Physical Chemistry A level OCR A
1/177
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Currently only has ALL of AS content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
Chemical vs physical properties of isotopes

What is relative isotopic mass?
Relative isotopic mass - The mass of an atom of an isotope compared to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
What is relative atomic mass?
Relative atomic mass (Ar) - The weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
What is relative molecular mass?
Relative molecular mass (Mr) - The average mass of a molecule compared to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
What is relative formula mass?
Relative formula mass - Used for ionic compounds. It is calculated by adding up the Ar values of all the ions in one formula unit.
What does a mass spectrum do?
Key facts about plotting a mass spectrum?
A mass spectrum plots the relative abundance of ions against their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z).

In a molecular sample in a mass spectrum, how do you find the molecular mass?
It is the right most significant peak.
Another peak beyond this may be caused by a different isotope in the molecule in trace amounts.
What is the empirical formula?
This formula gives the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound.
Charge of an electron?
1.6 × 10-19 C
A fact about any gas?
One mole of any gas at room temperature and pressure will occupy 24 dm3
Ideal gas equation?
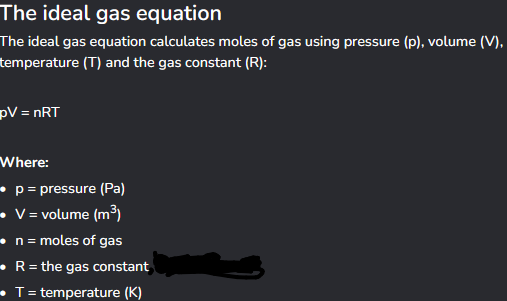
What is the gas constant?

8.3145 J mol-1 K-1
What is a theoretical yield?
The theoretical yield of a chemical reaction is the maximum mass of product that could be produced, assuming the reaction goes to completion with no loss of product.
What is actual yield?
Key fact and points about it?

What is percentage yield?
What can be said about its value?
Percentage yield is a measure of how efficient a reaction is, indicating how close the actual yield is to the theoretical maximum.

What is atom economy?

1st reaction type and its facts in relation to atom economy
Addition reactions
Two (or more) reactants combine to form a single product.
Since all the reactants are used in making the product, the atom economy is always 100%
2nd reaction type, and its facts in relation to atom economy.
Substitution reaction
Some atoms are displaced between reactants, generating at least 2 products: the desirable product and one by-product.
Think reducing copper with carbon.
Atom economy of such reactions are (always) less than 100%.
Advantages of a high atom economy?

What are acids?
They are species that give up protons (H+)
What are bases?
They are species that accept protons (H+)
How is ammonia a base?
It does not produce hydroxide ions directly, but it does stimulate water to do so:
NH_3+H_2O_{}\leftrightarrow NH_4^{+}+OH^{-}
Then:
NH_4^{+}+OH^{-}+HCl_{}\to NH_4Cl+H_2O
But since it starts and ends with water, that part can be removed:
NH_{3\left(aq\right)}+HCl_{\left(aq\right)}\to NH_4Cl_{\left(aq\right)}
What does the strength of an acid / alkali depend on?
If they fully ionise / dissociate in solution.
A strong acid will fully ionise / dissociate in solution, the reaction is not reversible:
HCl_{}\to H^{+}+Cl^{-}
A weak acid will partially ionise / dissociate in solution, this reaction is reversible:
CH_3OOH\leftrightarrow CH_3OO^{-}+H^{+}
4 Acid reactions with metals and their compounds

What is titration?
It is an analytical method used to determine the concentration of a solution of a known volume by adding a solution with a known concentration to it until neutralisation occurs.
How do you do a titration?

