monomers and polymers
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
what is a monomer?
one subunit, many of which join together chemically to make a polymer
what is a polymer?
large molecule, made of many monomers that are chemically joined together
what are some examples of monomers?
amino acids
glucose (monosaccharide)
nucleotides
fatty acids+glycerol
what are some examples of polymers?
proteins
starch (polysaccharide)
RNA/DNA (nucleic acid)
fats
what reaction joins monomers together?
condensation reactions
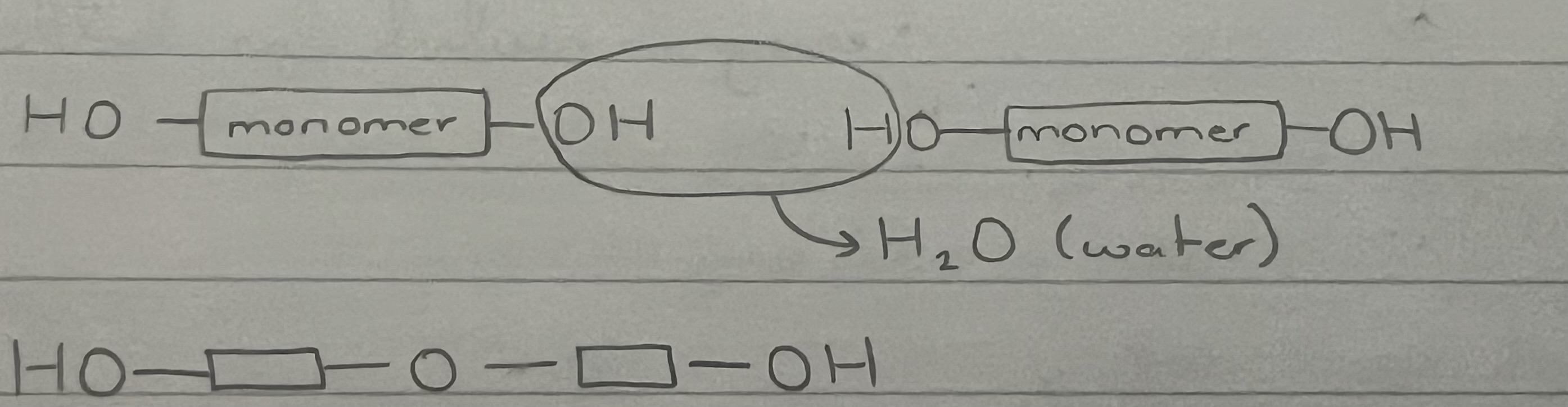
how do monomers join together through a condensation reaction?
monomers have a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to carbon in monomer (covalent bond)
what is a hydroxyl group?
an -OH covalently bonded to carbon (the oxygen forms the bond twice, once with H and once with the carbon)
what does a condensation reaction look like?
why are they called condensation reaction?
water is produced- do not happen spontaneously—> need enzymes to catalyse the reaction
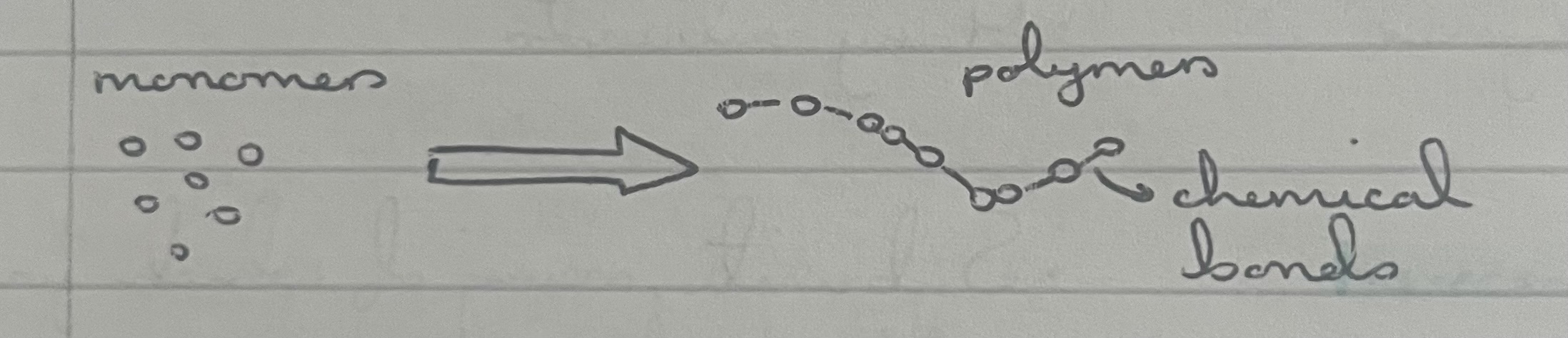
what is polymerisation?
lots of condensation reactions occurring to join lots of monomers together, producing a polymer
what is a hydrolysis reaction?
breaking the bond that links monomers, requires water (and enzymes)
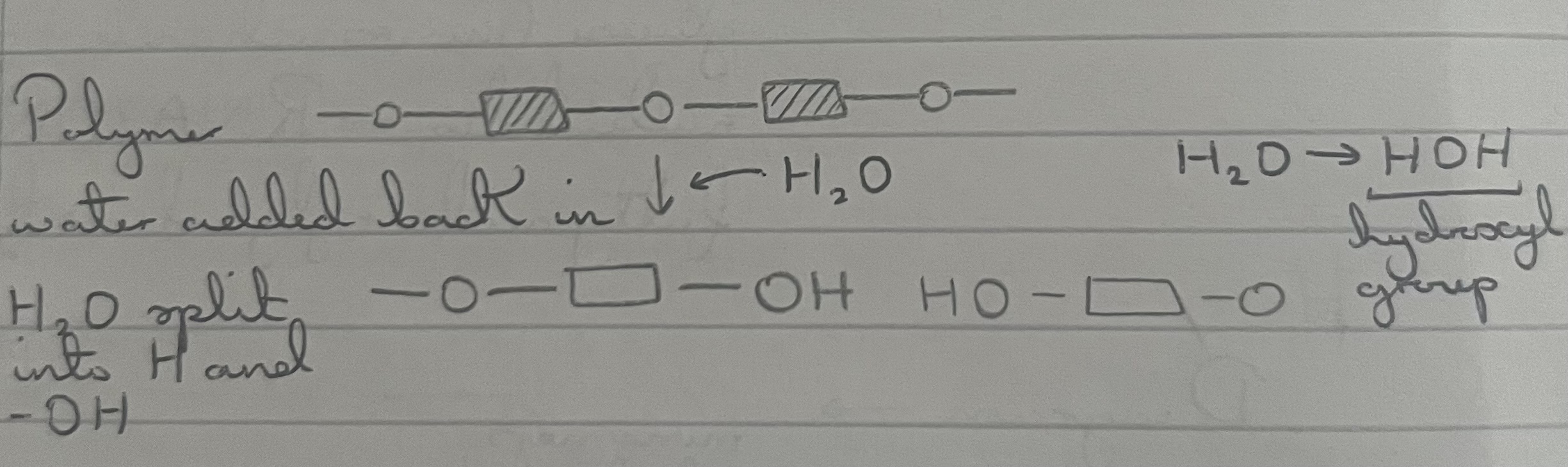
what are macromolecules?
large molecules of biological importance
what are triglycerides?
fats
not polymers
not made of many identical subunits (made of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids)