Breast, Lymphatics, & Female Genitalia
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What is breast tissue?
Fatty and glandular tissue that makes up the breast.
What is the nipple?
The protruding structure where milk ducts open.
What is the areola?
he pigmented area surrounding the nipple that contains Montgomery glands.
What are Montgomery glands?
Sebaceous glands in the areola that produce lubrication during breastfeeding.
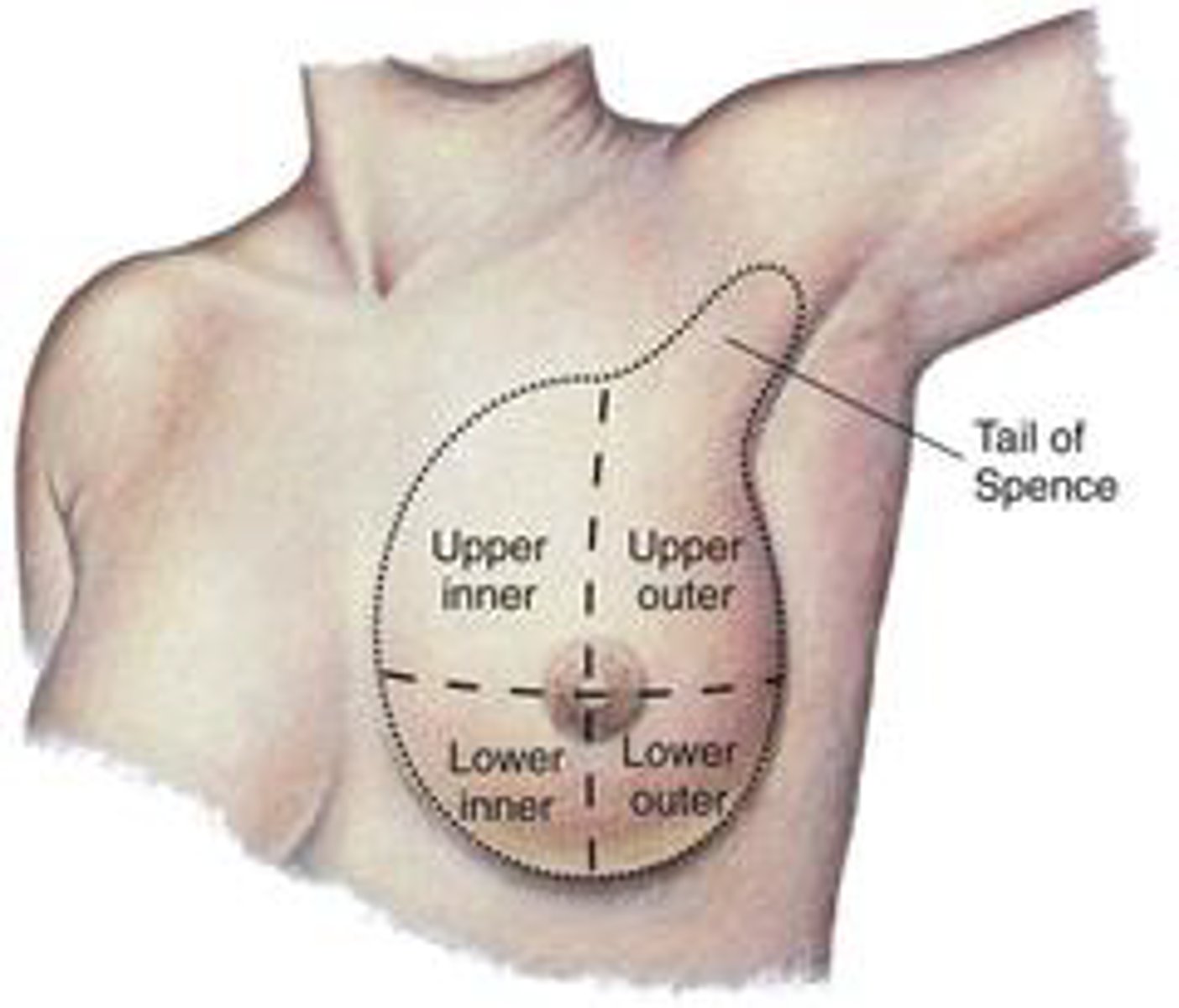
What are breast quadrants?
