[PT11] Terminologies
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:19 PM on 10/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
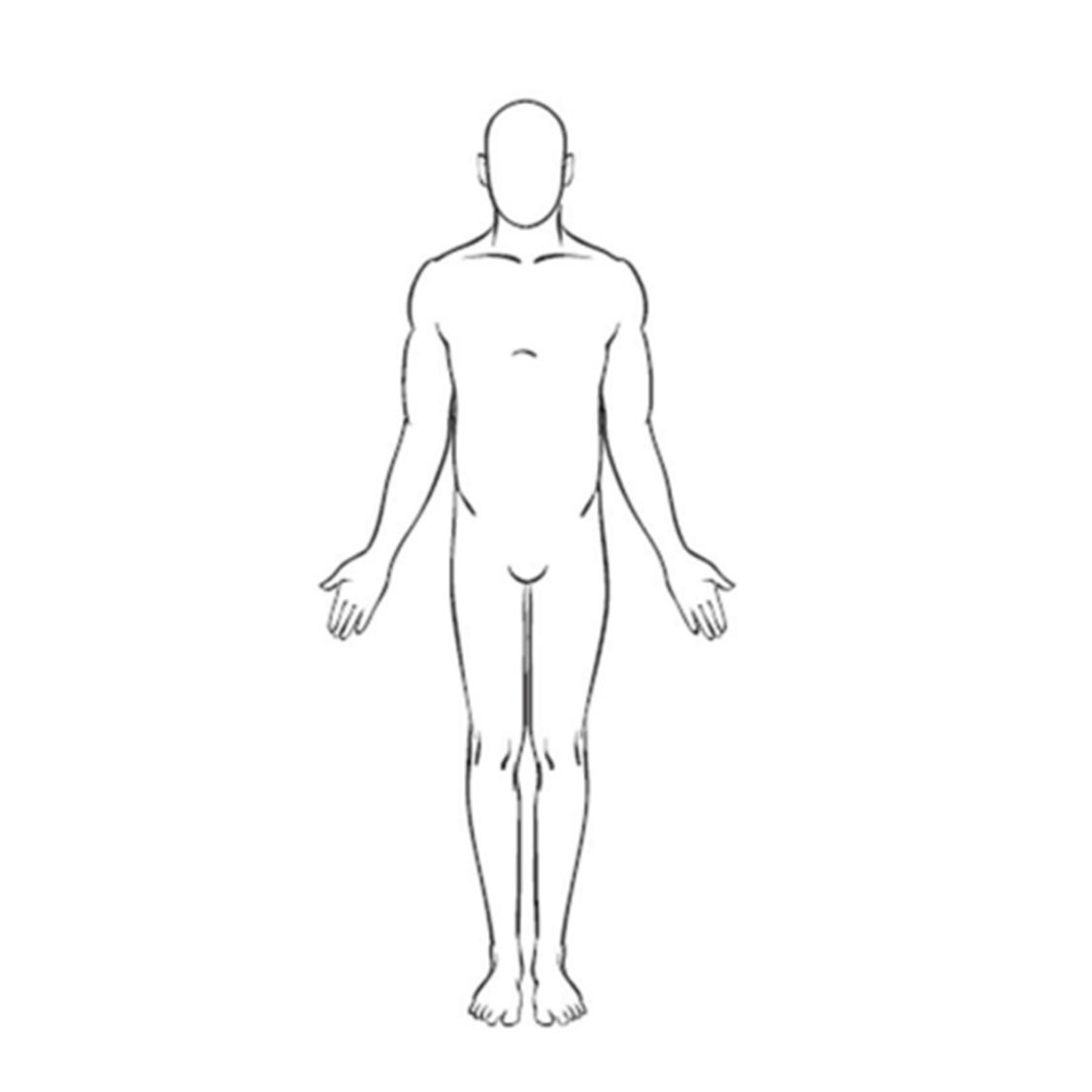
anatomical position
2
New cards
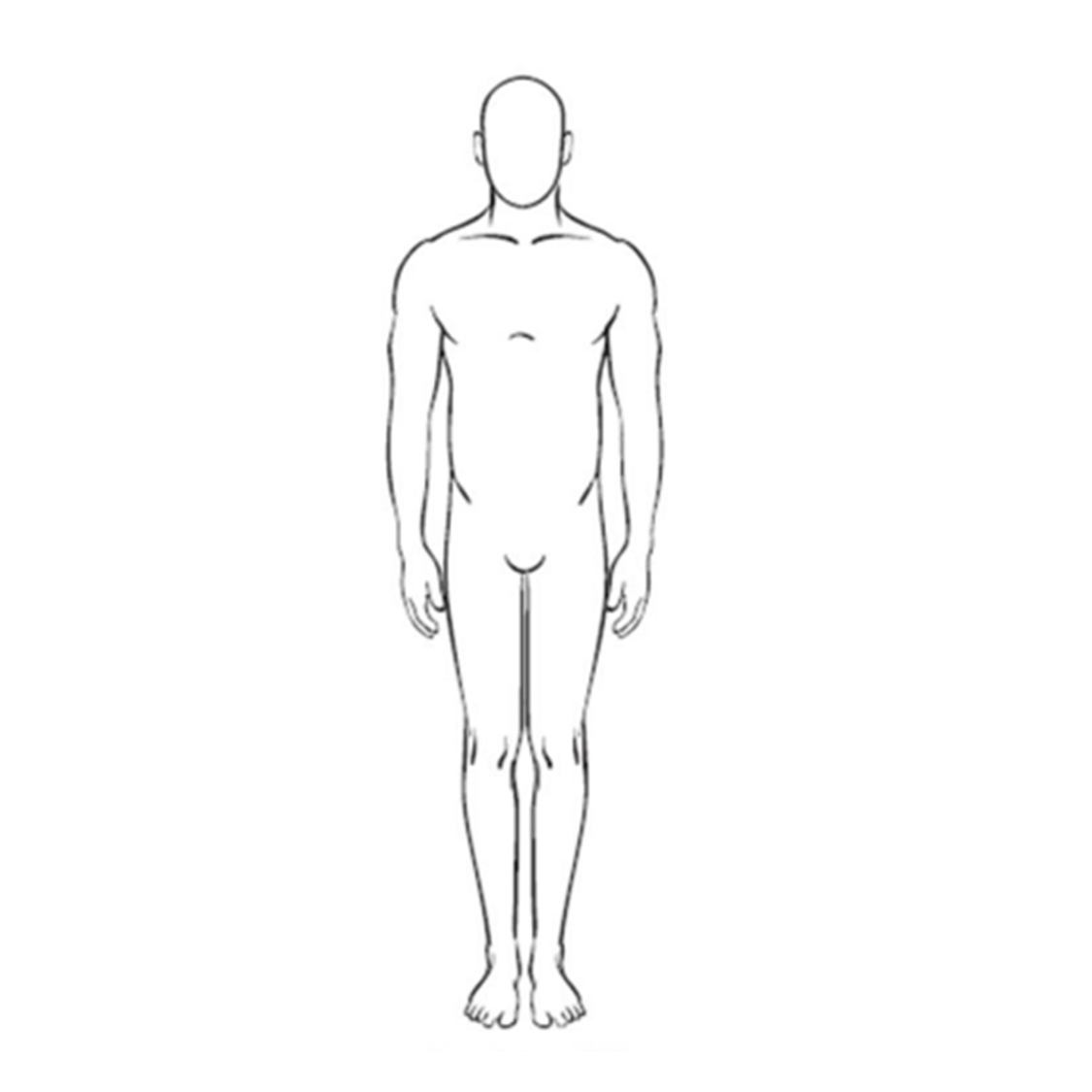
fundamental position
3
New cards
anterior
front surface of the body or structure
4
New cards
posterior
back surface of the body or structure
5
New cards
superficial
near the surface
6
New cards
deep
further from the surface
7
New cards
internal
nearer the inside
8
New cards
external
nearer the outside
9
New cards
lateral
away from the mid-line
10
New cards
medial
towards the mid-line
11
New cards
superior
situated above or towards the upper part
12
New cards
inferior
situated below or towards the lower part
13
New cards
proximal
nearest to the point of reference
14
New cards
distal
