Geriatric Dermatology
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
65
Old skin is any skin greater than or equal to __ years old
Intrinsic
aging due to a set of gradual physiological changes that are consequence of time and are under genetic and hormonal control
-skin may appear dry, fine lines and wrinkles
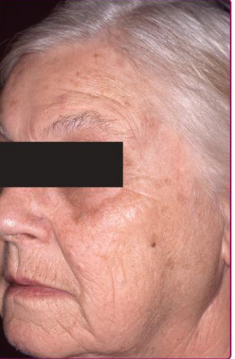
Extrinsic
dramatic structural and functional changes caused by exogenous factors like sun exposure
collagen, reduced, lipids, rete
Intrinsic Aging Skin
-Decreased _________ production
-_________ blood flow
-Lowered amounts of ______
-Loss of ___ ridges, which are epithelial projections into the dermis
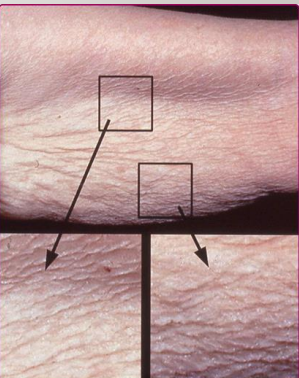
longer, accumulate, dry, shearing, bruised, broken
Microscopic View of Intrinsic Aging
-The epidermal turnover rate slows down with age, delaying epithelization after injury. Meaning it takes _______ for them to heal
-Older corneocytes __________, keeps the skin from looking youthful
-Altered biosynthesis of stratum corneum lipids → increased trans-epidermal water loss and defects in the permeability layer, meaning geriatric individuals are more likely to have ___ skin
-Thinned epidermis and flattening of epidermal-dermal junctions, making them more susceptible to ________/tearing
-Decreased elastic content in dermis and vasculature making them easily _________
-Dermis has sparse collagen and elastin fibers, sweat glands, and nerve endings
-Skin’s protective barrier is _____ down
intervention, UV, smoking, air
Extrinsic Aging Skin
-More amendable to __________ and preventative measures, unlike intrinsic aging
-__ radiation is the most powerful source, This can cause deep wrinkles, telangiectasias, and skin laxity
-Other risk factors include cigarette _________, diet, chemical exposure, trauma, and ___ pollutants
Pruritus
most common dermatologic complaint of the elderly population
-idiopathic in up to 30% of cases
-may be due to underlying systemic disease
emollients, antihistamines, steroids
Treatment of Pruritus
-___________ with methanol, camphor, phenol, or doxepin like Vaseline
-Consider oatmeal baths and oral ___________, be sure to avoid Benadryl
-Short term use of topical ________
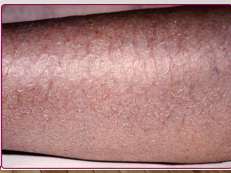
Xerosis
most common skin disorder in the elderly, mostly affecting the lower legs
-dry skin causing scaling, redness, and fissuring

Asteatotic eczema
inflammatory changes due to dry skin
-very itchy, more likely to have fissures and scales than xerosis
-worse in the winter
avoid, hydrate, after
Treatment of Xerosis and Asteatotic Eczema
-_____ aggravating factors
-________ the skin
-Avoid harsh soaps
-Stop using bath salts
-Moisturize immediately ______ the bath with Vasoline or anther emollient
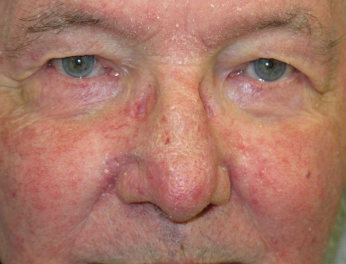
Seborrheic Dermatitis
faint erythematous patches with greasy scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands
-decreased immune response
-due to M. Furfur
