funds 30 promoting urinary elimination
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
anuria
absence of urine output or severe reduction
less than 100 mL over a 24-hour period
often a sign of kidney failure / complete obstruction
ogluria
decreased urine output
less than 400-500 mL of urine in adults over a 24-hour period
polyuria
production of abnormally large volumes of urine
more than 2.5 to 3 liters per 24 hours
hematuria
blood in urine
nocturia
need to wake up at night to urinate
cystitis
inflammation of bladder
dysuria
difficult, painful, or burning urination
residual urine
urine that remains in the bladder immediately after the person has finished voiding
usual urine output for an adult is:
30-70 mL/hr
if less than 30mL/hr, may have decreased tissue perfusion & decreased cardiac output
bladder empties when _ mL of urine is present (under voluntary control)
250 - 400 mL
if a pt has not voided in _ hours, it is concerning.
8
bladder can contain _ mL of urine
1000 - 1800 mL
at least 600 mL must be excreted daily to remove waste
average urine output is 1000 - 1500 mL daily
changes w aging
incontinence is not a normal part of aging
decrease in functioning nephrons
decrease in filtration rate
decreased bladder tone - nocturia
decreased bladder emptying increased residual
enlargement of prostate - urethral obstruction
normal urinary elimination

characteristics of normal urine

cystitis
inflammation of the bladder
causes: bacteria, injury, break in sterile technique
E. Coli is most common bacteria cause
s: frequency, urgency, dysuria, malaise, foul-smell urine, slight fever. elderly: altered mental
preventing cystitis & uti
increase fluid to 2500 - 3000 mL
avoid citrus
front to back wipe
avoid tight clothing and baths, wear cotton underwear
empty bladder after intercourse
empty bladder q2-3h
avoid sitting in wet bathing suit
urine specimens
send to lab within 5-10 min. after 15 mins, characteristic change
midstream (clean catch) specimen: to be sent for culture
given sterile cup, wipes, be told how to hold. keep labia open after cleaning until obtained. clean right, left, middle.
strained specimen: if renal calucli

24-hour urine specimen
specific container. all urine into container
if void in toilet by accident, specimen is invalid
must be refrigerated/ stored on ice
abnormalities found in urine

bladder palpation

assessing GU
usual pattern of elimination
incontinence / frequent urination
burning, sense or urgency?
time of day for elimination, nocturia?
total daily fluid intake, is I&O normal?
types of catheters
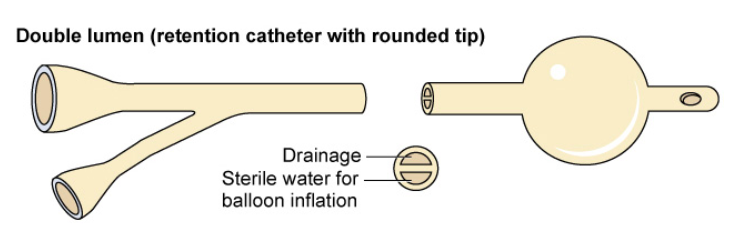
foley: indwelling
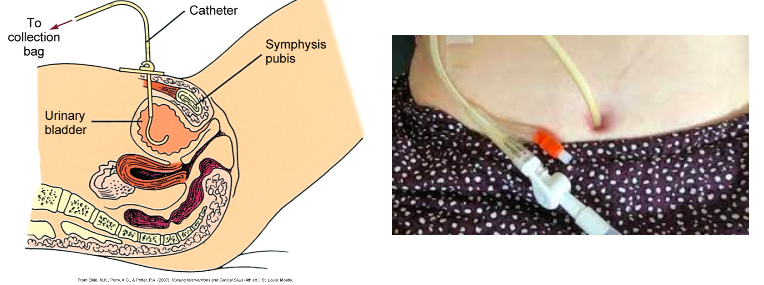
suprapubic: directly into bladder
coude: angle of the tip. prostate issue

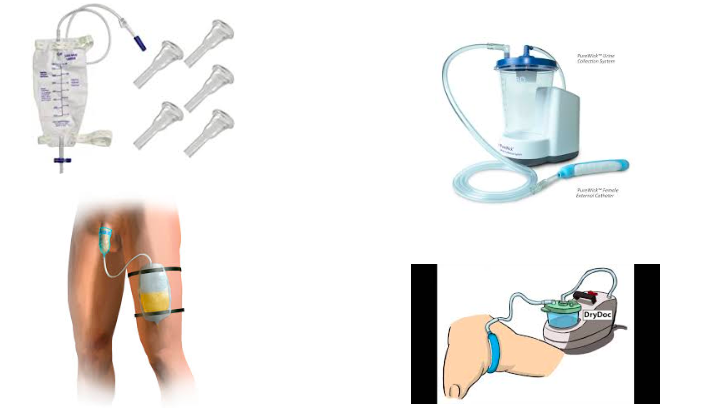
non-invasive ways to collect urine
condom catheter. has self adhesive. skin needs to be clean and dry, intact, & skin prep. leave 1-2 inch between tip and drain spout
pure wick:
foley catheter
double lumen. one inflates, other is for the drainage
come in French. smaller the number, the smaller the size
Male: 18-20 Fr
Female: 14-16 Fr
suprapubic catheter
surgically placed, directly into bladder
if pt has long-term urinary retention
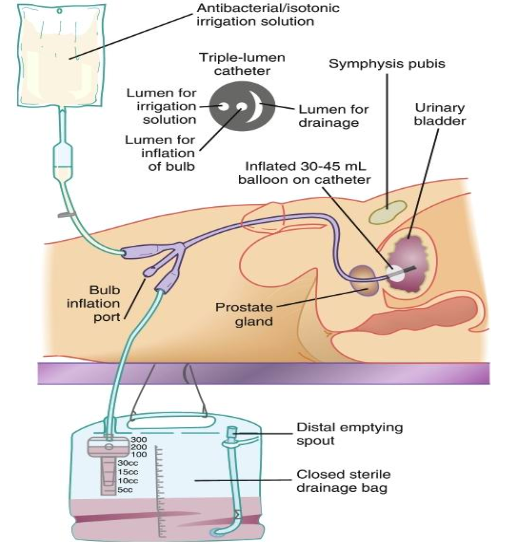
alock
triple lumen alcock with coude tip
one port for inflation, one for drainage, one for continuous bladder irrigation (CBI)
if had had urinary/ prostate surgery. for any big clots any big clots come out. flow rate is adjusted so drainage is light pink
volume going in has to be documented since that is not their urine output