furthest away from the point of reference
15
New cards
prone
lying face down in a horizontal position
16
New cards
supine
lying face up in a horizontal position
17
New cards
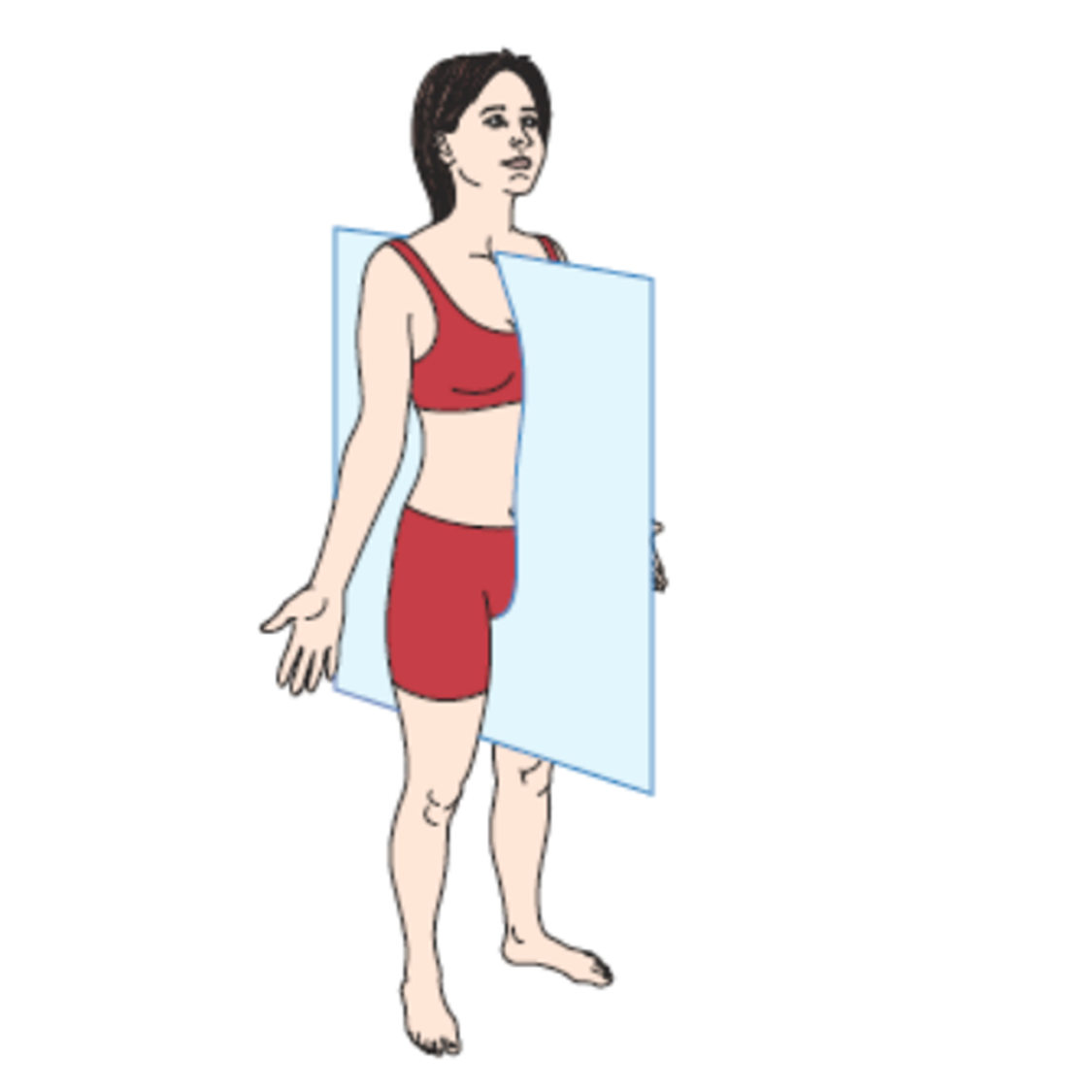
sagittal plane
18
New cards
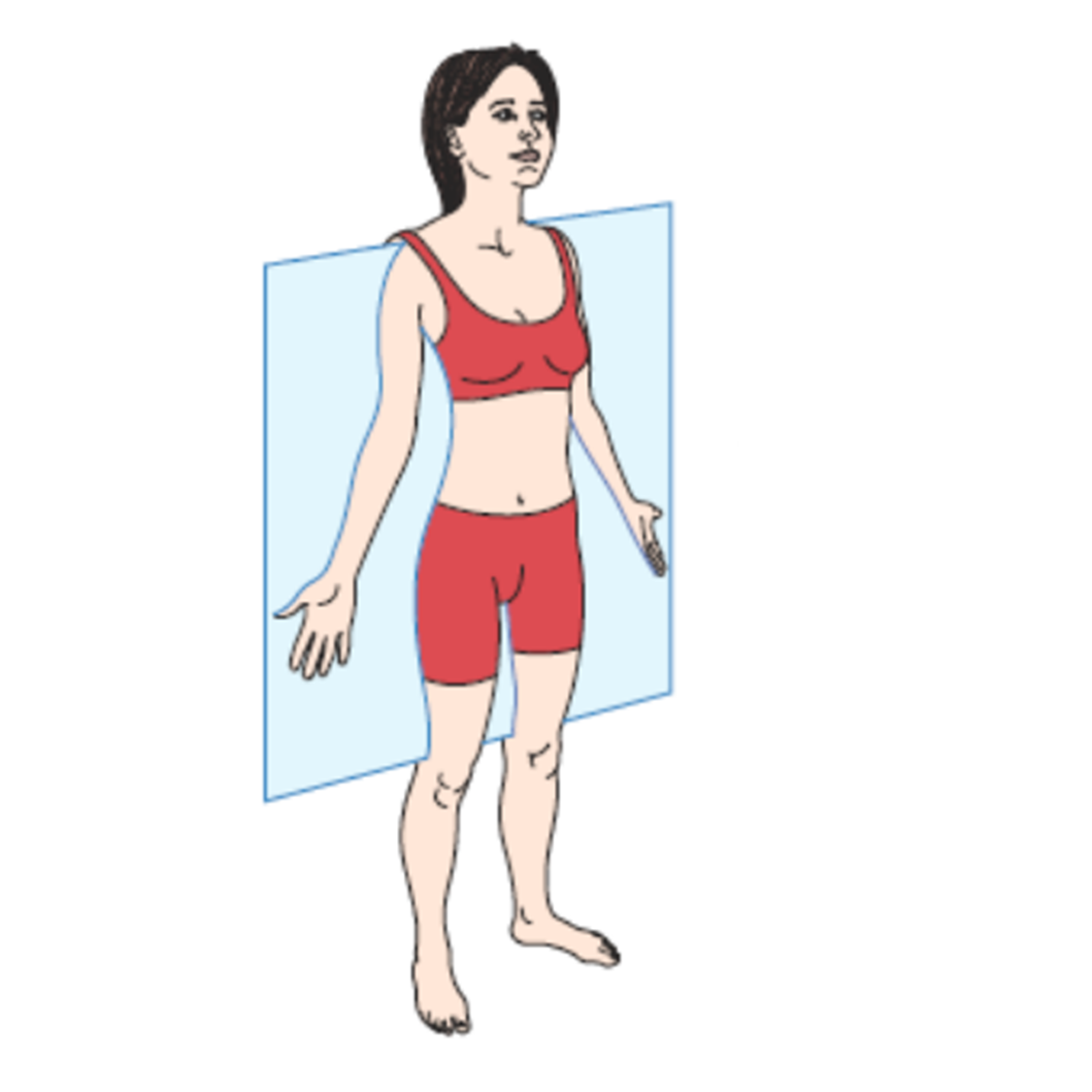
frontal/coronal plane
19
New cards
transverse plane
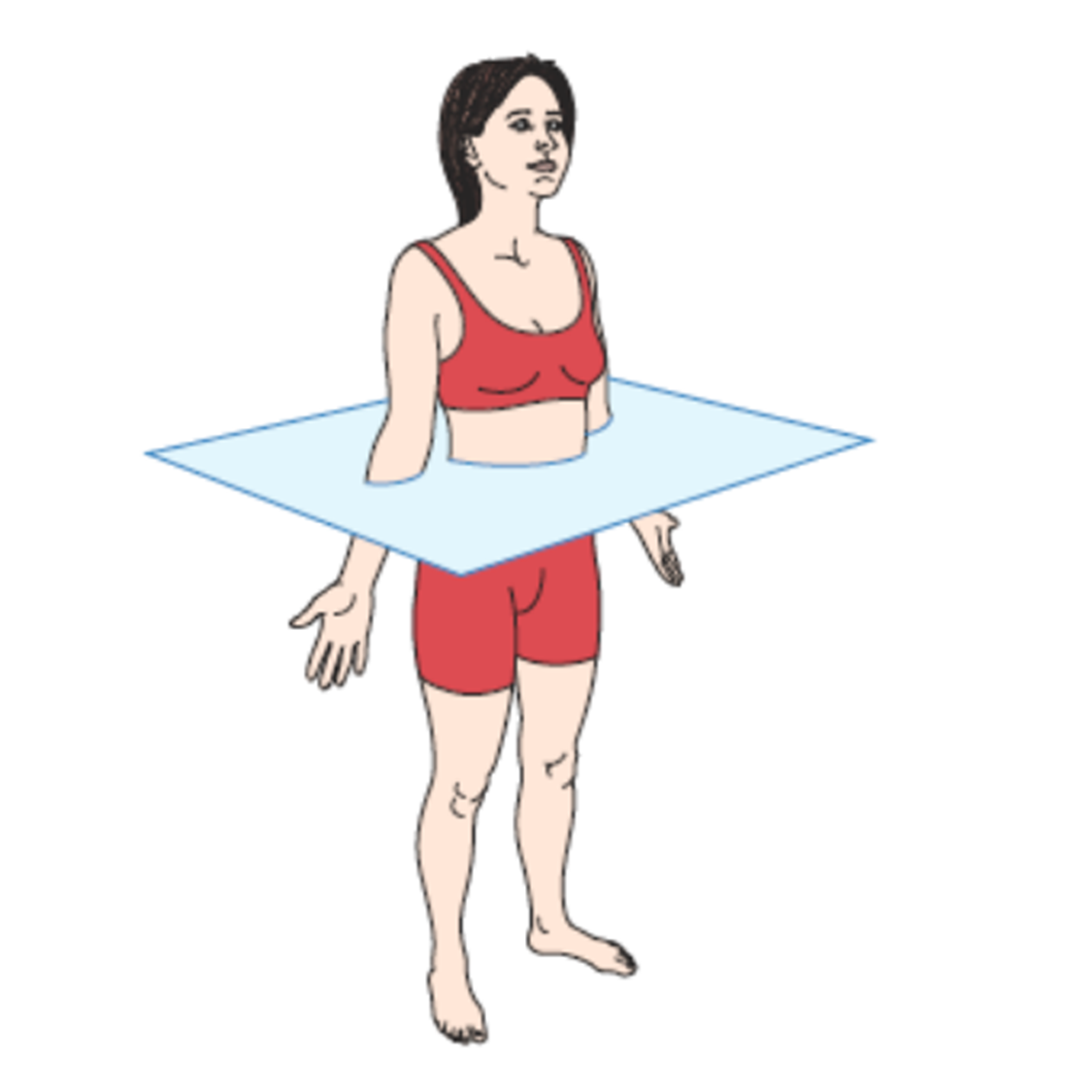
20
New cards
- head and neck
- trunk
- upper limbs
- lower limbs
- trunk
- upper limbs
- lower limbs
the anatomical regions of the body
21
New cards
cephalic
anatomical term for head
22
New cards
cervical
anatomical term for neck
23
New cards
cranial
anatomical term for skull
24
New cards
frontal
anatomical term for forehead
25
New cards
occipital
anatomical term for back of the head
26
New cards
ophthalmic
anatomical term for eyes
27
New cards
oral
anatomical term for mouth
28
New cards