How to read a burette.
The volume of the burette should be recorded to the nearest half division (nearest 1cm³).
There will be a meniscus, a curved surface of the liquid, caused by adhesive forces between the walls and the liquid.
Readings should be taken from the bottom of the meniscus.
What indicators should you use in titration?
What else is important?
Methyl Orange - This changed yellow to red when acid is added to an alkali, but stop at orange.
Phenolphthalein - Turns from pink in alkaline to colourless (or light pink) in neutral.
There should be a white tile under the conical flask to ensure easy readings.
How to prepare accurate known concentrations.
(A standard solution)
Measure the mass of the solute using a mass balance. You should measure the mass of the solute with the container before and after to get best results.
Dissolve it in distilled water in a beaker
Transfer it to a volumetric flask of a specific volume
Rinse the beaker several times, adding the rinsings to the flask (at least 3 times).
Using a pipette, top up the flask to the measurement line.
Invert the flask to allow for thorough mixing of the solution.
Label the flask clearly
Oxidation number rules (no oxygen or fluorine)
Pure element → 0
Ions → solve like an equation
The more electronegative element will have a negative oxidation number.
Oxidation number of Oxygen in its 3 oxides
Oxide = -2
Peroxide = -1
Superoxide = -0.5
The 2 OPs keep having after I deal with them.
If it is bonded to fluorine → +2
Oxidation number of Fluorine.
F2 → 0
Bonded → -1
Oxidation state of Hydrogen
Bonded with a non-metal → +1
Bonded with a metal → -1
Electronegativity series
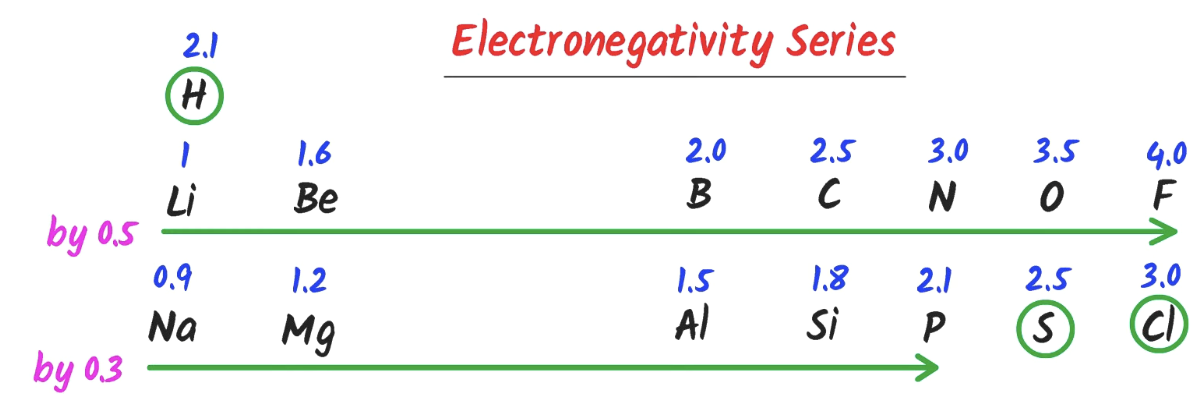
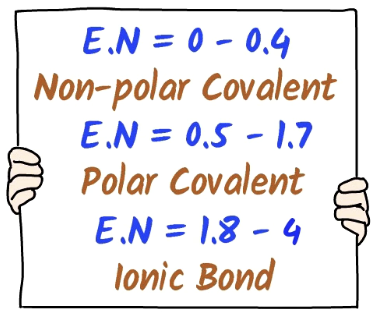
How can electronegativity be used to determine the bond type?
To determine the bond type, have a look at the difference in the E.N. numbers:
What is an oxidation number?
A measure of the number of electrons that an atom used to bond with atoms of another element.
Oxygen + Another element in an ion makes…
-ate, e.g.
Sulphate
Chlorate
What is oxidation?
What is reduction?
Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons), or an increase in oxidation state
Reduction Is Gain (of electrons), or a decrease in oxidation state
(Use oxidation numbers to figure this out)
What is an oxidising agent?
What is a reducing agent?
An oxidising agent accepts electrons, and is itself reduced.
A reducing agent donated electrons, and is itself oxidised.
(Use oxidation numbers to figure this out)
What are orbitals?
2 other facts about them?
They are regions with high probabilities of finding an electron.
They are defined as a region around the nucleus that can accommodate up to two electrons with opposite spins.
Electrons within orbitals in the same shell have an equal energy level.
What is mol dm-1 also shown as?
M
How do electron shells work at A-Level (x3)?
Shells further from the nucleus hold electrons with higher energy levels than those closer.
Each shell is defined with a principal quantum number (starting from 1).
Electron shells are split into subshells as well:
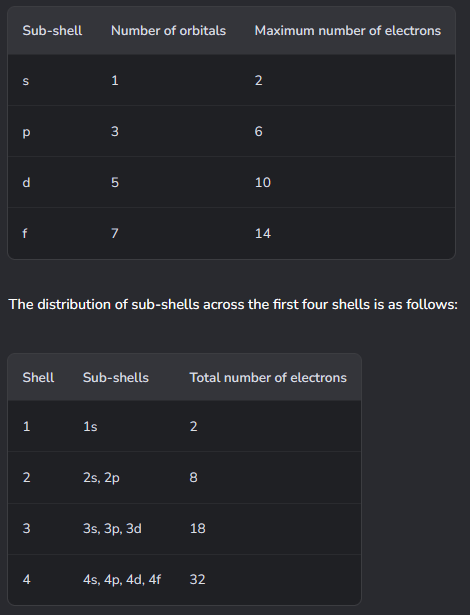
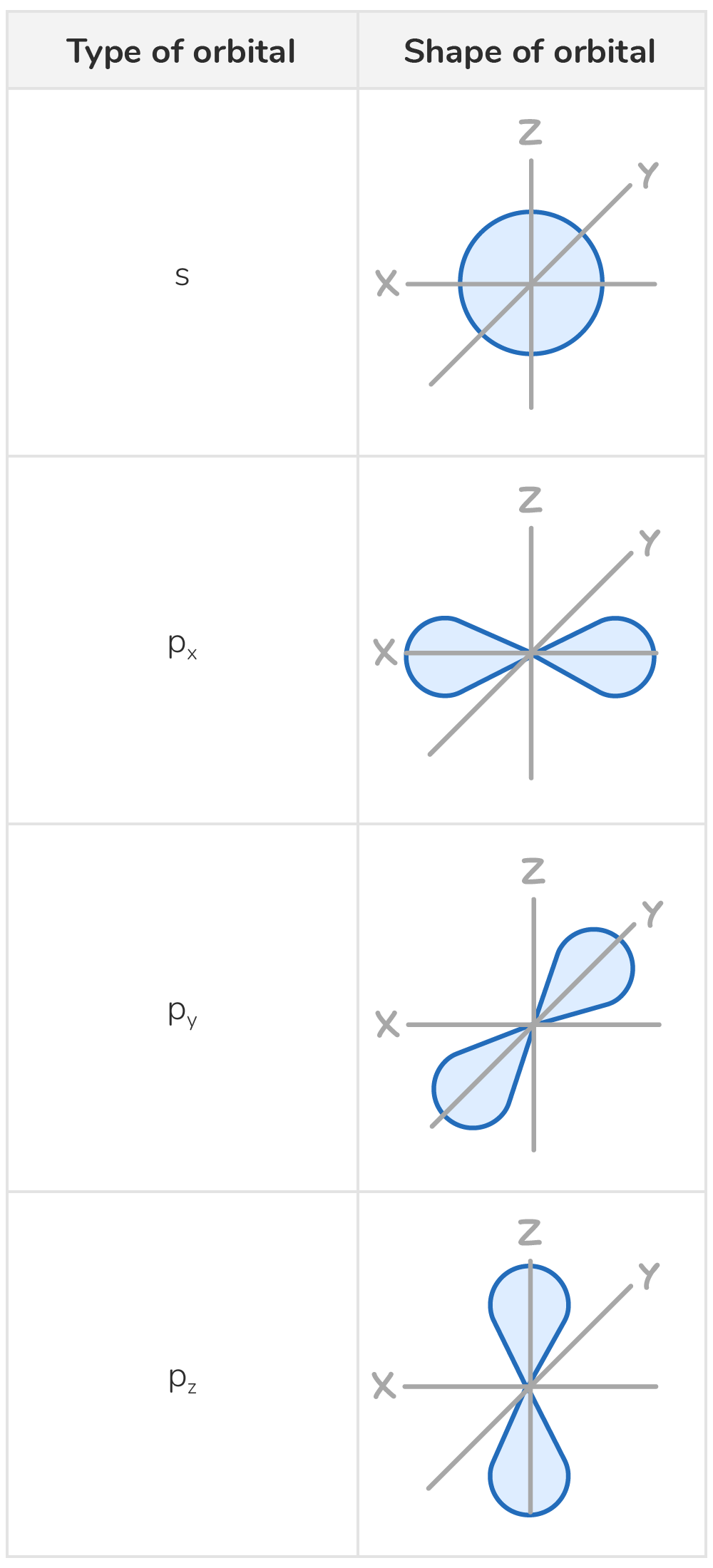
Specifics about s and p orbitals.
S orbitals are spherical.
P orbitals are dumbbell shaped.
How to represent electron configurations.

