Human Phys Exam II
4.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:12 PM on 3/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
1
New cards
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord; receives input from sensory neurons and directs the activity of motor neurons
2
New cards
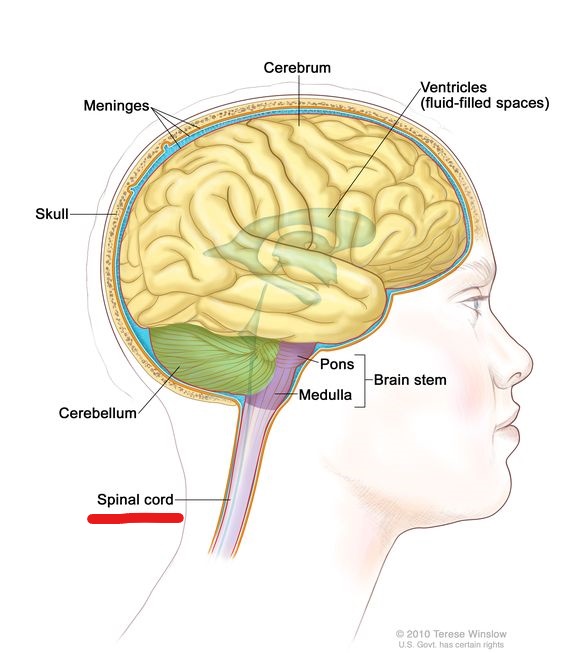
spinal cord
3
New cards
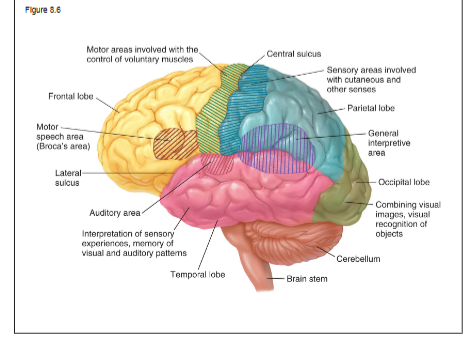
brain stem
\
4
New cards
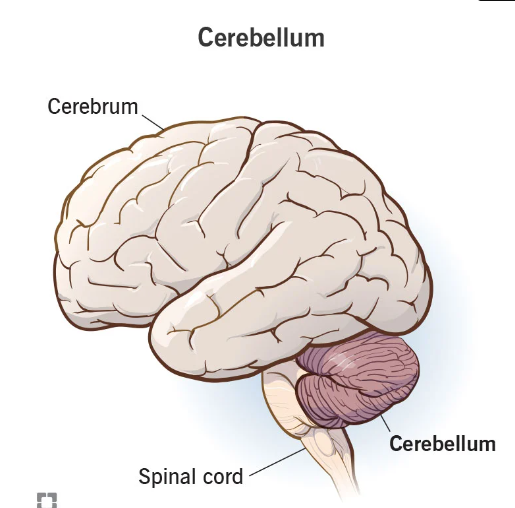
cerebellum
5
New cards
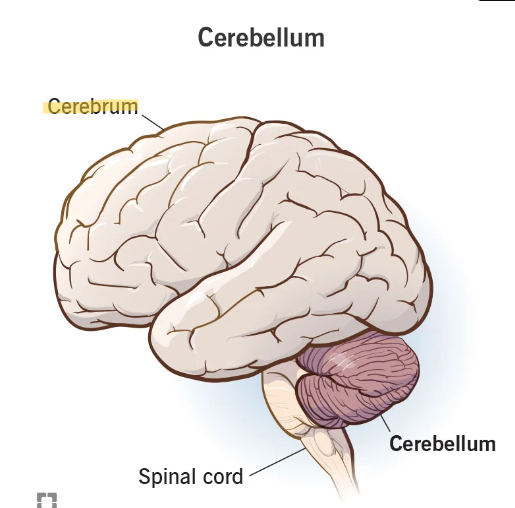
cerebrum
6
New cards
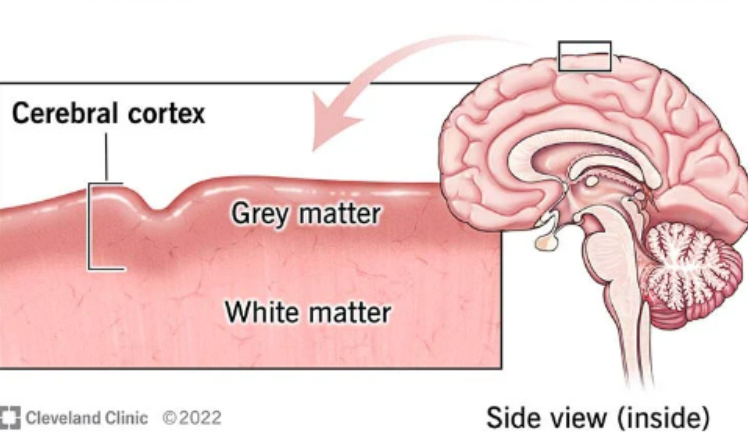
cerebral cortex
cerebral cortex, composed of gray matter and underlying white matter. The cerebral cortex is characterized by numerous folds and grooves "
\
“bark” of the brain -- where cerebral neurons are located
\
“bark” of the brain -- where cerebral neurons are located
7
New cards
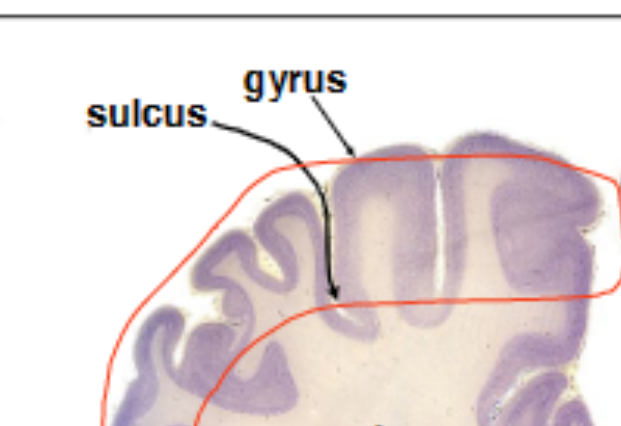
gyrus
An elevated fold
8
New cards
sulcus
the depressed groove between two gyri
9
New cards
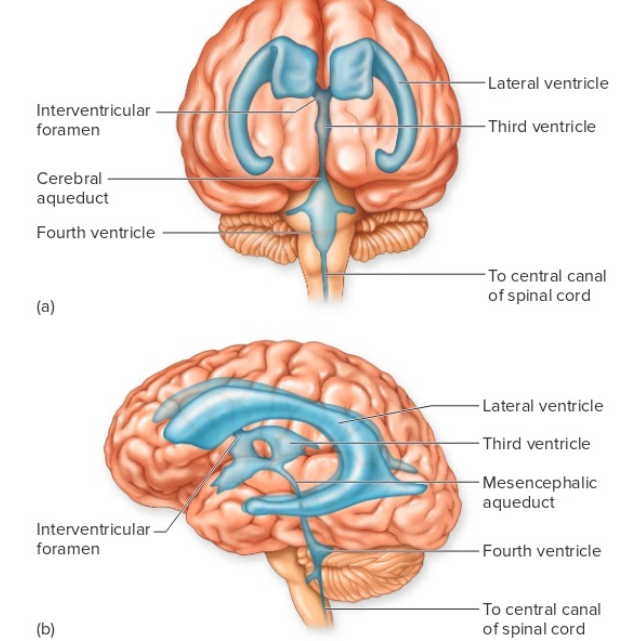
Ventricles
cavities of the brain filled with cerebral spinal fluid
10
New cards
Central canal
cavity of the spinal cord filled with CSF
11
New cards
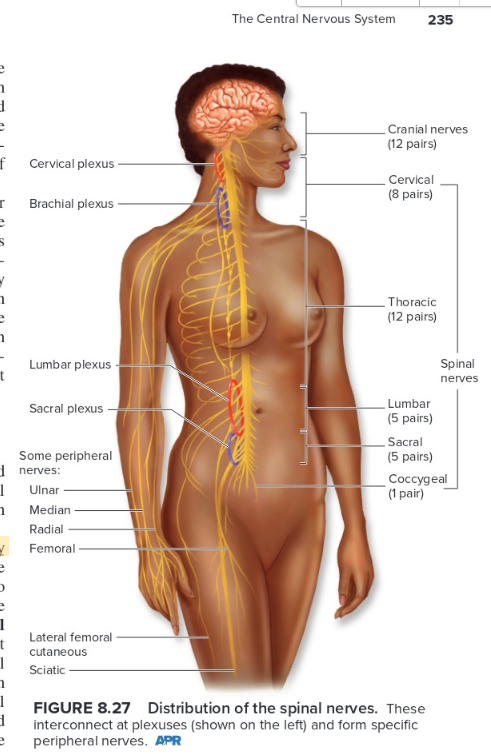
spinal nerves
Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve composed of sensory and motor fibers
12
New cards