The four sections (upper outer, upper inner, lower outer, lower inner) used to describe locations of findings.
What is the upper outer quadrant?
The quadrant of the breast where most tumors occur.
What is the Tail of Spence?
An extension of breast tissue into the axilla; the most common site for breast cancer.
What is glandular tissue?
Tissue responsible for producing and transporting milk.
What is lactation?
The production and secretion of breast milk.
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
Removes microorganisms, absorbs lipids, and returns excess fluid to the bloodstream.
What is lymphatic reabsorption?
Returning excess interstitial fluid to circulation.
What is lipid absorption in the lymphatics?
Process where lacteals in the small intestine absorb dietary fats.
What is the expected skin appearance on the breast?
Smooth, even color, possible veins or striae.
What are normal breast variations?
Veins, striae, scars, gynecomastia, atrophy.
What is expected in the areola and nipples?
Round, smooth, no crusting or drainage.
What is expected in the axillae?
No rash, edema, or discoloration.
What is peau d'orange?
Orange-peel breast skin caused by cancerous lymph obstruction.
What is nipple retraction?
Nipple pulled inward—possible malignancy.
What is unilateral breast edema?
Swelling on one side; sign of infection or cancer.
What are abnormal nipple findings?
Crusting, scaling, discharge, rash.
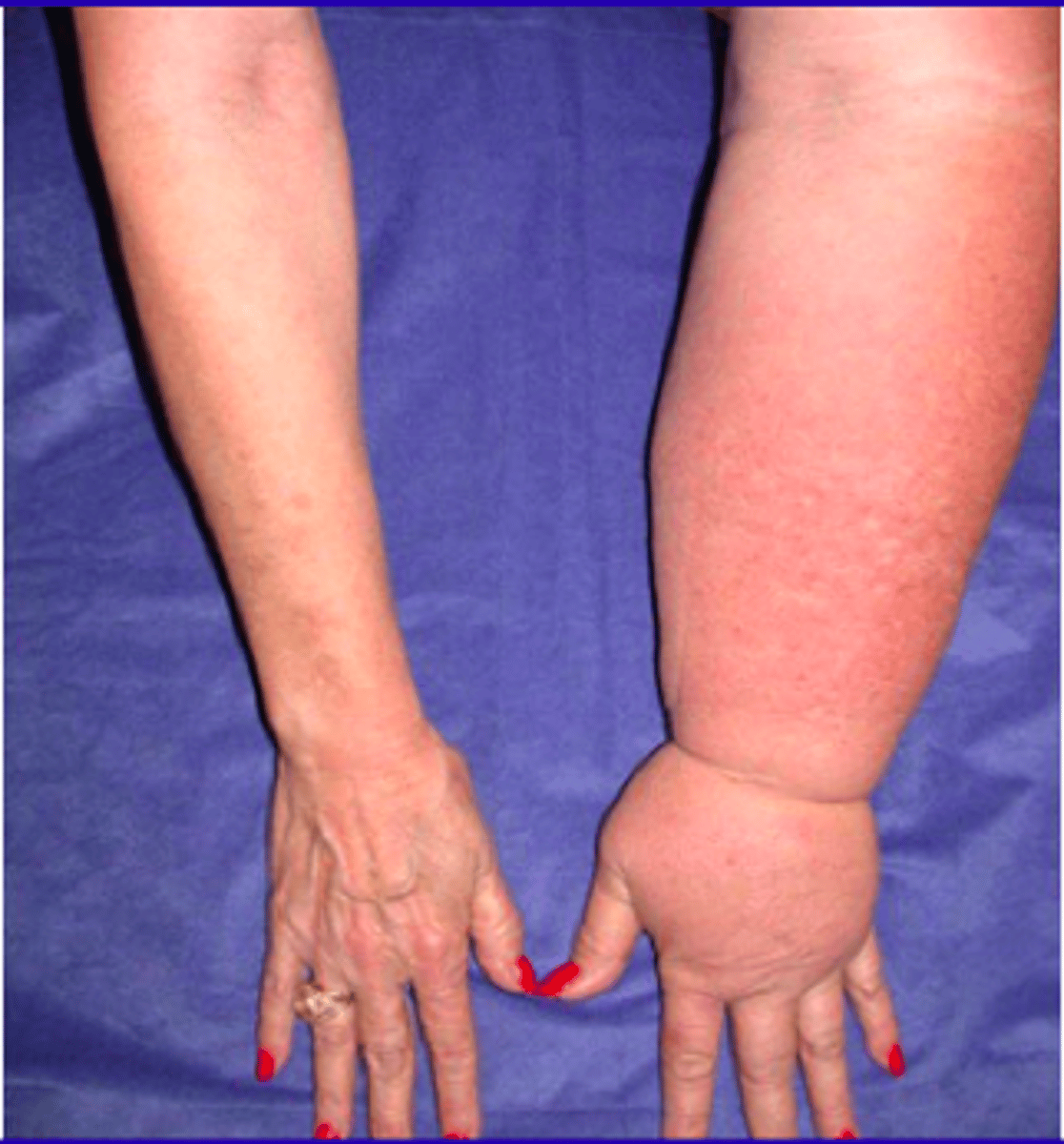
What is post-mastectomy lymphedema?
Swelling from lymph buildup; avoid BP or IV in that arm.
What breast changes require further evaluation?
Shape change, contour change, unilateral vein dilation, rash, skin dimpling, masses.
What subjective tools are used for breast pain?
PQRST or OLD CARTS.
