WSU Bio 315 Lab Exam 3
1/386
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
387 Terms
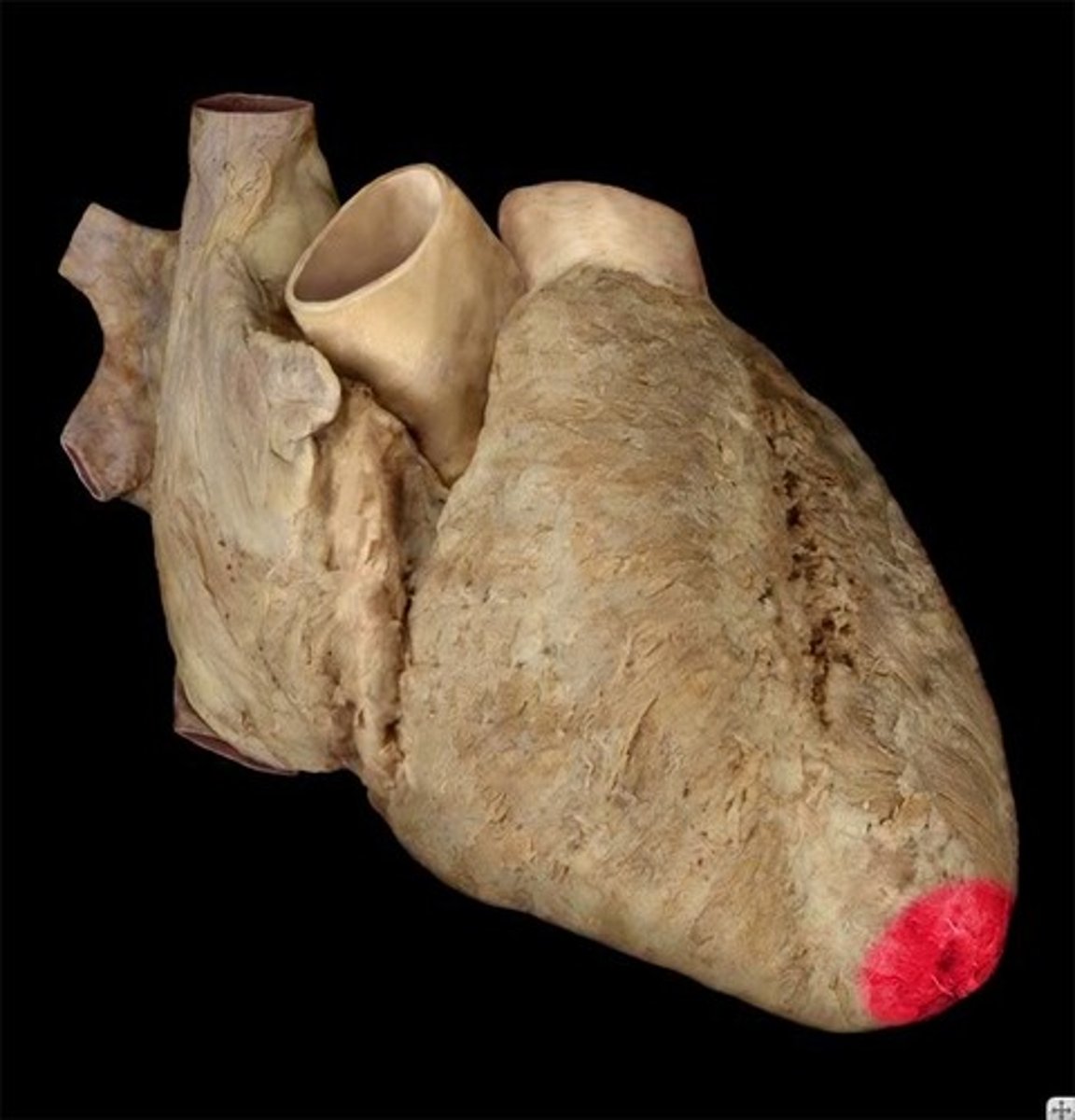
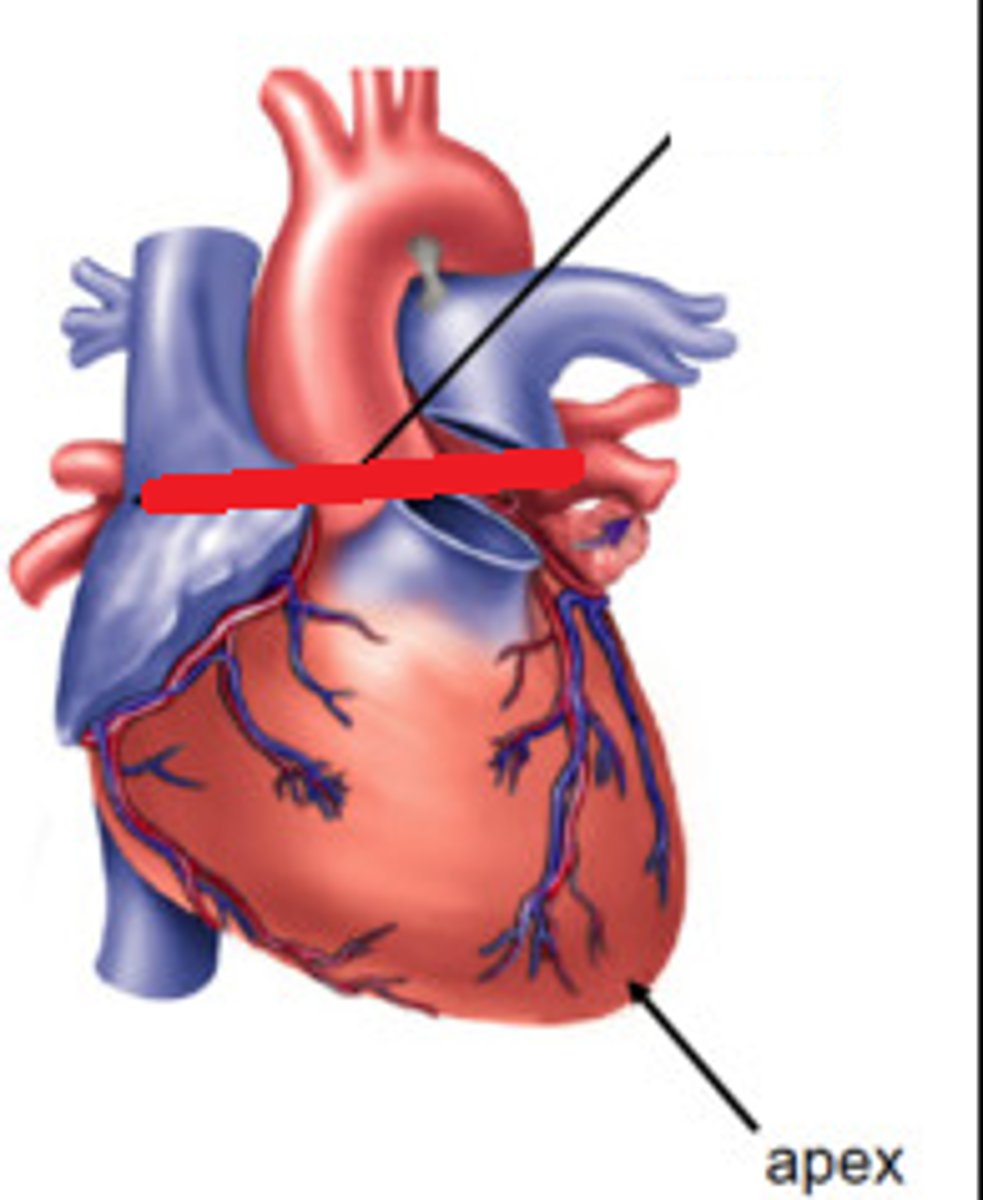
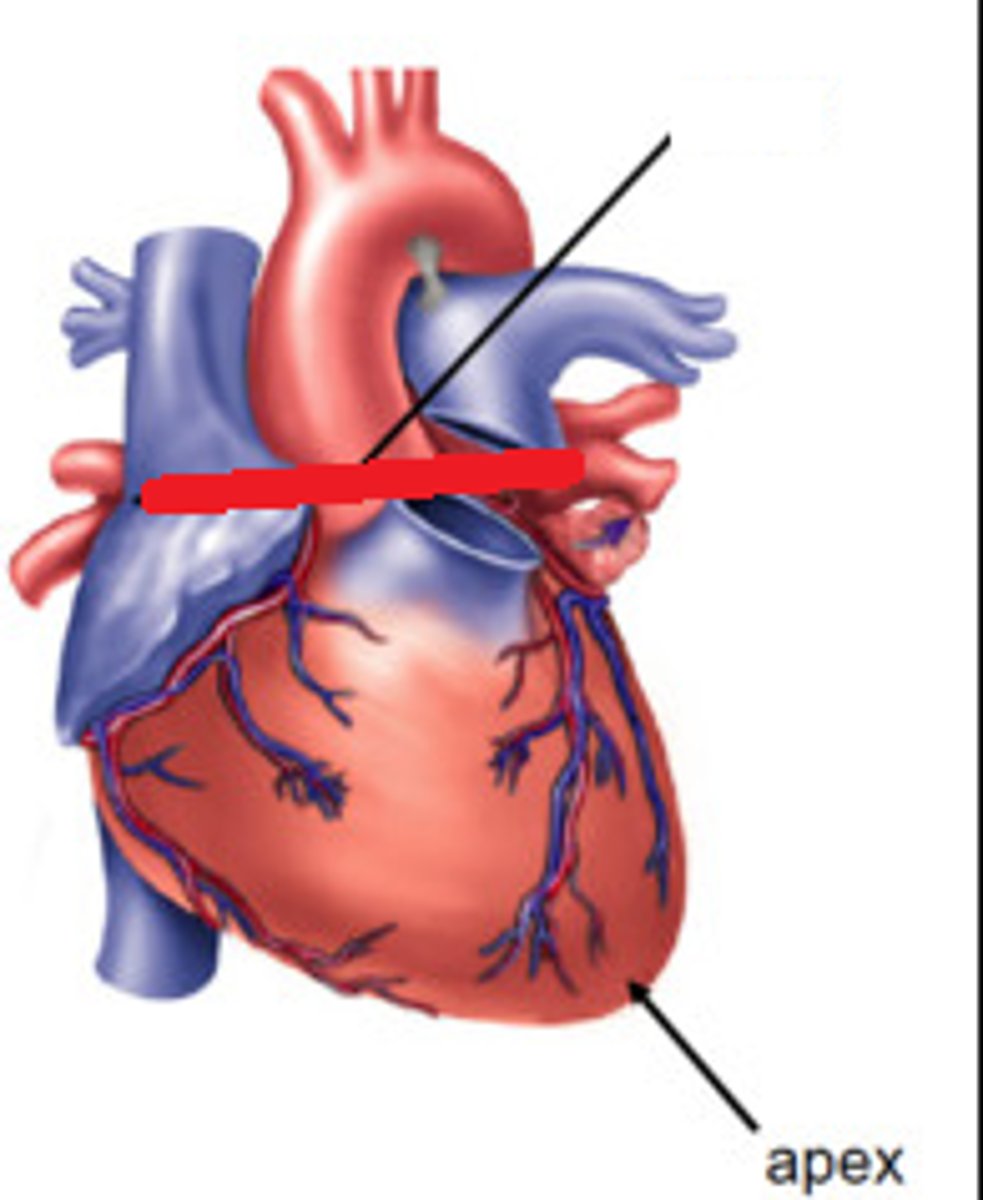
Apex of the heart
lower tip of the heart (feature)
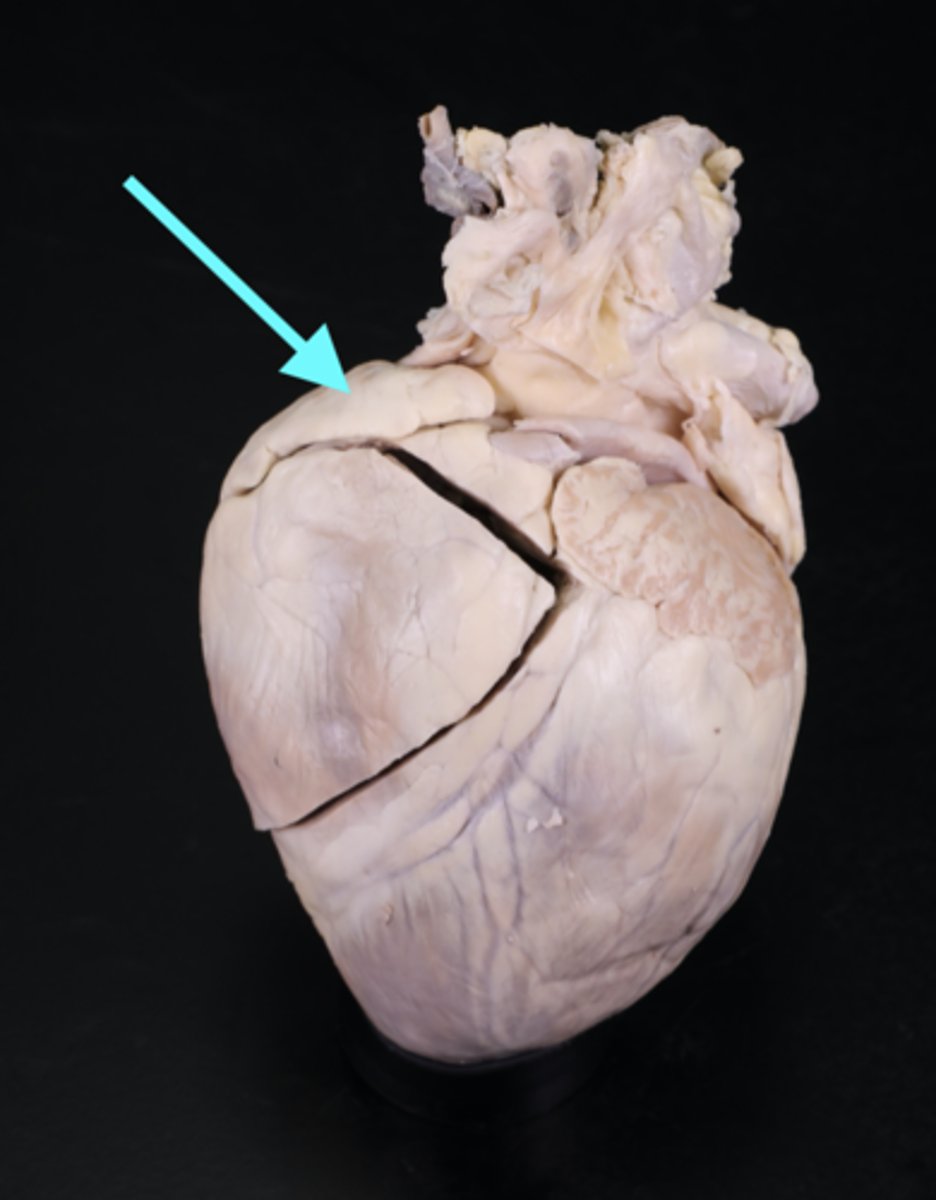
Base of heart
faces posterior of the apex. formed by the left atrium (feature)
Right atrium of heart
top angle on right side
Right auricle of the heart
above the right atrium, black numb
Left atrium of the heart
left side top part
Right ventricle
Right Lower chamber of the heart
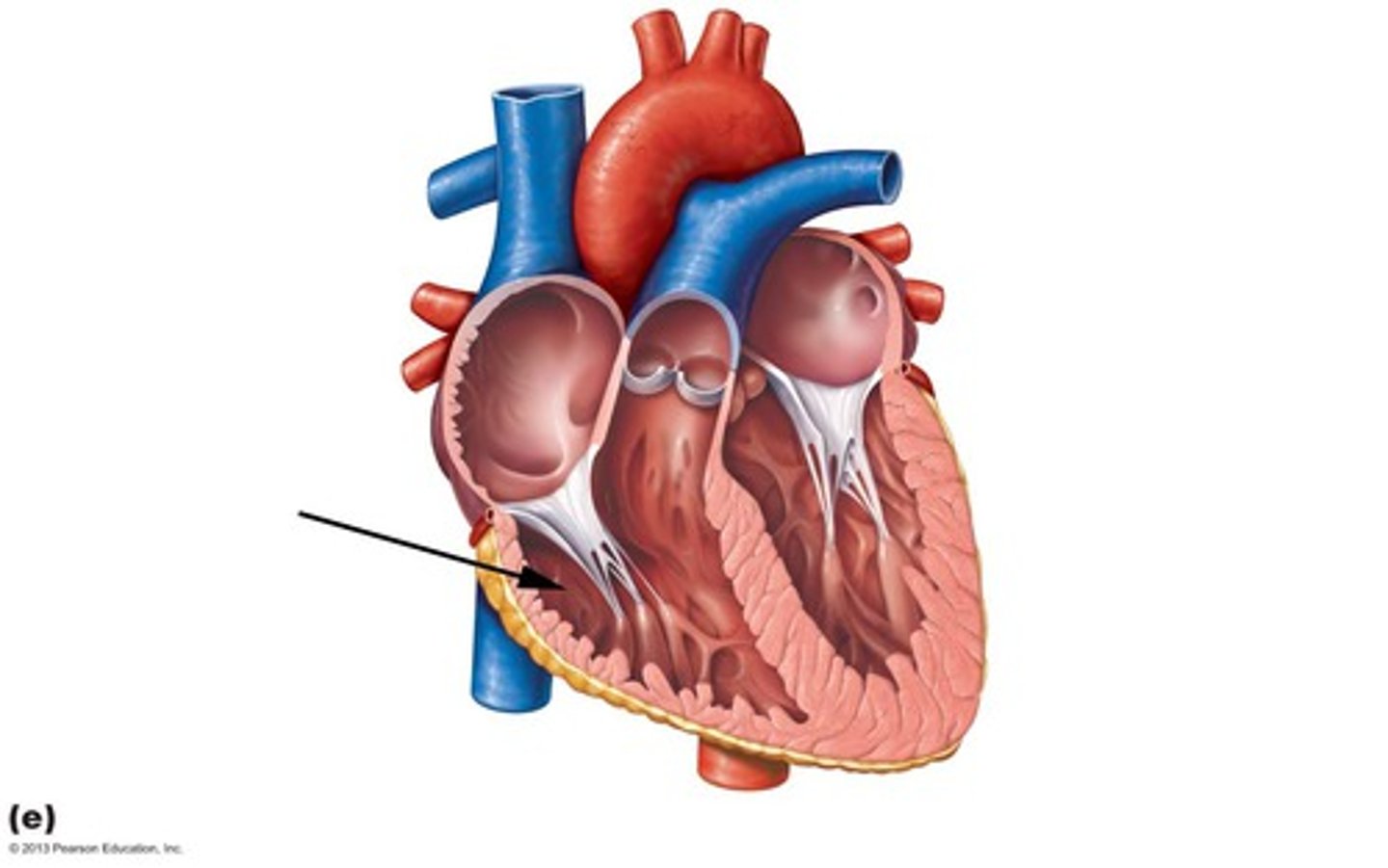
left ventricle
left lower chamber of the heart
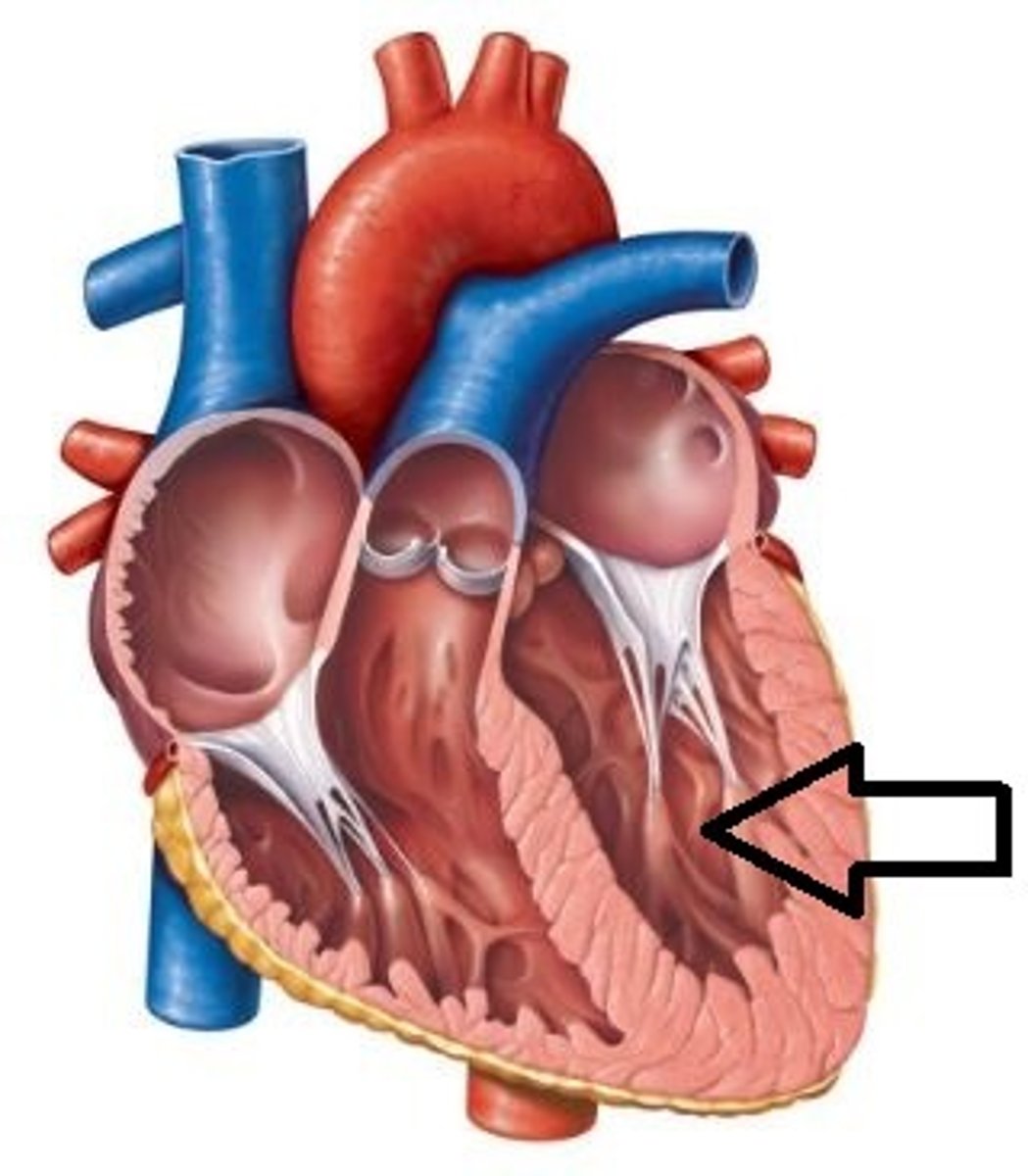
anterior surface of the heart
Formed mainly by the right ventricle (region)
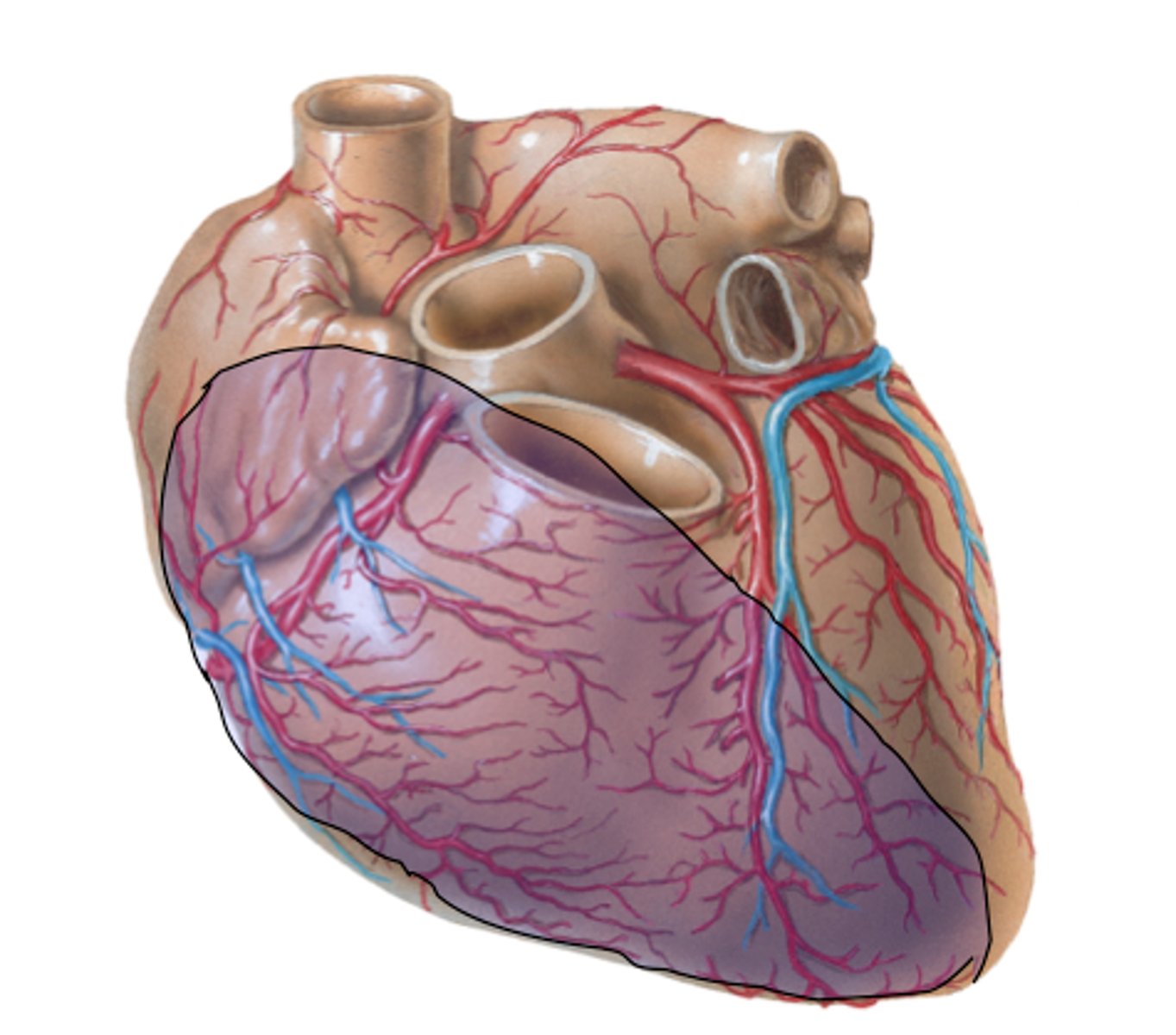
diaphragmatic surface of the heart
Formed by left and right ventricles. Sits on the diaphragm. Posterior view
right and left pulmonary surfaces of the heart
face the lungs. formed by right atrium and left ventricle, respectively.
Opposite when looking at anterior side
