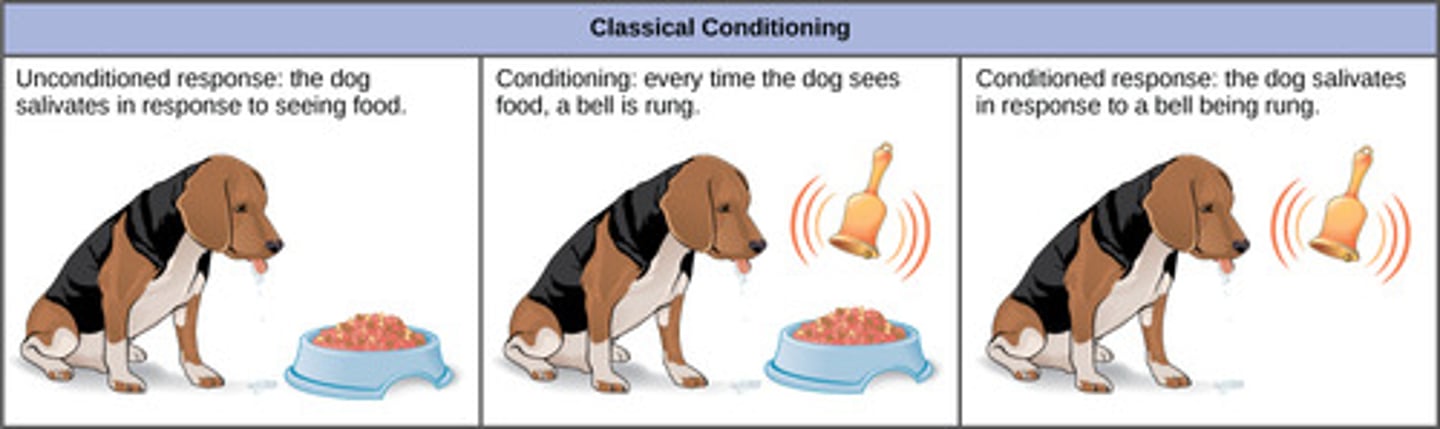
When the stimulus of a bell repeatedly paired with the presentation of food, it is called what?
conditioned stimulus
(Note: classical conditioning)
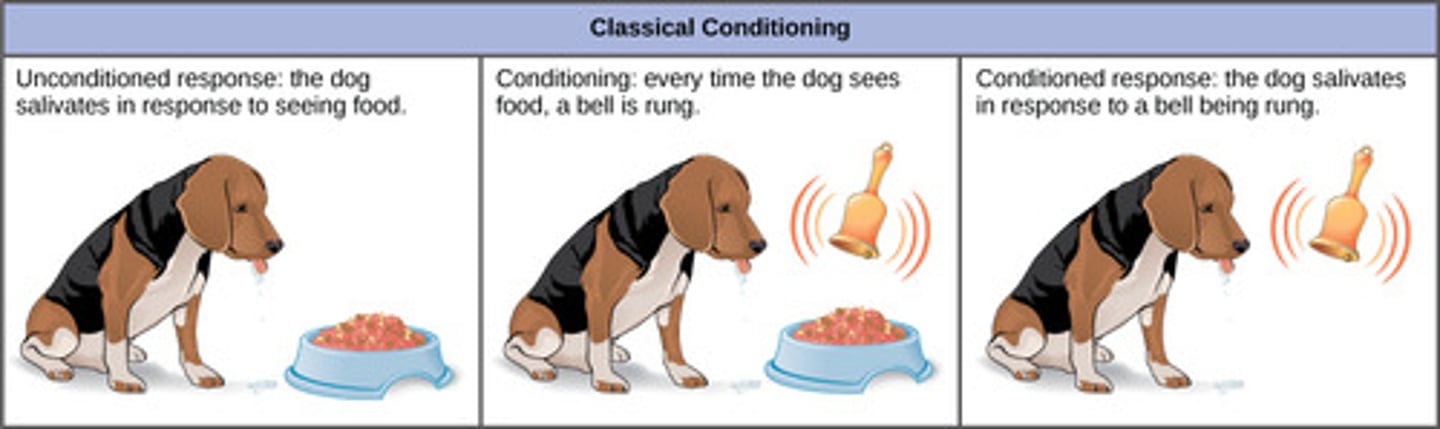
When dog salivation is caused by a conditioned stimulus (bell ring), it is now called what?
conditioned response/reflex
(Note: classical conditioning)
What form of associative learning occurs when an animal connects its own behavior with either a punishment or reward?
operant conditioning
(AKA: trial-and-error learning)