cranial nerves
Cranial nerves are classified as either sensory, motor, or mixed
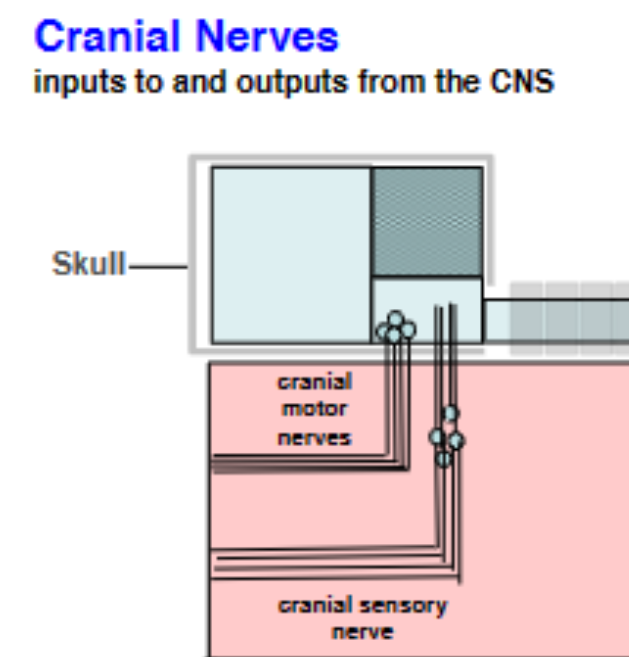
13
New cards
Know the 4 lobes of the brain
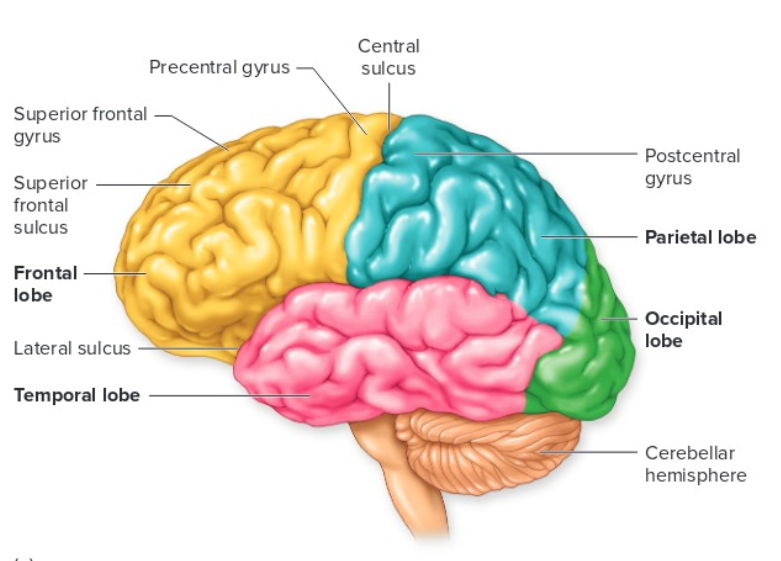
14
New cards
central sulcus
separates parietal and frontal lobes
15
New cards
lateral sulcus
separates frontal lobe from temporal lobe
16
New cards
motor and somatosensory cortex
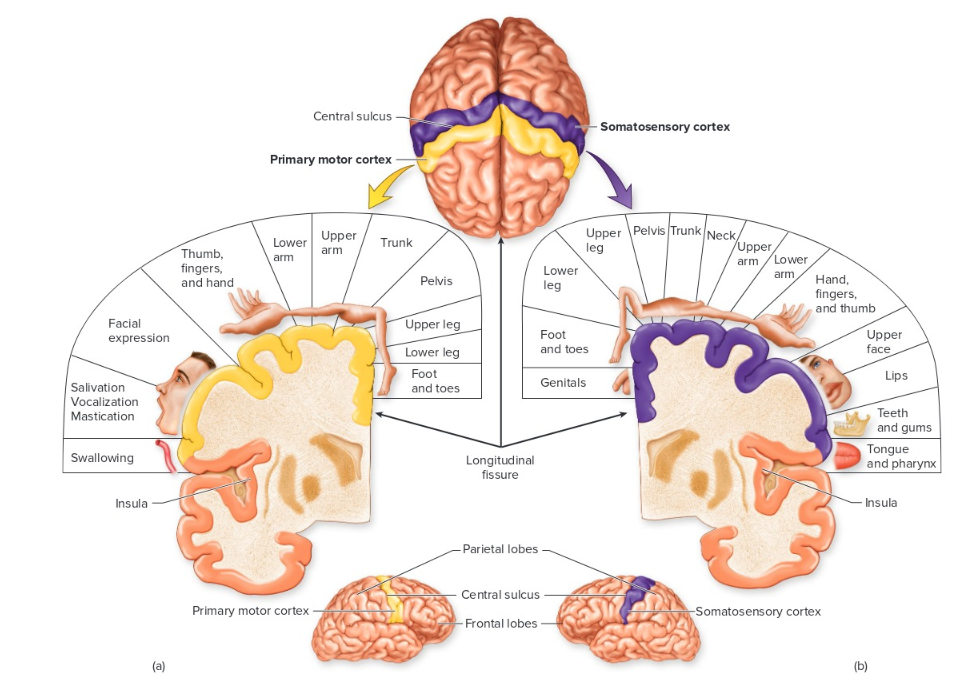
17
New cards
visual receptive field
the part of the visual field that affects the activity of a particular ganglion cell can be considered its receptive field
18
New cards
photoreceptors
in the retina (rods and cones) and synapses with other neurons in the retina
respond to light
respond to light
19
New cards
photoreceptor mechanism
Chemical interaction affects ionic permeability of sensory cells
20
New cards
chemoreceptors
sense chemical stimuli in environment or blood. Examples are taste buds, olfactory epithelium and aortic and carotid bodies
21
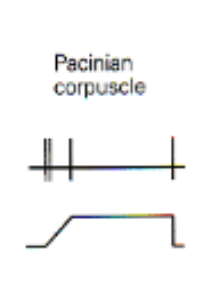
New cards
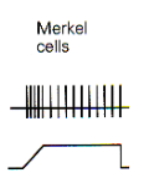
chemoreceptors mechanism
Chemical interaction affects ionic permeability of sensory cells
22
New cards
thermoreceptors
respond to heat and cold
23
New cards
receptive field of a neuron serving cutaneous sensation
the area of skin that, when stimulated, changes the firing rate of the neuron
24
New cards