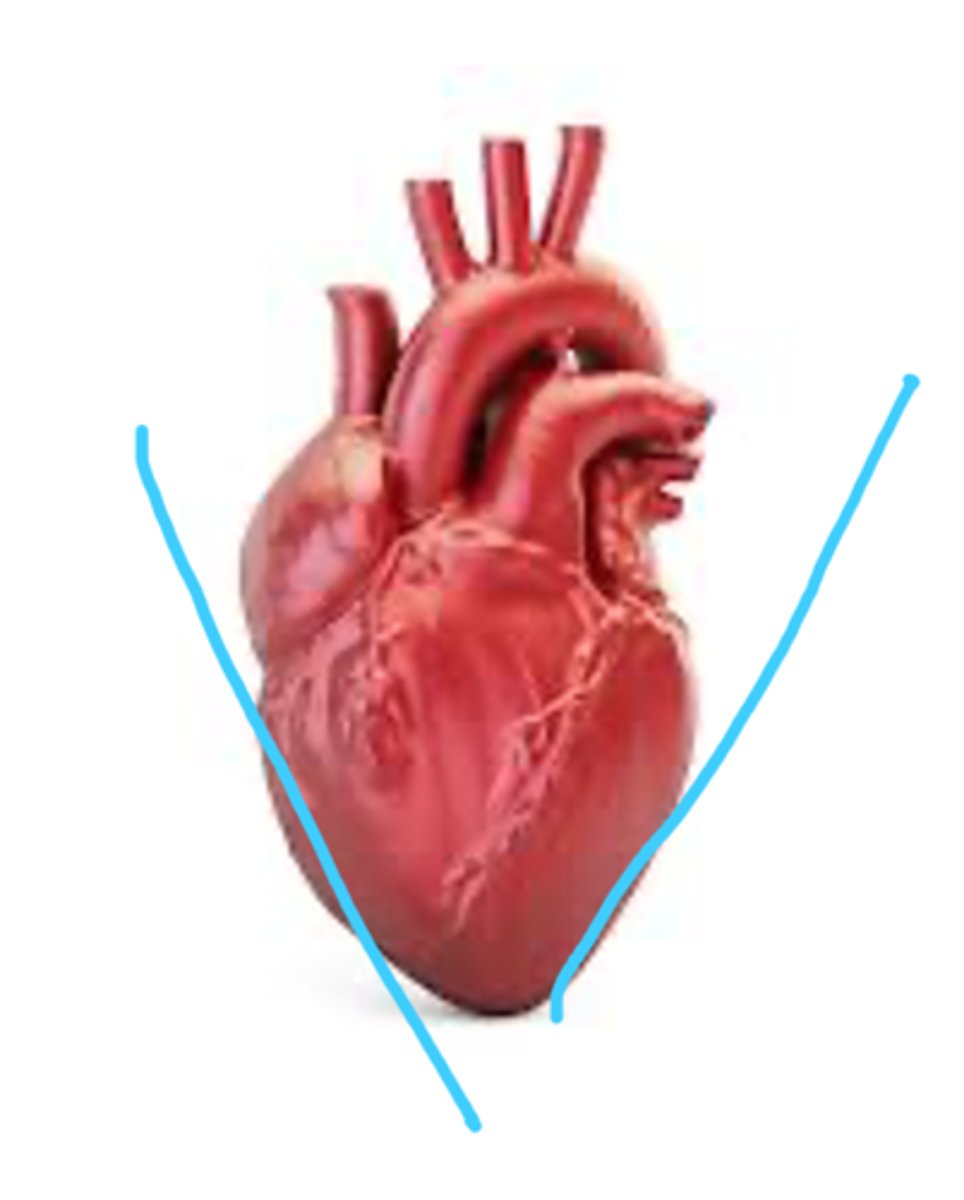
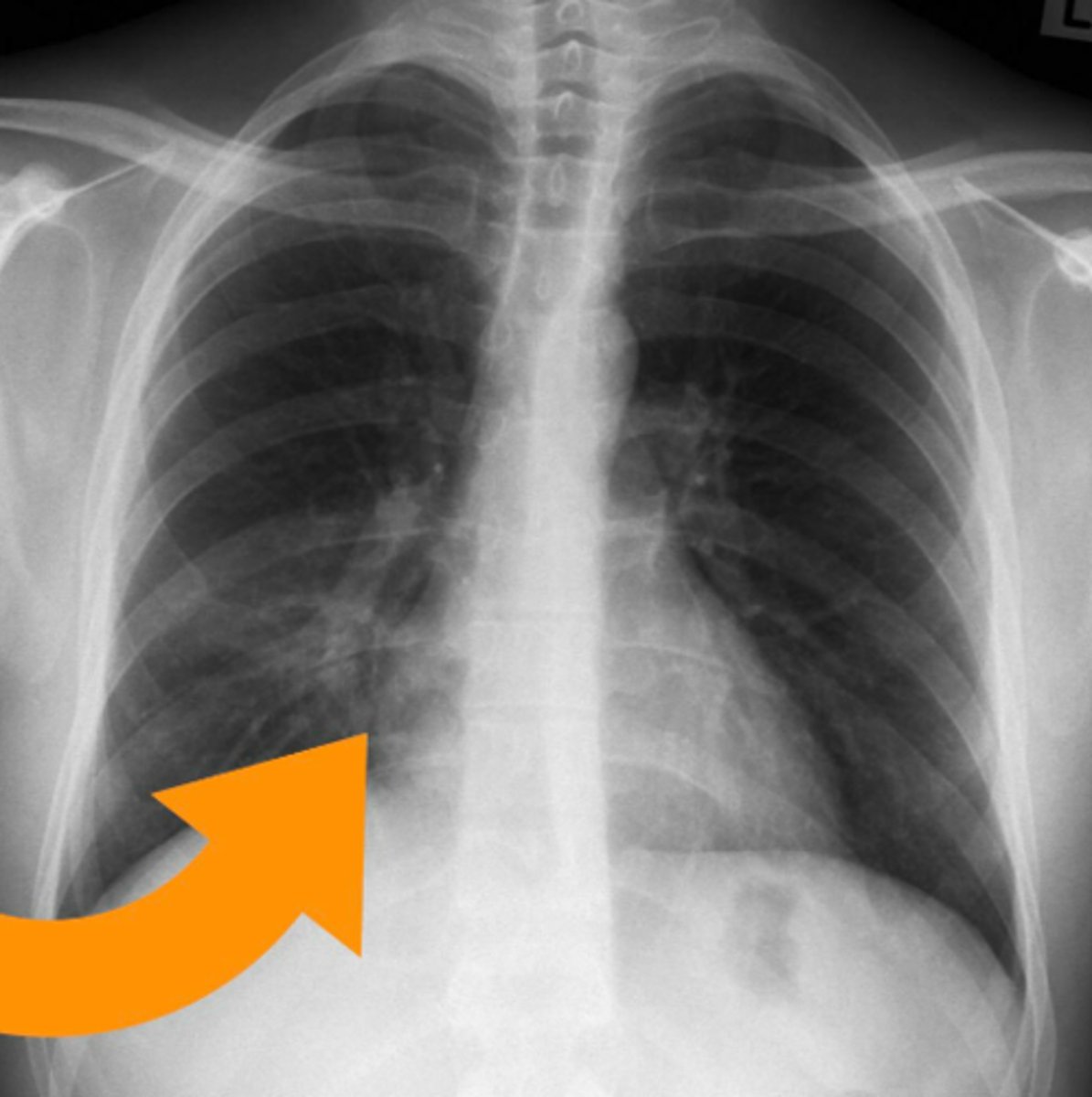
right boarded of the heart
convex shape, formed by right atrium (on x-ray)
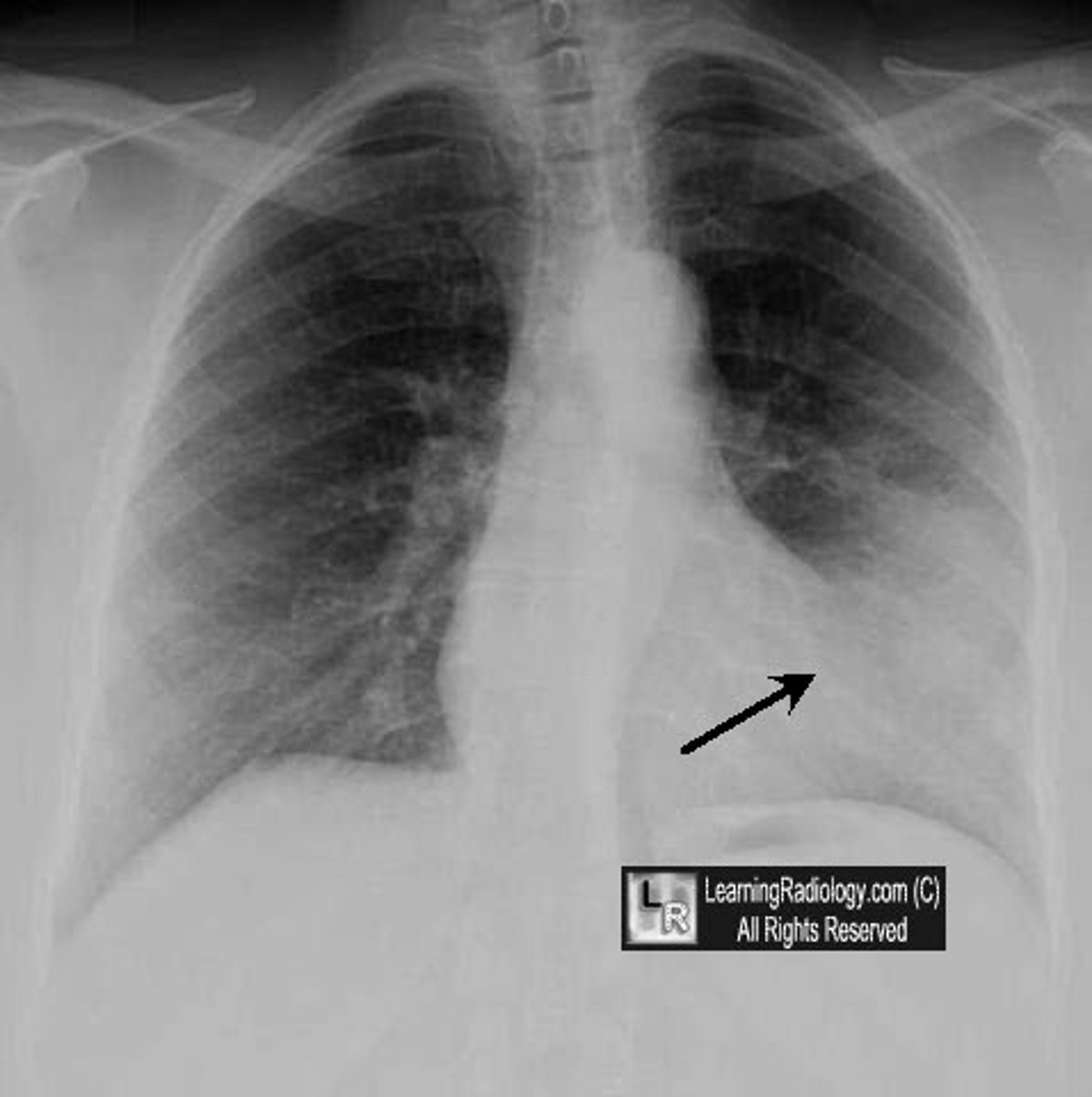
left boarder of the heart
almost vertical, formed mainly by the left ventricle (on x-ray)
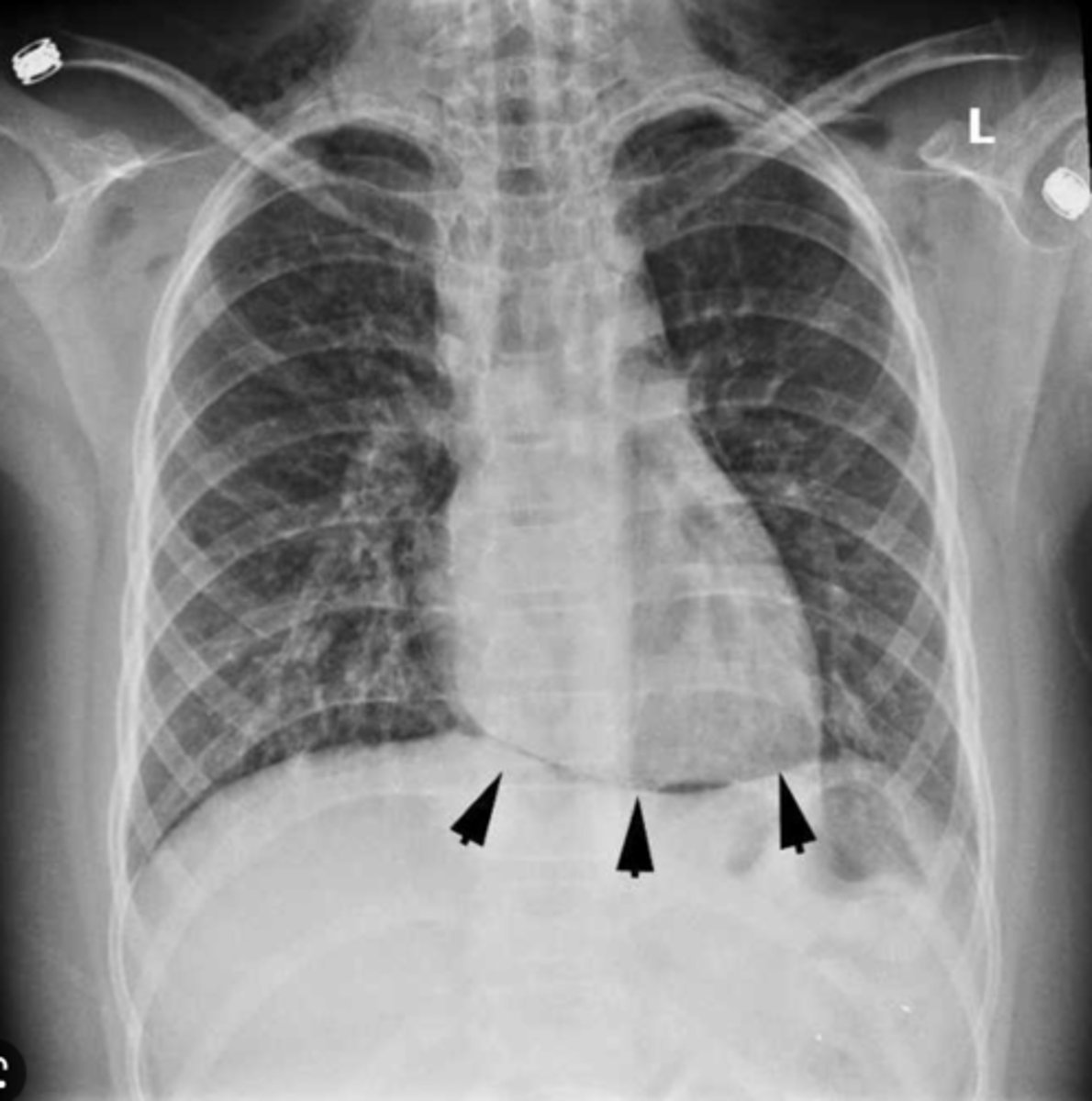
inferior boarded of the heart
horizontal, formed mainly by right ventricle (on x-ray)
superior boarder of the heart
boarder above the heart (on x-ray)
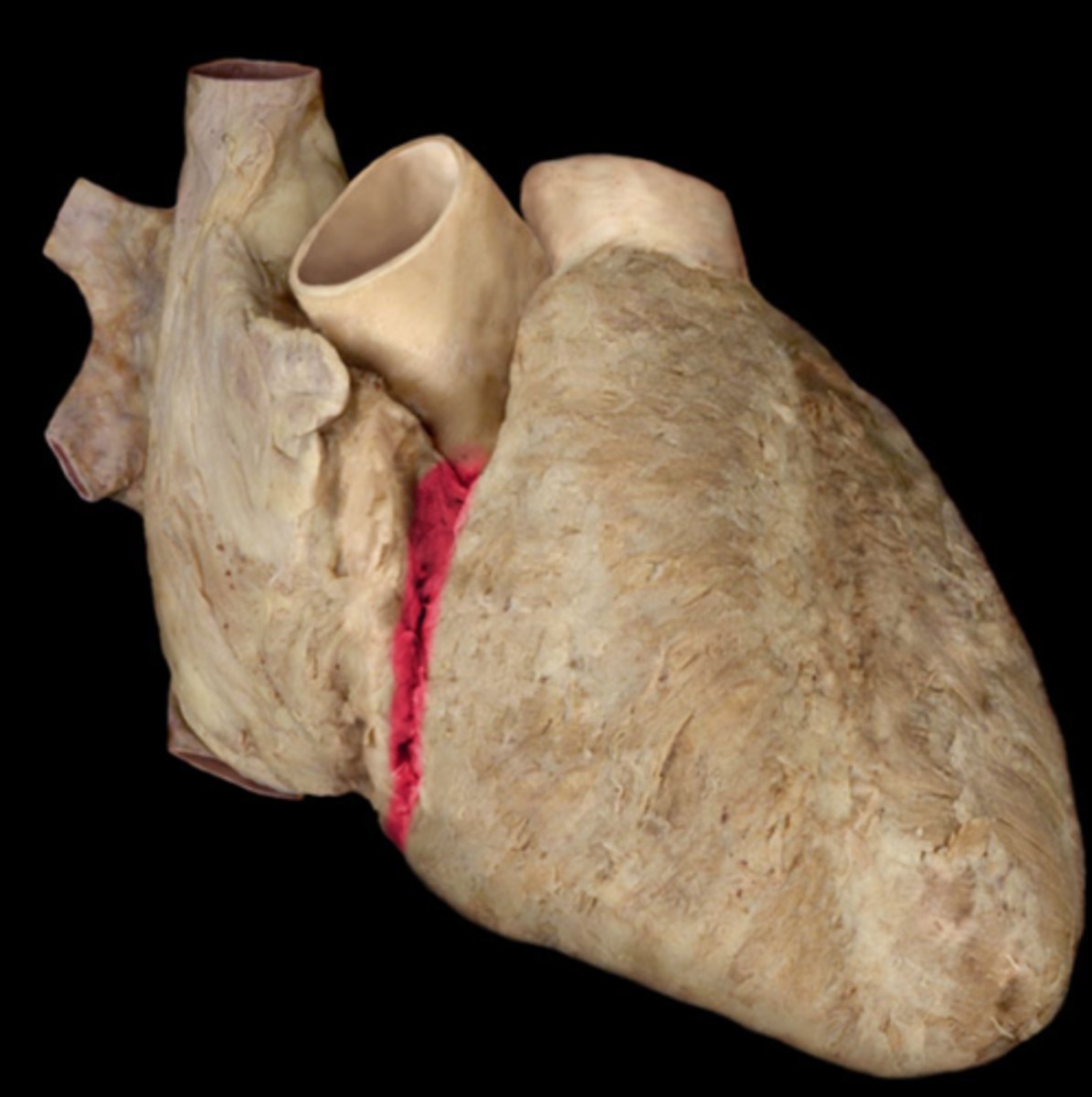
coronary sulcus
marks the junction of the atria with the ventricles (depression)
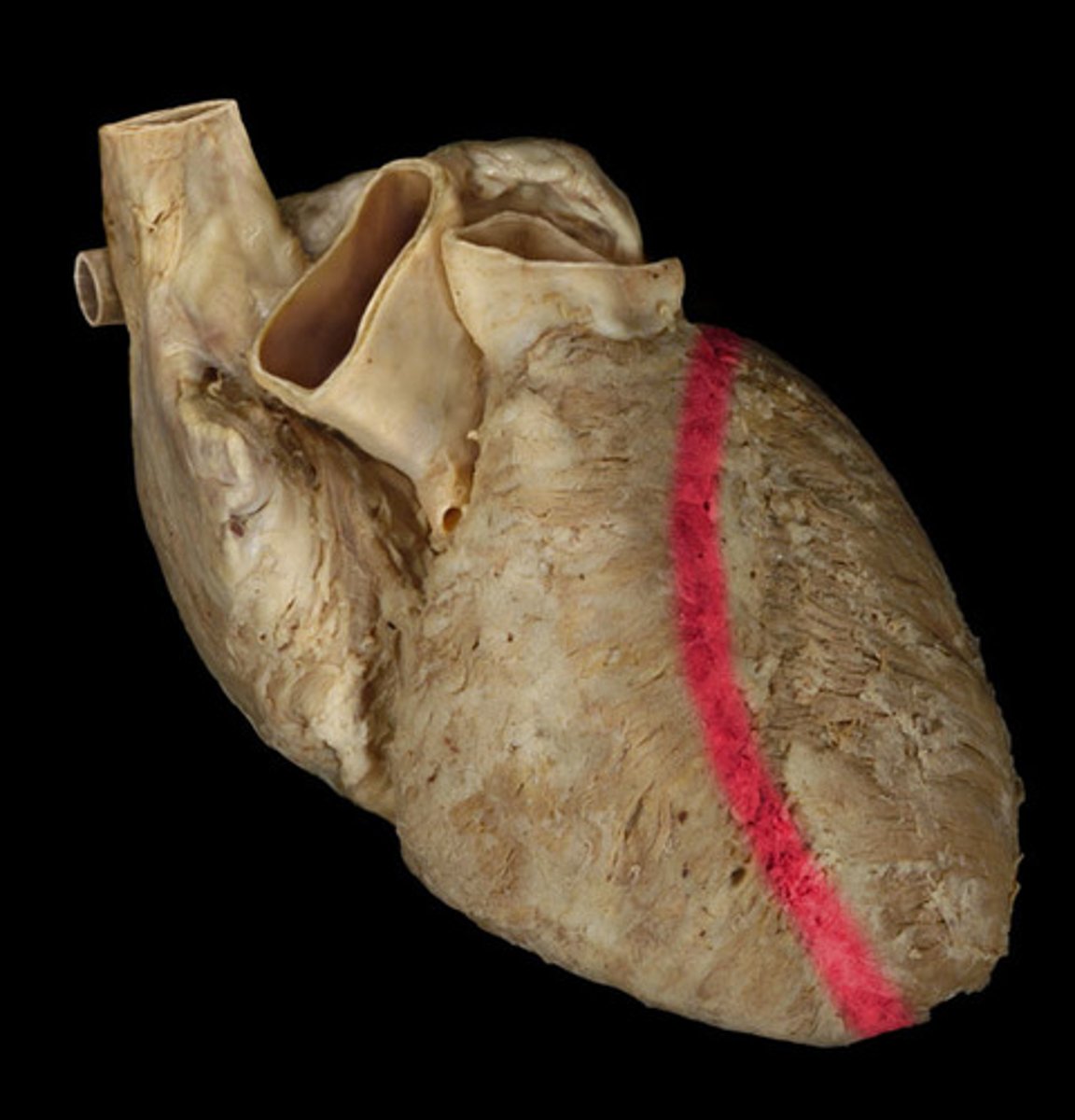
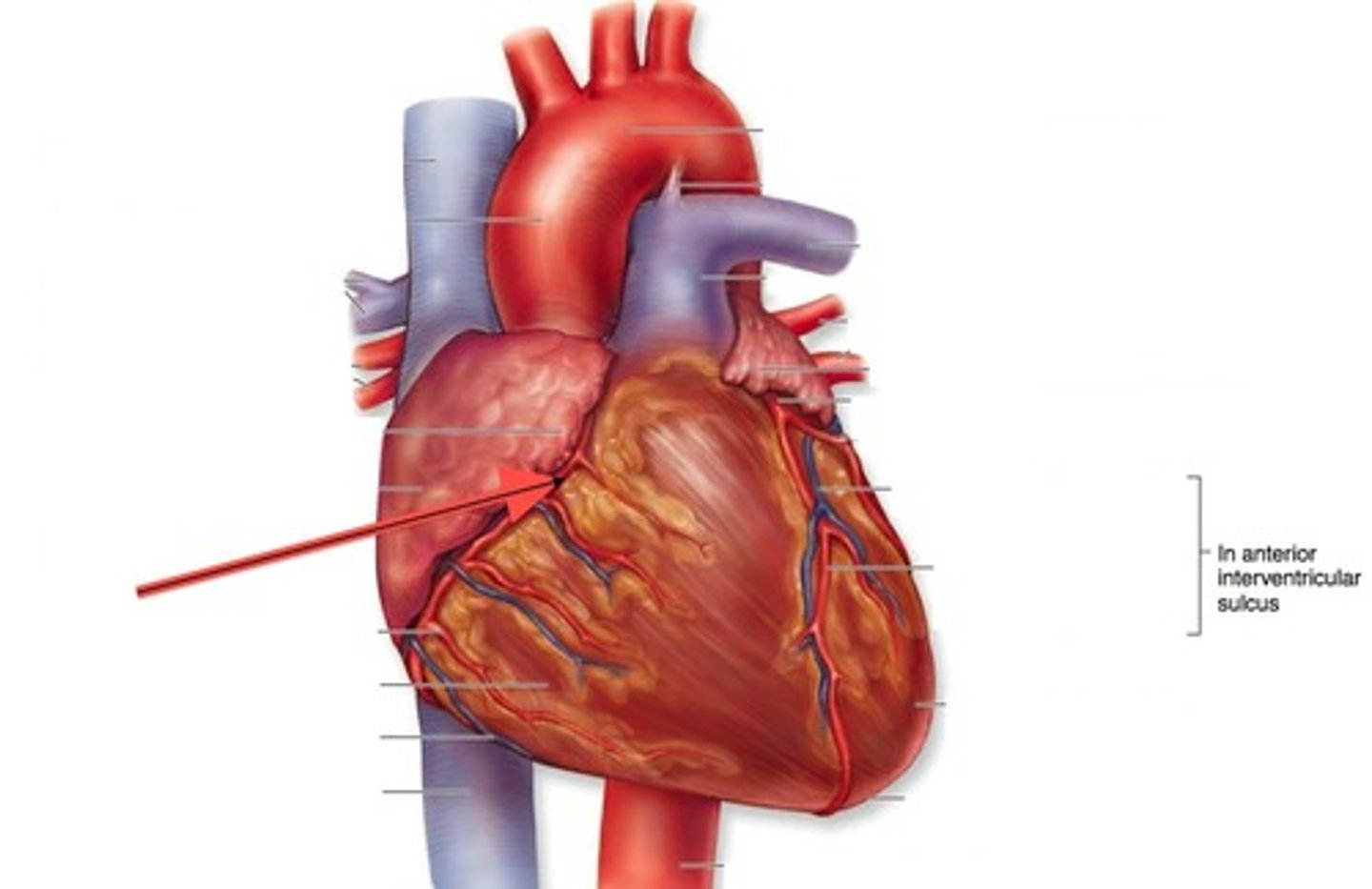
anterior interventricular sulcus
the junction between right and left ventricles
anterior side (depression)
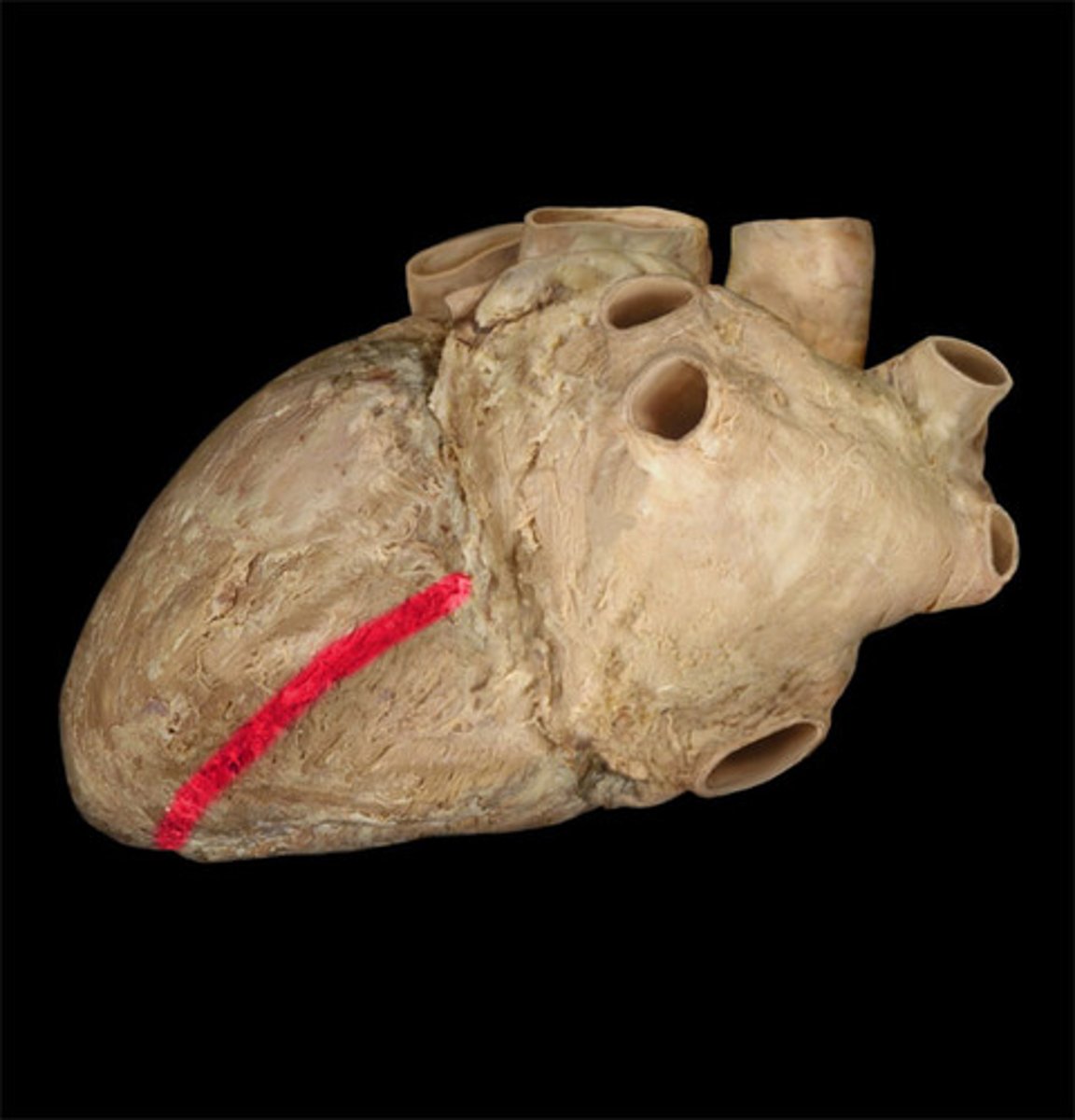
posterior interventricular sulcus
marks the boundary between the ventricles posteriorly
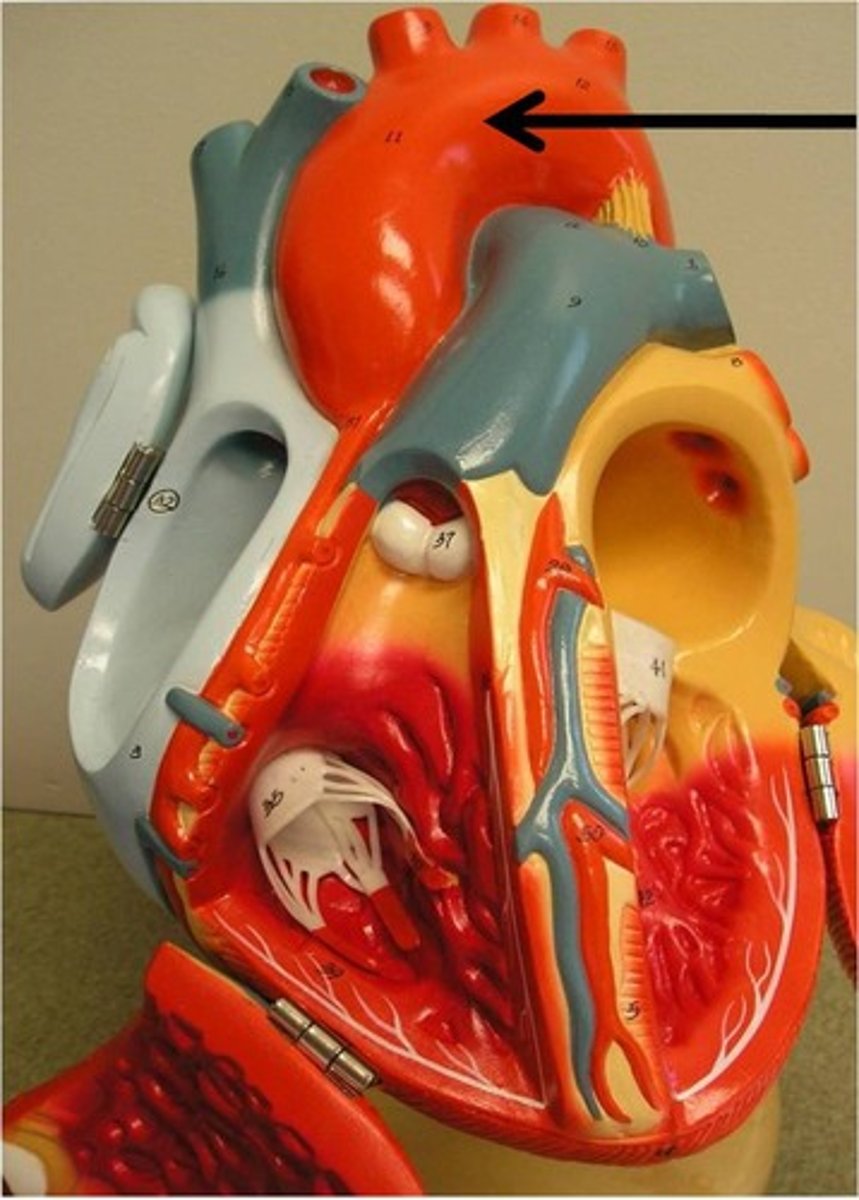
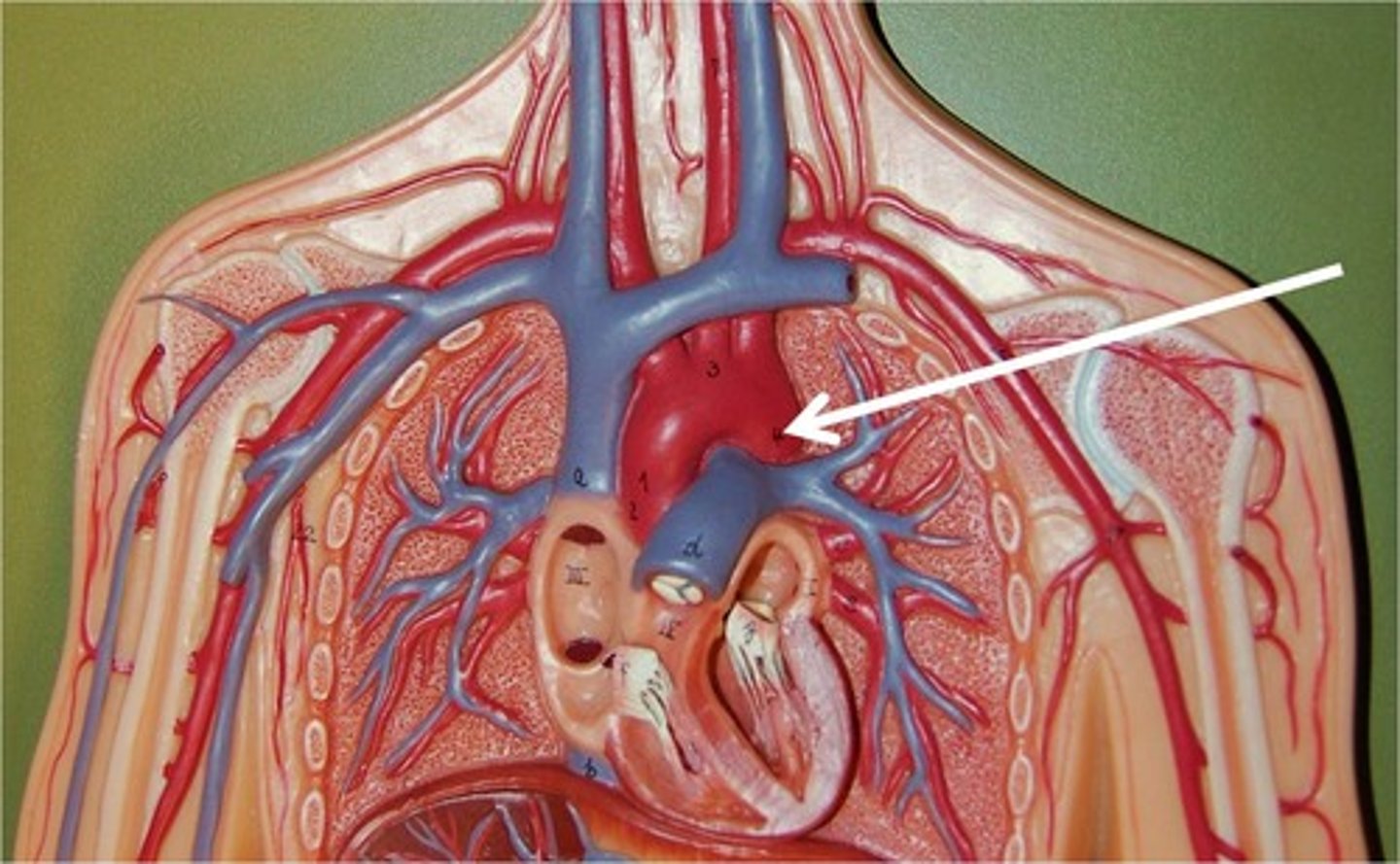
aorta
leaves the left ventricle
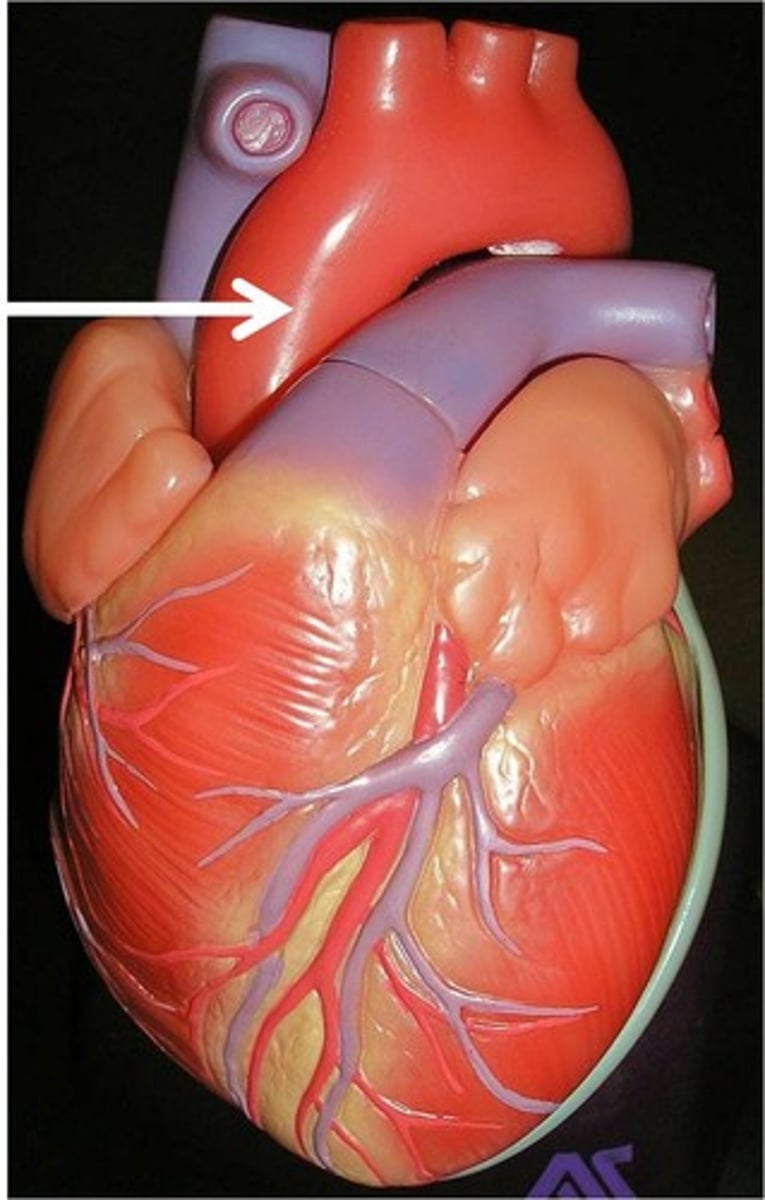
acending aorta