In operant conditioning, what occurs in an animal's behavior if it is rewarded?
the behavior will increase in frequency
In operant conditioning, what occurs in an animal's behavior if it is punished?
the behavior will decrease in frequency
What action in operant conditioning involves adding something bad to decrease a behavior?
positive punishment
(Ex: giving a slap)
What action in operant conditioning involves taking away something good to decrease a behavior?
negative punishment
(Ex: not giving a treat)
What action in operant conditioning involves adding something good to increase a behavior?
positive reinforcement
(Ex: giving a treat)
What action in operant conditioning involves taking away something bad to increase a behavior?
negative reinforcement
(Note: removing a shock collar from an obedient dog)
What event occurs when a learned behavior is reversed in the absence of reinforcement?
extinction
(Note: operant conditioning)
What is the recovery of a conditioned response to a conditioned stimulus after a previously extinguished response called?
spontaneous recovery
What form of associative learning involves associating landmarks with a specific location?
spatial learning
(Note: remember if location is dangerous or safe)
What is learned behavior that allows an animal to disregard meaningless stimuli?
habituation
In habituation, it allows individuals to ignore which events known to be inconsequential and remain focused on meaningful events?
repetitive events
What is an increased response to repeated stimuli?
sensitization
(Note: opposite of habituation)
What process occurs when an animal copies the behavior of another animal without having experienced any feedback themselves?
observational/social learning
What process occurs when an animal is exposed to a new situation, but still perform a behavior that generates a positive outcome?
insight
What processes provide a mechanism to learn new behaviors in response to unexpected events without receiving reinforcement?
observational learning and insight
(Note: reduces time for behavior acquisition)
Some behaviors appear to be learned but actually only require what process to occur?
maturation
(Note: actually innate behaviors)
What process involves adaptive responses to the environment?
learning
In higher animals, the capacity for learning is closely associated with what metric?
degree of neurological development
What are daily cycles of behavior?
circadian rhythms
What occurs when an organism responds to stimuli similar to the original stimulus but not identical to the original conditioned stimulus?
stimulus generalization
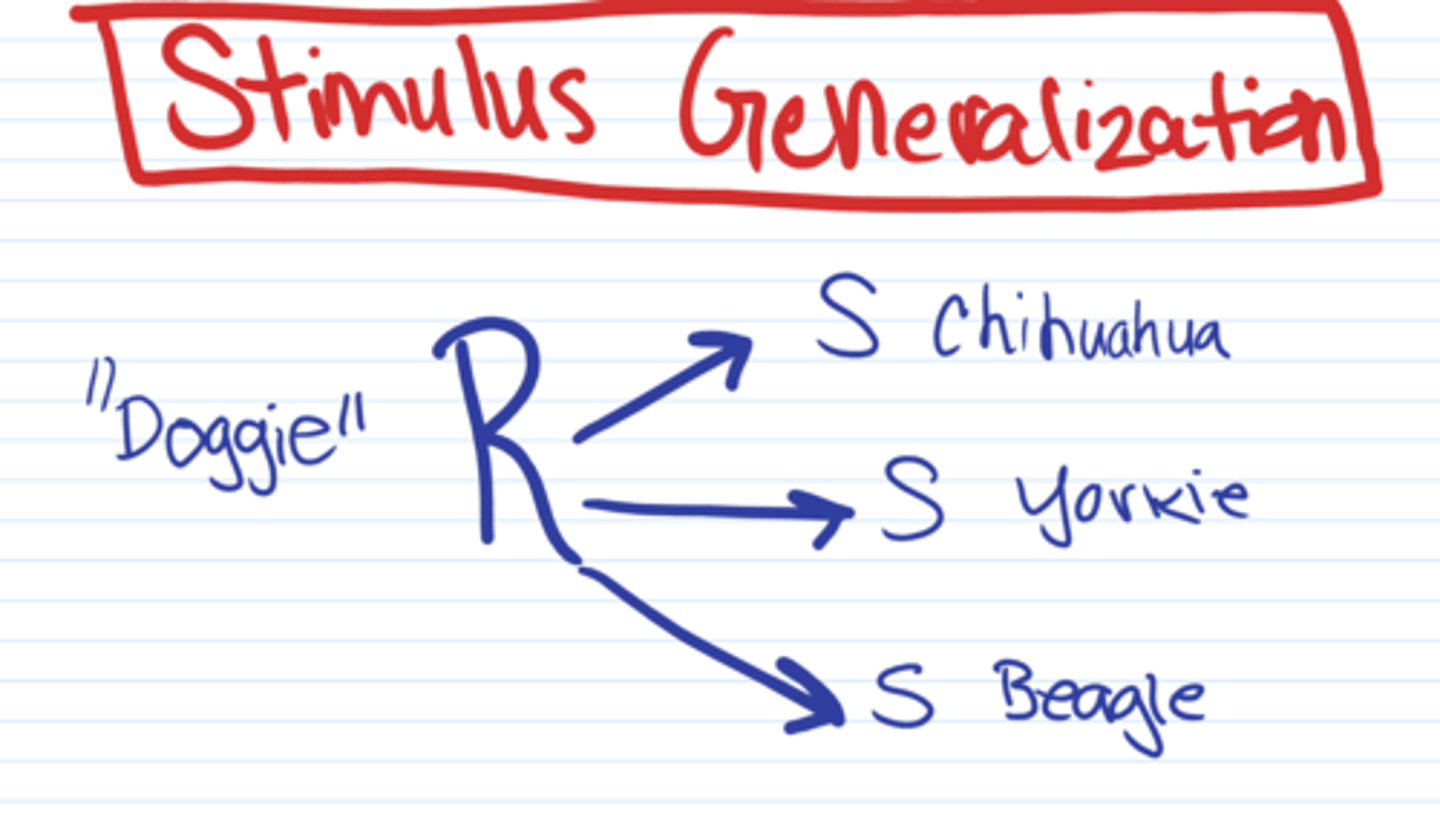
What is the ability of the learning organism to differentially respond to slightly different stimuli ?
stimulus discrimination