mechanoreceptors
stimulated by mechanical deformation of the receptor plasma membrane
examples are touch and pressure receptors in the skin and hair cells within the inner ear
examples are touch and pressure receptors in the skin and hair cells within the inner ear
25
New cards
mechanoreceptor mechanism
Deforms plasma membranes of sensory dendrites or deforms hair cells that activate sensory nerve endings
26
New cards
nociceptors
pain receptors that depolarize in response to stimuli that accompany tissue damage
27
New cards
nociceptors mechanism
Damaged tissues release chemicals that excite sensory endings
28
New cards
proprioceptors
includes the muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, and joint receptors. These provide a sense of body position and allow fine control of skeletal movements
29
New cards
Somatotopy
Cortical neurons are arranged in same topology as peripheral receptive fields on the skin, to make up homunculus. Areas with denser receptive fields have bigger cortical representation (more neurons dedicated to processing)
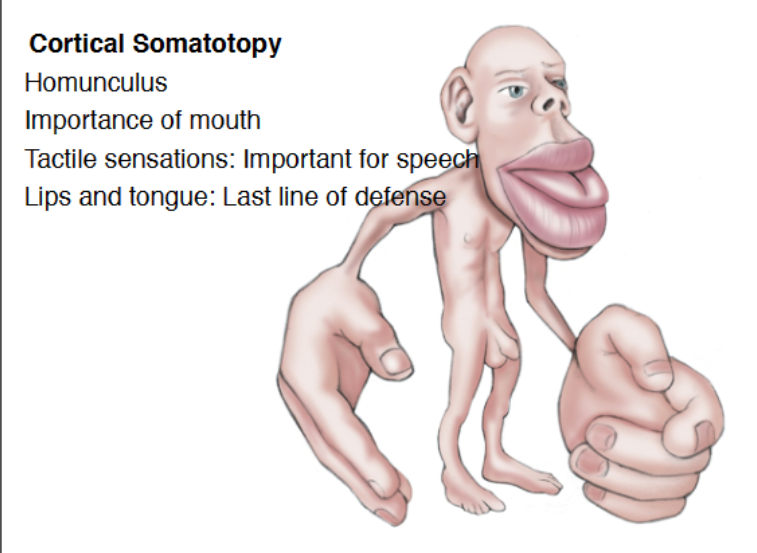
30
New cards
tonotopy
Transduction of sound frequency into spatial location
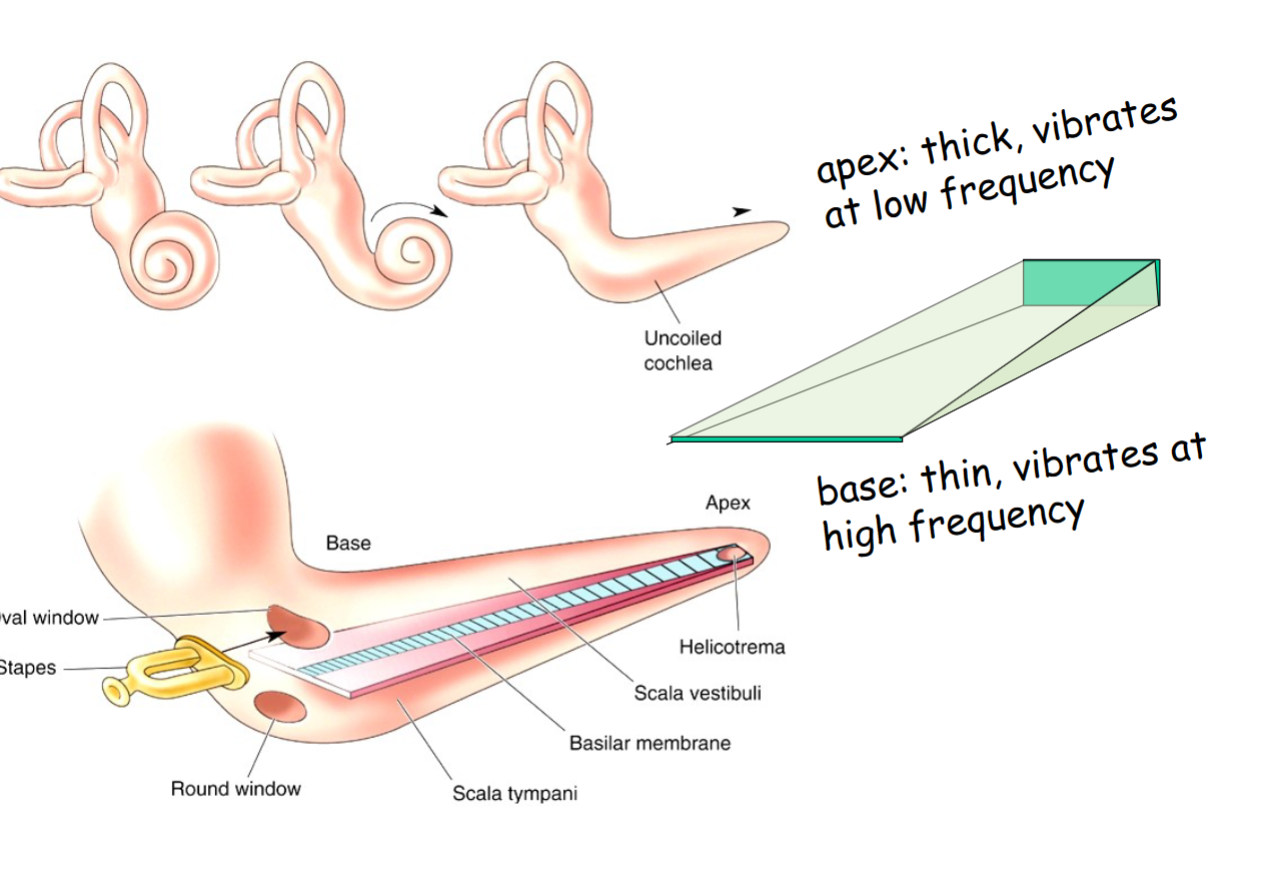
In cochlea, the apex is thick and responds to low freq
base is thin and responds to high freq
In cochlea, the apex is thick and responds to low freq
