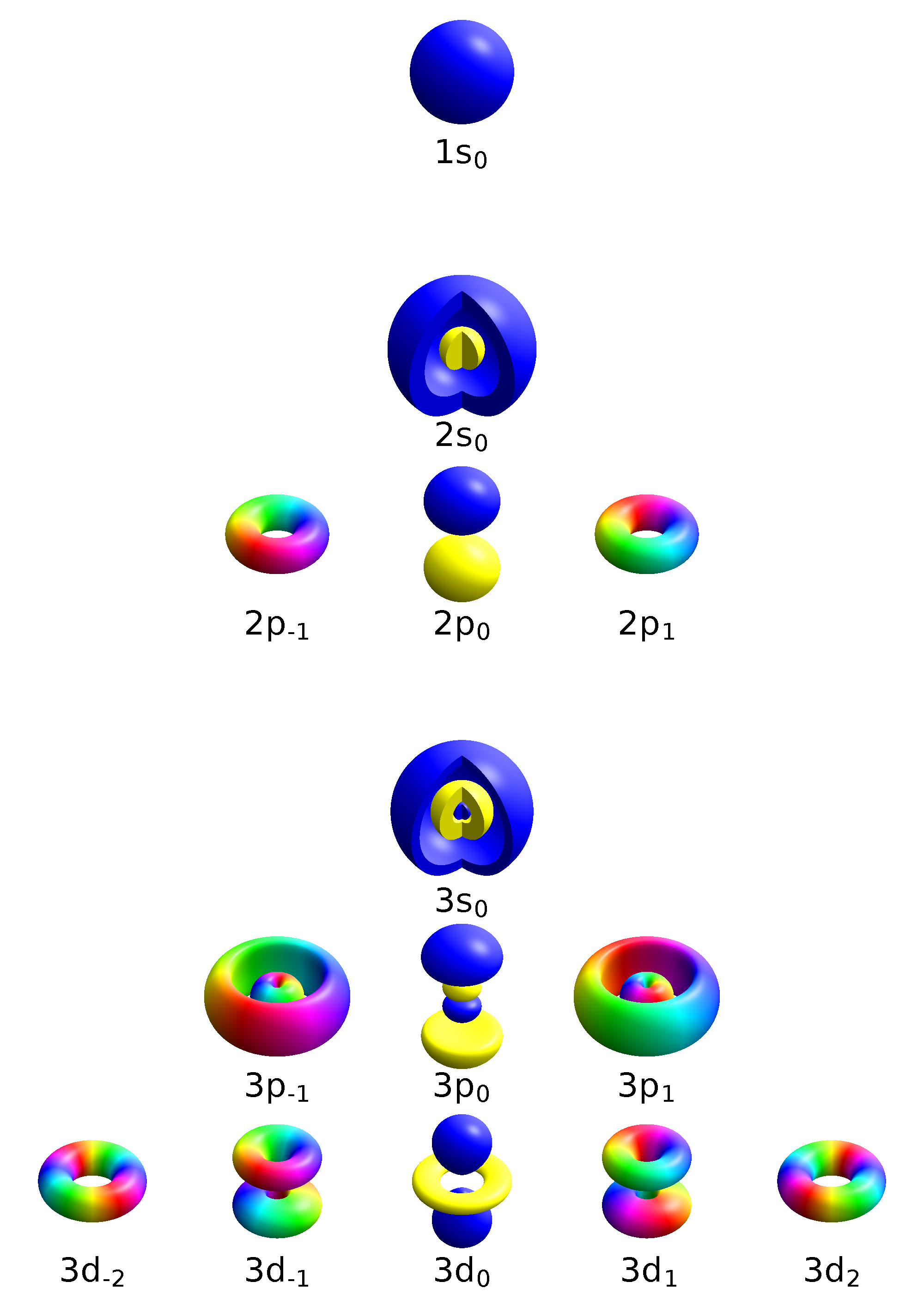Electrons in Atoms
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chemistry materials and nano technology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
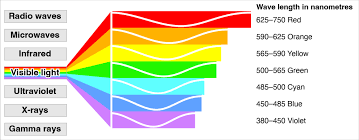
Visible light
the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye, ranging from approximately 400 to 700 nanometers in wavelength.
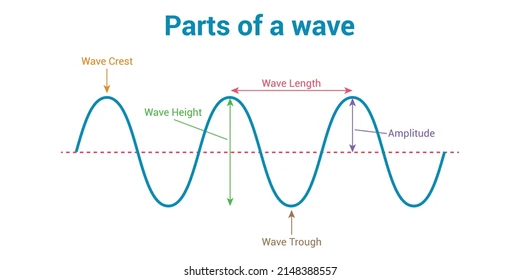
Waves
repetitive disturbances that transfer energy through space or matter.