What is a gradient where the further a stimulus is from the original conditioned stimulus, the lesser of the magnitude of response in the animal?
generalization gradient
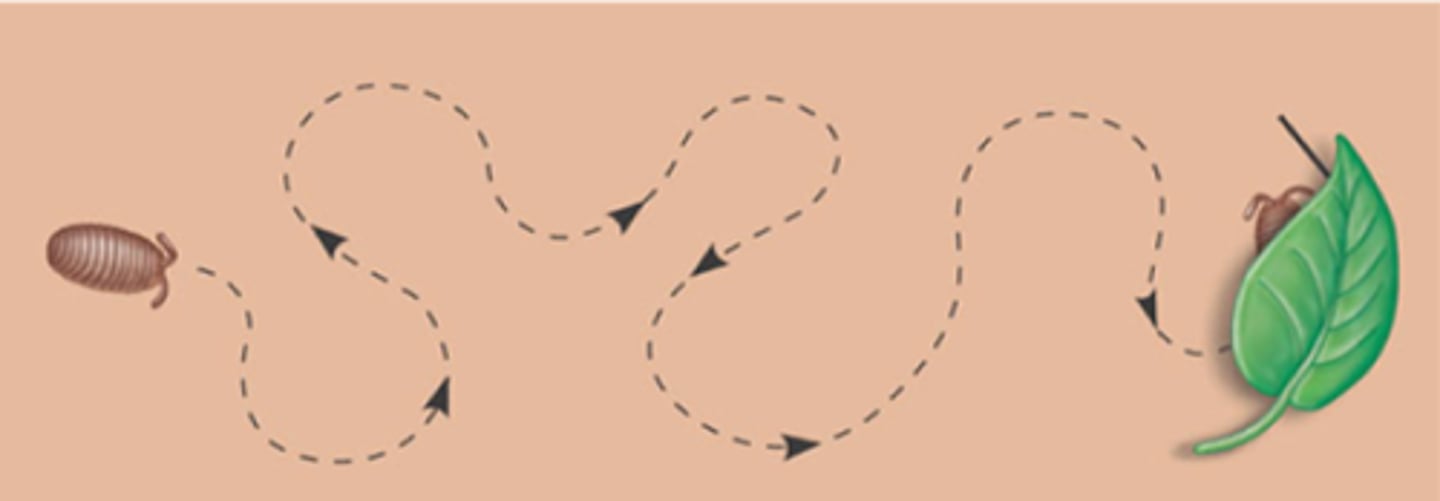
What is an undirected (without direction) change in the speed of an animal’s movement in response to a stimulus?
kinesis
(Note: an animal can
slow down in a favorable
environment and speed
up in an unfavorable
environment)
What is a directed movement in response to a stimulus, either toward or away from the stimulus?
taxis
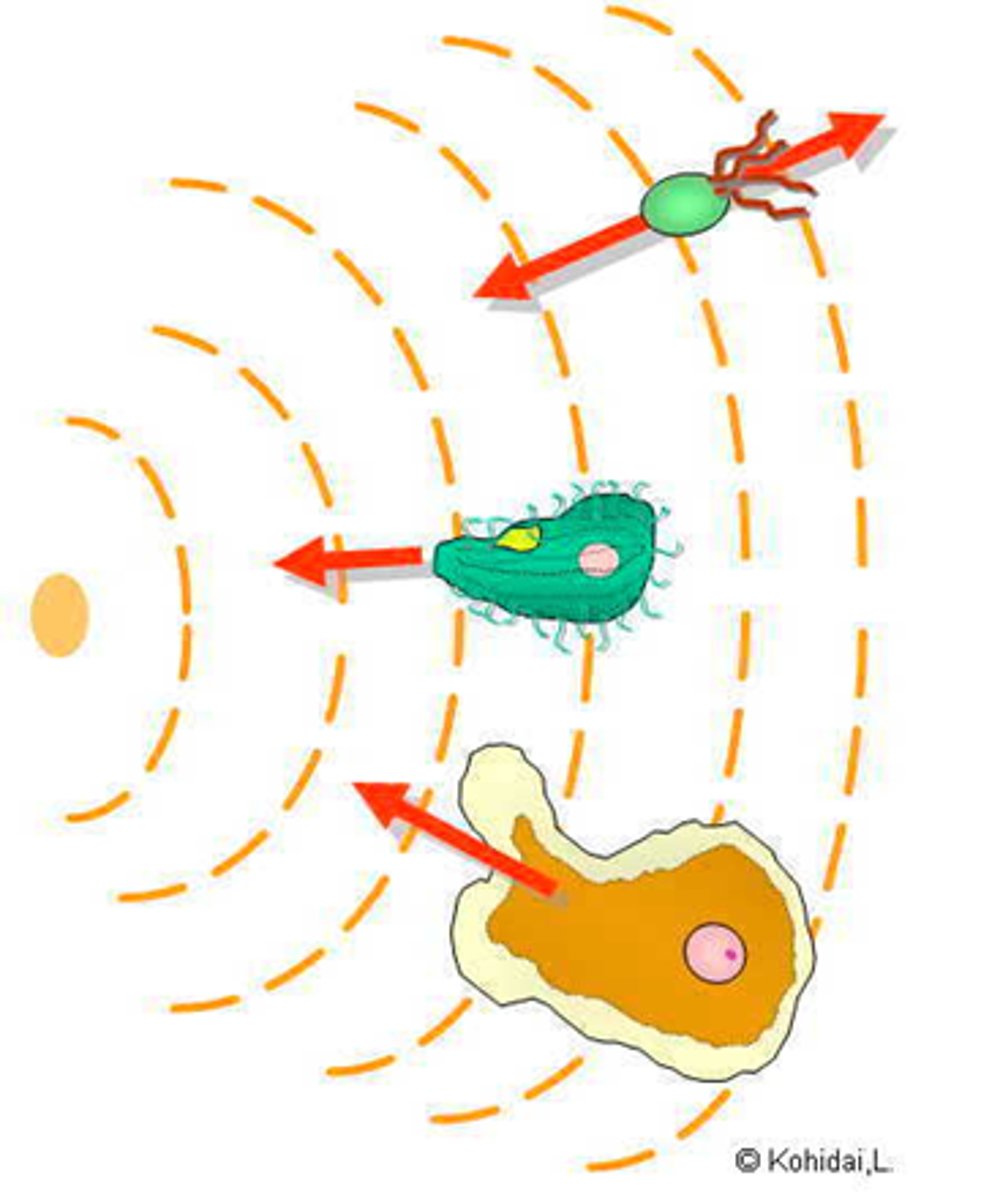
What is the movement toward light?
phototaxis