right side, going up (portion)
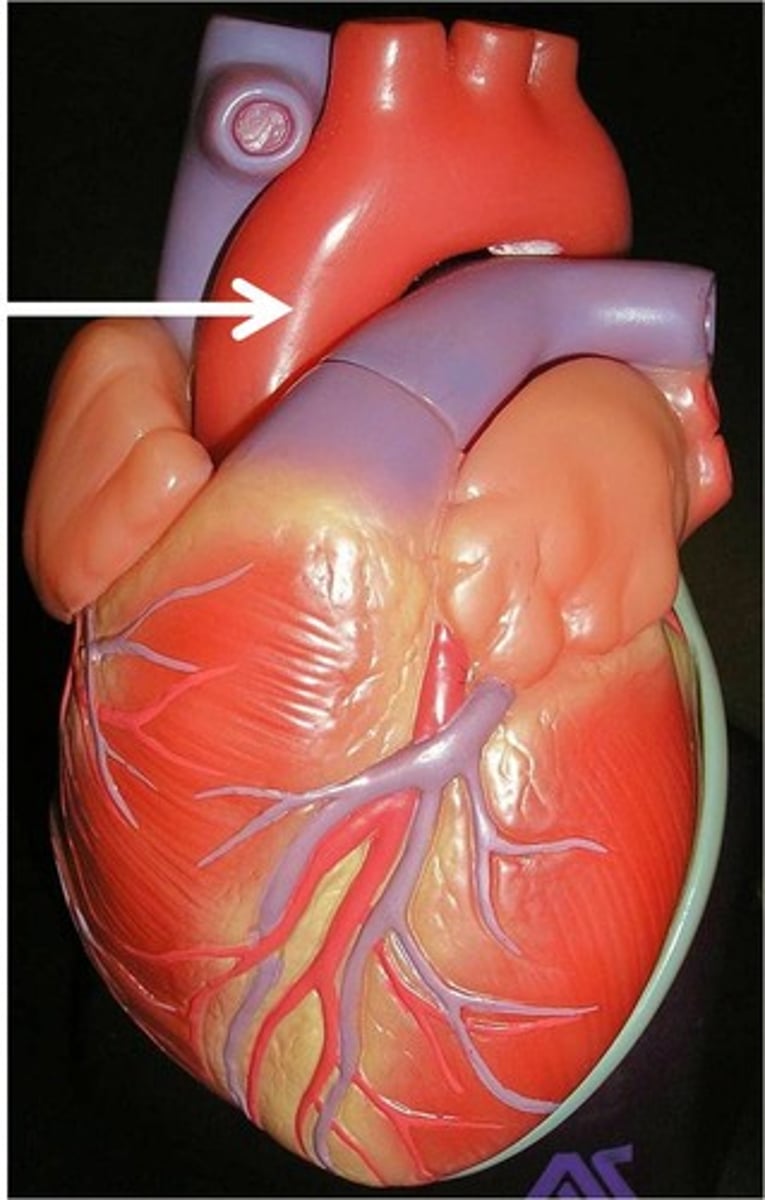
arch of aorta
'C' shape, arching over
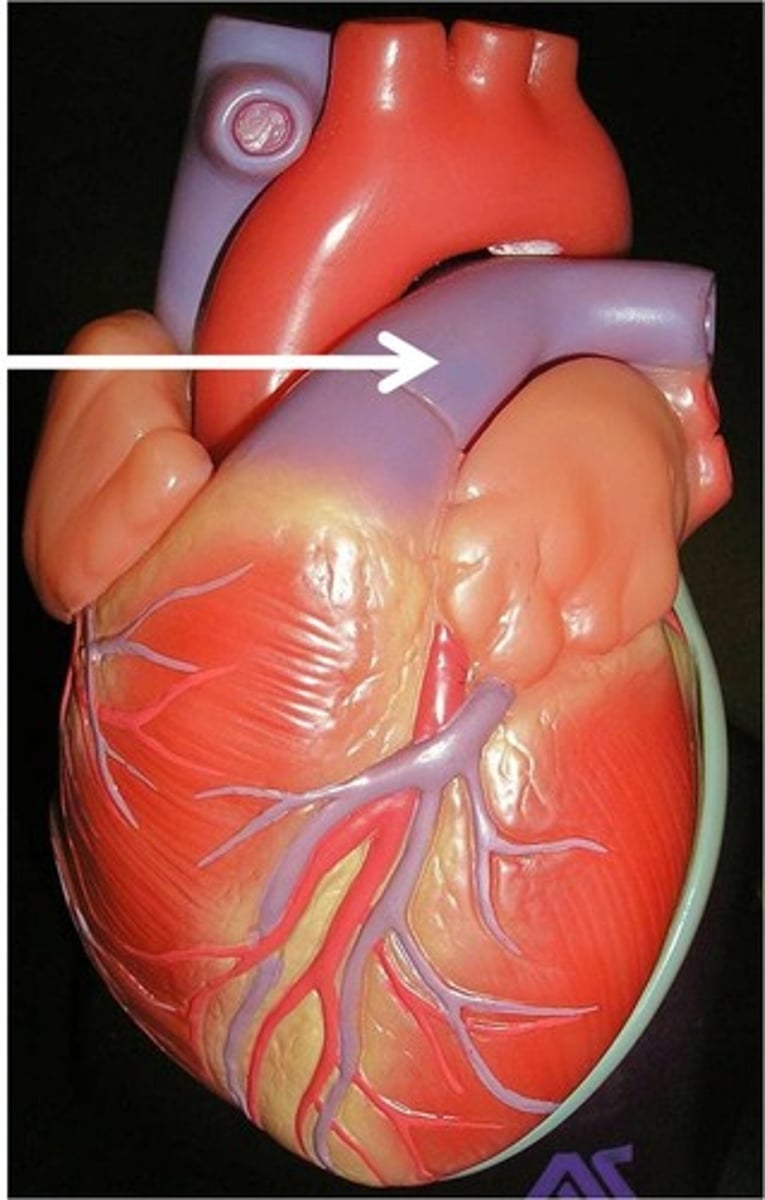
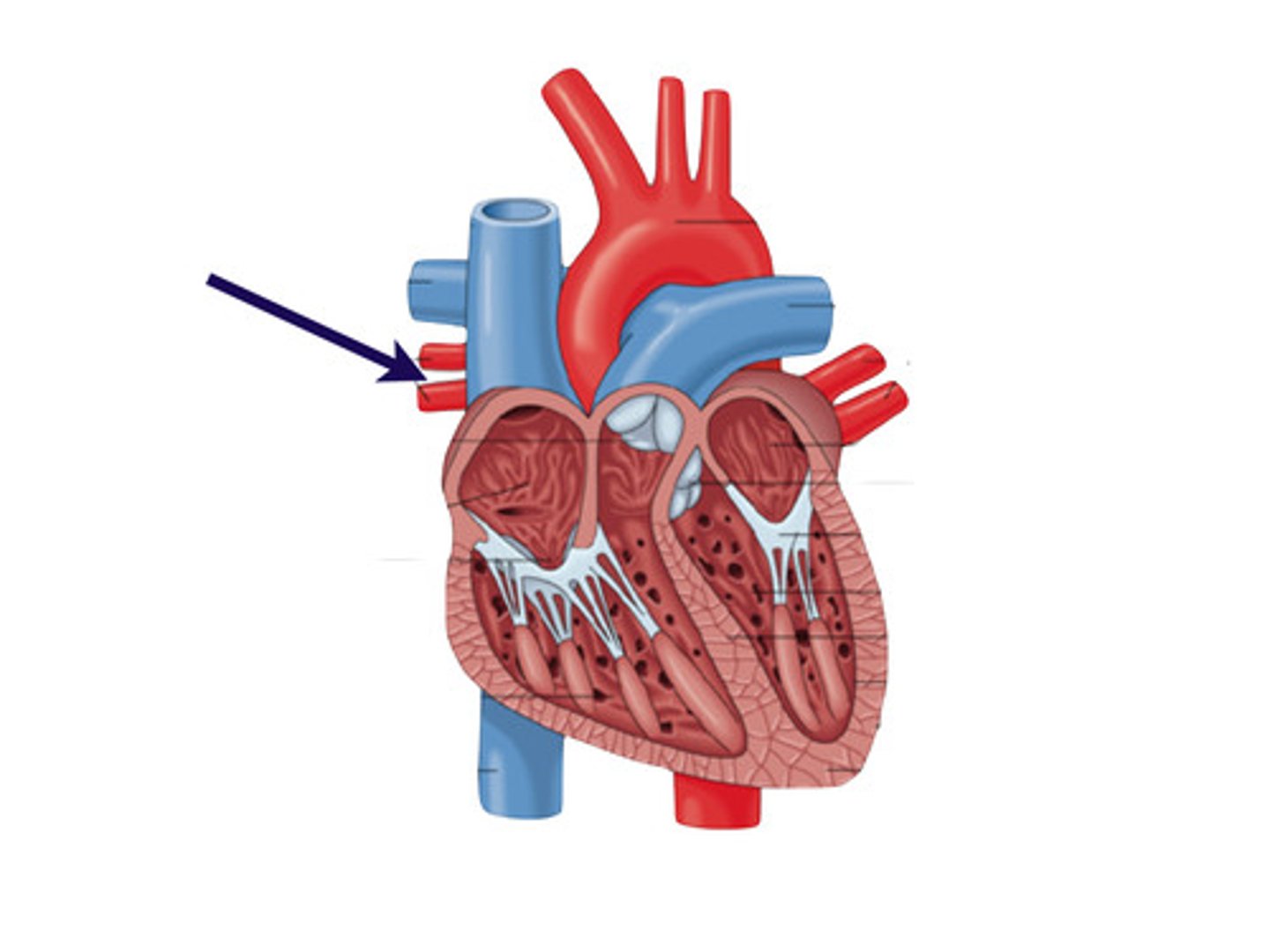
pulmonary trunk
leaves the right ventricle (collective structure)
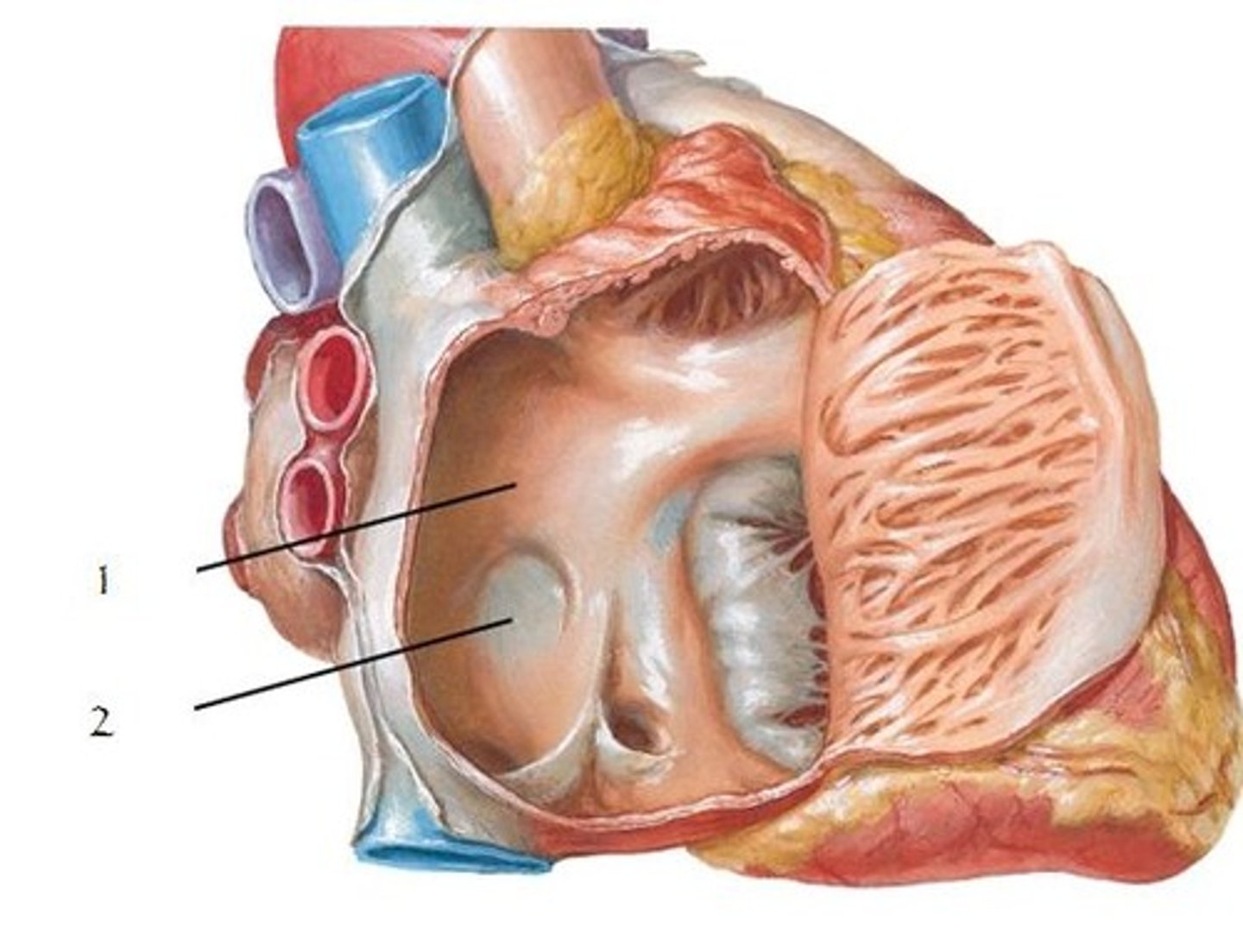
left pulmonary artery
Identify the vessel
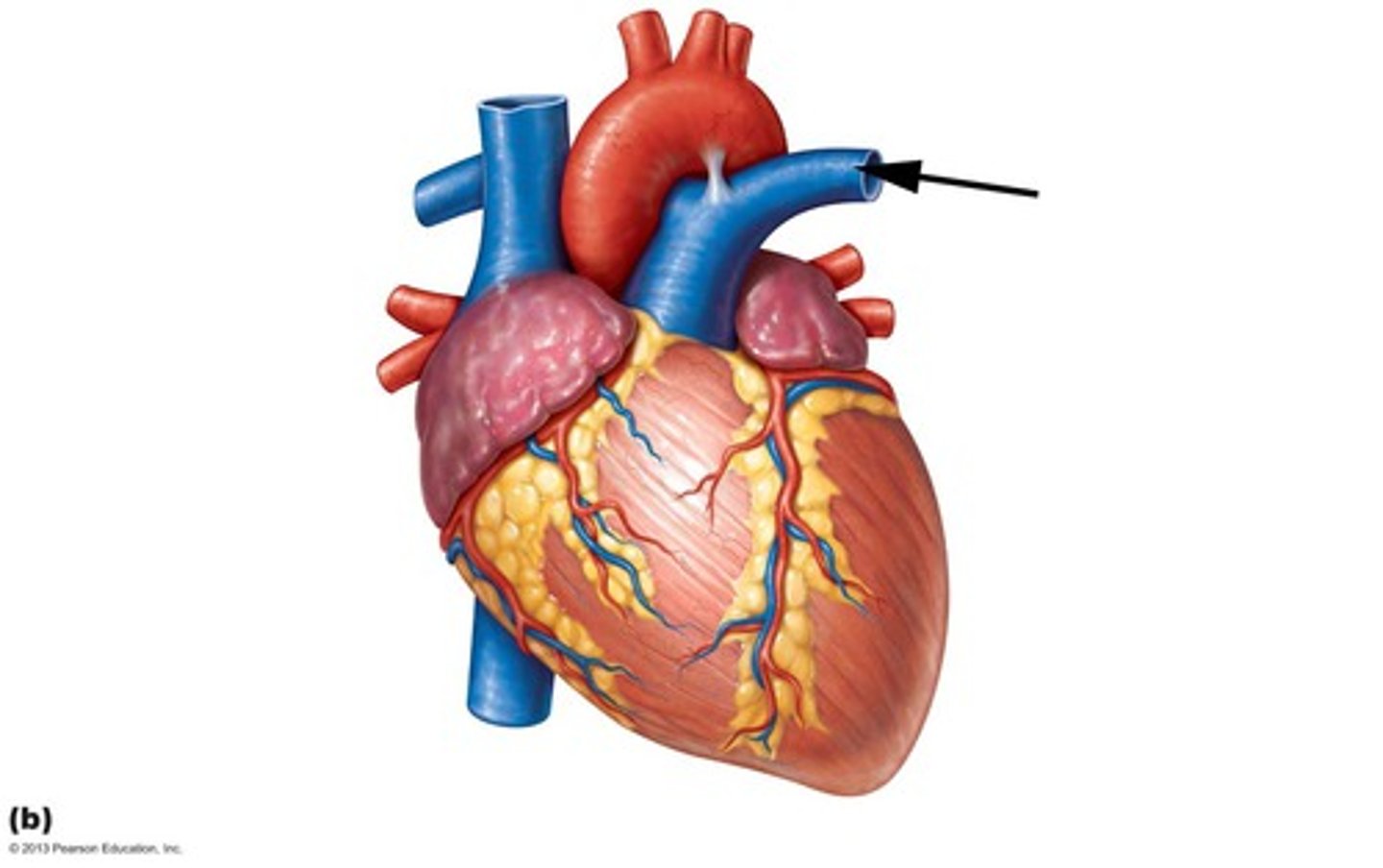
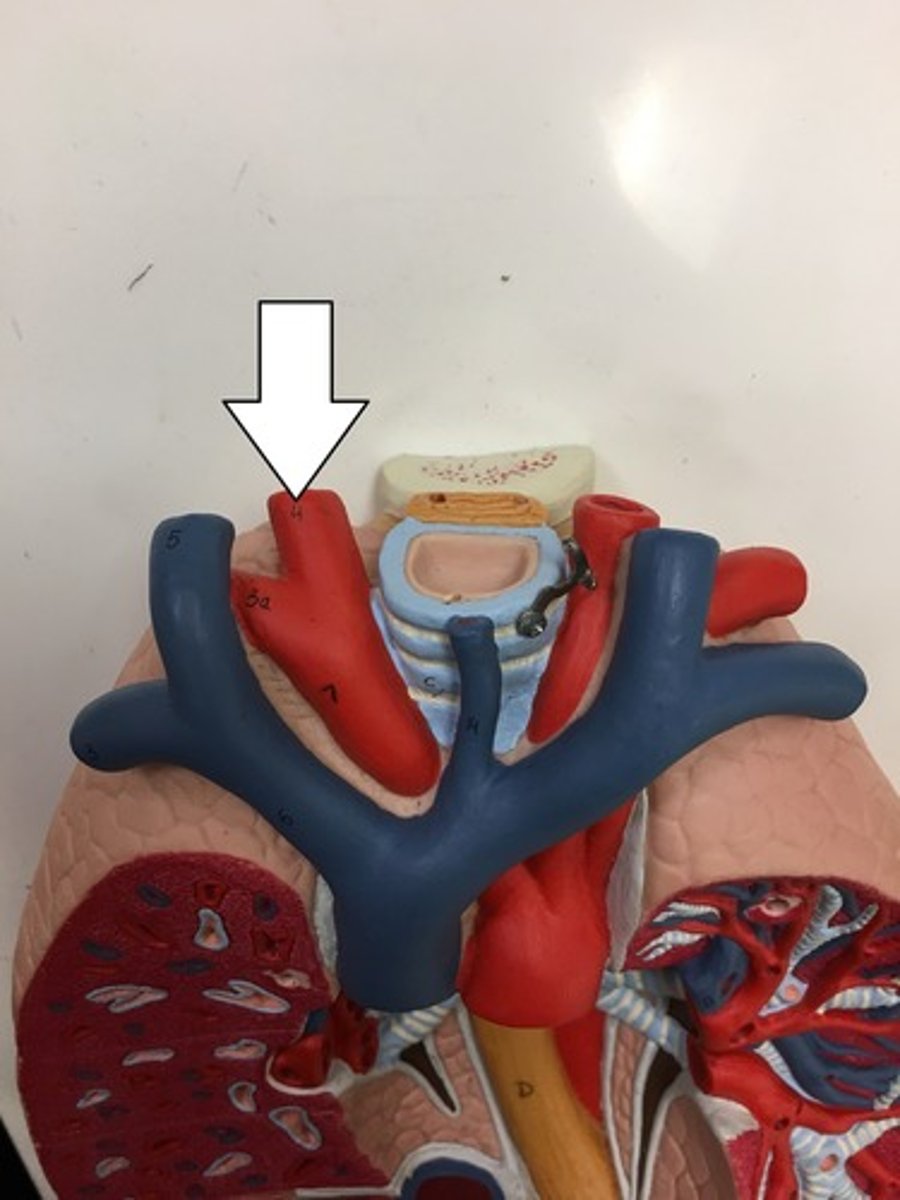
right pulmonary artery
Identify the vessel
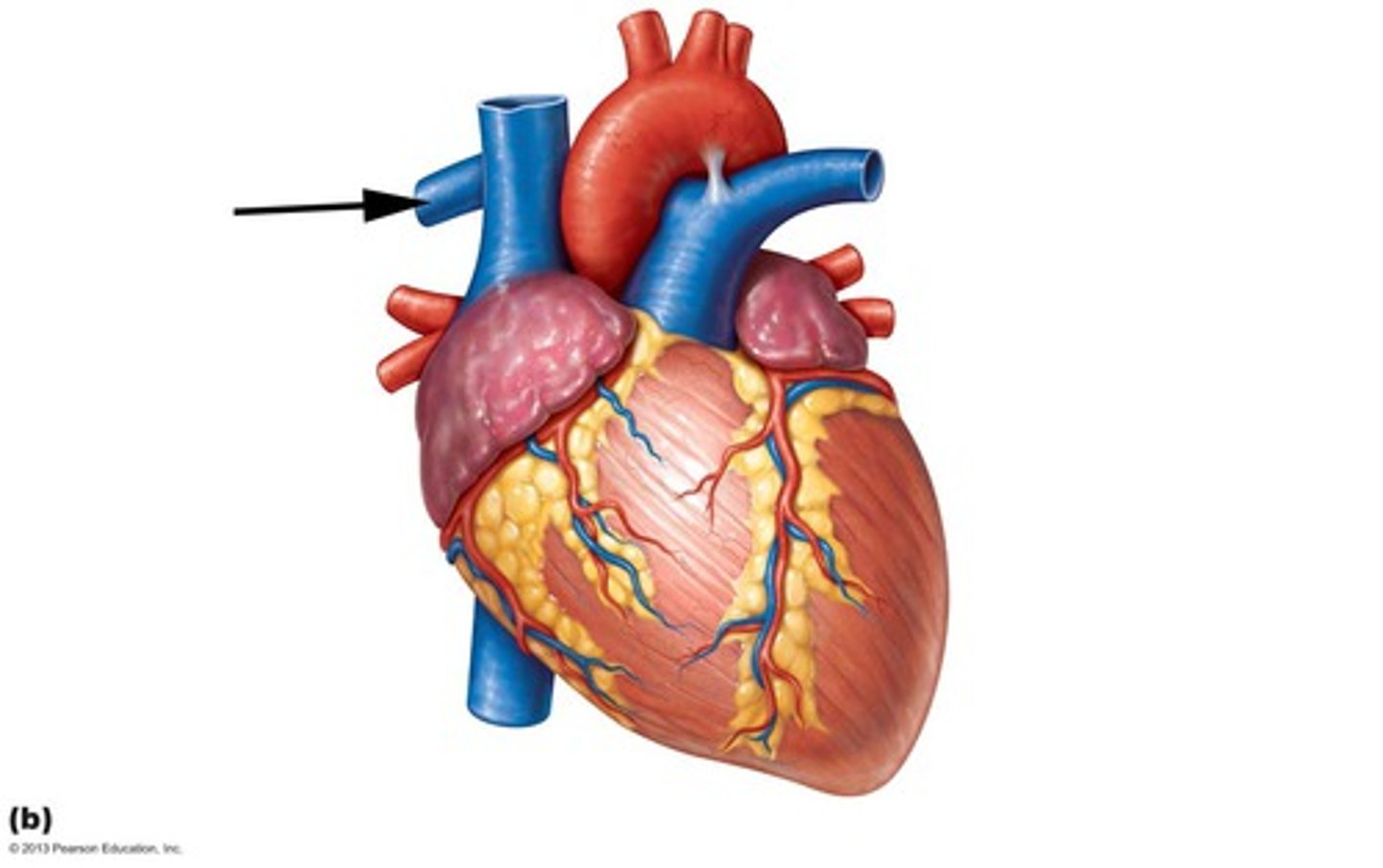
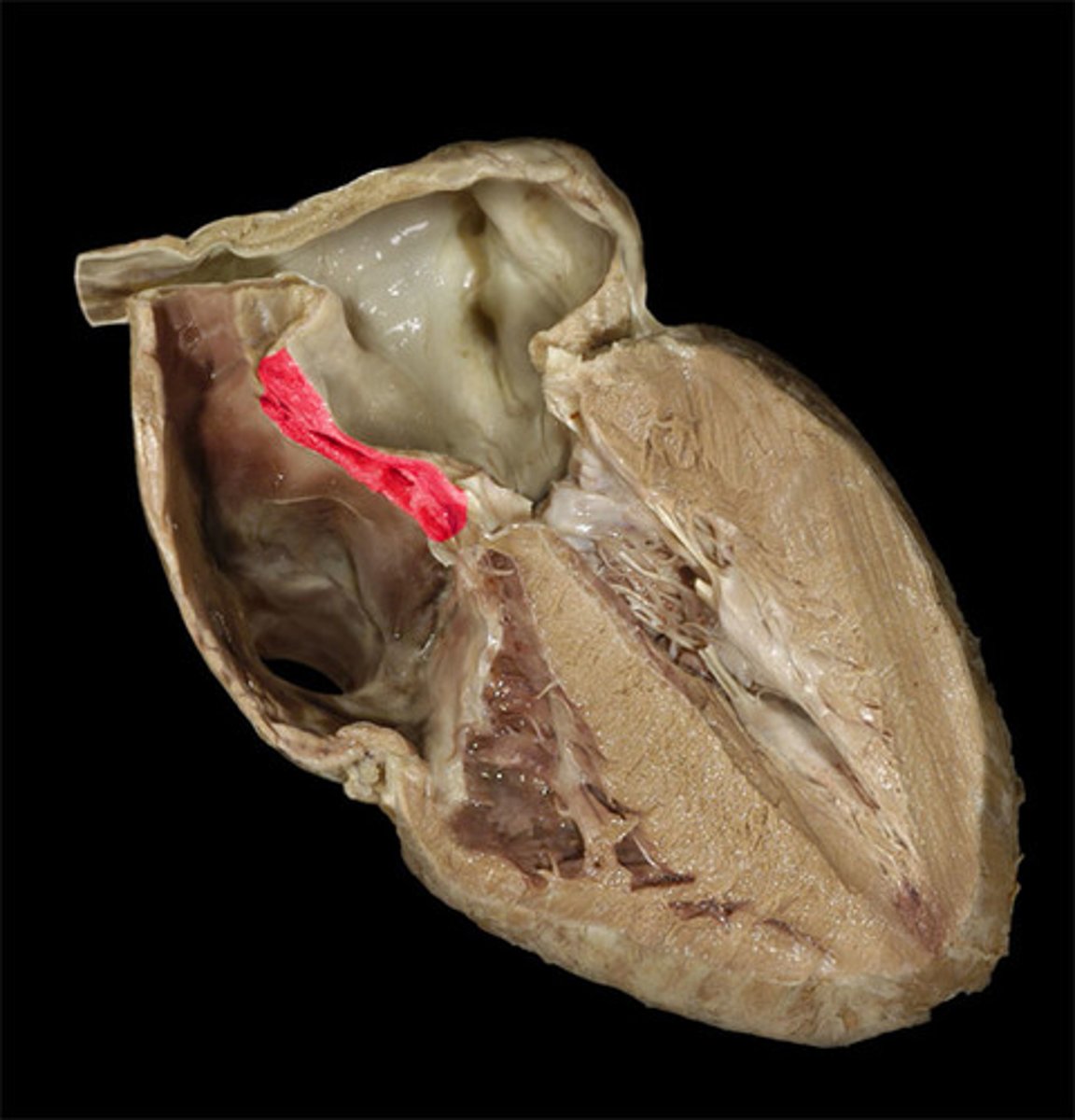
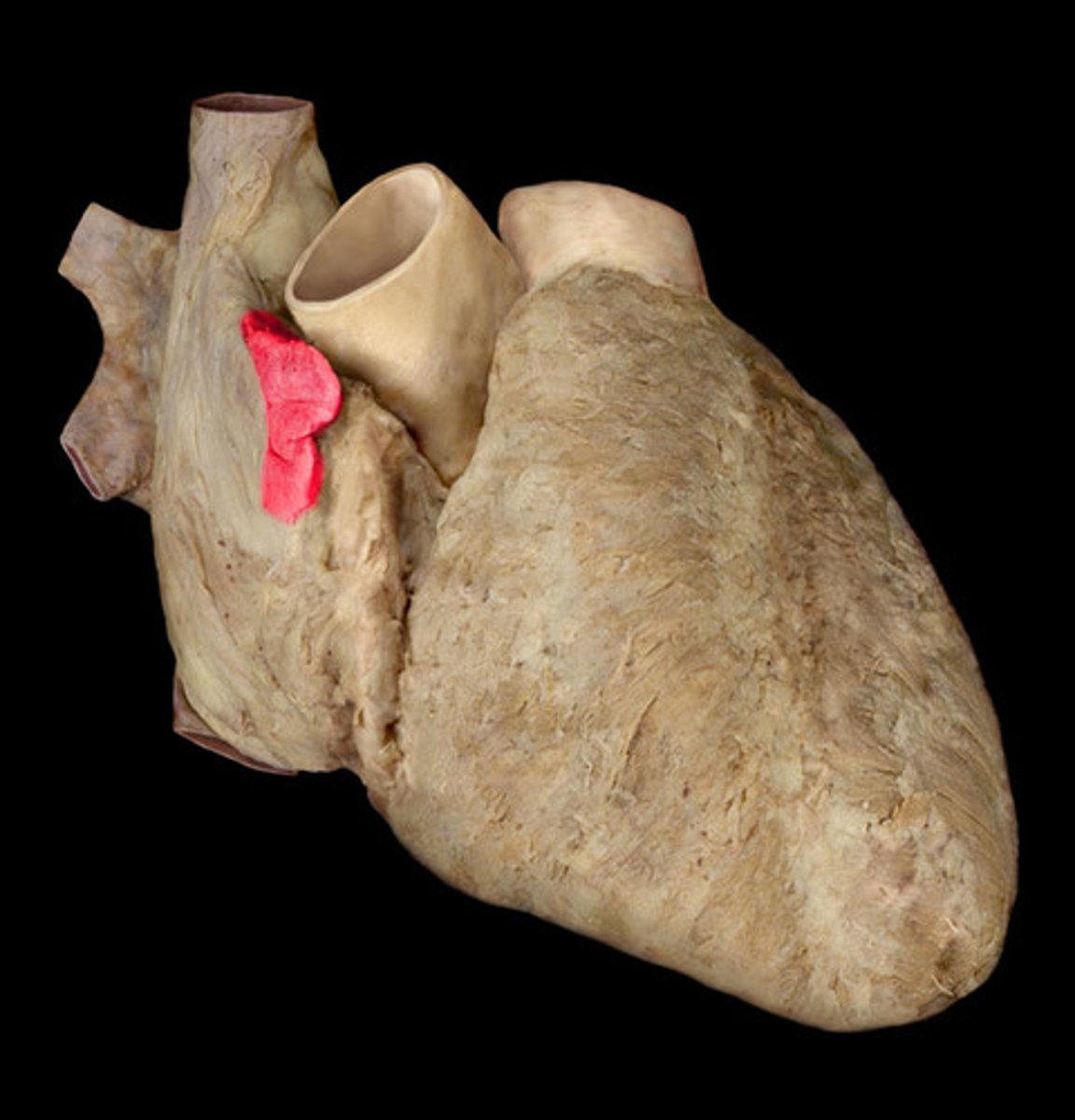
ligamentum arteriosum
vestige of the fetal ductus arteriosus, which shunted blood in the pulmonary trunk away from the lungs in the fetus
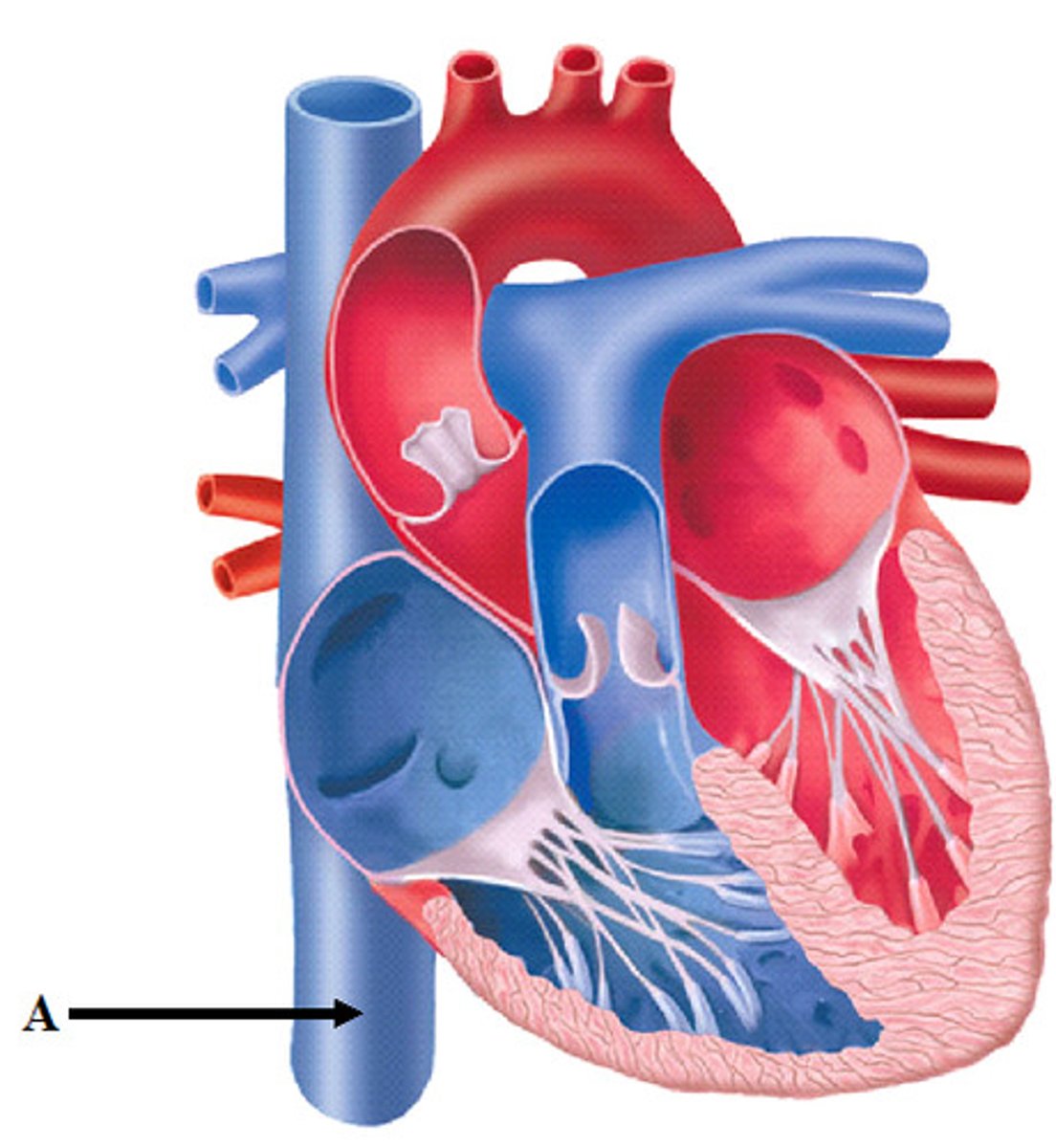
superior vena cava
the vena cava drain into the right atrium
posterior side, upper part
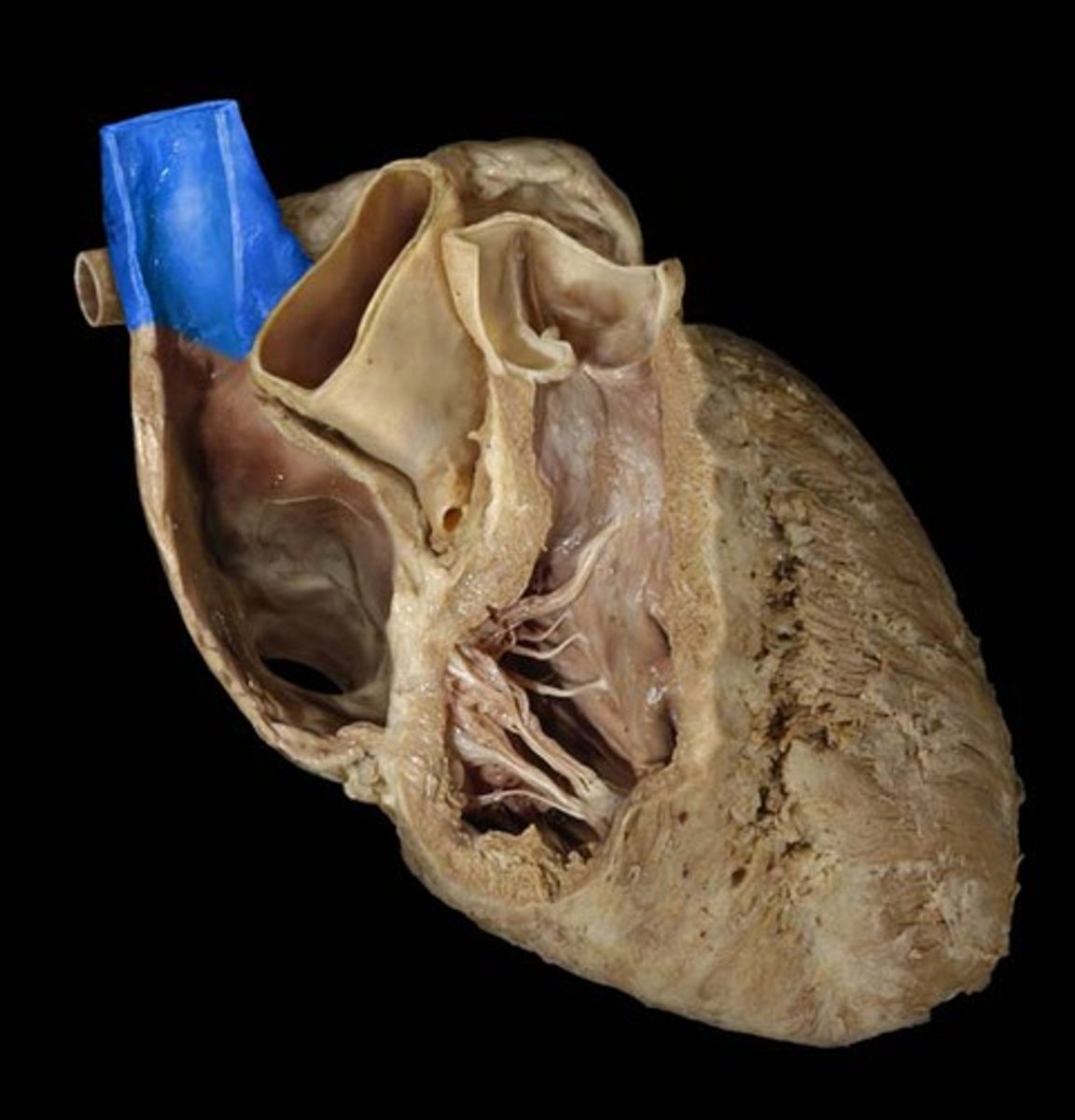
inferior vena cava
posterior side, large bottom opening
pulmonary veins
drains to the left atrium
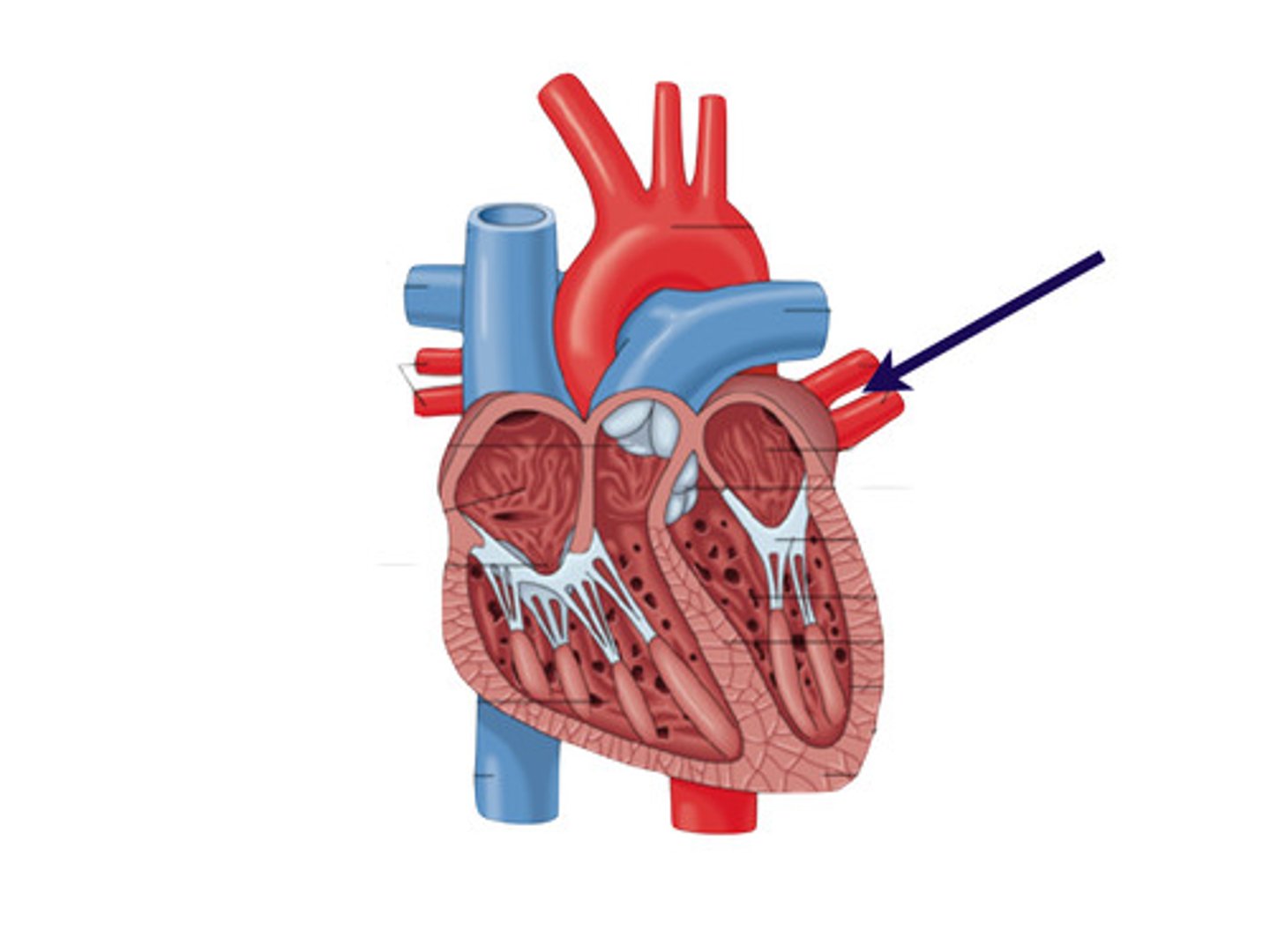
left superior and inferior pulmonary veins
what is this structure?