Energy levels of the orbitals.
See diagram, but note the 4s subshell is filled before the other ones.

How to do electron orbitals.
Electrons first occupy different orbital spaces before doubling up
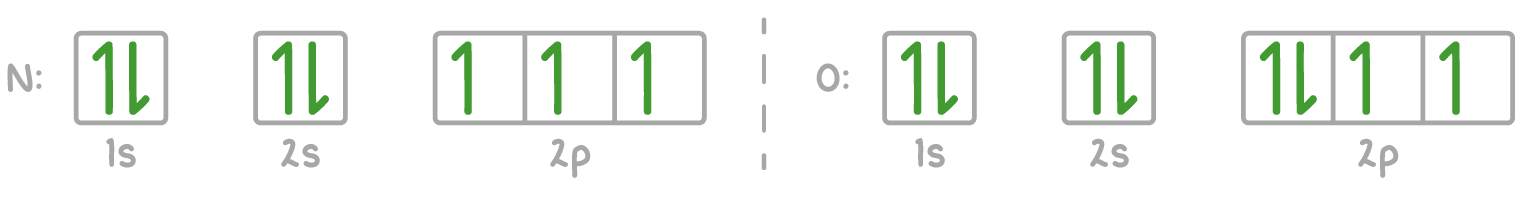
Electrons fill up from the least energy orbitals
How to simplify the electron configuration number notation.
Use noble gases to abstract lower orbitals’ states.
For example, calcium's configuration (1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2) is abbreviated as [Ar] 4s2, where [Ar] represents 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6.
What is the electron configuration of copper?
Why is it different?
Another element

The 3d subshell is more stable when entirely full.
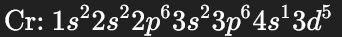
Ethanoic acid vs Di-ethanoic Acid
Simple explanation to why transition elements can form ions with many different charges.
Unlike main group elements, transition elements have partially filled d sub-shells, enabling them to form multiple ions with different charges. For example, iron can form both Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions:
Fe2+: [Ar] 3d6
Fe3+: [Ar] 3d5
When transition elements undergo ionisation, the 4s electrons are lost before the 3d electrons. The similar energies of the 3d and 4s sub-shells allow for successive ionisations in many transition elements, resulting in the formation of ions with varying charges.
The structure of ionic compounds

