N209 - Hair, Skin & Nails
1/90
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Macule/patch (primary)
solely color change, flat and circumscribed.
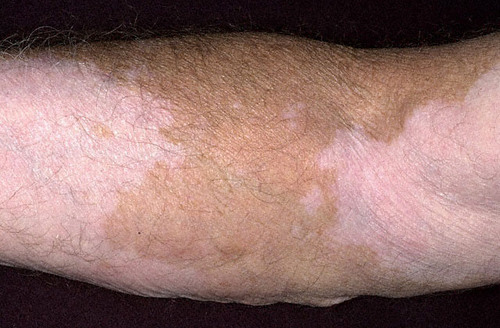
e.g., freckles, petechiae, Mongolian spot, vitiligo
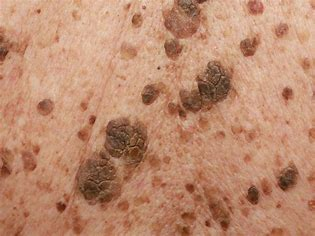
Papule/plaque (primary)
something you can feel (solid, elevated, circumscribed) caused by the superficial thickening of the epidermis.
e.g., moles, warts, psoriasis
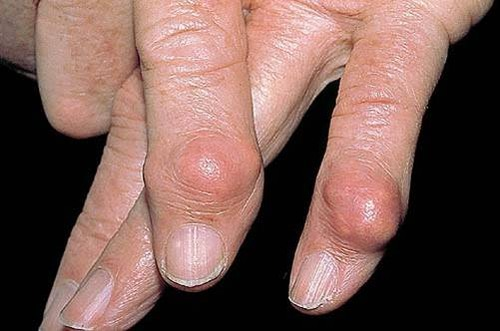
Nodule/tumor (primary)
vesicle/bulla (primary)
elevated cavity containing free fluid.
e.g., herpes zoster (shingles), contact dermatitis, burns, friction blisters
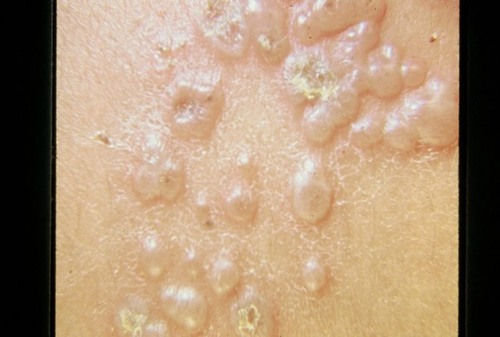
pustule (primary)
turbid fluid (pus) in the cavity.
e.g., impetigo, acne
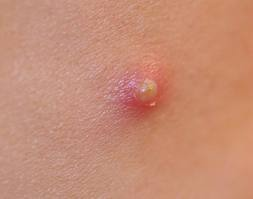
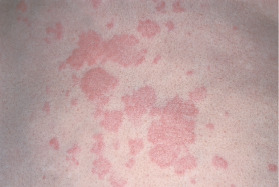
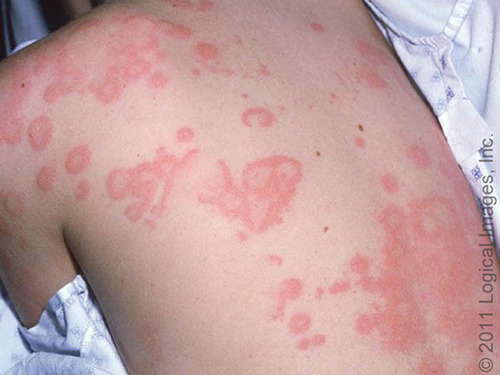
wheal (primary)
e.g., mosquito bite, allergic reaction
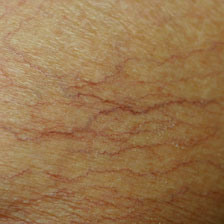
telangiectasia (primary/vascular)
caused by dilation of blood vessels that are visible on the skins surface
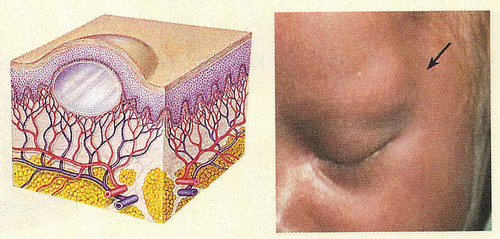
cyst (primary)
encapsulated fluid-filled cavity in dermis or subcutaneous layer
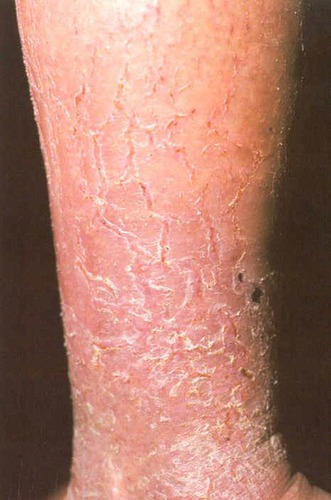
scale (secondary)
compact, desiccated flakes of skin from shedding of dead excess keratin cells
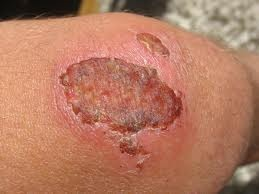
