BU2 2.3 HEATING SYSTEM
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Conduction
Heat transfer through solid material
[Heat-reflecting roofs, insulation, and energy efficient windows will help to reduce]
Radiation
Heat transfer in the form of visible and non-visible light
Convection
The heat from walls and ceiling reaches body within an enclosed space or room
[Hot air naturally rises, carrying heat away from the walls and causing it to circulate throughout the interior side of the structure]
Heating
The process of raising the temperature of an enclosed space for ensuring the comfort of the occupants.
[By regulating the ambient temperature, this also serves to maintain a building's structural, mechanical and electrical systems]
Greece
Who invented Central Heating?
** but it was the ROMANS who developed it further
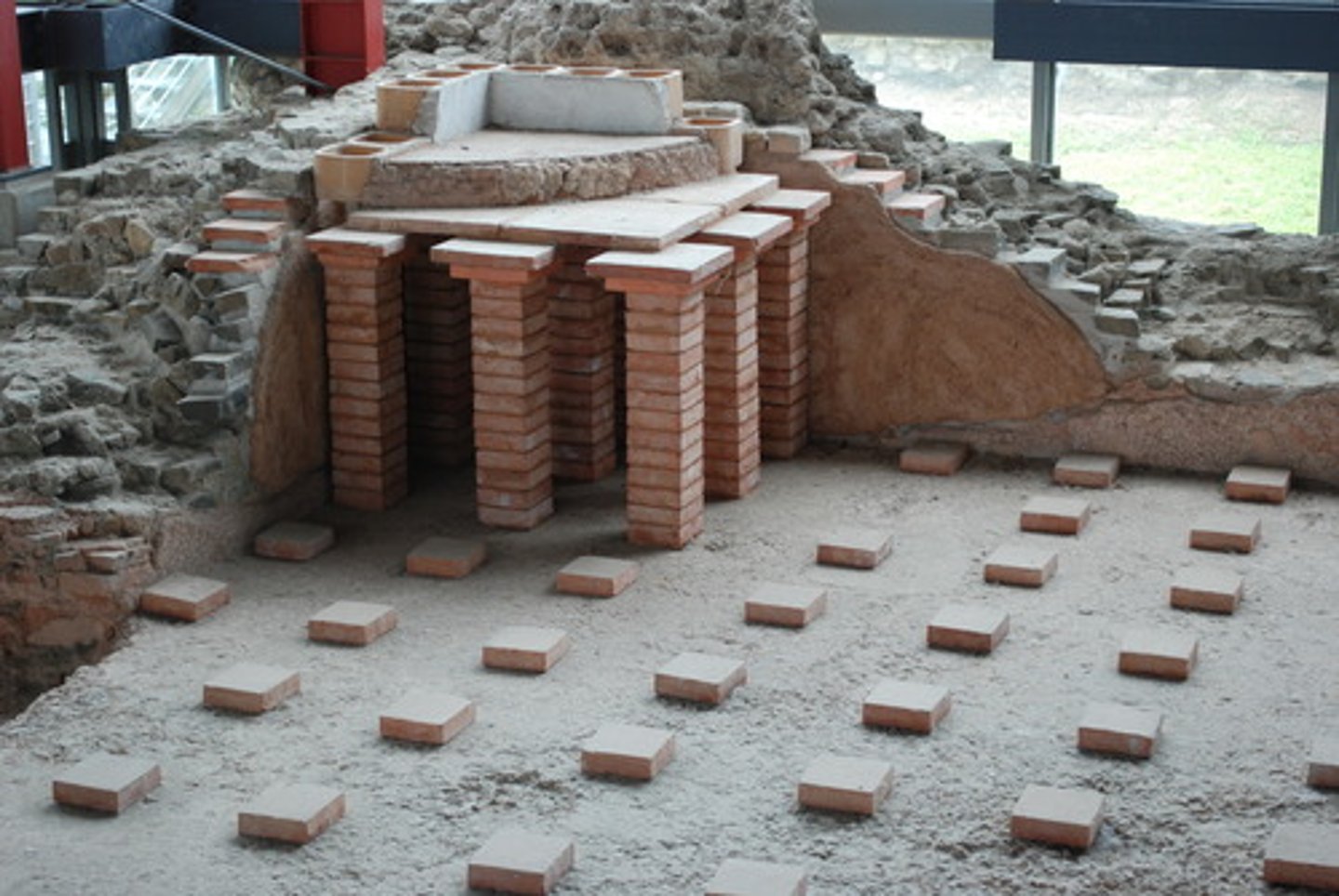
Hypocaust system
- air heated by furnaces through empty spaces under the floors and out of pipes in the walls.