Properties related to ionic structure
High melting and boiling points - The strong electrostatic attractions between the positive and negative ions in the giant lattice must be overcome for the lattice to break apart; this requires a lot of energy.
Conduct electricity when molten or in solution - When melted or dissolved, the ions can move freely and carry electric charge through the liquid.
Do not conduct electricity as solids - In the solid lattice structure, the ions are firmly locked in place and unable to move to carry electric charge.
Dissolve in water - Water molecules, which are polar, attract the charged ions in the lattice via ion-dipole forces, pulling them away from the lattice and dissolving the structure.
What impacts the strength of an ionic bond?
Ionic charge: Higher charges (e.g. Mg²⁺ vs Na⁺) give stronger electrostatic attraction.
Ionic radius: Smaller ions pack closer, so the attraction is stronger.
Charge density (combination of charge and size): A small, highly charged ion has high charge density, so it attracts the opposite ion more strongly.
What is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is the strong electrostatic attraction formed between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms.
This bonding creates a stable molecule - a group of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds.
What is covalent bond strength
This depends on how much energy is needed to break the bonds, this is expressed in kJ mol-1
This value is called bond enthalpy
What is dative covalent bonding also known as?
What is this bond?
Coordinate bonding
Both shared electrons come from just one of the bonding atoms, rather than 1 from each.
What impacts the strength of a covalent bond?
Bond Enthalpy depends on:
Bond length: Shorter bonds are stronger because the nuclei are closer together, so the electrostatic attraction between the shared electrons and nuclei is greater.
Bond multiplicity: Multiple bonds (double, triple) are stronger (and shorter) than single bonds, because more electrons are being shared.
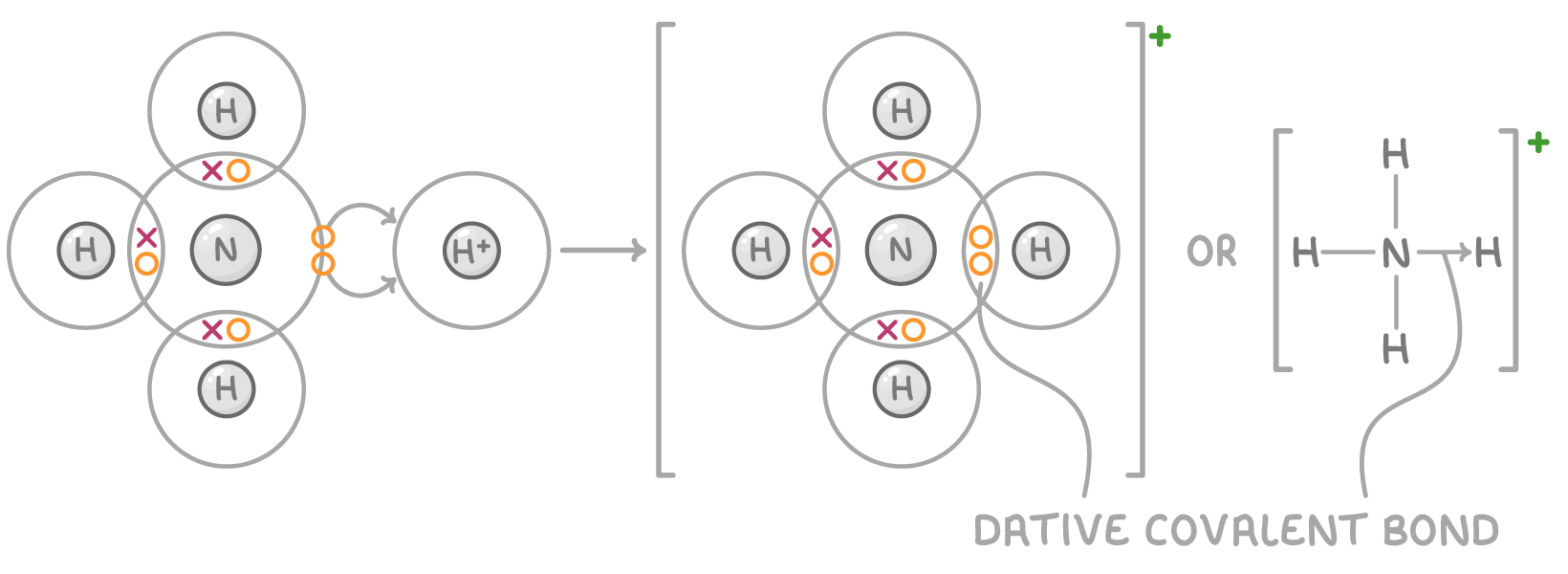
What is needed for a dative covalent bond to form?
One atom (A) must have a lone pair of electrons to donate.
The other (B) must be electron deficient (must have an incomplete electron shell).
An arrow is used to show the donation A to B
This happens in the formation of the ammonium ion:
Tell me about metallic structures
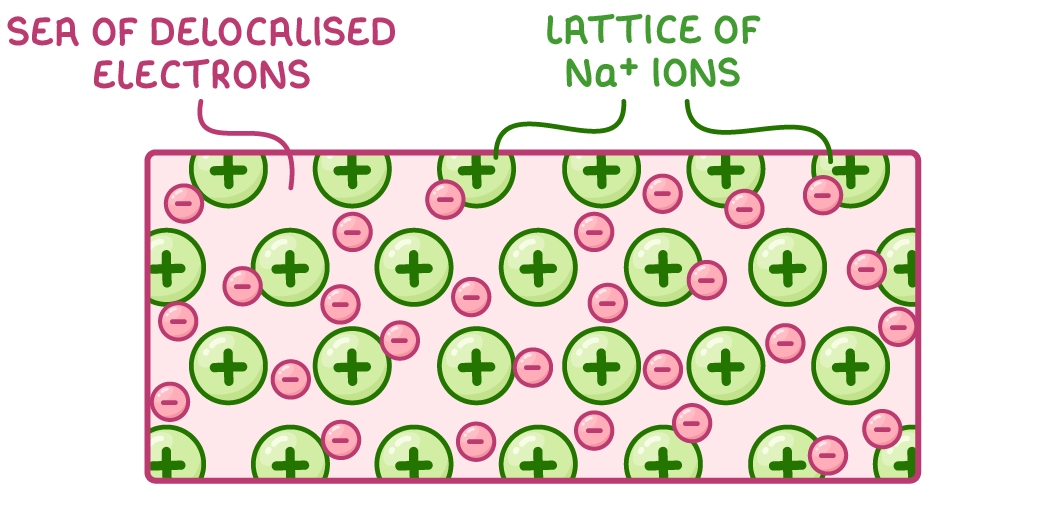
Metals exist as giant lattice structures made up of:
Positively charged metal cations (e.g. Na+, Mg2+)
Delocalised electrons that move freely between the cations
The outer electrons of metal atoms leave to become delocalised, resulting in positively charged metal cations.