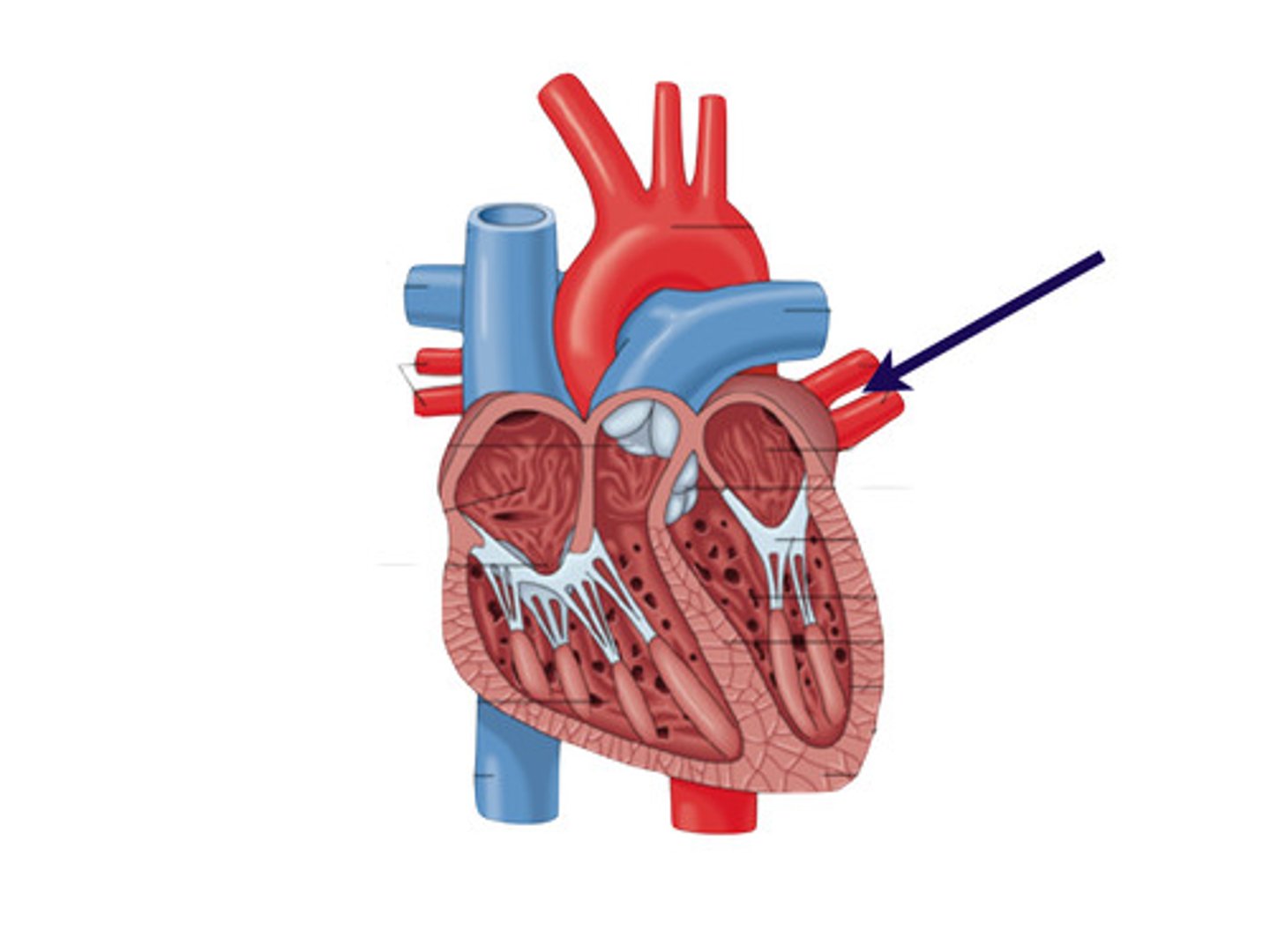
right superior and inferior pulmonary veins
what is this structure?
coronary arteries
The only branches of the ascending aorta
anterior
collective structure
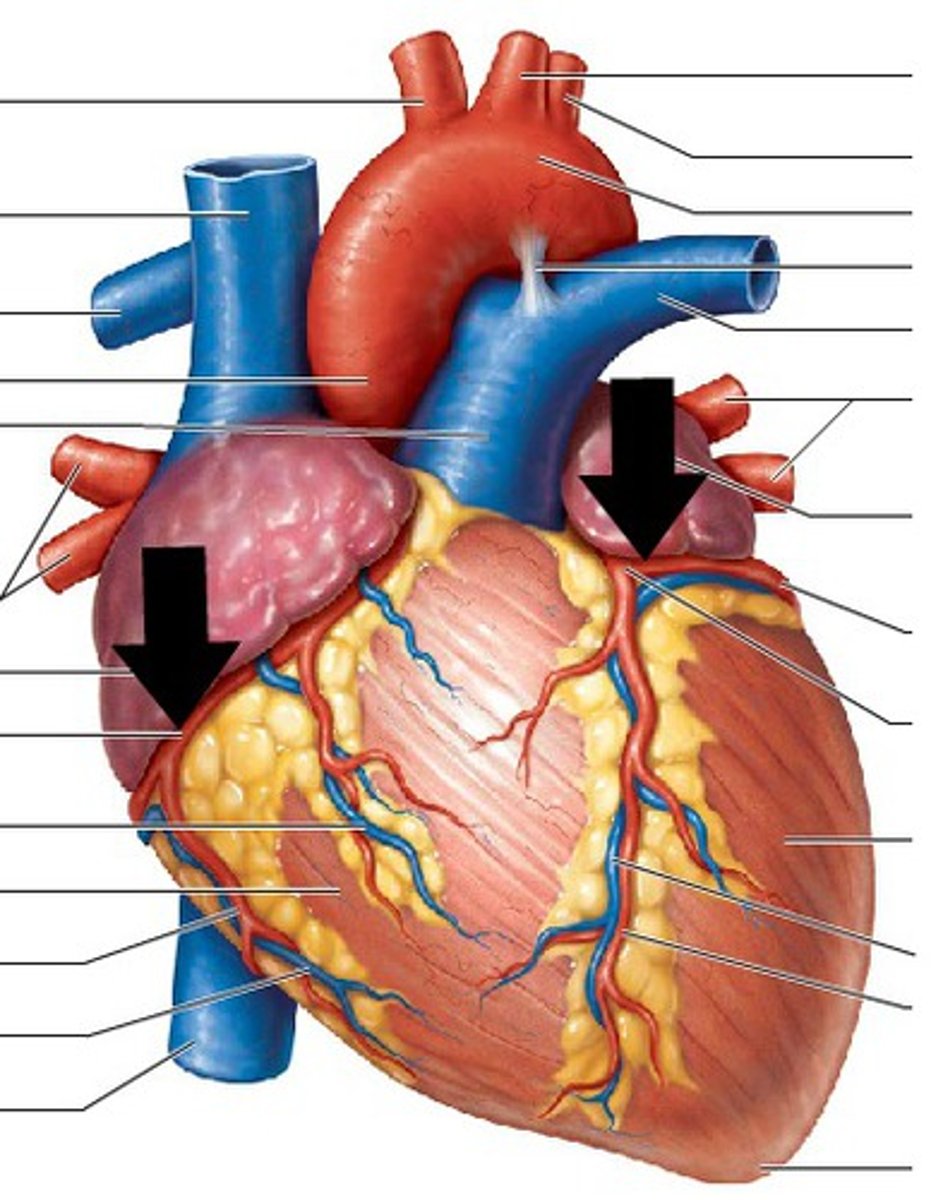
right coronary artery
artery vascularizing the right side of the heart
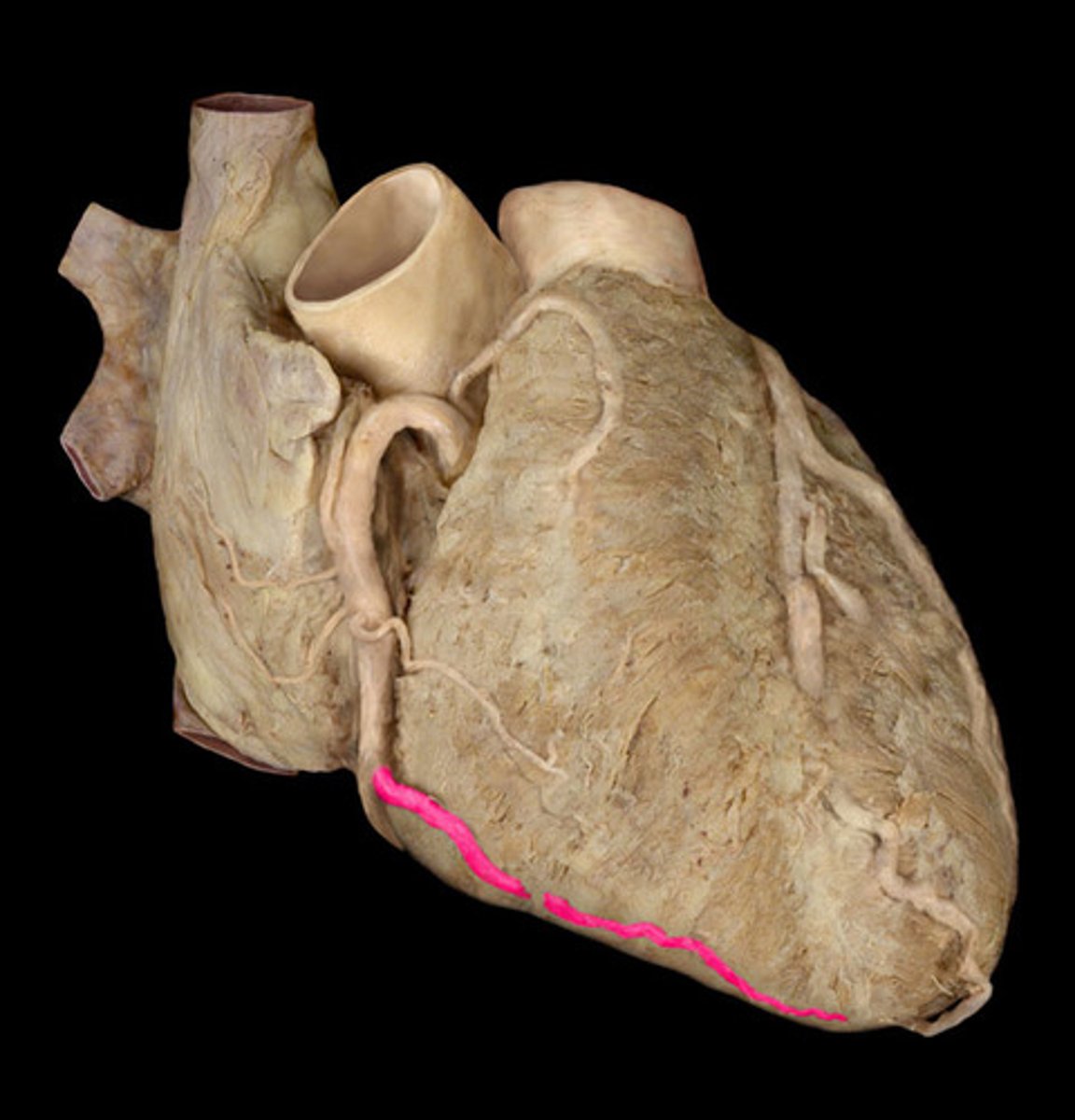
right marginal artery
along the inferior boarder of the heart
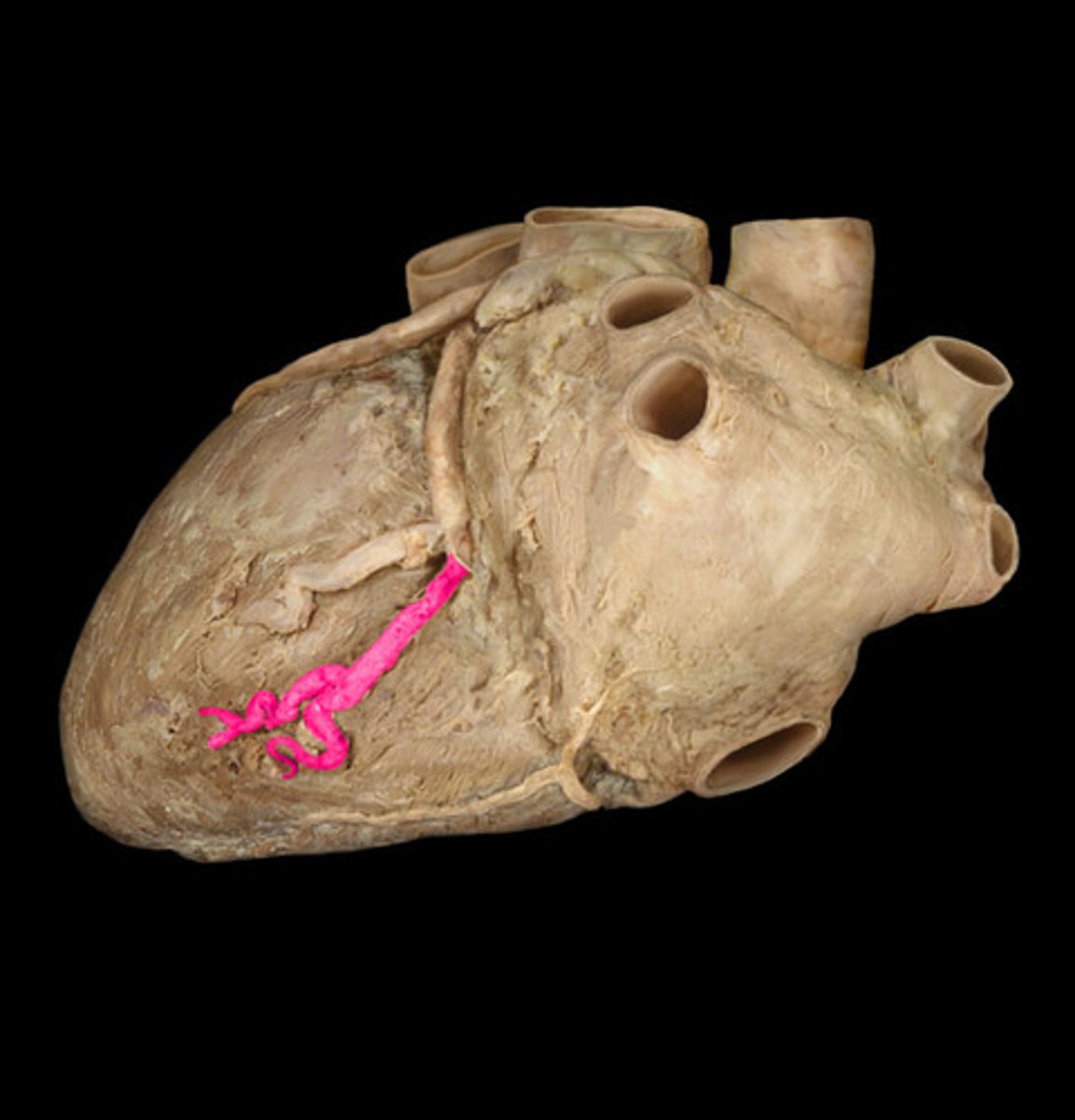
posterior interventricular artery
in the posterior interventricular sulcus
left coronary artery
left side of the heart, wraps around the front
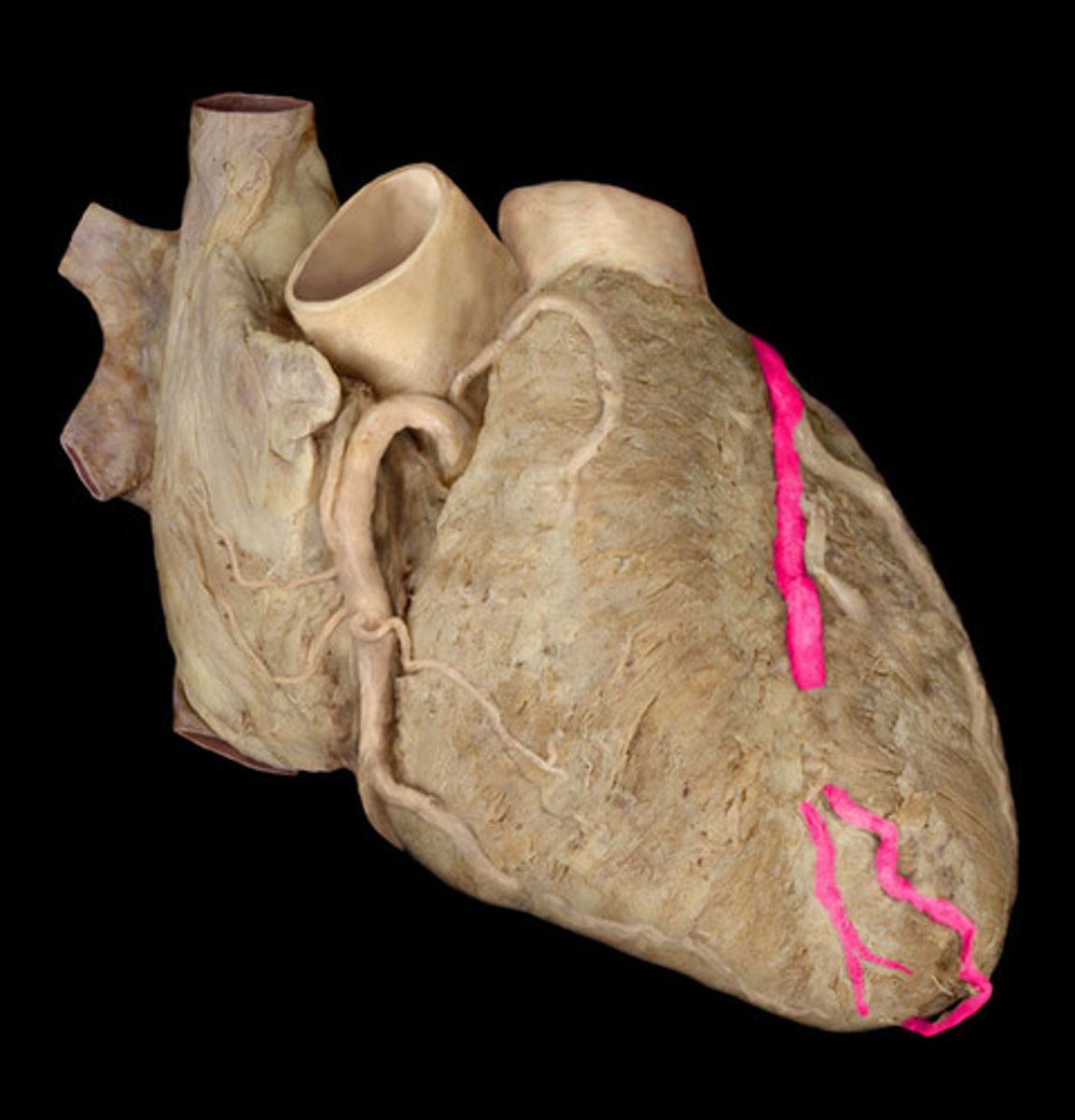
anterior interventricular artery
in the anterior interventricular sulcus
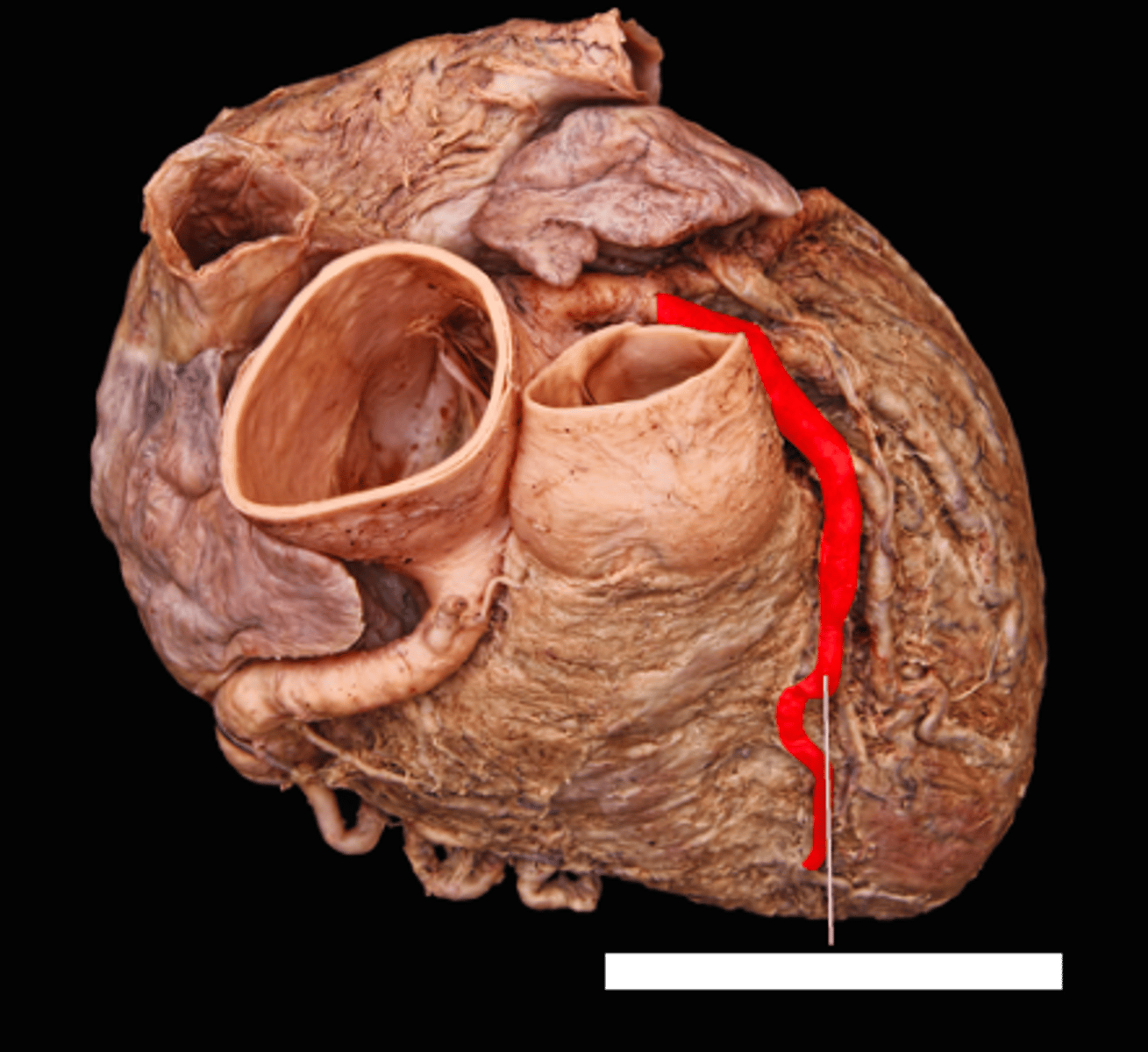
circumflex artery
bends around the heart
left side, looks like ramen noodles
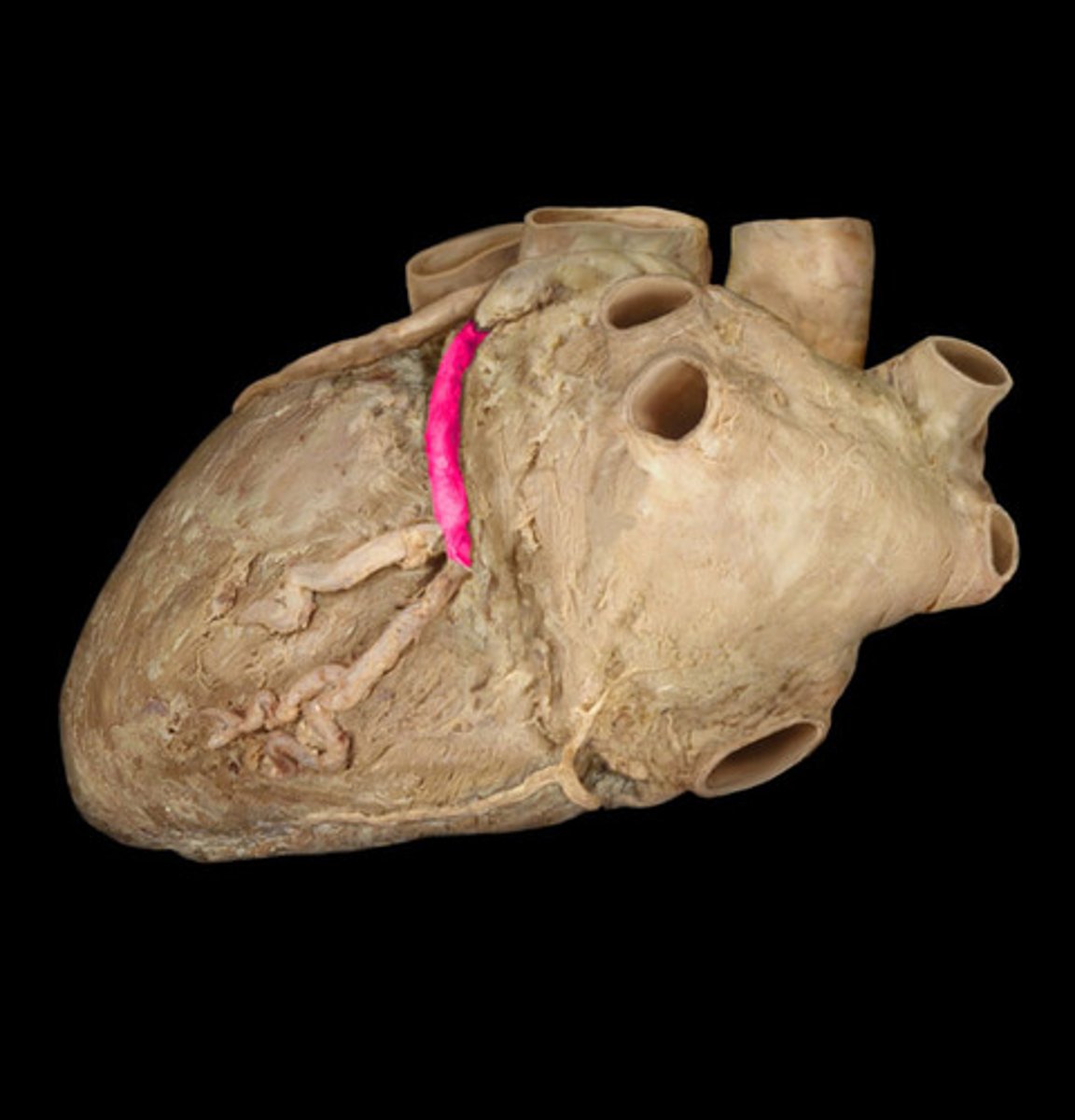
right atrium
most of right ventricle
part of left ventricle
SA and AV nodes
the right coronary artery supplies....
Left atrium
most of the left ventricle
part of the right ventricle
the interventricular septum
the left coronary artery supplies...
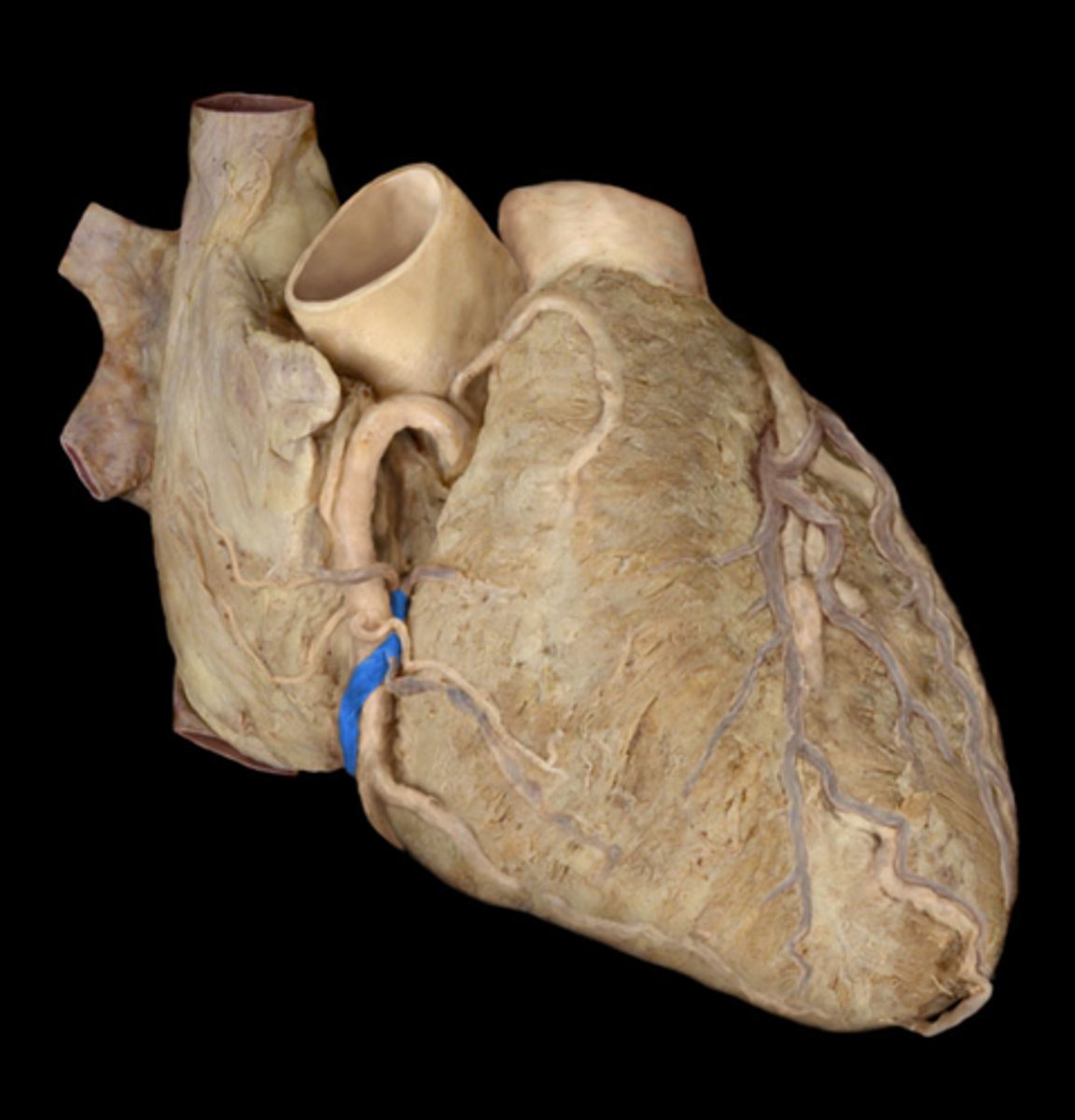
cardiac veins
collects deoxygenated blood from heart muscle tissue empty into right atrium (posterior side)
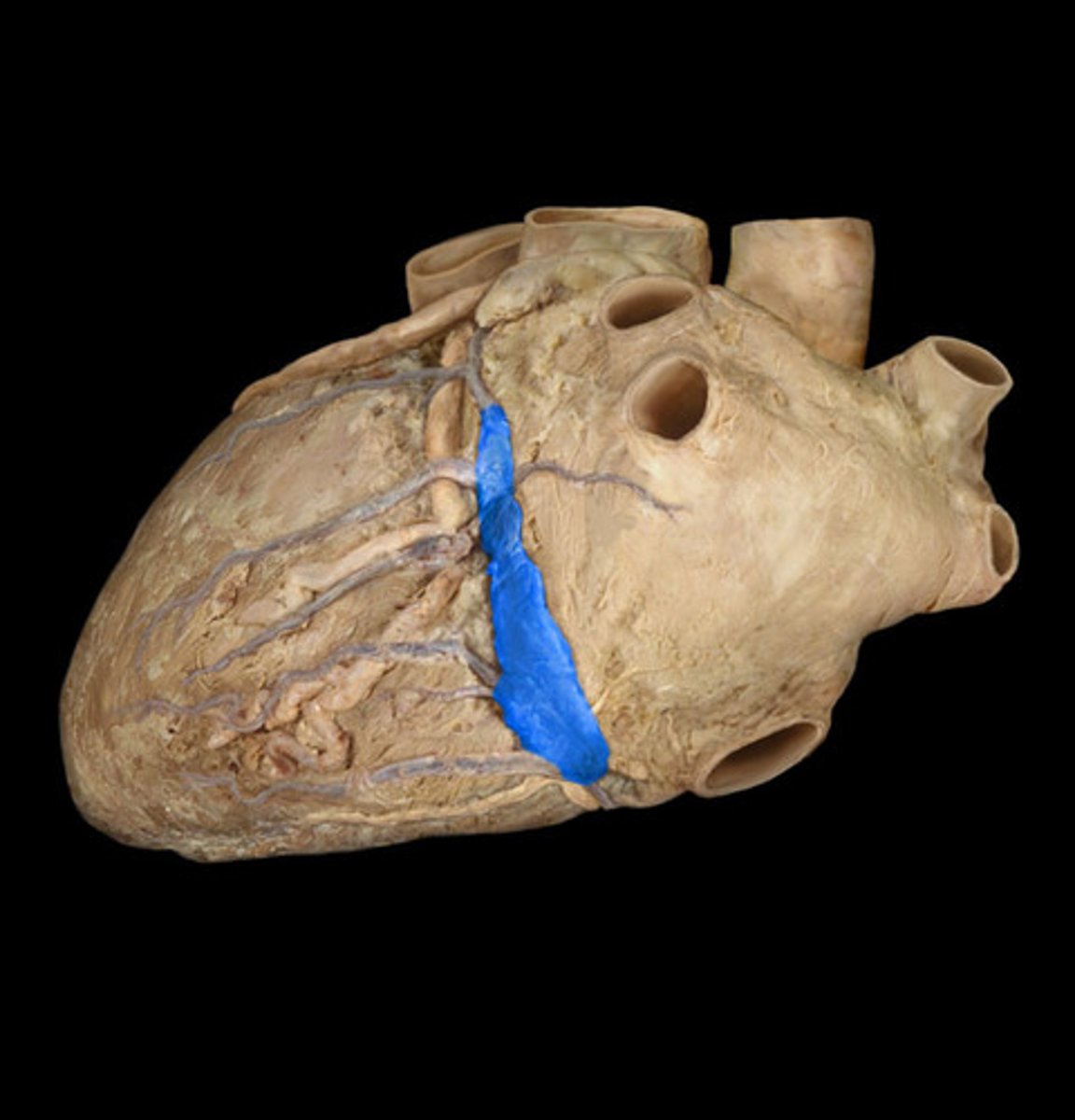
coronary sinus
largest vein of the heart, in the posterior coronary sulcus
middle of the 'T'
great cardiac vein
begins in the anterior interventricular sulcus
left side of the 'T'
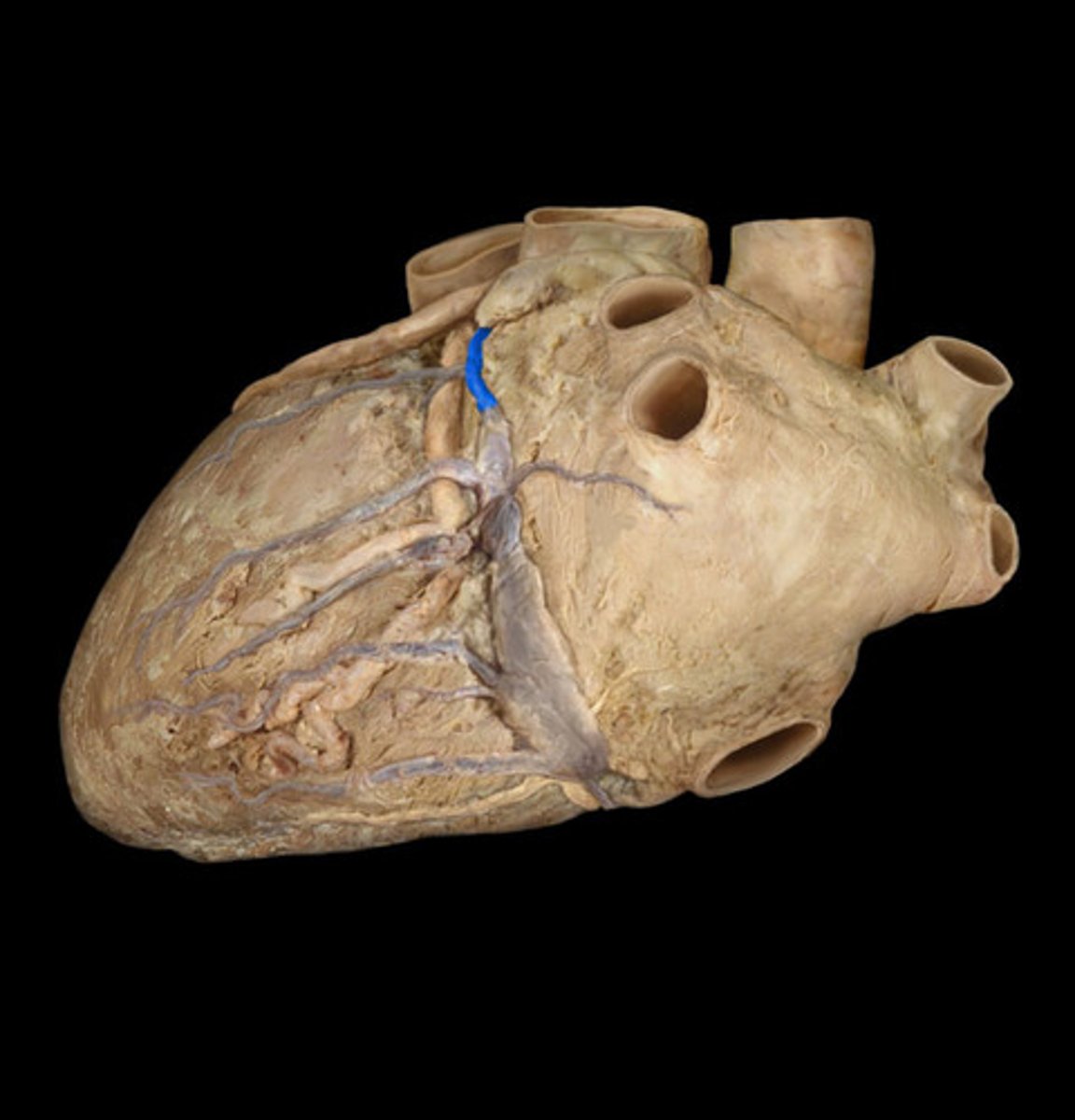
middle cardiac vein
posterior interventricular sulcus
middle string coming out of sinus
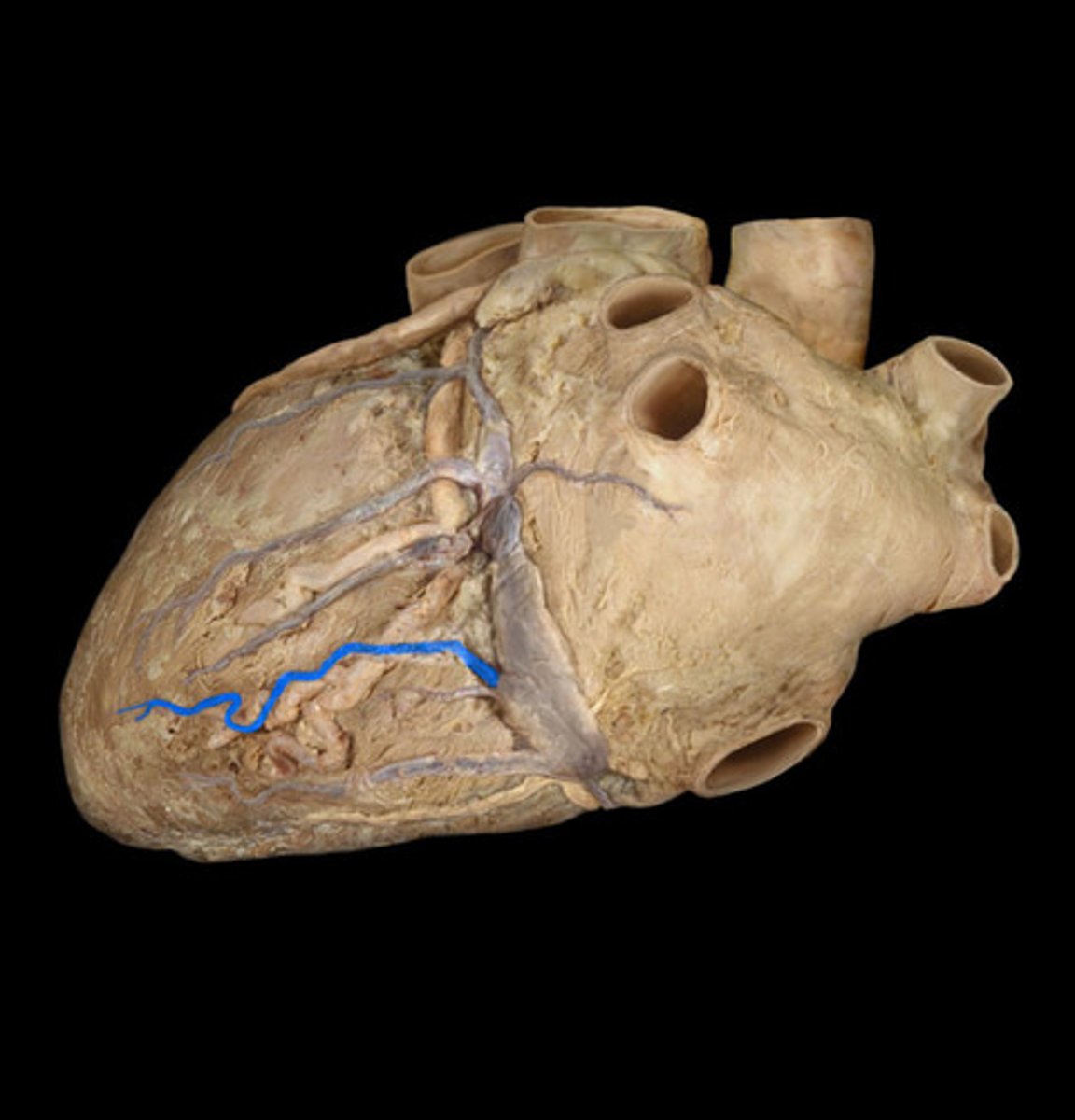
small cardiac vein
anteriorly along the inferior border of the heart
right side of the 'T'
fibrous pericardium
attaches to the great vessels above and is fused below to the superior surface of the diaphragm (covering)
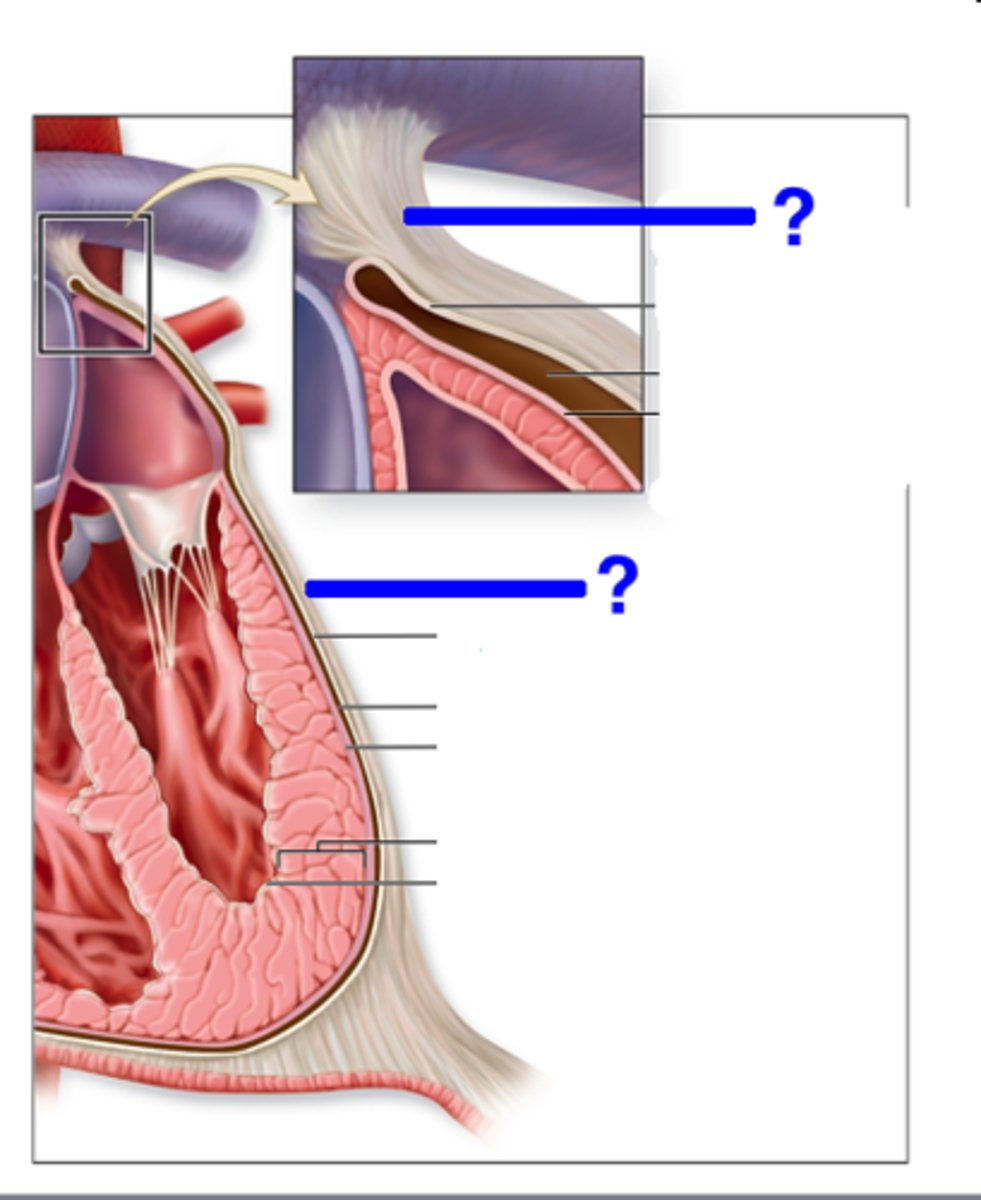