crust (secondary)
the thickened, dried-out exudate left when vesicles/pustules burst or dry up
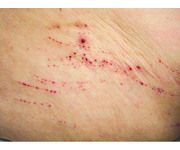
excoriation (secondary)
self-inflicted abrasion; superficial; scratches from intense itching
erosion (secondary)
scooper-out, shallow depression. loss of epidermis
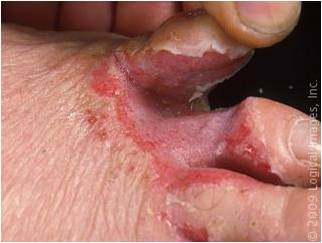
scar (secondary)
normal tissue is lost and replaced with collagen (CT) after a skin lesion (permanent change)
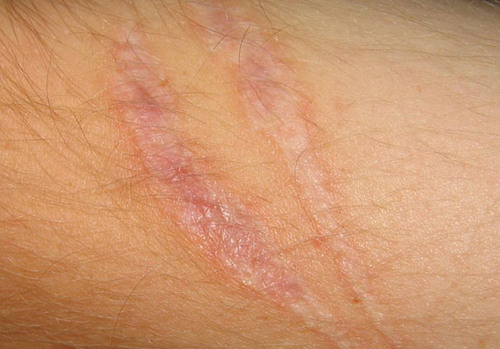
keloid (secondary)
benign excess of scar tissue beyond sites of original injury
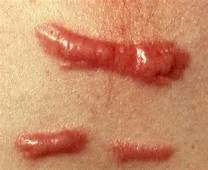
ulcer (secondary)
deeper depression extending into dermis.
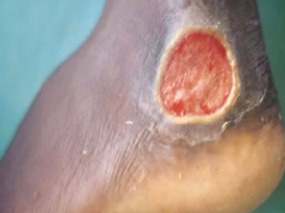
atrophy (secondary)
skin is depressed with a loss of tissue (thinning of the epidermis).
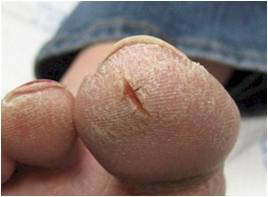
fissure (secondary)
linear crack with abrupt edges that extends into the dermis.
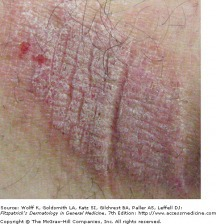
lichenification (secondary)
thickening of the skin from irritation or rubbing.
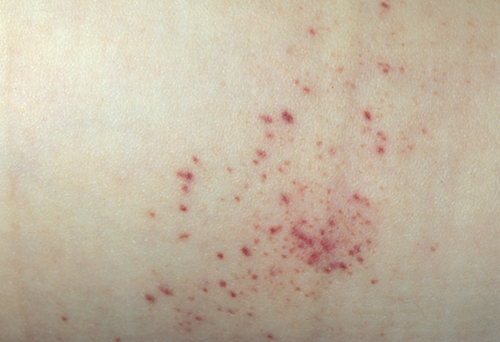
petichiae (vascular)
tiny purple or red spot caused by bleeding into the skin
spider telangiectasia (vascular)
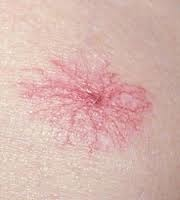
purpura (vascular)
confluent and extensive patch of petechiae and ecchymosis
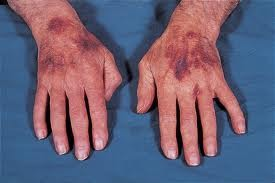
ecchymoses (vascular)
bleeding into tissue.