base is thin and responds to high freq
31
New cards
rapidly adapting (phasic)
responds best to onset and offset of stimulus
32
New cards
slowly adapting (tonic response)
continue to respond to continuous stimulus
33
New cards
feature extraction
this concept includes knowing when is vertical, horizontal, and oblique in your hand. Or when your body knows where and how to reach something using your proprietors and visual input. Or when hear something and visual input helps you understand what they are saying. Another example is smelling popcorn and remembering a random movie
34
New cards
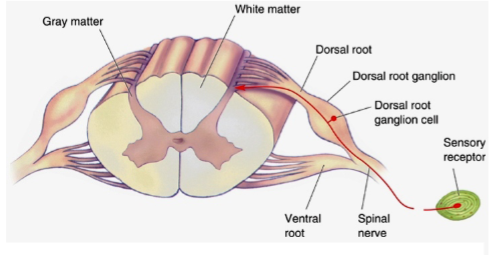
dorsal root
composed of sensory fibers
35
New cards
ventral root
composed of motor fibers
36
New cards
dorsal root ganglion
contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons.
37
New cards
ventral horn of spinal cord
the cell bodies of lower motor neurons are located here
38
New cards
anatomy of spinal cord
39
New cards
Two-point Touch
determines density of receptive fields. Two points are put on skin and when the subject can distinguish its two points, the mm apart tells the receptive field. ie 2mm on thumb = small and abundant receptive fields. Compared to the 42 mm of the back which shows less frequent receptive field
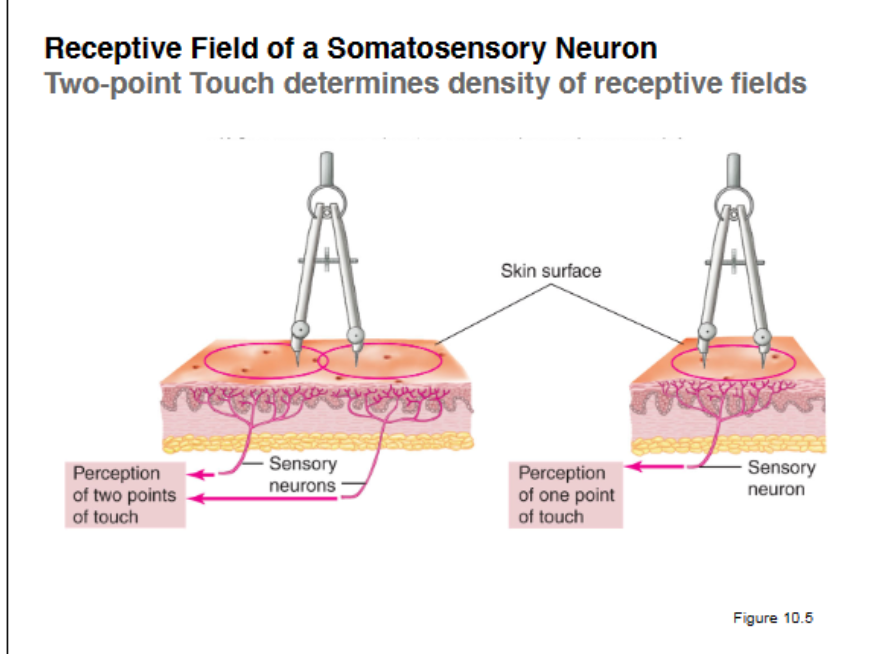
40
New cards
dermatome
each spinal sensory nerves have a receptive field .