- first ever HVAC system
- invented by the Romans

Wood
The earliest fuel used, though in places where only moderate warmth was needed, such as China, Japan, and the Mediterranean
Charcoal
________ was used because it produced much less smoke
Flue or Chimney
The ________ or ___________ appeared in Europe by the 13th Century and effectively eliminated the fire's smoke and fumes within the enclosed area
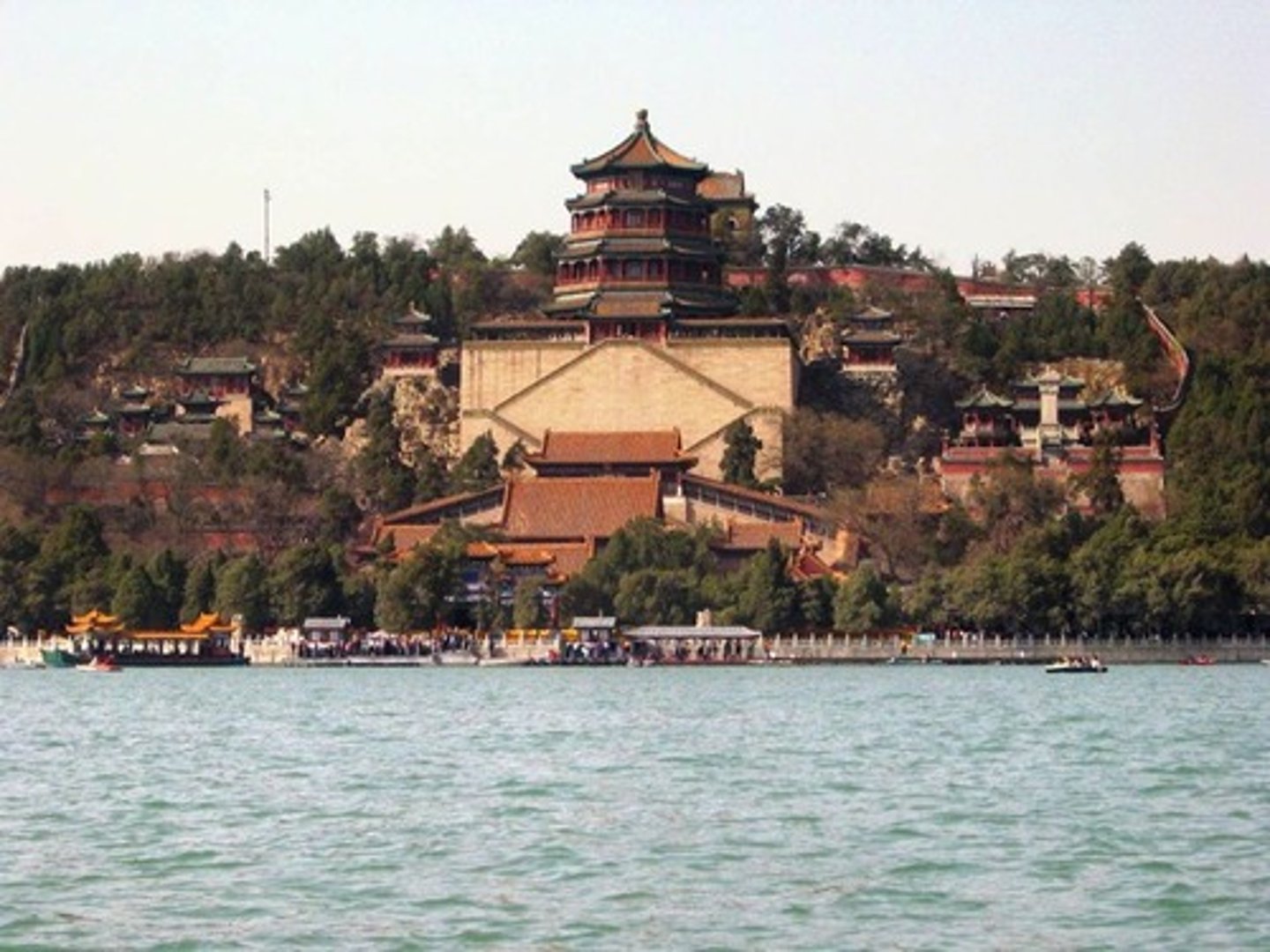
Hydrological Based System
Russian Engineers designed a ____________ __________ ___________ for central heating.