What are breast cancer risk factors?
BRCA genes, obesity, early menarche, family hx, inactivity, late menopause, hormone use.
When does breast cancer screening typically begin?
Around age 40 (depends on guidelines).
What are cervical cancer screening guidelines?
Every 3-5 years from ages 21-65.
What STI prevention methods are recommended?
Condoms, cotton underwear, no douching, front-to-back wiping.
What are toxic shock safety rules?
Change tampons every 8 hours; alternate pads/tampons.
What is the vulva?
The collective external female genital structures.
What is the mons pubis?
A fatty pad that cushions and protects the pubic bone.
What are the labia majora?
The outer, larger skin folds protecting the vulva.
What are the labia minora?
The inner, smaller folds surrounding the vestibule.
What is the vestibule?
Area between labia minora containing the urethral and vaginal openings.
What is the urethral meatus?
External opening of the urethra.
What is the vaginal orifice?
The external opening of the vagina.
What are Skene's ducts?
Glands producing mucus near the urethra.
What are Bartholin's glands?
Glands that secrete mucus into the vaginal opening.
GPAL
gravida (pregnancies), (para) births after 20 wks, abortions (interrupted pregnancy), living children
What does a Pap smear assess?
Cervical cell abnormalities; begin age 21
What is candidiasis?
Yeast infection with white, curd-like discharge.
What is trichomoniasis?
STI with foul odor and frothy discharge.
What is bacterial vaginosis?
Infection causing thin discharge and fishy odor.
What age does cervical cancer screening begin?
21 years old.
What is the HPV vaccine for?
Prevents cervical, anal, and genital cancers/warts.
What prevents toxic shock syndrome?
Changing tampons every 8 hours.