What is the difference between kinesis and taxis?
1. kinesis = random movement
2. taxis = directional movement
What is the long-distance, seasonal movement of animals?
migration

What are usually the stimuli for migration?
1. availability of food
2. degradation of environment

What process is used in species recognition, mating behavior, and organizing social behavior?
communication
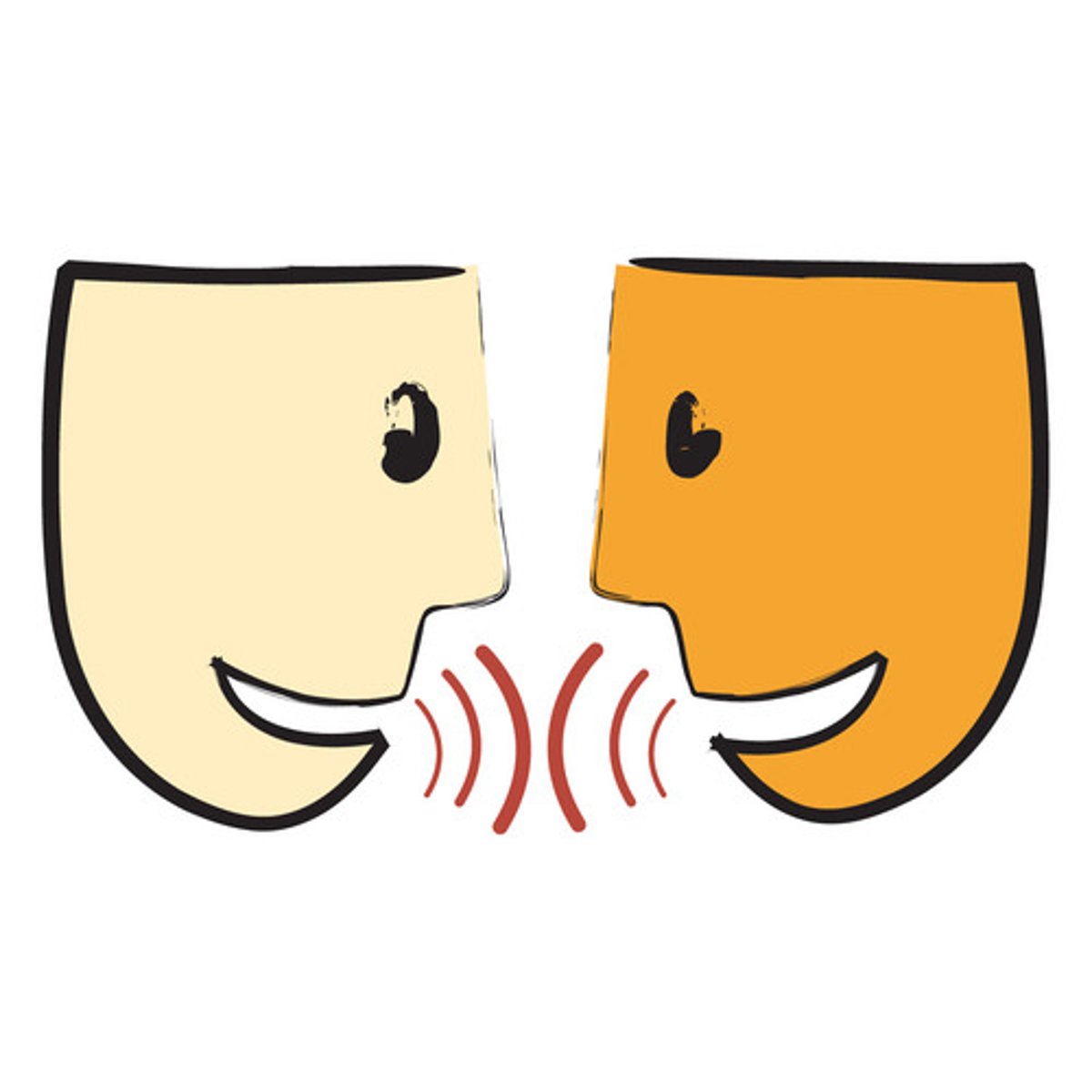
Which communication uses chemicals called pheromones?
chemical communication

