CIS macro economics final
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
yeah
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Scarcity
The fundamental economic problem of having seemingly unlimited human wants in a world of limited resources, leading to the need for choices and trade-offs.
Opportunity Cost
the loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen.
factors of production
land, labor, entrepreneurship, and capital.
Command Economy
In a command economy, the government or central authority makes all the economic decisions. They control what goods and services are produced, how they are produced, and who gets them. This type of system is often found in socialist or communist countries.
Example: North Korea.
Market Economy
A market economy is driven by supply and demand with little or no government intervention. Individuals and businesses make economic decisions based on their own interests. Prices, production, and distribution of goods are determined by competition in the market.
Example: The United States, although it is more accurately described as having a mixed economy.
Traditional Economy
In a traditional economy, economic decisions are based on customs, beliefs, and traditions. This system relies on agriculture, fishing, hunting, and gathering, and barter is often used for trade. These economies are typically found in rural and farm-based areas.
Example: Indigenous tribes in Africa and South America.
Mixed Economy
A mixed economy combines elements of both market and command economies. While private individuals and businesses have the freedom to make many economic decisions, the government intervenes in certain areas to regulate and guide the economy.
Example: Most modern economies, including the United States, the United Kingdom, and Germany.
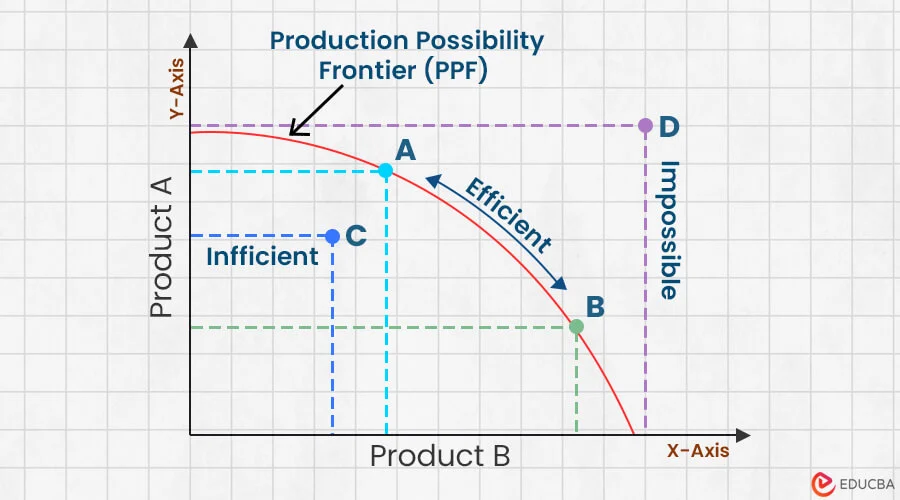
Production Possibilities Curve
shows production possibilities and how to most efficiently do it
households in circular flow model
Provide labor, land, and capital to businesses (factors of production).
Receive income in the form of wages, rent, and dividends.
Businesses in circular flow model
Produce goods and services using the factors of production provided by households.
Sell goods and services to households, receiving revenue in return.
Government
Collects taxes from households and businesses.
Provides public goods and services, and redistributes income through welfare programs.
Resource Market:
Households sell factors of production (labor, land, capital) to businesses.
Businesses pay for these resources (wages, rent, interest).
Product Market:
Businesses produce and sell goods and services to households.
Households buy goods and services from businesses, spending their income
Government Interaction:
Government collects taxes from both households and businesses.
Government provides public goods and services to households and businesses.
Externalities
costs or benefits of economic activities that affect third parties who did not choose to incur those costs or benefits. They can be either positive or negative and are considered market failures because their effects are not reflected in market prices
Negative Externalities
These occur when the production or consumption of a good or service imposes a cost on a third party. Common examples include pollution, noise, and traffic congestion.
Positive Externalities
These occur when the production or consumption of a good or service generates benefits for third parties. Examples include education, vaccination, and public parks.
public goods
goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous, meaning that one person's use of the good does not reduce its availability to others, and people cannot be prevented from using the good
GDP calculation
GDP = Consumption + Investment + Government spending +( exports − imports)
Nominal GDP
Measures the value of all final goods and services produced within a country at current market prices. It does not account for inflation.
It can be misleading if there are significant changes in price levels over time.
