Chapter 10 Test
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What are traits?
Characteristivs such as hair color, eye color etc...
What are chromosomes?
Instructions for each trait that are located in the nucleus of the cells
What are genes?
Segments that DNA are organized into
What do genes control?
The production of a protein
How many genes do chromosomes contain?
Hundreds.
How many chromosomes do humans cells have?
46
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
23
What are homologous chromosomes?
chromosomes that make up pairs.
Why do organisms produce gametes with half the number of chromosomes?
To maintain the same number of chromosomes from generation to generation.
What is the symbol n
It represents the number of chromosomes in a gamete
What is a haploid cell?
A cell with n chromosomes
What is a diploid cell?
A cell that contains 2n chromosomes
What is meiosis
A type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell and produces gametes.
What happens in interphase?
Chromosomes replicate and chromatin condenses
What happens during prophase I
pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs
How many chromatids are in one chromosome
two
What is synapsis?
A process where homologous chromosomes condense and they are bound together.
What is crossing over?
Chromosomal segments are exchanged between a pair of homologous chromosomes.
What does crossing over produce?
an exchange of genetic information.
What happens during metaphase I
chromosome centimeres attach to the spindle fibers and homologous chromosome line up as a pair at the equator.
What happens during anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. The chromosome number is reduced from 2n to n when the homologous chromosomes separate.
What happens during telophase I
Chromosomes reach the cell's opposite poles. Cytokinesis occurs.
What happens during prophase II
A second set of phases begins as the spindle apparatus forms and the chromosomes condense.
What happens during metaphase II?
Chromosomes are positioned at the equator. Meiosis II involves a haploid number of chromosomes.
What happens during anaphase II?
Sister chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere by spindle fibers and move toward the opposite poles of the cell.
What happens during telophase II?
The chromosomes reach the poles, and the nuclear membrane and nuclei reform.
What results in cytokinesis?
four haploid cells, each with n number of chromosomes.
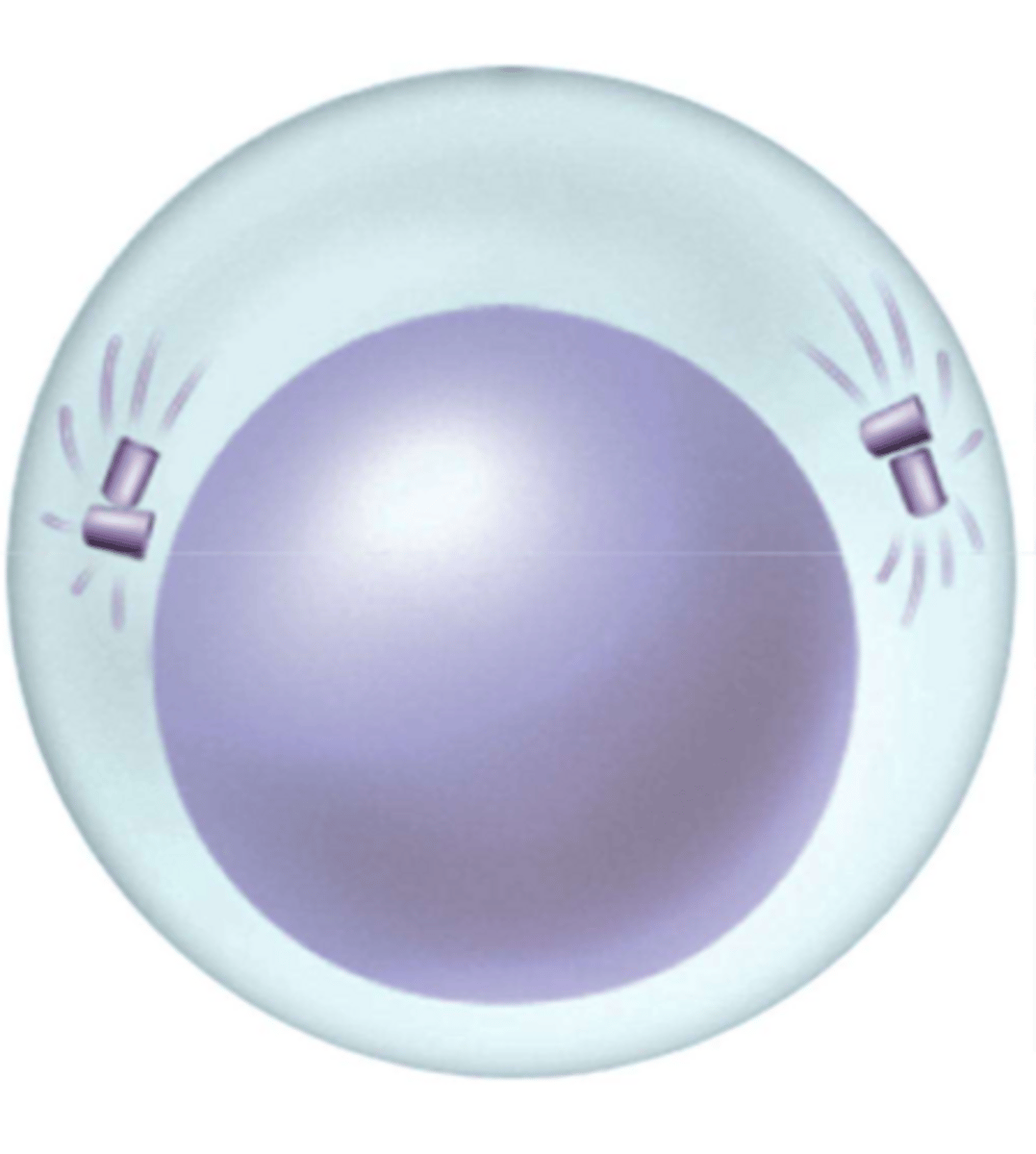
What phase is this?
