Molecular Basis of Inheritance
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:52 PM on 2/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
DNA
the substance of inheritance, is the most celebrated molecule of our time. Hereditary information is encoded in DNA and reproduced in all cells of the body
2
New cards
DNA program
m directs the development of biochemical, anatomical, physiological, and (to some extent) behavioral traits
3
New cards
Fredrick Griffith
The discovery of the genetic role of DNA began with research by (----) in 1928
4
New cards
Erwin Charga
reported that DNA composition varies from one species to the next and the number of A and T bases are equal and the number of G and C bases are equal
5
New cards
Nucleotides
are the building blocks of DNA
6
New cards
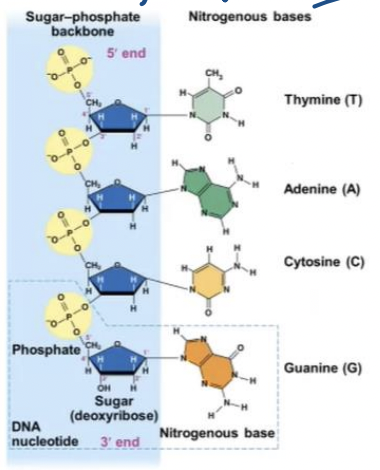
Thymine & Adenine & Cytosine & Guanine
Four Nitrogenous Bases
7
New cards
double helix
shape of the DNA
8
New cards
A – T (U) & G – C
Complementary base pairing
9
New cards
antiparallel
strands of a DNA double helix are said to be "-------" because the have the same chemical structure, but are opposite in direction
10
New cards
acts as a template
Since two strands of DNA are complementary, each strand (--------) for building a new strand in replication
