Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology, Anatomy and Physiology, nervous system, Nervous system physiology and anatomy
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
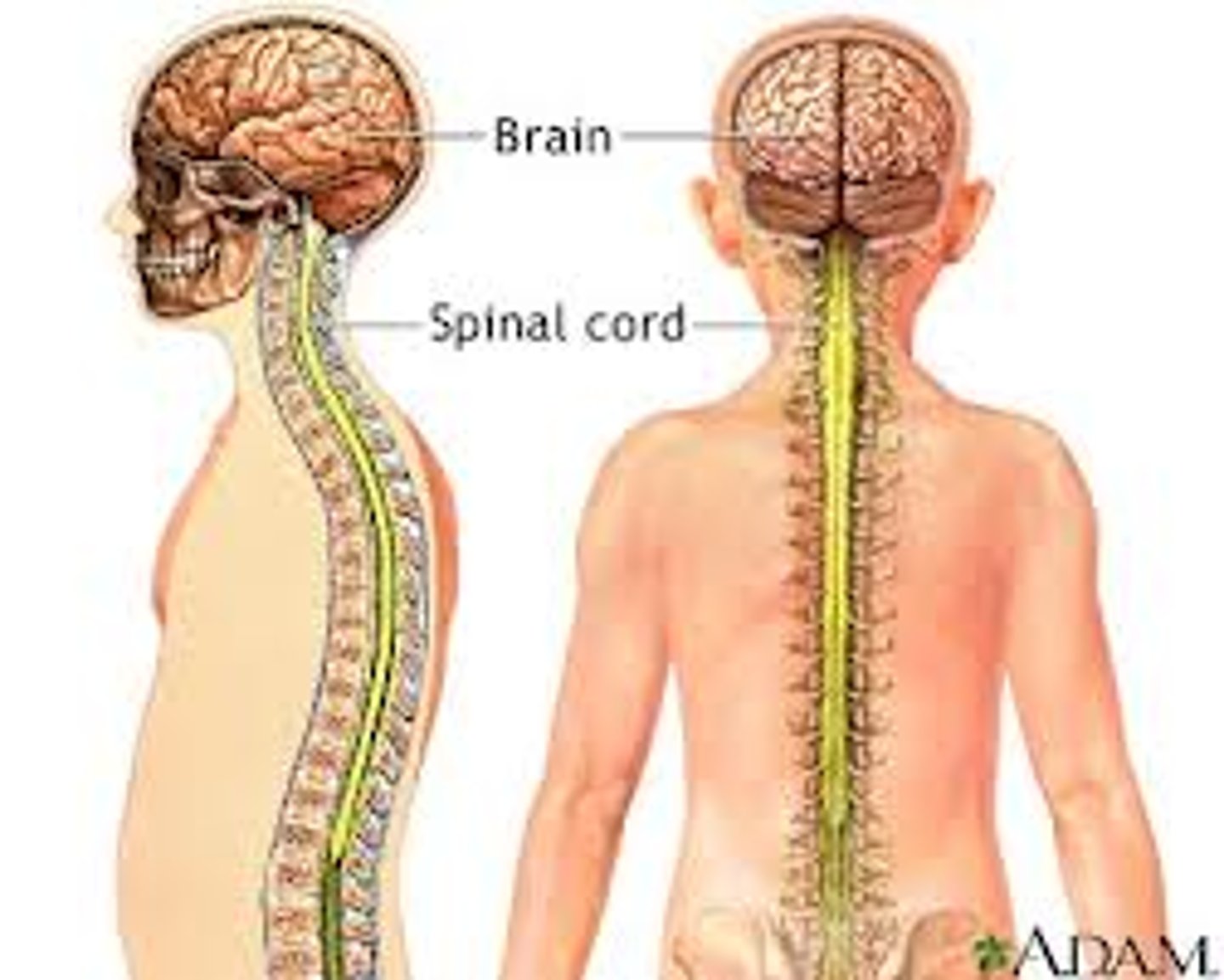
spinal cord
a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column
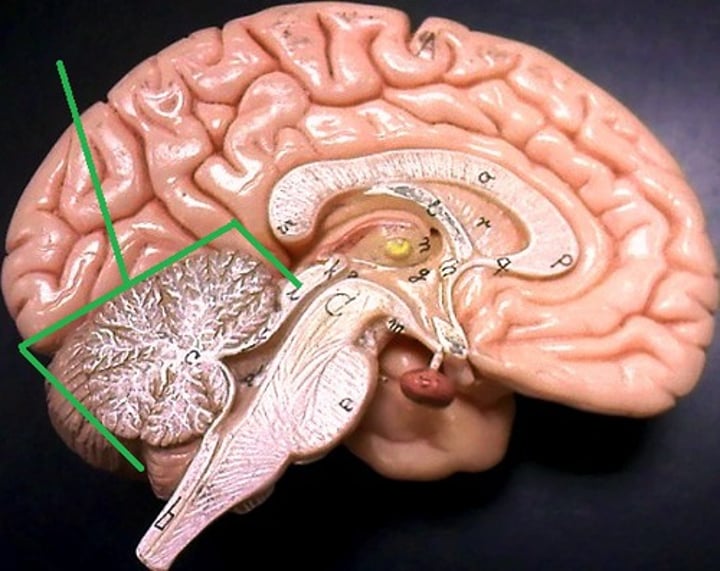
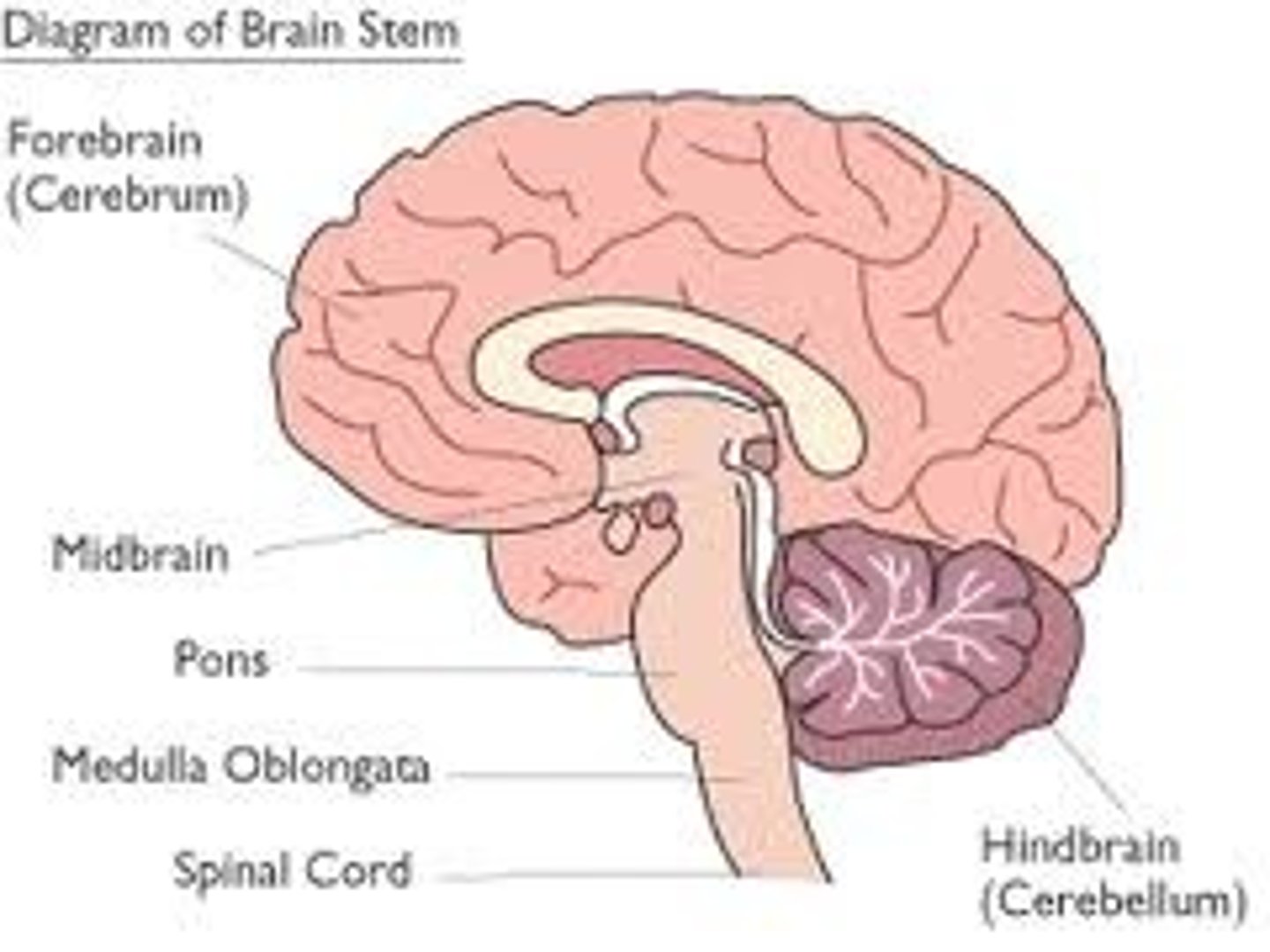
cerebellum
a major feature of the hindbrain responsible for body movements and balance
cerebrum
the principal and most anterior part of the brain in vertebrates, located in the front area of the skull and consisting of two hemispheres, left and right, separated by a fissure
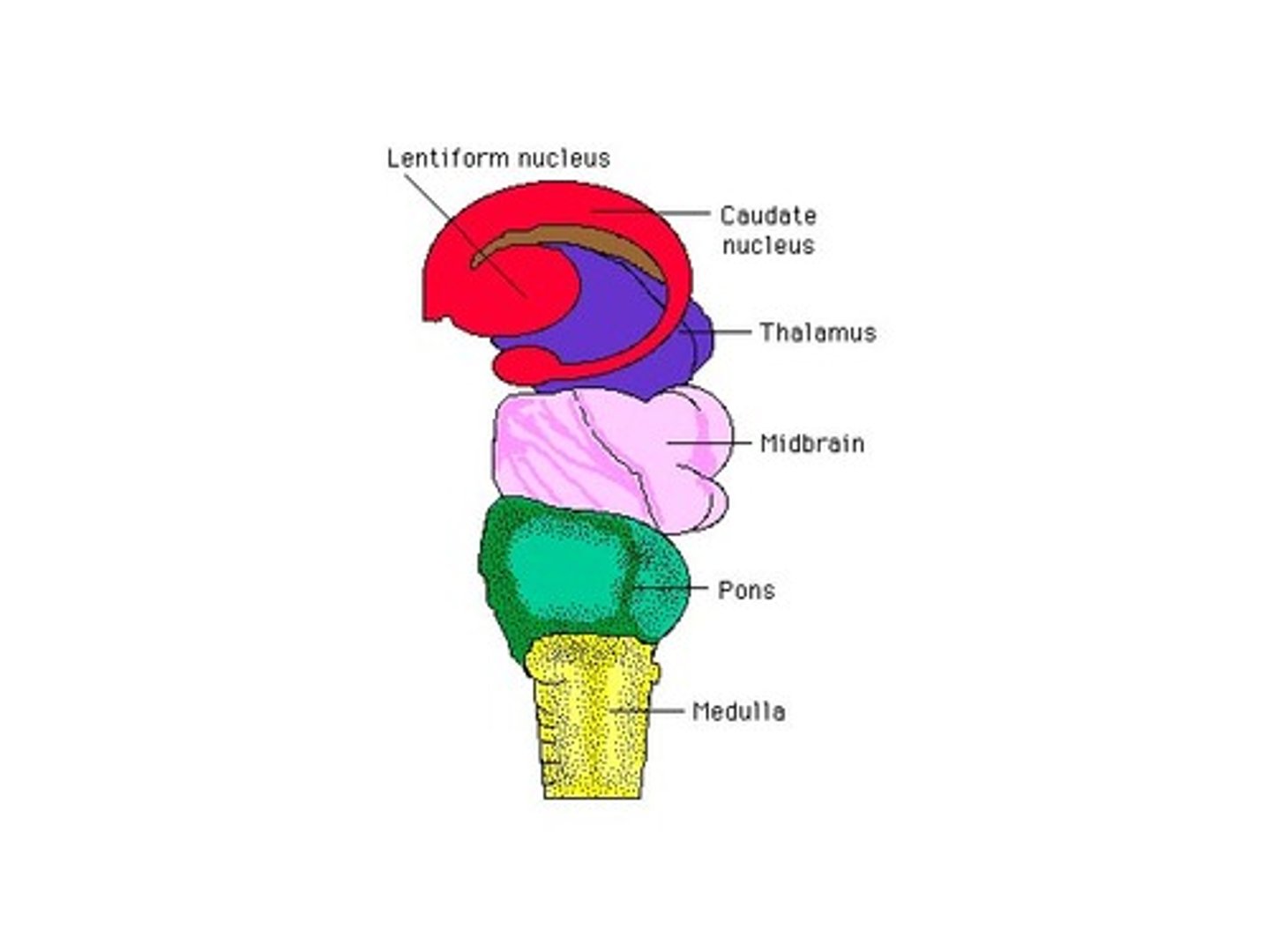
midbrain
relays sensory and motor impulses; serves important functions in motor movement, particularly movements of the eye, and in auditory and visual processing.