Real GDP
Measures the value of all final goods and services produced within a country, adjusted for inflation. It reflects the actual quantity of goods and services produced.
Real GDP is a more accurate measure of economic growth because it removes the effect of price changes.
GDP Growth Rate
The GDP growth rate is the percentage change in GDP from one period to another, typically expressed on an annual basis.

Frictional Unemployment
Short-term unemployment that occurs when people are between jobs or entering the workforce for the first time. It is often voluntary and can result from the time taken to search for a new job that better matches their skills and preferences.
Structural Unemployment
Occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills of workers and the requirements of available jobs. It can be caused by technological changes, shifts in consumer demand, or other factors that change the structure of the economy.
Cyclical Unemployment
Results from economic downturns or recessions. During these periods, demand for goods and services decreases, leading to a reduction in production and, consequently, a rise in unemployment.
Seasonal Unemployment
Happens when industries experience regular seasonal fluctuations in demand. Workers in these industries, such as agriculture, tourism, and retail, may be unemployed during off-peak seasons.
Full Employment
refers to the situation where all available labor resources are being used efficiently, and the only types of unemployment are frictional and structural. Cyclical unemployment is minimized.
Natural Rate of Unemployment
level of unemployment that exists when the economy is at full employment. It includes frictional and structural unemployment but excludes cyclical unemployment.
Counted as Unemployed
Individuals who are actively seeking work and are available to start a job.
Those who have been laid off and are waiting to be recalled to a job.
Not Counted as Unemployed
Discouraged workers who have stopped looking for work because they believe no jobs are available for them.
People who are not actively seeking work, such as retirees, students, and homemakers.
Part-time workers who are seeking full-time employment are counted as employed, but they may be underemployed.
unemployment rate equation

Consumer Price Index (CPI)
measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services, such as transportation, food, and medical care. It is used to calculate inflation by comparing the current prices of the basket to the prices in a base year. CPI is one of the most commonly used indicators for measuring inflation.
Nominal Values
These are values expressed in current prices, without adjusting for inflation. For example, nominal GDP is the value of all goods and services produced in an economy at current prices.
Real Values
These are values that have been adjusted for inflation, reflecting the true purchasing power. For example, real GDP accounts for changes in price levels and provides a more accurate measure of economic growth.
Real Value Calculation
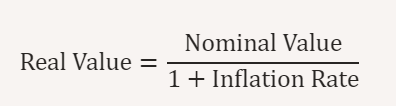
Borrowers
Helped by Inflation
Businesses with Price Flexibility
Helped by Inflation
Savers
Hurt by Inflation
Fixed-Income Earners
Hurt by Inflation
Lenders
Hurt by Inflation
Changes in Consumer Spending
Increase in consumer confidence or wealth (e.g., stock market boom) shifts AD to the right.
Decrease in consumer confidence or wealth (e.g., recession) shifts AD to the left.
Changes in Investment Spending
Increase in business investment due to optimistic future expectations shifts AD to the right.
Decrease in business investment due to pessimistic future expectations shifts AD to the left.
Government Policies
Expansionary fiscal policy (e.g., tax cuts, increased government spending) shifts AD to the right.
Contractionary fiscal policy (e.g., tax increases, reduced government spending) shifts AD to the left.
Net Exports
Increase in exports relative to imports (e.g., weaker domestic currency) shifts AD to the right.
Decrease in exports relative to imports (e.g., stronger domestic currency) shifts AD to the left.
Changes in Input Prices
Decrease in the cost of production (e.g., lower raw material prices) shifts AS to the right.
Increase in the cost of production (e.g., higher raw material prices) shifts AS to the left.
Changes in Technology
Technological advancements that improve productivity shift AS to the right.
Technological setbacks or inefficiencies shift AS to the left.
Supply Shocks
Positive supply shocks (e.g., favorable weather conditions) shift AS to the right.
Negative supply shocks (e.g., natural disasters) shift AS to the left.
Government Policies
Policies that reduce production costs (e.g., tax incentives, deregulation) shift AS to the right.
Policies that increase production costs (e.g., higher corporate taxes, strict regulations) shift AS to the left.
Aggregate Demand
the total quantity of goods and services demanded across the economy at various price levels. same equation as GDP
components of Aggregate supply
Labor, Capital, Technology, Natural Resources, Human Capital, and Government Policies