INSY 2303 Exam 3 Karen Scott
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
Critical Path
In a PERT chart, the sequence of task that takes the shortest amount of time to complete
Colocation Center
Where several corporations lease space and equipment in a facility designed to hold and protect computer systems and data
Data Center
Is a specialized facility designed to hold and protect computer systems and data
Application Development Tool
Software that can be assembled into the application software for an information system, contains many of the ingredients necessary for quickly and easily developing the model for an information system
SDLC
Software Development Life Cycle
1. Planning
2. analysis
3. design
4. implementation
5. maintenance
order of SDLC phases
planning phase (Purpose )
To create a project development plan
planning phase (Main activities)
Assembling the project team, justifying the project, choosing a development methodology, developing a project schedule, producing a project development plan
analysis phase (Purpose )
To produce a list of requirements for a new or revised informations system
the analysis phase (Main activities)
Studying the current system, determining system requirements, writing a requirements report
Design Phase (Purpose )
To decide how to build a system to fulfill the needs determined in analysis/planning phase
design phase (Main activities)
Design the user interface, system interfaces, network, databases
development stage (Purpose )
Where the developers code and build the application according to design documents
Purpose of implementation stage
Initiated after the system has been tested and accepted by the user to deploy and enable operations of the new information system in the production environment
maintenance phase (Purpose )
Occurs after the product is in full operation, includes software upgrades, repairs, and fixes the software if it breaks
Feature Creep
An undesirable occurrence during informations systems development when users, customers, or designers attempt to add features after the final specifications have been approved
JAD - Joint application design
based on the idea that the best informations systems are designed when end users and systems analysts work together on the project as equal partners
BI - Business intelligence
an integrated set of technologies and procedures used to collect and analyze data pertaining to sales, production, and other internal operations of a business in order to make better business decisions
Object-Oriented Methodology
An approach to system development that regard the elements of a system as a collection of objects that interact with each other to accomplish tasks
UML
Unified modeling language
· Class Diagram
· Use Case Diagram
· Sequence Diagram
UML includes
Class Diagram
Provides the name of each Brecht, a list of each object's attributes, a list of methods, and an indication of the associations between the objects.
Use Case Diagram
Documents the users of an informations system and the functions they perform. The people who use this system are called actors, any task they perform is called a use case.
Sequence Diagram
Depicts the detailed sequence of interactions that take place for a use case. Such as searching, selecting, or adding.
Arrow
Symbolizes data flow in a class diagram
success factors
System requirements, the criteria for successfully solving problems identified in an information system, they also serve as an evaluation checklist at the end of the project
System Conversion
refers to the process of deactivating an old information system and activating a new one
AKA "cutover" or "to go live"
Unit Testing
As each application module is completed, it undergoes __________ to ensure that it operates reliably and correctly
Integration Testing
______________ is performed to ensure that the modules operate together correctly
System Testing
ensures that all the hardware and software components work together
MRP - material requirements planning
-a production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes
- calculates material acquisition plans needed to meet production plans and customer demand.
-ensure materials are available for production and products are available for delivery to customers
Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
graphically illustrates how data moves through an information system
Process
A routine that changes data by performing a calculation in a class diagram
Gantt Chart
Shows the duration of development tasks as they occur overtime
WBS -Work breakdown structure
breaks a complete task into a series of sub tasks
PERT - Program Evaluation and Review Technique
used to analyzing the time needed to complete each project task
JIT - Just in time
a manufacturing system in which the parts are needed to construct a product are received at the assembly site only as needed
Horizontal Market
Any computer program that can be used by many different kinds of businesses (like an accounting program)
payroll, inventory monitoring, income and expenses tracking
Example of horizontal market software
Vertical Market
a software application designed to meet the needs of a specific market segment or industry,
such as medical record keeping software for use in hospitals.
example of vertical market software
vertical
horizontal
+______ market is More specific than a _______ market
Turnkey system
Hardware and application software designed to offer a complete information system solution. These solutions may be designed for in-house installation or as a cloud-based system.