Interphase

What phase is this?
Prophase I
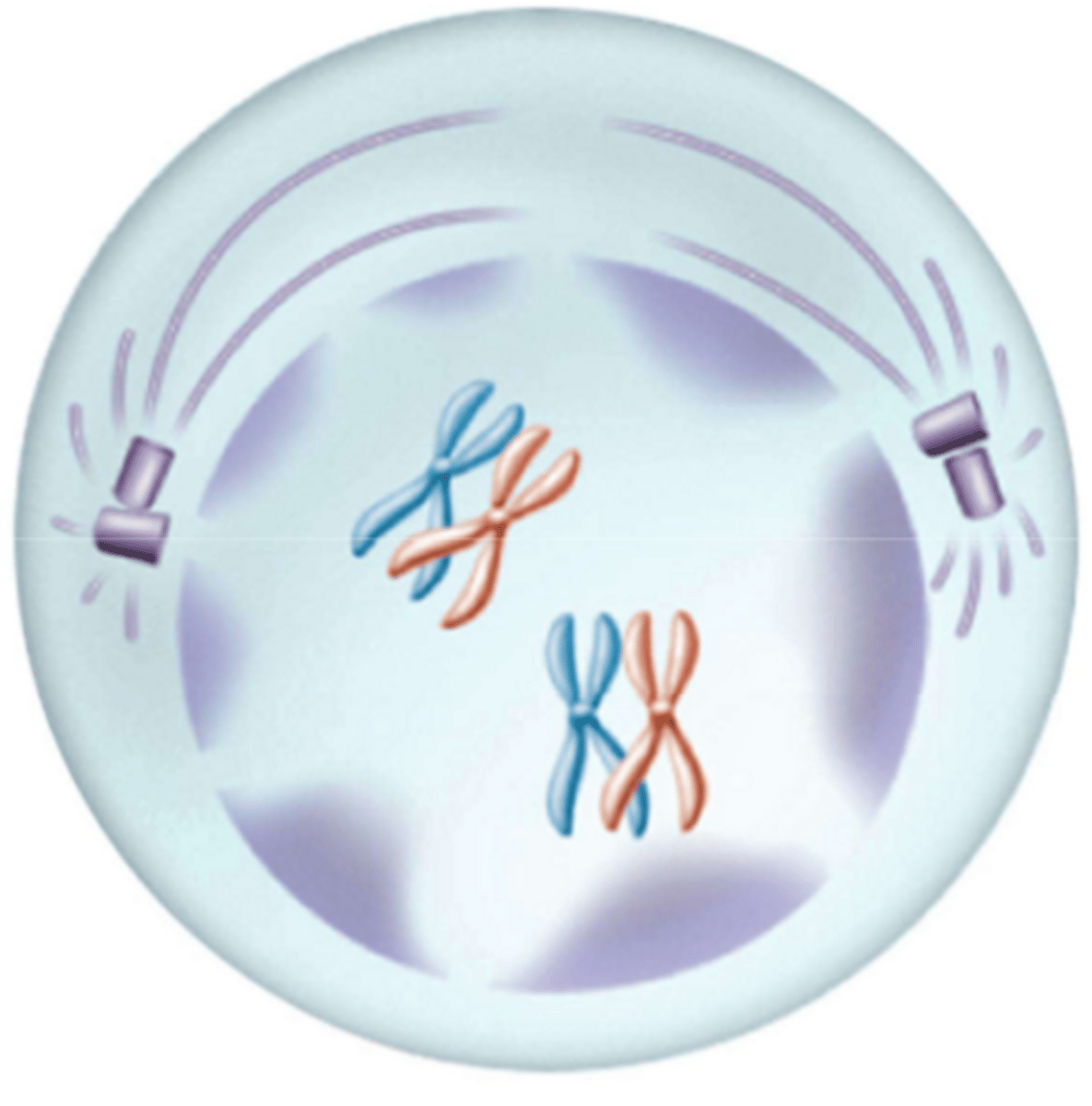
What phase is this?