serous pericardium
a closed sac
both sides; cover on the heart + flap
collective structure
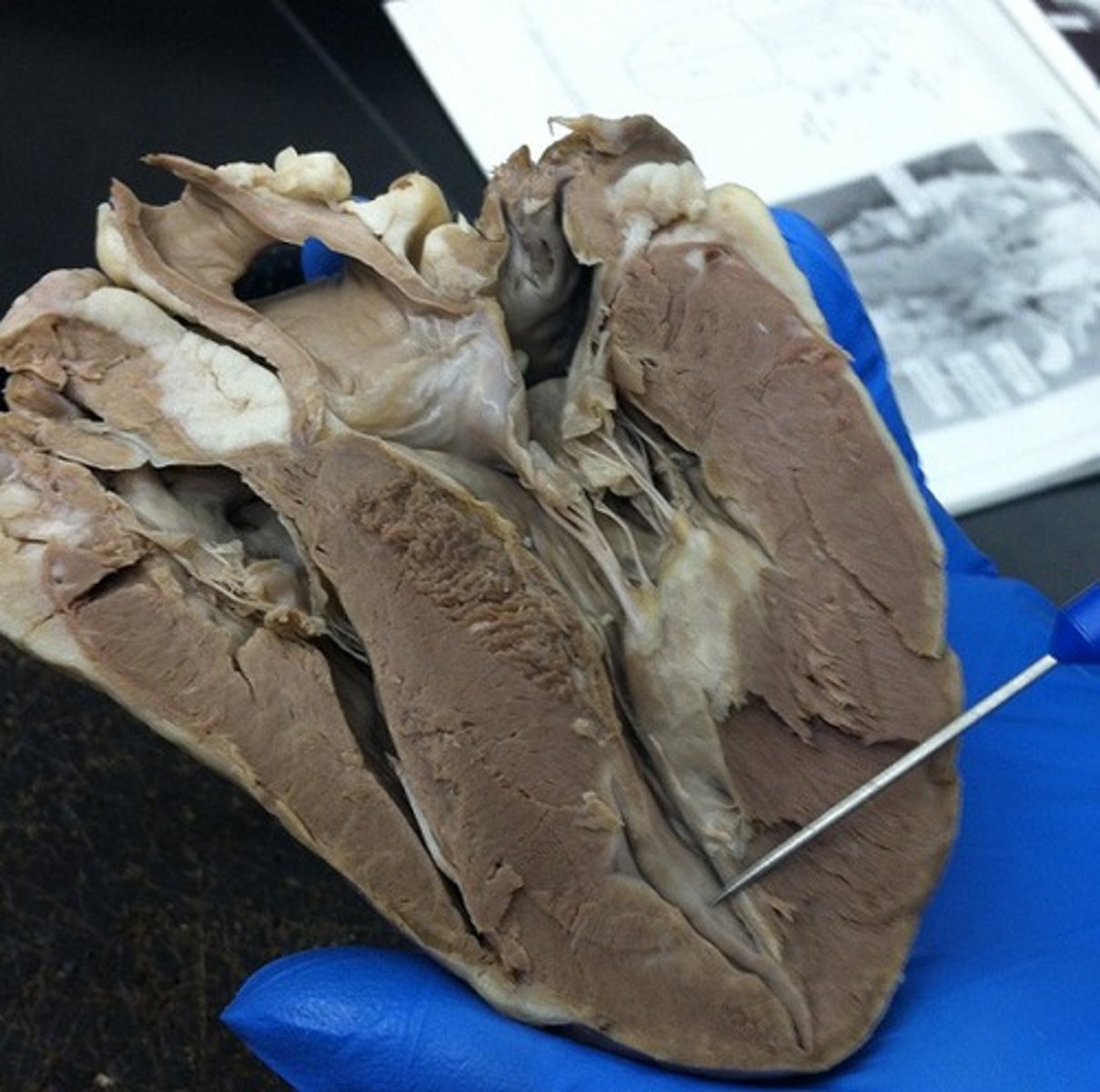
parietal layer of the serous pericardium
fused to fibrous pericardium
back part of the layer when flipped back (feature)
visceral layer of serous pericardium
the outer layer of the heart wall (feature)
pericardial cavity
a potential space surrounding the heart between the parietal and visceral layers of the serous pericardium
transverse pericardial sinus
behind the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk-connects the left and right sides of the pericardial cavity
oblique pericardial sinus
a blind "cul-de-sac" posterior to the heart-surrounded by the pulmonary veins, the SVC, and the IVC
endocardium
the simple squamous epithelium that lines the heart (layer)
inside part
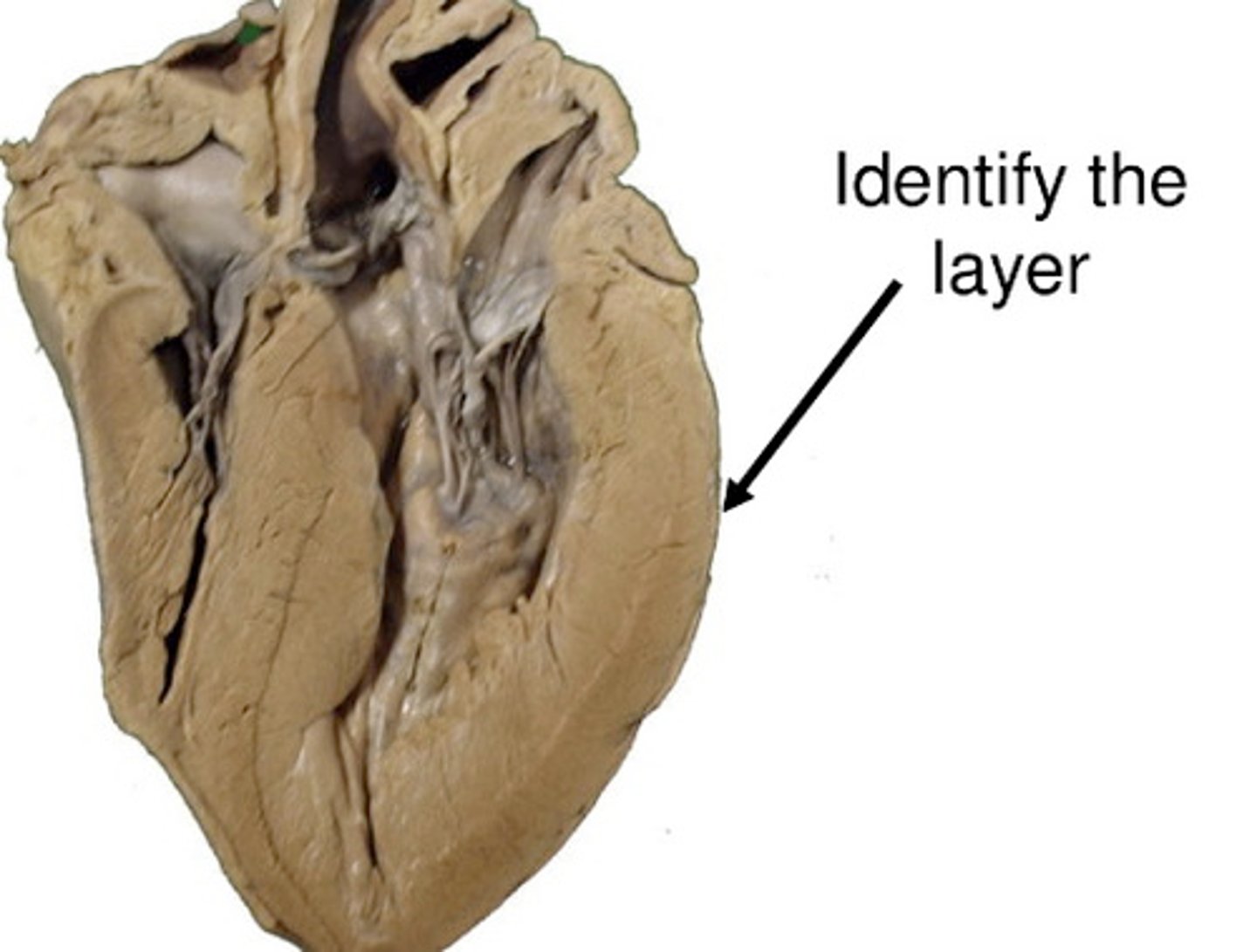
myocardium
cardiac muscle tissue
thick middle layer of the heart (layer)
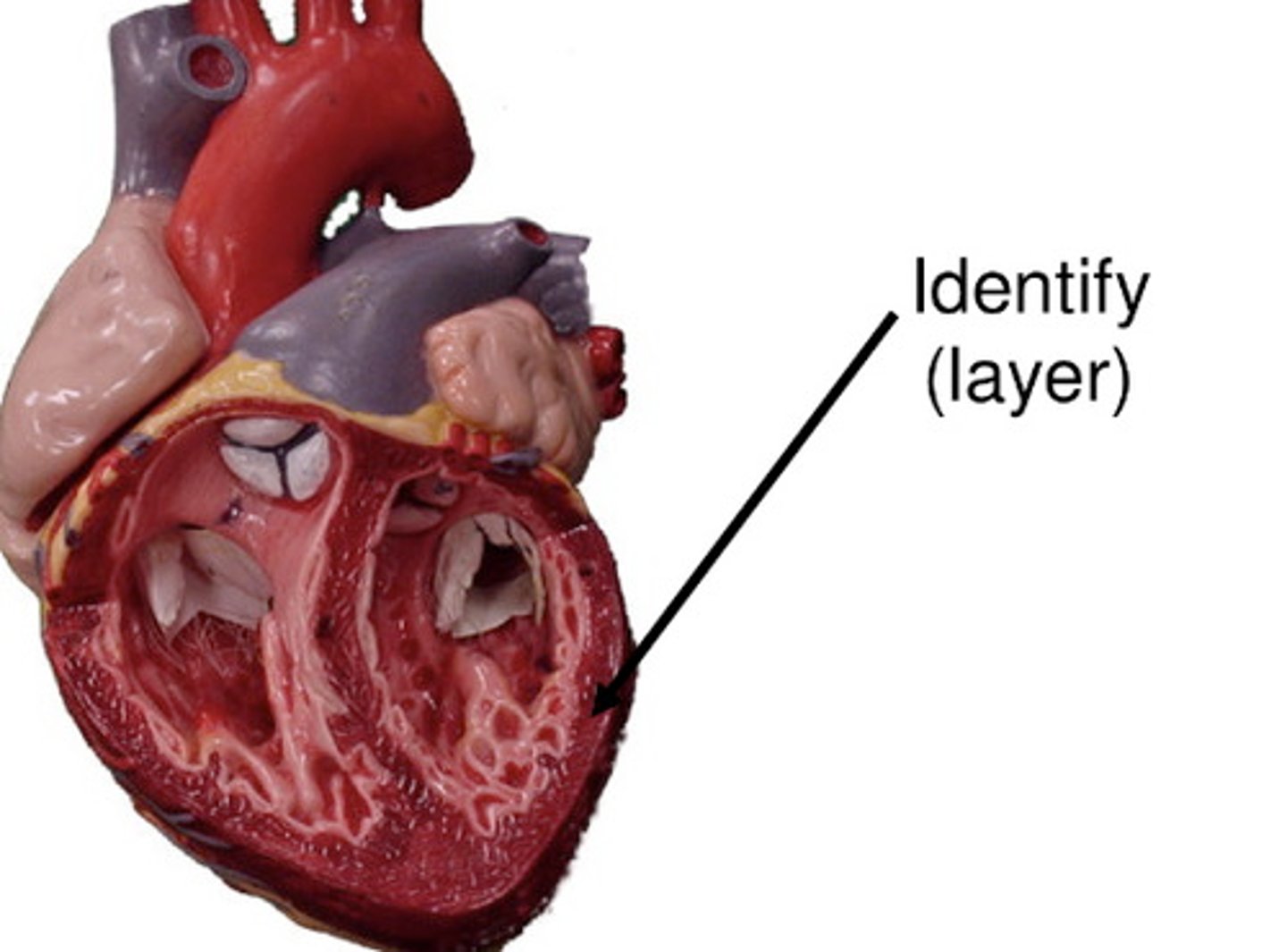
epicardium
outer layer of the heart
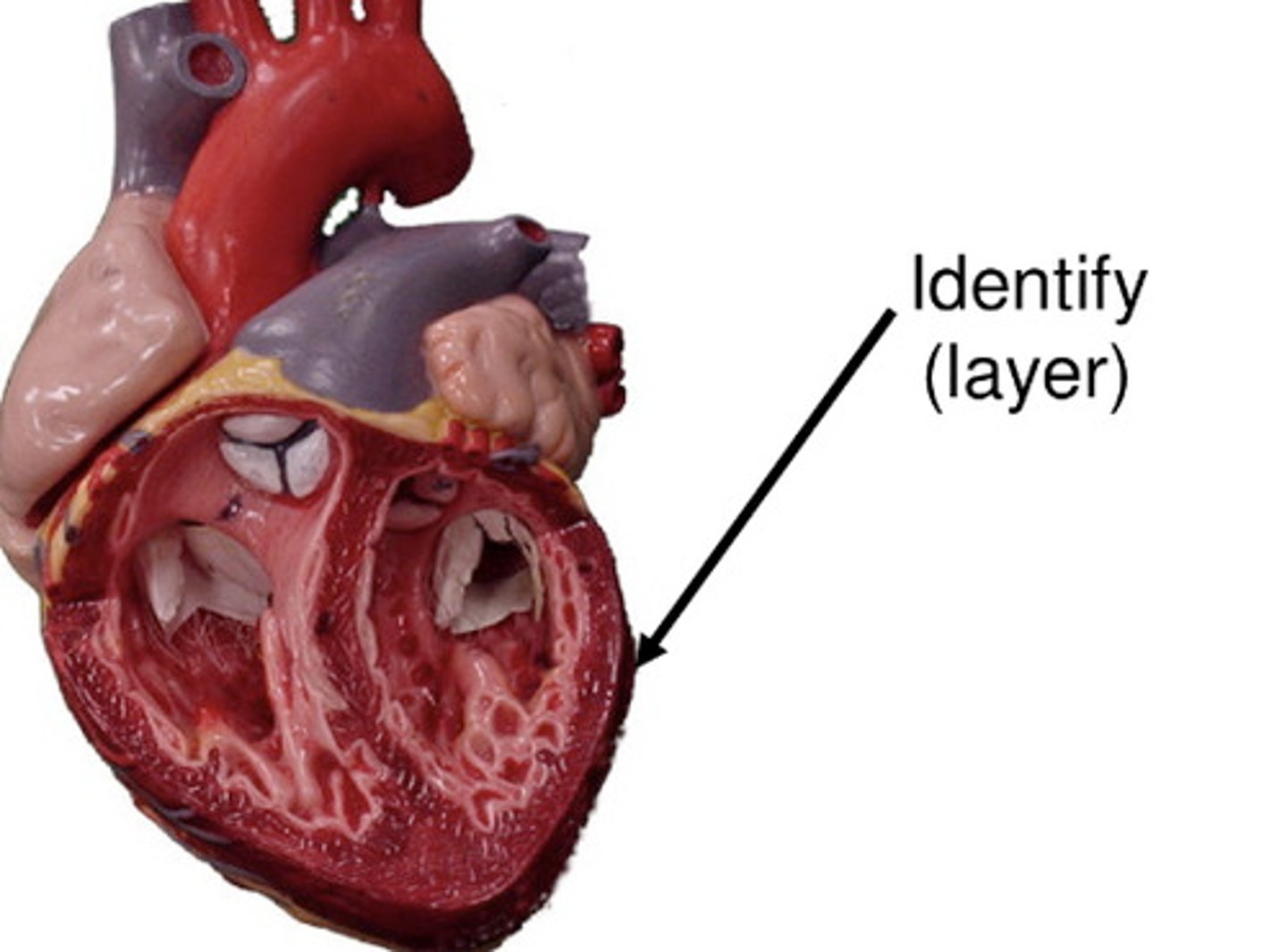
interatrial septum
separates the right and left atria
fossa ovalis
Name this structure located in the right atrium.
oval depression
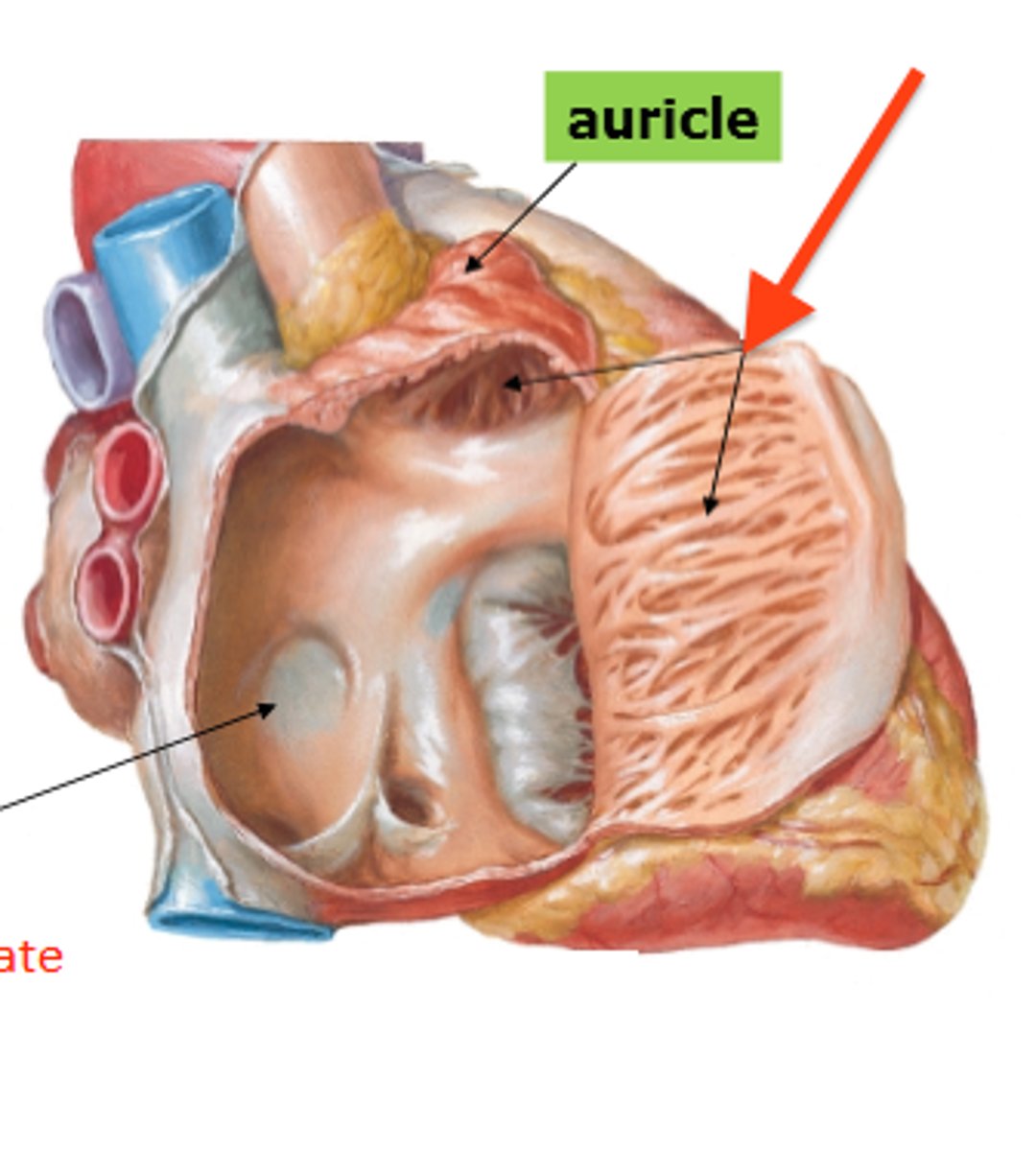
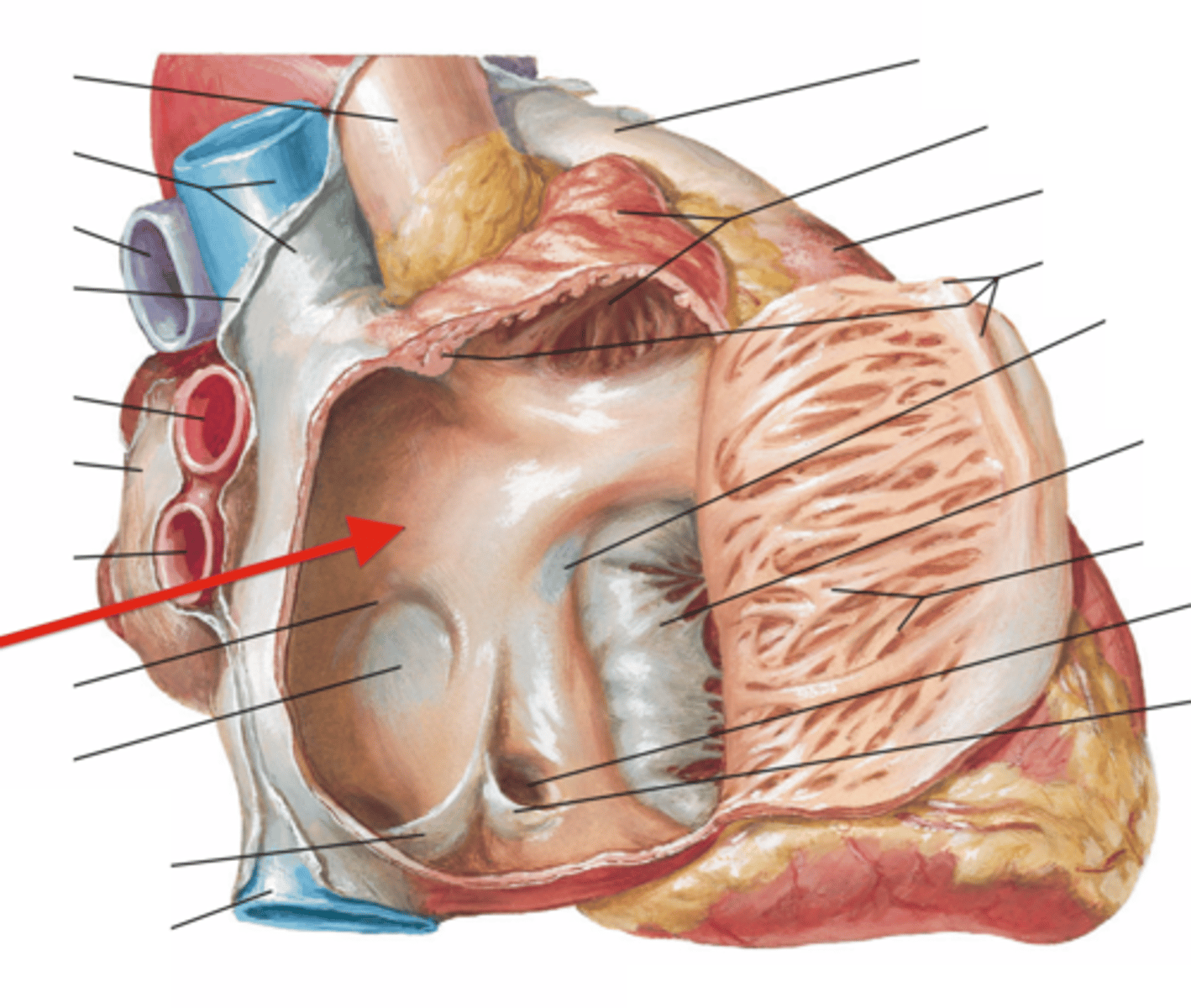
right auricle
Identify the flap.
dog ear looking
pectinate muscle
muscle that lines the walls of the atrium
striated muscle
sinus venarum
Smooth part of right atrium
below pectinate muscle
opening of the superior vena cava
anterior side opening, above the aorta (space)
opening of the inferior vena cava
posterior side coming down from the heart (space)
opening of the coronary sinus
returns venous coronary circulation to right atrium
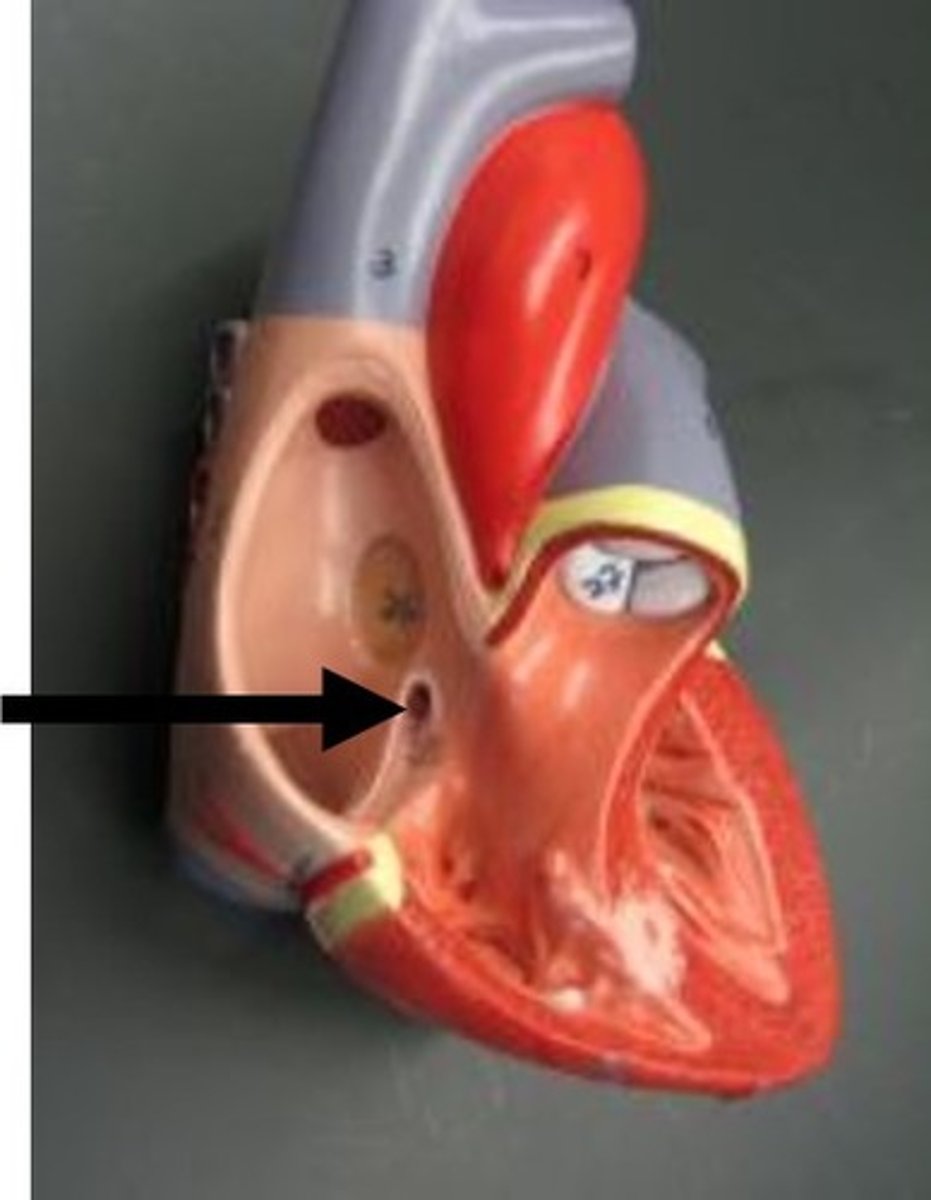
left auricle
Identify the flap.
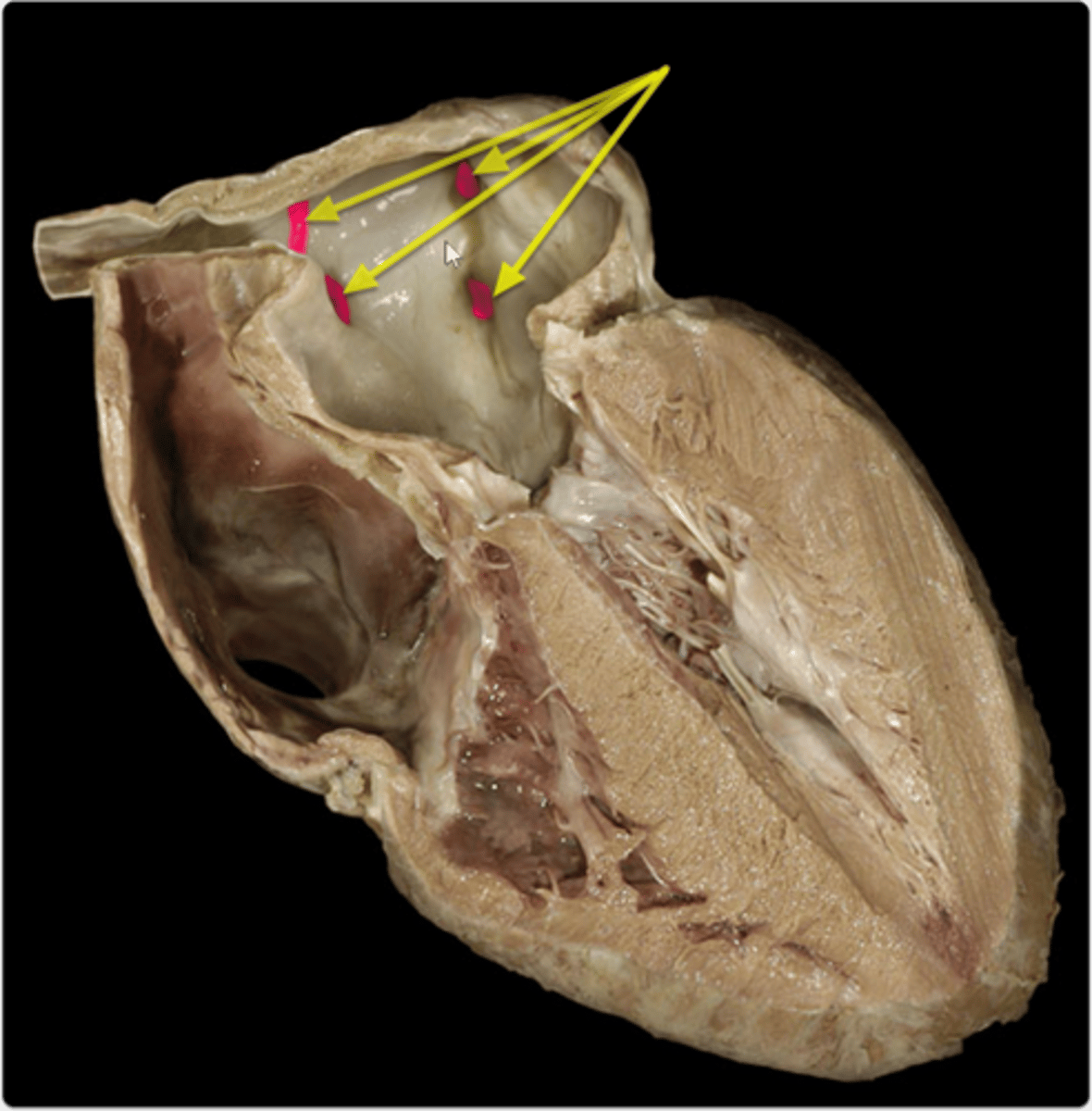
opening of the pulmonary veins
Found inside the left atrium.