E-Commerce
Refers to business transactions that are conducted electronically over a computer network
· B2C
· C2C
· B2G
· B2B
E-Commerce types
B2C
Business to consumer, the process in which businesses sell to consumers
C2C
Consumer to consumer, the process in which consumers sell to other consumers
B2B
Business to business, the process of selling merchandise or services from one business to another
B2G
Business to government, an exchange of products, services, or information between businesses and governments
Amazon & Zappos
B2C online store front example:
eBay and Etsy
C2C online store front example:
Expert System
Computerized advisory programs that imitate the reasoning processes of experts in solving difficult problems and give solution to the given question
ERP - Enterprise resource planning
a suite of software modules that integrate major business activities. All combine into ERP Central Database
knowledge-based system
expert system aka
· Knowledge Base
· Inference Engine
· Knowledge Engineering
Expert System:
Knowledge base
Stored in a computer file and can be manipulated,
_____________ holds the facts and rules for an expert system
Inference Engine
The knowledge base can be manipulated using an _____________________ , this is software that can analyze a knowledge base or expert system
fuzzy logic
a technique used by an expert system to deal with imprecise data by incorporating the probability that the input information is correct.
Uses confidence level to determine something allowing for multiple possible truth values to be processed through the same variable.
Knowledge engineering
The process of designing, entering, and testing the rules in an expert system
TPS vs. DSS
TPS: Provides a way to collect, store, process, display, modify, or cancel transactions
