P8 b: liposomes
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is micellisation?
Spontaneous assembly of amphiphilic molecules into micelles at slightly higher (but still low) concentrations.
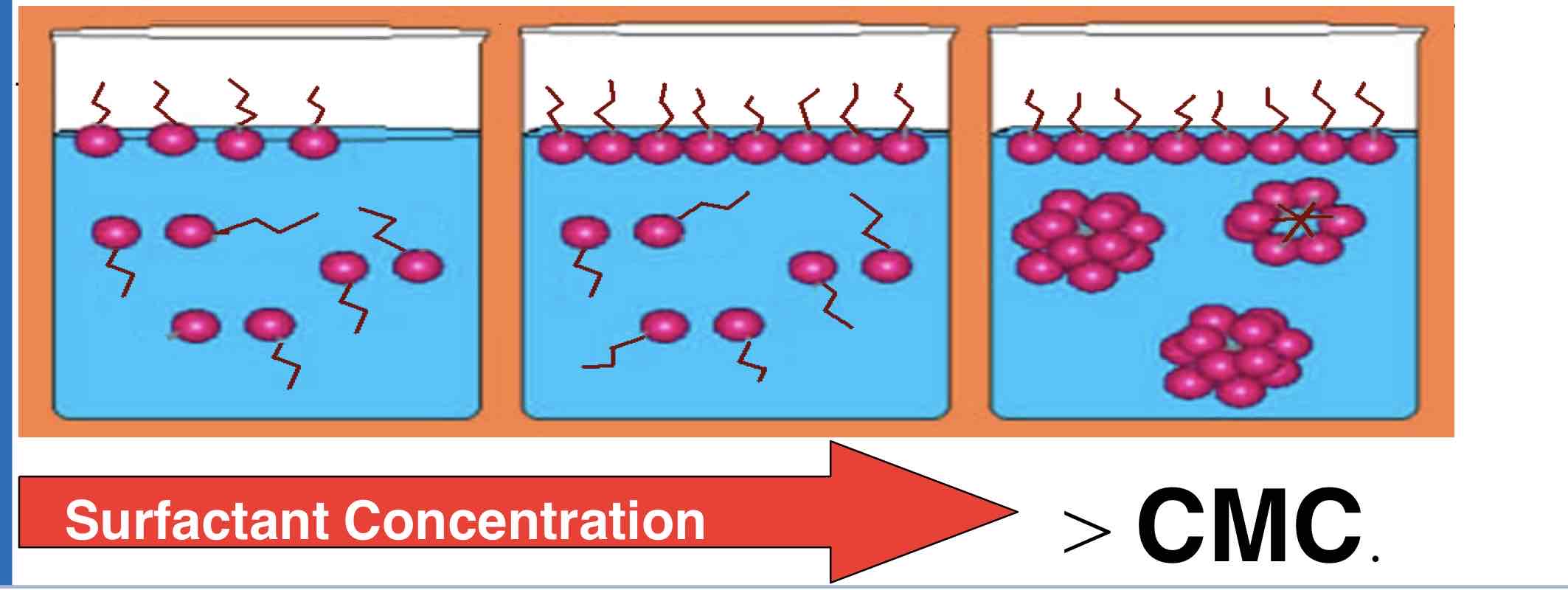
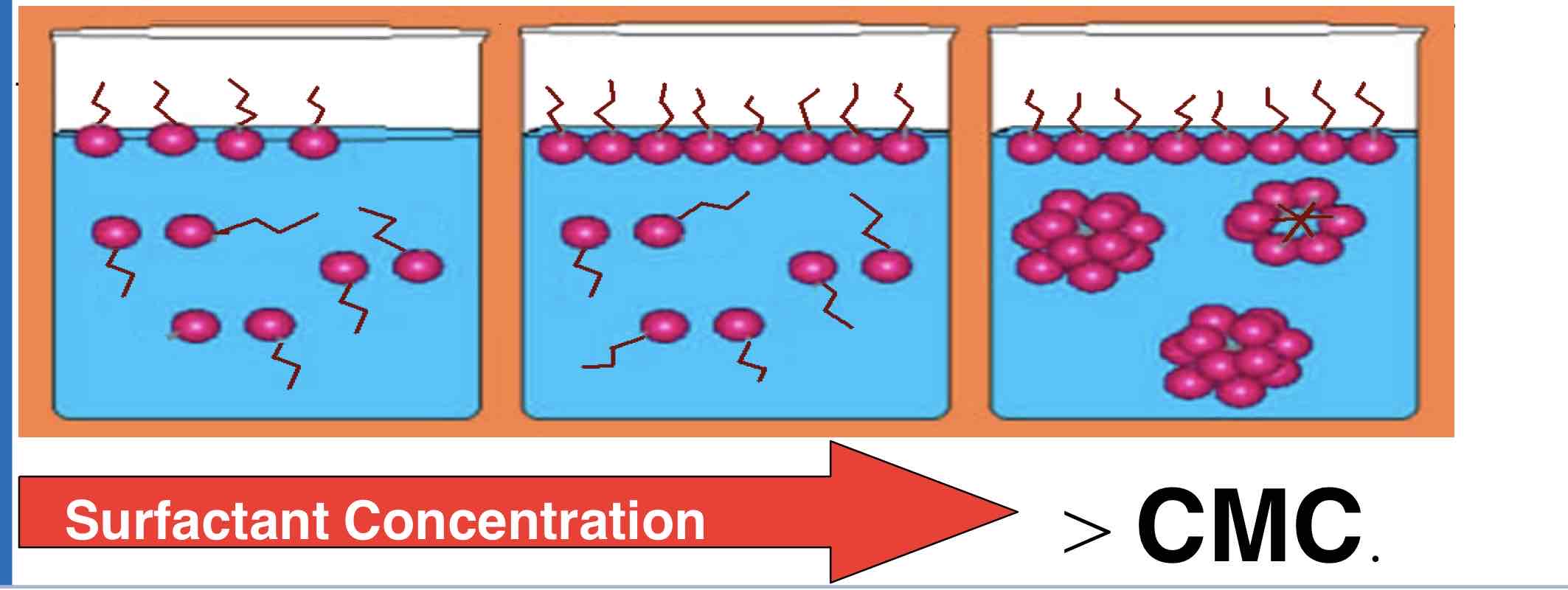
What happens to amphiphillic molecules during micellsiation?
Amphiphilic molecules hide their hydrophobic tails inside the micelle core whilst exposing the hydrophilic surface to the surrounding aqueous solution
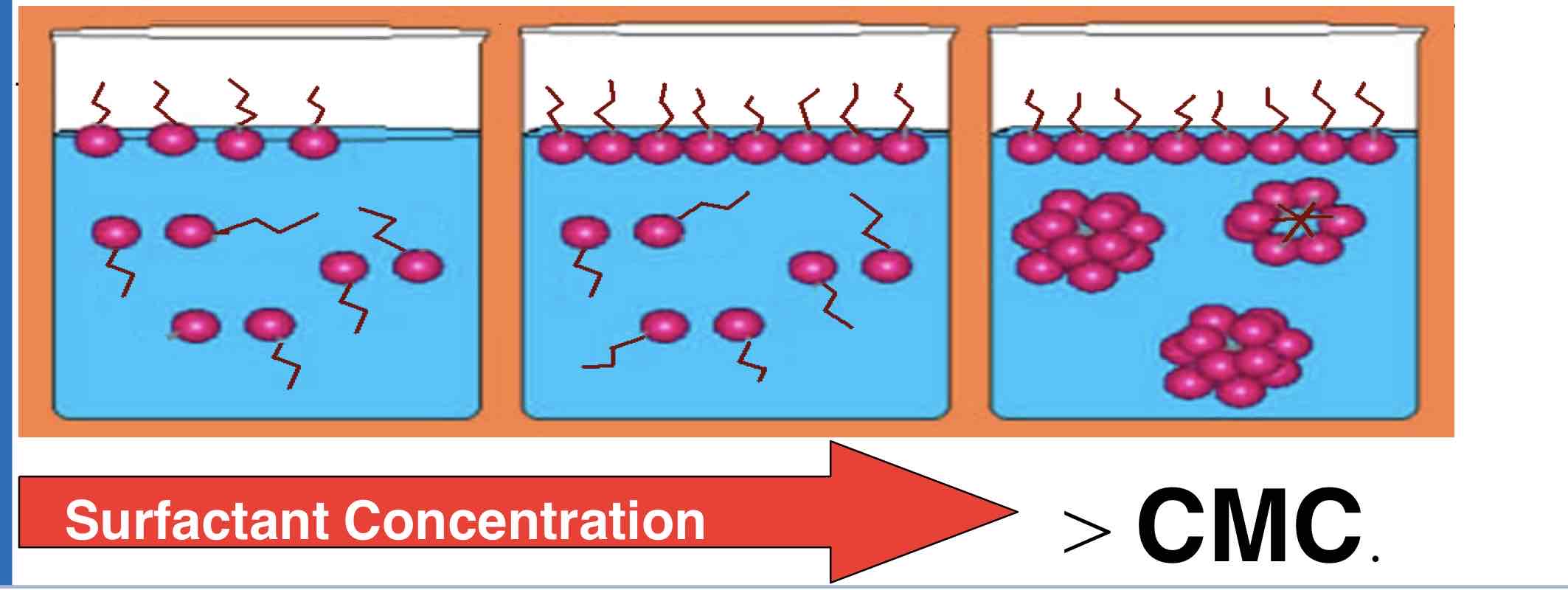
How are micelles formed during micellisation?