Metaphase I
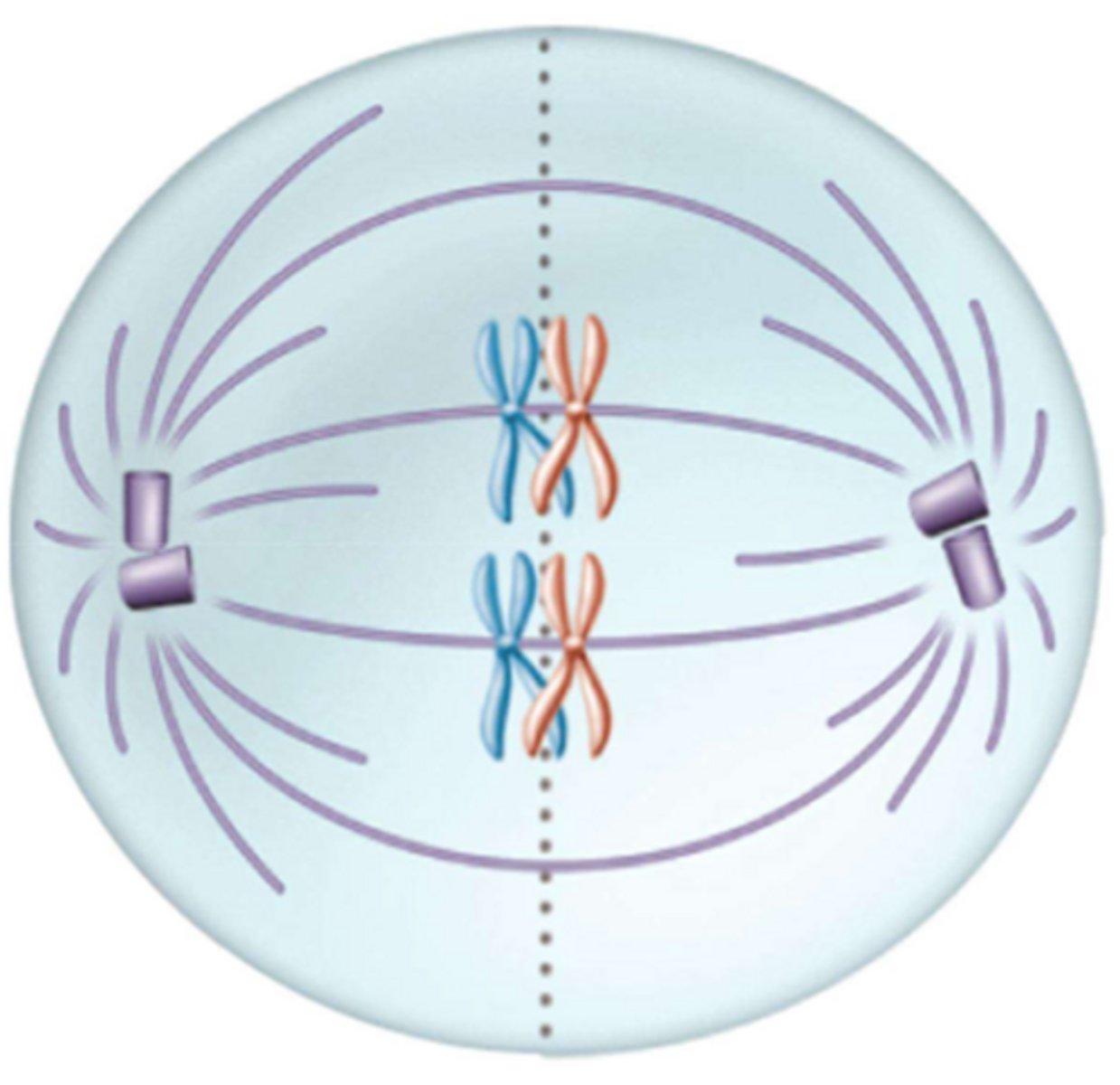
What phase is this?