11
New cards
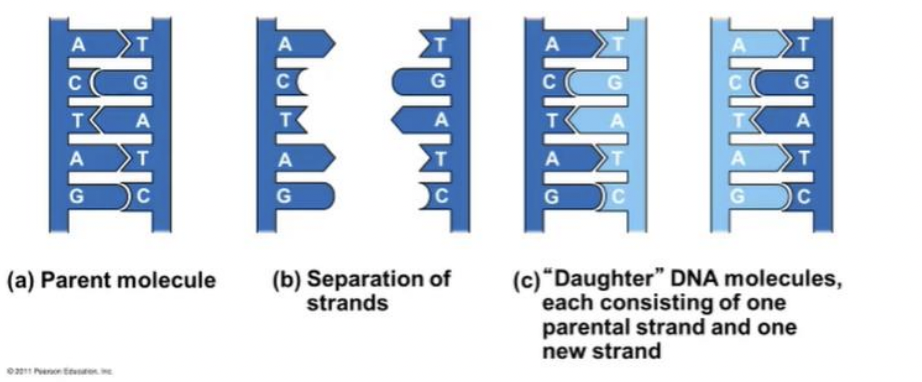
DNA replication
the parent molecule unwinds, and two new daughter strands are built based on base-pairing rules
12
New cards
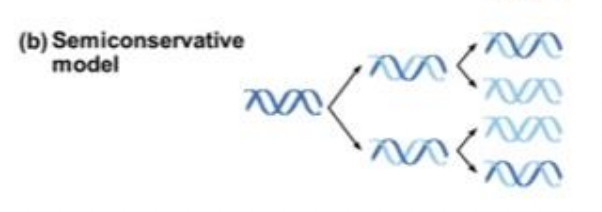
Semiconservative Model
model of replication that predicts that when a double helix replicates, each daughter molecule will have one old strand (derives or “conserves” from the parent molecule) and one newly made strand
13
New cards
origins of replication
Replication begins at particular sites called
14
New cards
Bubble
the two DNA strands are separated, opening up a replication “---------”
15
New cards
replication fork,
At the end of each replication bubble is a “--------” a Y-shaped region where new DNA strands are elongating
16
New cards
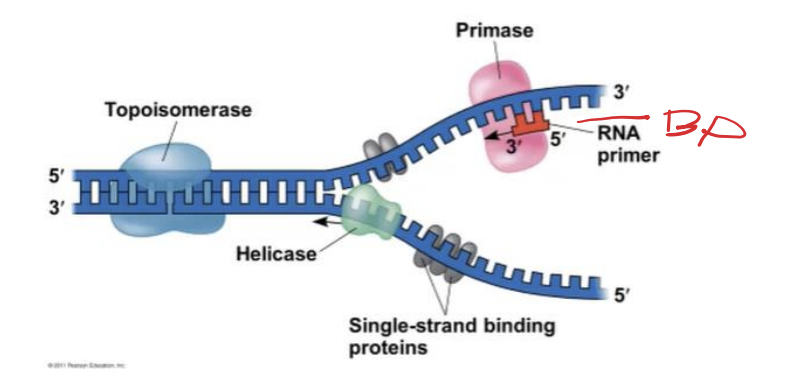
Helicases
are enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks
17
New cards
Single-strand binding proteins
bind to and stabilize single-stranded DNA
18
New cards
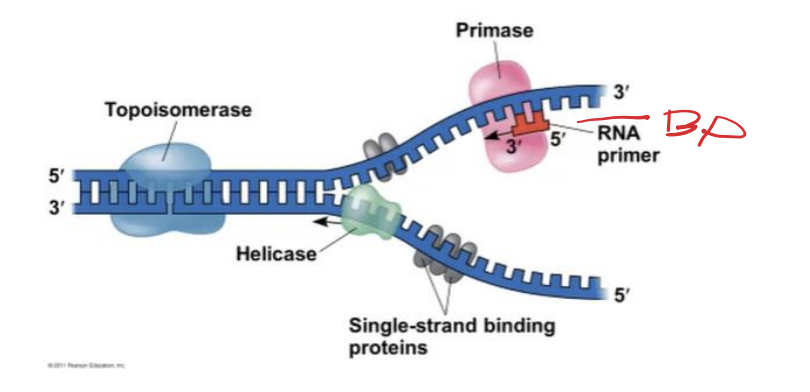
Topoisomerase
corrects “overwinding” ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
19
New cards
short RNA primer
The initial nucleotide strand is
20
New cards
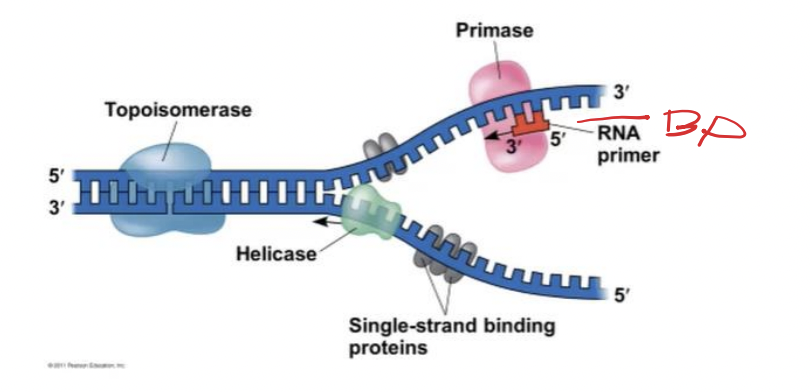