Quantum
the minimum amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction.

Light
electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye, encompassing a range of wavelengths from visible light.

Photoelectric effect
Situations in which electrons are emitted from a material when it absorbs light, This light shines on the metal material, This electrons are emitted from the metal material called “photoelctron”.
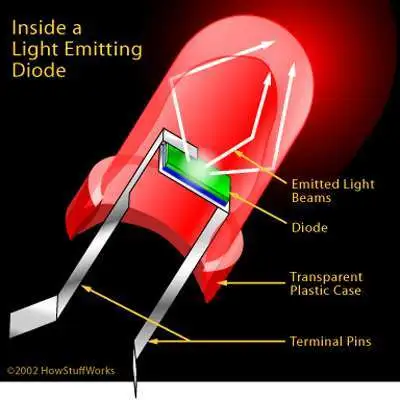
Emitted light
This process releases energy in the form of photons, producing visible light.
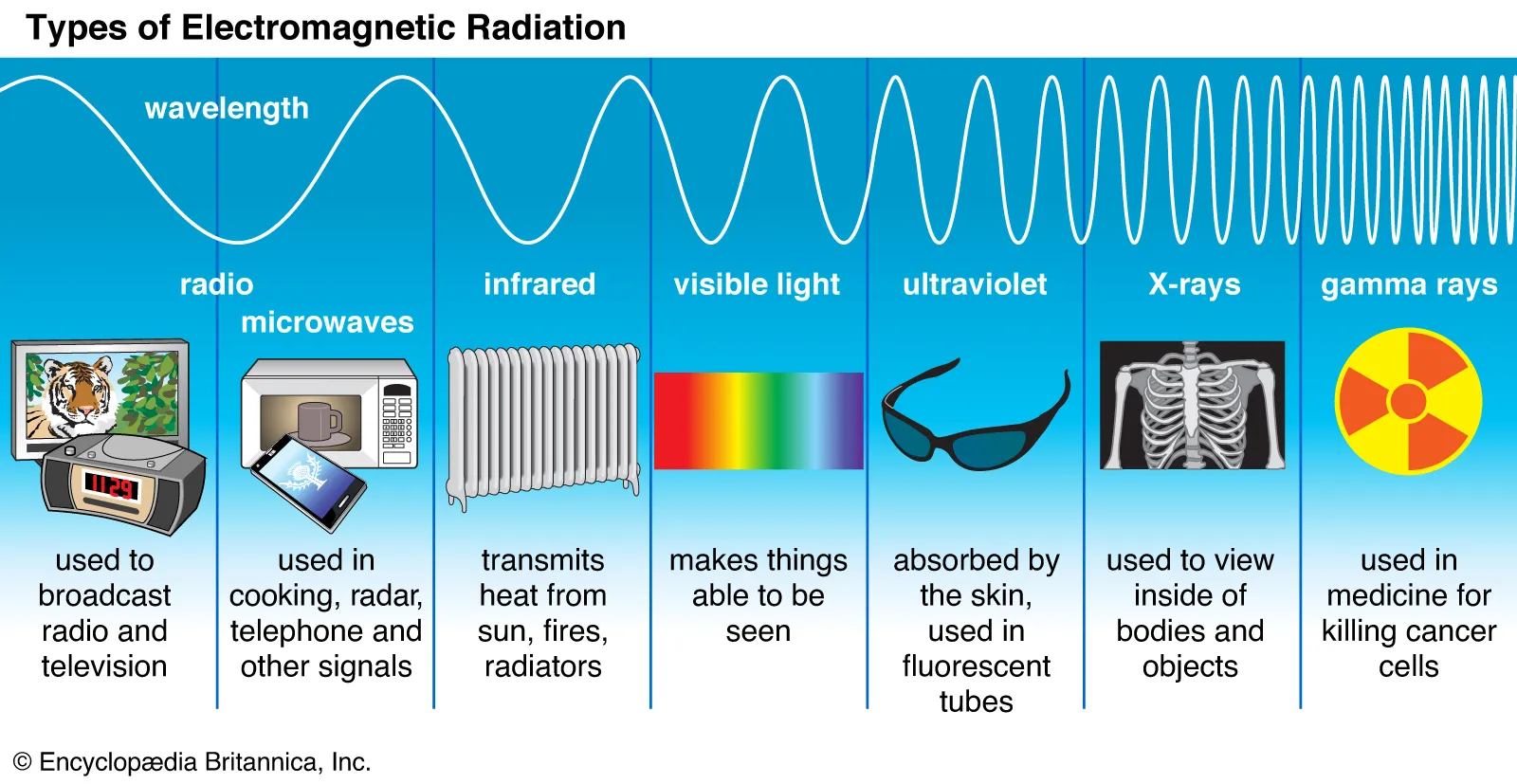
Electromagnetic radiation
Energy waves that include visible light, radio waves, and X-rays.