What are chemicals that trigger reversible behavioral changes?
releaser pheromones
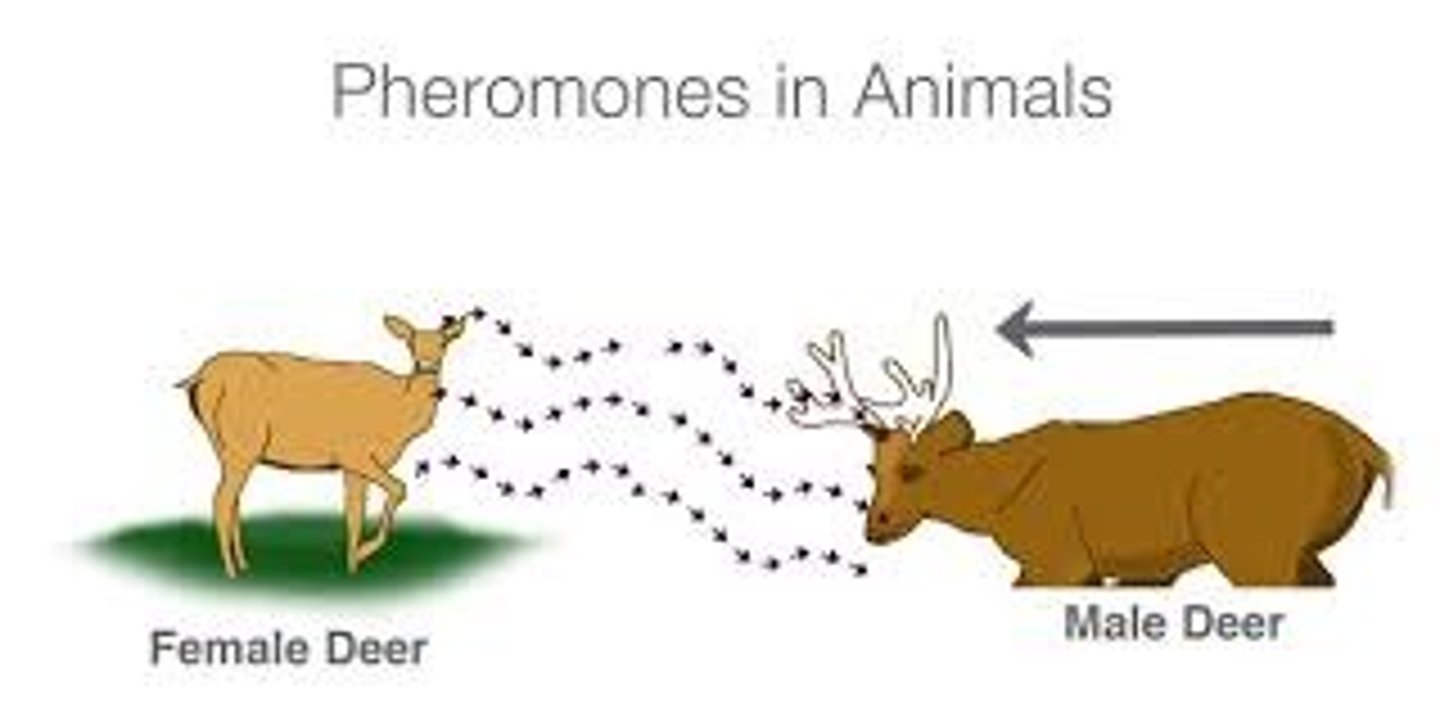
What are chemicals that cause long-term physiological (and behavioral) changes?
primer pheromones
What are the two methods of interacting with pheromones?
1. smell
2. ingestion
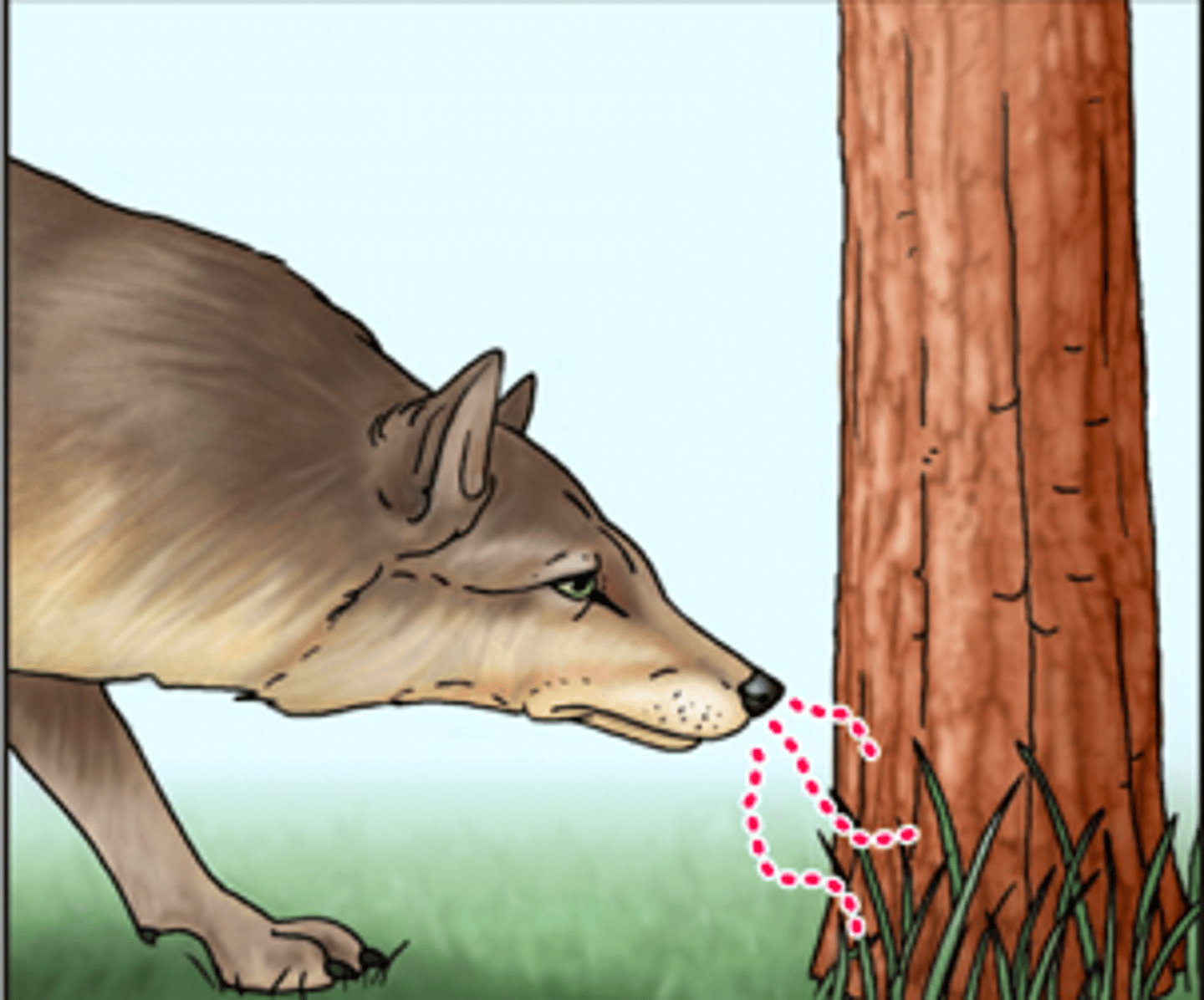
What are the functions of pheromones?