HSV-2
herpes, cluster of small vesicle w/ erythema, painful, erupt on glans, forskin, or anus. They rupture to form superficial form ulcers; mild tingling, shooting pain in legs and butt; treating orally with anti-viral
Syphailitic chancre
solitary, ulcer, painless, treated with penicillin
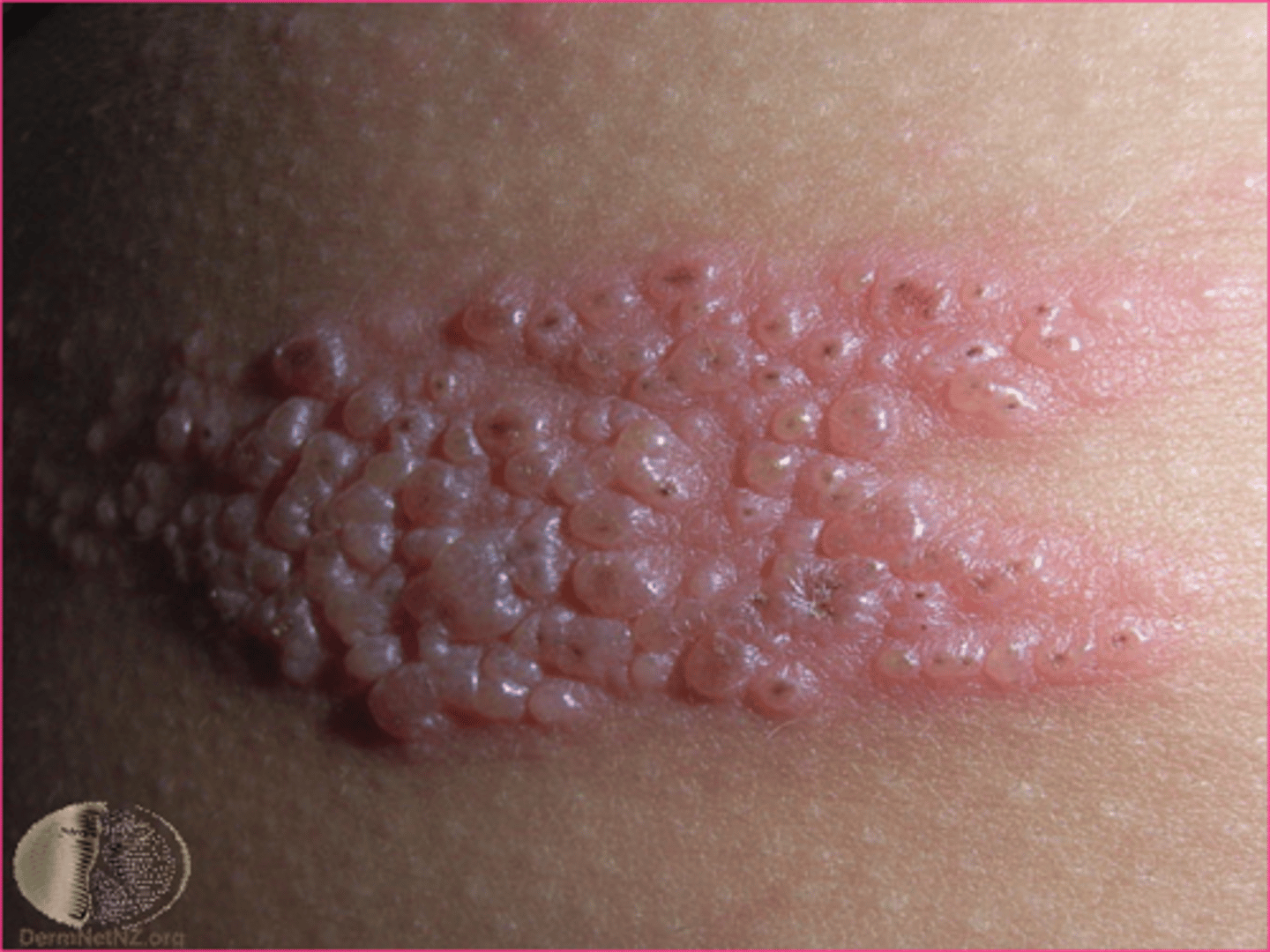
Genital warts
painless, soft, moist; MOST COMMON, caused by early onset, use of contraceptives, multiple partners; cause bed HPV, high risk for cervical cancer in women = Gardasil series of 3 shots for 9-26 years old in boys
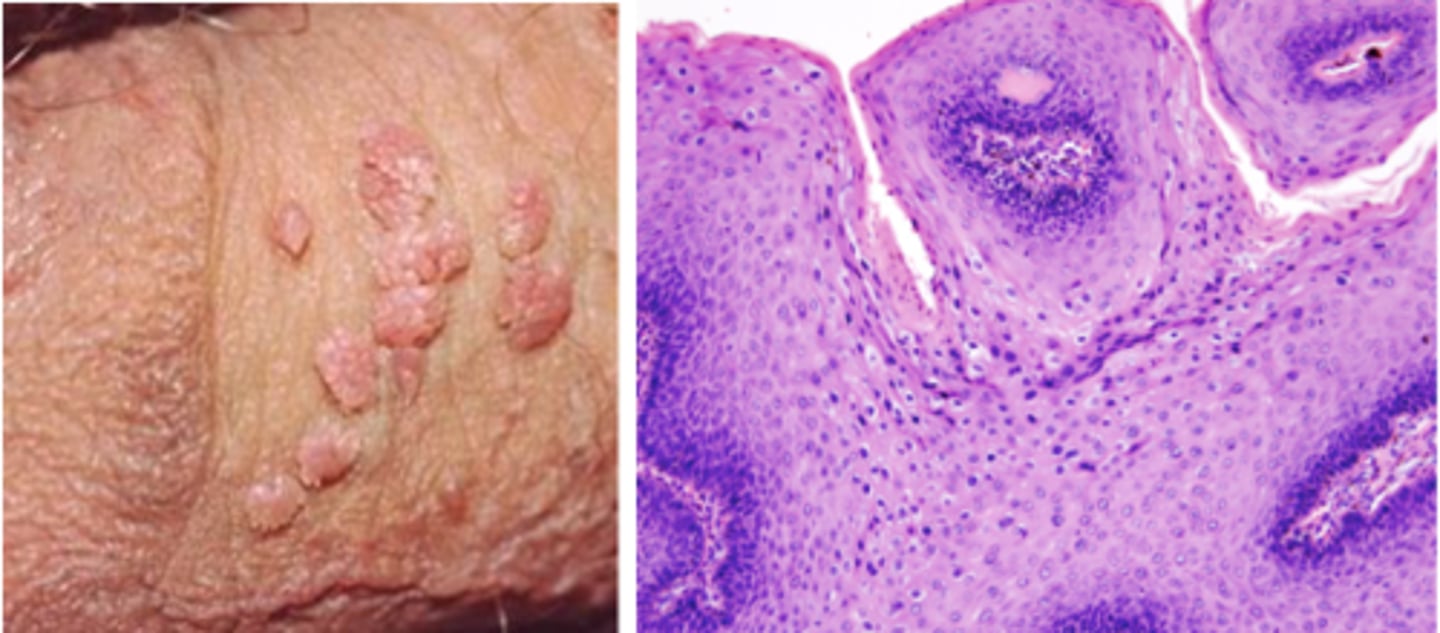
Uretheritis (possibly chlamydia)
painful, burning, discharge, cloudy urine; must notify partners between last 60 days and report to health department; treated with anitbiotics
G: yellow/green discharge
C: creamy, white discharge
Expected findings of lymph nodes
soft, mobile, nontender
Unexpected findings of lymph nodes