Formed by spontaneous forming of amphiphilic molecules into spheres.
What happens to assemblies of amphiphilic molecules at higher concentrations?
higher concentrations, assemblies of amphiphilic molecules become ordered.
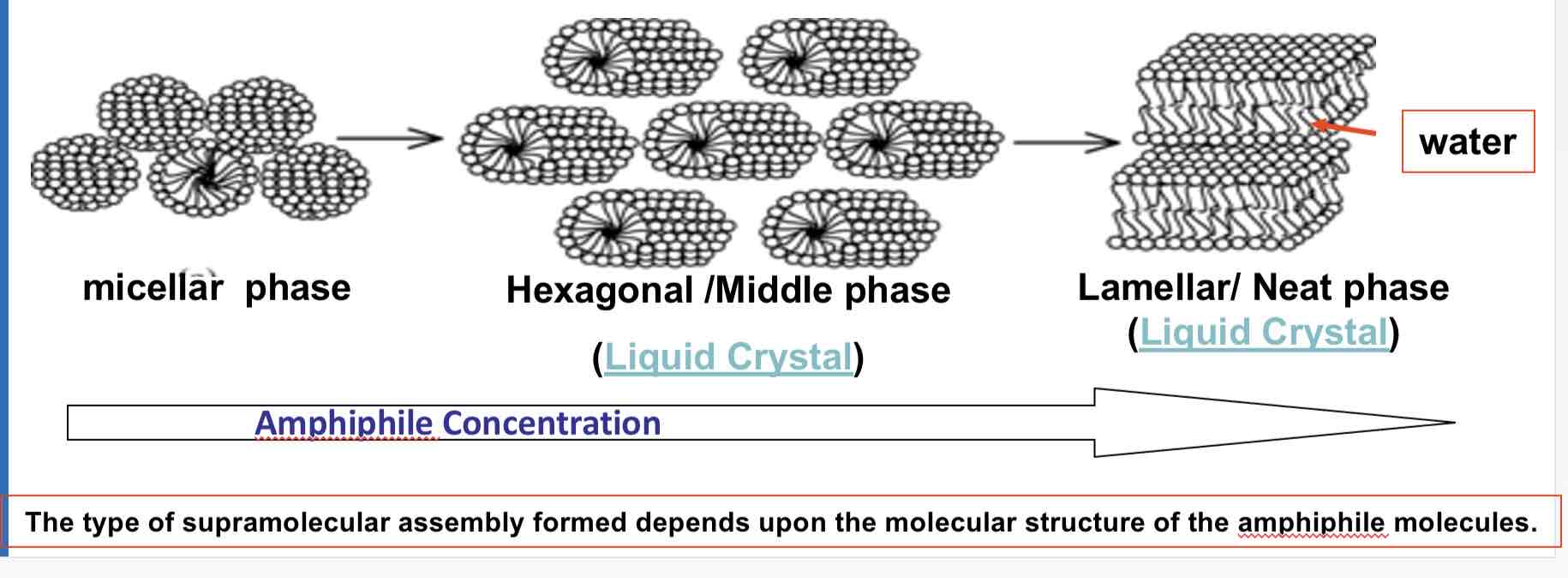
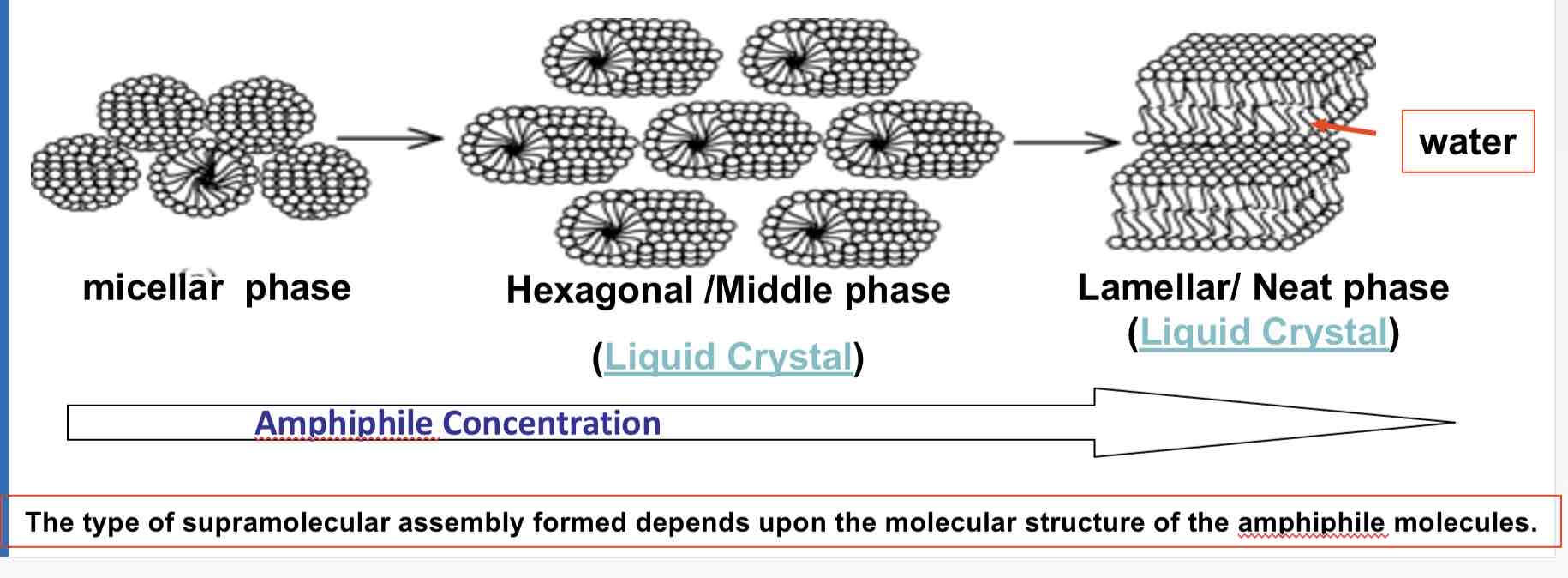
What is a hexagonal columnar phase?