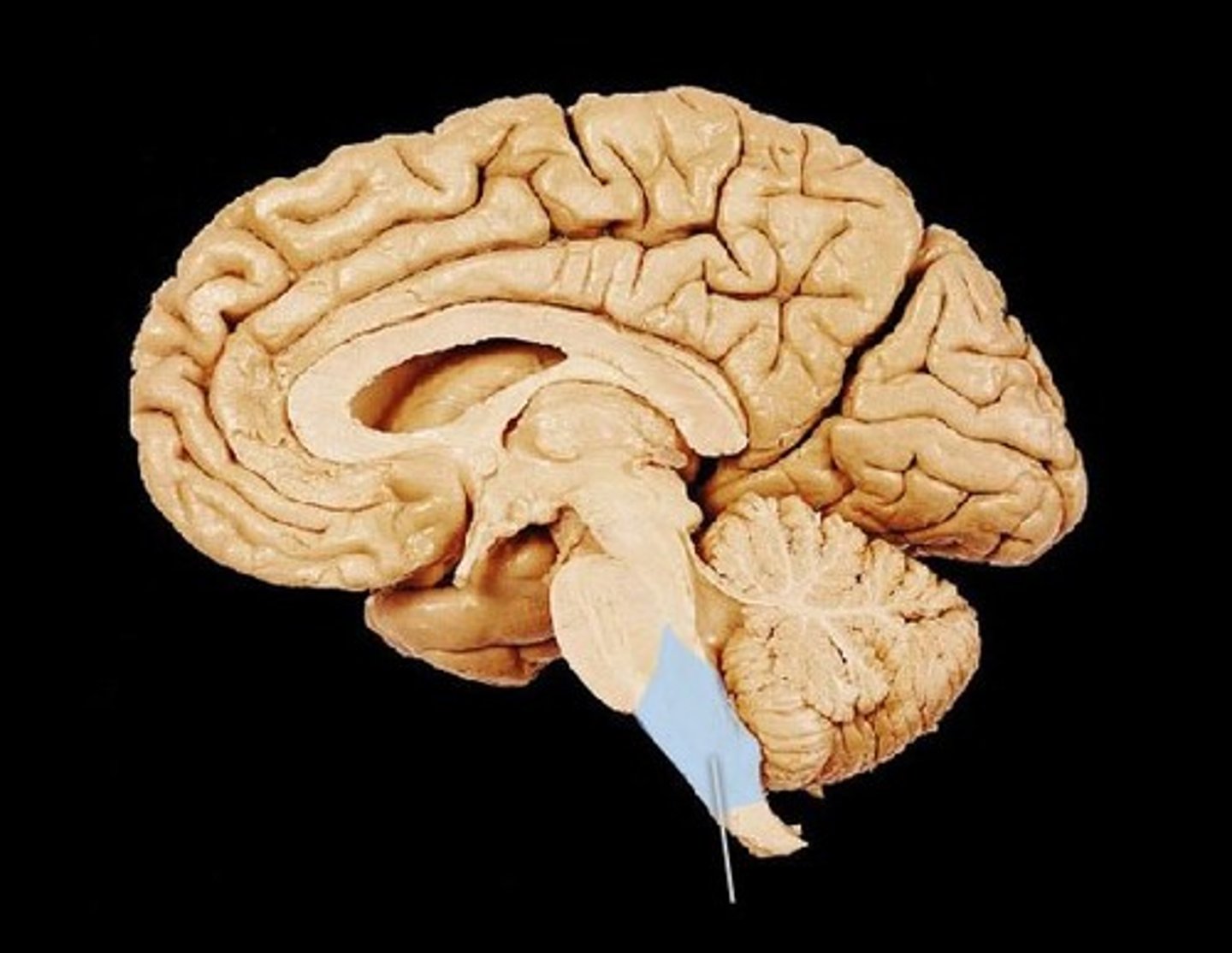
pons
part of the brain stem, assists with regulation of breathing
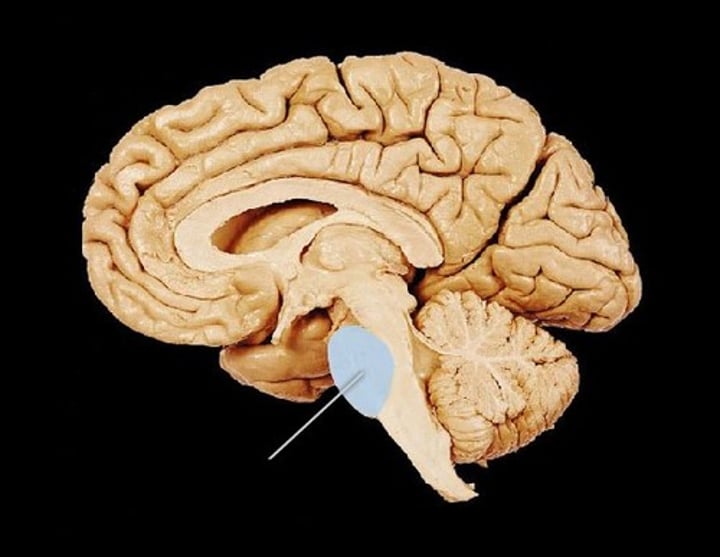
medulla oblongata
part of brain stem, regulates heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing, and controls the reflexes of coughing, sneezing, and vomiting
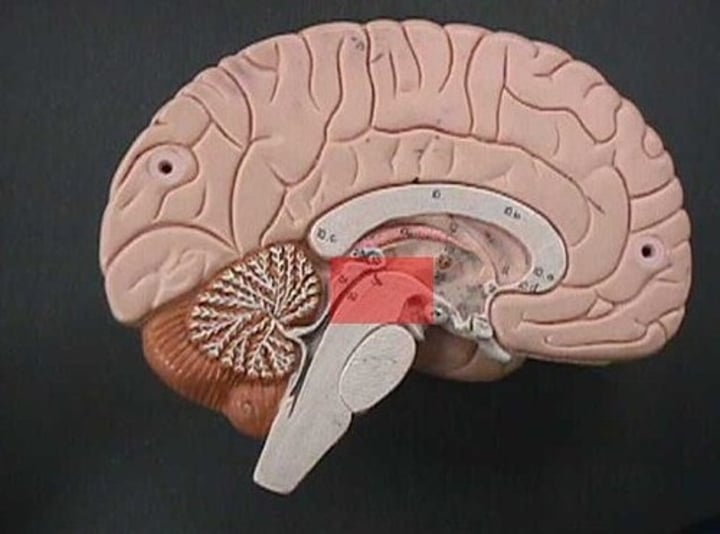
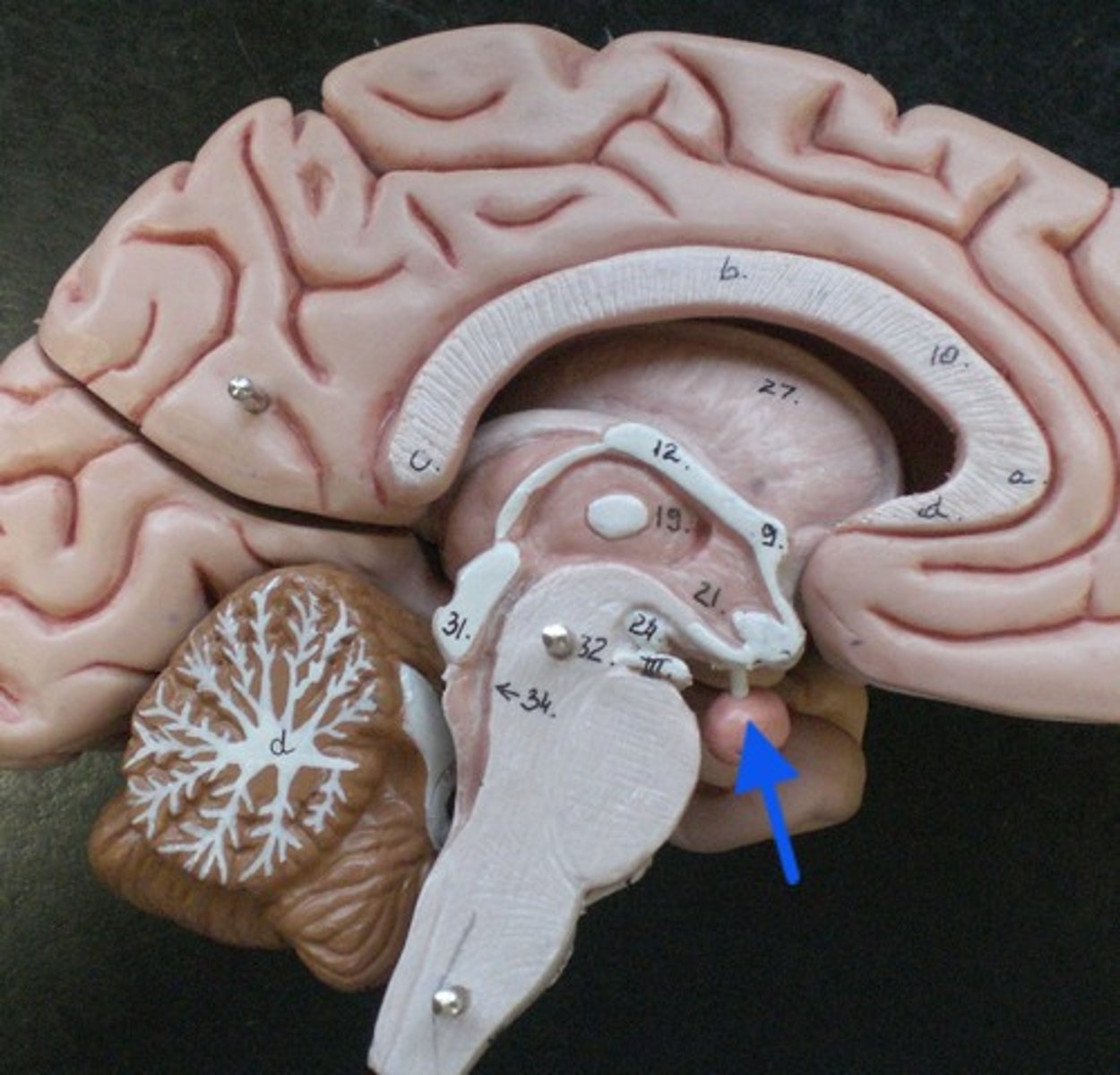
pituitary gland
a pea-sized structure located at the base of the brain, just below the hypothalamus, to which it is attached via nerve fibers. It is part of the endocrine system and produces critical hormones, which are chemical substances that control various bodily functions
hypothalamus
lower portion of diencephalon which acts as an autonomic center regulating metabolism, heart rate, blood pressure, thirst, hunger, energy level, and body temperature
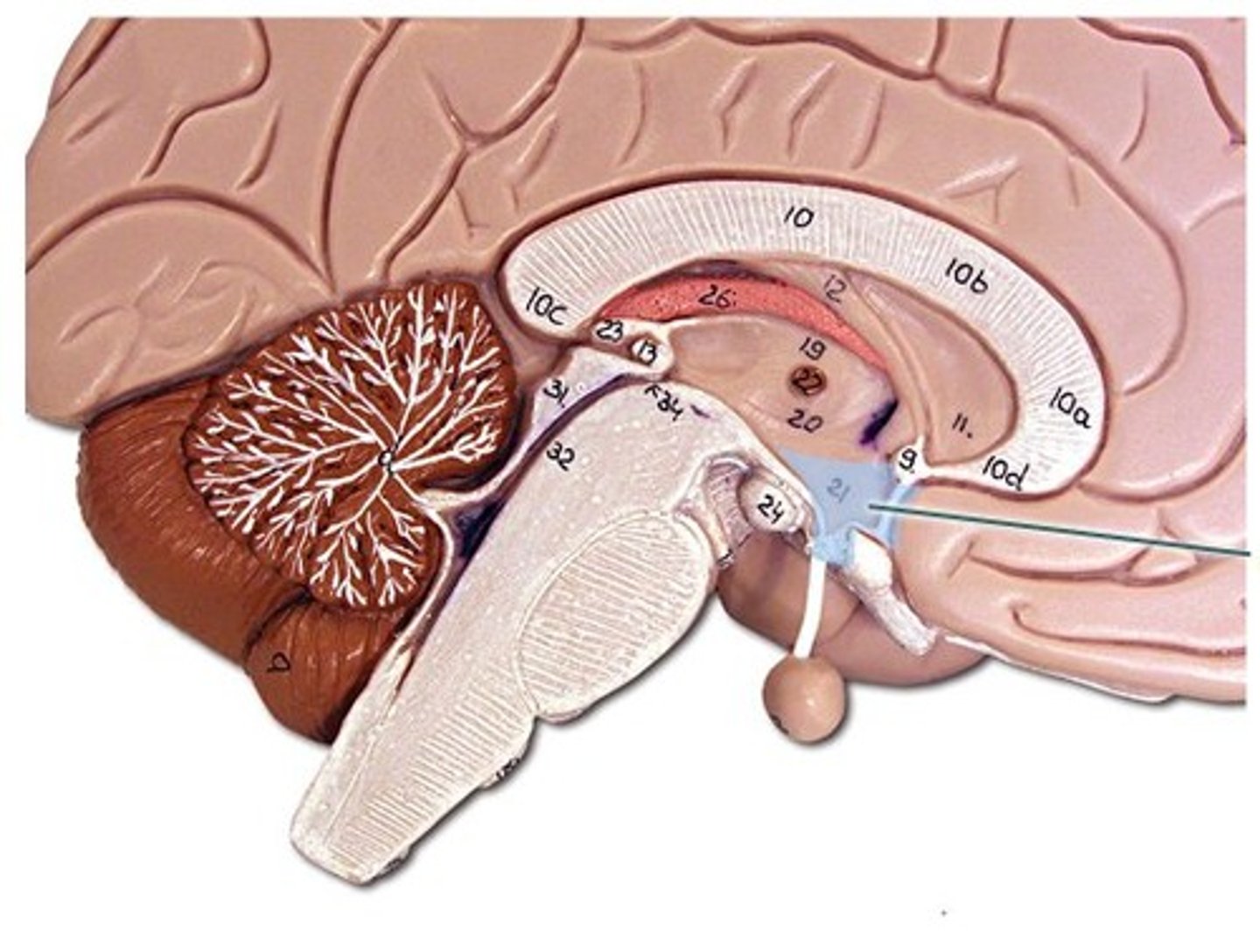
thalamus
middle portion of diencephalon which relays sensory impulses up to the sensory cortex (aka the cerebrum); regulates sleep and consciousness
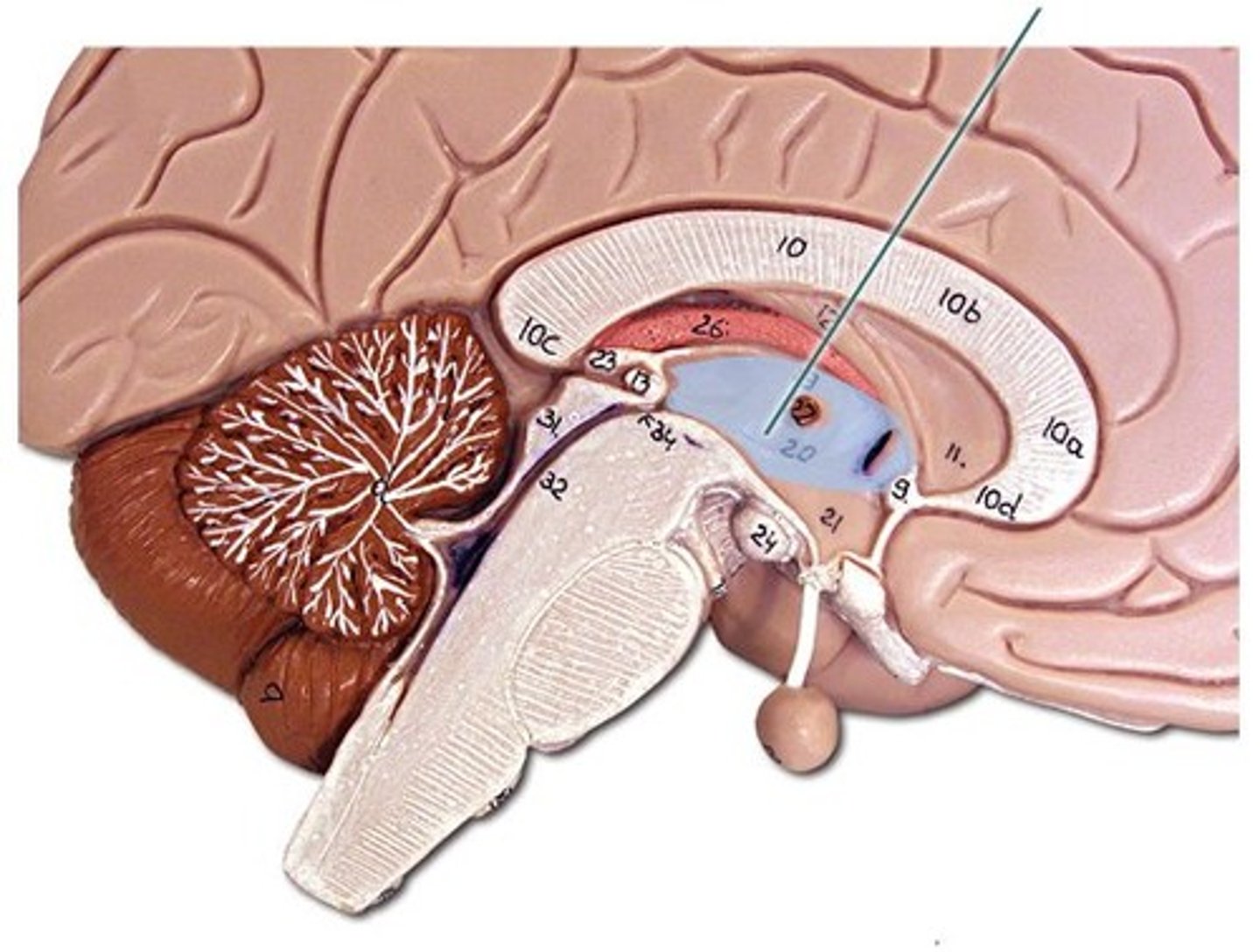
epithalamus
upper portion of diencephalon that regulates hormones secreted by the pineal gland. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns
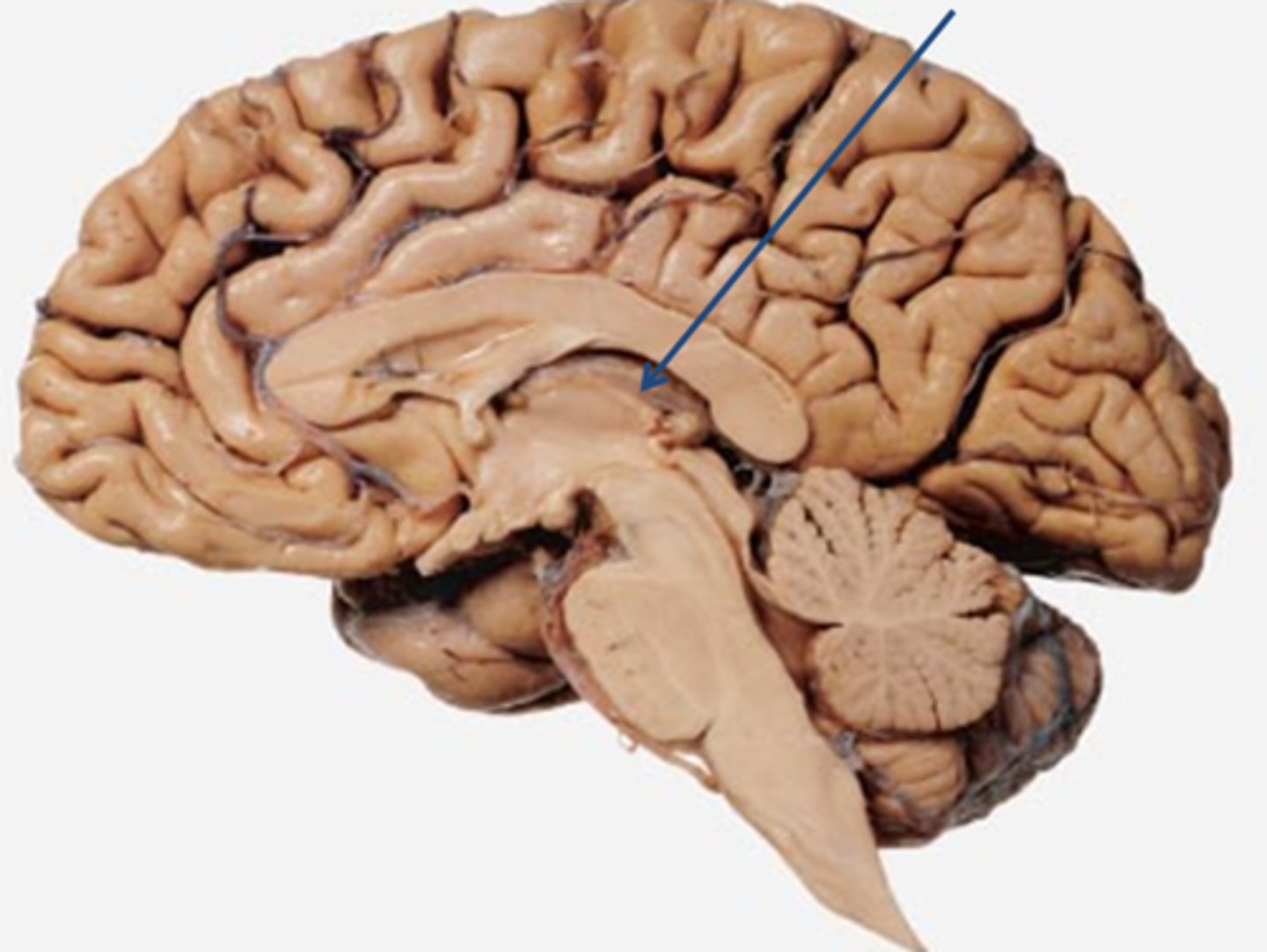
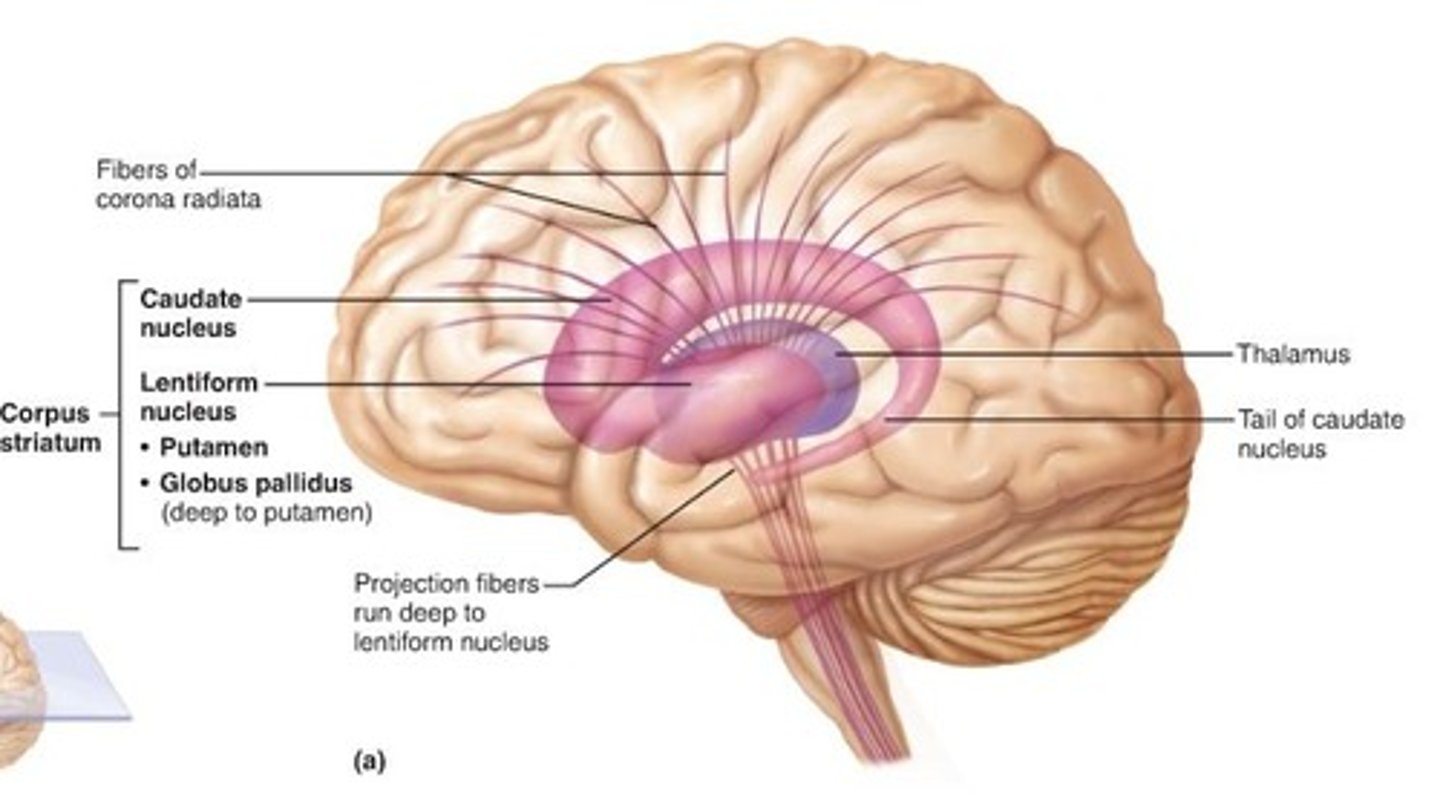
striatum
structure lying at the base of the forebrain which is a critical component of the motor and reward systems. Coordinates decision-making, motivation, and reinforcement.
corpus callosum
a thick band of nerve fibers that divides the cerebral cortex lobes into left and right hemispheres and acts as the connection between the two.