nasal
anatomical term for nose
29
New cards
axillary
anatomical term for armpit
30
New cards
costal
anatomical term for ribs
31
New cards
mammary
anatomical term for breast
32
New cards
pectoral
anatomical term for chest
33
New cards
vertebral
anatomical term for backbone
34
New cards
abdominal
anatomical term for abdomen
35
New cards
gluteal
anatomical term for buttocks
36
New cards
inguinal
anatomical term for groin
37
New cards
lumbar
anatomical term for lower back
38
New cards
pelvic
anatomical term for pelvis/lower part of abdomen
39
New cards
umbilical
anatomical term for navel
40
New cards
perineal
anatomical term for area between anus external genitalia
41
New cards
pubic
anatomical term for pubis
42
New cards
brachial
anatomical term for upper arm
43
New cards
carpal
anatomical term for wrist
44
New cards
cubital
anatomical term for elbow
45
New cards
forearm
anatomical term for lower arm
46
New cards
palmar
anatomical term for palm
47
New cards
digital
anatomical term for fingers/toes
48
New cards
femoral
anatomical term for thigh
49
New cards
patellar
anatomical term for front of knee
50
New cards
pedal
anatomical term for foot
51
New cards
plantar
anatomical term for sole of foot
52
New cards
popliteal
anatomical term for hollow behind knee
53
New cards
osteokinematics
deals with the relationship of the movement of bones around a joint axis (e.g., humerus moving on scapula)
54
New cards
arthrokinematics
deals with the relationship of joint surface movement (e.g. humeral head’s movement within glenoid fossa of scapula)
55
New cards
flexion
is the bending movement of one bone on another, causing a decrease in the joint angle
56
New cards
hyperextension