2 probes through the tubes, posterior side
collective structure
interventricular septum
separates ventricles
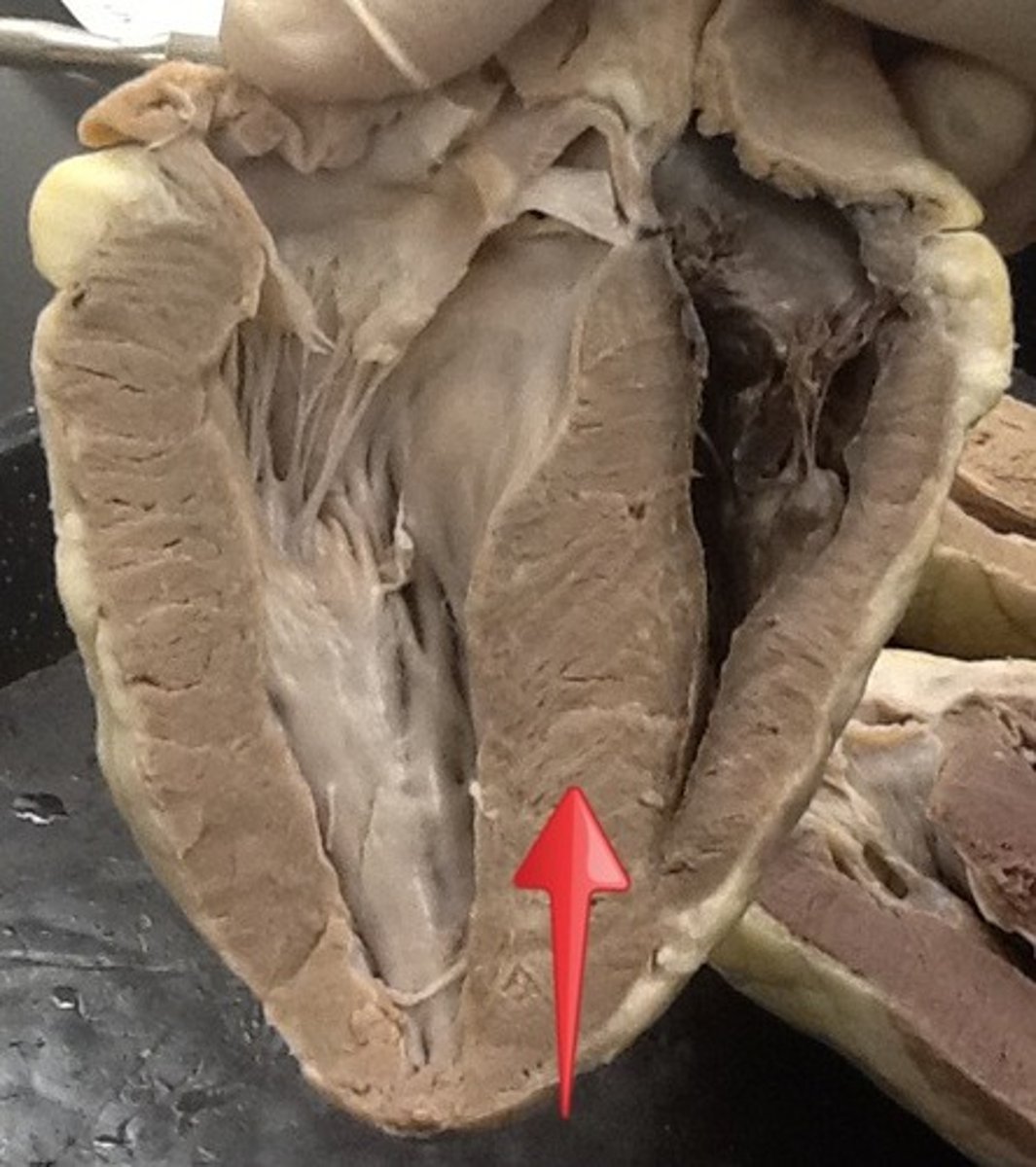
muscular part of interventricular septum
Most of the septum is thick. This is the thick part
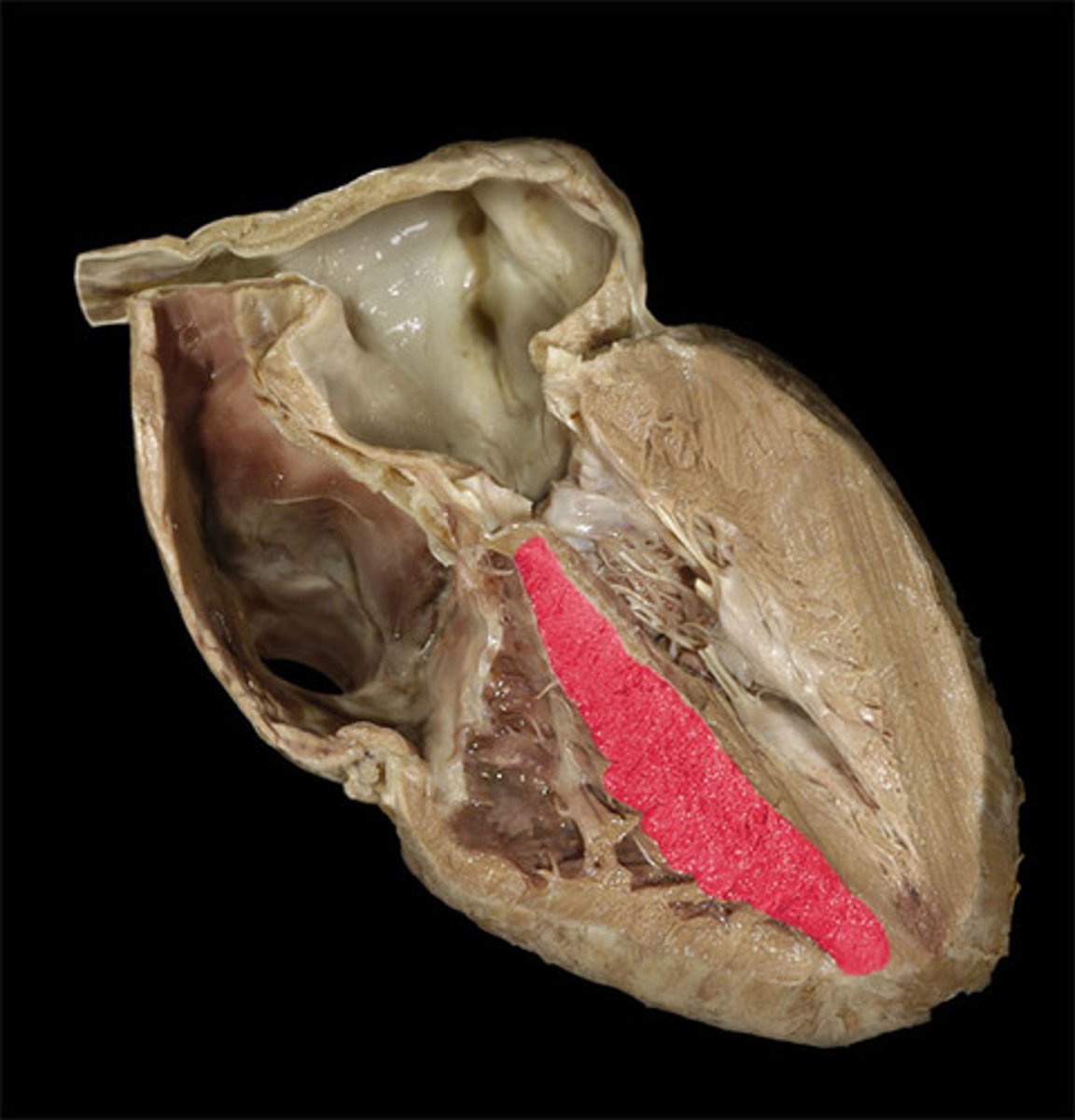
membranous part of the interventricular septum
thin upper-most part of the septum
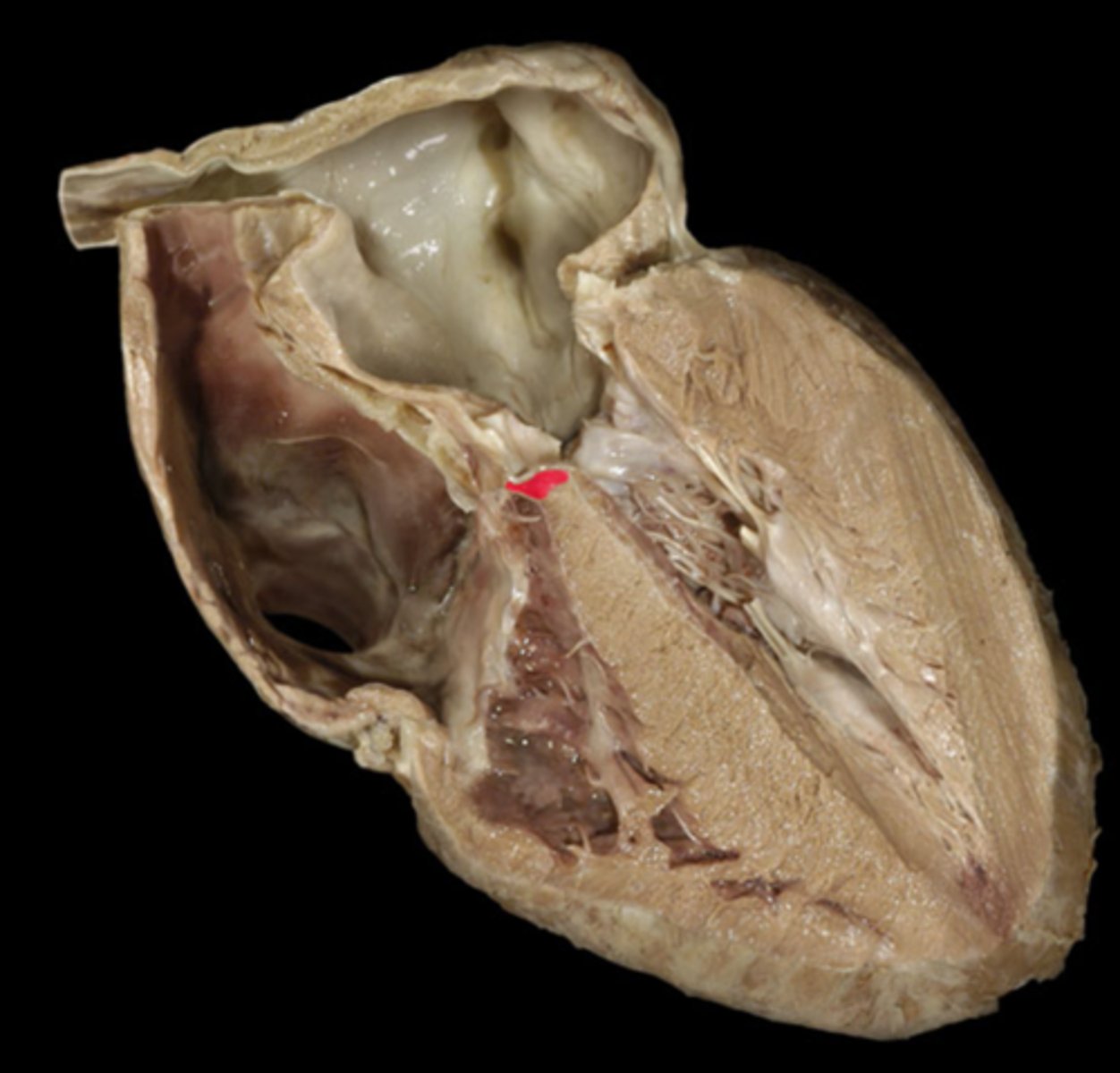
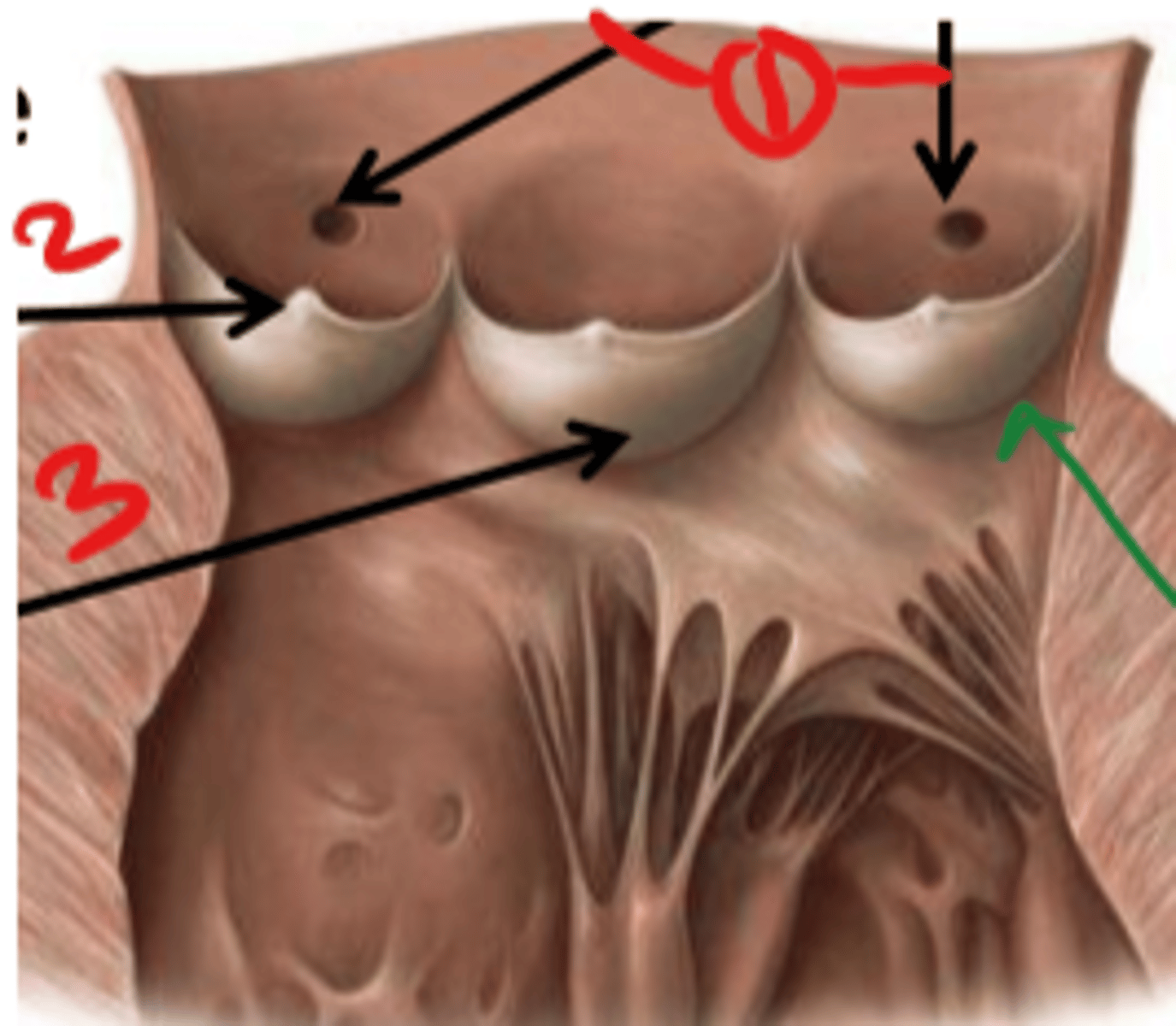
Right atrioventricular orifice
opening from right atrium to right ventricle
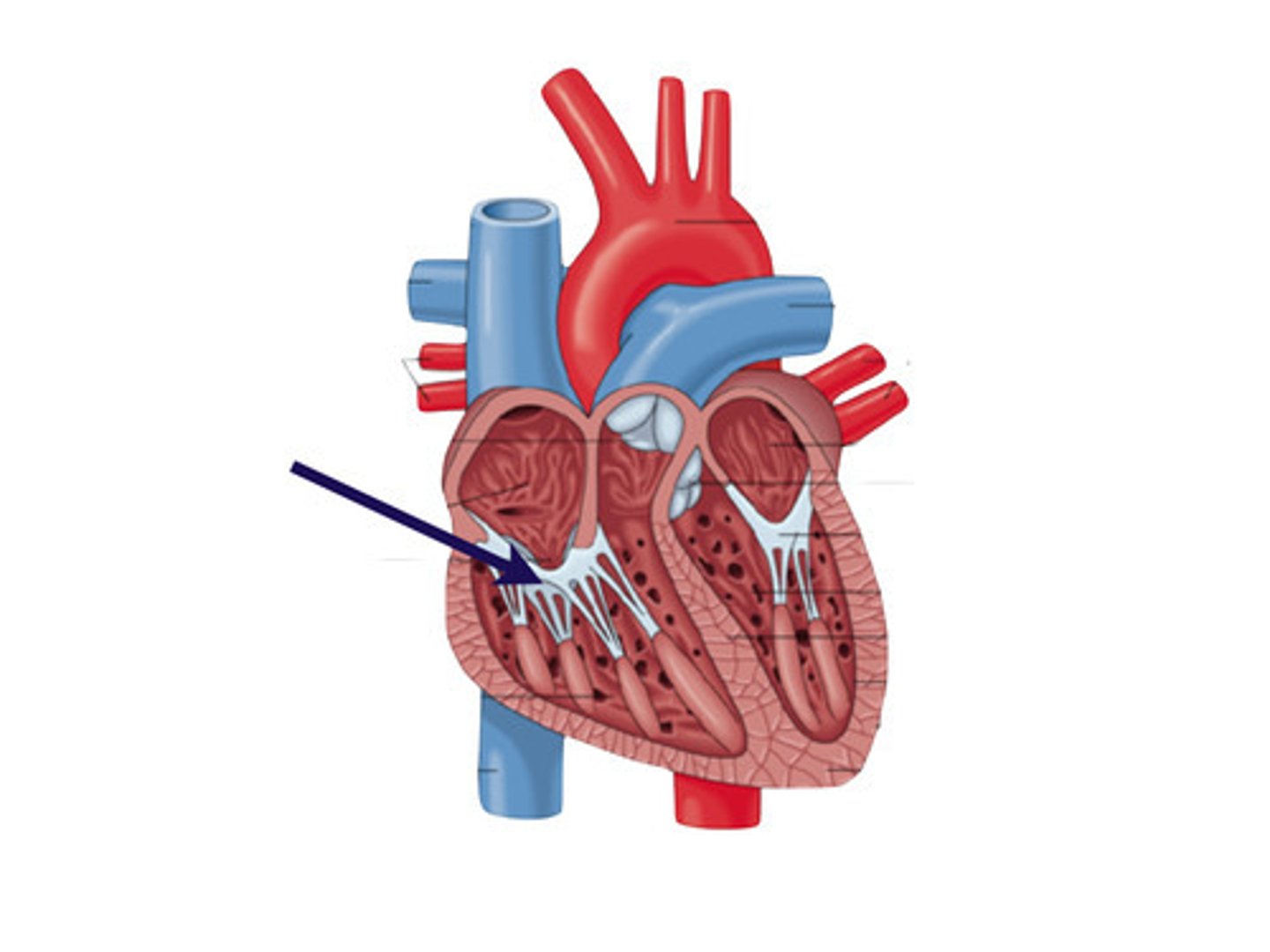
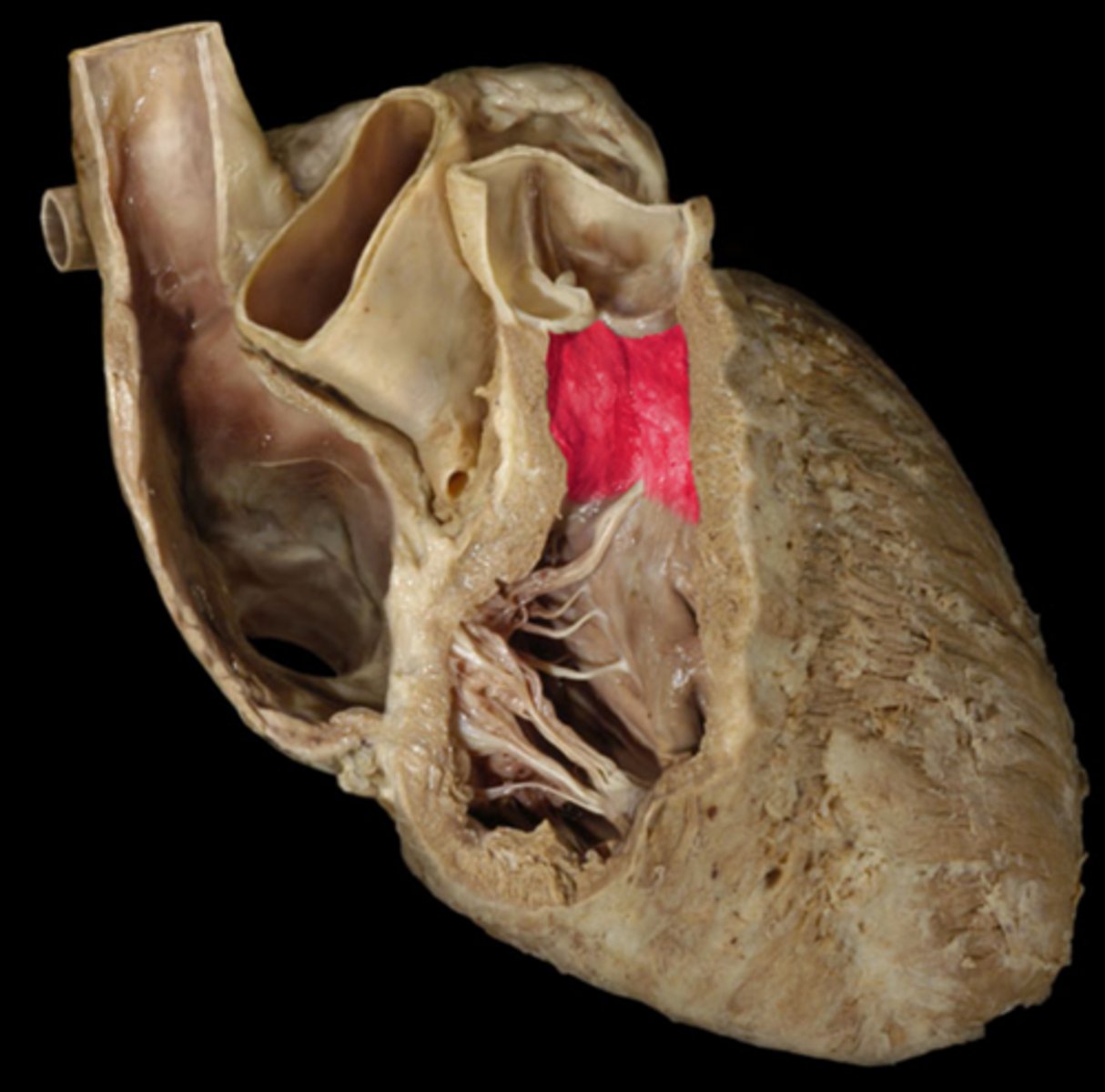
tricuspid valve
3 cusps. closes as pressure rises in the ventricle to prevent backflow of blood
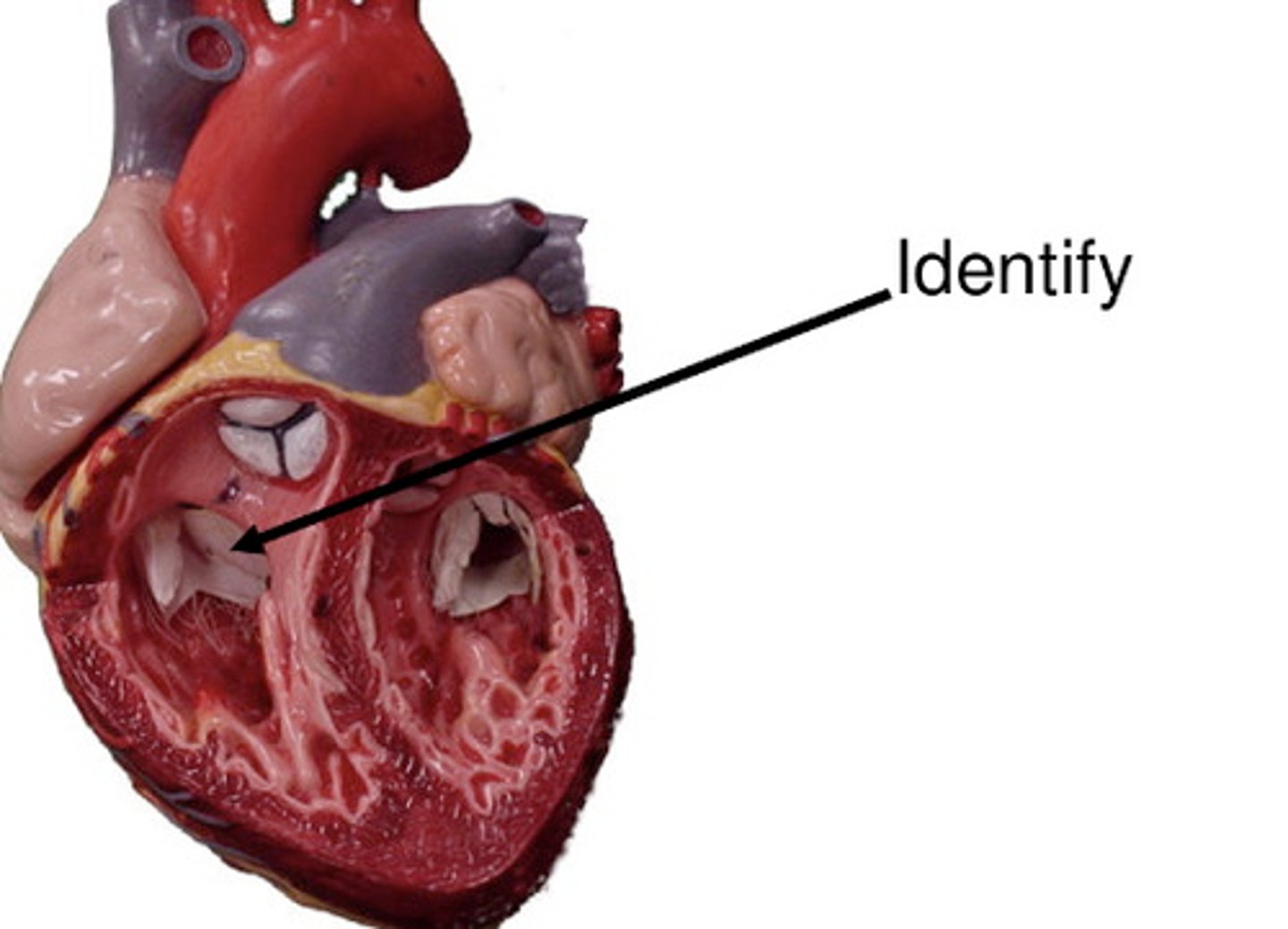
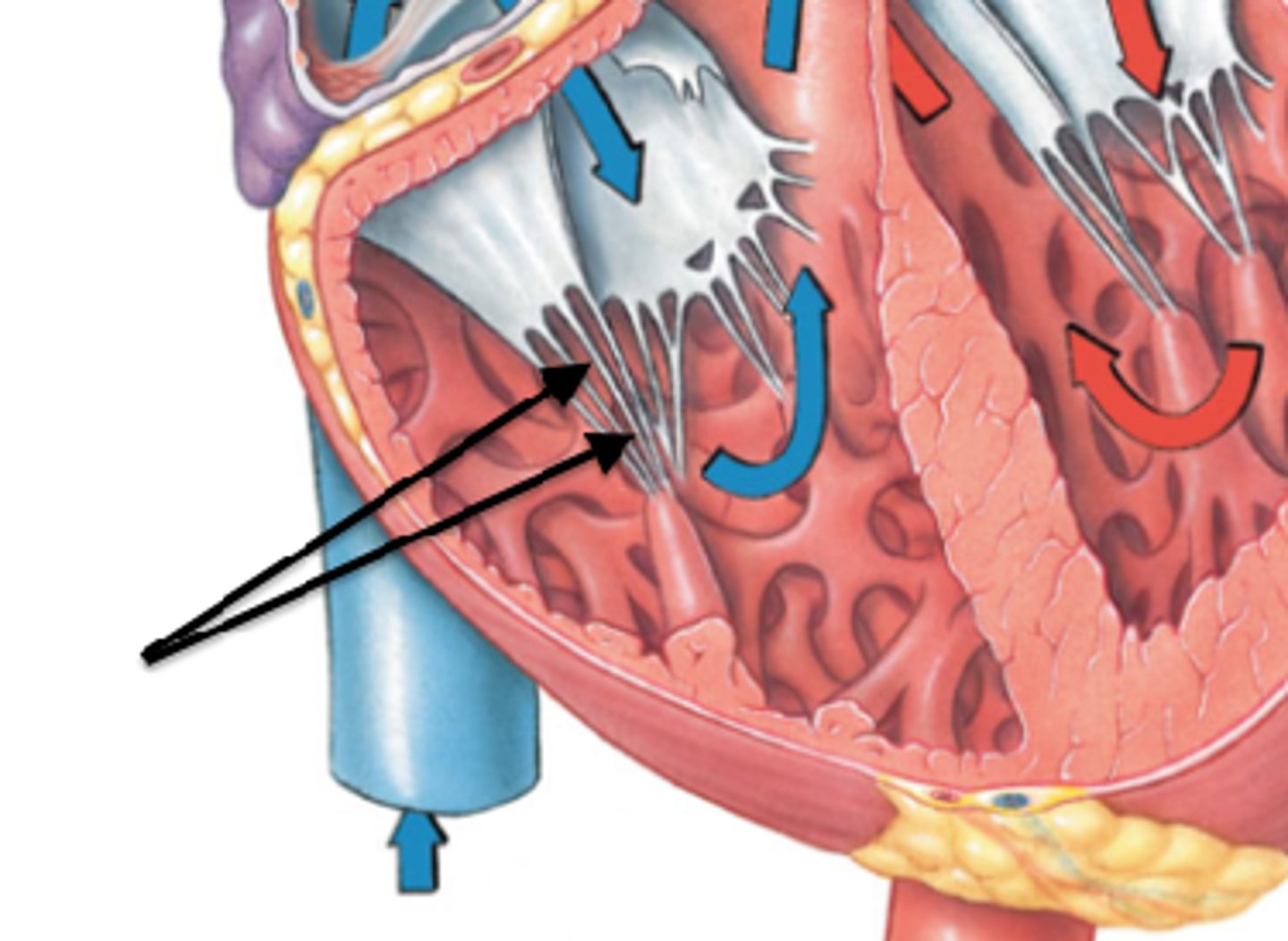
papillary muscles (3)
they tug at your heart strings
carrot
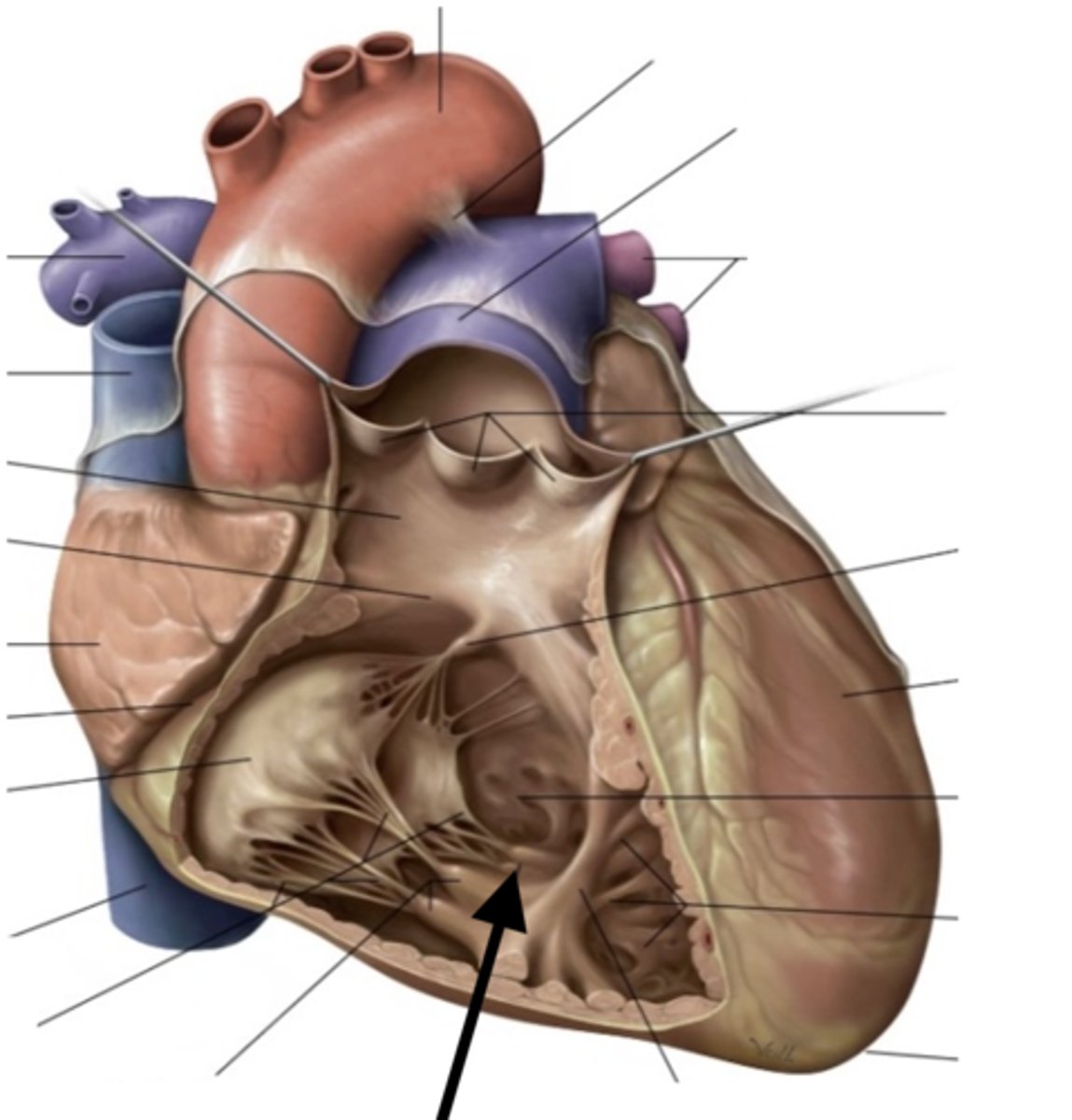
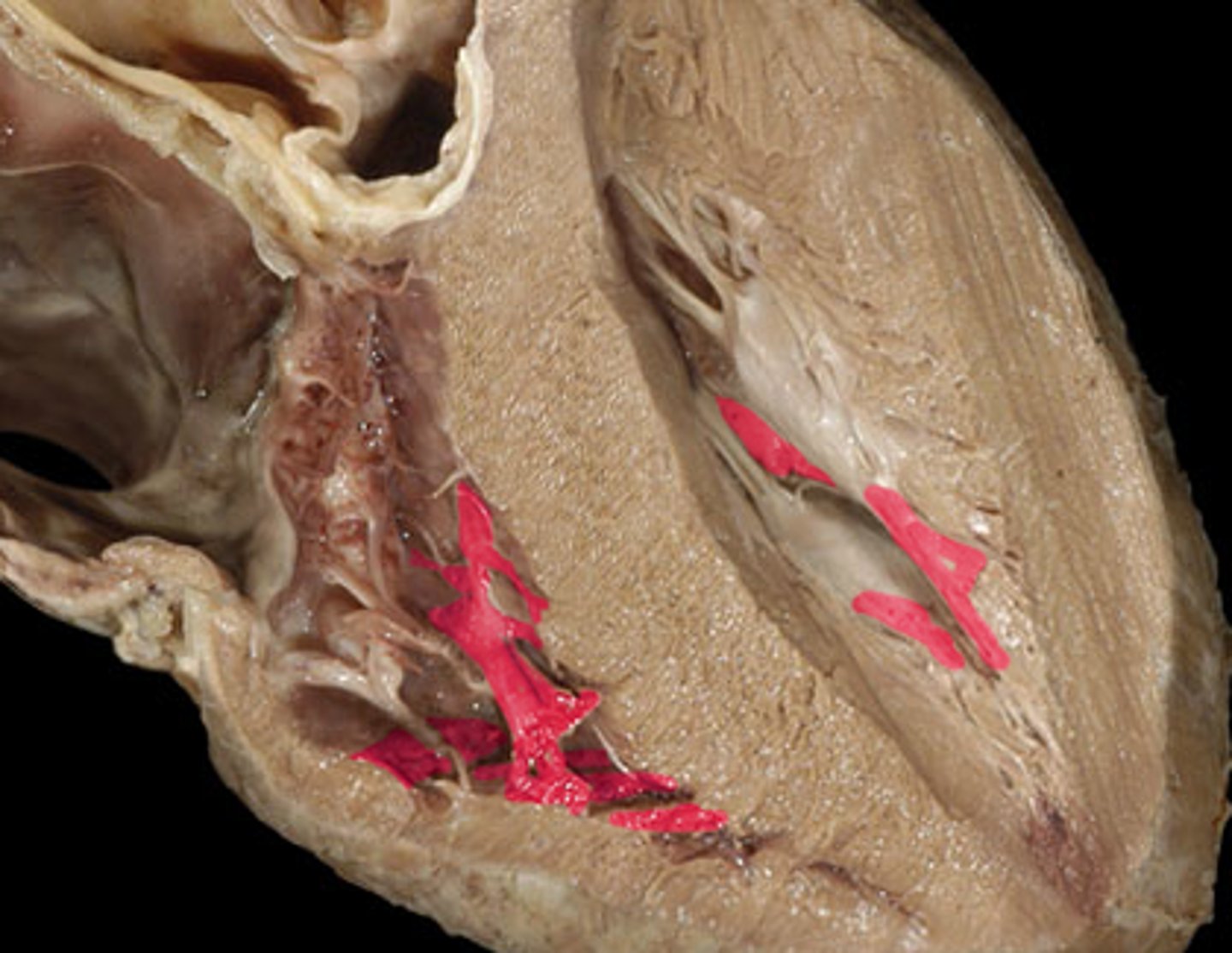
tendinous cords
heart strings
trabeculae carneae
ridges of cardiac muscle
conus arteriosus
cone-shaped part of the ventricles that leads into the pulmonary trunk (narrowing)
opening of the pulmonary trunk
What is this space?