primase
An enzyme that can start from scratch and adds nucleotides one at a time using the parental DNA as a template
21
New cards
DNA polymerases
Enzymes that catalyze the elongation of new DNA
22
New cards
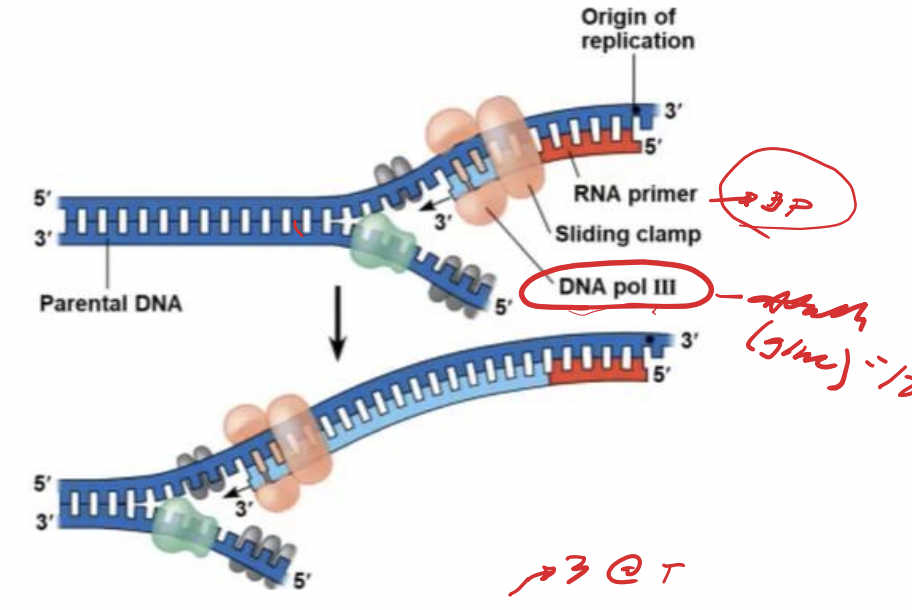
5’ to 3’ direction
DNA polymerases add nucleotides only to the free 3-prime end of a growing strand; therefore, a new DNA strand can elongate only in the (--------)
23
New cards
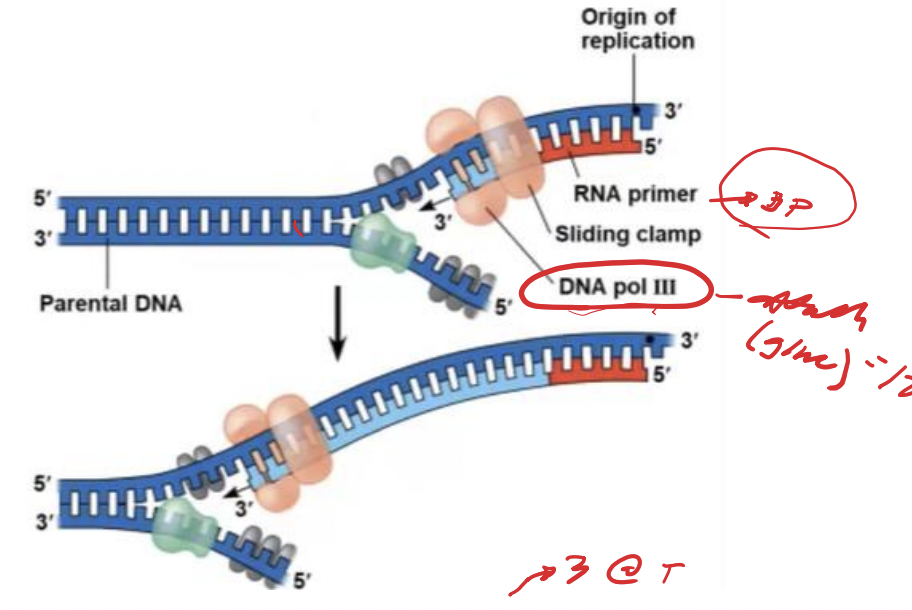
leading strand
Along one template strand of DNA, the DNA polymerases synthesizes a -------- continuously, moving toward the replication fork
24
New cards
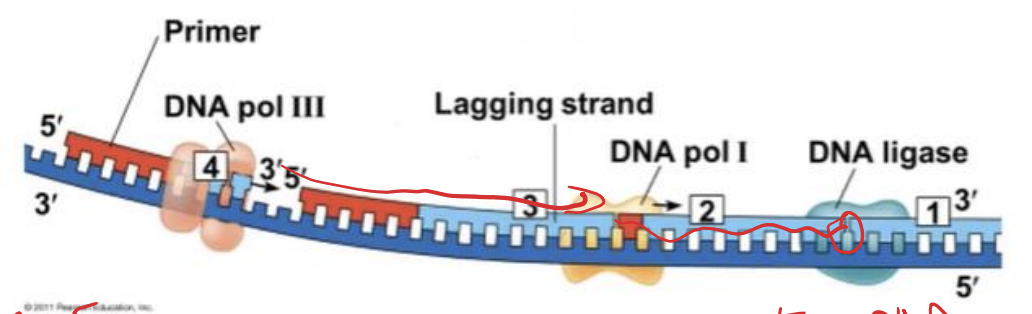
lagging strand
To elongate the other new strand, called the (-------), DNA polymerase must work in the direction away from the replication fork
25
New cards
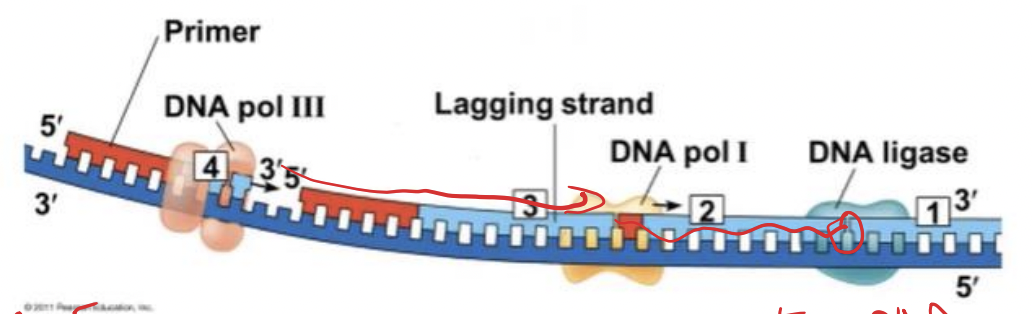
Okazaki fragments
The lagging strand is synthesized as a series of segments called (---------), which are joined together by DNA ligase
26
New cards
mismatch repair
In (--------) of DNA, repair enzymes correct error in base pairing
27
New cards
28
New cards
RNA
is the bridge between genes and the proteins for which they code
29
New cards
Transcription