no change with pressure (doesn’t blanch) and tenderness
complete exam
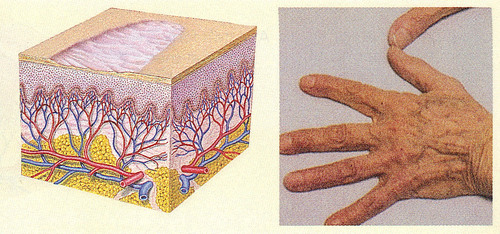
assessment of the skin is integrated throughout as you move through each system
starts w hands and fingernails
separate areas w skinfold (common sites for irritation)
Regional Exam
help the person remove clothes & assess the skin as one entity.
reveals distribution patterns (overall impression of the skin)
ABCDEF
asymmetry
border irregularity - notched, scalloped, or poorly defined border
color variation - multi-colored/different shade
diameter - >6mm
elevation or evolution - sudden change or appearence
funny looking
What are the danger signs (abnormal characteristics) of pigmented lesions?
purple to yellow-green areas
no change w pressure
soreness
How does ecchymosis appear in light skin?
difficult to see (darker area)
no change w pressure
tender
How does ecchymosis appear in dark skin?
pallor
the red-pink tones from oxygenated Hbg are lost & the skin takes on a white complexion
Etiology
anemia (decreased hematocrit)
shock/fear/anxiety (vasoconstriction)
arterial insufficiency
albinism (total absence of pigment)
vitiligo (patchy depigmentation)
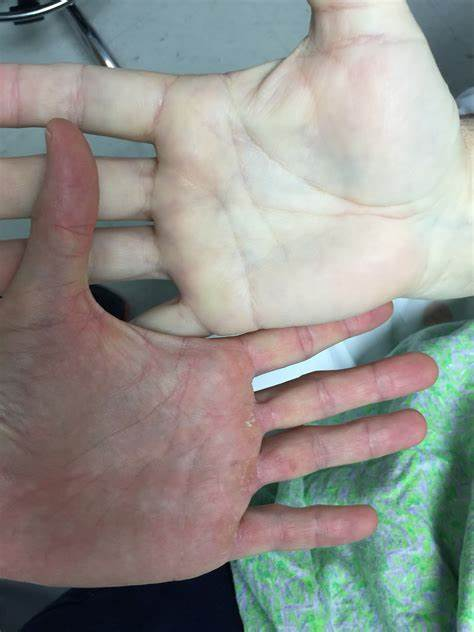
lack of color to the face
pale lips
no red tones
How does pallor appear in light skin?
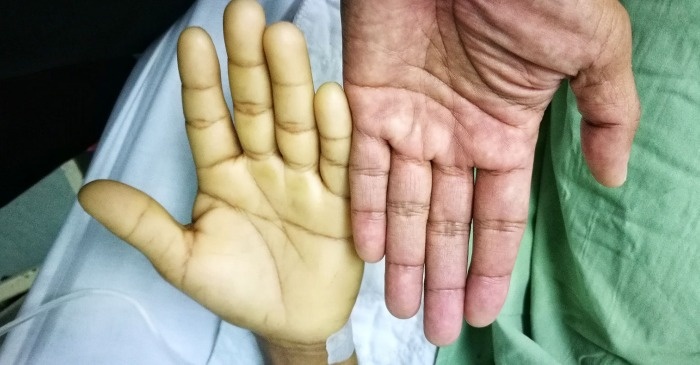
yellow-brown
ashy-grey
How does pallor appear in dark skin?
erythema
= intense redness of the skin from excess blood in the superficial capillaries (surface of the epidermis)
expected with fever, inflammation, & emotions in the cheeks, neck and upper chest
redness may not be visible, but you can palpate for heat and swelling
How does erythema appear in dark skin?
