1.3 Nutrition and Food Tests 🥗
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Biology Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Cells, Living Processes & Biodiversity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
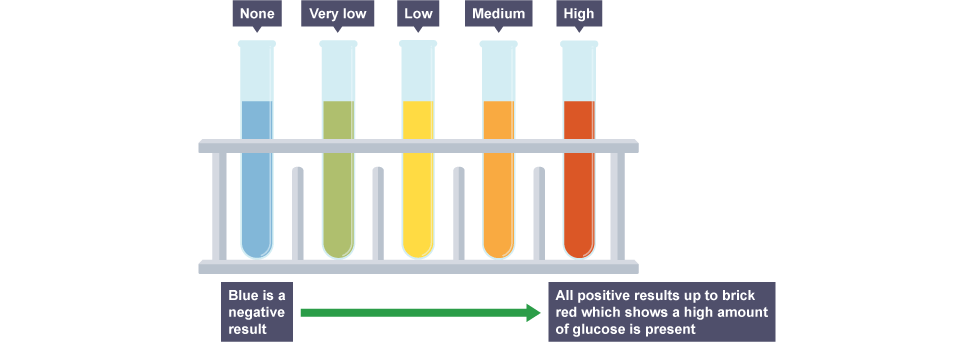
Benedict's reagent
turns from blue to brick-red when heated in presence of sugar
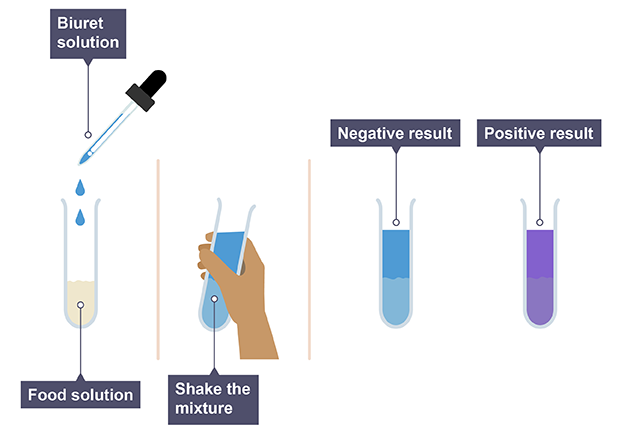
Biuret reagent
Turns from blue to lilac/purple in the presence of proteins
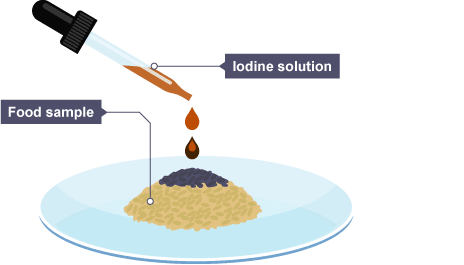
Iodine test
Turns from yellow-brown or orange to blue-black in the presence of starch
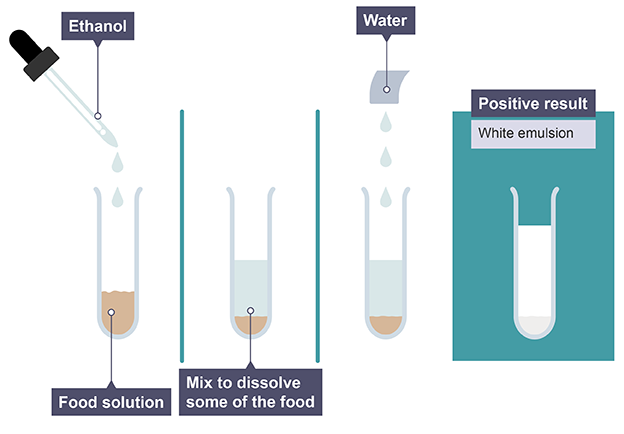
Ethanol and water
when shaken will turn from colourless to a milky-white emulsion in the presence of lipids
Balancing energy
energy content of food eaten must be equal to energy needs as excess energy will be stored as fat
Specific heat capacity
energy to raise mass of substance by 1 degree
water = 4.2 J/g/°C
Digestion
uses energy from respiration to break down large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules
Carbohydrates
Provide energy for chemical reactions and can break down into chains of sugars
Simple carbohydrate examples (energy)
Sugars, glucose and lactose
raise blood glucose levels fast and produce quick elevation in energy
Complex carbohydrate examples (storage)
Cellulose, starch and glycogen
raise blood glucose levels slowly and produce more lasting elevation in energy
Proteins
building blocks of cells and tissues that can break down into amino acids
Uses of proteins
can be structural e.g in muscle
or functional e.g enzymes/ antibodies
How are proteins used
Long chains of amino acids are separated and connected again to form different arrangements
Lipids
fats and oils that can break down into glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Uses of lipids
very good as energy storage with 1 gram containing double the energy of carbohydrates/ protein
What are biological molecules made up of
all contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen but proteins also have nitrogen