One DRG approx. for each vertebra:
receptive fields of one DRG = dermatome
One DRG approx. for each vertebra:
receptive fields of one DRG = dermatome
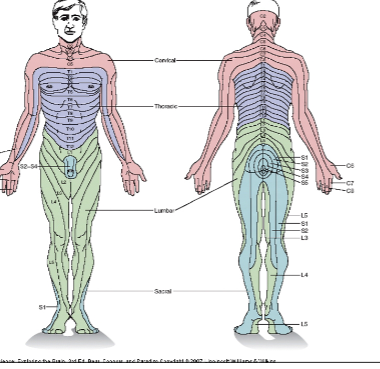
41
New cards
shingles/chicken pox
Infection by neural virus (herpes zoster) that lives in DRG cells
42
New cards
Hair Cells of inner ear
Mechanoreceptors that detect vibration (audition)
Bending of stereocilia (due to vibration) opens K+ channels. Because endolymph is high in K+, K+ rushes into hair cell to cause depolarization=action potentials
Bending of stereocilia (due to vibration) opens K+ channels. Because endolymph is high in K+, K+ rushes into hair cell to cause depolarization=action potentials
43
New cards
Utricle
detects linear acceleration, using otoliths as inertial mass to detect gravity and starting/stopping during linear motion
44
New cards
semicircular canals
detect rotational acceleration in each of 3 planes. Sloshing of endolymph around the canal; deforms cupula which bends hair cells.
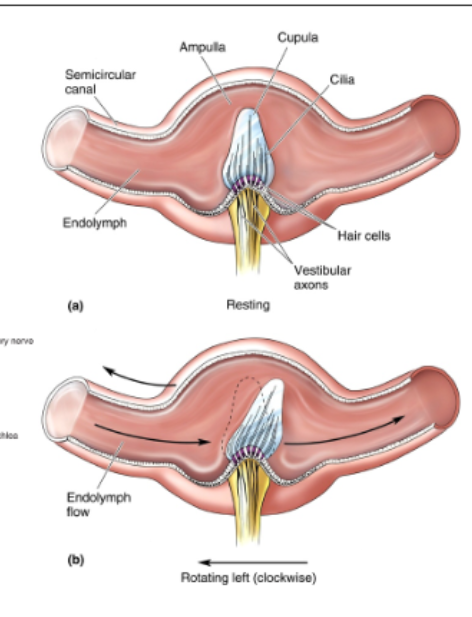
45
New cards
the cochlea and vestibular apparatus of the inner ear
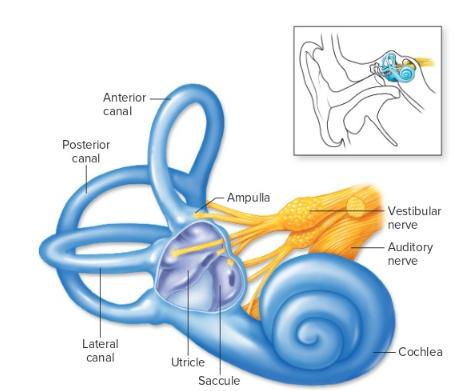
46
New cards
basic anatomy of the outer, middle, and inner ear
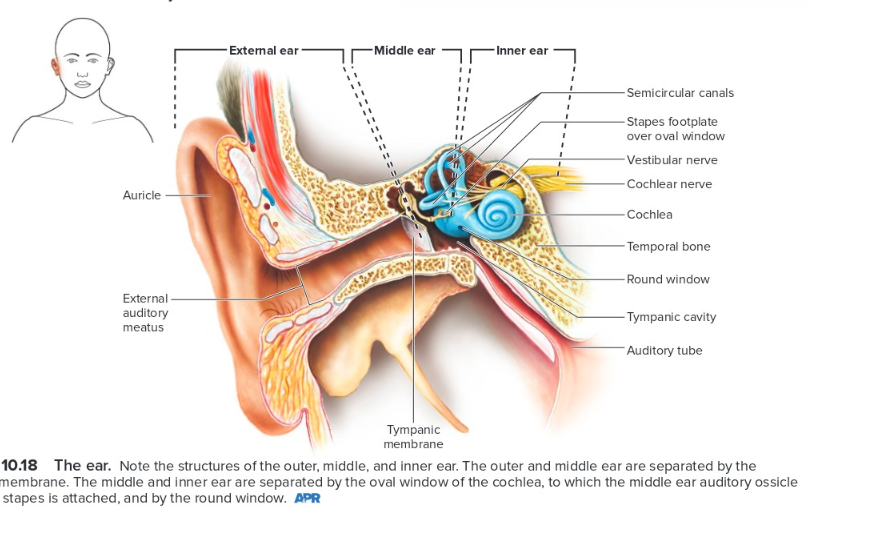
47
New cards
Understand the frequency response of the basilar membrane
Vibrations of oval window -> vibrations in endolymph -> vibration of basilar membrane
48
New cards
frequency response of the basilar membrane
Response of basilar membrane varies across its length.
Low frequency sound vibrates apex of cochlea.
High frequency sound vibrates base of cochlea
Low frequency sound vibrates apex of cochlea.