DSS:
helps people make decisions by directly manipulating data from external sources, generations statistical projection, and creating data models of various scenarios
TPS - Transaction processing system
Provides a way to collect, store, process, display, modify, or cancel transactions
Structure
TPS is Structure or Non-structure?
DSS - Decision Support System,
helps people make decisions by directly manipulating data from external sources, generations statistical projection, and creating data models of various scenarios
OLTP vs Batch Processing
OLTP:
a transaction is processed in real time as it is entered.
Batch processing:
A processing system that involves holding a group of transactions for processing until the end of a specified period of time.
OLTP - Online transaction processing
a transaction is processed in real time as it is entered.
Batch Processing
A processing system that involves holding a group of transactions for processing until the end of a specified period of time.
OLTP rather than batch processing
most modern transaction processing systems use ______ rather than batch processing.
1. summary report
2. exception report
Managers depend on reports produced by an MIS to make routine business decisions based on 2 reports:
Summary report
combines, groups, or totals data. Useful in tactical and strategic planning, useful for annual sales
Exception Report
contains information that is outside of normal or acceptable ranges
Ad Hoc Report
responds to unplanned requests for non-routine information needs, custom reports
CHAP 10
Database/ Database Models
collection of information
1. Hierarchical
2. Network
3. Relational
4. O-O
Types of Database Models
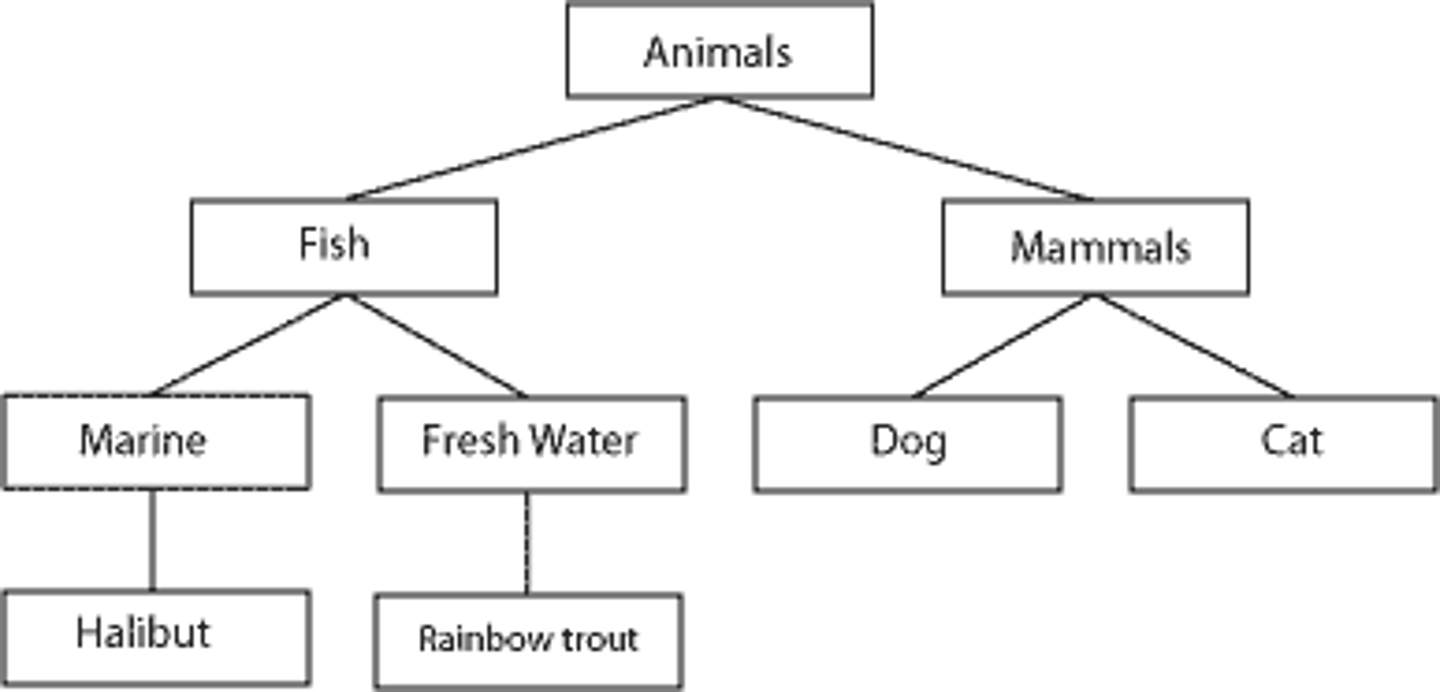
Hierarchical database model