is the synthesis of RNA using information in DNA
30
New cards
Translation
is the synthesis of a polypeptide, using information in the mRNA
31
New cards
Transcription
produces messenger RNA (mRNA)
32
New cards
Ribosomes
are the sites of translation
33
New cards
primary transcript
A (-----) is the initial RNA transcript from any gene prior to processing
34
New cards
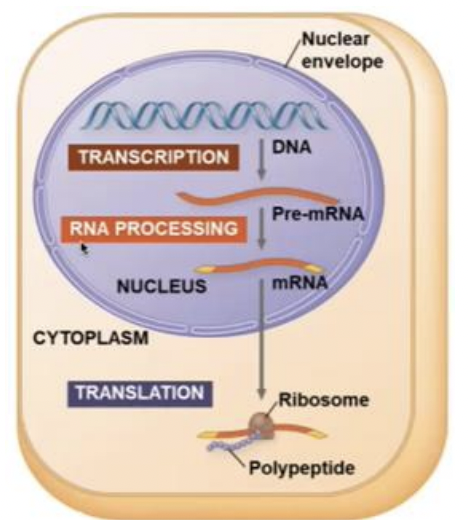
DNA -> RNA -> PROTEIN
The central dogma is the concept that cells are governed by a cellular chain of command:
35
New cards
RNA polymerases
RNA synthesis is catalyzed by (---------) which pries the DNA strands apart and join together the RNA nucleotides
36
New cards
uracil , thymine
RNA synthesis follows the same base-pairing rules as DNA, except that (--------) substitute for (----------)
37
New cards
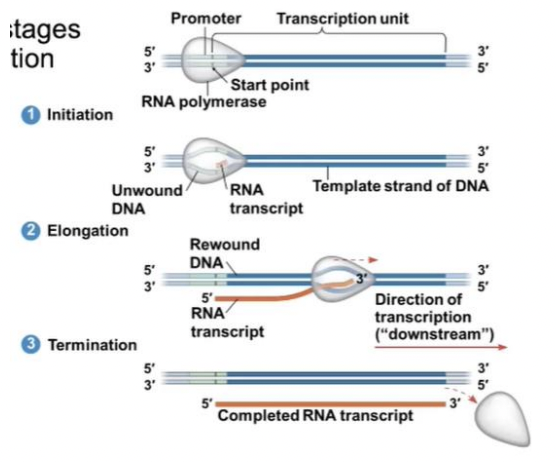
Initiation, Elongation, & Termination
The three stages of transcriptions
38
New cards
modify pre-mRNA (RNA processing)
Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus (-----------) before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm
39
New cards
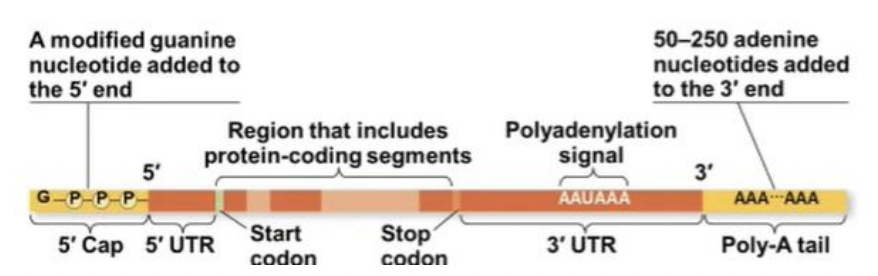
The 5’ end receives a modified nucleotide 5’ cap & The 3’ end gets a poly-A tail
Each end of a pre-mRNA molecule is modified in a particular way:
40
New cards
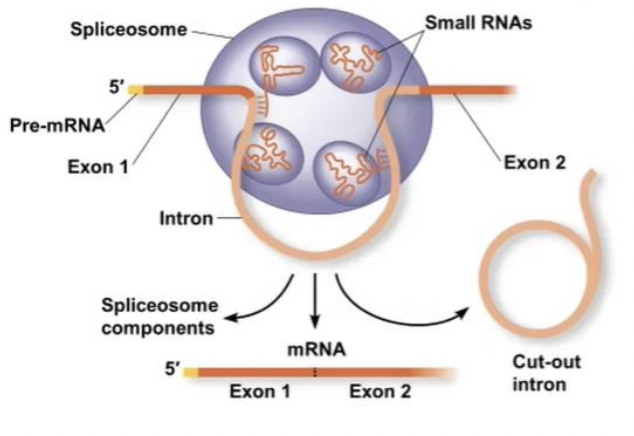
spliceosomes
RNA splicing is carried out by
41
New cards
codons
The mRNA base triplets, called (-------), are read in the 5’ to 3’ direction
42
New cards
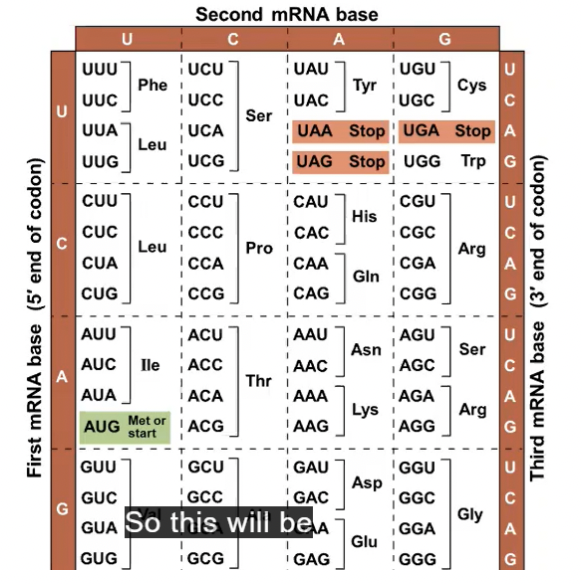
amino acid (one of 20)
Each codon specifies the (----------) to be placed at the corresponding position along a polypeptide
43
New cards
Translation
is a complex process in terms of its biochemistry and mechanics
44
New cards
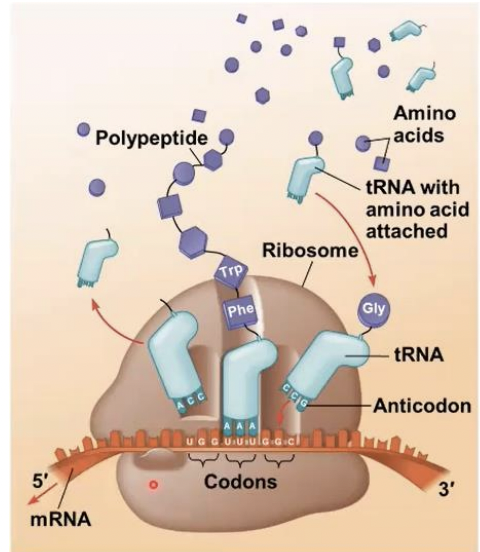
transfer RNA (tRNA)
A cell translates an mRNA message into protein with the help of
45
New cards
amino acids , polypeptide
tRNAs transfer (--------) to the growing (--------) in a ribosome
46
New cards
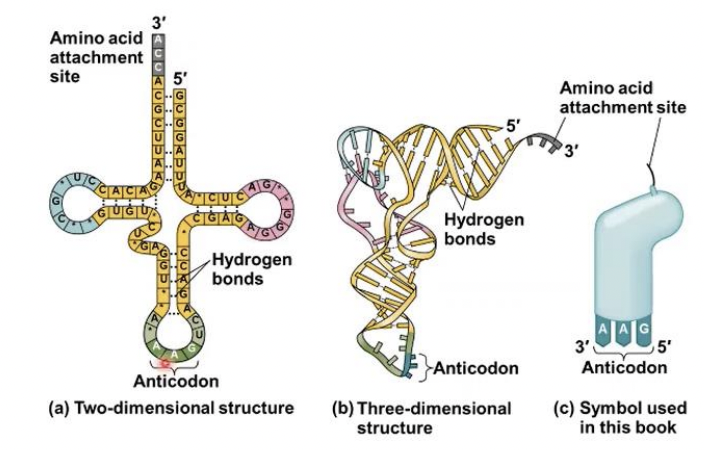
amino acid & anticodon
each molecule of tRNA carries a specific (----------) & (-----------) on each of its two ends
47
New cards
two steps
accurate translation requires how many steps?
48
New cards
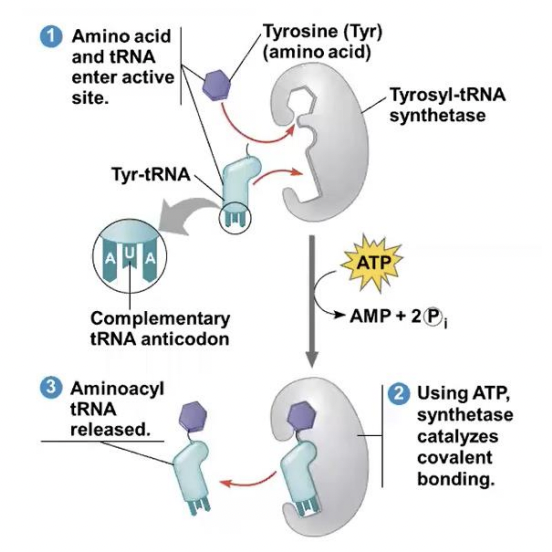
First step of accurate translation
Correct match between a tRNA and an amino acid, done by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
49
New cards
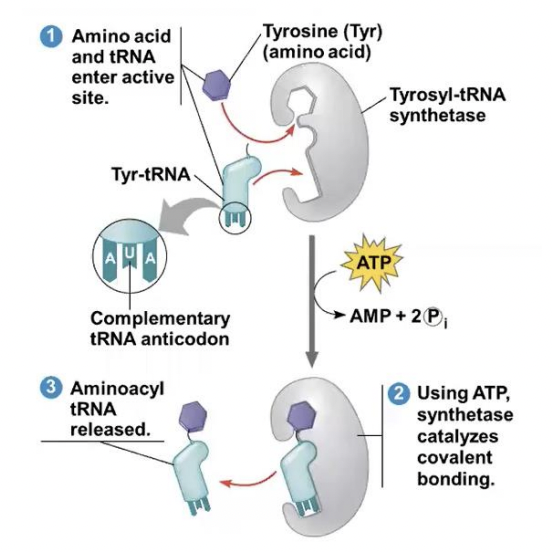
second step of accurate translation