enlargement > 1 cm, hard/fixed, painful palpation, matted together
Indications of cancer
Dimpling
Edema
Inflammation
Unilateral rash
Peau d'orange: breast resembling skin of an orange
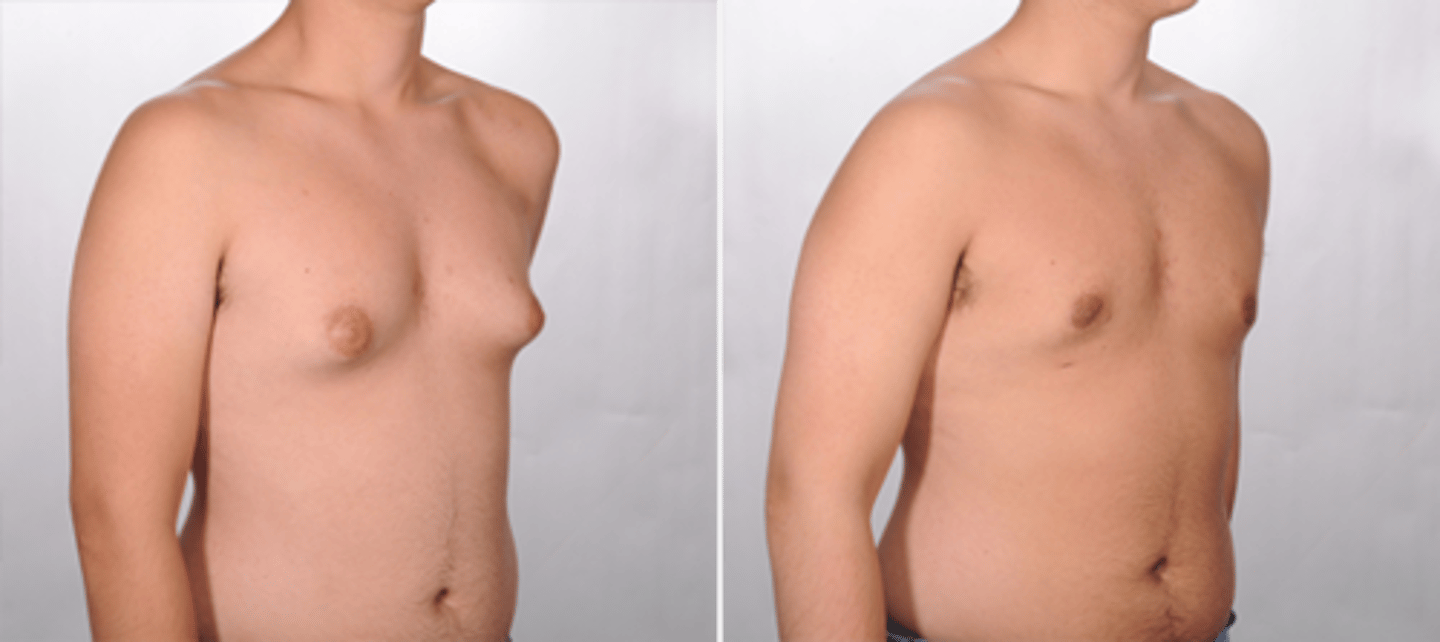
Gynecomastia in male
caused by weight gain, med, hormones
Risk factors for cervical cancer
HPV, smoking, immunosuppression, chlamydia, diet low in fruits and vegetables, overweight, multiple full-term pregnancies, poverty,family history
Safe sexual practice
Natural methods
Barrier methods
Pharmacological methods
Implanted devices
Surgical interventions
Sexually transmitted infection prevention and screening
Abnormal breast finding
Assessment:
Change in breast size, shape, contour
Unilateral superficial vein dilation, inflammation, edema
Nipple drainage
Enlarge lymph nodes
Change in presentation, orientation of nipple
Rash on nipple or areola
Dimpled or retracted areola
Visible palpable lump
Collect subjective data: PQRST or OLD CARTS
Document
What is subjective data for a breast assessment?
Information the client reports, including breast pain or tenderness, changes in appearance, swelling, lumps, rashes, nipple discharge (color, odor, timing), menstrual-related breast changes, breastfeeding history, hormone therapy use, history of breast disease or trauma, past surgeries (augmentation, reduction, mastectomy, biopsies), family history of breast cancer, and changes in lymph nodes.
What is objective data for a breast assessment?
Observed or measured findings including breast symmetry, skin condition, nipple appearance, presence of masses or tenderness, swelling, rashes, discoloration, dimpling, peau d'orange, nipple retraction, discharge, lymph node enlargement, and axilla inspection for edema, lymphedema, rash, or abnormal lesions.
When is a flat or inverted nipple considered normal?
When present since puberty without recent change.