a database model in which record types are arranged as a hierarchy or tree, of child nodes that can have only one parent node. Allows one to one or one to many relationships
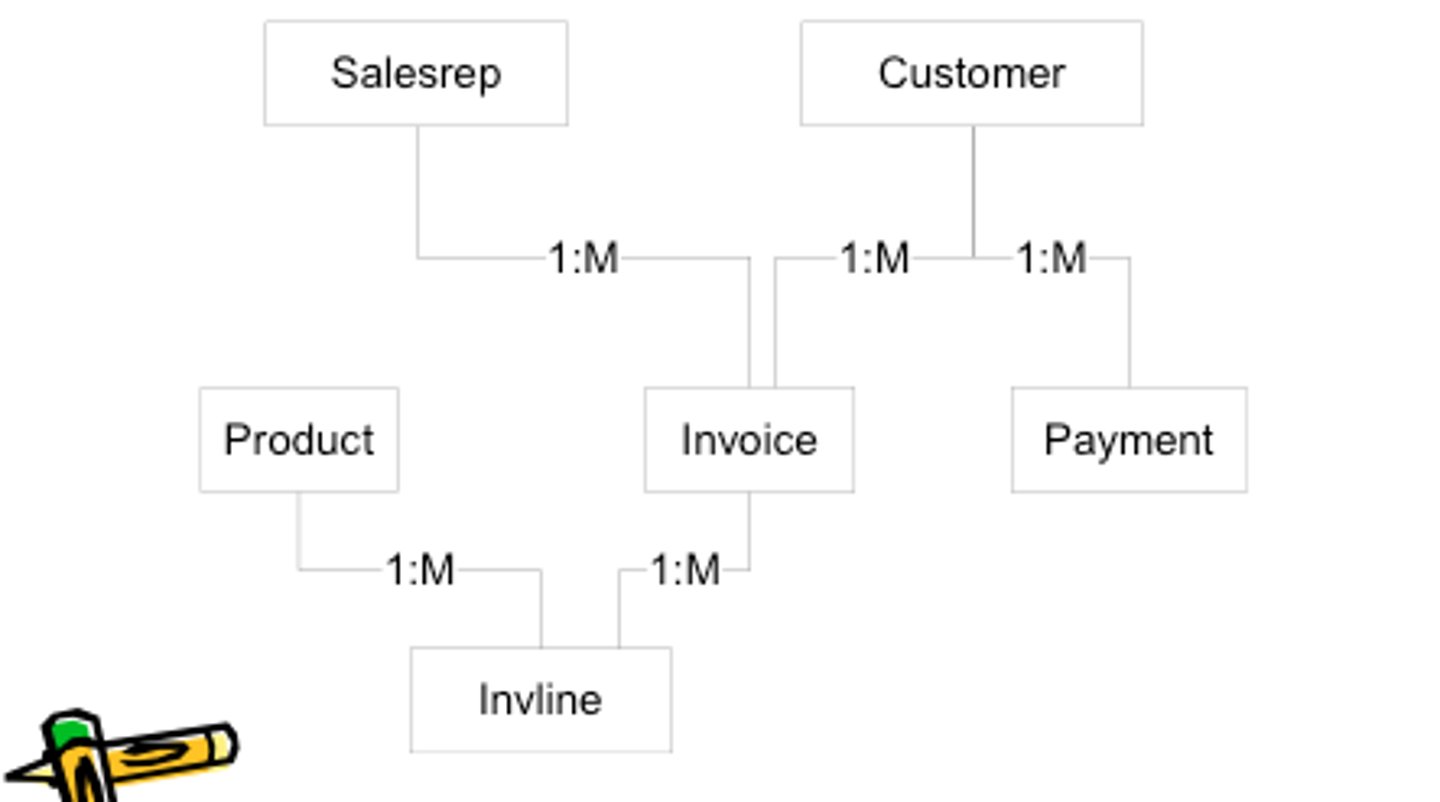
Network Database Model
type of database where multiple records or files can be linked to multiple owner files and vice versa (upside down- each member information is the branch linked to the owner at the bottom of the tree)
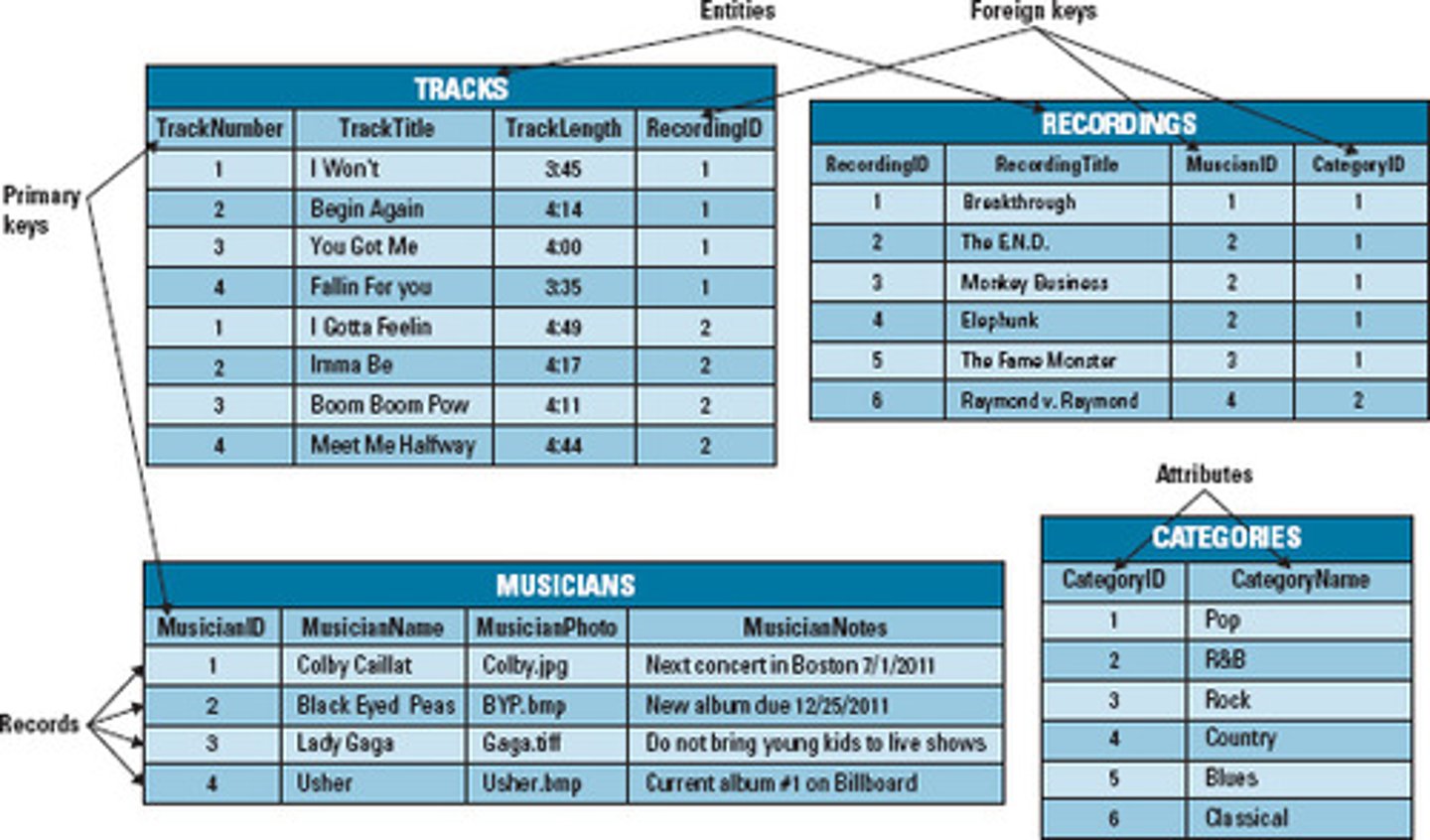
Relationship Database Model
an association between data that's stored in different record types
stores data in a collection of related tables, each table is a sequence of records, similar to a flat file, all the records in a table are of the same record type, each row of a table is a record and each column is equal to a field. Relationships are specified by joining common data stored in records from different tables
O-O (Database Model)
database which is organized around objects rather than actions, and data rather than logic
DBMS - database management system
software that manages data stored in a database, such as Microsoft Access, works with many kinds of data
Data Independence
separating the data from the programs that manipulate it, supported by modern database tools
Data Redundancy
the amount of data that is duplicated in a database
Normalization
a process that helps database designers create a database structure that minimizes storage space and increases processing efficiency
Operational Database vs. Data Warehouse
Operational database
is used to collect, modify, and maintain data on a daily basis
Data warehouse
a collection of information organized for analysis. _______________________ can combine operational databases with data from other databases. It is a repository for data from more than one database.
Big Data