High frequency sound vibrates base of cochlea
49
New cards
Receptive Field of Auditory Neuron
tuned to characteristic frequency. Neuron’s response (rate of action potentials) reflects intensity of sound at characteristic frequency
50
New cards
Cochlear Implants
reproduce function of basilar membrane
and hair cells: stimulate auditory nerve endings at
appropriate point in cochlea to ==reproduce tonotopic
mapping of missing hair cells==
and hair cells: stimulate auditory nerve endings at
appropriate point in cochlea to ==reproduce tonotopic
mapping of missing hair cells==
51
New cards
Rods vs Cones
Because bipolar cells receive input from the convergence of many rods (a), and because a number of such bipolar cells converge on a single retinal ganglion cell, rods maximize sensitivity to low levels of light at the expense of visual acuity. By contrast, the 1:1:1 ratio of cones to bipolar cells to ganglion cells in the fovea (b) provides high visual acuity, but sensitivity to light is reduced"
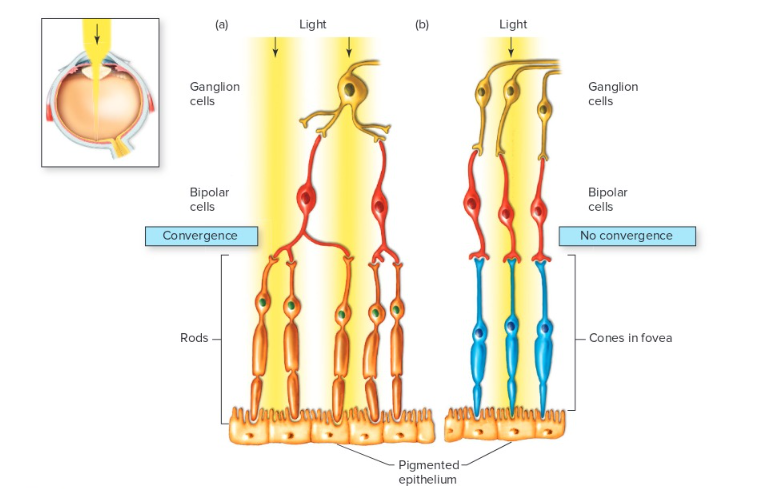
52
New cards
Bipolar cells
synapse onto ganglion cells
53
New cards
Ganglion cells
project to brain via optic nerve (cranial nerve 2)
54
New cards
Optic Disk
**the blind spot**, Optic Nerve leaves eye and central artery & vein enter eye and interrupts retina, so no photoreceptor cells
55
New cards
Cones
contain photopigment photopsins:
either S (short blue), M (medium green) or L( long red)
High-light level, high density in fovea, so detail vision
either S (short blue), M (medium green) or L( long red)
High-light level, high density in fovea, so detail vision
56
New cards
Rods
contain light-sensitive photopigment protein rhodopsin; grayscale, low-light level, night vision, peripheral vision
57
New cards
Summary of Dark Current & Activation of Rhodopsin
1. Rod Photoreceptors have cGMP-gated Na+ channels on their plasma
membrane.
2. In the dark, cGMP levels are high, so Na+ channels are open.
3. In-rush of Na+ depolarizes photoreceptor cell, so it releases **more** neurotransmitter in the dark.
4. Light activates rhodopsin in the disk membranes by altering configuration of retinal (vitamin A).
5. Rhodopsin is a G-protein coupled receptor (activated by light, not a ligand).
Activated G-proteins activate a phosphodiesterase that breaks down cGMP.
6. So in light, cGMP levels fall. cGMP-gated Na+ channels close.
7. Photoreceptor cell becomes hyperpolarized, so it releases **less**
neurotransmitter in the light.
58
New cards
On center ganglion cells
firing increases when light is shown in the center
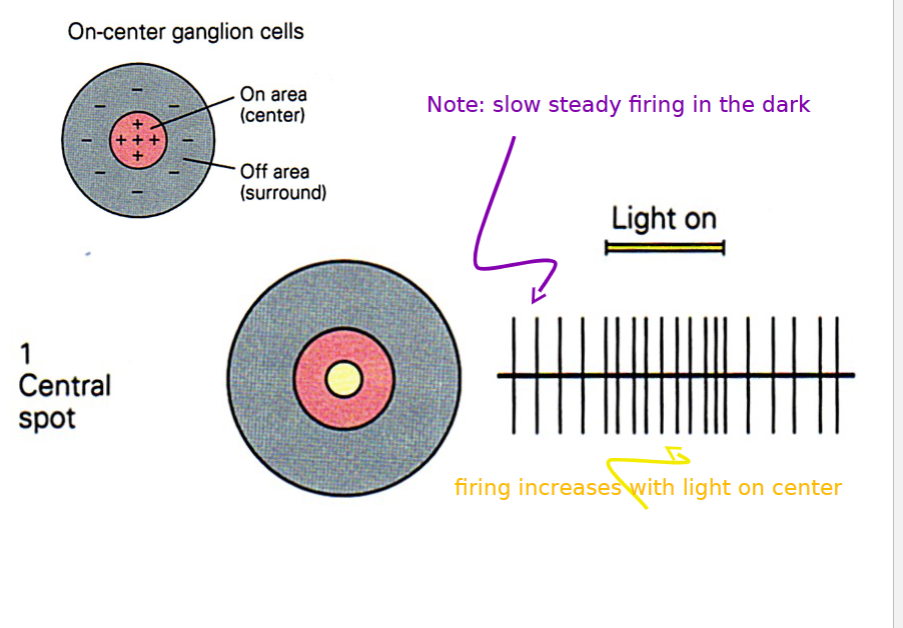
59
New cards
off center ganglion cells
increases firing with surround illumination