Anaphase I
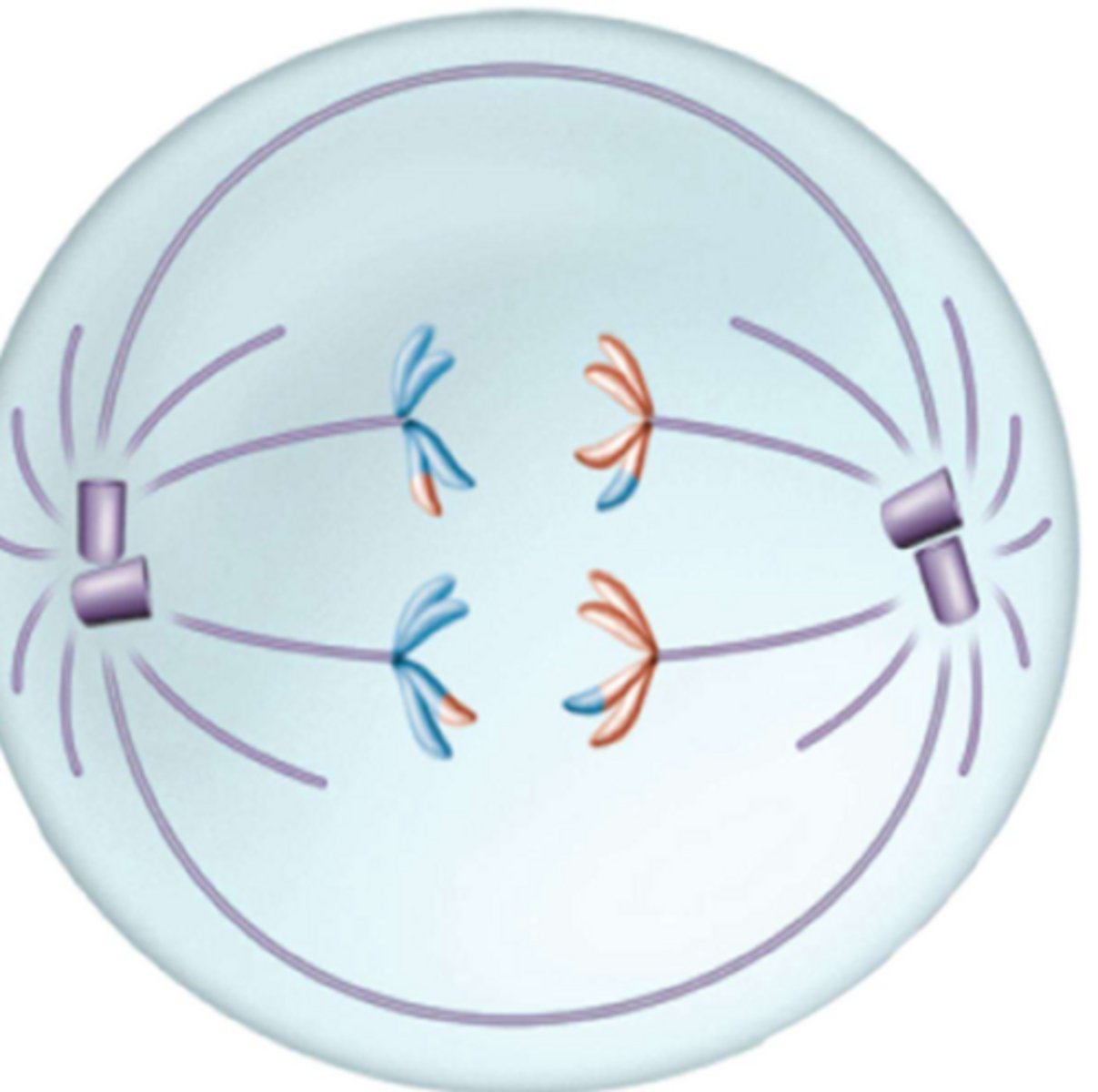
What phase is this?
Telophase I
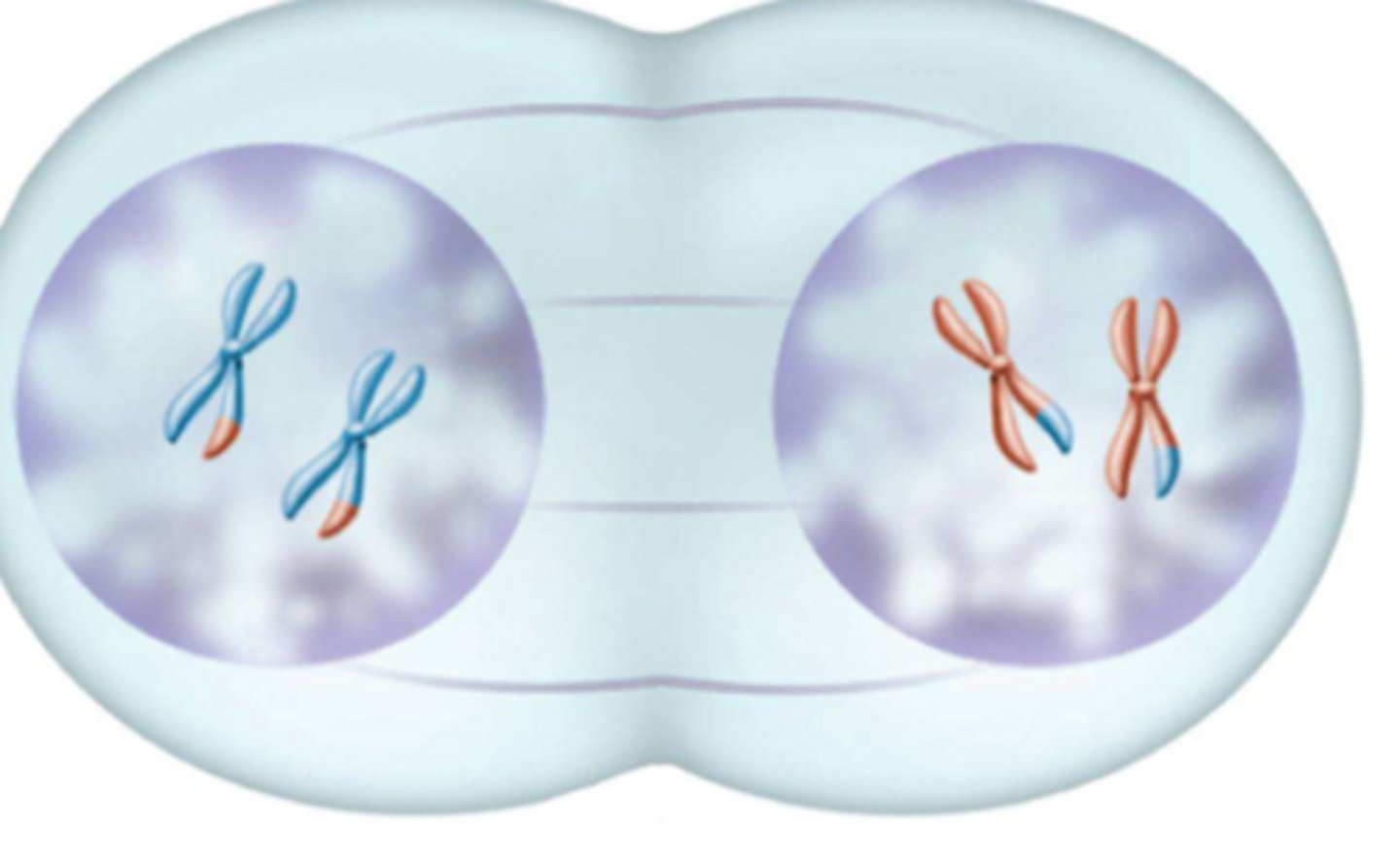