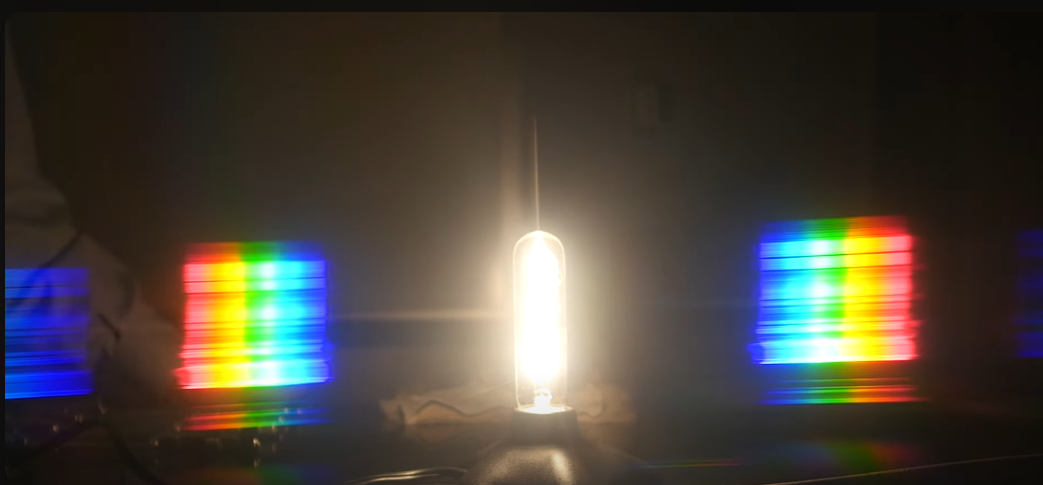

Atomic emission spectum
A spectrum of light emitted by atoms when they transition from higher to lower energy states, resulting in characteristic wavelengths.
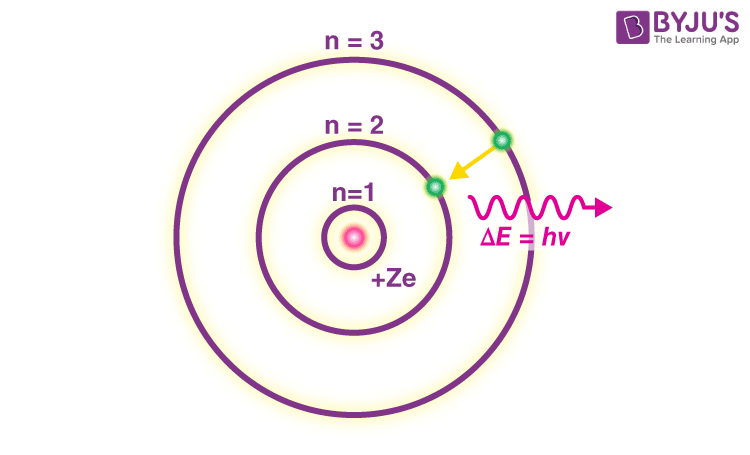
Bohr’s Model
A model of the atom that depicts electrons in fixed orbits around the nucleus, with energy levels quantized.

spectrum line of hydrogen
The distinct wavelengths of light emitted by hydrogen atoms when they transition between energy levels, creating a unique spectral pattern.