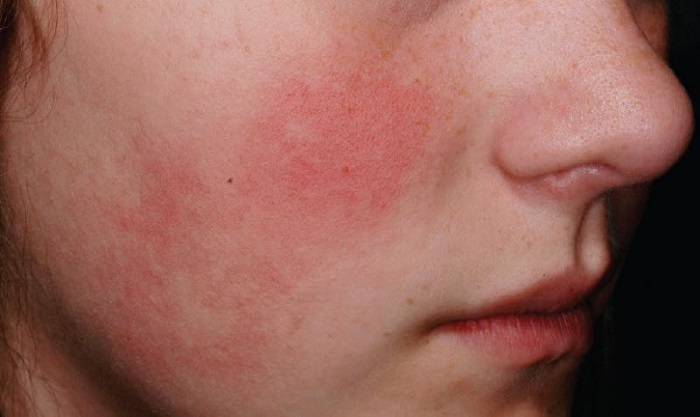
redness associated with heat (blanches with pressure)
How does erythema appear in light skin?
cyanosis
bluish-mottled color from decreased perfusion (= high levels of deoxygenated blood)
occurs with shock, cardiac arrest, chronic bronchitis, heart failure
occurs with decreased LOC (bc there is decreased oxygen to the brain)
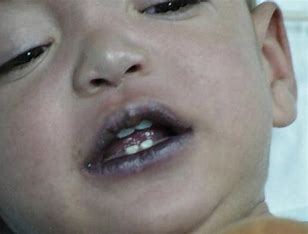
a bluish tinge to the lips, nose, cheeks, ears and oral mucosa
How does cyanosis appear in light skin?
ashy-grey lips and tongue
How does cyanosis appear in dark skin?
there is not enough Hb present to color the skin
Why can a person who is anemic have hypoxemia without ever looking blueish?
they cannot oxygenate the massive amounts of RBCs, but there is adequate oxygenation for the body to function properly.
Why can a person with polycythemia look blue without being hypoxemic?
Jaundice
yellowish skin color that signals a rising bilirubin in the blood
occurs with hepatitis, cirrhosis, sickle-cell disease, transfusion reaction, hemolytic diseases.

visible on the sclera, hard palate, palms and soles
How does Jaundice appear in dark skin?
hypothermia
generalized coolness induced in surgery, fever, and cardiac arrest
localized coolness expected with poor blood flow in areas (such as with PAD)

Hyperthermia
generalized warmness with increased metabolic rate (such as with fever and after exercise)
localized warmness associated with trauma, sunburn, and infection

diaphoresis
=profuse sweating
accompanies an increased metabolic rate (from heart attack, anxiety, pain)

dehydration
visible in the oral mucous membranes (will be dry)

no, this is a normal finding
A dark-skinned pt. has dry/ashy skin. Is this patient necessarily dehydrated?
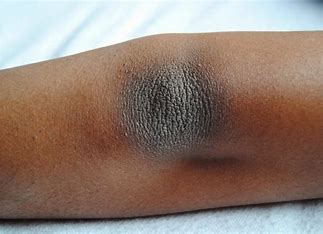
hyperthyroidism
With what condition would the pt. have smooth, velvety skin?
hypothyroidism
With what condition would the pt. have rough, dry, & flaky skin?
corns & calluses
an overgrowth of epidermis from excessive pressure from the friction of work & weight bearing (overuse of skin)
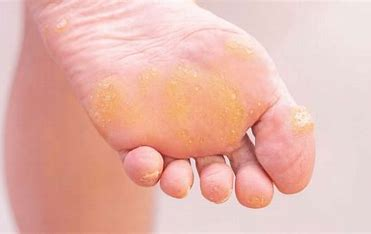
the skin becomes thin and shiny
How does arterial insufficiency (in OA) effect the skin?