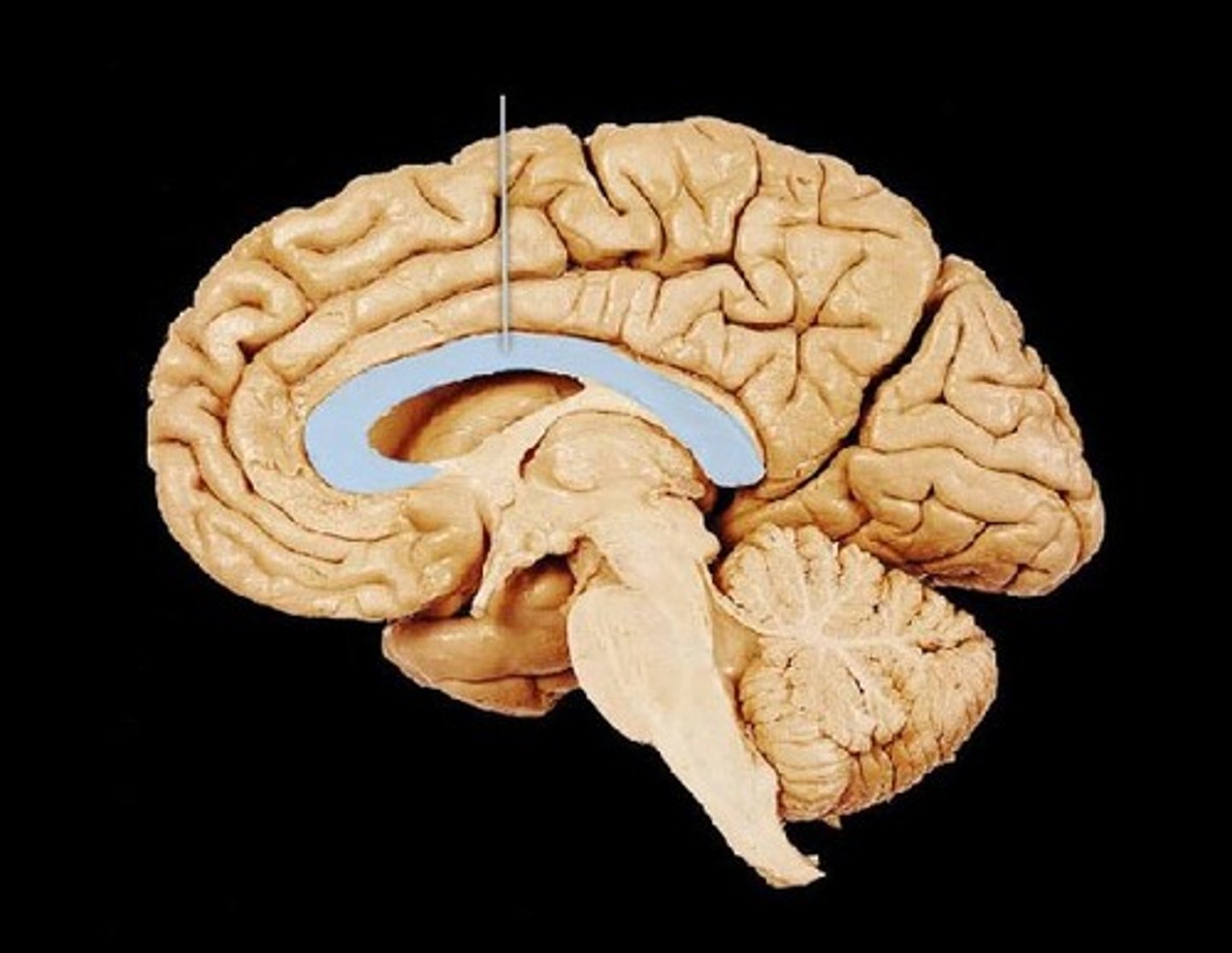
meninges
three layers of protective tissue between the brain and skull
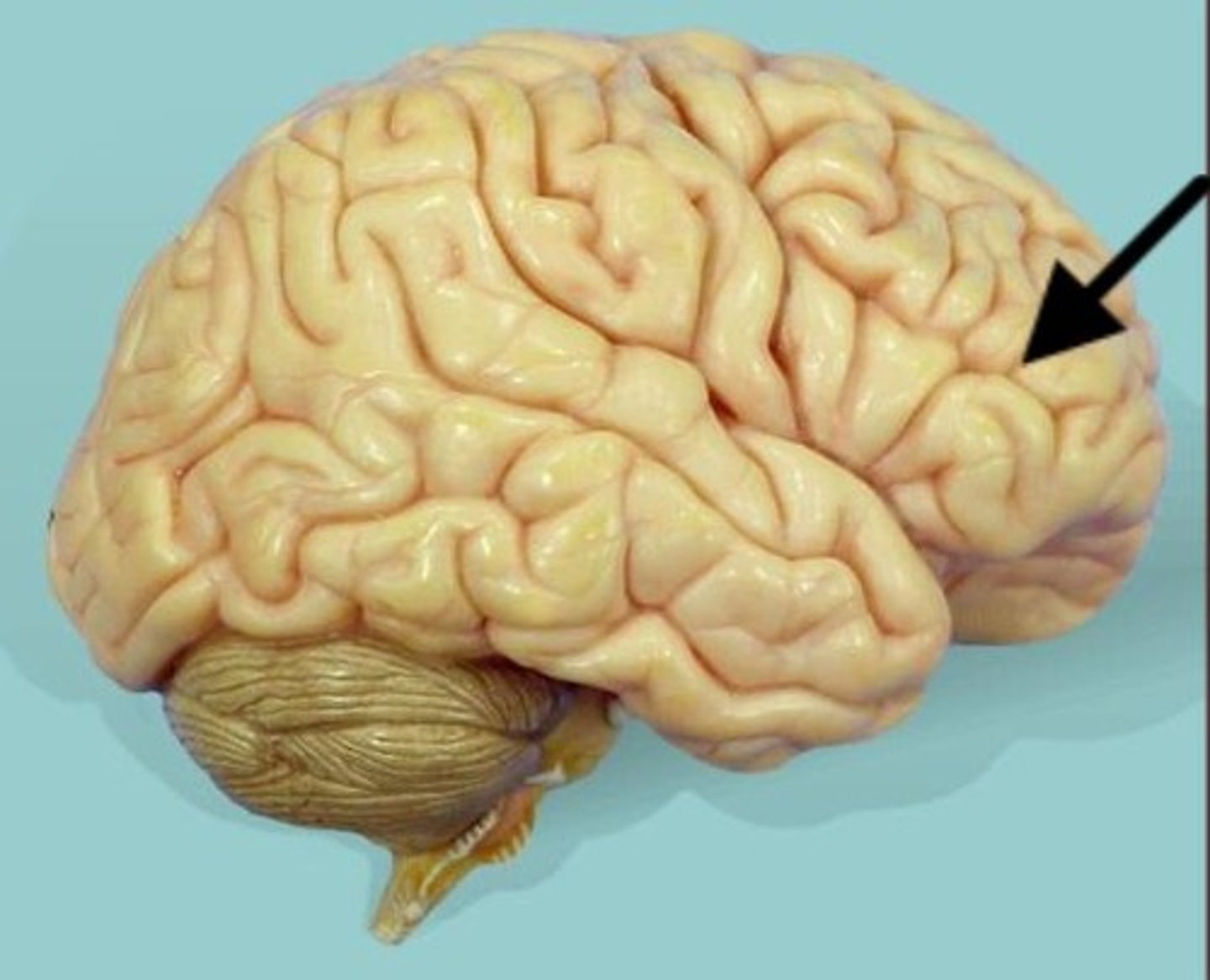
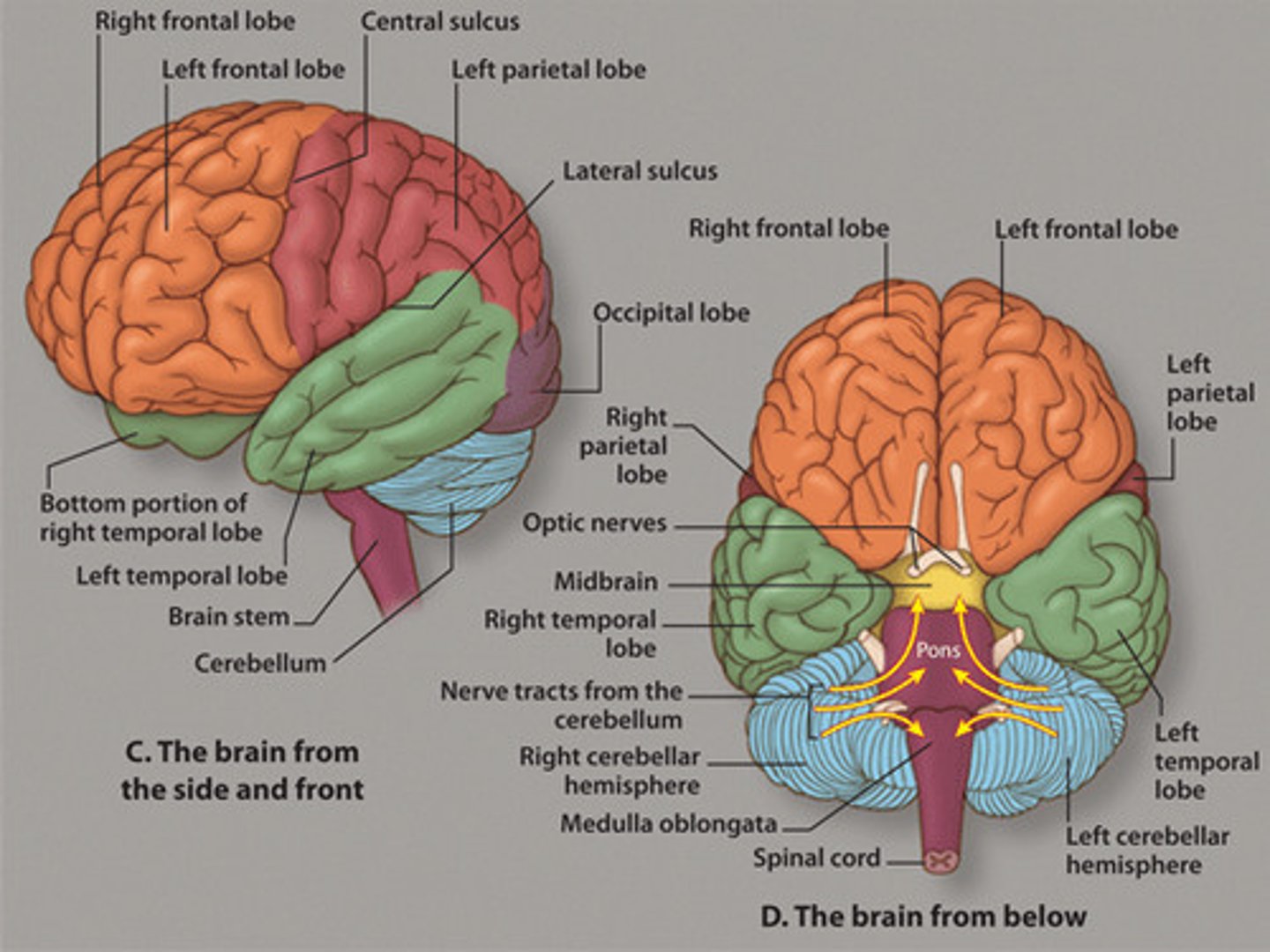
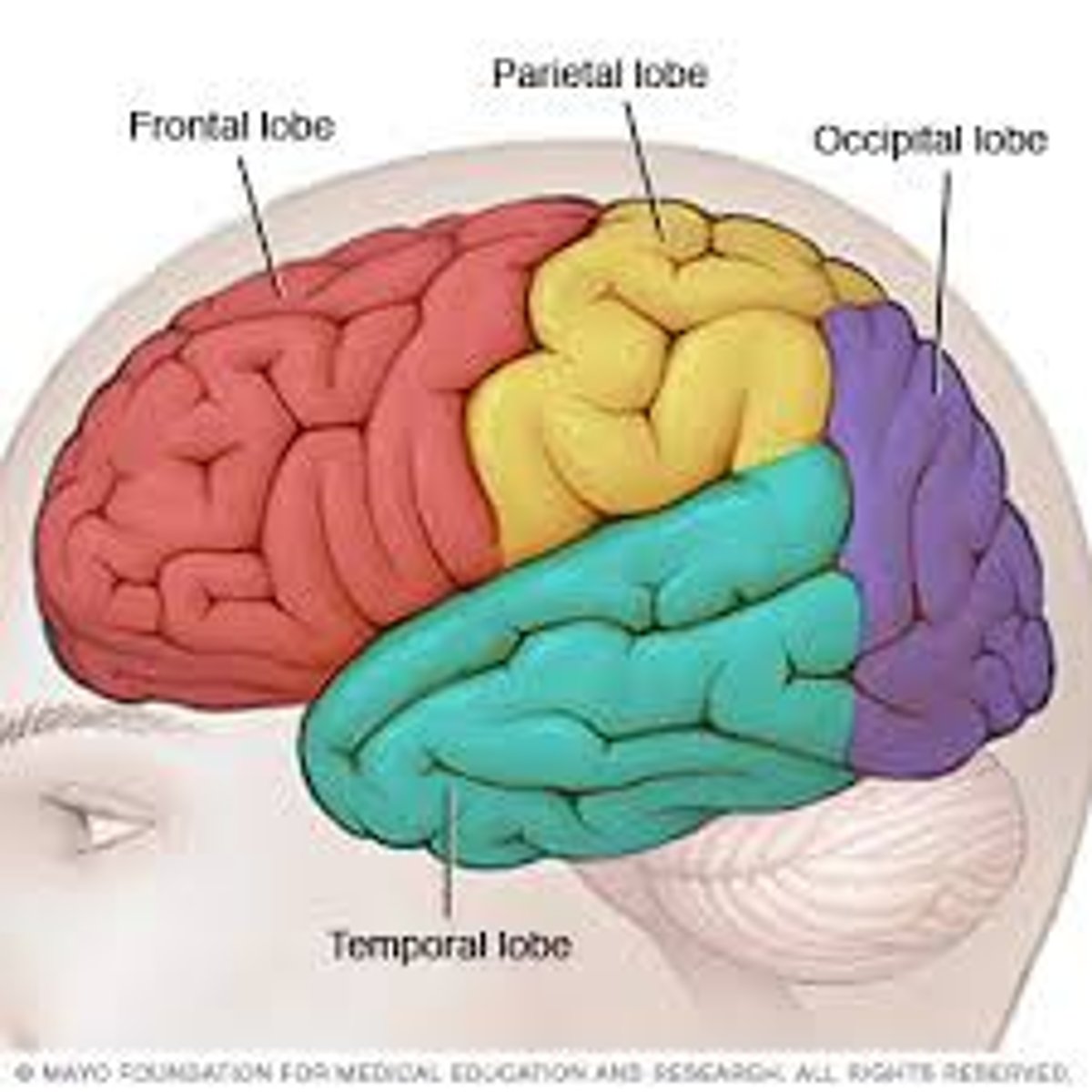
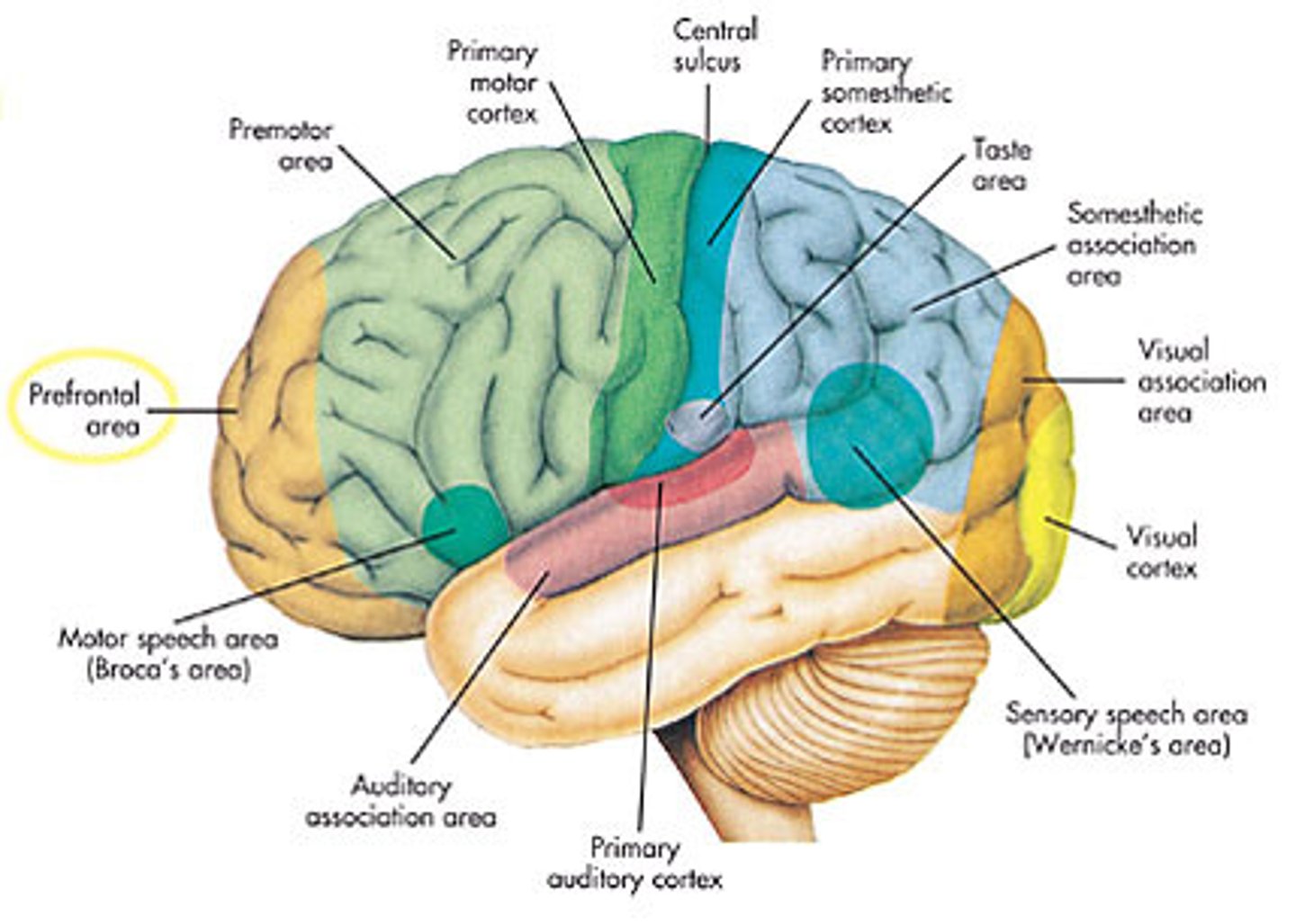
frontal lobe
cerebrum lobe responsible for memory, intelligence, behavior, emotions, motor function, and smell
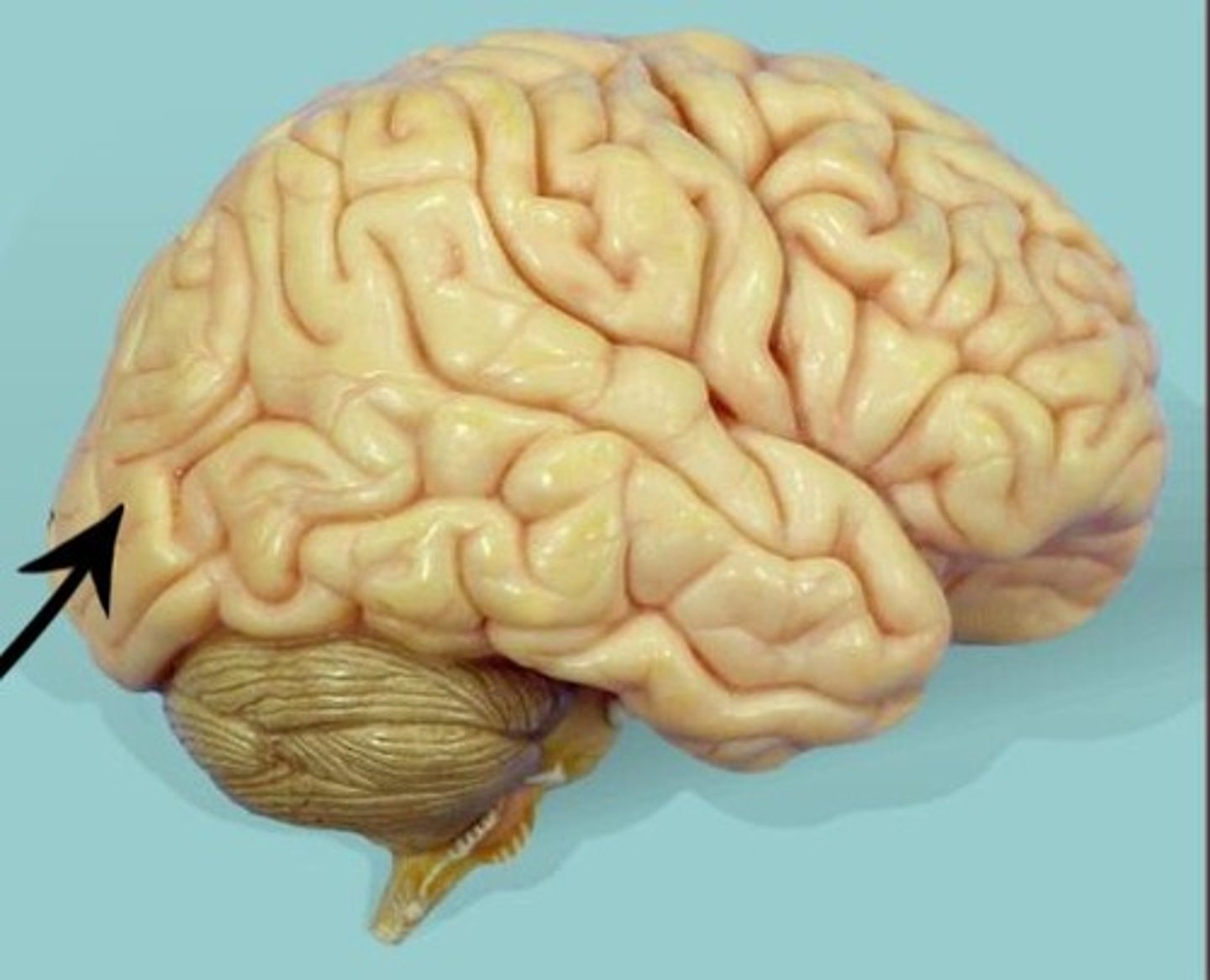
occipital lobe
cerebrum lobe responsible for vision and speech
parietal lobe
lobe responsible for somatic sensations (pain, touch, temperature perception), and speech
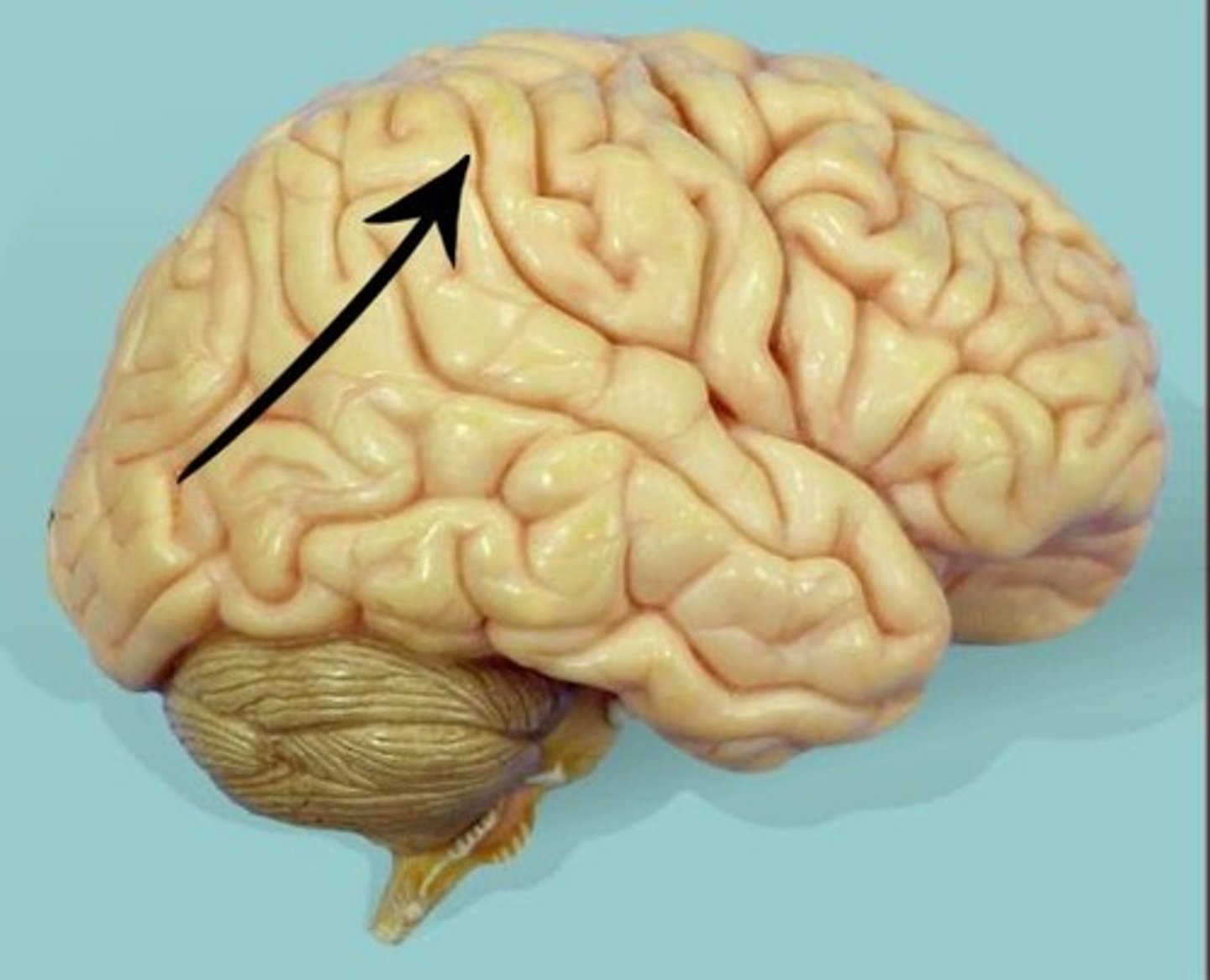
temporal lobe
lobe responsible for hearing, smell, memory, speech, and emotion
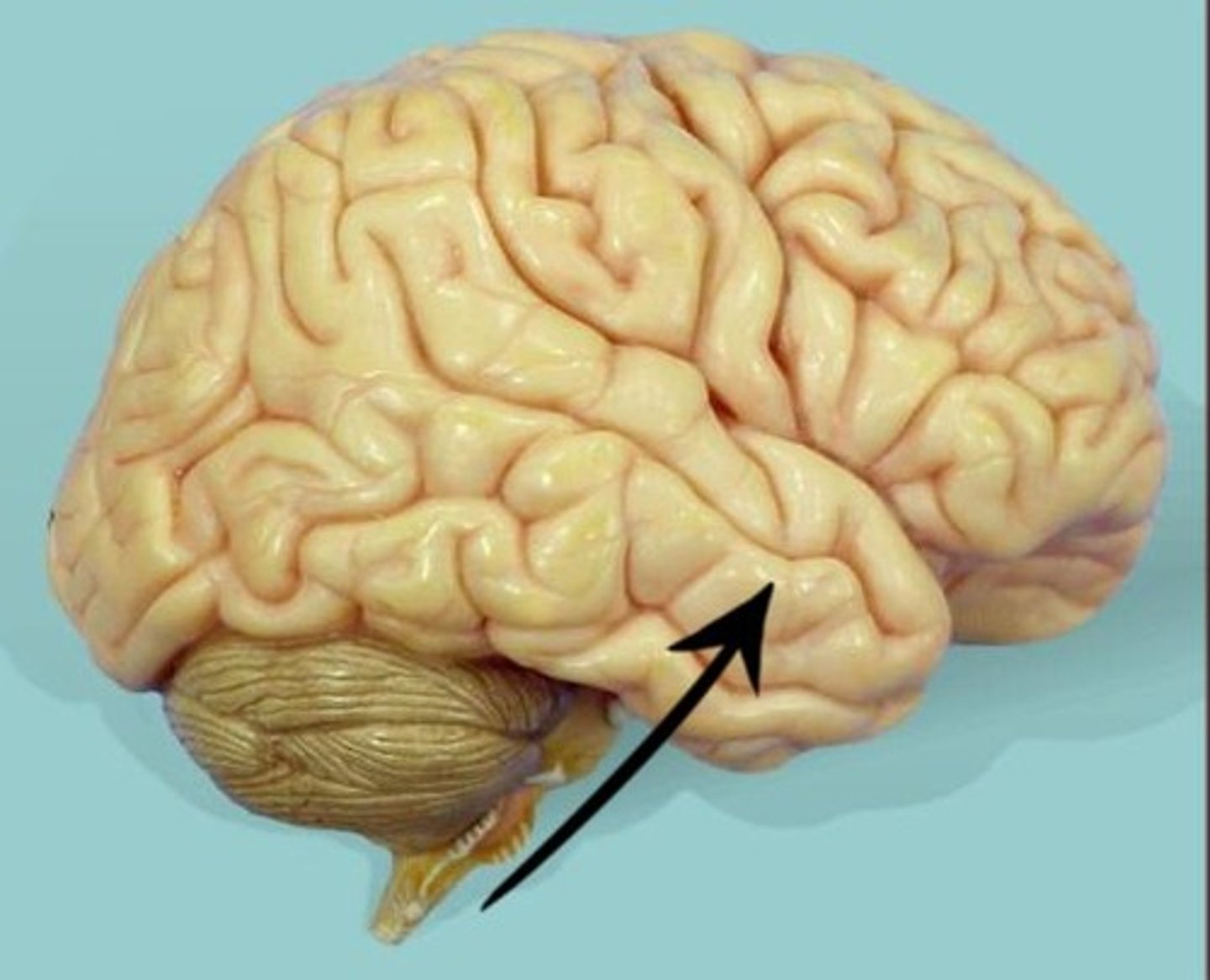
brain stem
Portion of brain that contains the pons, medulla oblongata, and the beginning of the spinal cord, controls the flow of messages between the brain and the rest of the body, and it also controls basic body functions
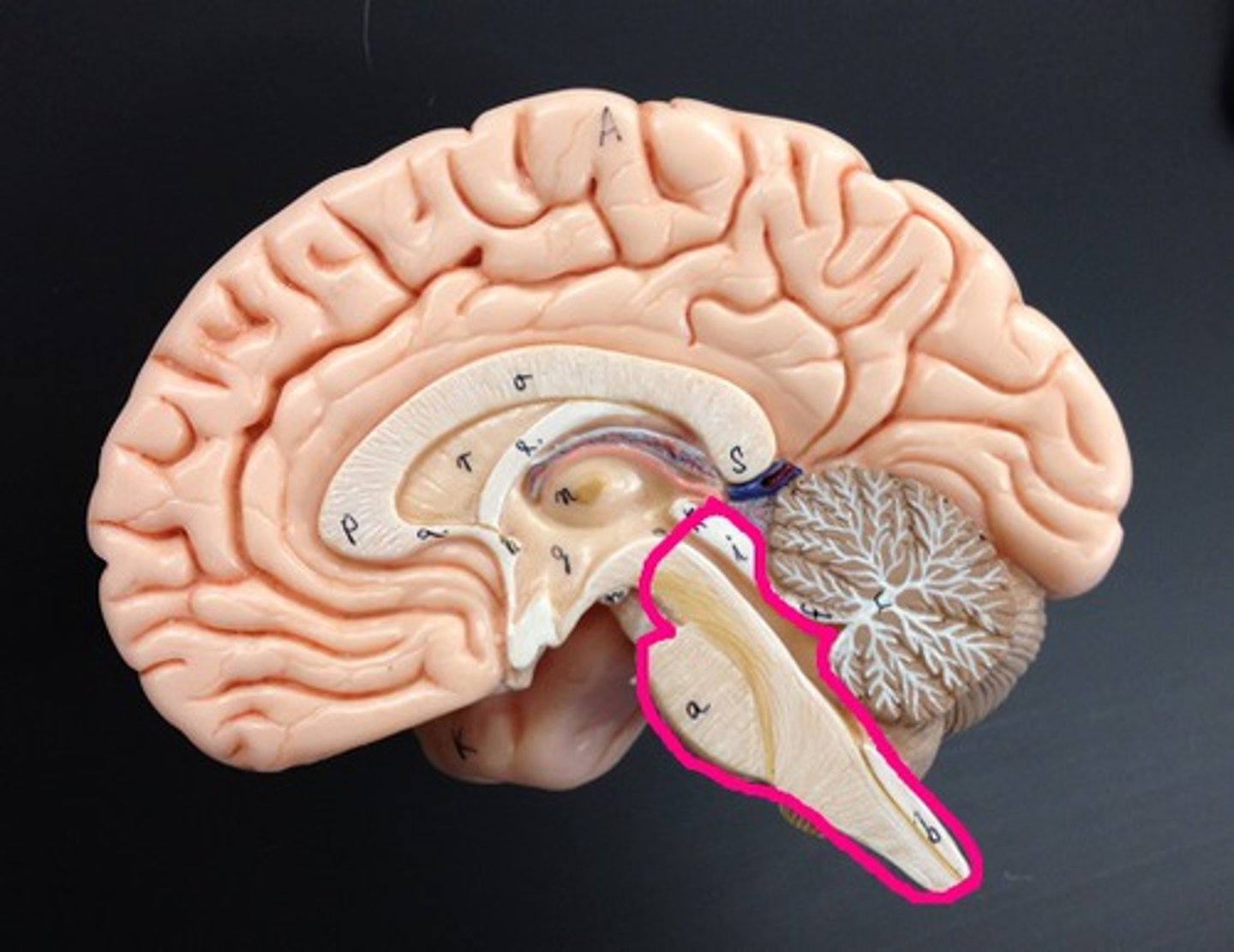
Broca's area
area on left frontal lobe responsible for tongue and lip movements
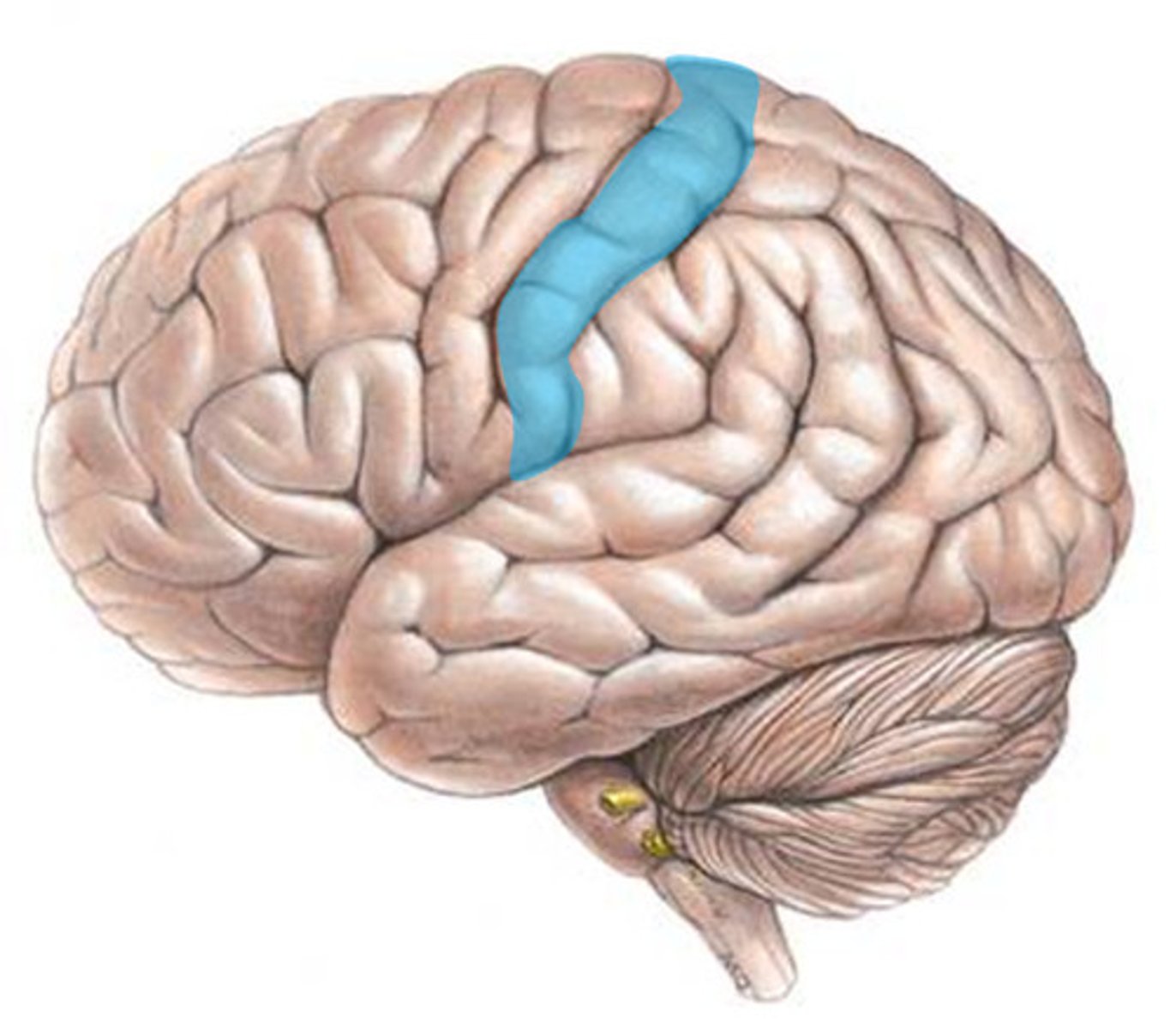
primary motor cortex
area in frontal lobe responsible for sending impulses to muscles
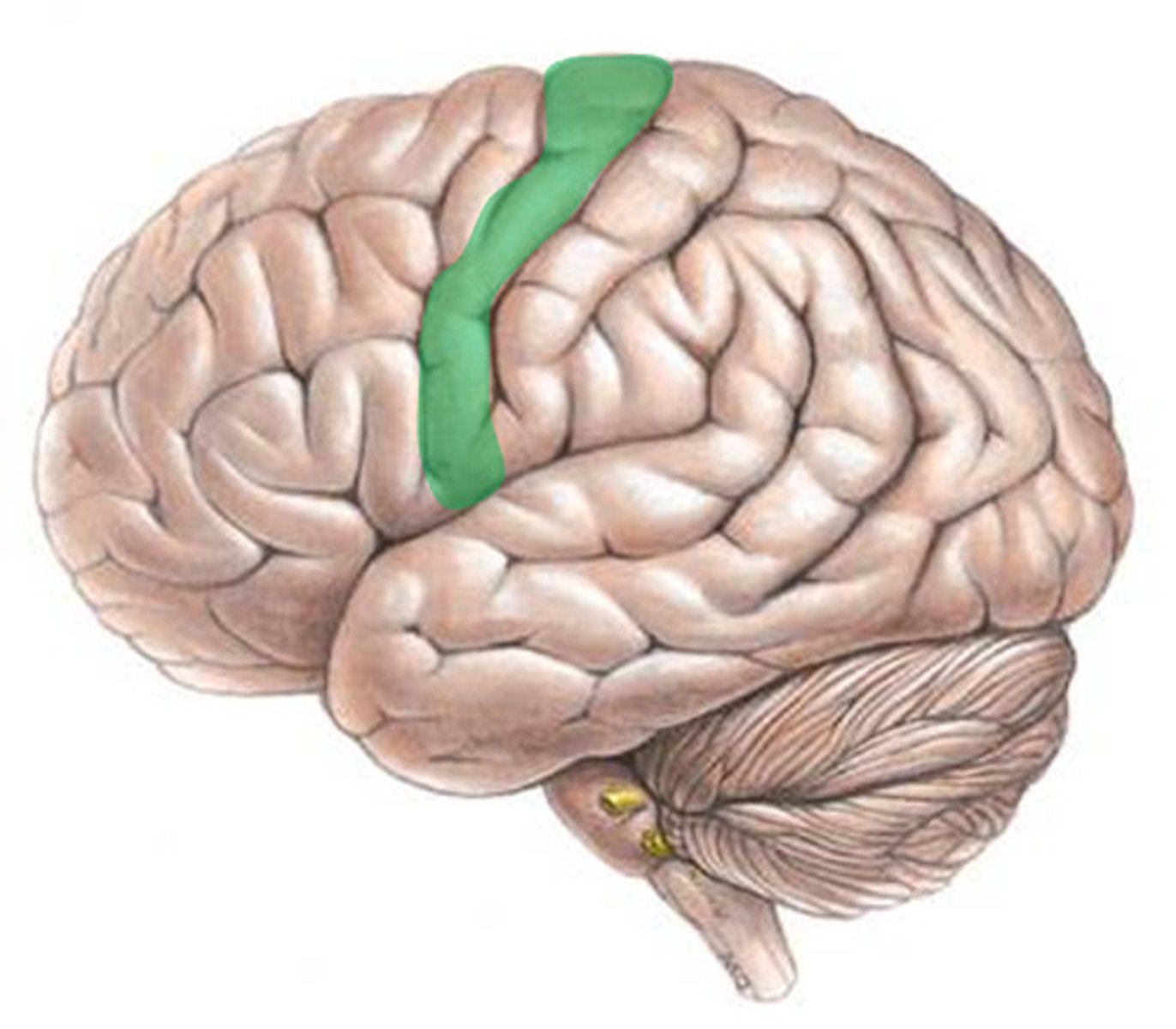
primary somatic sensory cortex
area in parietal lobe responsible for interpreting sensory impulses from the body
dura mater