1. territorial markers
2. alarm symbols
3. sex attractants
4. reproductive maturity accelerators
Which communication is conveyed via visual displays?
visual communication
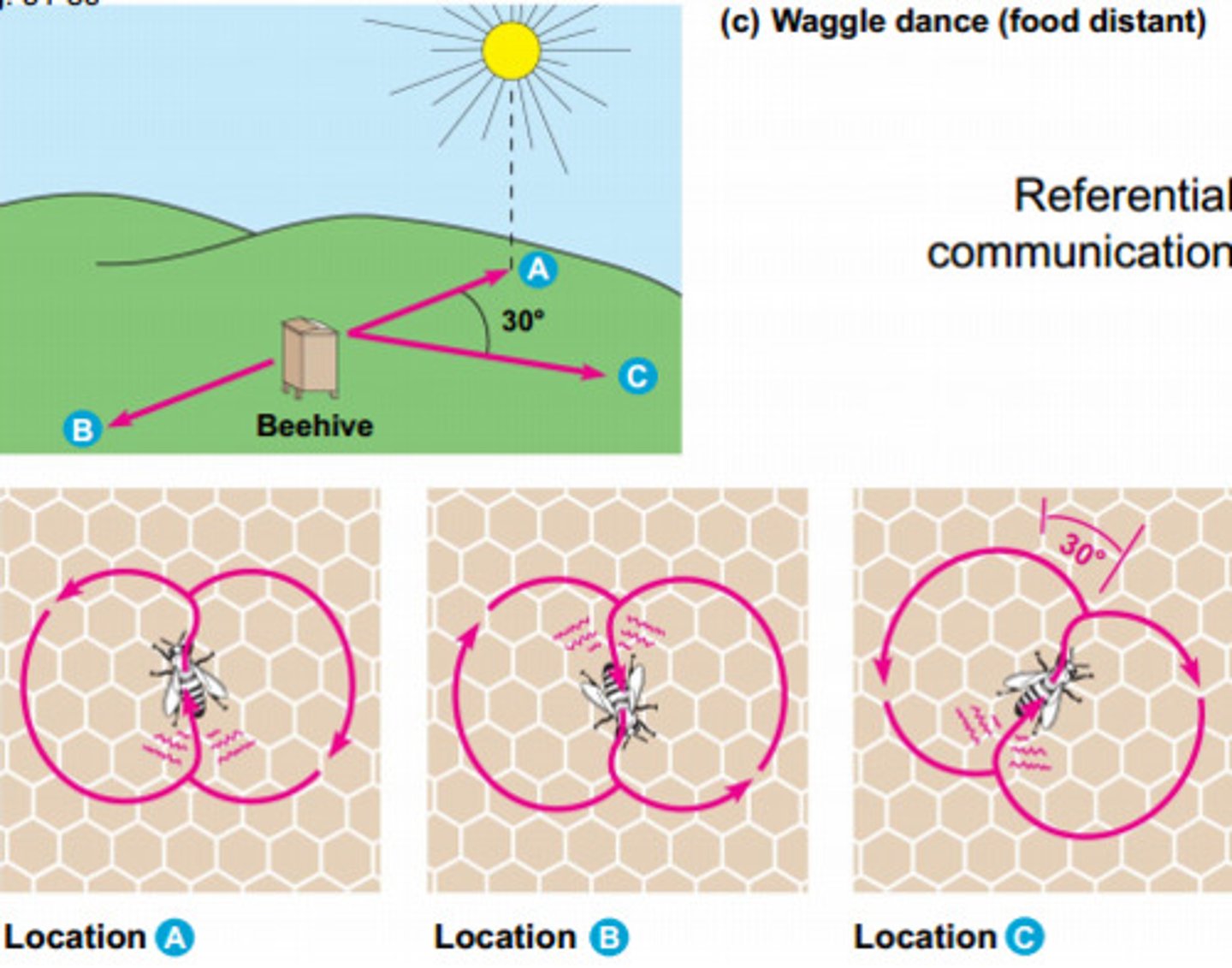
Visual displays are often employed in which scenarios?
1. to signify aggression
2. courtship
What behaviors occur when an animal competes for territory, food, or a mate?
agnostic behaviors