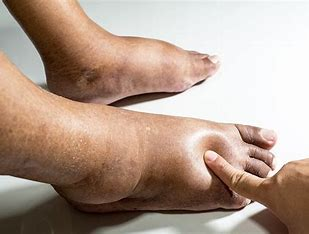
edema
fluid in the interstitial tissues (not normally present) that shows in dependent body parts (whichever way gravity pulls)
normal skin color is masked bc fluid lies b/t the surface and pigmented/vascular layer
mobility & turgor
= elastic nature of the skin
indicates hydration status
Mobility
= ease of the skin to rise
turgor
= ability of the skin to return to place (normal = 3-5 sec)
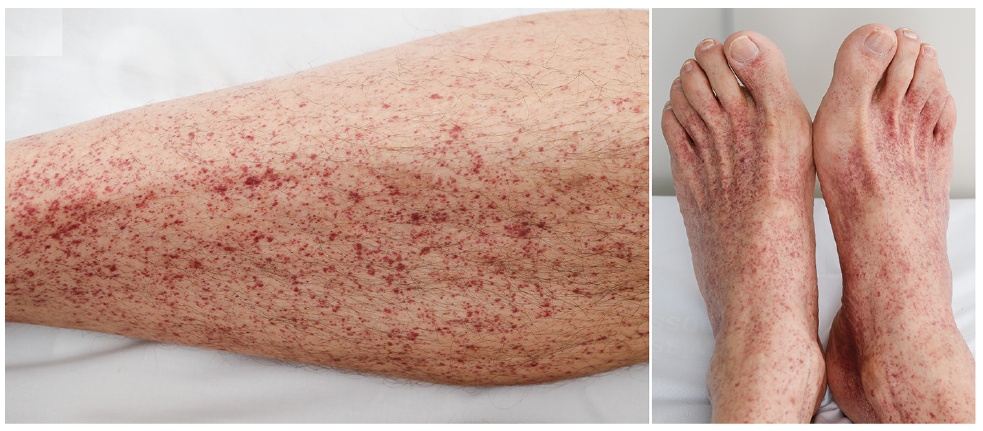
petechiae
= intradermal bleeding (tiny areas)
Primary Lesions
= a lesion developed on previously unaltered skin
e.g., blister
Secondary Lesion
= when a lesion changes over time or changes bc of scratching/infection
e.g., crusted blister
generalized
lesion is widespread over the body (e.g., found on face, abdomen, legs, back)
Universal
lesion is over the entire body
Bizzare
lesion is irregularly distributed or geographically patterned
contact dermatitis
= local inflammatory reaction to an irritant in the environment or an allergy
e.g., poison ivy
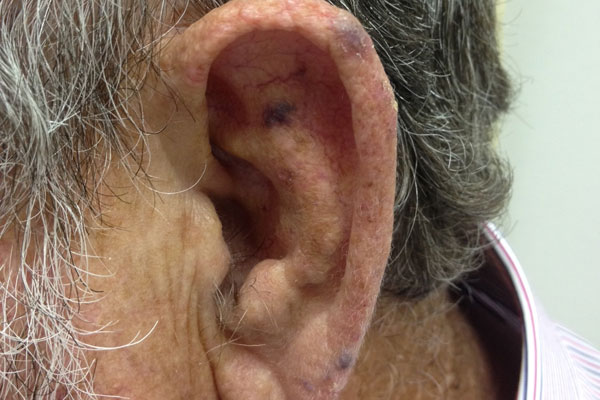
venous lake
= a blue-purple dilation of venules and capillaries on the face of OA
candidiasis
= common cause of diaper dermatitis; infection in the genital area marked by scaling patches
impetigo
= highly contagious bacterial infection of skin, most common in infants and children
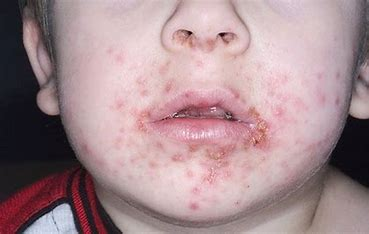
Herpes Zoster (shingles)
caused by a reactivation of the dormant virus of chickenpox
small, grouped vesicles emerge along the route of cutaneous sensory nerve (zosteriform)
skin cancer
the most diagnosed cancer in the US =
men
_____ are three times more likely to get melanoma on the scalp, face and ears
legs
the most common site for melanoma in women is the _______
basal cell carcinoma
most common type of skin cancer, occurring on sun-exposed areas of the face, ears, scalp, and shoulders.
squamous cell carcinoma
arise from actinic keratosisor de novo. usually on hands or head.
malignant melanoma
mole/macule that transforms into cancer
fine vellus hair
(peach fuzz) coats the body
coarse terminal hair
thick hair on the scalp, pubic axilla, and male face
endocrine abnormalities
what does absent or sparse genital hair suggest?
Hirsutism
= excess body hair in females following a male distribution pattern
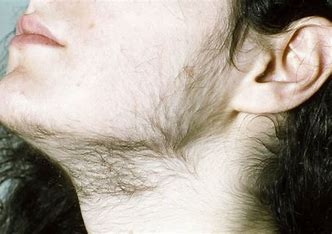
excess circulating androgens
from genetic or adrenal/ovarian disorders
what causes Hirsutism?
toxic alopecia
patchy, asymmetric loss of hair caused by chemotherapy or radiation.
growing hairs are lost and resting hairs are spared.
regrowth occurs after chemotherapy is stopped.