What phase is this?
Prophase II
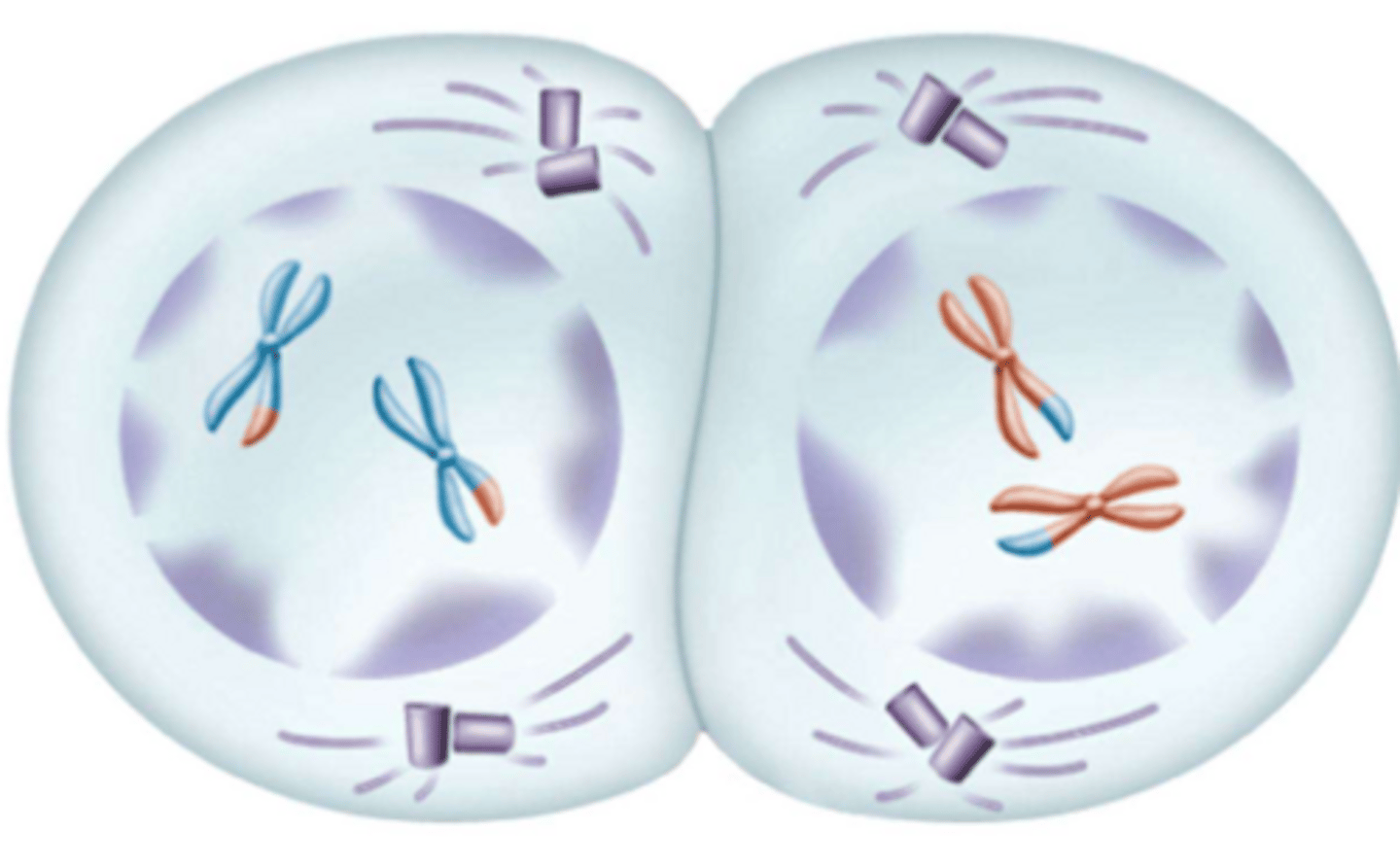
What phase is this?