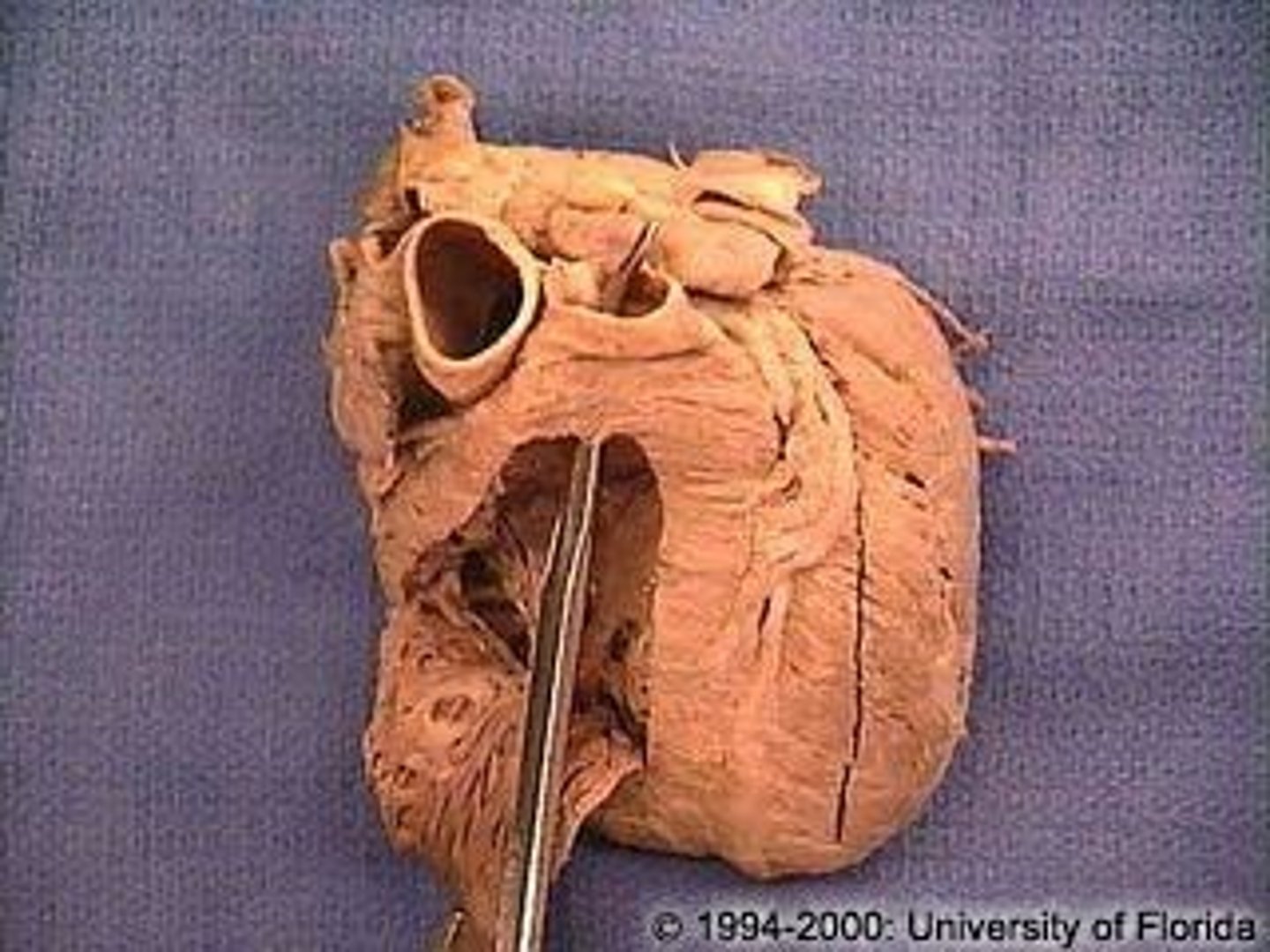
pulmonary valve
valve between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery
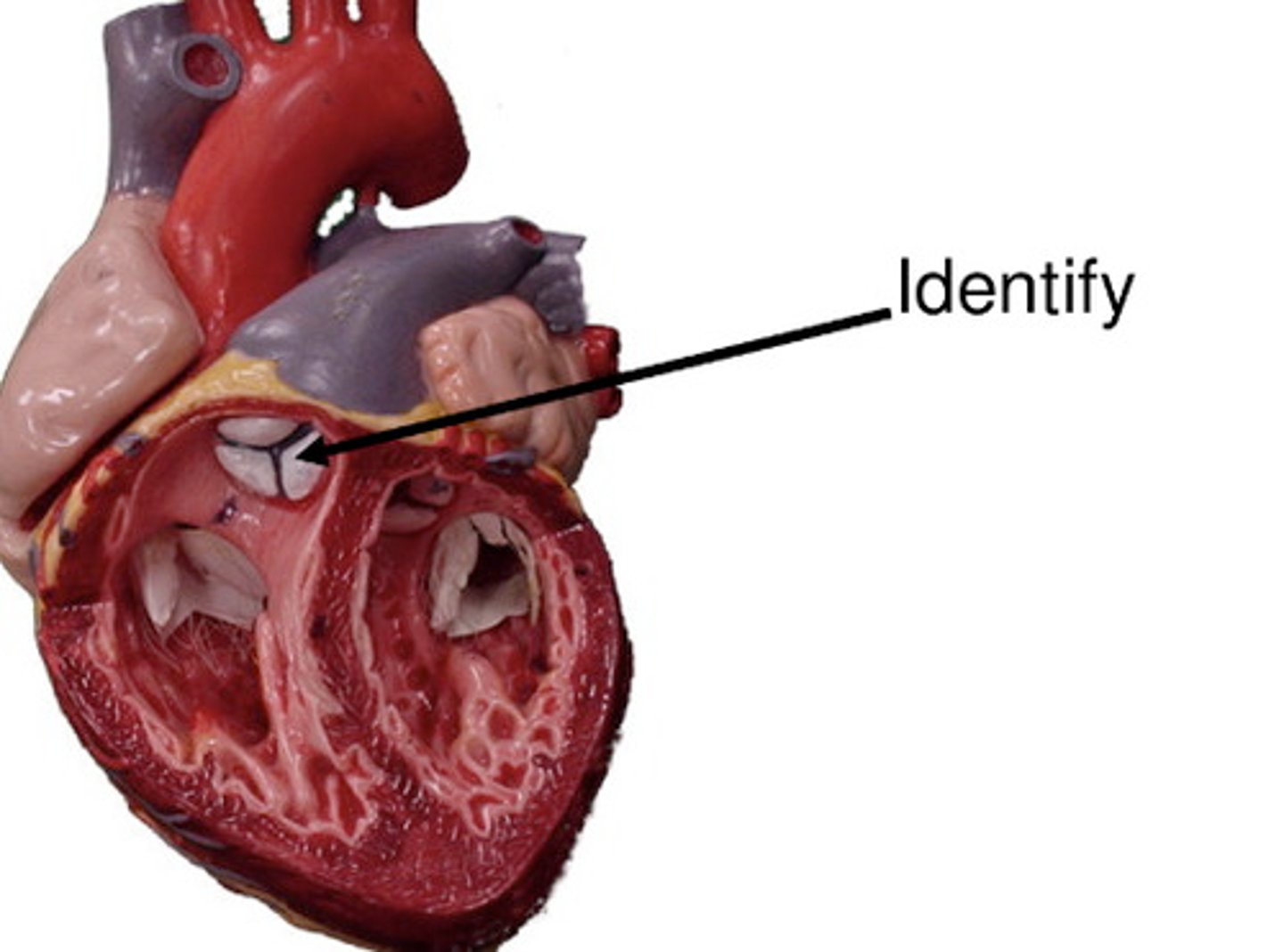
semilunar cusps
half moon shaped flaps of the endocardium
left atrioventricular orifice
opening between left atrium and left ventricle
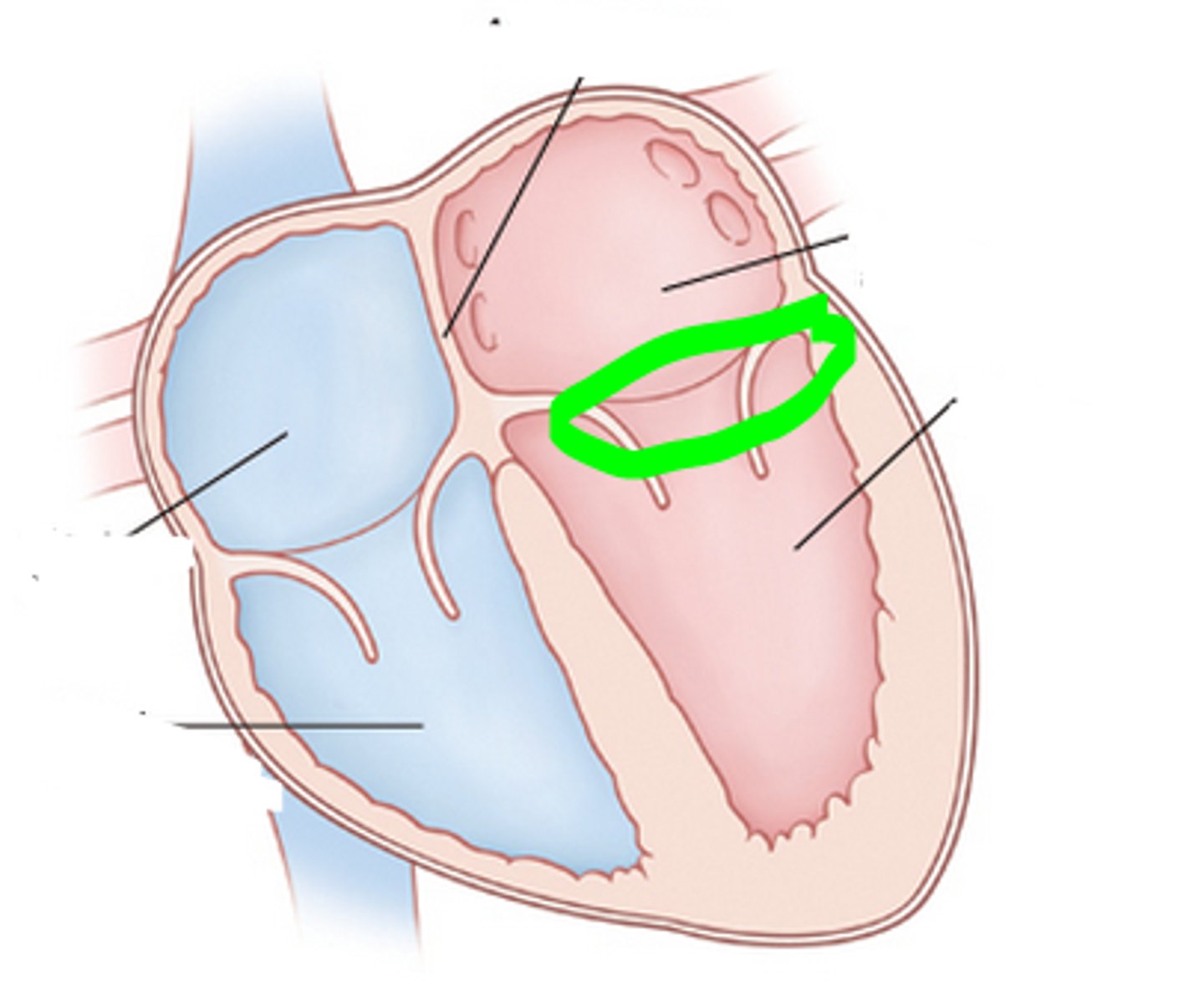
mitral valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle; bicuspid valve
shaped like a bishops hat
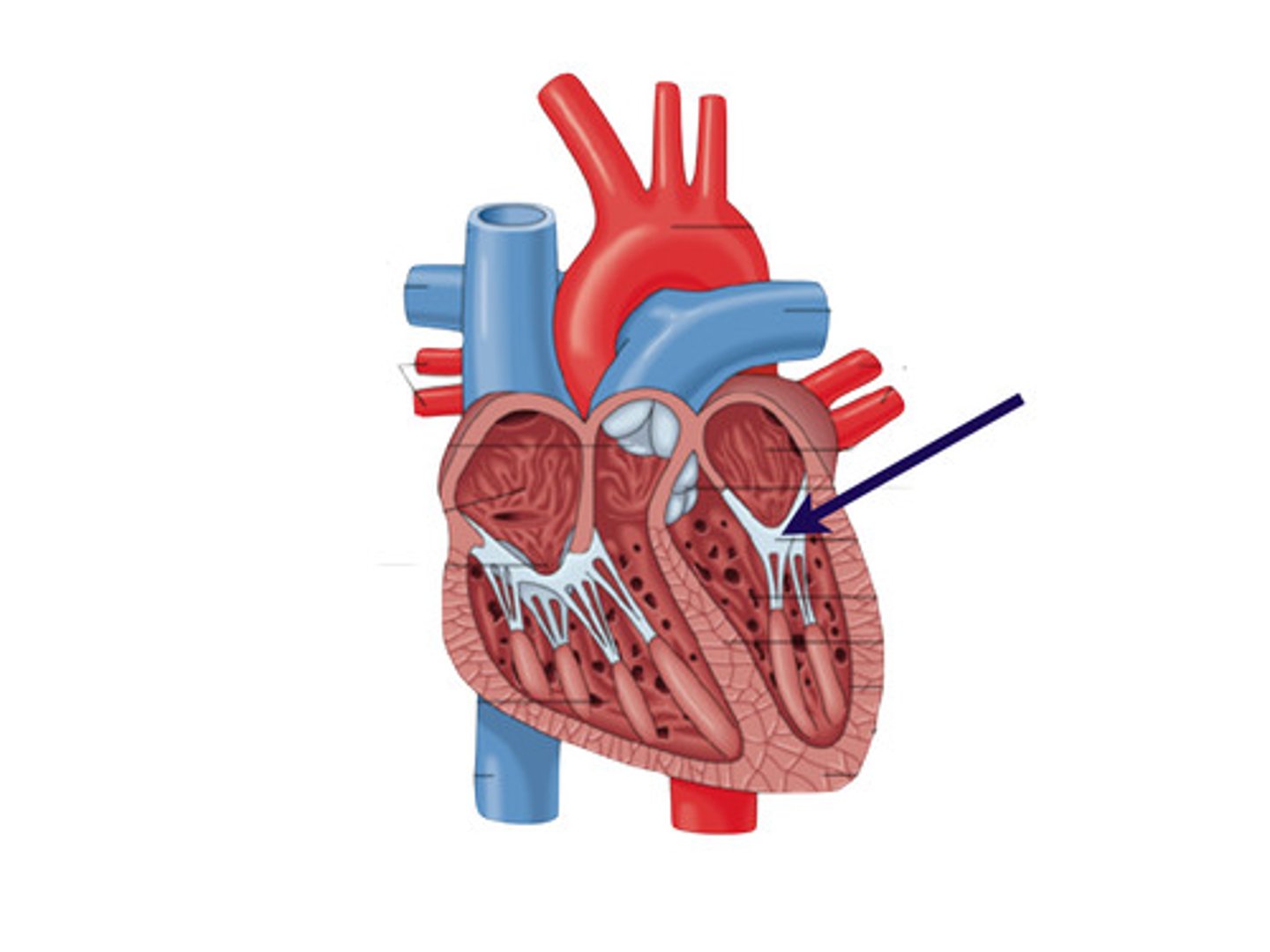
aortic vestibule
the narrowing "outflow part" of the ventricle leading to the ascending aorta
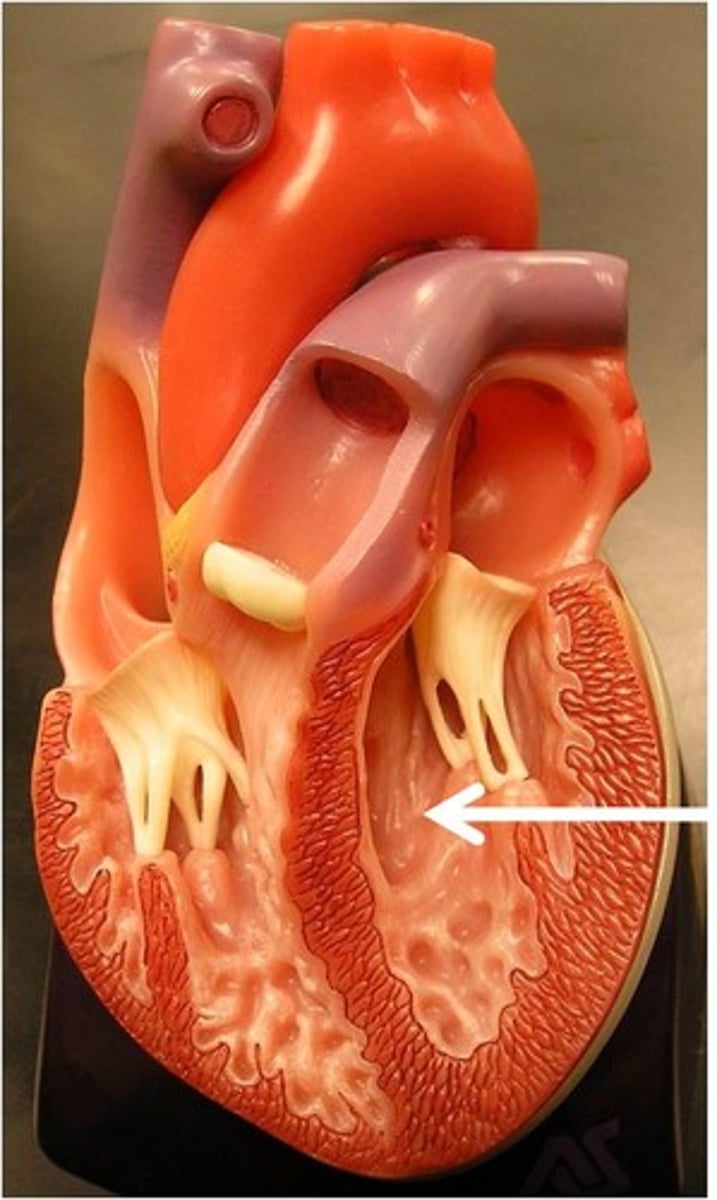
opening of ascending aorta
probe going through the aorta
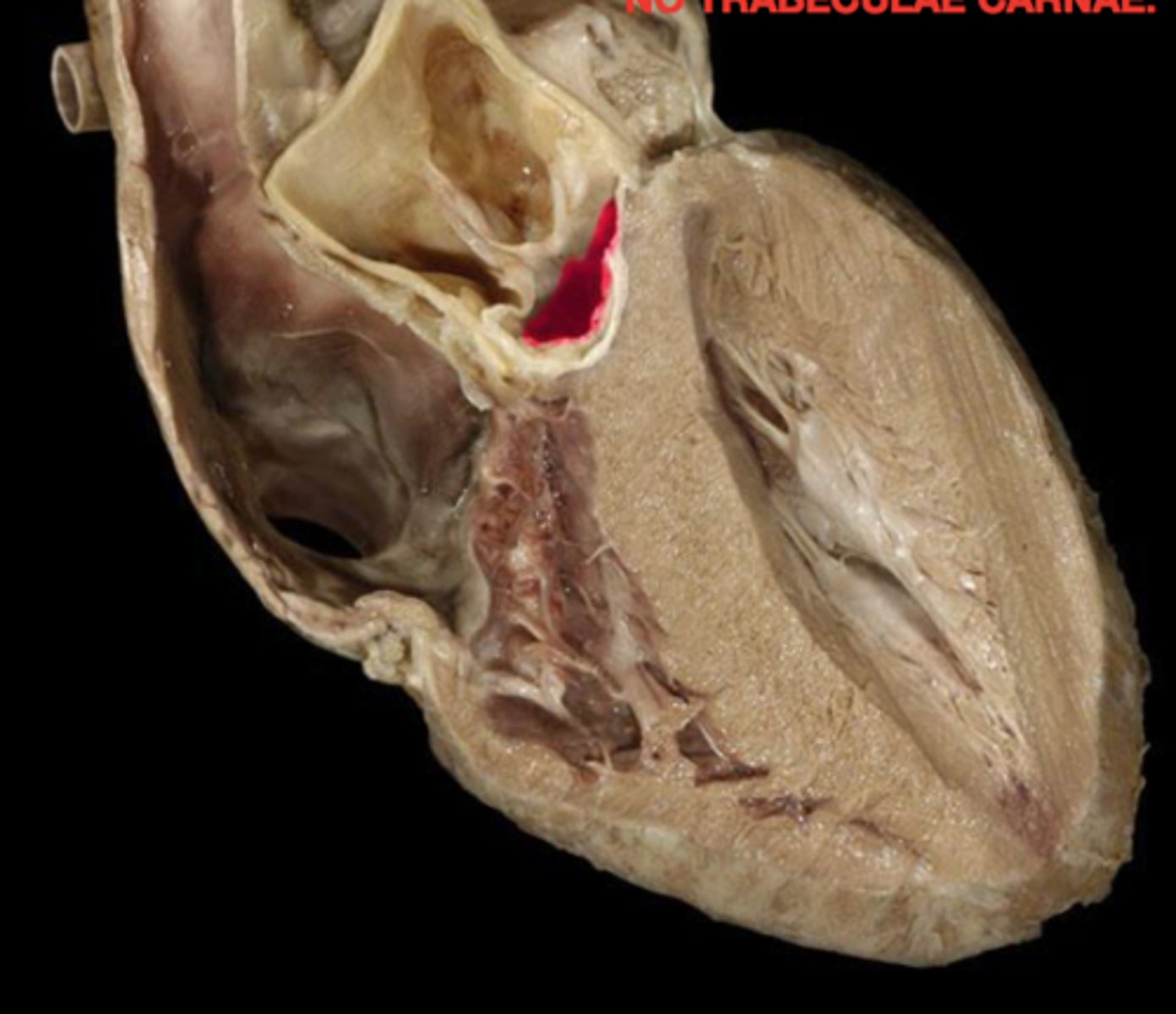
aortic valve
all three cusps make up the...
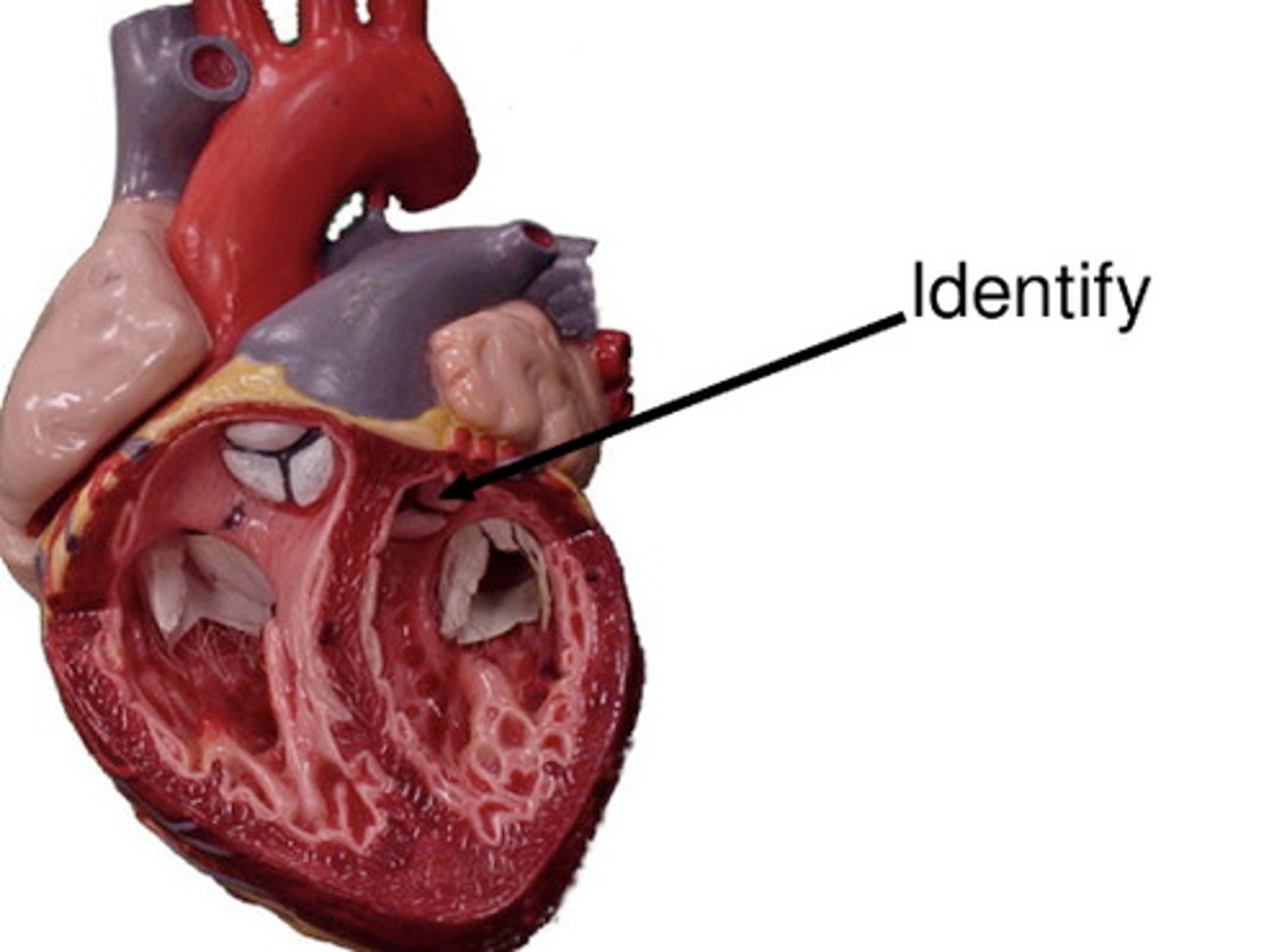
tricuspid valve (3)
mitral valve (2)
the atrioventricular valves consist of...
1. sino-atrial node
2. atrioventricular node
3. atrioventricular bundle
4. purkinje fibers
what is the order of the conducting system of the heart?
superior vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, L+R pulmonary artery, lungs, L+R pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta, rest of the body
circulation of blood through the heart
ascending aorta
right and left coronary arteries branch from here (portion)
arch of the aorta
curved part of aorta
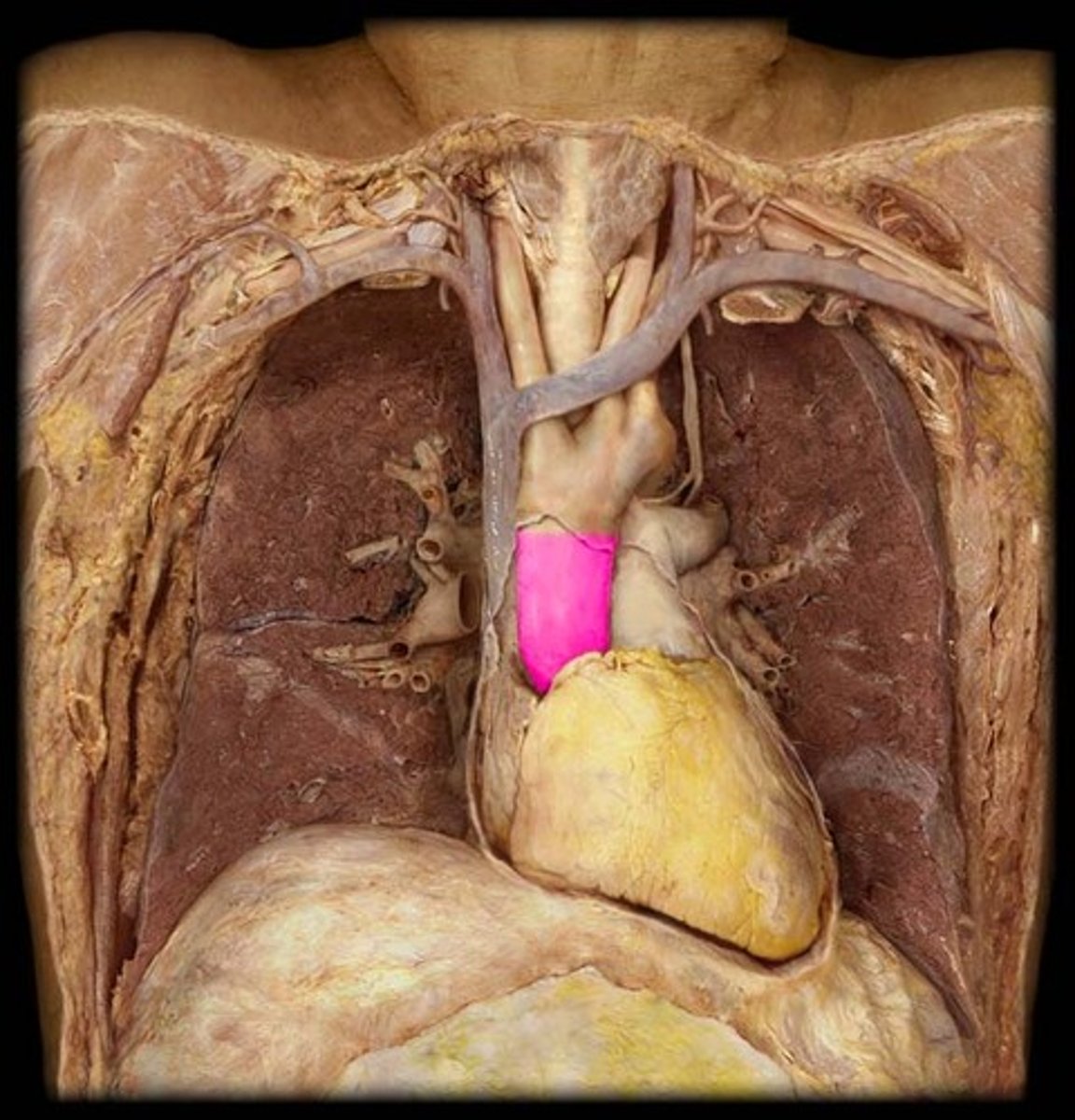
brachiocephalic artery
first branch off aortic arch
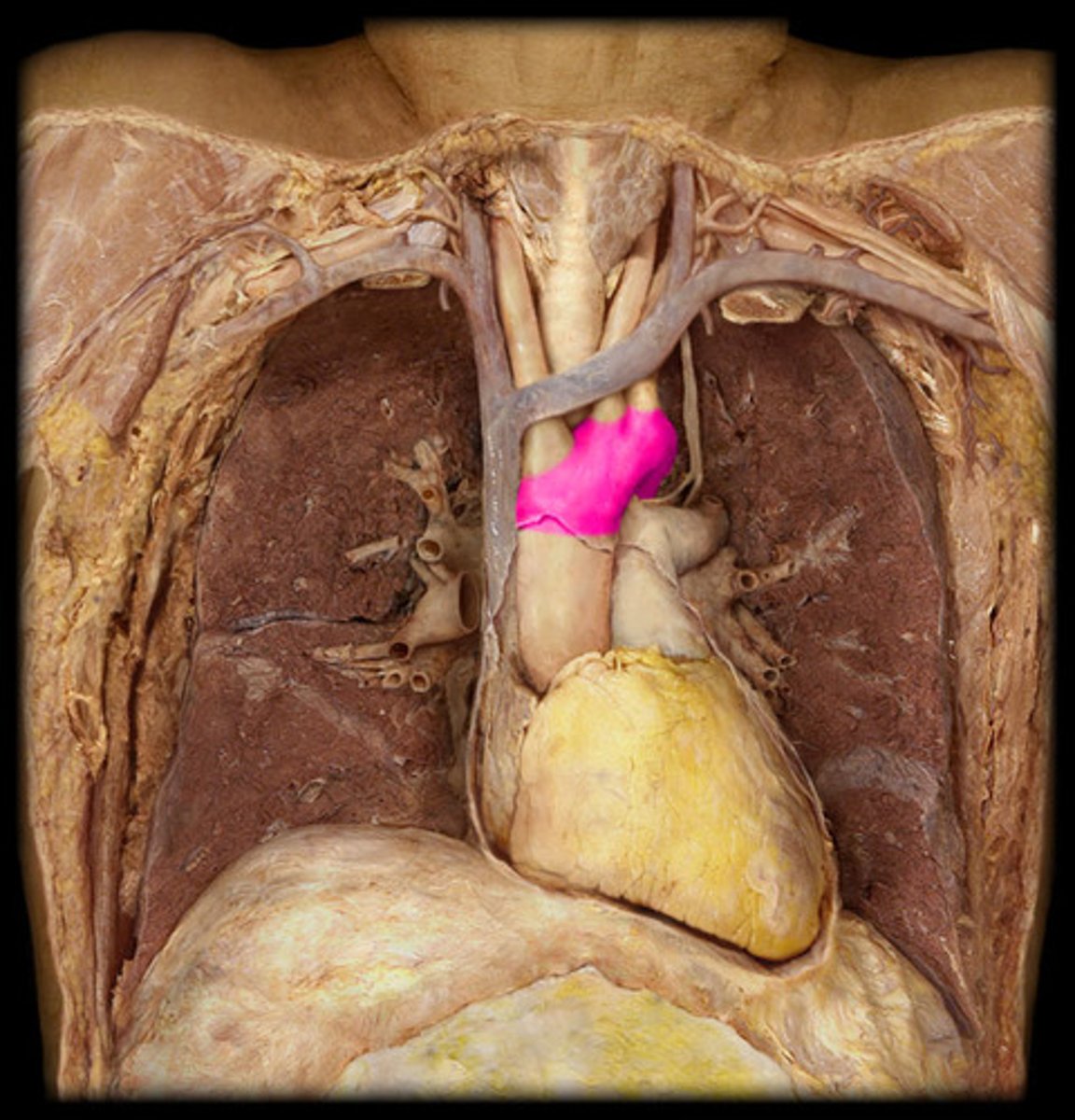
right common carotid artery
branches off brachiocephalic artery
supplies blood to right side of head and neck
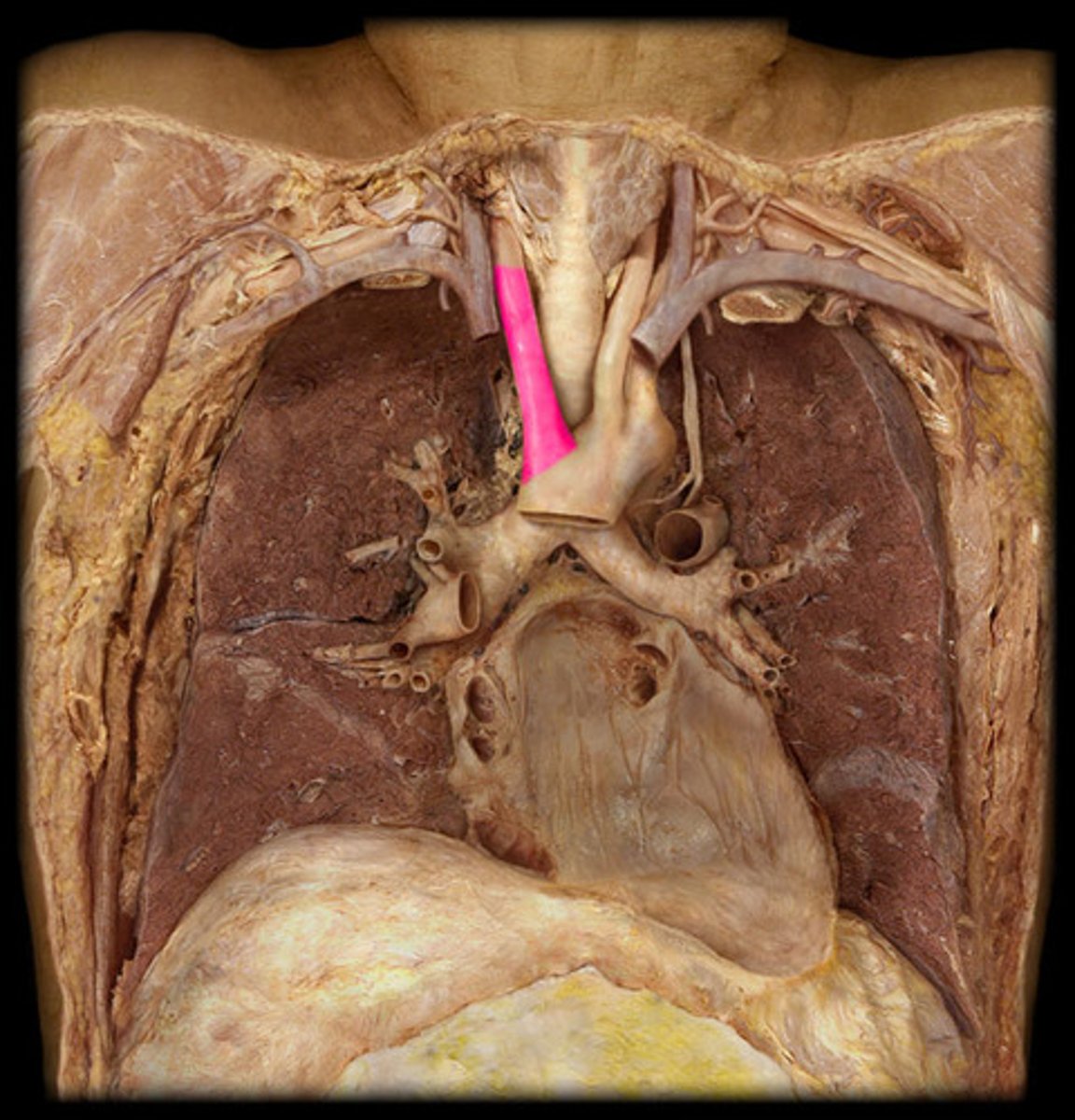