phase is a typical phase where amphiphiles form long cylinders with a hydrophilic surface arranged into a roughly hexagonal lattice.
This is also known as the "middle soap phase."
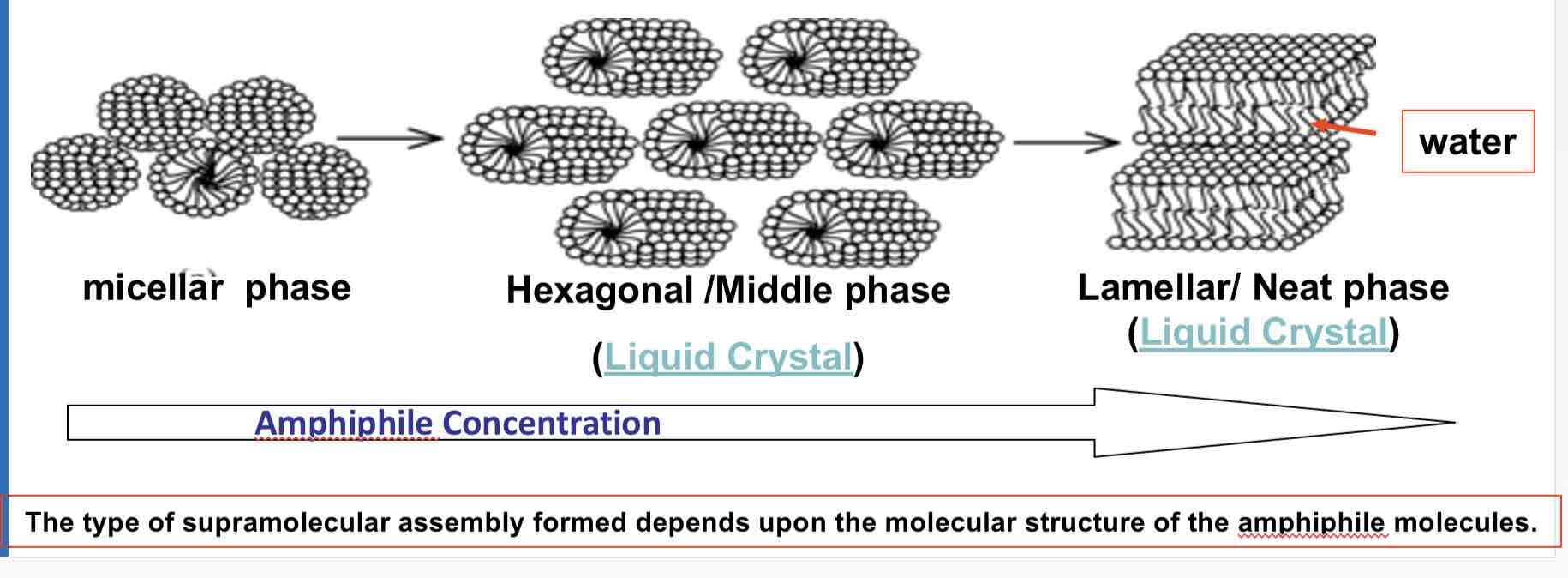
What is a lamellar phase?
lamellar phase, also known as the "neat soap phase,"
may form at still higher concentrations,
wherein extended sheets of amphiphiles are separated by thin layers of water