Metaphase II
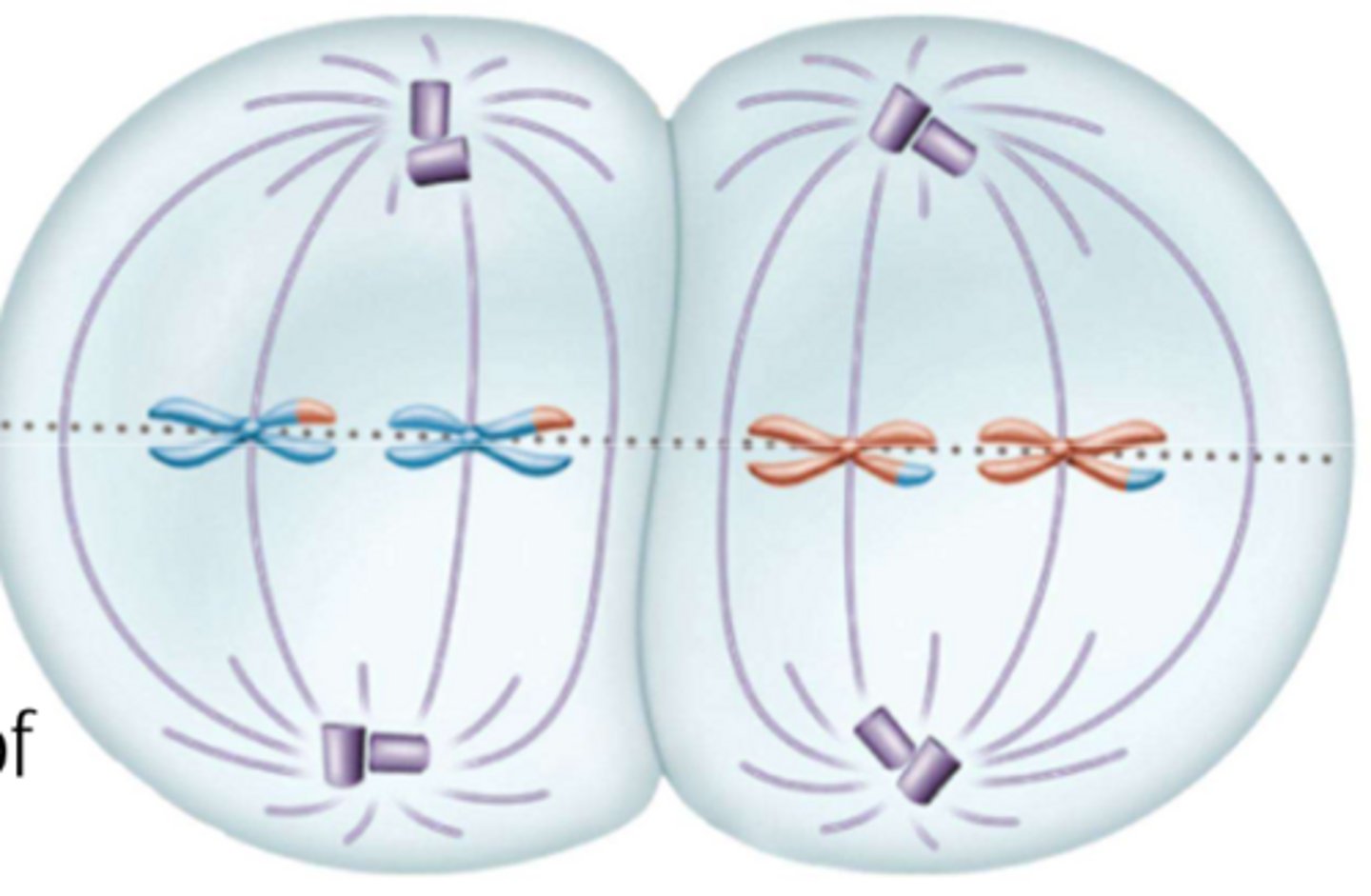
What phase is this?