Ex. The Summer Palace (1710 - 1714) of Peter the Great in Saint Petersburg

Coal-fired boilers
- A central heating used during the 19th century when the Industrial Revolution increased
- delivered hot steam to rooms by means of standing radiators

Ducted warm air
A method of heating that displaced steam in most newly built structures during the 20th century
Hot water
Another method of heating that succeeded steam in Great Britain and much of the European continent during the 20th century
Heating system
Replaces heat that is lost through the shell of the structure
British Thermal Unit (BTU)
Heat is measured in ______________
Heating plant
Part of a heating system where fuel is converted into useful heat
Distribution System
Part of a heating system that deliver heat to where it is needed
Controls
Part of a heating system that regulates when and how the system runs and when it turns off
Appliance
A component of a heating system that generates heat (fuel may be burned)
Medium
A component of a heating system that transfers heat such as PIPES OR DUCTS
Emitting apparatus
A component of a heating system that releases the heat by convection or radiation or both
1. Central Heating System
2. Direct Heat
3. Radiant floor heat
4. Ductless, Mini-Split, Multi-Split
5. Combined heat and power or cogeneration
The 5 Types of Heating System
Central Heating System
A Type of Heating System
- generate heat by transforming CHEMICAL ENERGY in fuel into THERMAL ENERGY and transferring that energy to air, water, or steam, which then gets delivered throughout the building.
- provides warmth to the whole interior of a building from one point to multiple rooms.
1. Furnaces
2. Conventional Gas Furnace
3. Boilers
4. Heat Pumps
4 Examples of the Central Heating System