Which agnostic behavior involves fighting between animals?
aggression

Which agnostic behavior involves an animal yielding to another?
submission

Which communication utilizes sound?
auditory

Sounds are commonly used for communication in which scenarios?
1. long distances
2. through water
3. at night
What conditions are sounds used to convey?
1. warn danger
2. communicate reproductive readiness
3. species recognition
4. warning against rivals
Which agnostic behavior involves intimidation?
threats
Which communication involves touch?
tactile

In which scenarios is tactile communication common?
1. social bonding
2. infant care
3. grooming
4. mating
The goal of which behavior is to maximize the amount of food eaten and to minimize energy expenditure and risk?
foraging

Foraging involves which activities?
1. eating
2. searching for food
3. recognizing food
4. capturing food
Why do some animals form herds, flocks, and schools?
they can cooperate
and carry out a
behavior more
successfully as a group

Which benefit of a herd involves hiding most individuals from view?
concealment

Which benefit of a herd involves taking turns foraging and watching for predators?
vigilance
Which benefit of a herd involves shielding young or mobbing a predator?
defense
What group of animals enables members to corner and successfully attack large prey?
pack

What visual stimuli help animals find favored or plentiful food by using a specific, perhaps abbreviated ‘image’ of the target?
search images

Where did agnostic behavior originate?
competition for food, mates, or territory
Why is agnostic behavior ritualized?
to minimize injuries and time spent in contests
What is the social construct involving different levels of power and status depending on an individual's rank in the group?
dominance hierarchies
(Note: hierarchies minimizes
fighting for food and mates)

What is a linear order of status used to describe the dominance hierarchy in chickens?
pecking order

What is the active possession and defense of territory to ensure adequate food and place to mate?
territoriality
What is seemingly unselfish behavior that appears to reduce the fitness of an individual?
altruistic behavior
Which type of fitness does altruistic behavior increase?
inclusive fitness
What is the fitness of an individual plus its relatives who share some identical genes?
inclusive fitness
What is natural selection that increases inclusive fitness?
kin selection
What process occurs when unrelated members of the same species help each other?
reciprocal altruism
(Note: occurs in species with stable social groups that are likely to meet again)
What is the equation for Hamilton's rule?
rB > C
What does the r represent in rB > C (Hamilton's rule)?
the genetic relatedness between the altruist and the relative
What does the B represent in rB > C (Hamilton's rule)?
the amount of genes the relative can pass on after it is helped by an altruist
What does the C represent in rB > C (Hamilton's rule)?
the altruist's direct fitness
(Note: number of genes that animal can pass on by itself without relatives)
What is the principle that for natural selection to favor an
altruistic act?
Hamilton's rule
Under what conditions can altruistic behavior occur according to Hamilton's rule?
when (r) and (B) is multiplied and is greater than (C)
What is a pacifying social behavior that seeks to pacify aggression or to avoid being attacked by showing an inferior social stance?
appeasement behavior
(e.g. moving/turning away)
Which mating system involves one male mating with one female?
monogamy

Which mating system involves one individual mating with multiple members of the opposite sex?
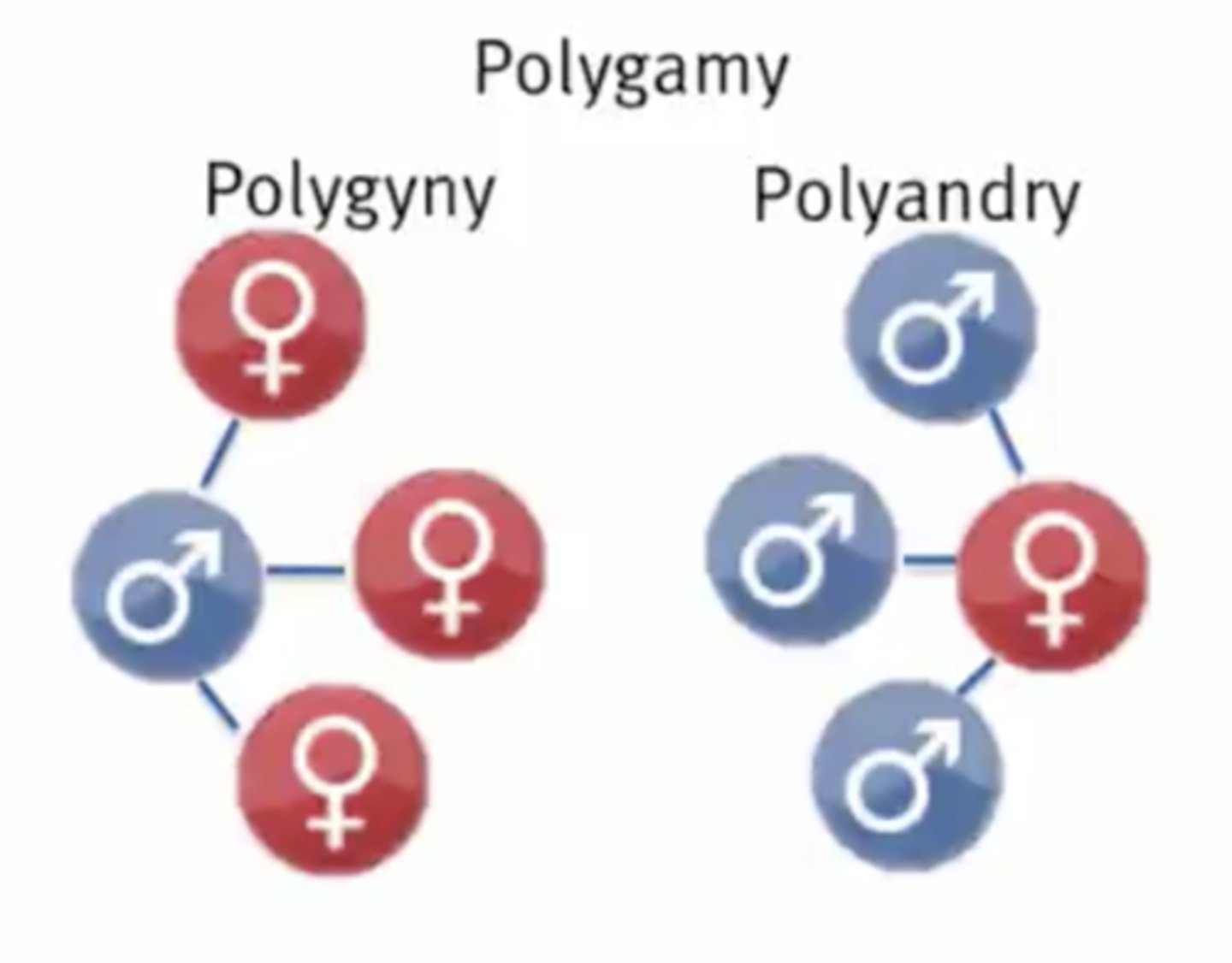
polygamy