60
New cards
black and white slide
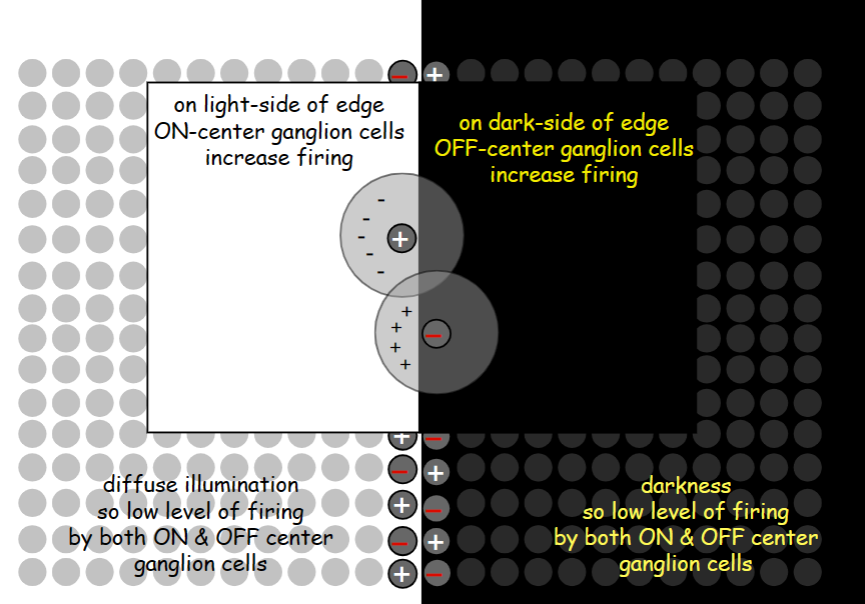
61
New cards
left vison goes to
right cortex
62
New cards
right vision goes to
left cortex
63
New cards
lesion at retina
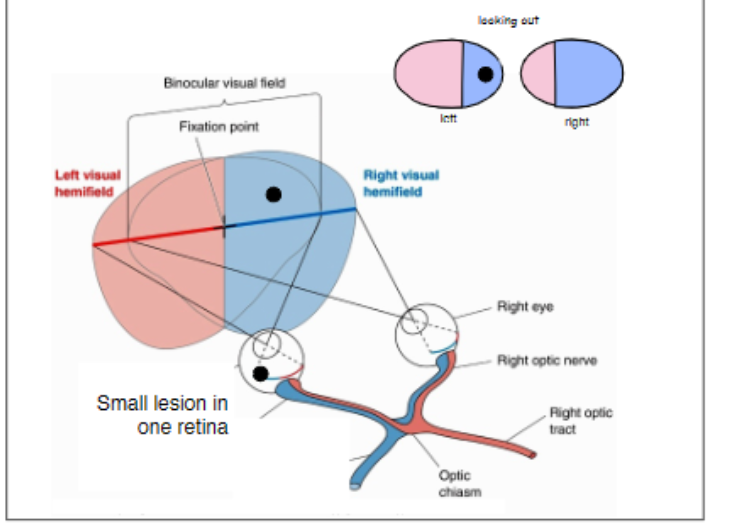
64
New cards
cut at left optic nerve
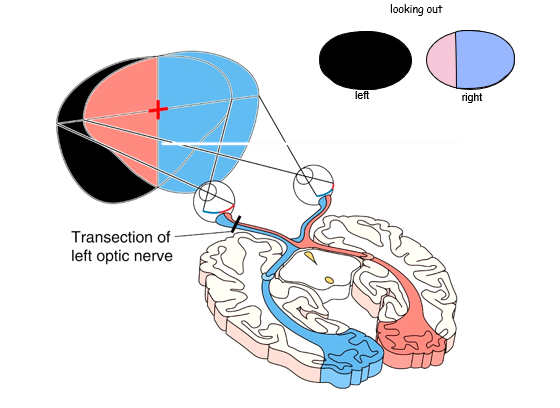
65
New cards
cut at left optic tract
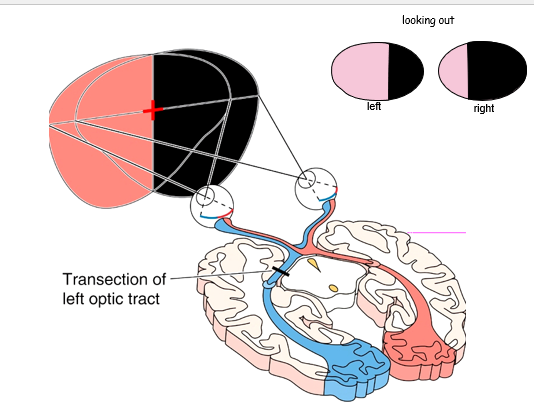
66
New cards
loss of left visual cortex
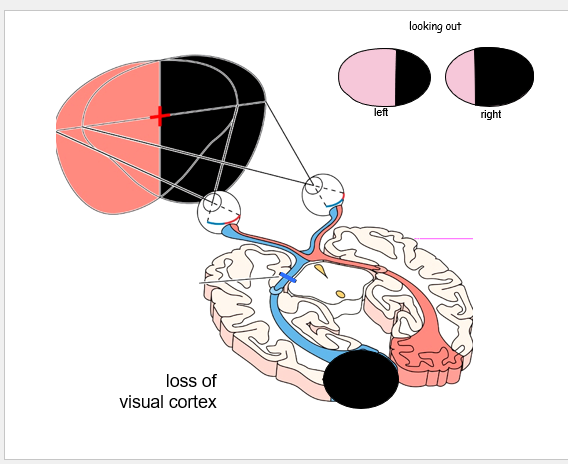
67
New cards
cut at optic chiasm
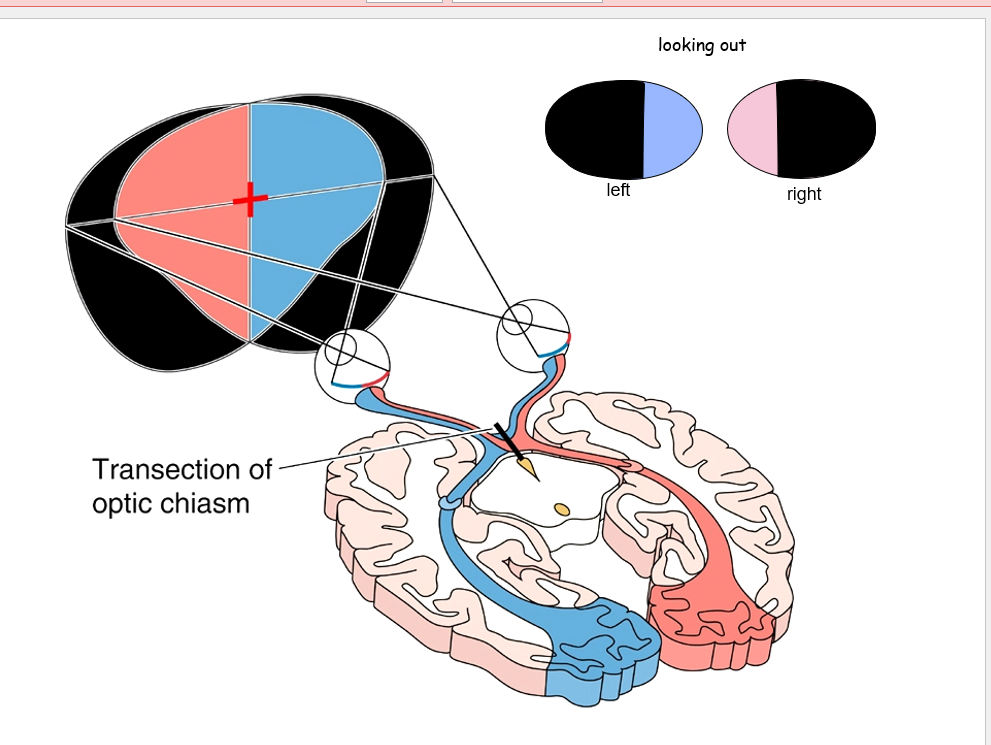
68
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
Nerves from spinal cord run to chain ganglia or collateral ganglia and then to glands and smooth muscle
Nerves from spinal cord run to chain ganglia or collateral ganglia and then to glands and smooth muscle
69
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
Nerves from brainstem and spinal cord run to glands and smooth muscle
Nerves from brainstem and spinal cord run to glands and smooth muscle
70
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system neurotransmitters
Preganglionic nerves release Acetylcholine (ACh) to stimulate nicotinic receptors
\
Postganglionic cells release Norepinephrine (NE) to stimulate or inhibit target tissues via adrenergic receptors
\
==exception==: sympathetic fibers to sweat glands use ACh.
\
Postganglionic cells release Norepinephrine (NE) to stimulate or inhibit target tissues via adrenergic receptors
\
==exception==: sympathetic fibers to sweat glands use ACh.
71
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system neurotransmitters
Preganglionic nerves release Acetylcholine (ACh) to stimulate nicotinic receptors
Postganglionic cells release Acetylcholine (ACh) to stimulate or inhibit target tissues via muscarinic receptors
Postganglionic cells release Acetylcholine (ACh) to stimulate or inhibit target tissues via muscarinic receptors
72
New cards
atropine
blocks muscarinic receptors (what’s used at the opthamlogist)
73
New cards
alpha and beta blockers
blocks adrenergic receptors
74
New cards
examples of sympathetic nervous
system affects the body
system affects the body
bronchi dilate, heartbeat increases, blood flow to the muscles, pupil dilate,
75
New cards
example of parasympathetic nervous system
bronchi constrict, pupils constrict, digestion
76
New cards
Know the (general) location of the preganglionic cell bodies and the ganglionic cell bodies
Paraganglion cell bodies are in the spinal cord/brain stem.
Ganglionic cell bodies are in the ganglia.
Ganglionic cell bodies are in the ganglia.
77
New cards
Adrena medulla