Furnaces
Example of a Central Heating System
- works by blowing heated air through ducts that deliver the warm air to the room throughout the structure via air registers or grills.
- This type of heating system is called a DUCTED WARM-AIR or
FORCED WARM-AIR distribution system. It can be powered by electricity, natural gas, or fuel oil
Conventional Gas Furnace
Example of a Central Heating System
- consists of a furnace with a naturally aspirating gas burner.
- The combustion passes through the furnace where they pass heat across a heat exchanger and are exhausted to the outside through a flue pipe and vent
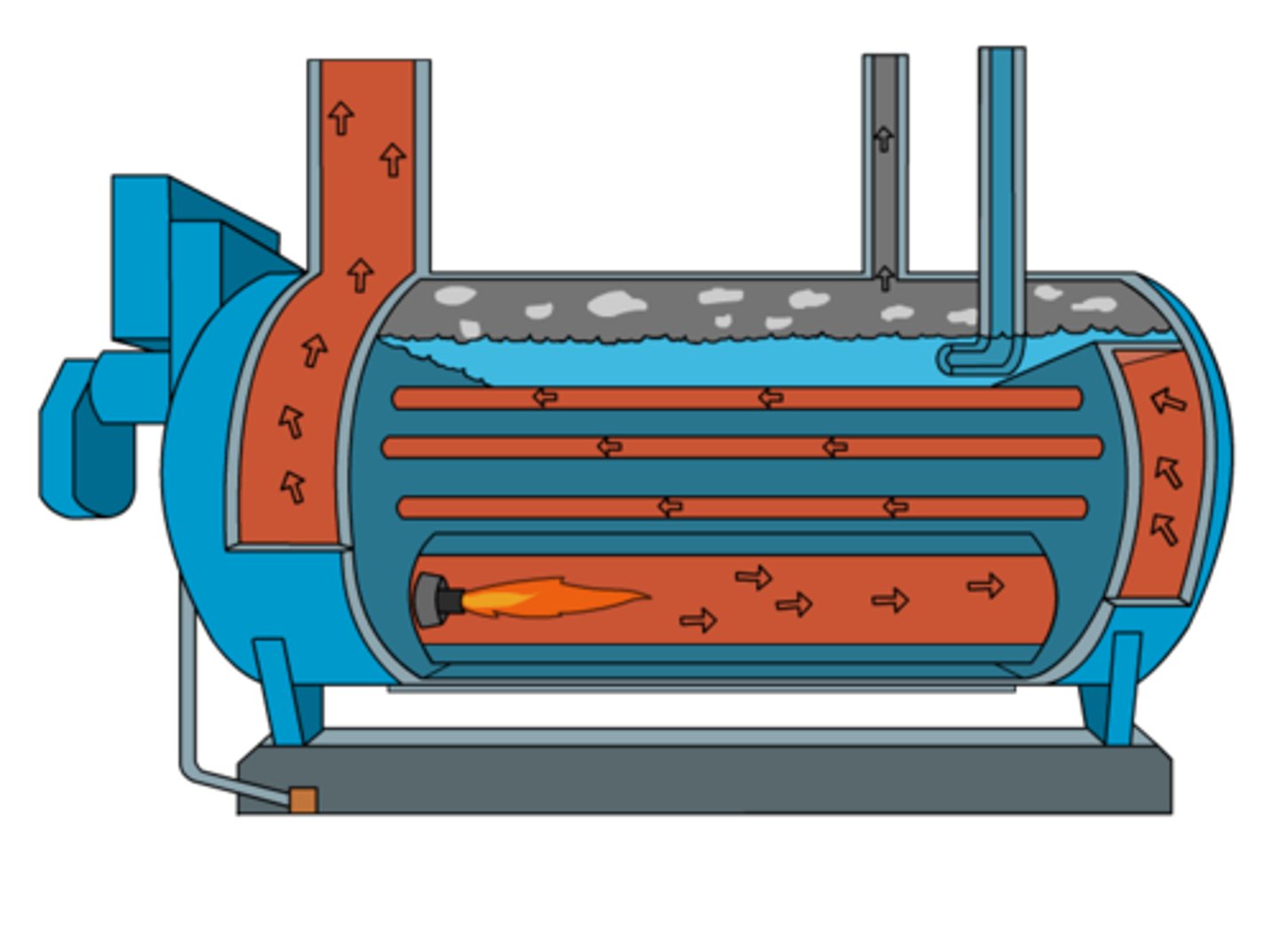
Boilers
Example of a Central Heating System
- special purpose water heaters
- distribute the heat in hot water, which gives up heat as it passes through radiators or other devices in rooms throughout the structure.
- Heat water, and provide either hot water or steam for heating. Steam is distributed via pipes to steam radiators, and hot water can be distributed via baseboard radiators or radiant floor systems or can heat air via coil.
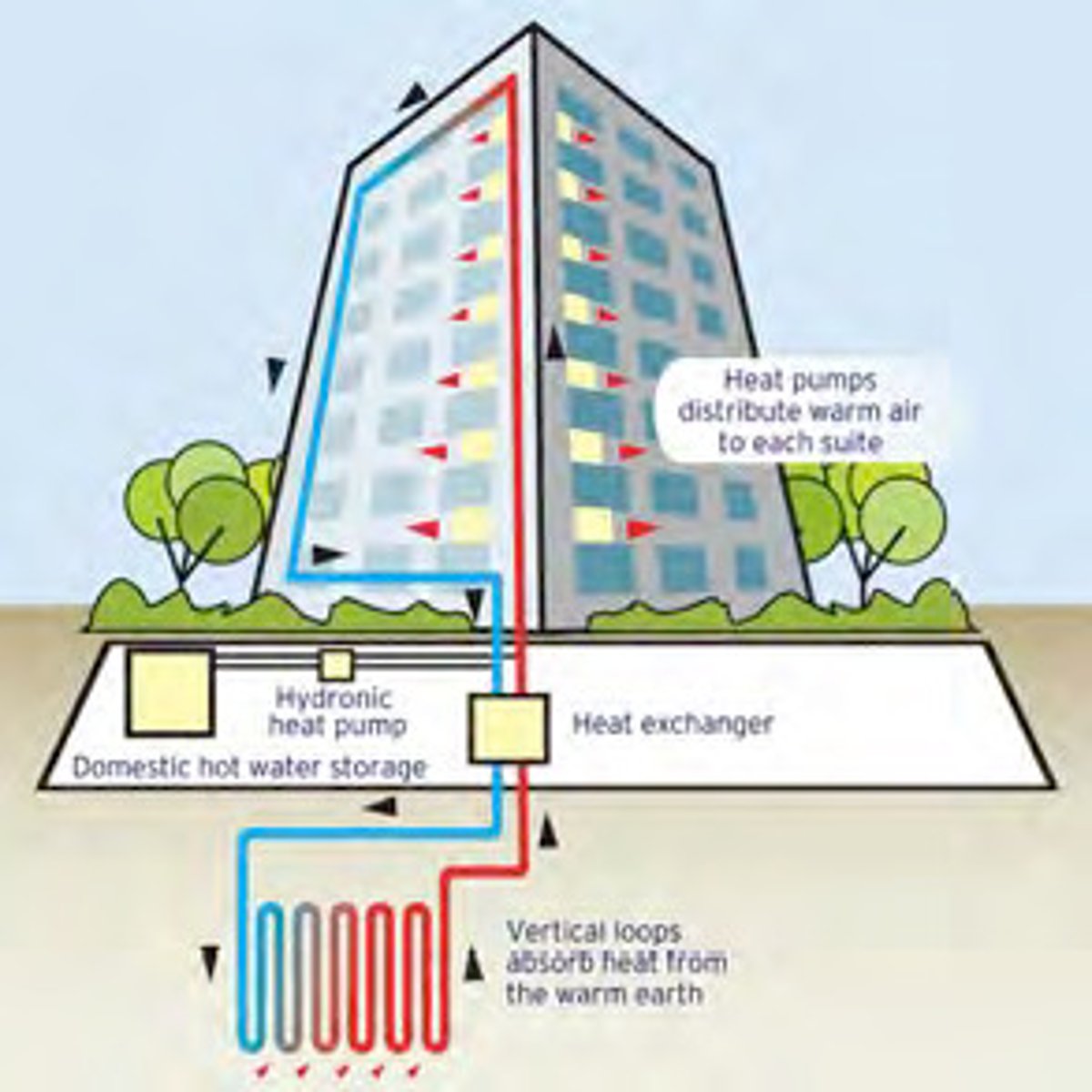
Heat Pumps
Example of a Central Heating System
- two-way air conditioners.
- In summer, air conditioner works by moving heat from the relatively cool indoors to the relatively warm outside.
- In winter, the heat pump reverses its function, scavenging heat from the cold outdoors with the help of an electrical system and discharging the heat inside the structure.
Direct Heat
A Type of Heating System
- the process when heat is generated directly within a material by passing an electric current through it, by causing controlled EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS, or by exciting atoms or molecules inside the material by ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