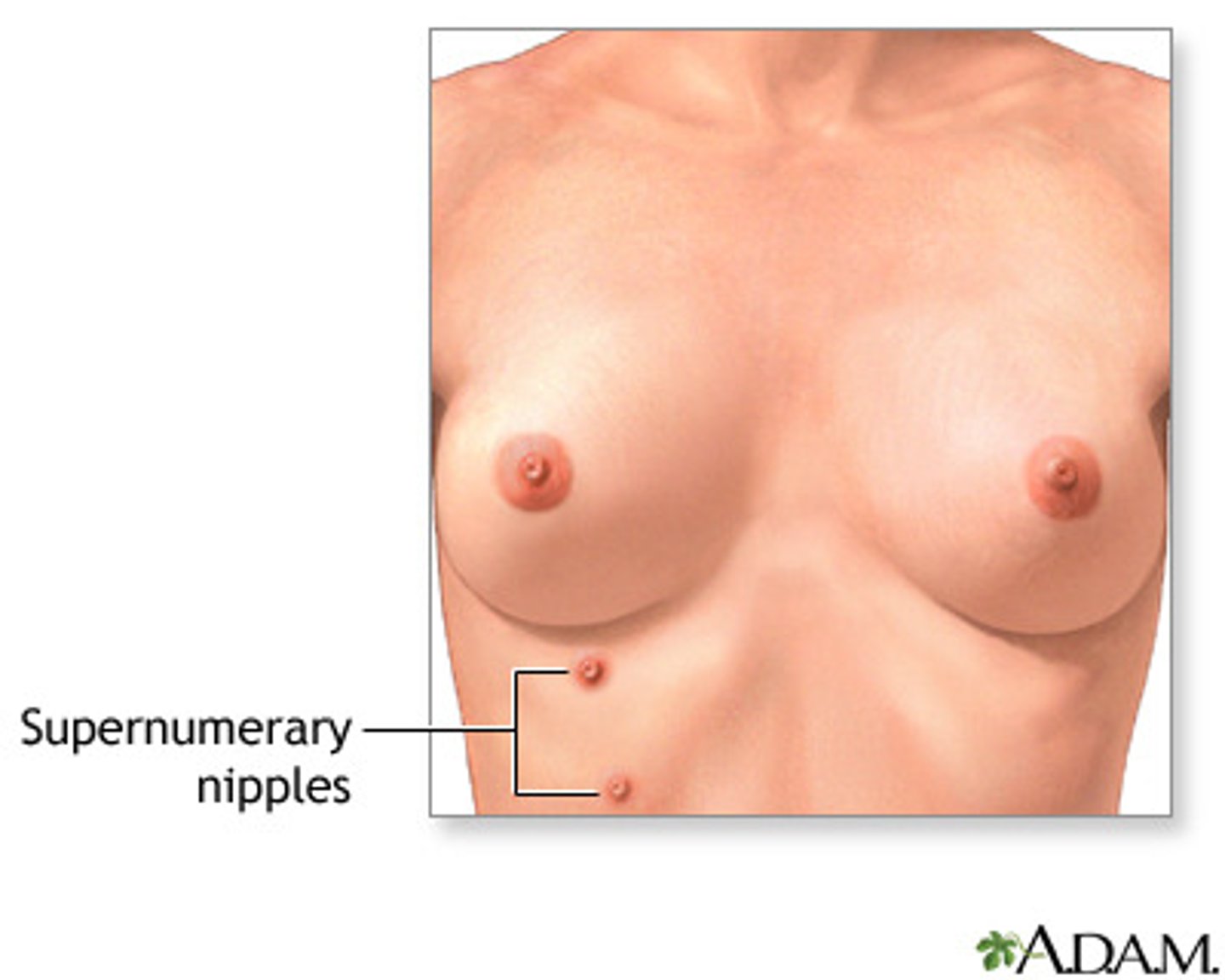
What is a supernumerary nipple?
An extra nipple along the embryonic milk line that may appear like a mole.
What does deeply pigmented, very smooth axillary skin suggest?
Conditions such as diabetes or polycystic ovary disease.
When should menstruating clients perform breast self-exams?
4-7 days after the start of their menstrual period.
What is an inframammary ridge?
A firm ridge of compressed breast tissue along the lower breast; an expected finding.
What are current mammogram recommendations for low-risk clients?
Every 2 years from age 50 to 74.
When should high-risk clients consider starting mammograms?