releases norepinephrine and epinephrine when stimulated by the sympathetic ; adrenal medulla are embryologically related to postganglionic sympathetic neurons,
78
New cards
pupil dilation
Sympathetic nerves cause dilation of pupil by stimulating pupillary dilator muscle (NE beta-adrenergic receptors)
79
New cards
pupil constriction
Light via optic nerve (II) stimulates parasympathetic nerve (III) to constrict pupillary sphincter muscle (ACh muscarinic receptors)
80
New cards
Hidrosis
Sympathetic postganglionic neurons synapse onto sweat glands in the skin
Sympathetic neurons release ACh (not NE) to stimulate sweating
Sympathetic neurons release ACh (not NE) to stimulate sweating
81
New cards
Horner’s Syndrome
Damage to sympathetic nerves on one side of neck
Unilateral (one-sided) constriction of pupil, anhydrosis (lack of sweat), flushing
Unilateral (one-sided) constriction of pupil, anhydrosis (lack of sweat), flushing
82
New cards
Organophosphates
insecticides that block cholinesterase enzyme -> enhanced ACh
neurotransmission at all synapses
Treated with atropine to block effects of elevated ACh
neurotransmission at all synapses
Treated with atropine to block effects of elevated ACh
83
New cards
the pupil receptors
muscarinic ACh (constriction) vs
beta-adrenergic receptors (dilation)
beta-adrenergic receptors (dilation)
84
New cards
adrenal gland receptors
nicotinic Ach receptors
85
New cards
heart receptors
muscarinic Ach (slow)
beta-adrenergic receptors (speed up)
beta-adrenergic receptors (speed up)
86
New cards
sweat gland receptors
muscarinic Ach receptors
87
New cards
sympathetic chain ganglion receptors
nicotinic Ach receptors
88
New cards
parasympathetic ganglion receptors
nicotinic Ach receptors
89
New cards
cocaine
enhance adrenergic receptors
90
New cards
The cell bodies of the parasympathetic preganglionic neurons are located in the:
brainstem and spinal cord
91
New cards
The cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons are located in the:
spinal cord
92
New cards
If the setpoint for body temperature is elevated above normal, then a person will:
feel cold, start shivering, put on a sweater
93
New cards
Meissner’s Corpuscle
small receptive field with rapid adaption
94
New cards
Pacinians’s Corpuscle
Large receptive field with rapid adaption
95
New cards
Merkels Disk
small receptive field, slow adaption
96
New cards
Ruffini’s ending
large receptive field with slow adaption
97
New cards
small receptive field size =
responds to light touch
98
New cards
large receptive field size=
deep receptors responds to stronger force
99
New cards
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobe
100
New cards
Motor cortex
located in front of central sulcus