right subclavian artery
passes to the upper limb, deep to the clavicle
into the arm
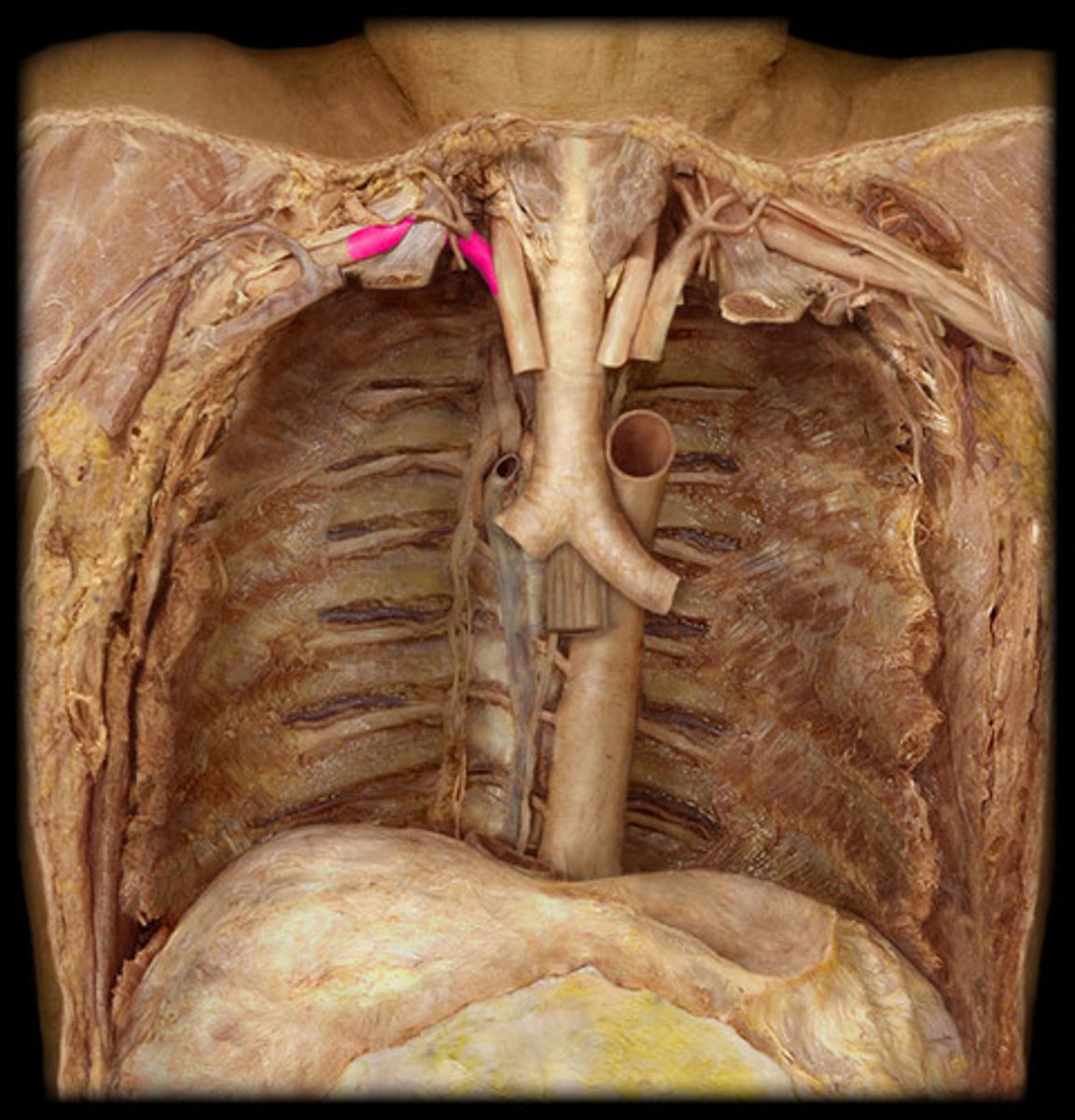
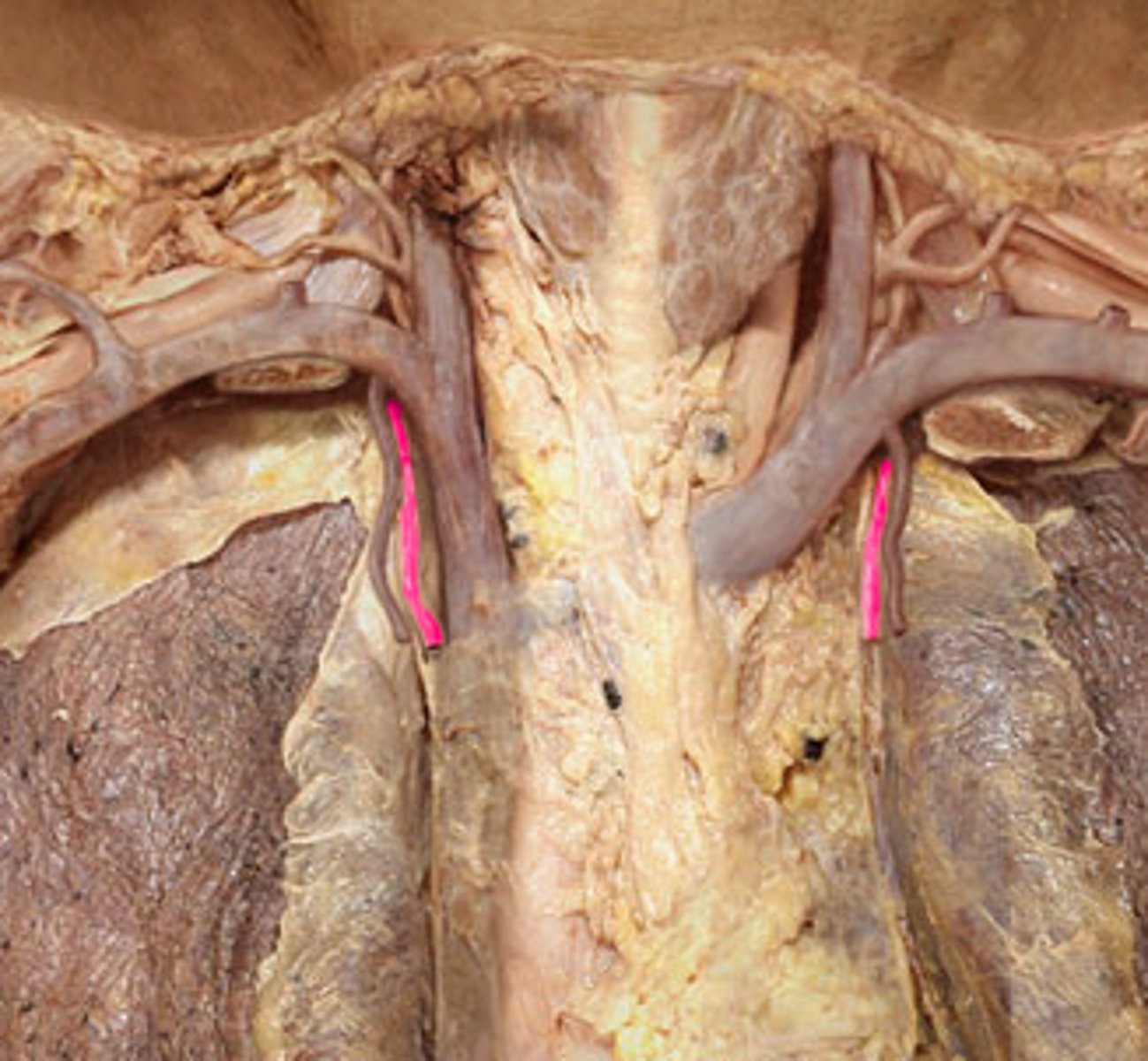
R. internal thoracic artery
runs deep to the costal cartilages to supply the anterior chest walls
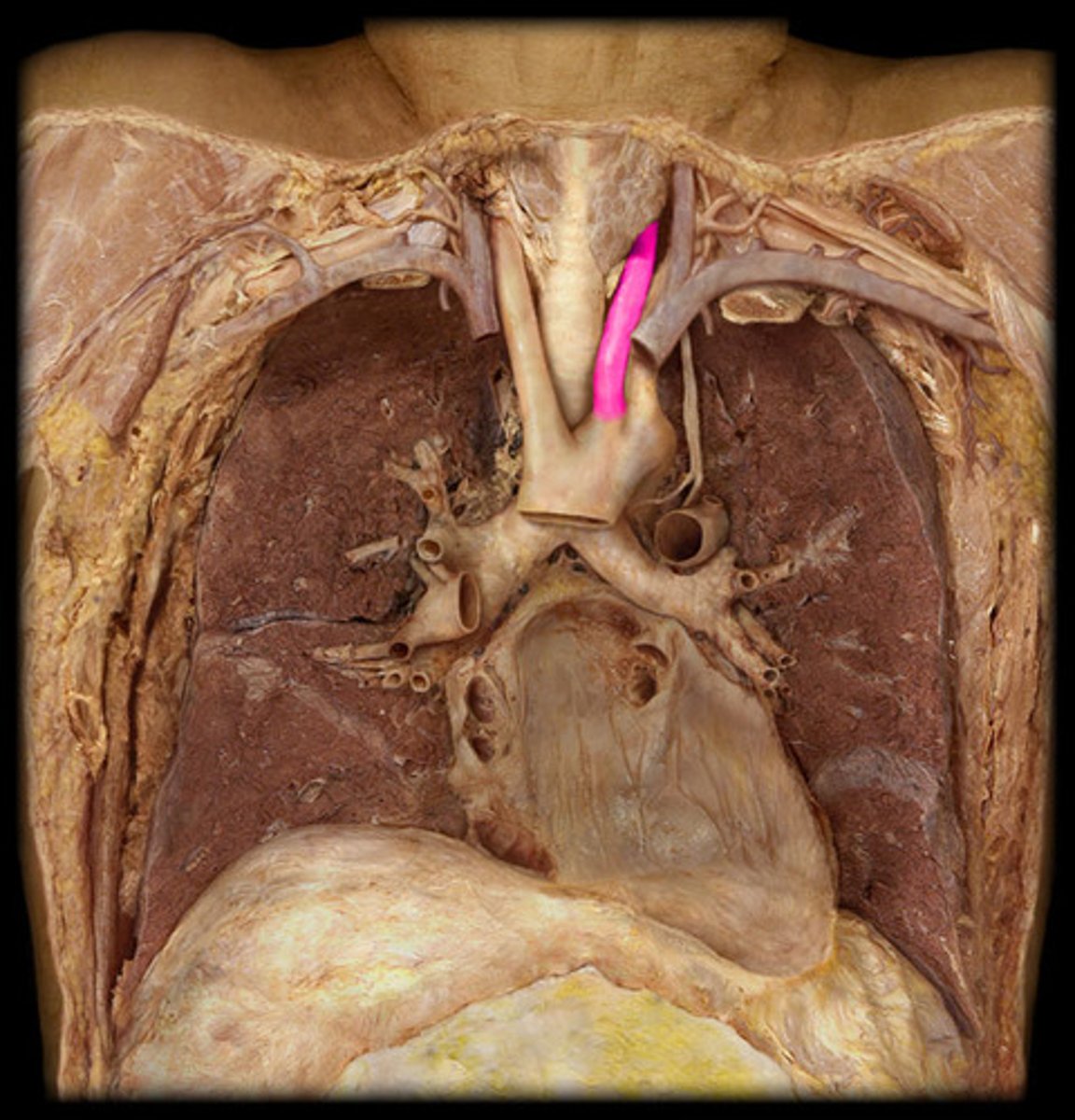
L. common carotid artery
second branch off the aortic arch
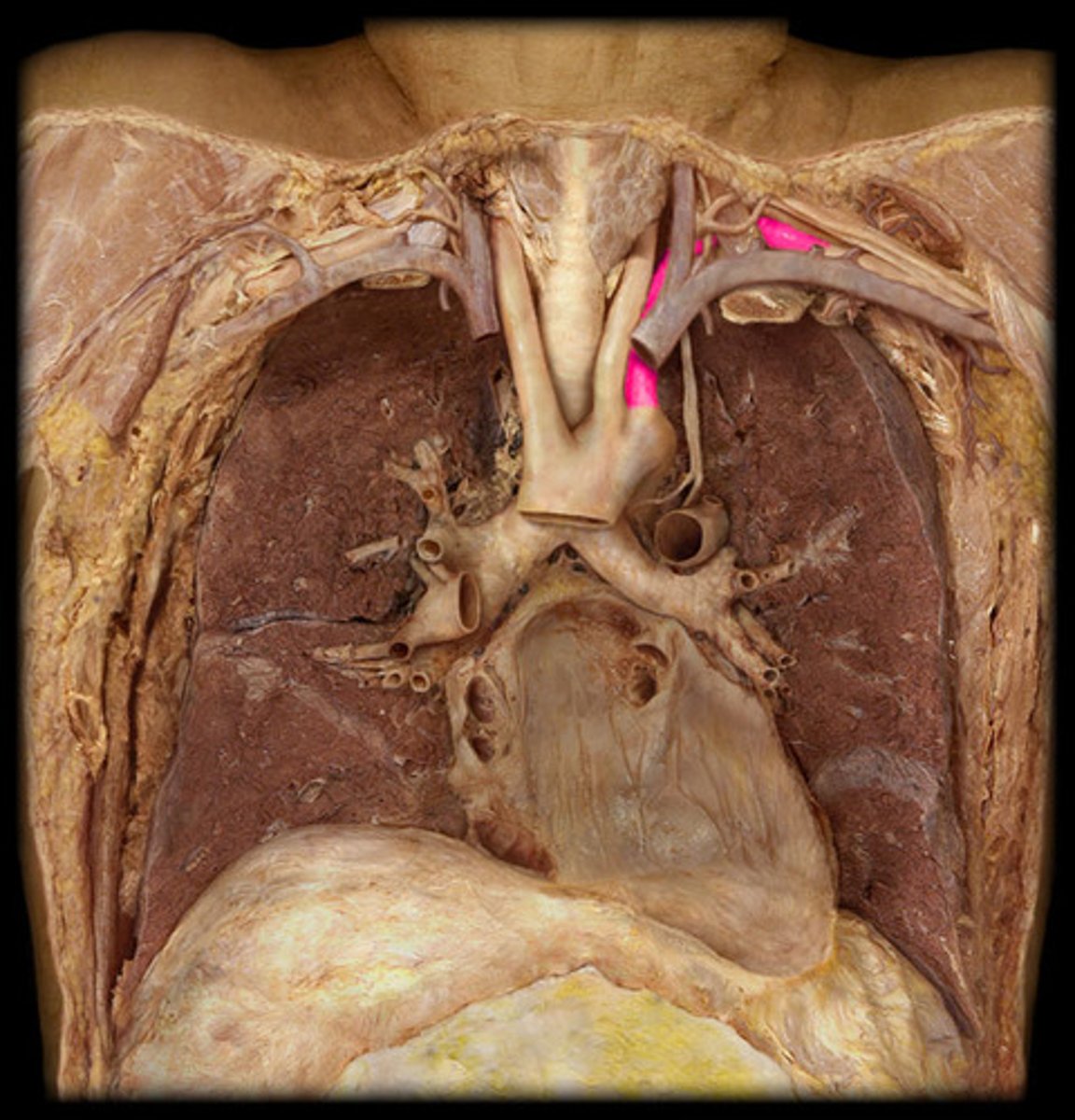
L. subclavian artery
third branch of the aortic arch
L. internal thoracic artery
comes off the l. subclavian, going towards the thorax
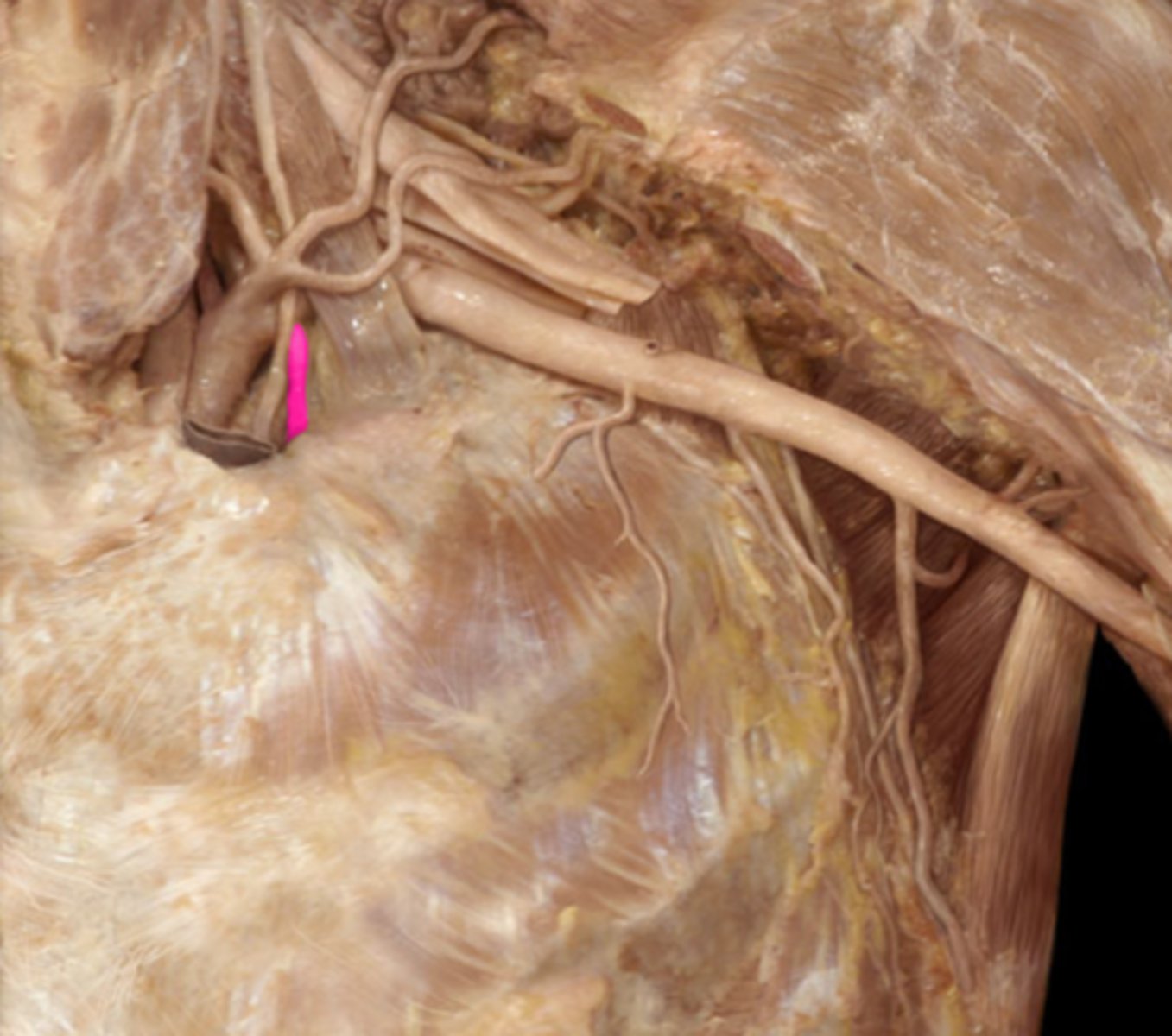
descending aorta
deep to the inferior vena cava; the largest artery of the body; carries blood away from the heart down the midline of the body
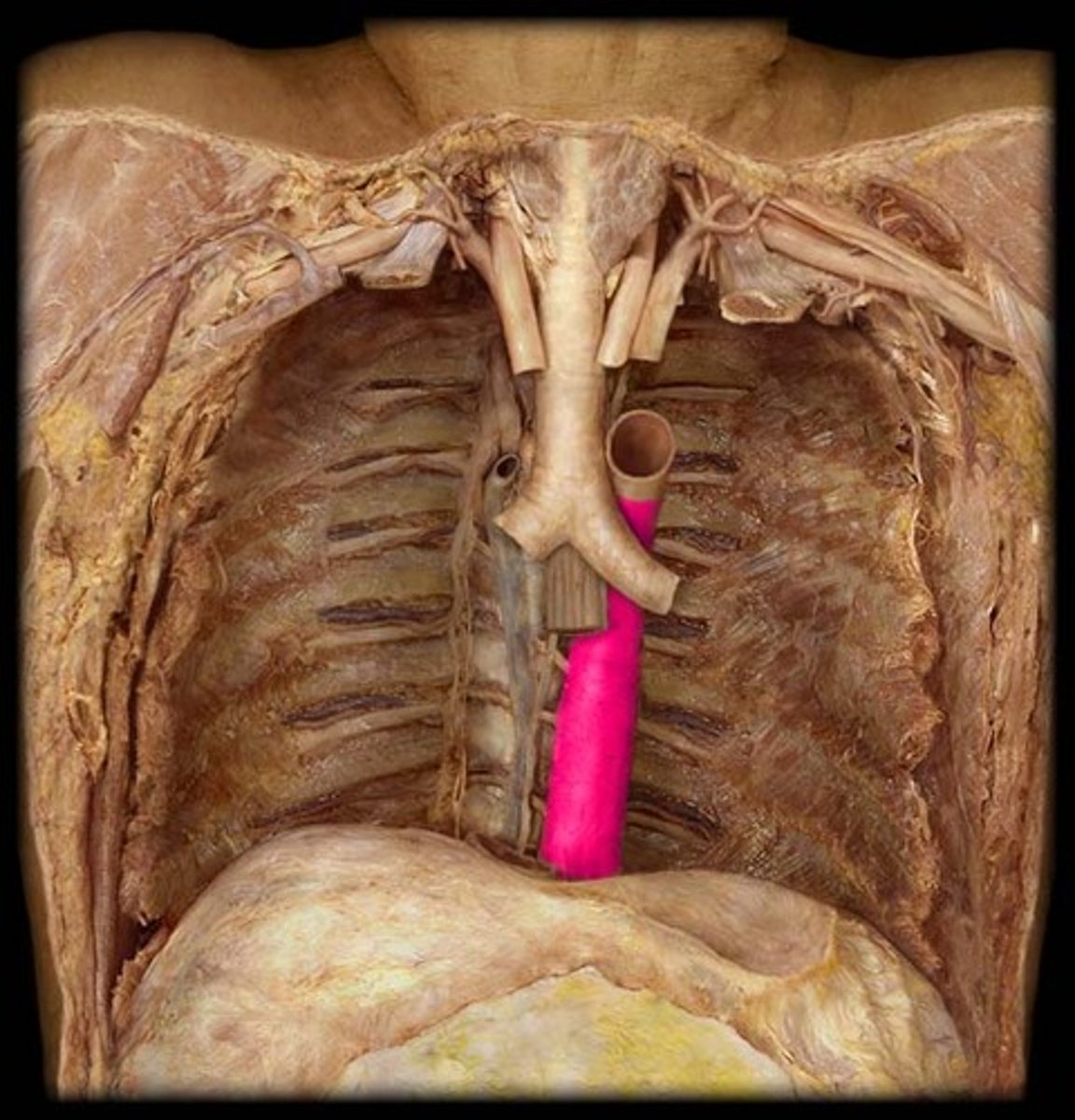
thoracic aorta
travels downward through the thorax
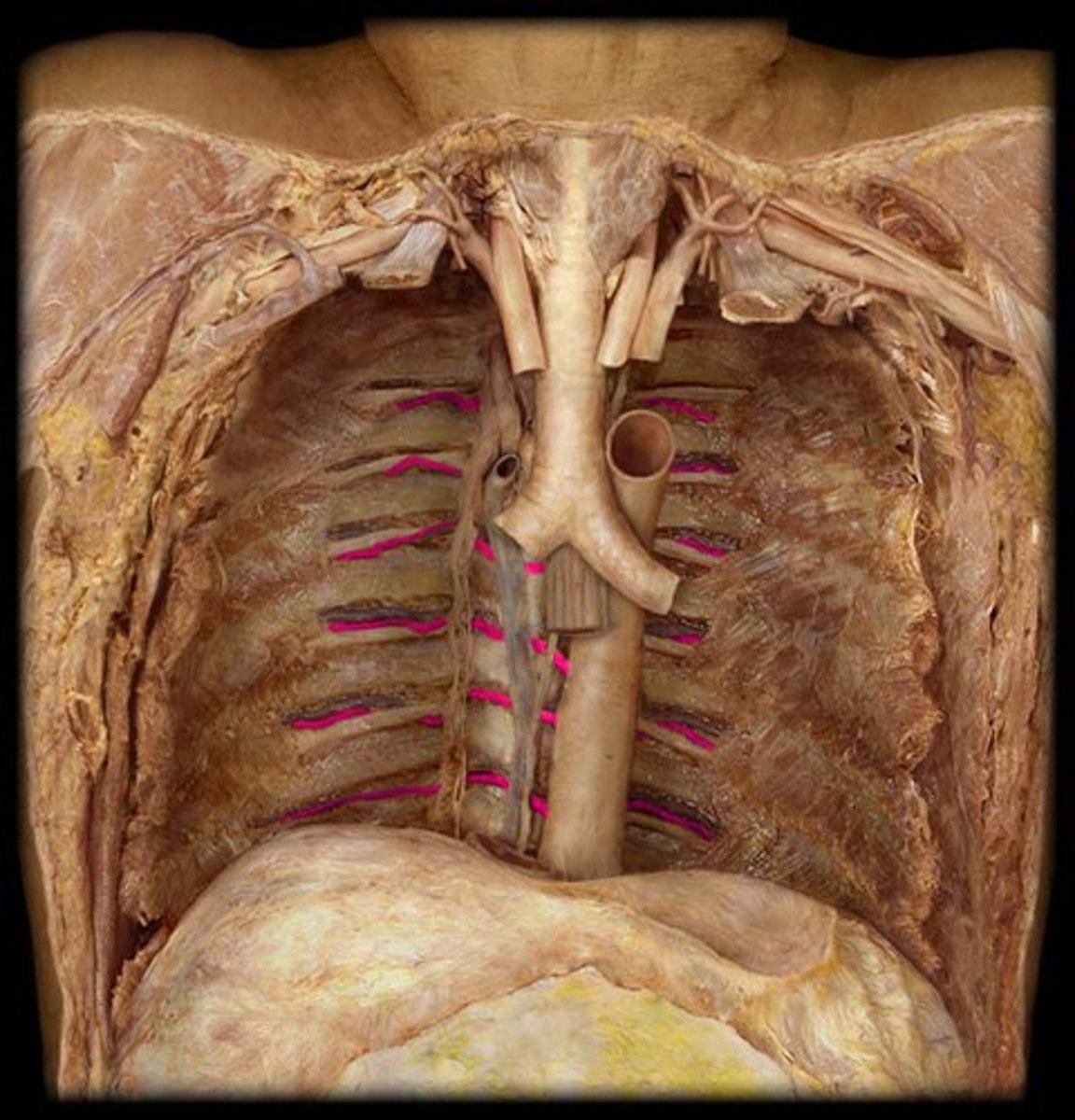
left posterior intercostal arteries
enters the 3rd through 11th intercostal spaces, supplies the chest wall
abdominal aorta
continuation of the thoracic aorta that runs through the abdominal cavity
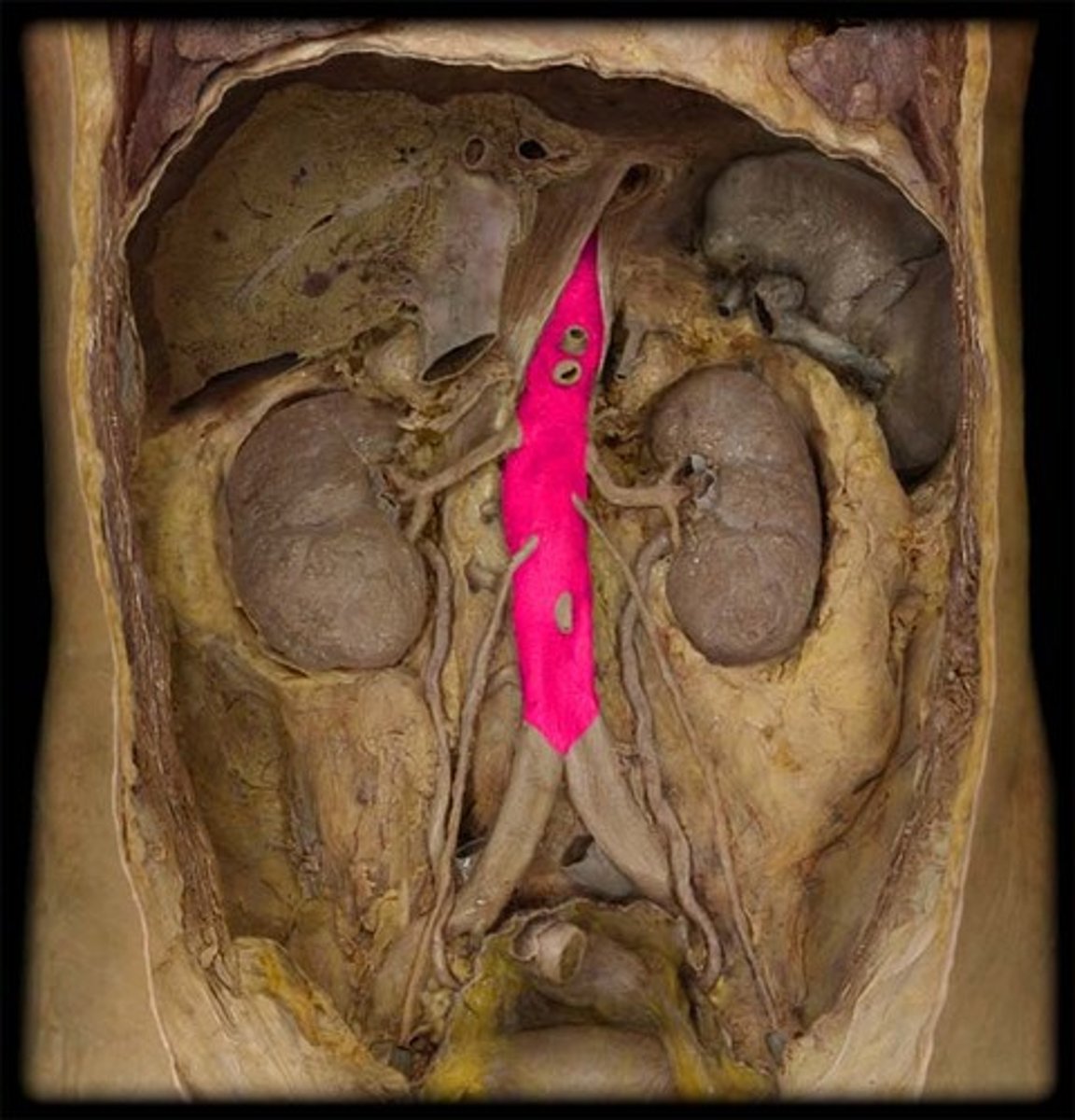
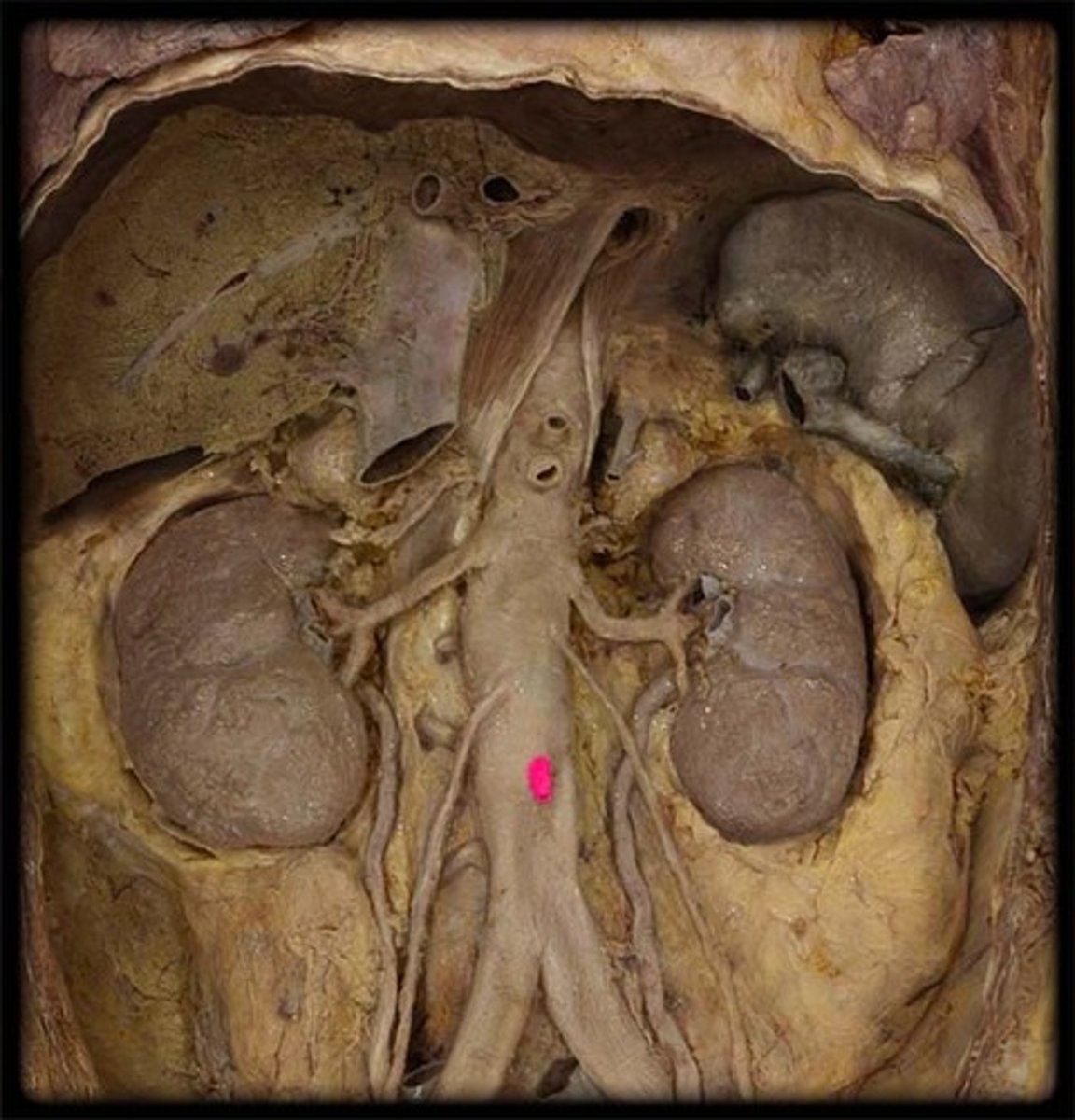
renal arteries
The two small branches of the abdominal aorta that supply the kidneys
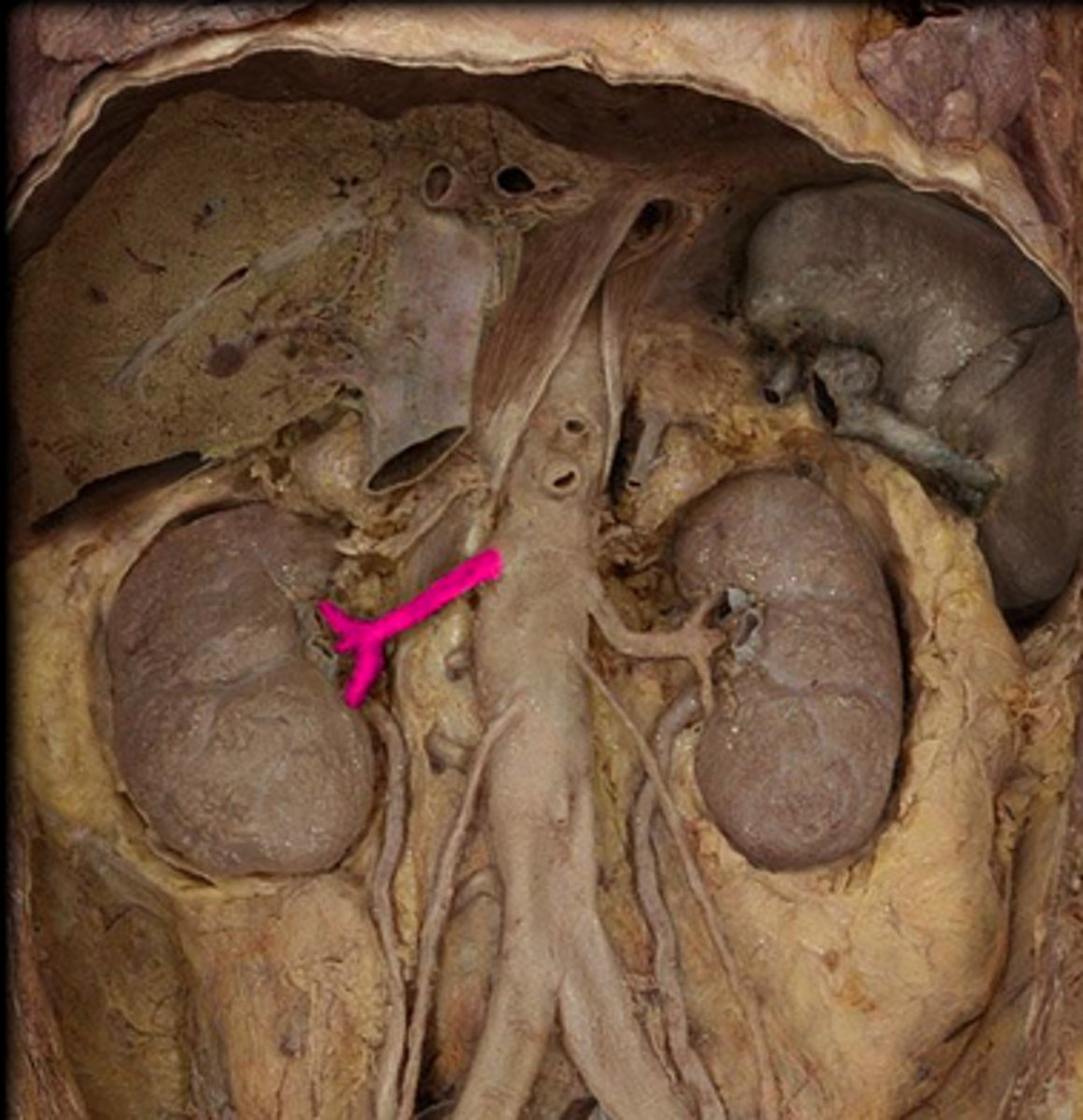
celiac trunk
Large unpaired branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies the liver, stomach, and spleen. 1st
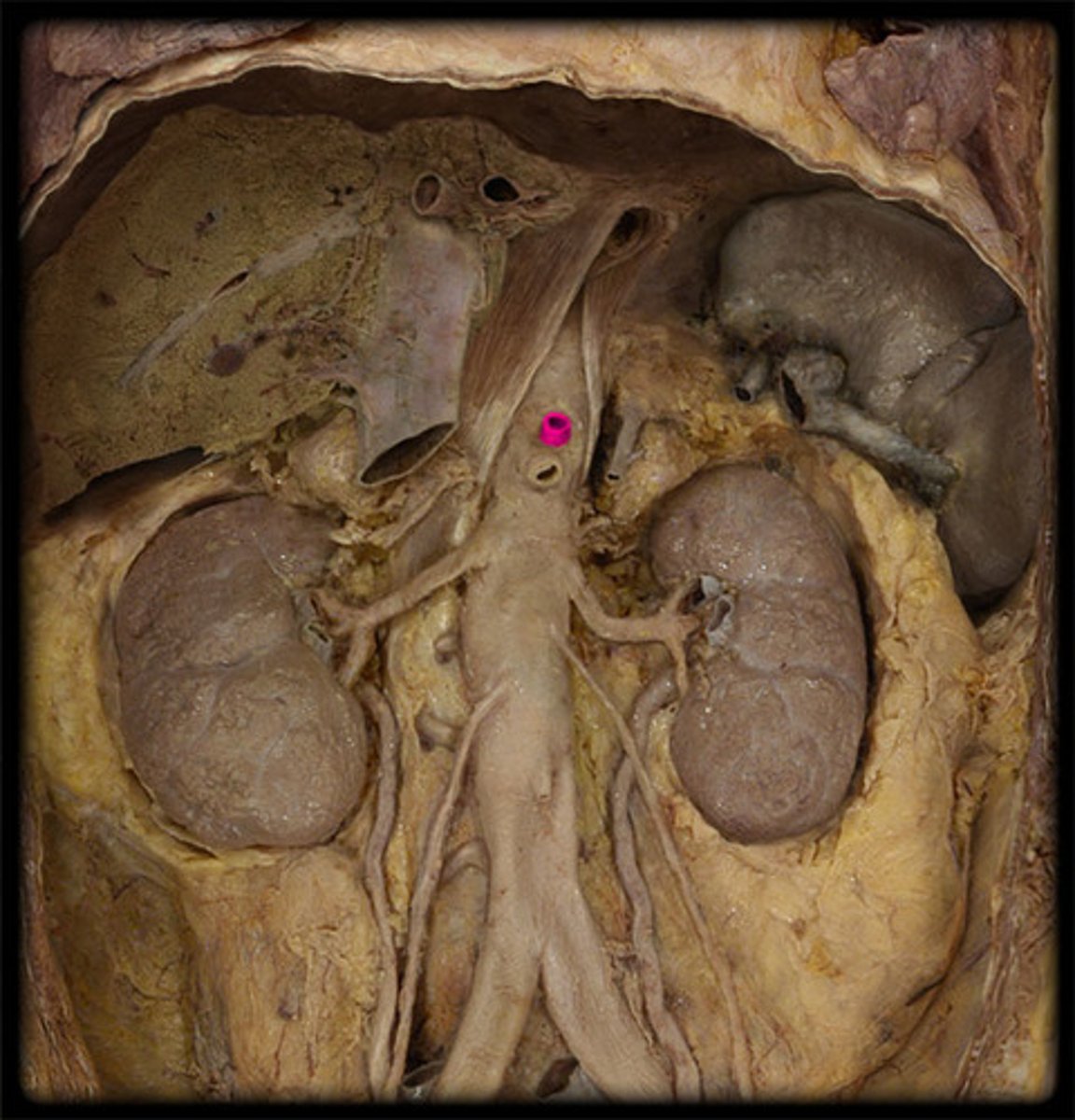
superior mesenteric artery
unpaired. to middle digestive tube. below celiac trunk. 2nd
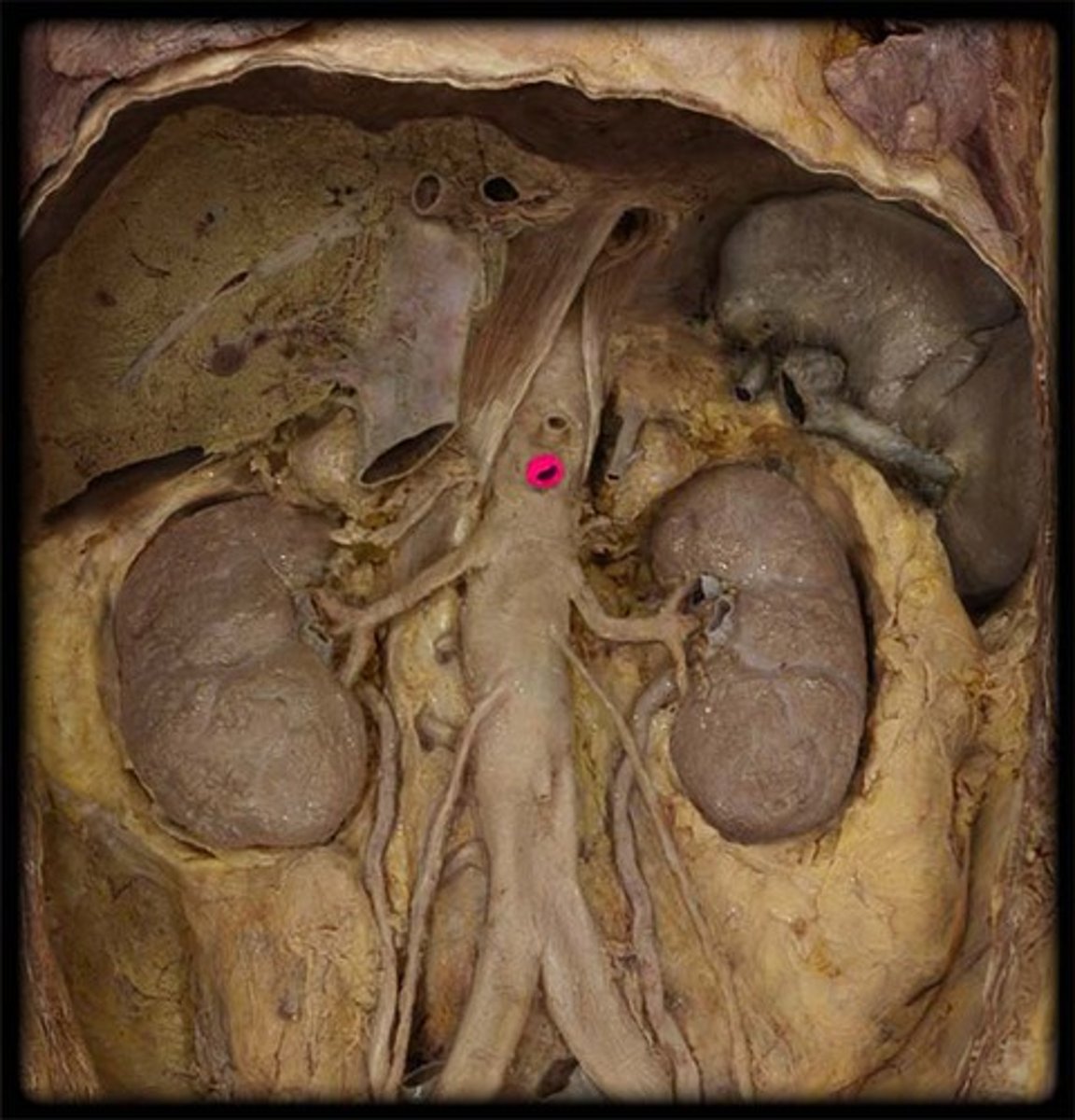
inferior mesenteric artery
unpaired. to lower digestive tube. cord like, 3rd