outermost meninges layer
arachnoid mater
middle meninges layer
pia mater
inner meninges layer
sensory input
also known as the afferent pathway; the gathering information about changes in the environment
integration
process of interpreting sensory input and deciding motor output
motor output
also known as the efferent pathway; the response sent from the CNS to the rest of the body
CNS
composed of brain and spinal cord
PNS
composed of all other nerves and sensory receptors
autonomic NS
involuntary control of cardiac adn smooth muscles
Somatic NS
voluntary control of skeletal muscles
parasympathetic
part of autonomic N.S. responsible for involuntary daily functions
sympathetic NS
part of the autonomic N.S. responsible for response to potential danger
neuroglia
neuron supporting cells of the nervous system
Astrocytes
neuroglia that protects neurons from harmful substances in the blood
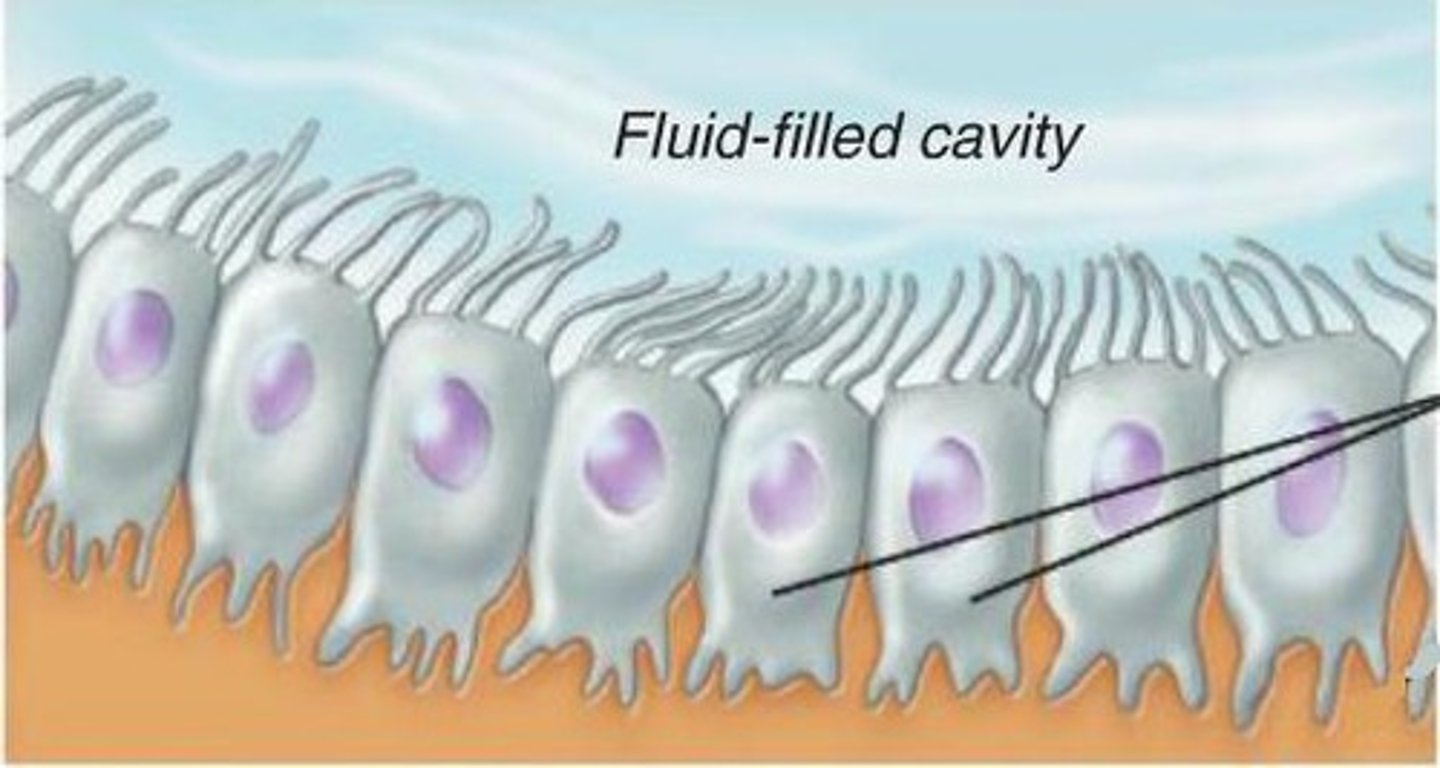
ependymal
neuroglia that form a protective covering around the spinal cord and cavities of the brain
oligodendrocytes
neuroglia that produce myelin sheaths around nerve fibers in the CNS
Schwann cells
neuroglia that produce myelin sheaths around nerve fibers in the PNS
Satellite cells
neuroglia that cushion neurons of the PNS
dendrites
conduct impulses toward the cell body of a neuron
axons
conduct impulses away from the cell body of a neuron
myelin sheath