A correct match between the tRNA anticodon and an mRNA codon
50
New cards
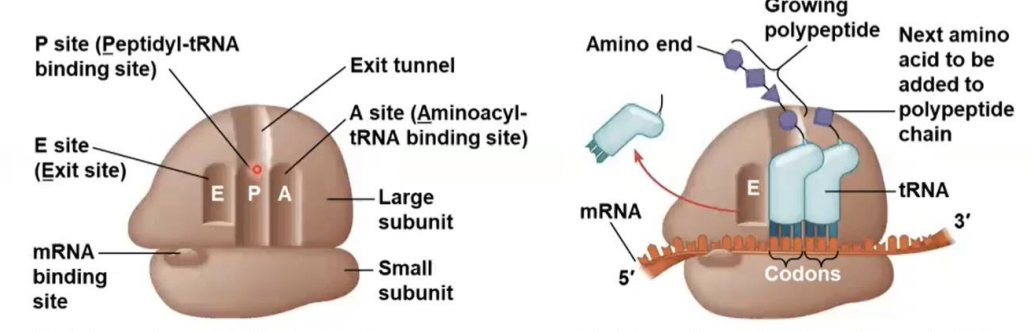
three sites
how many binding sites does ribosomes have for tRNA
51
New cards
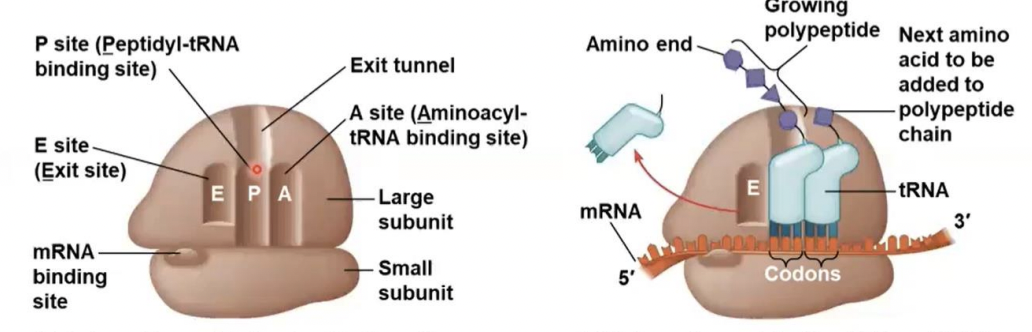
P site
this site Holds the tRNA that carries the growing polypeptide chain
52
New cards
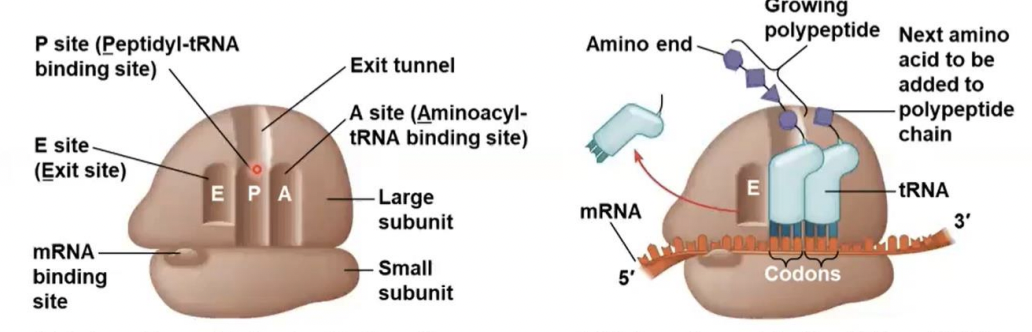
A site
this site Holds the tRNA that carries the next amino acid to be added to the chain
53
New cards
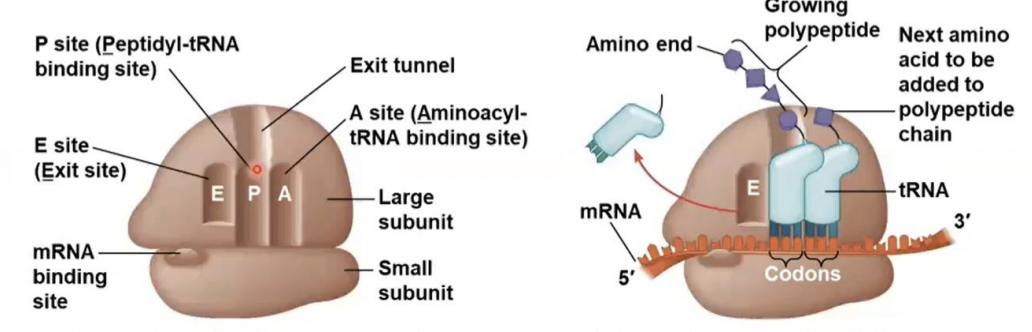
E site
Is the exit side, where discharged tRNAs leave thee ribosome
54
New cards
Initiation, Elongation & Termination
the stages of translation
55
New cards
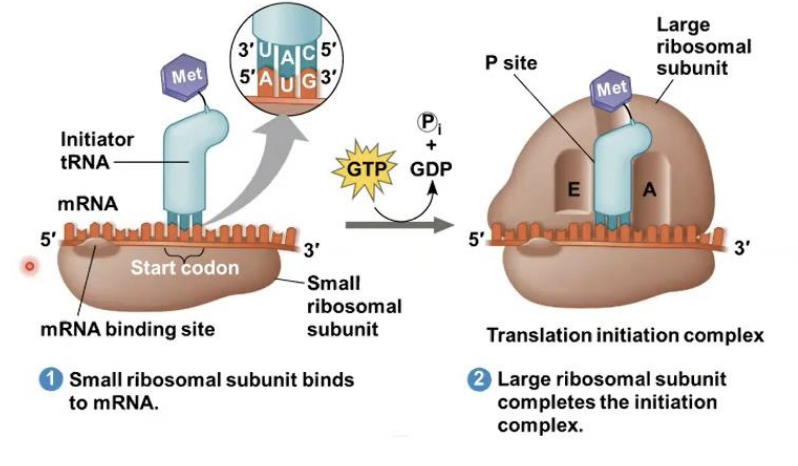
Initiation
stage of translation where it brings together mRNA, a tRNA with the first amino acid, and the two ribosomal subunits
56
New cards
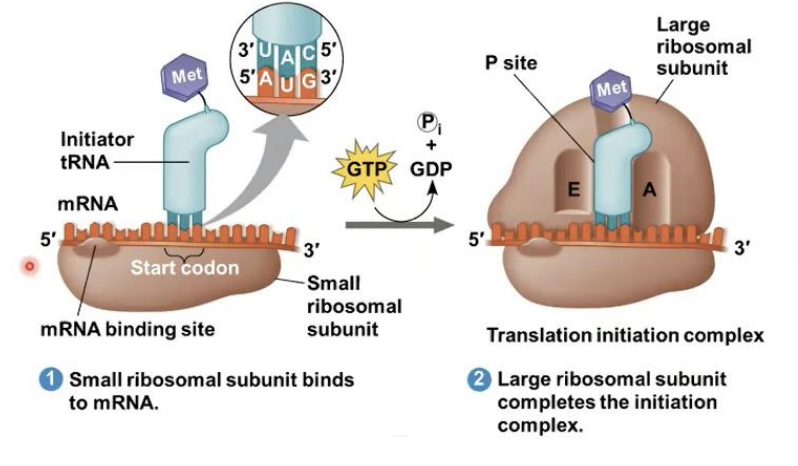
Initiation
stage of translation where this happens : First, a small ribosomal subunit binds with mRNA and a special initiator tRNA • Then the small subunit moves along the mRNA until it reaches the start codon (AUG)
57
New cards
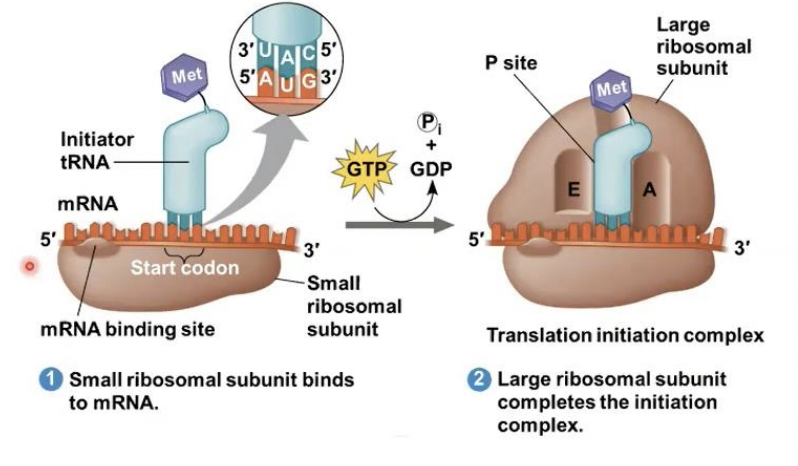
Initiation factors
proteins called (---------) bring in the large subunit that completes the translation initiation complex