sulfide, shampoo, corticosteroids
Treatment of Seborrheic Dermatitis
-Head: selenium _______ / zinc pyrithione _________
-Antifungals
-Topical ______________
coin-shaped, KOH, xerosis, steroids
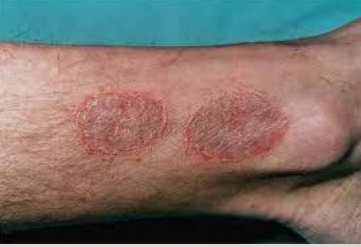
Nummular Dermatitis
-Defined by pruritic oval or _____-_______ plaques on the lower extremities
-___ prep may be helpful in making the diagnosis. You should expect negative results
-Often associated with low humidity, ________, or emotional stress
-Treatment: topical ________ and emollients
medications, nickel, avoidance
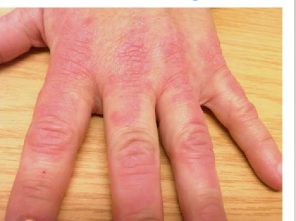
Contact Dermatitis Causative Agents and Treatment
-Certain __________ (neomycin), parabens, dyes, plants, rubber, and _______ are the most common allergens
-____________ of allergen, emollients, or mild corticosteroids
-Presentation may be less severe in geriatric patients because of their decreased ability to mount an immune response
polypharmacy, maculopapular, pruritis, removal
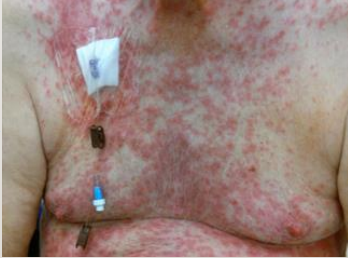
Drug Eruptions
-The elderly are more susceptible because of __________, meaning they take a lot of medications
-Clinical Manifestations: systemic, erythematous, morbilliform, _____________ eruptions. Often associated with _________
-Can happen months or years later OR immediately after taking drug
-Treatment: ________ of offending agent, topical corticosteroids, and oral antihistamines
susceptible, impetigo, scabies, pedis, zoster
Skin Infections in the Elderly
-Elderly are more ___________ to aggressive and life-threatening infections
-Bacterial: ________ and folliculitis caused by staphylococci, as well as cellulitis
-Parasitic: ________, which is overlooked as itching. Be sure to check your patient’s feet
-Fungal: tinea ____ is the most common fungal infection, onychomycosis is also quite common, may see cutaneous candidiasis more often in the elderly
-Viral: most common viral infection is Herpes ______, which causes shingles
reactivation, prodromal, midline, dermatome, neuralgia
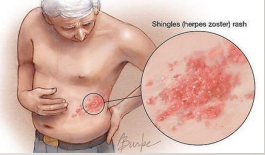
Herpes Zoster aka Singles
-____________ of varicella-zoster virus
-Clinical Manifestation: _________ pain → crops of vesicles on an erythematous edematous base in a unilateral distribution that does not cross the _______. The lesions follow a __________.
-Begin antiviral treatment within 72 hours to decrease the likelihood of post-herpetic _________ (PHN)
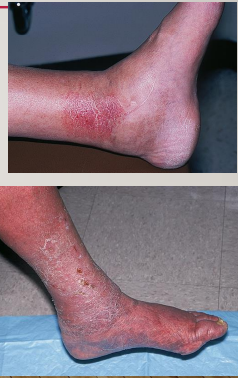
Stasis Dermatitis
eczema due to venous insufficiency
-pruritic erythematous lesions/scales in the lower extremities of patients with chronic, dependent edema.
-more common in patients with DM or arteriosclerosis
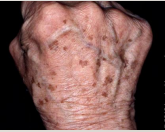
Seborrheic Keratosis
benign tumor of epithelial origin
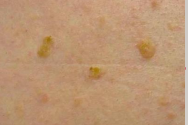
Solar letigines (sun spots)
hyperpigmented macules on sun exposed areas of fair skinned people
Basal Cell Carcinoma
most common skin malignancy