Anaphase II
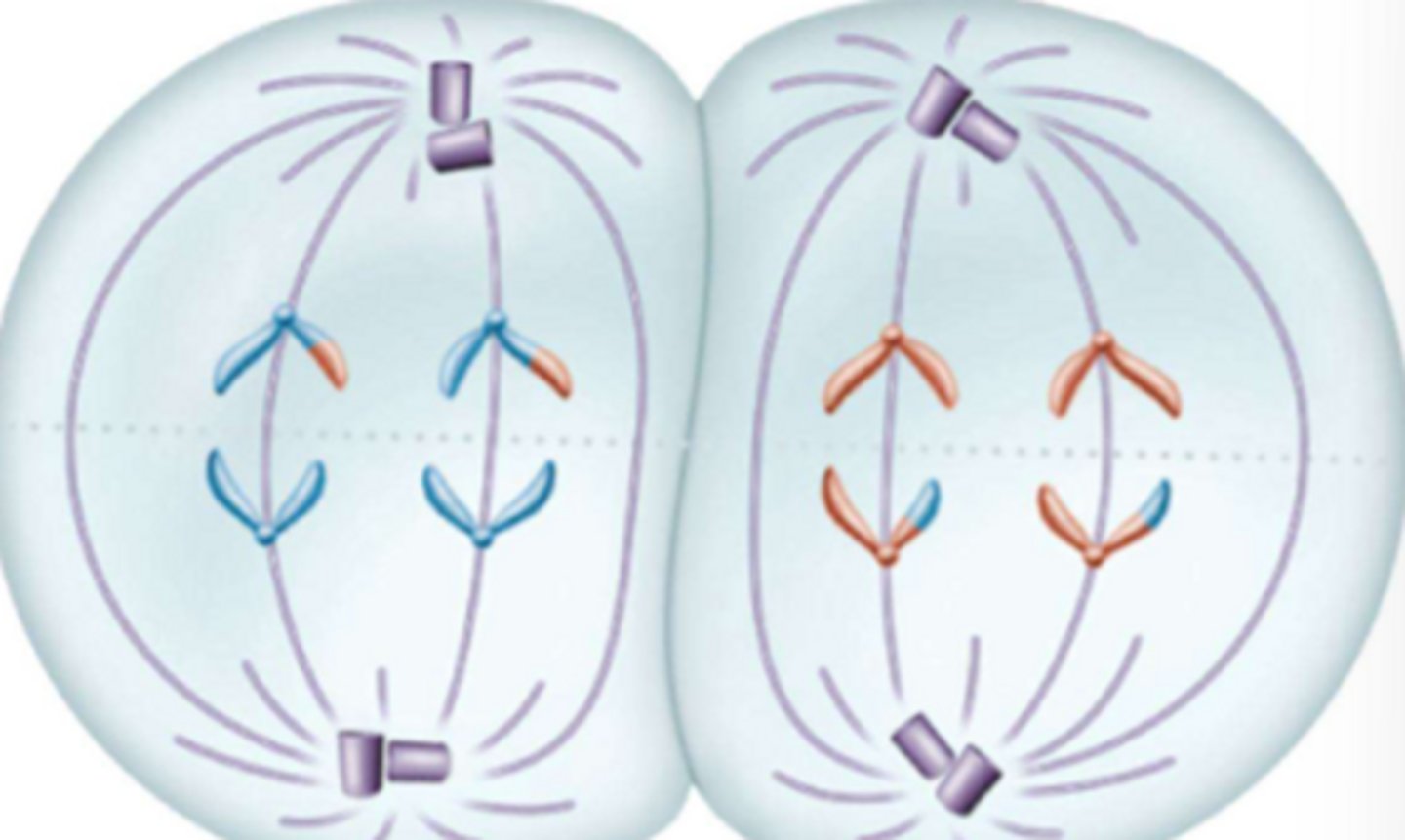
What phase is this?