Here is sodium as an example:
What is a metallic bond?
Metallic bonding refers to the electrostatic attractions between positively charged metal ions (e.g. Na+, Mg2+) and negatively charged delocalised electrons.
These metallic bonds are very strong and hold the metals in their lattice structure.
What are the 3 factors that impact the strength of a metallic bond.
The number of delocalised electrons per atom. The more of these, the stronger the electrostatic forces between the negative electrons and positive cations. (Opposite charges attract).
Charge of the metal cation. The higher this, the larger the charge difference between a cation and an electron, leading to stronger electrostatic forces, and a stronger bond.
Radius of the metal cation. This can lead to higher charge density (Charge density = charge on the ion ÷ volume of the ion). The smaller the atomic radius, the closer the delocalised electrons are to the attractive positive nucleus, leading to a stronger metallic bond.
Properties of metals, and how this results from their metallic bonding
High melting and boiling points - The strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the positively charged metal cations and the sea of delocalised electrons must be overcome for the lattice to break apart; this requires large amounts of energy.
Good conductors of electricity and heat - The delocalised electrons can flow freely through the lattice to transfer charge and heat energy.
Malleable and ductile - Layers of the cation lattice can slide over one another when the metal is hammered or pulled because there are no bonds locking individual cations together.
Insoluble - The strength of the metallic bonding prevents water or other solvent molecules from pulling the cations away from the lattice structure and dissolving the metal.
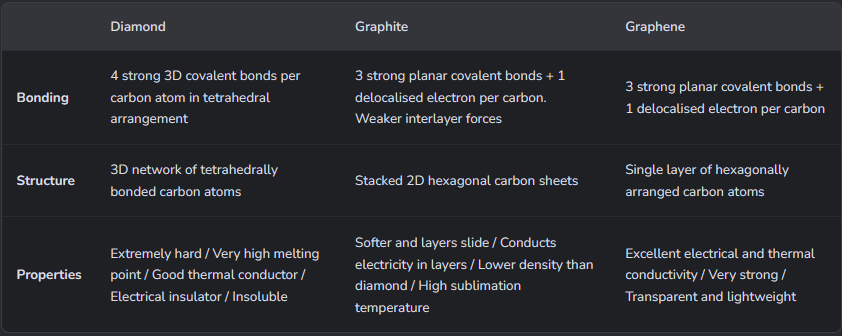
Give the 3 common allotropes of carbon, and their properties.
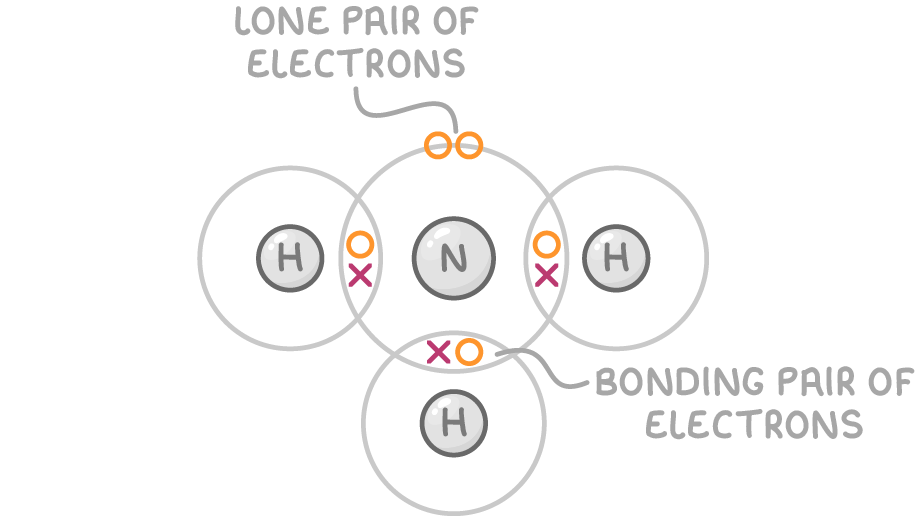
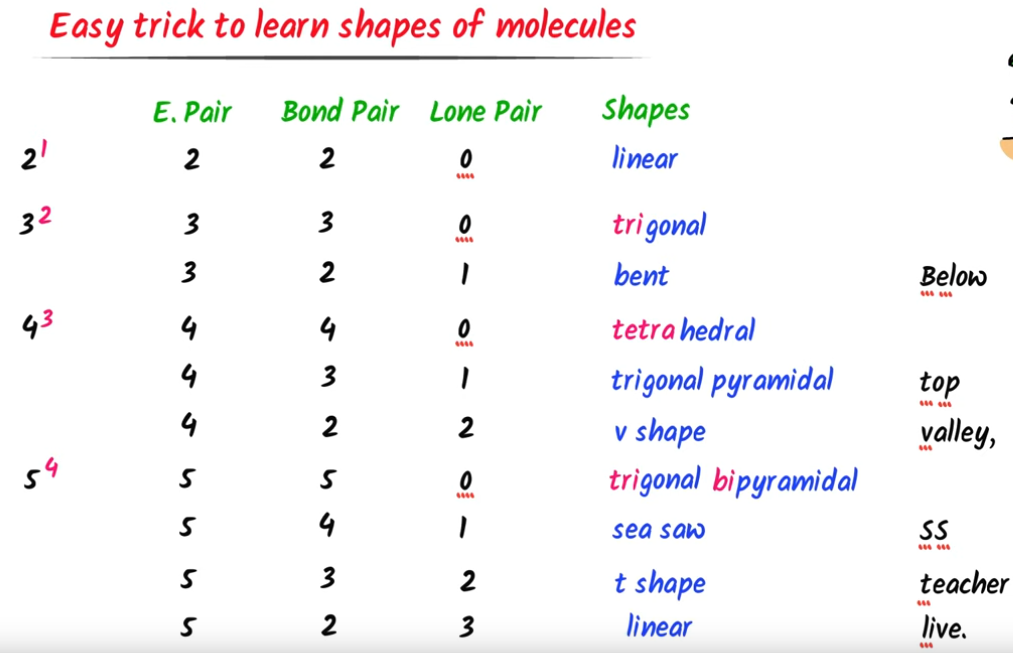
Two types of electron pairs
Bonding pairs - Involved in forming covalent bonds with other atoms.
Lone pairs - Not involved in bonding and remain on the central atom.
Molecular shape table
Hydrogen bonded to a metal, what is it called?
Hydride
What is the “expansion of the octet”?
In A-Level, we can deal with elements with more than 8 electrons in their outer shell, allowing them to form even more bonds, e.g. SF6.
Conversely, there are some that are stable with few bonds, e.g. BF3.
How many bonds can each group form?
This only applies to Period 3 and below.
Group 5: 3 or 5
Group 6: 2,4 or 6
Group 7: 1, 3, 5, 7
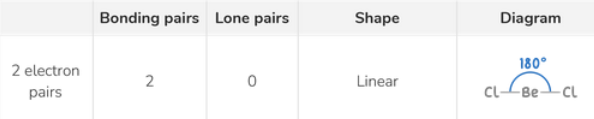
Molecular shape for 2 electron pairs
Molecular shape for 3 electron pairs