58
New cards
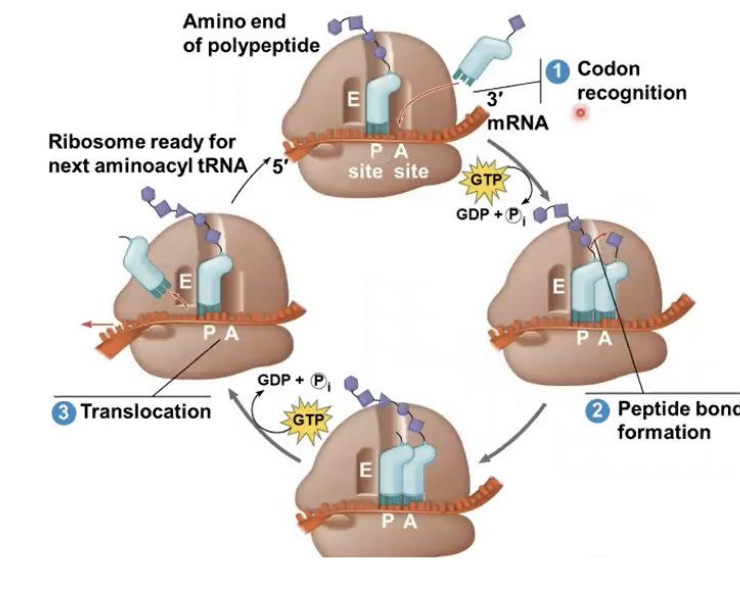
Elongation
stage of translation where : ribosome ready for aminoacyl tRNA , codon recognition , peptide bond formation and translocation
59
New cards
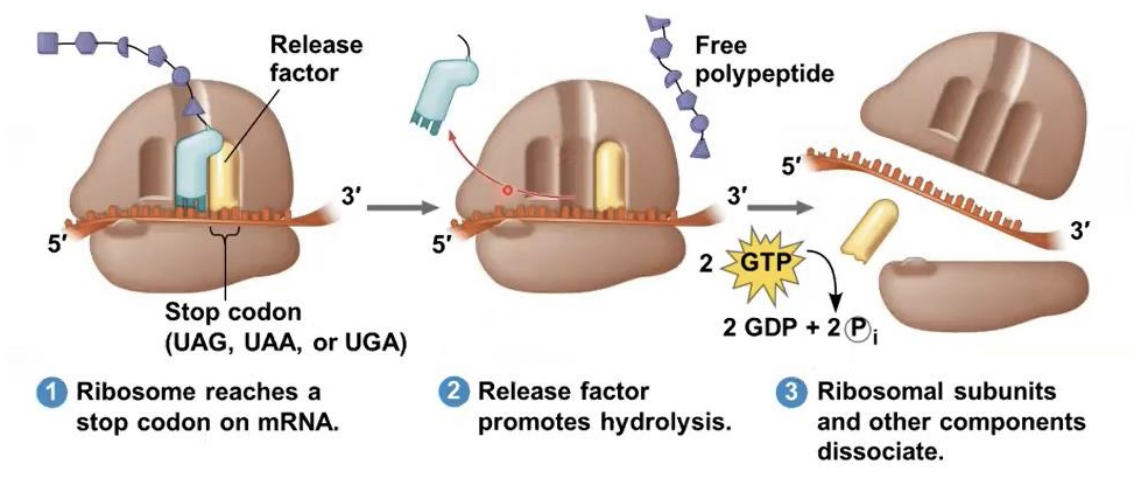
Termination
stage of translation where it occurs when a stop codon in the mRNA reaches the A site of the ribosome
60
New cards
Mutations
are changes in the genetic material of a cell or virus
61
New cards
Point mutations
are chemical changes in just one base pair of a gene
62
New cards
abnormal protein
The change of a single nucleotide in a DNA template strand can lead to the production of an
63
New cards
genetic disorder or hereditary disease
If mutation has an adverse effect on the phenotype of the organism the condition is referred to as a
64
New cards
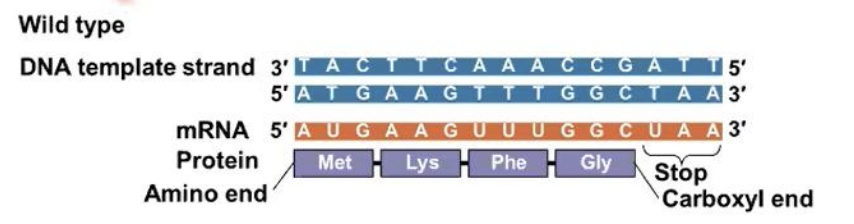
nucleotide-pair substitution
A (-----------) replaces one nucleotide and its partner with another pair of nucleotides
65
New cards
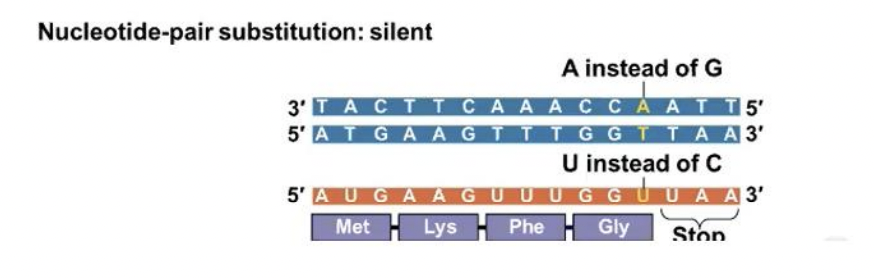
Silent mutations
they have no effect on the amino acid produced by a codon because of redundancy in the genetic cod
66
New cards
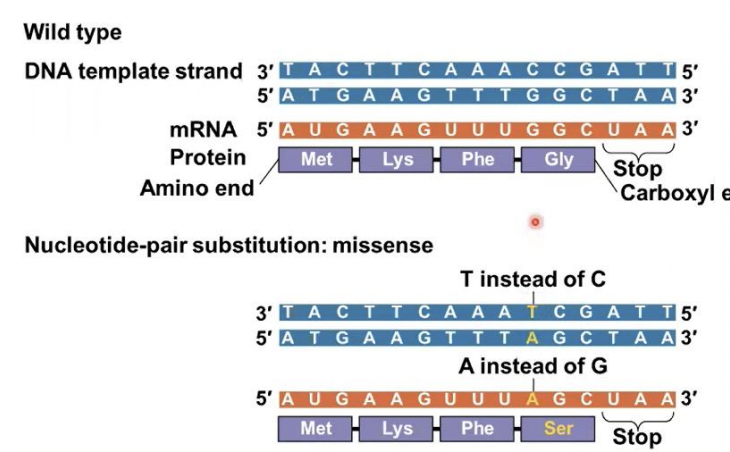
Missense mutations