Liposome generation
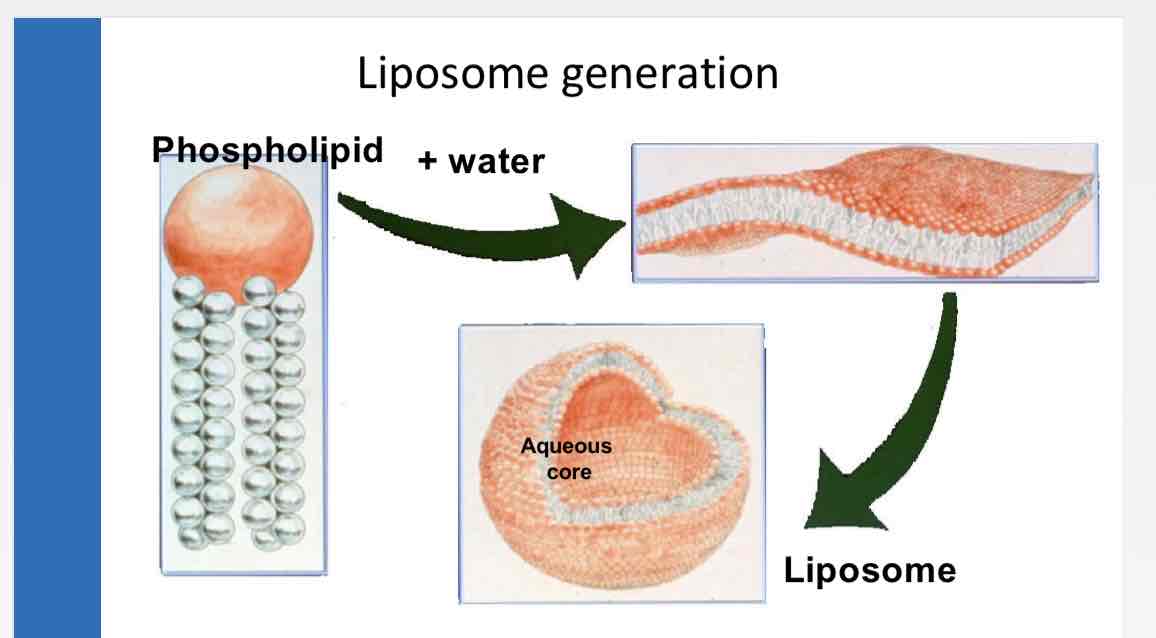
What are liposomes?
structures made of lipids. Lipids form bilayer. Hydrophobic tails facing inside. Hydrophilic heads facing outwards. Arrangement creates boundary with water containing core is within the lipid bilayer.
How are lipid molecules typically arranged in liposomes?