- refers to gas wall heaters, floor heaters, and room heaters. Unlike gas furnaces, these DO NOT USE DUCTS to move air throughout a structure but rather provide heat directly to the area where they are installed
1. Gas-Fired Space Heaters
2. Electric Space Heaters
3. Fireplaces
3 Examples of Direct Heat
Gas-Fired Space Heaters
Example of Direct Heat
- includes wallmounted, free standing, and floor furnaces, all characterized by their lack of ductwork and relatively small heat output.
- Because this system lacks ducts, this is recommended for warming a single room
Electric Space Heaters
Example of Direct Heat
- include "oil-filled" and "quartz-infrared" heaters (portable) that convert electric current from the wall socket directly into heat
- designed to focus heat in a single room or small zone. This works by expelling hot air through a fan, which naturally rises and forces colder air to the floor. This process helps to circulate heat and warm the space effectively
Fireplaces
Example of Direct Heat
- can be electric-powered or wood-burning.
- An electric-powered fireplace is one of the most efficient ways to heat rooms faster; this mimics a burning coal, wood or natural gas and are safe to use.
Radiant floor heat
A Type of Heating System
Systems that circulate warm water in tubes UNDER THE FLOOR. This warms the floor, which in turn warms the room
Ductless, Mini-Split, Multi-Split
A Type of Heating System
Heat pumps that distribute energy through REFRIGERANT LINES instead of water or air.
Combined heat and power or cogeneration
A Type of Heating System
Uses small generator to meet electric demand and recover the waste heat to heat the structure and make domestic hot water