these mutations still code for an amino acid, but not the correct amino acid
67
New cards
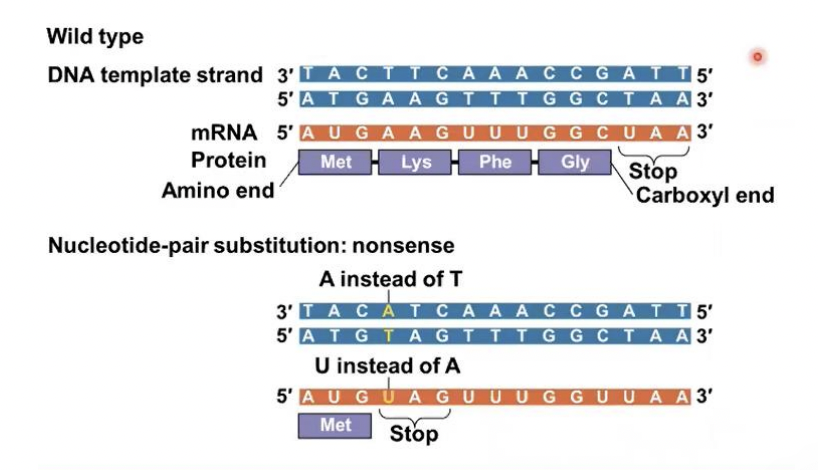
Nonsense mutations
these mutations change an amino acid codon into a stop codon, nearly always leading to a nonfunctional protein
68
New cards
Insertions
are additions s of nucleotide pairs in a gene
69
New cards
deletions
are losses of nucleotide pairs in a gene
70
New cards
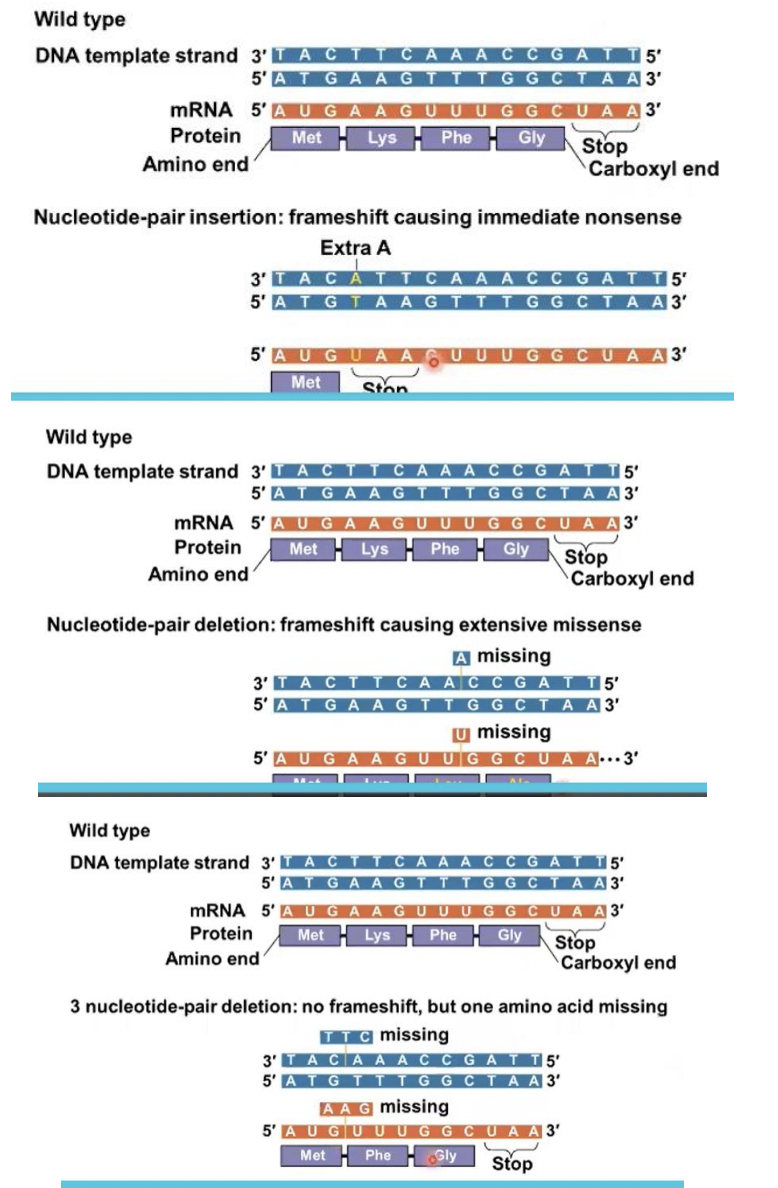
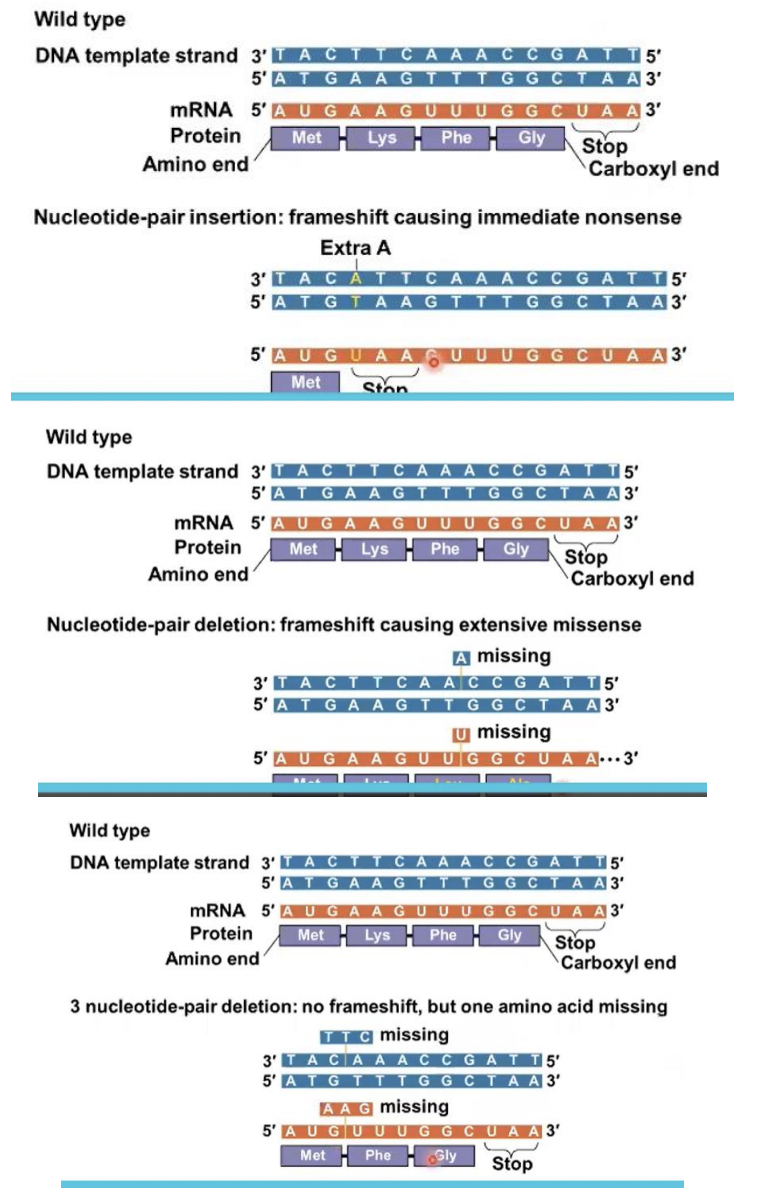
frameshift mutation
Insertion or deletion of nucleotides may alter the reading frame, producing a
71
New cards
frameshift mutation
These mutations have a disastrous effect on the resulting protein more often than substitutions do
72
New cards
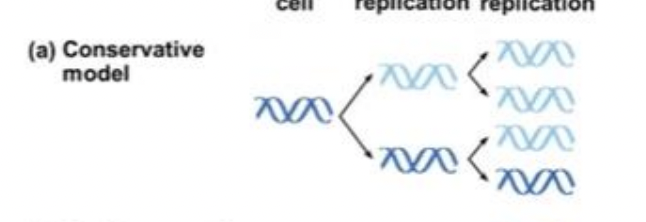
Conservative Model
this type of model tells us that would produce two helices, and among them, one contains entirely old DNA while the other contains entirely new DNA
73
New cards
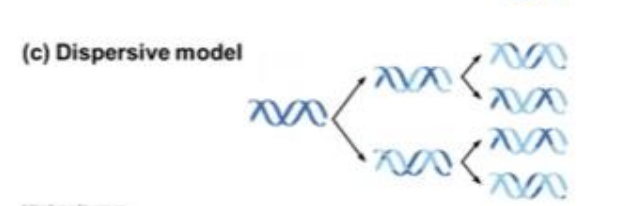
Dispersive Model
this type of model tells us that every round of replication would result in hybrids, or DNA double helices that are part original DNA and part new DNA
74
New cards
Conservative, Semi conservative, & Dispersion Models
three models of DNA replication