the continuation of extension beyond the anatomical position
57
New cards
palmar flexion
flexion at the wrist
58
New cards
plantar flexion
flexion at the ankle
59
New cards
dorsiflexion
extension of wrist or ankle joints
60
New cards
abduction
movement away from the midline of the body
61
New cards
adduction
movement toward the midline
62
New cards
horizontal abduction
the shoulder joint is flexed to 90 degrees and then abducted
63
New cards
horizontal adduction
the shoulder is adducted from this 90-degree position
64
New cards
radial deviation
the hand moves laterally, or toward the thumb side
65
New cards
ulnar deviation
the hand moves medially from the anatomical position toward the little finger side at the wrist
66
New cards
inversion
moving the sole of the foot inward at the ankle
67
New cards
eversion
moving the sole of the foot outward at the ankle
68
New cards
supination
rotation of the forearm so that it faces the palm of the hand forward, or anteriorly
69
New cards
pronation
rotation of the forearm wherein the palm is facing backward, or posteriorly
70
New cards
rotation
movement of a bone or part around its longitudinal axis
71
New cards
medial rotation/internal rotation
type of rotation wherein the anterior surface moves inward toward the midline
72
New cards
lateral rotation/external rotation
type of rotation wherein the anterior surface moves outward away from the midline
73
New cards
circumduction
motion that describes a circular cone-shaped pattern
74
New cards
(1) flexion
(2) aBduction
(3) extension
(4) aDduction
(2) aBduction
(3) extension
(4) aDduction
the four joint motions of circumduction
75
New cards
lateral bending/lateral flexion
when the trunk moves sideways/sideward motion