Lipid molecules in liposomes are usually phospholipids, such as lecithin, which have a hydrophilic head group and two hydrophobic chains (tails).
How do lipid molecules spontaneously orient in water to form liposomes?
water, lipid molecules spontaneously orient
Gives most stable conformation,
hydrophilic head-group facing outward into the aqueous environment
lipid chains oriented inward, avoiding the water phase, resulting in bilayer structures.
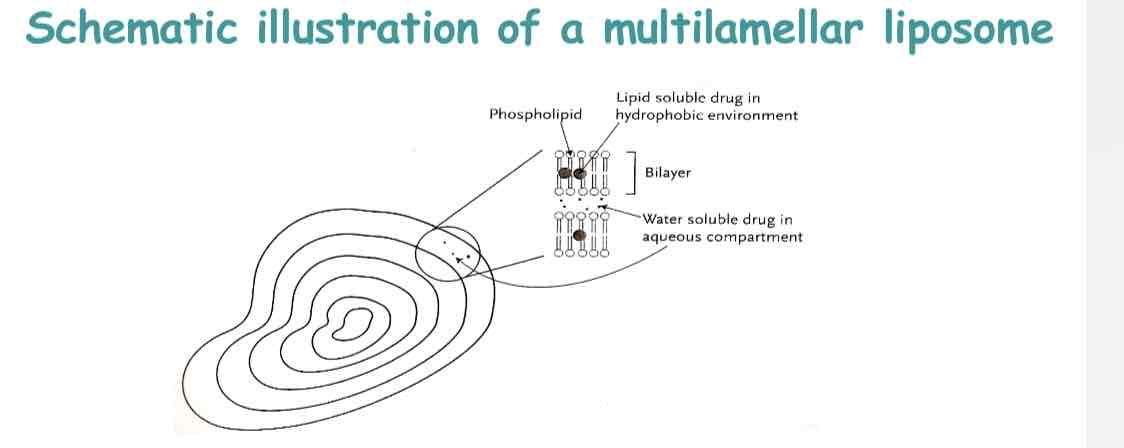
What are the two main structural types of liposomes?
Either multilamellar = with multiple layers of lipid bilayers surrounding the water core,
Or unilamellar= with only 1 layer of lipid bilayer surrounding the water core.
Schematic illustration of a multilamellar liposome
Liposomes are attractive drug carriers
Strongly lipophilic drugs fully buried in lipid bilayer
(i.e. membrane-entrapped drugs)
Strongly hydrophilic drugs sequestered in the aqueous interior of the liposome (i.e. Entrapped or encapsulated drugs)
Drugs with intermediate logP partition between the lipid & aqueous phases (i.e. membrane-associated drugs)
What type of drugs can liposomes carry?
Both water soluble and lipid soluble drugs
Like anti-tumour, Antimicrobial agents for example.
What lipid components are used in pharmaceutical liposomes?
Phosphatidylcholine (PC), a natural phospholipid= major lipid component used
What influences the rigidity, stability and permeability of liposome bilayer?
Type and quality of lipids
How does presence of cholesterol affect liposome bilayer rigidity?
It rigidifies liposome bilayers
What is advantage of using more rigid bilayer systems in liposome formulations?
More rigid bilayer system = when cholesterol is present= more stable and can retain drug entrapped in bilayer for longer periods.
When might a formulation require a more fluid bilayer system?
When a more rapid release of the entrapped drug is needed.
What is a stabiliser for liposome stability?
Cholesterol
Why are liposomes attractive as carriers for drugs?
Liposomes are attractive as drug carriers because their lipid composition is biocompatible and biodegradable.
What are the advantages of liposomes made from natural phospholipids?
Liposomes composed of natural phospholipids are biologically inert, weakly immunogenic, and have low intrinsic toxicity. They can distribute throughout the body and target specific receptors.
Meaning —> are natural blobs that body doesnt mind. Don’t cause much reaction from immune system, not toxic, can spread all over body and latch onto specific places.
What are conventional liposomes used for?
neutral or negatively charged, are mainly used for passive targeting to the cells of the MPS (mononuclear phagocyte systems).
What are sterically stabilised liposomes used for and what makes them unique?
Sterically stabilised liposomes, also known as 'stealth' liposomes, are coated with hydrophilic substances and are used to prolong their circulation times in the body.
How are immunoliposomes different from conventional and sterically stabilised liposomes?
also known as 'antibody-targeted' liposomes, can be either conventional or sterically stabilised and are used for active-targeting purposes.
purpose of cationic liposomes?
what makes them diff?
are positively charged,
used for delivering genetic material.
Conventional liposomes
typically made of phospholipids and/or cholesterol, and they protect enclosed molecules from breaking down.
How do conventional liposomes target specific tissues?
Conventional liposomes can passively target tissues with leaky blood vessels, like the liver and spleen
What happens when conventional liposomes are injected into the bloodstream?
When injected intravenously, conventional liposomes are quickly taken up by certain immune cells in the liver and spleen, removing them from circulation.
When is it useful to target the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS) with liposomes?
Conventional liposomes are used when targeting the MPS is the goal. This can include delivering drugs to fight infections or delivering immunomodulators to activated macrophages in cancer treatments.
Long circulating liposomes
The most popular way to produce long-circulating liposomes is
to covalently attach the hydrophilic polymer, polyethylene glycol
to the liposomes bilayers.
The highly hydrated PEG group create a steric barrier against interactions with molecular and cellular components in the biological environment.
E.g. Doxil TM , (Johnson & Johnson), (Doxorubicin entrapped in peggylated liposomes) – stable in blood stream, prolonged circulation.à Approved for Kaposi’s sarcoma
The next slide shows how ‘PEGylation’ of liposomes can extend their blood circulation profile.
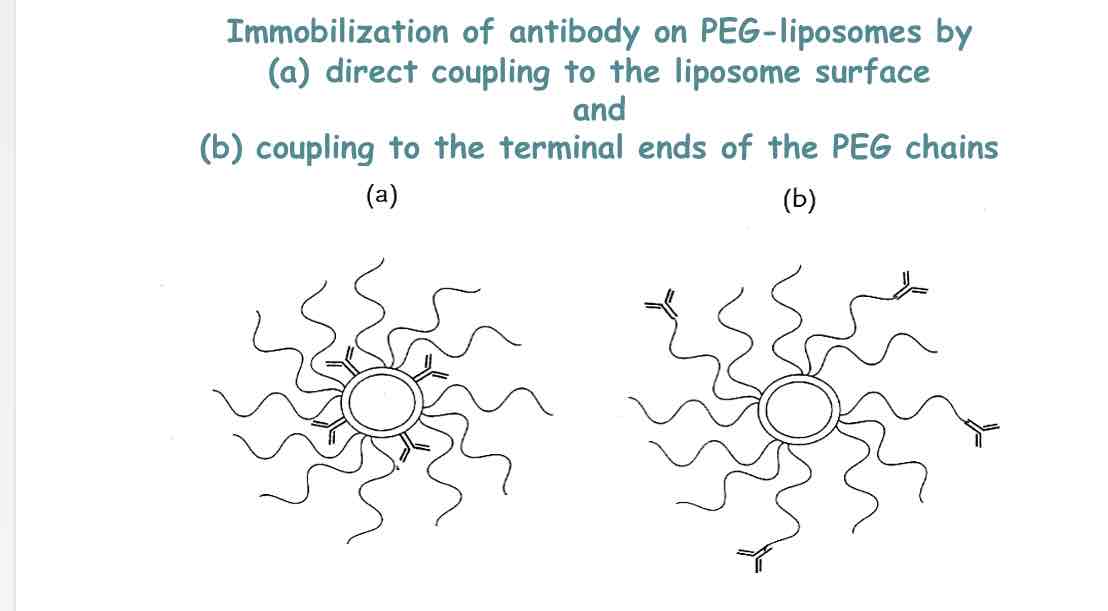
Immuno-liposomes
Immunoliposomes feature antibodies on their surface for improved binding to target sites.
Their main application is targeted delivery of anticancer drugs.
Long-circulating versions can be made, though direct antibody coupling may face steric hindrance.
Using a bi-functional PEG linker can overcome steric hindrance, coupling liposomes and antibodies separately.
Explain what this is
Cationic liposomes
Cationic liposomes are a recent advancement in delivering genetic material, showing promise for therapeutic applications.
These liposomes interact with and compact DNA, potentially forming complex structures with a lipid bilayer.
Toxicity of liposome formulations
Most liposome formulations are very well-tolerated
Cationic liposomes may activate complements and induce adverse effects via IV route.
PEGylated liposomes may induce a transient reaction upon injection in a subset of patients.