insulating material on axon fibers that increase the rate of impulse transmission
neurotransmitter
a chemical messanger that sends a message from the axon terminals to a muscle or nearby neuron
synaptic cleft
a gap between axon terminals and nearby muscles or neurons
Nodes of Ranvier
areas on an axon without a myelin sheath; also known as gray matter
action potential
another name for a nerve impulse
depolarization
the inflow of sodium ions resulting in a more positive environment inside the neuron and the propagation of an action potential.
repolarization
the outflow of potassium ions resulting in the return of a more positive environment outside the neuron.
refractory period
time between the start of an action potential and repolarization
fissure
a deep grove in the brain
Meningitis
inflammation of the meninges causing pin-point rashes, fever, photophobia, etc.
Streptococcus pneumonia
The cause of meningitis
Botox
The use of toxins to block nerve signals from the brain to targeted muscle area
describe the major functions of the brain stem...
the brain stem regulated vital basic functions like regulation of heart rate, breathing, sleeping, and eating
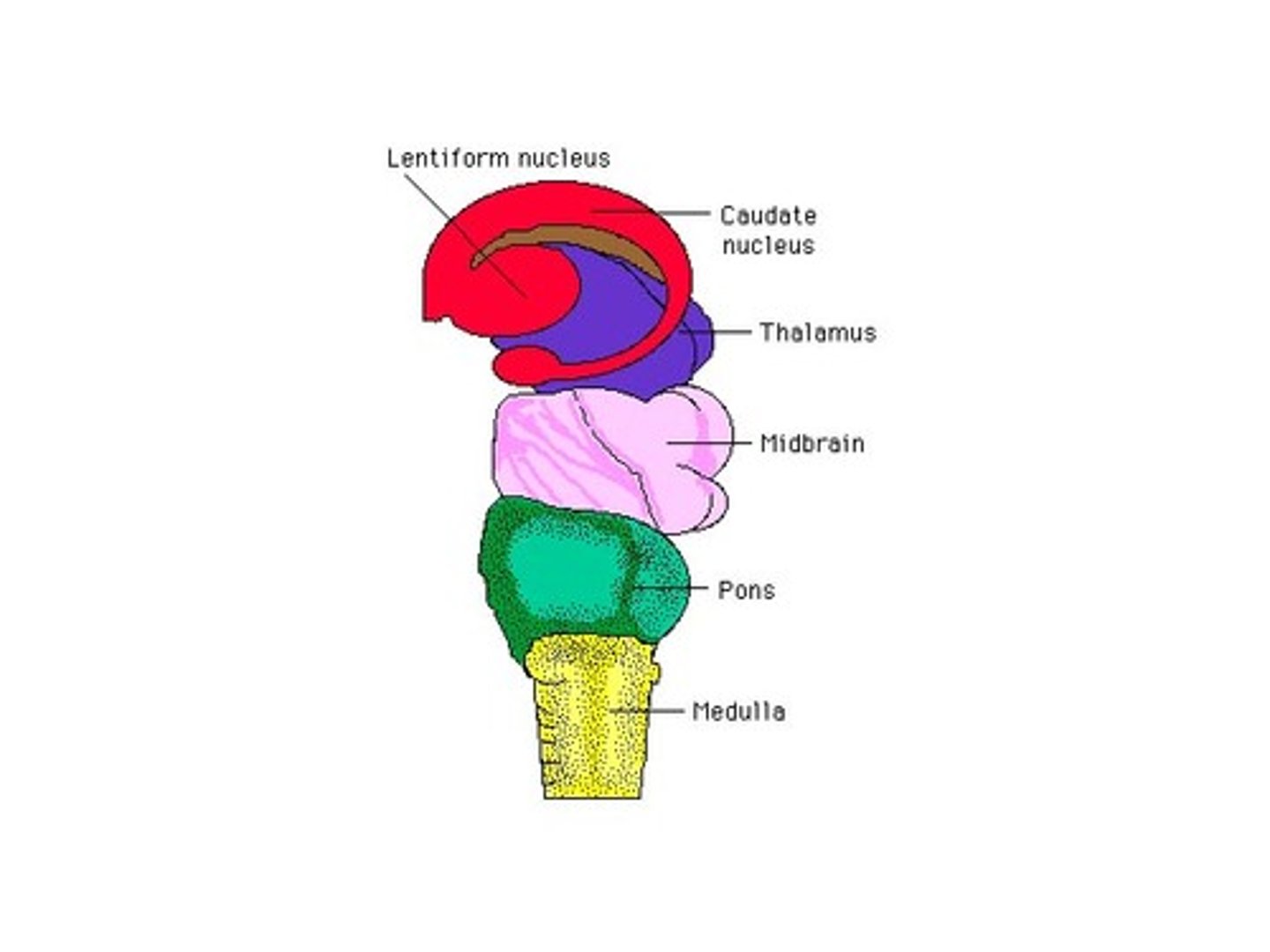
describe the major functions of the medulla...
carries out and regulates life sustaining that are done involuntarily (without thinking).
describe the major functions of the pons...