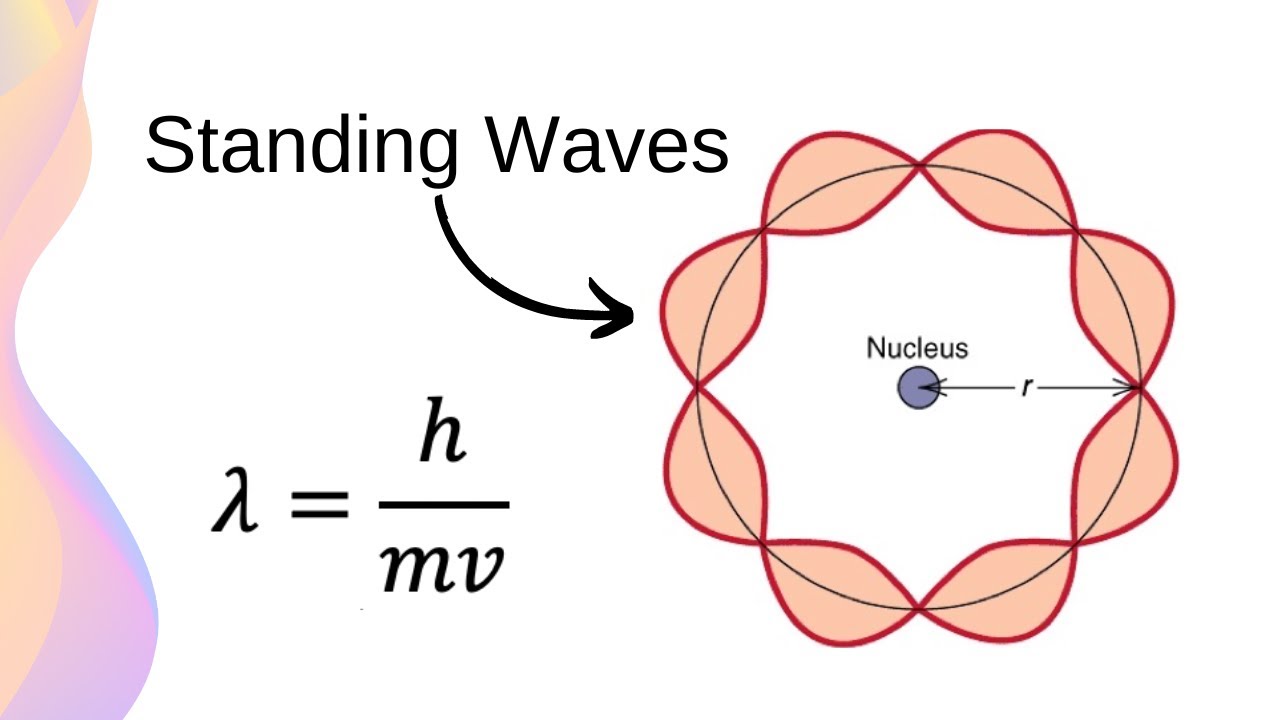
De Broglie Wave Equation
The equation that relates the wavelength of a particle to its momentum. The equation: lambda = h/p or lamba = h/mv.
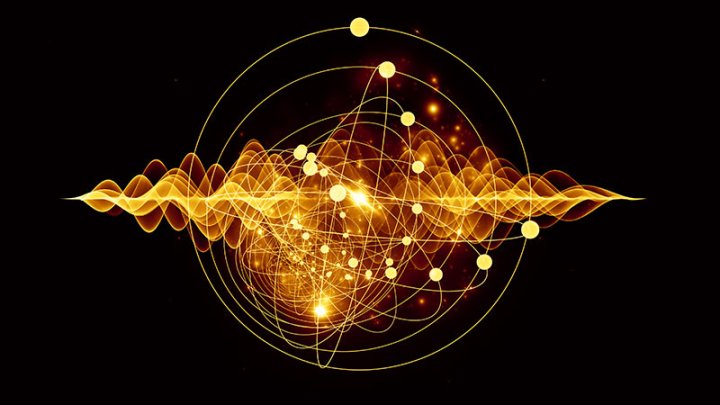

Quantum mechanics
the study of the motion of objects that are atomic or subatomic in size and therefore(thus) demonstrate wave-particle duality(double). electrons exist simultaneously as both a particle and wave and can’t definitely locate a particle.
Classical mechanics
The size and mass of the objects involved effectively cover(obscures)any quantum effects.
Quanta
the atomic level where the particles motion is described by gaining or losing the discrete amounts.
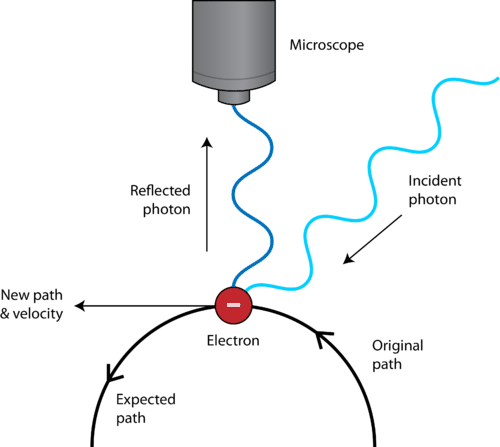
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and the velocity of a particle. Photons and electrons have quite the same energy.