What type of polygamy involves one male mating with multiple females?
polygyny
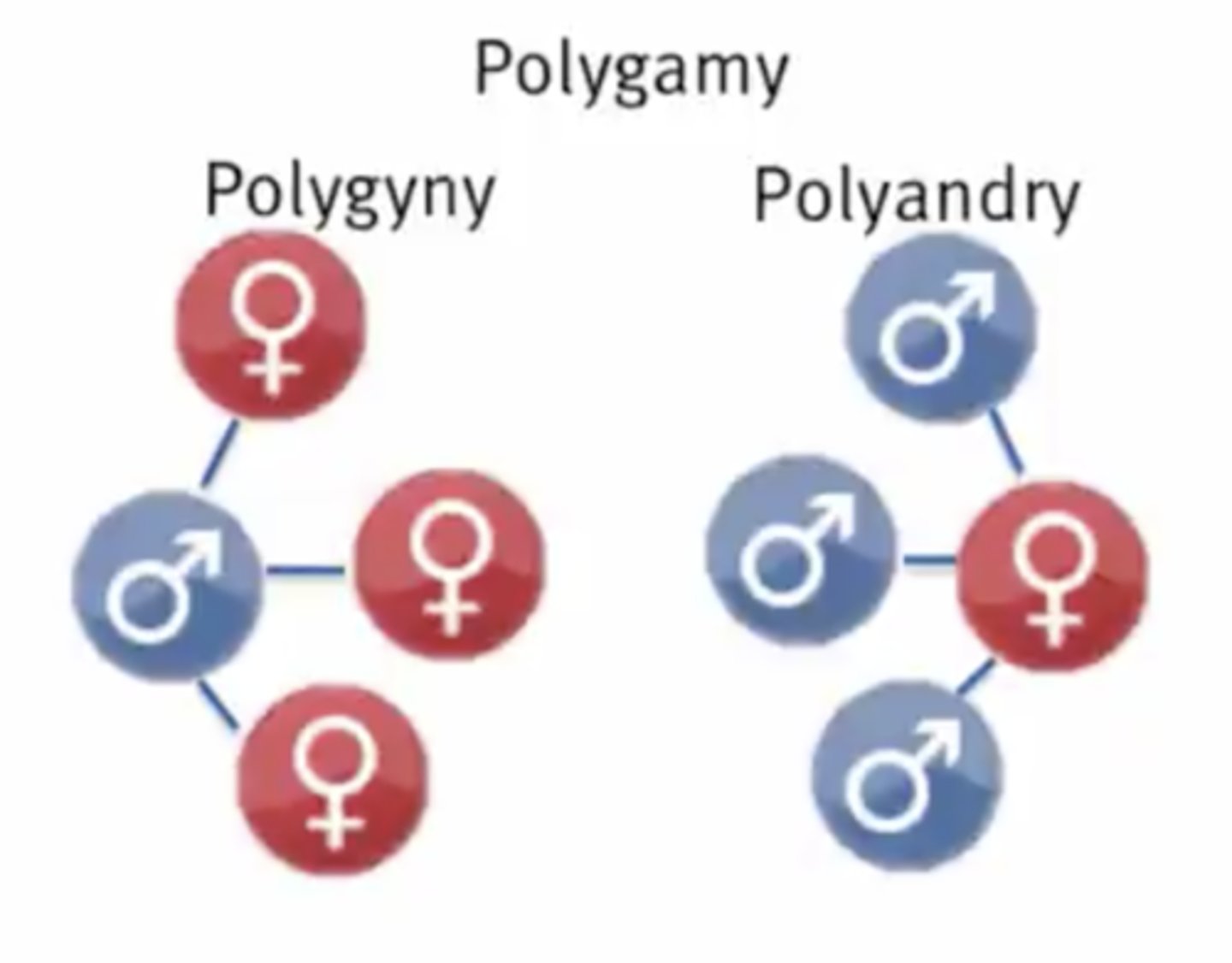
What type of polygamy involves one female mating with multiple males?
polyandry
What occurs when individuals in a population copy the mate choice of others?
mate-choice copying
What theory refers to the successful outcome of mating depending on dynamic, constantly shifting strategies of all the individuals involved?
game theory
How is game theory described in evolutionary terms?
fitness of a particular behavioral phenotype is influenced by the behavior of other phenotypes in population
Which reproductive approach is a one-shot, big-bang reproduction in which many offspring are produced in a single opportunity?
semelparity

Which reproductive approach involves repeated reproduction?
iteroparity