At age 40, based on provider recommendation or personal choice.
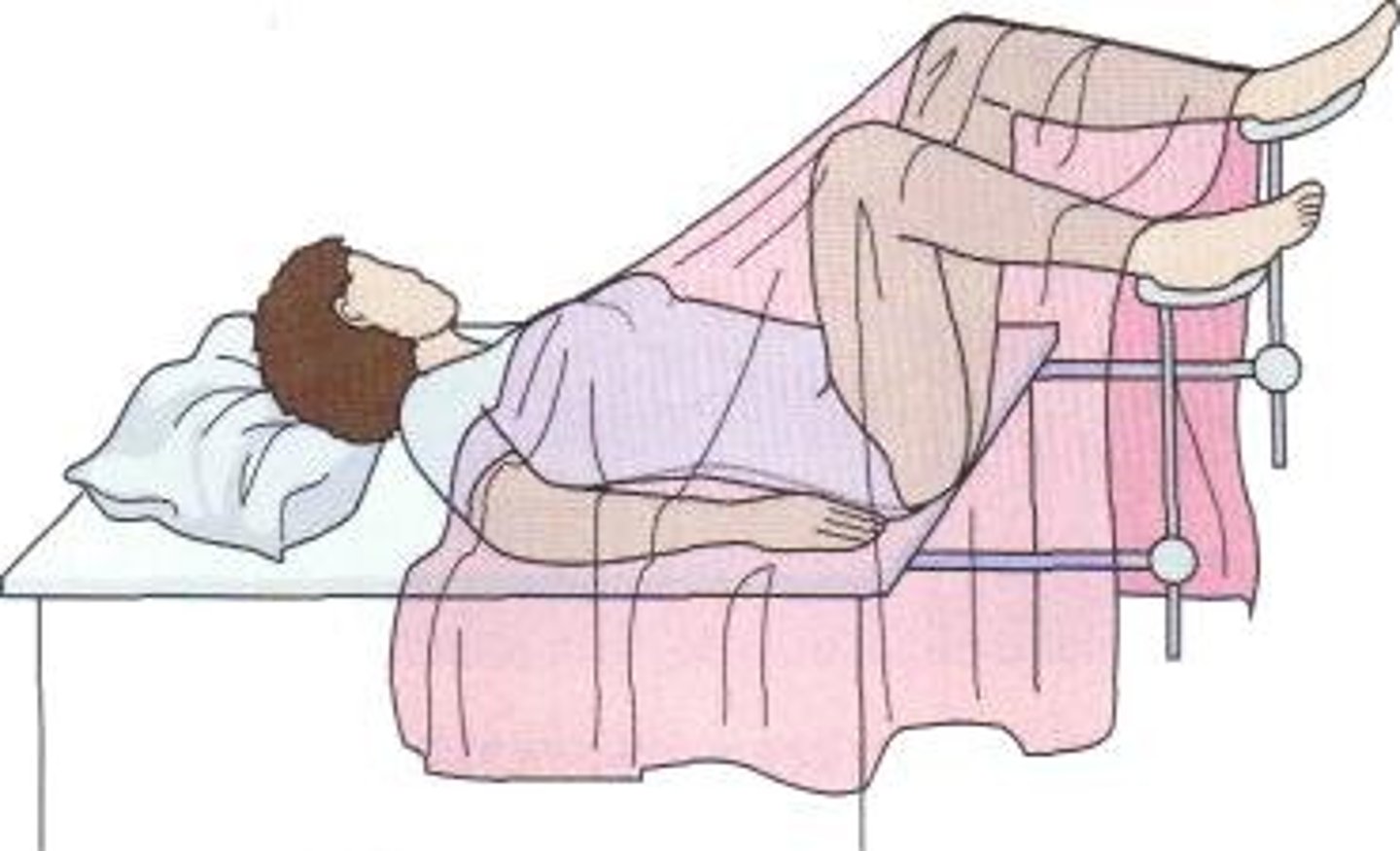
lithotomy position
A supine position with the knees flexed and thighs abducted with the feet usually held in straps or stirrups.