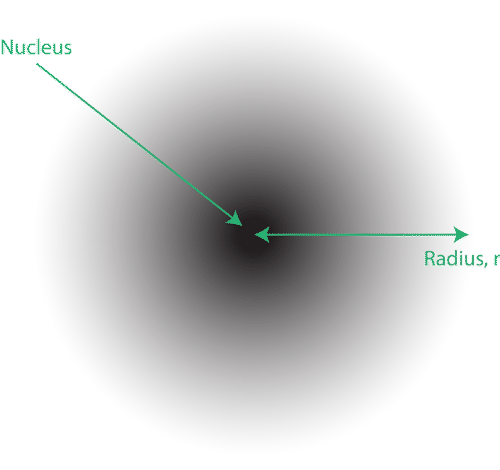
Quantum Mechanical Atomic Model
The location of the electron can only be given as a probability that the electron is somewhere in a certain area. This is known as “wave function”. The location of the electrons in quantum mechanics model known as “electron cloud”
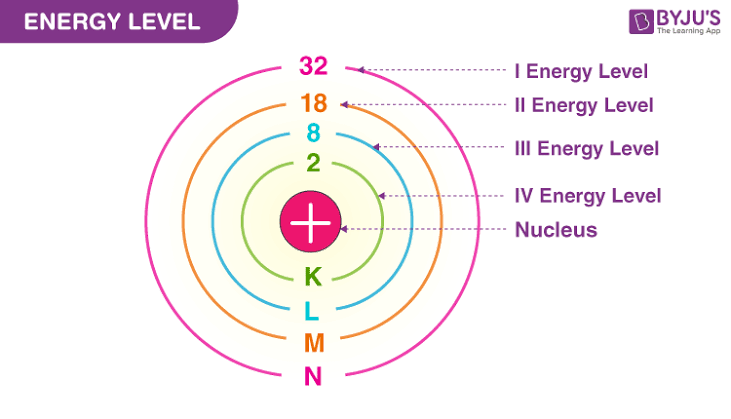
Energy level
This is known as electron shells are fixed distances from the nucleus of an atom where electrons may be found. Electron shells at higher energy will contain more electrons. Electrons are always added to lowest shells first then higher.
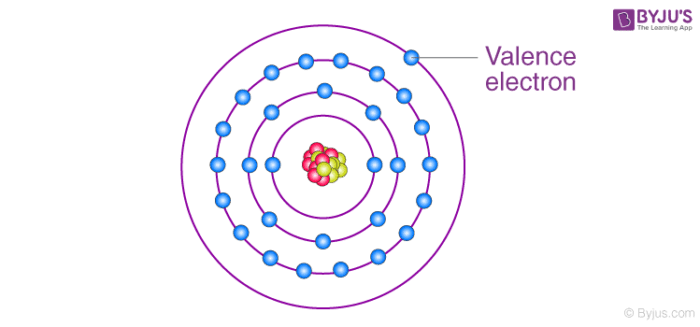
Valence electrons
The last shell at the last shell( this message not true in some transitions metal).
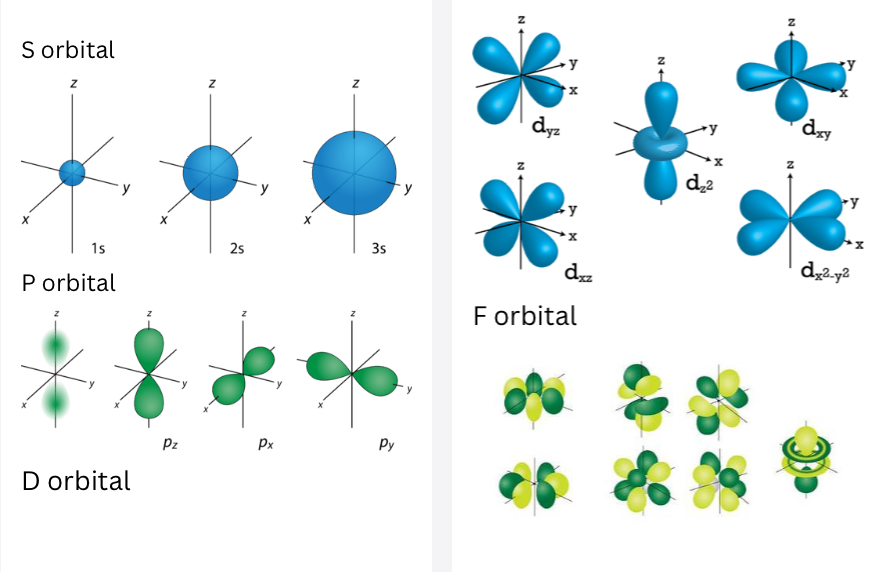
Orbitals
There are four different classes of electron orbitals. Quantum numbers can describe the arrangement of electrons, this process with something called electron configuration.