connects the upper and lower parts of the brain
temporal lobe
responsible for processing auditory information from the ears
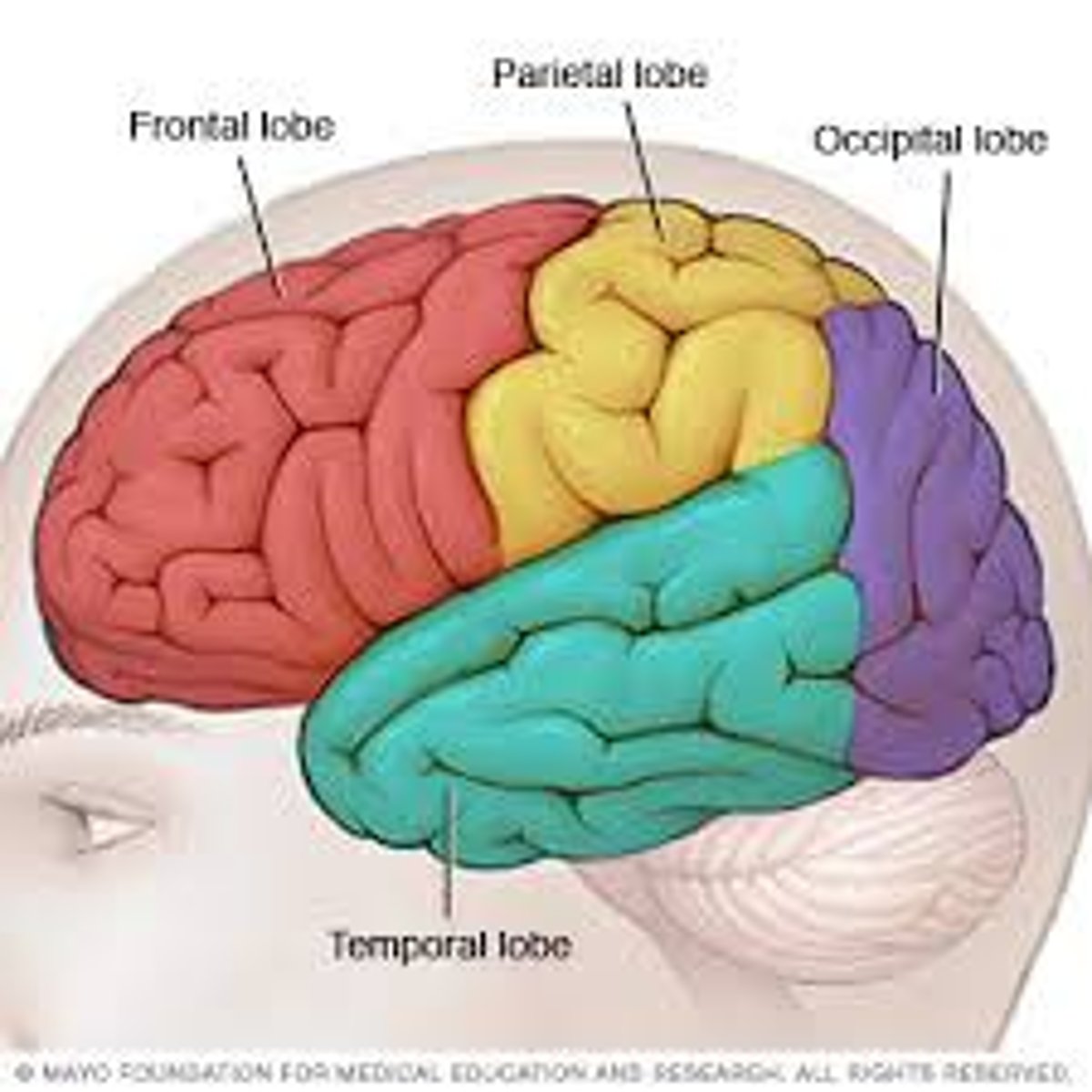
parietal lobe
processes sensory things that have to do with temperature, touch, and taste
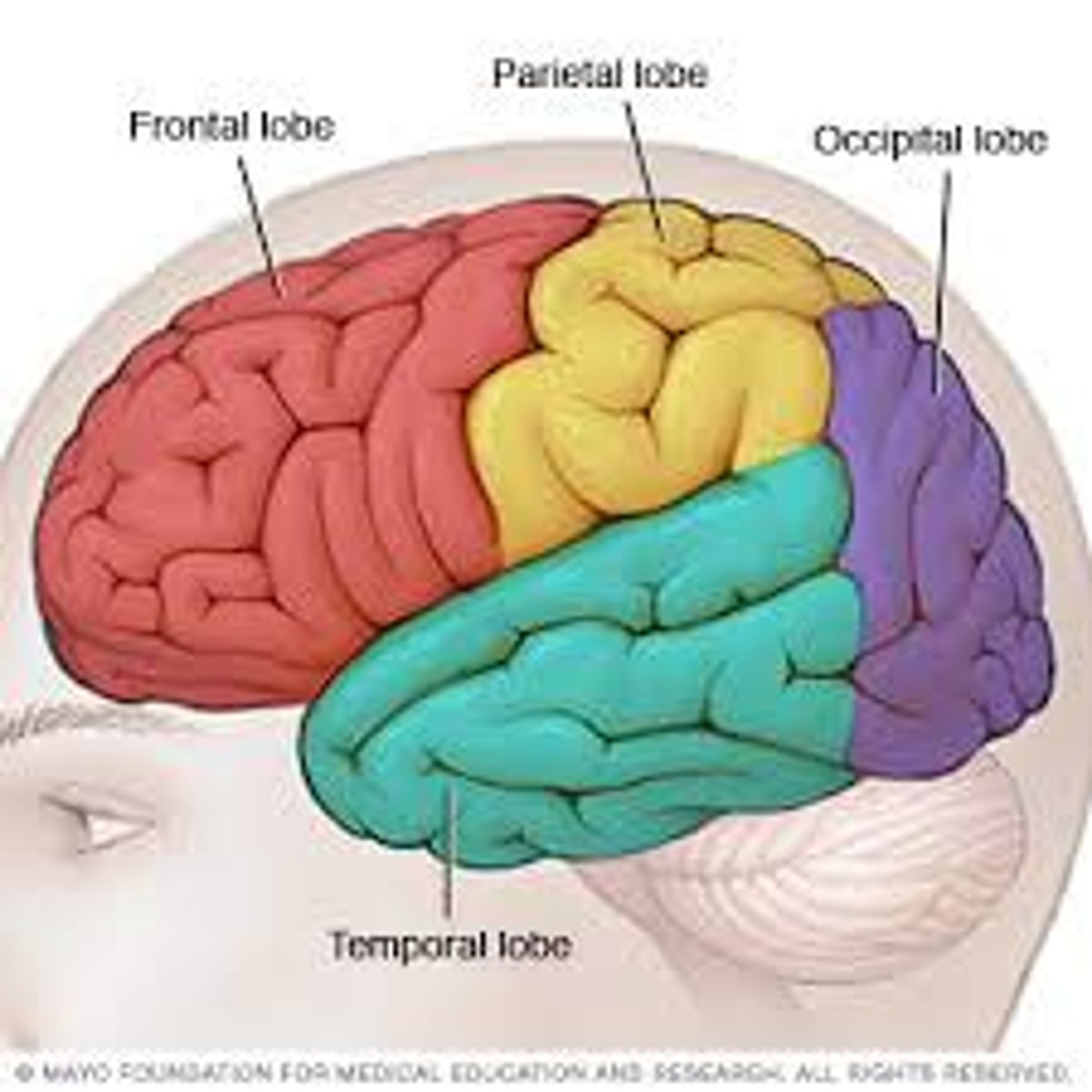
frontal lobe
carries out higher mental processes such as thinking, decision making, and planning. (This is where our personality is formed
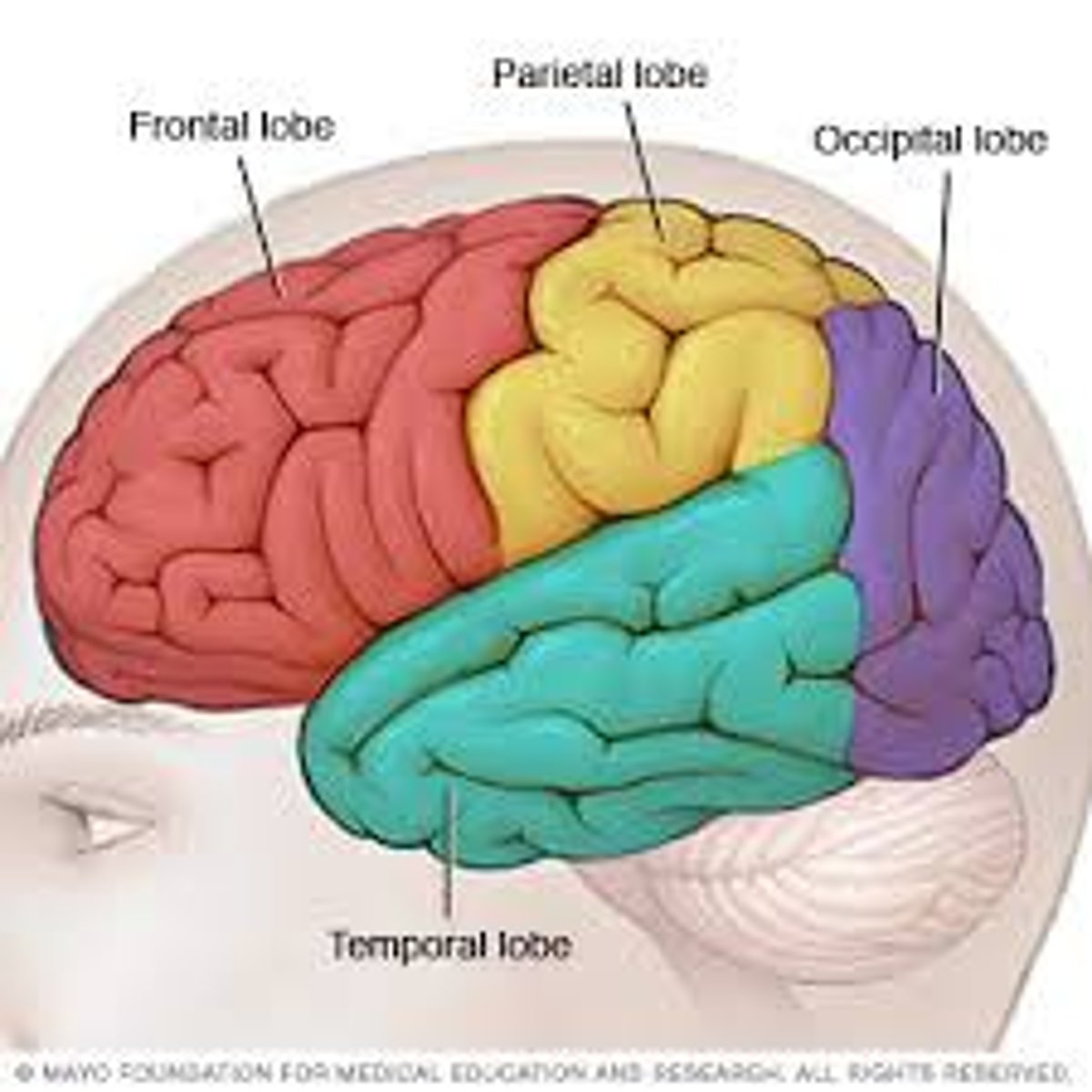
occipital lobe
responsible for processing visual information from the eyes. It helps you correctly understand what you are seeing
how does nicotine affect the nervous system?
Nicotine acts on the CNS and PNS. The rapid affects of nicotine include faster respiration, construction of arteries, and it stimulates the central nervous system
describe the major functions of the cerebral cortex
the cerebral cortex is where the four lobes are located
pituitary gland
it is referred to as the body's "master gland" because it controls the activity of most other hormone-secreting glands
hypothalamus gland
the section of the brain responsible for the production of many of the body's essential hormones. It's chemical substances help control different cells and organs
what is a gland?
a gland is an organ that synthesizes a substance
what hormones do the Hypothalamus Gland produce?
it produces dopamine and somatostaton
how does caffeine affect the nervous system?
caffeine is an odorless, but bitter, white powder that has the ability to stimulate the CNS
how does alcohol affect the nervous system?
alcohol can contract brain tissues, destroys brain cells, as well as depresses the CNS
how does marijuana affect the nervous system?
tetrehydrocannabinol (THC) acts on the cannabinoid receptors which are found on neurons in many places in the brain. It affects the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and cerebellum
what is the job of the spinal cord?
the spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of the neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body
the cerebrum cortex is...
associated with higher brain function such as thought and action
what hormones come from the pituitary gland?
the adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) stimulates the production and release of cortisol from the cortex and the andrenal gland.
the growth hormone (GH) participates in regulating the body's metabolism
what hormones do the thalamus produce?
anti-diuretic hormone
ADH travels in the blood stream to you kindneys so more water is reabsorbed into your blood
oxytocin
stimulates the uterine muscles to contract
what is a thalamus gland?
the thalamus serves as a relay station for impulses traveling to and from the spinal cord, brain stem, cerebellum, and cerebrum
describe the major functions of the cerebellum...
responsible for balance and coordination of muscles and the body. It is extremely important for being able to preform everyday voluntary things
what is a hormone?
hormones are chemical substances that act like messenger molecules in the body
describe the function of each sense organ...