Telophase II
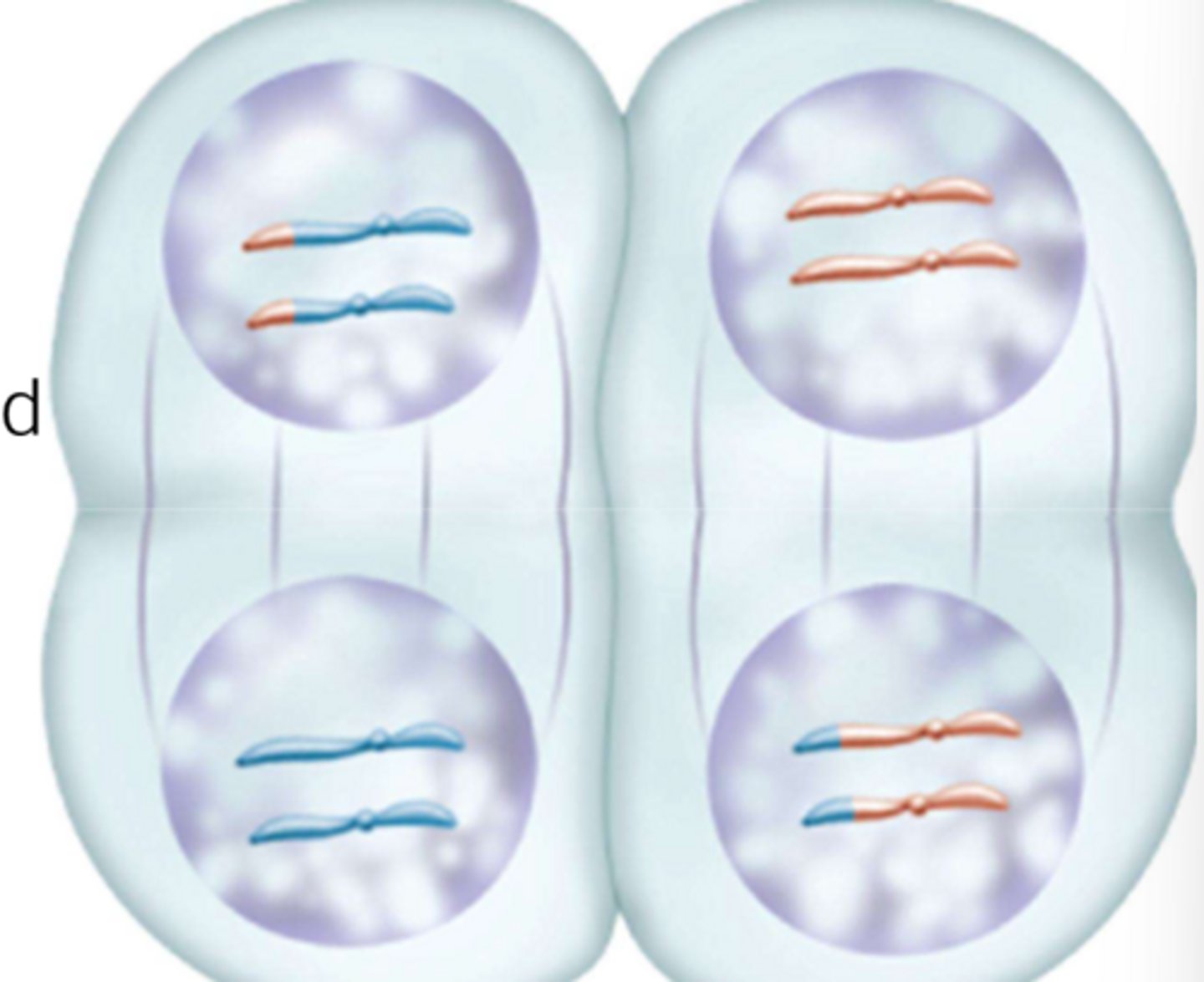
What is the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis?
Mitosis consists of one cell division that produces identical cells. Meiosis consist of two cell divisions that produce haploid daughter cells that are not genetically identical.
What does meiosis results in?
genetic variation.
When is genetic variation produced?
It is produced during crossing over and during fertilization when gametes randomly combine.
What is asexual reproduction?
When an organism inherits all of its chromosomes from a single parent and it is genetically identical to its parents.
What is inheritance or heredity?
The passing down of traits to the next generation.
What was one trait that Mendal noticed?
Seed color.
What are the seven different types of traits Mendal studdied?
seed or pea color, flower color, seed pod color, seed shape or texture, seed pod shape, stem length, flower position
What is an allele
an alternative form of a single gene
What is a genotype?
An organism's allele pairs
What is a phenotype?
The observable characteristics
What is the law of segregation?
A law that states that the two alleles for each trait separates during meiosis.
What happens during fertilization?
two alleles for that trait unite
what is another name for heterozygous organisms?
hybrid
What is a monohybrid cross?
a cross that involves hybrids for a single trait
What is a dihybrid cross?
The simultaneous inheritance of two or more traits in the same plant.
What is the law of independent assortment
A law that states that random distribution of alleles occurs during gamete formation
What do Punnett squares predict?
the possible offspring of a cross between two known genotypes.
what is the phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross?
9:3:3:1
What is genetic recombination?
The new combination of genes produced by crossing over and independent assortment
what is n in a 2n formula
the number of chromosome pairs
What are linked genes?
Genes that are located close to each other on the same chromosome
What is an exception to Mendel's law of independent assortment?
Gene linkage
What is polyploidy?
occurrence of one or more extra sets of all chromosomes in an organism