refers to huge collections of data that are difficult to process, analyze, and manage using conventional database tools
Hadoop
is a file system developed in 2005, that handles millions of files distributed across multiple server nodes, deployed by many of the world's biggest web sites.
MapReduce
a second NoSQL technology that efficiently accesses the dataset (used by Hadoop), _________________ sends the processing logic to the data and only returns the result.
Data Mining
refers to computer algorithms that analyze information to discover previously unknown and potentially useful information, including relationships and patterns, the data accessed by data mining and other analysis techniques is often stored in the data warehouse. Can reveal relationships that may not be anticipated or expected.
Distributed Database
a database that consists of two or more files located in different sites either on the same network or on an entirely different network, portions of the database are stored in multiple physical locations and processing is distributed among multiple database nodes
Cardinality
refers to the number of associations that can exist between two record types for example, many albums can be rap, but the reverse is not true
Relationship
the association data that's sorted in different record types
ERD -entity relationship diagram,
the relationship between record types are depicted graphically with this
SQL Commands
Processed by the DMBS and are issued using computer program big languages designed for databases, also called query languages
· CREATE
· INSERT
· UPDATE
· DELETE
· JOIN
· SELECT
SQL/SQL Commands:
CREATE
create a database or table
INSERT
add a record
UPDATE
change data in a field
DELETE
remove a record from a table
JOIN
use the data from two tables