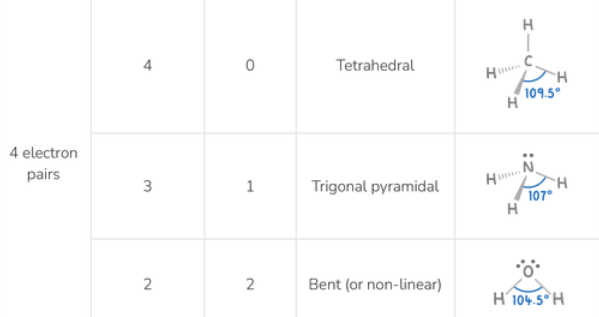
Molecular shape for 4 electron pairs
Molecular shape for 5 electron pairs

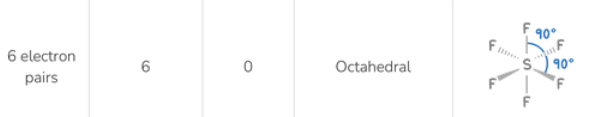
Molecular shape for 6 electron pairs
Grades of repulsion for electron pairs
Bonded & Bonded < Bonded & Lone < Lone & Lone
Bond angle reduced by about 2.5° per lone pair
Factors that impact electronegativity.
Atomic radius: the smaller this, the closer the electrons are to the attractive positive nucleus, leading to stronger electrostatic attraction → more electronegativity.
Nuclear charge: higher → stronger pull on electrons.
Shielding: The inner shell electrons can shield the outer shell electrons → less attraction on the incoming electron.
Trend for electronegativity across a period.
Nuclei charge increases significantly
So electrostatic force of attraction on the outer shell electron(s) increases.
This outcompetes the increasing atomic radius (which should decrease attraction)
So electronegativity increases
Trend of electronegativity down a group.
Atomic radius increases significantly
Electrostatic force of attraction on the outer shell(s) electron decreases.
This outcompetes the increasing nuclei charge (which should decrease attraction)
So electronegativity decreases
Explain why polar bonds form.
The difference in electronegativity of the two bonded atoms causes unequal forced on the electrons.
The bonding electrons are more strongly attracted to the more electronegative ion.
The unequal sharing of electrons makes the bond polar
Features of polar bonds.
Polar bonds have a permanent electric dipole.
This refers to the separation of positive and negative charges within a polar bond or molecule, caused by unequal electron sharing.
In a polar bond, the more electronegative ion gains a slight negative charge, and the other gains a slight positive charge
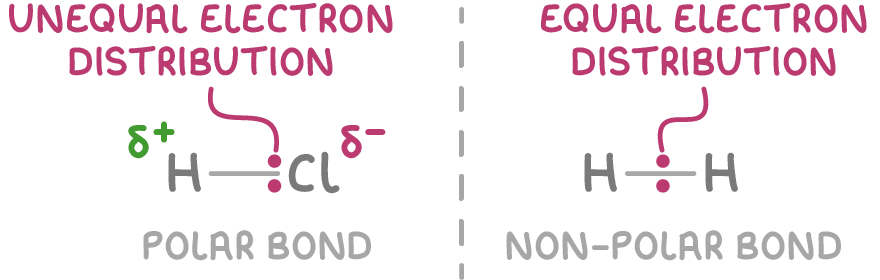
This will not occur if a species is bonded to one of its own. (O2)
What decides if a molecule is polar, or not?
The bonds have to be polar.
AND the dipoles should not cancel each other out.
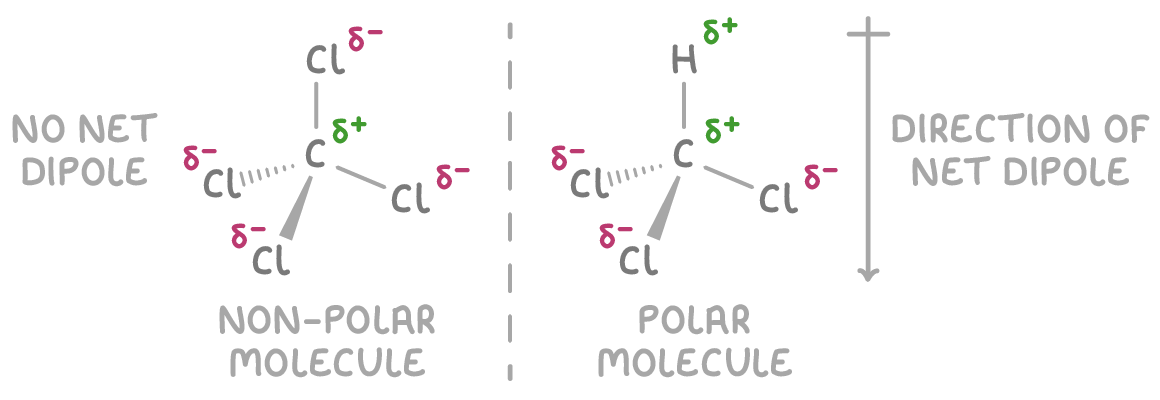
A symmetric molecule like CH4 will have no polarity or net dipole because the dipoles all cancel out.
An asymmetric molecule, like CHCl3, will be polar as the charges do not cancel out.
Early attempts at organising elements
In the early 1800s there were 2 main ways:
by chemical and physical properties
by relative atomic mass
What did the 1st guy do?
Johann Döbereiner identified triads of elements with similar properties and relative atomic masses in between the others.
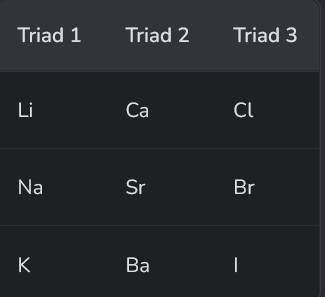
However, this was not really that accurate
What did the 2nd guy do?
John Newlands
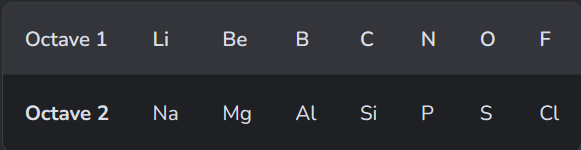
However it was not very accurate
What did the 3rd guy do?

The gaps he left, and the predictions he made were found to be accurate.
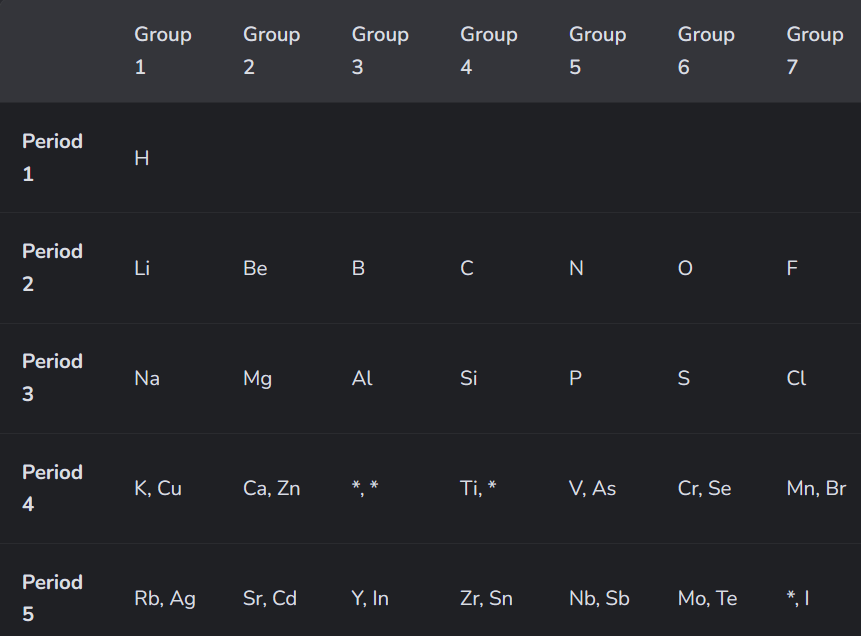
What did the 4th guy do?

The modern periodic table?
It has periods (rows)
And groups (columns)
What does chlorate(V) mean?
Oxidation state of +5
ClO3-
What is ionisation?
Removing one or more electrons from an atom or molecule.
This is endothermic.
What is the first ionisation energy?
The energy required to knock off 1 electron from each atom in 1 mole of gaseous atoms, to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions.