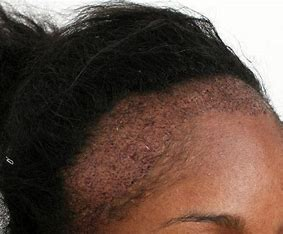
traction alopecia
breaks off due to prolonged tractions/pulling.
cause = mechanical
effects one-third of African American women.
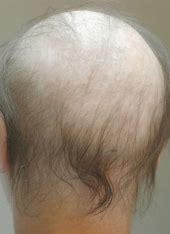
Androgenic Alopecia
male and female pattern baldness which occurs slowly over years, usually a family history of hair loss.

the hair becomes thin throughout the scalp (no bald spots)
How does androgenic alopecia present itself in women?
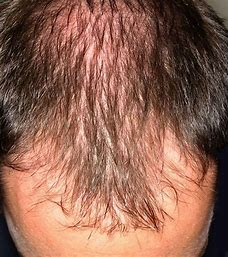
the hair loss starts at the temples, then an enlarging bald spot @ the top of the head
How does androgenic alopecia present itself in men?
~160
@ what degree should the nail base be in normal nails?
clubbing
What does a nail bed @ 180 degrees or more indicate?
onychauxis
nail thickening or hypertrophy caused by trauma, psoriasis, fungal infections, or PVD.
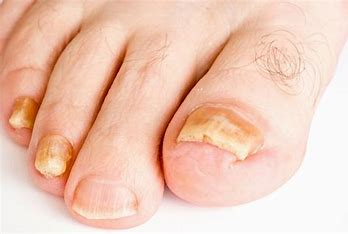
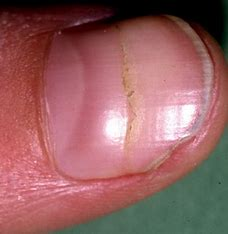
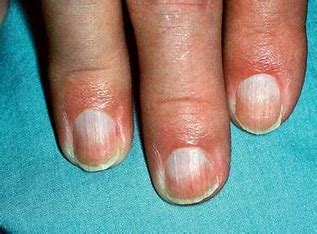
splinter hemorrhage
= red/brown linear streaks from damage to nail bed capillaries
occurs with bacterial endocarditis, trauma, or sport-related injury
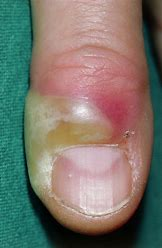
paronychia
= red, swollen, tender inflammation around the nails
most common nail complaint
acute = bacterial infection
chronic = fungal infection from a break in the cuticle
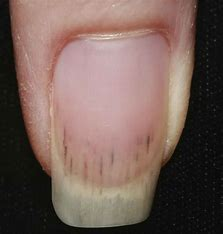
Beau Lines
= transverse furrow or groove associated with malnutrition, anemia, infection, trauma
pitting
sharply defined pitting and crumbling of nails with distal detachment
occurs with psoriasis, PVD, and TB
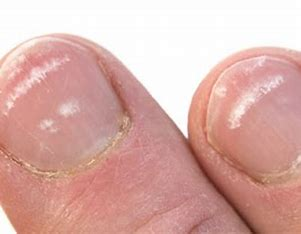
white spots
from mild trauma, infection, or zinc deficiency
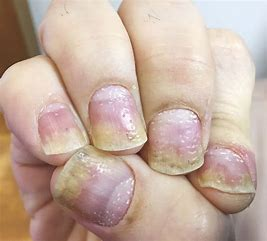
terry nails
¾ of nail is white with a narrow pink band
occurs with liver failure, renal failure, DM, CHF
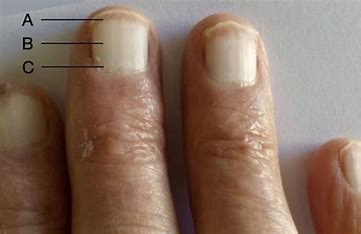
half and half nails
half the nail is white
indicates renal failure
seborrheic keratosis
large lesions that are waxy, thick, wart-like (in OA)