touch-skin
smell-nose
taste-tongue
hearing-ear
sight-eyes
cerebral palsy
A congenital disorder of movement, muscle tone or posture due to abnormal brain development...the cerebral cortex is affected
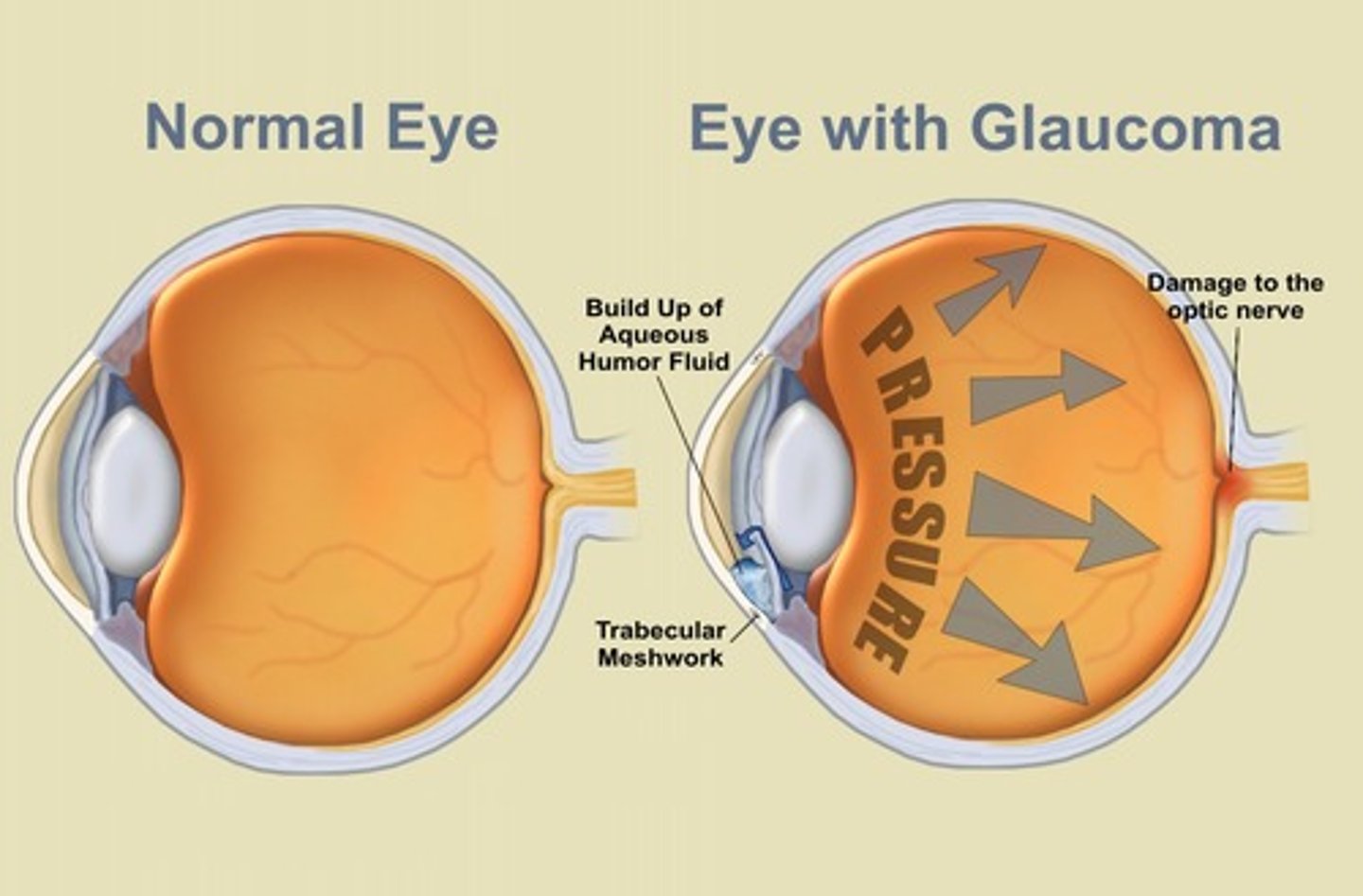
glaucoma
a group of eye conditions that can cause blindness. The visual cortex is affected
epilepsy
Also known as seizure disorder, it is a disorder in which nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, causing seizures
multiple sclerosis
a disease in which the immune system eats away at the protective covering of the nerves. The brain and spinal cord are affected
Alzheimer's disease
a progressive disease that that destroys memory and other important mental functions. The condition affects the cerebral cortex and hippocampus
Parkinson's disease
a disorder of the CNS that affects movement, often including tremors
Nervous system
Major communication system in the body. Functions in sensing, processing, communicating between the cells throughout the entire body
Central Nervous system
Consists of the brain and spinal cord
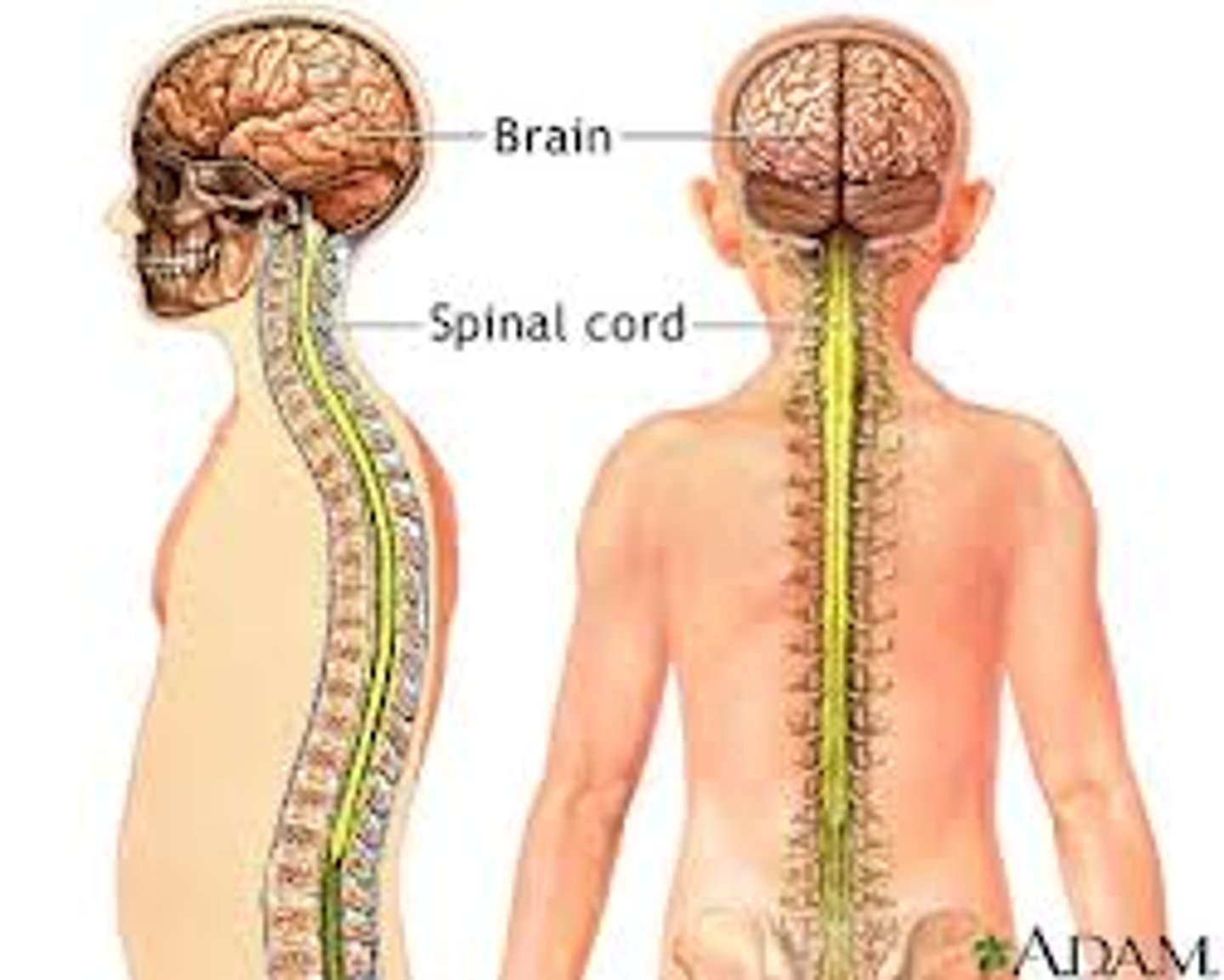
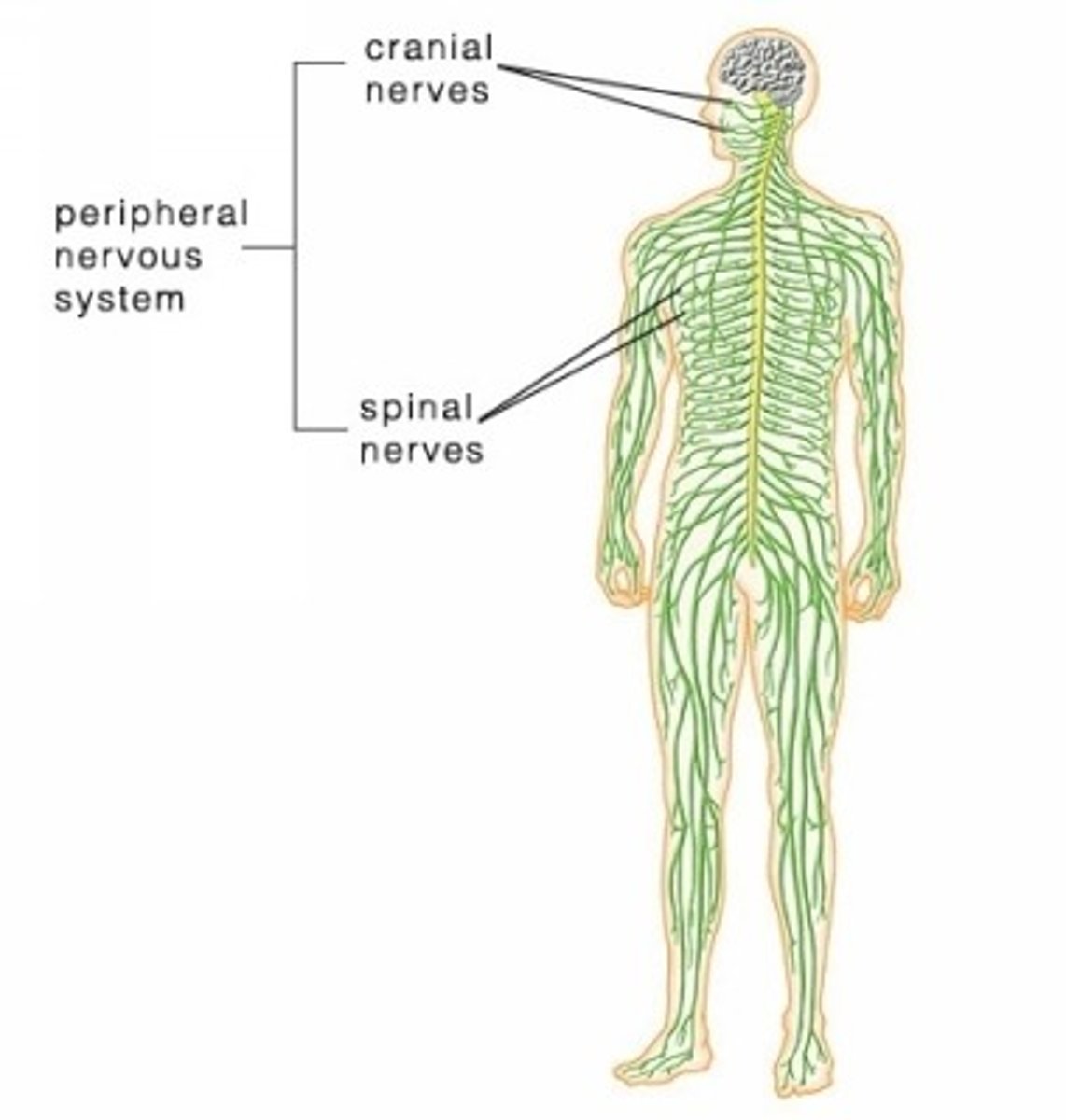
Peripheral nervous system
Extends from the spinal cord out to the entire body. Touch and feeling travels through neurons in the peripheral nerves through the afferent pathway to the spinal cord/brain
Afferent pathway
Input. Away from the periphery to the CNS. Brain functions as the integrator. Includes somatic, special, and visceral senses
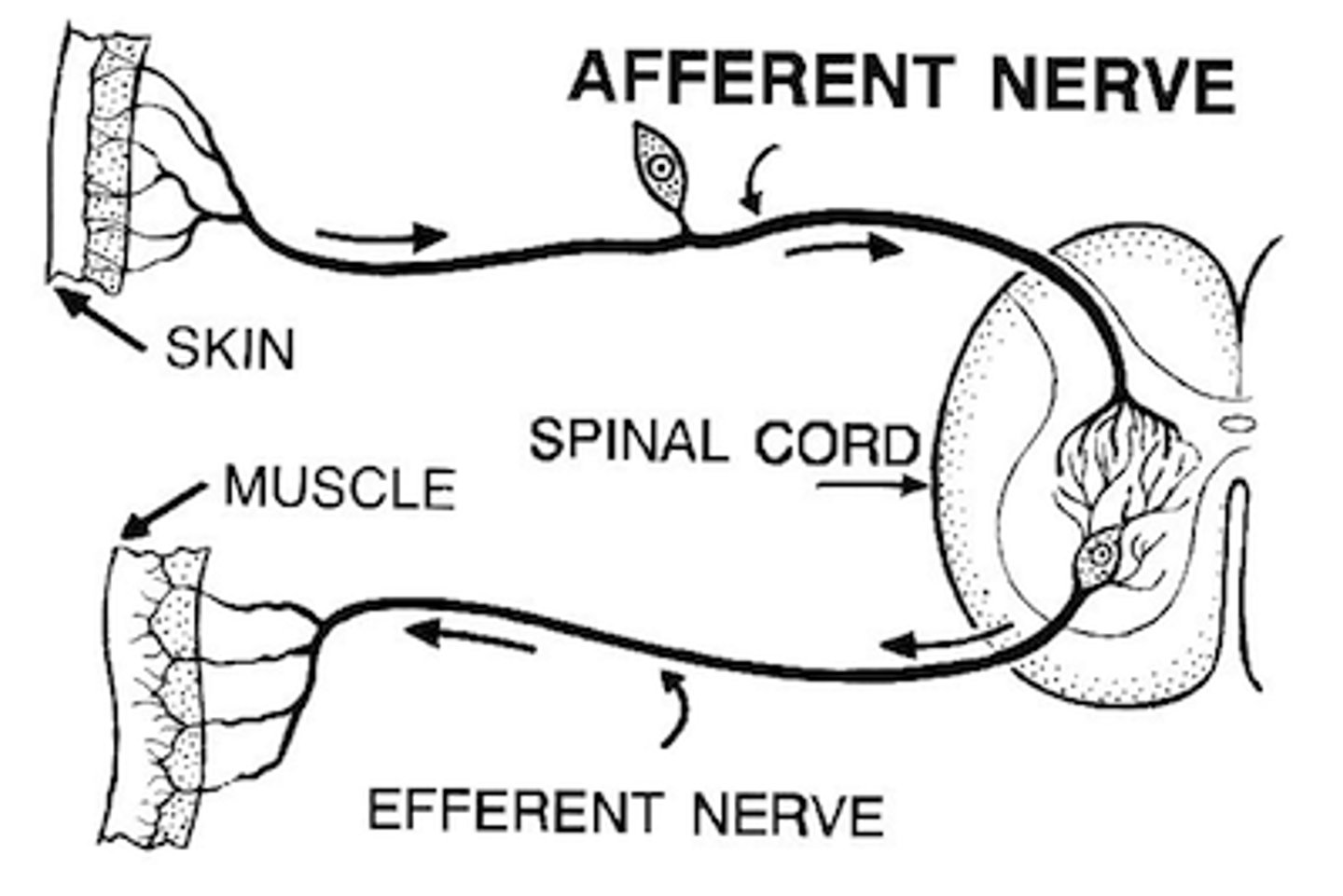
Efferent pathway
Output. Leaves the CNS and travels to the periphery. Includes somatic and automatic nervous systems and sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways
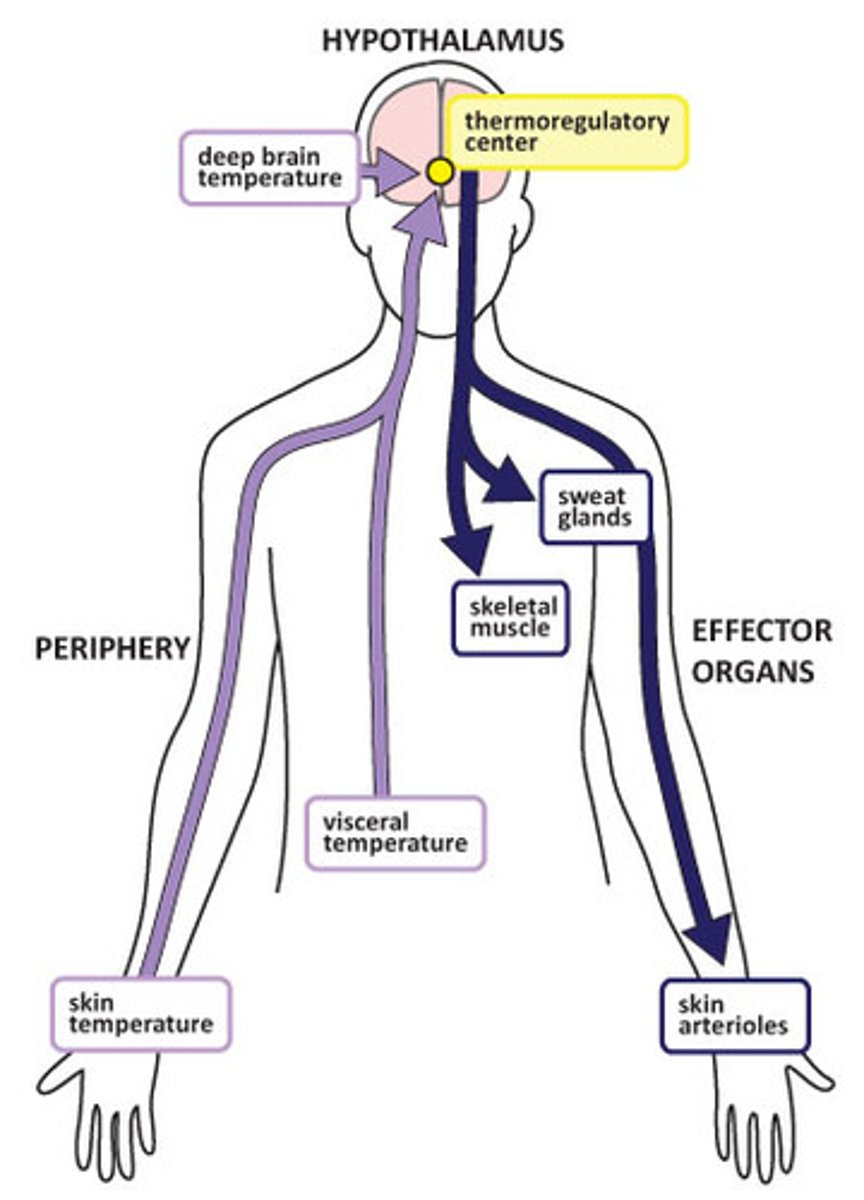
Somatic response
Signals travel from the brain down efferent pathway to muscles/neruons
Neurons
Interconnect and communicate with each other. From the brain to spinal, to peripheral nerves, to the effector organs to allow us to react to our surroundings. Use electrical and chemical signals
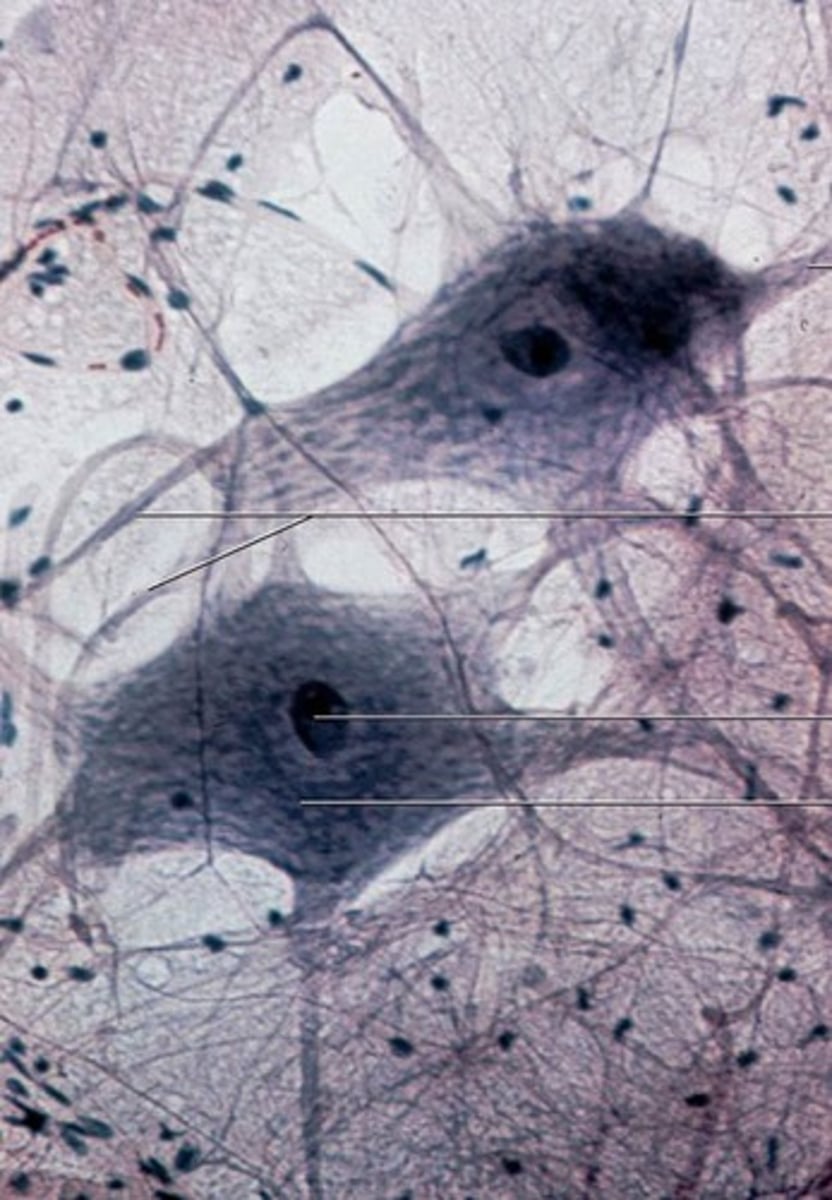
Action potential
Sending of message leads to chemical release (neurotransmitter)
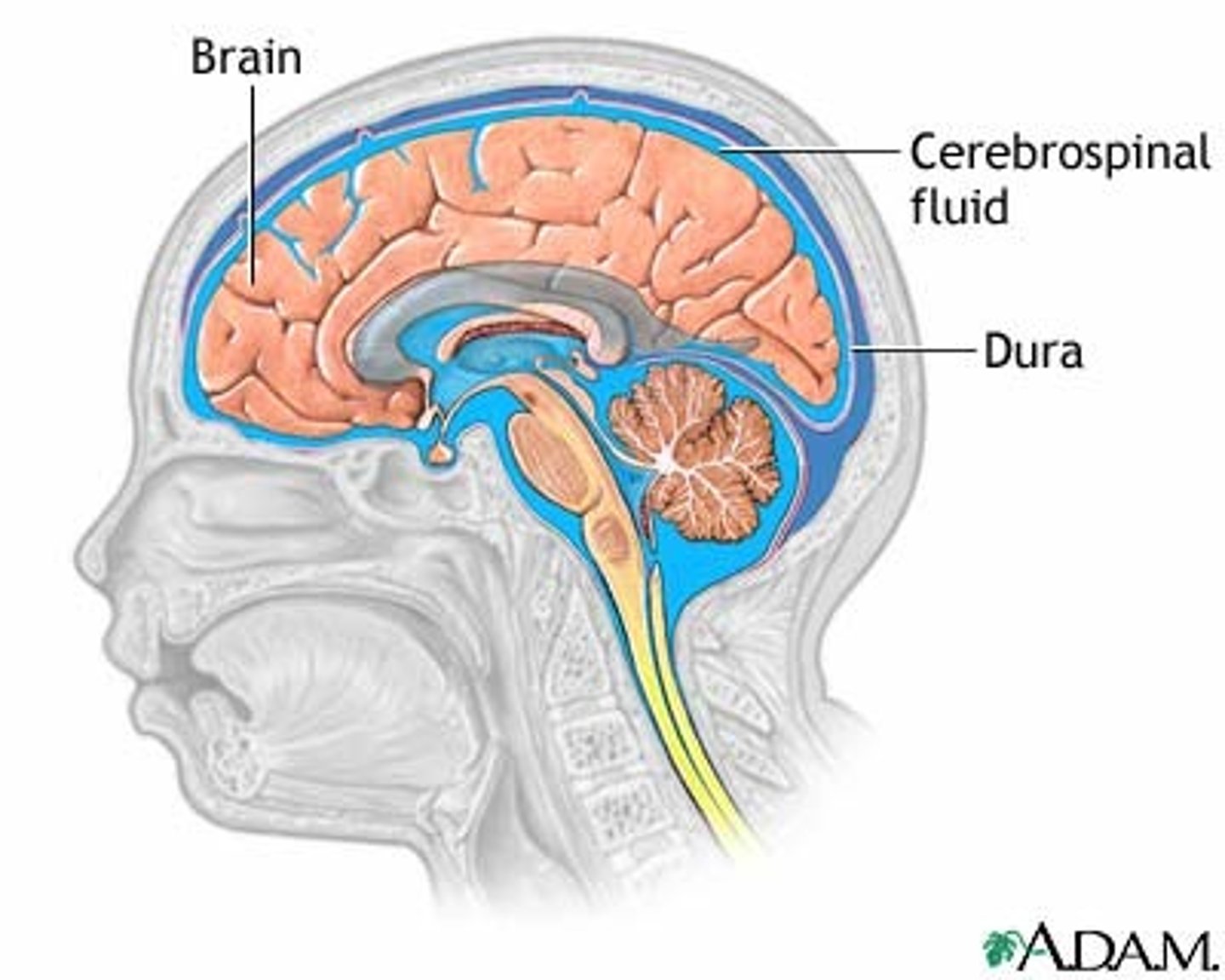
Brain and spinal cord
Delicate/semisolid structures that require support and protection. Bone (skull, vertabrae), meninges (membranes), fluid (CSF)
Ventricles
Cavities filled with CSF, lined with ependymal cells
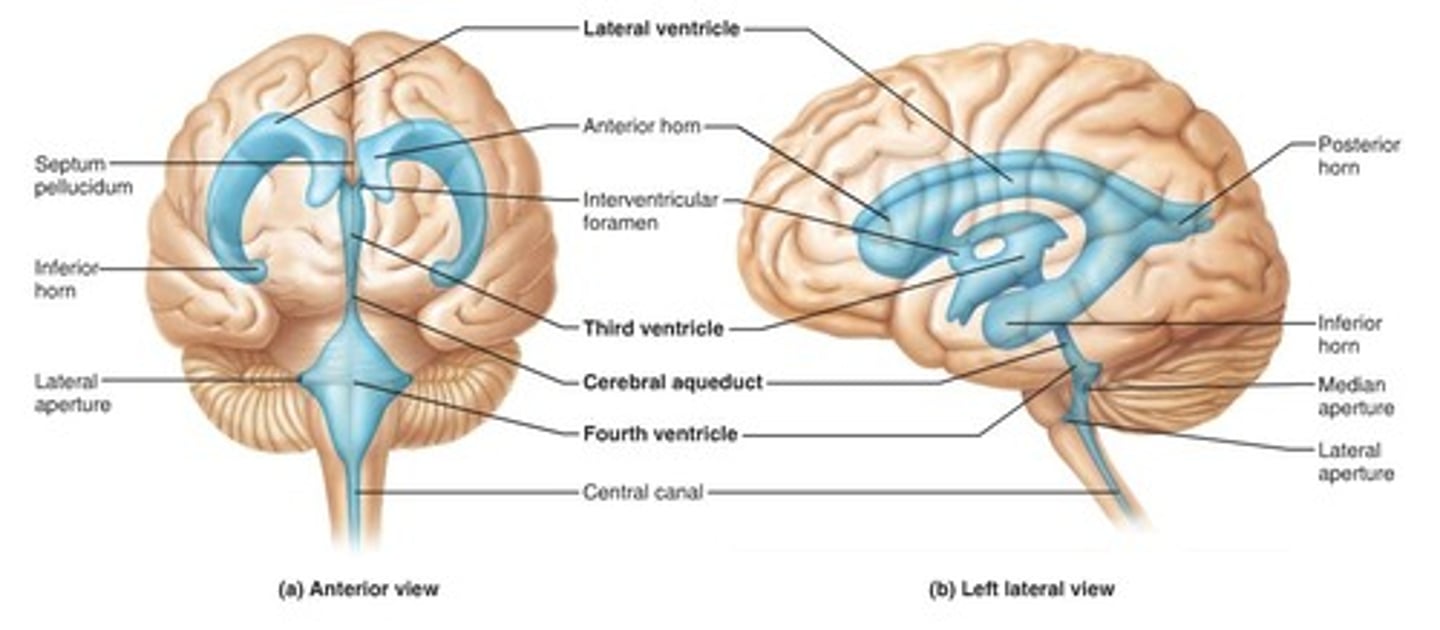
CSF
Secreted from support cells (glia). Support the brain, regulate cell environment. Circulates through ventricular system. Produced by choroid plexus ependymal cells, supports/cushions against trauma, regulates environment of the brain
Glia
Support cells. More numerous than neurons. Always making CSF
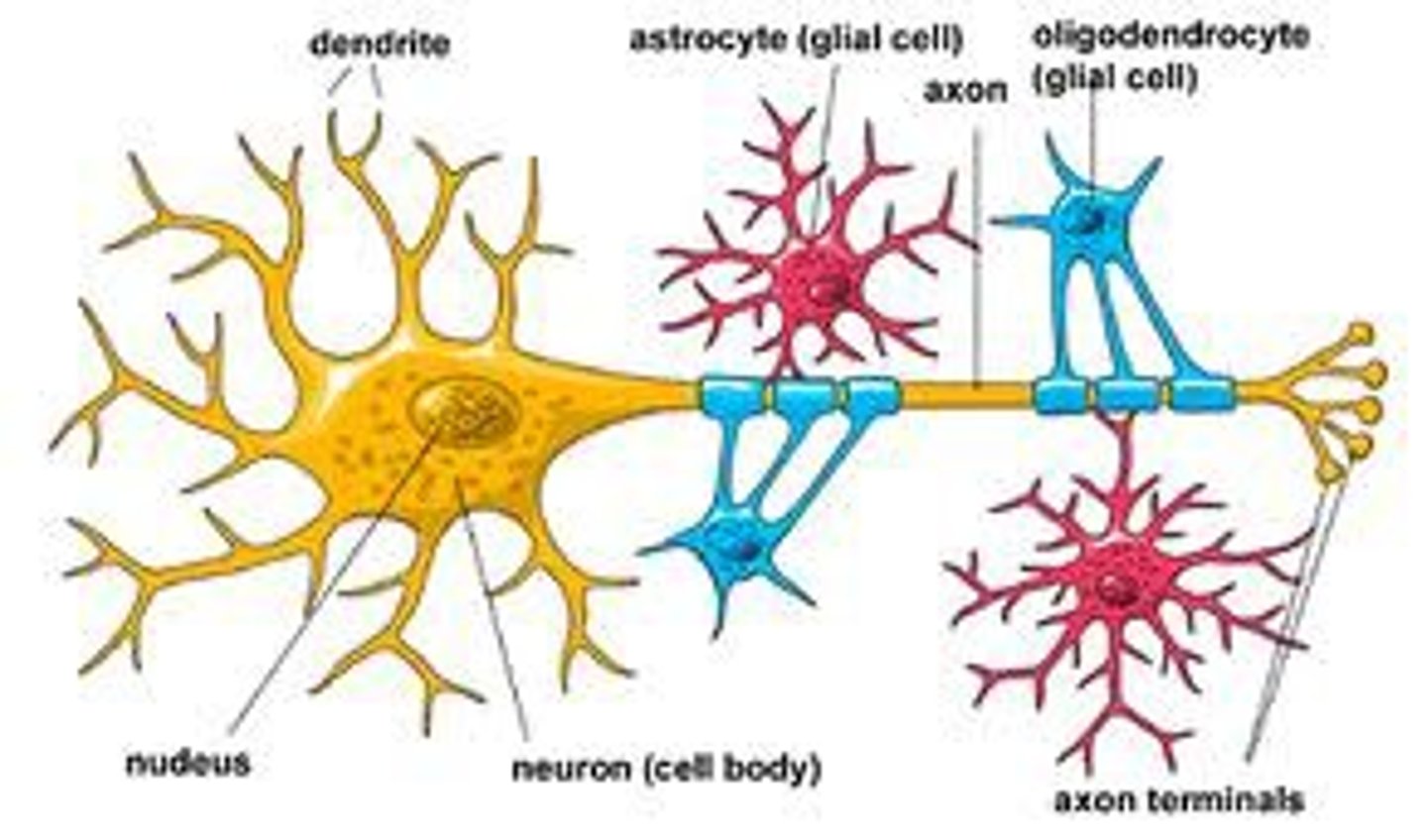
Astrocytes
Regulate extracellular environment (ions, neurotransmitters). Guide developing neuronal processes
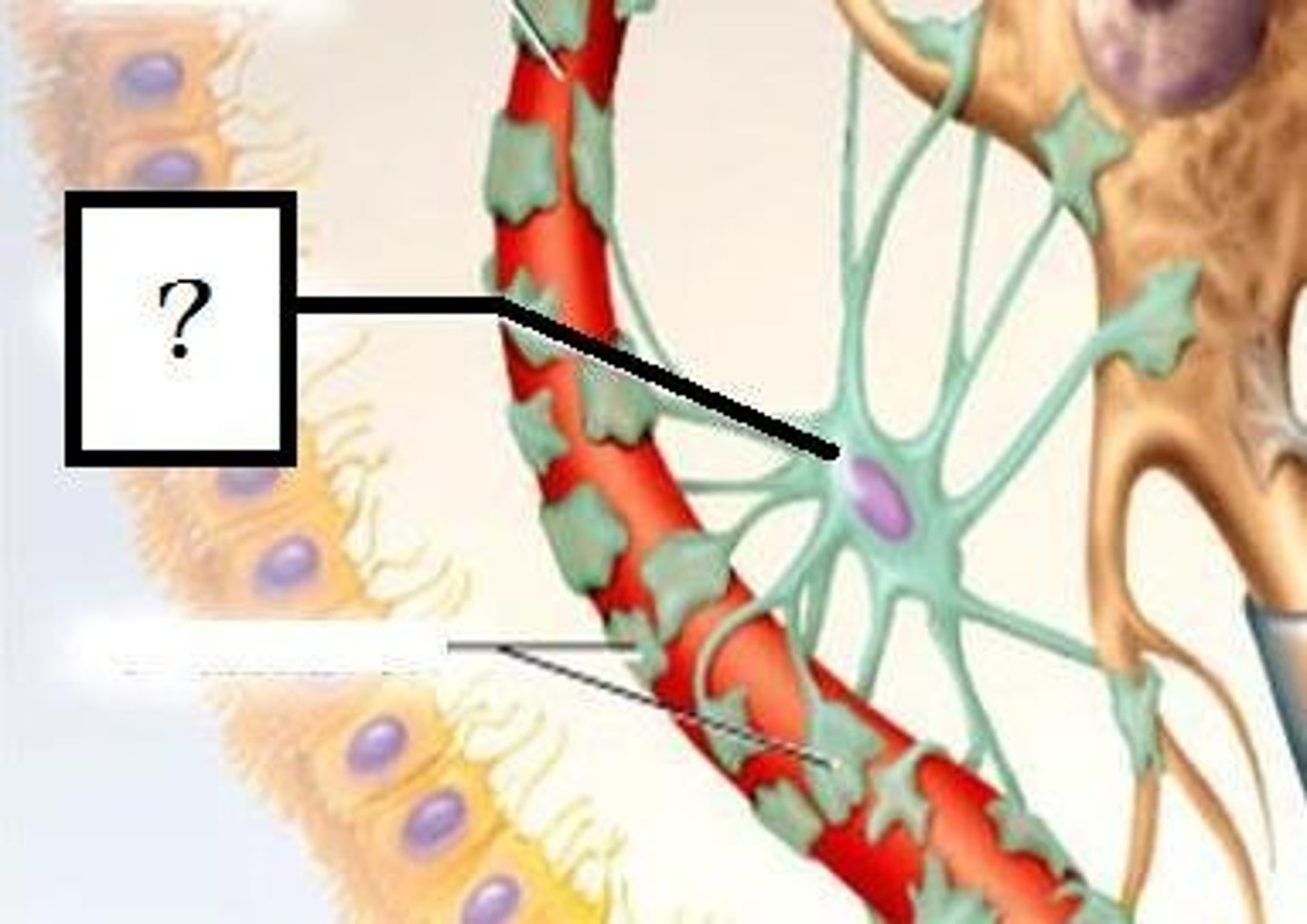
Microglia
Immune function (phagocytize bacteria and debris, release cytokines)

Oligodendrocytes
Myelinate central nerves multiple nerves at a time
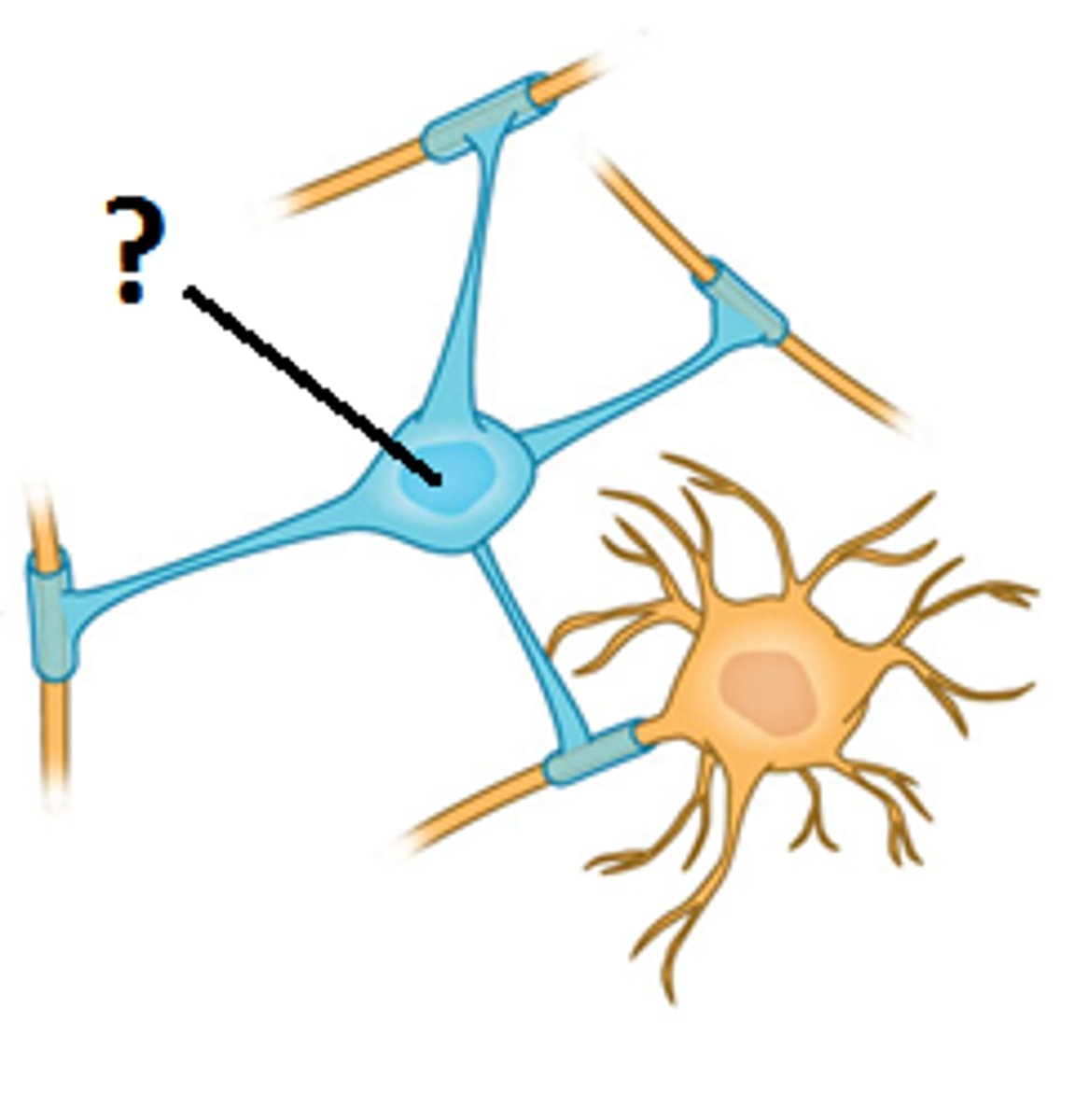
Myelin
Protect axon from outside ions. Act like electrical tape. Made from schwann cells in the periphery and oligodendrocytes in the CNS
Ependymal cells
Secrete CSF, ions, proteins, etc. Line the ventricles