What does ionisation energy depend on?
How strongly the outermost electron is attracted to the positive nucleus.
What factors impact ionisation energy?
Nuclear charge: The higher this, the higher the charge difference between the electrons and the nucleus, meaning a higher electrostatic force of attraction.
Atomic radius: The closer the outmost electrons are to the nucleus, the stronger the electrostatic charge.
Electron Shielding: The inner shell electrons reduce the electrostatic form of attraction between the positive nucleus and the outermost shell of electrons
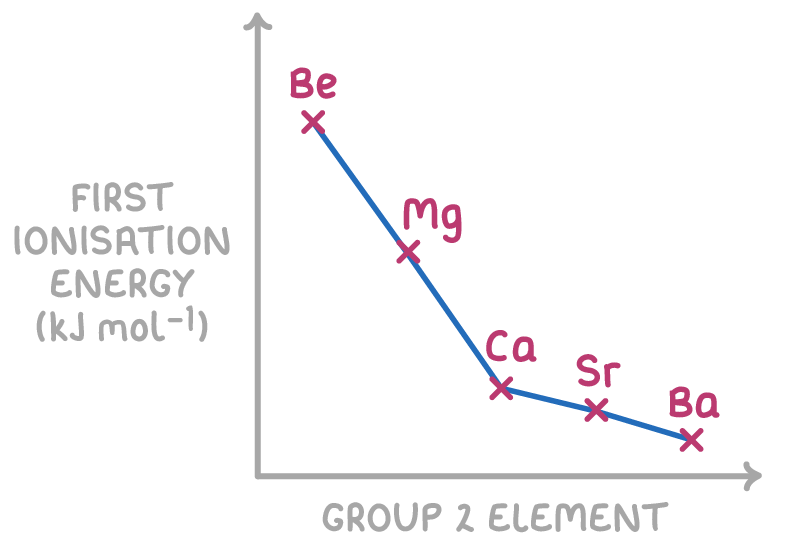
Tell me about trends in 1st ionisation energy: down a group
The increase in atomic radius, and the increase in the electron shielding, cause the ionisation energy to decrease, outweighing the increase in the nuclear charges.
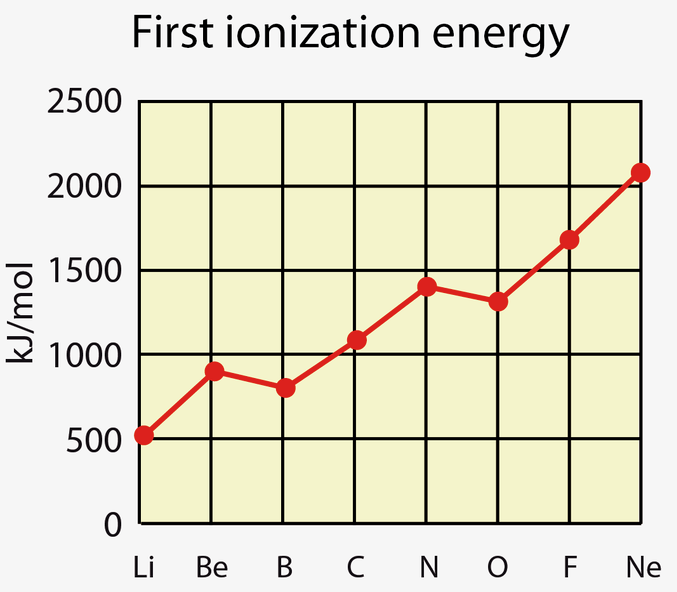
General trend with ionisation energies across a period
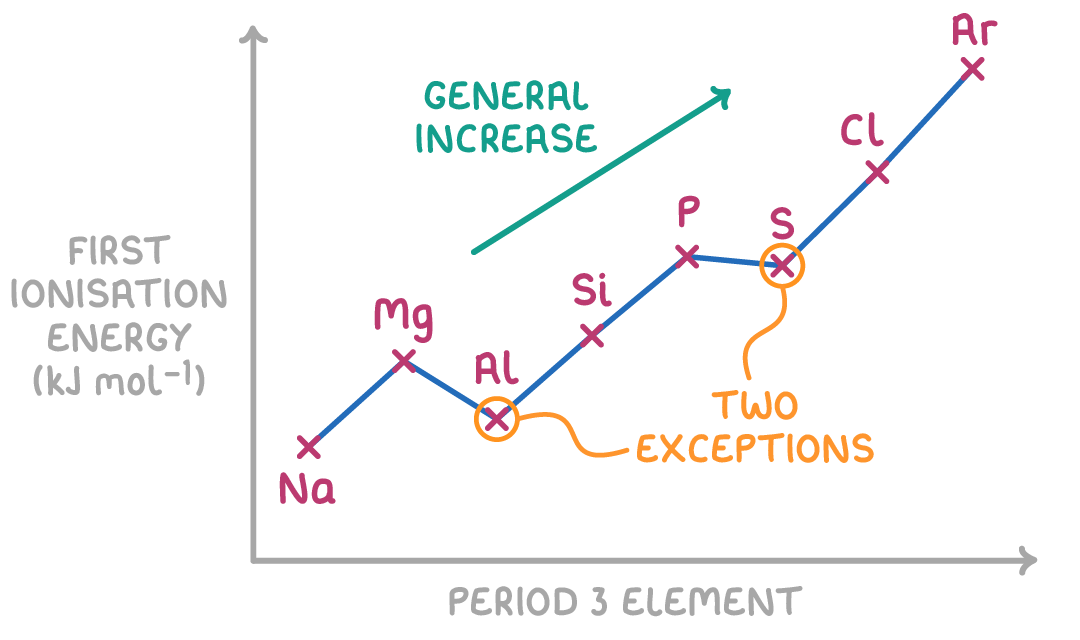
Generally:
Nuclei charge increases significantly
So electrostatic force of attraction on the outer shell electron(s) increases.
This outcompetes the increasing atomic radius (which should decrease attraction)
So electronegativity increases
Describe the 1st exception with ionisation energies across a period.
Group 2-3
This is because the outmost electron is in the p orbital, not the s.
This means that this electron has a slightly higher energy level.
Resulting in it being further away from the attractive nuclear charge, decreasing its attraction to the positive nucleus.
This also means that there is more shielding from the s orbital electrons.
Thus, less energy is needed to ionise the atom.
Describe the 2nd exception with ionisation energies across a period.
Group 5-6
In group 5, the electron is removed from a singly occupied orbital.
However, in group 6, the electron is removed from full orbital.
This means that there is greater electron-to-electron repulsion.
Thus, less energy is needed to remove this electron: the ionisation energies decrease.
What are successive ionisation energies?
This is when electrons are removed sequentially from an atom.
The definitions follow a clear pattern.
The second ionisation energy is the energy required to knock off 1 electron from each 1+ ion in 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions, to form 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions.
The third ionisation energy is the energy required to knock off 1 electron from each 2+ ion in 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions, to form 1 mole of gaseous 3+ ions.
Explain the change in successive ionisation energies, when you stay in the same electron shell.
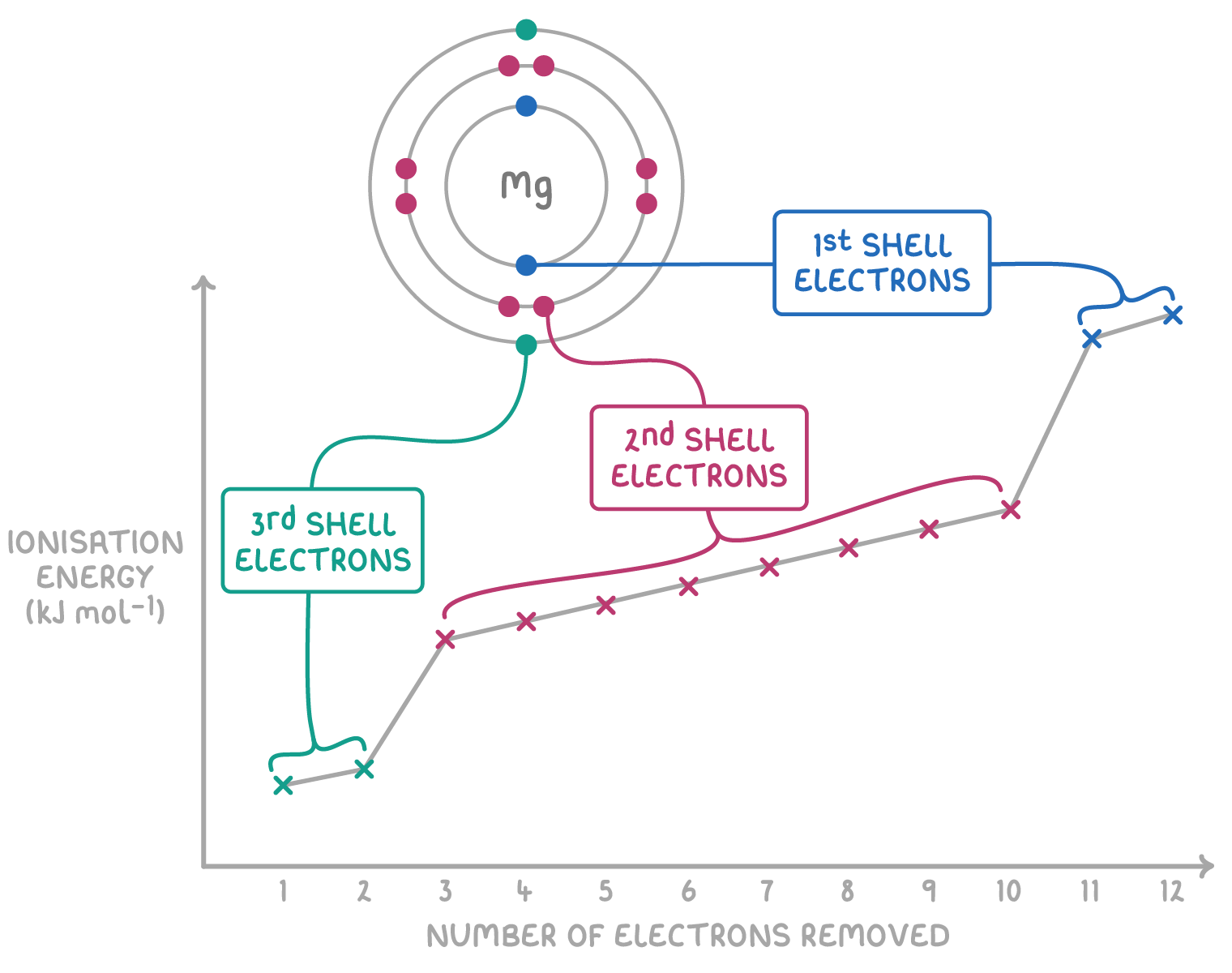
As you remove electrons from the same shell, the remaining electrons experience a larger electrostatic force of attraction to the nucleus (the atomic radius also increases).
So the energy required to remove the next electrons in the same shell is only slightly greater.
Explain the change in successive ionisation energies, when you go across electron shells.
When you reach the inner shell electron, there will be a big increase in the ionisation energy.
This is because the attraction to the positive nucleus is much greater for the inner shell electron, as it is much closer.
Atomic radius trend
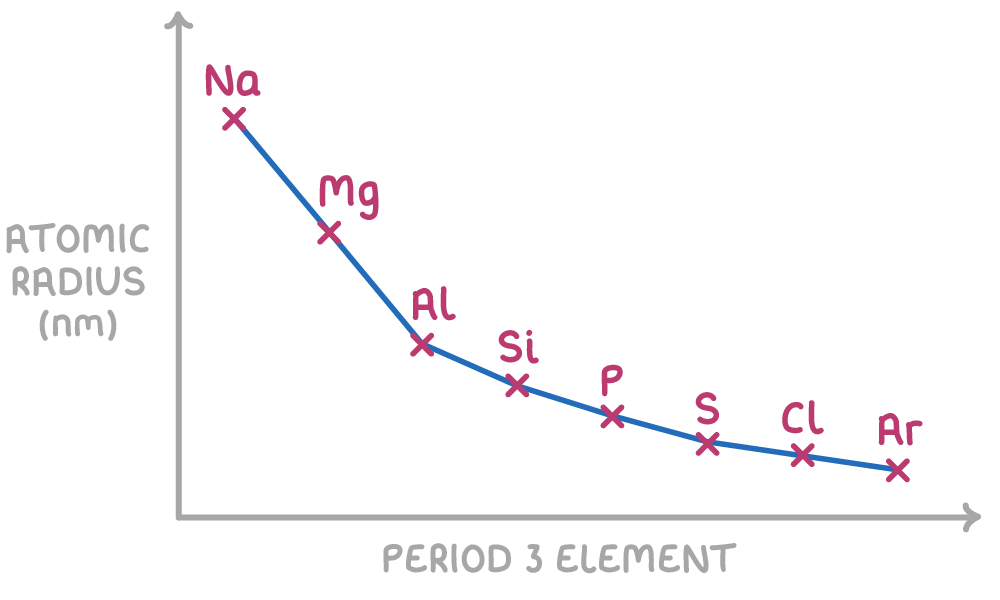
Protons are added to the nucleus, so the nuclear charge increases.
Electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outer shell electrons increases
SO the outer shell electrons are drawn in closer
The electrons added across the period go to the outer shell, so change in shielding in minimal for the inner electrons.
Thus with a large increase in nuclear charge, and minimal change in shielding, the atomic radius decreases.

Water of Crystallisation