Unit/Exam 1 Foundations of Nursing
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Cardiac Output (CO)
amount of blood pumped into the circulatory system by the heart within one minute
Stroke Volume (SV)
is the amount of blood ejected by the ventricle during one heart contraction (60-100 normal)
Blood Viscosity
The resistance of a liquid to flow, aka “thickness” of blood
atherosclerosis
hardening of the arteries
Peripheral vascular resistance
PVR = how hard it is for blood to flow through the blood vessels
Think of it as how tight or relaxed the vessels are.
High PVR → vessels are narrow/tight
Low PVR → vessels are wide/relaxed
Contractility
The force required to eject blood from the left ventricle and if the heart can do this efficiently or not.
Preload
the amount of blood inside the ventricles before they contract. (this can effect stroke volume and blood pressure)
Afterload
amount of resistance, or constriction, that the heart must overcome to eject the blood into the systemic circulation
Orthostatic Hypotension
A decrease in blood pressure that occurs upon standing, especially from a lying or sitting position. A significant drop in the blood pressure caused by a change in position.
tachycardia vs bradycardia
higher then normal range heart rate
lower then normal range heart rate
apical pulse
The heart rate that is heard or felt at the apex of the heart,
pulse sites in the body
Temporal – At the temple, just lateral to the eye, above the zygomatic (cheek) bone
Carotid – On either side of the neck, between the trachea and sternocleidomastoid muscle
Apical – Left chest at the 5th intercostal space, midclavicular line (auscultated, not palpated)
Brachial – Inner aspect of the upper arm, between the biceps and triceps (antecubital space)
Radial – Thumb side of the wrist, just below the base of the thumb
Ulnar – Little-finger side of the wrist (less commonly used)
Femoral – In the groin, where the thigh meets the trunk
Popliteal – Behind the knee, in the popliteal fossa
Posterior Tibial – Behind and slightly below the medial malleolus (inner ankle)
Dorsalis Pedis – Top of the foot, lateral to the extensor tendon of the great toe
eupnea
respiratory rate and rhythm that are normal or within range for a specific patient
Cheyenne - Stokes
Irregular respirations beginning with rapid shallow breaths and then deep breaths followed by apnea
Kussmaul Respirations
Deep, rapid respirations (metabolic acidosis)
Normal Vital Signs Range
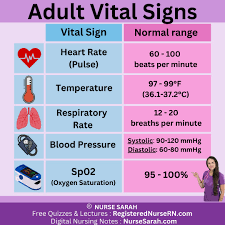
Pacemaker of the heart
SA node
What would indicate orthostatic hypotension
A decrease of 20 millimeters of mercury ion the systolic pressure with a position change indicates what
Blood Pressure Readings
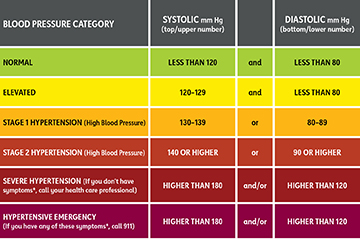
Pulse Rate Ranges by Age
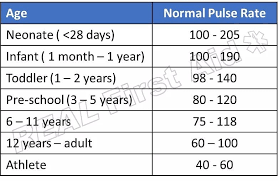
Respiratory Rate (different ages)

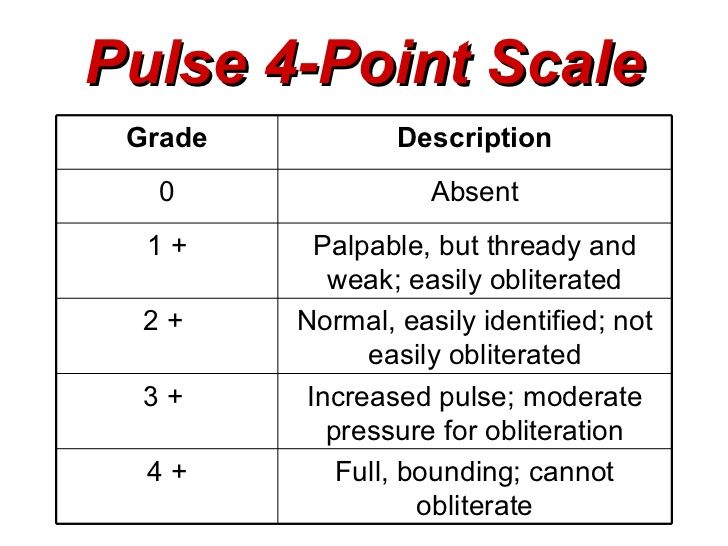
Pulse 4 point scale
A nurse is caring for a client who has a heart rate of 120/min. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Instruct the client to bear down like they are having a bowel movement. (valsava maneuver can regualte heart rate)
A nurse is assessing a 3-month old infant during a well-child visit. Which of the following actions should the nurse take when assessing the apical pulse?
Place the stethoscope over the 4th intercostal space to the left of the sternum.
Pulse Deficit
Apical - Radial Pulse = ????
anticoagulant medication
Medications that inhibit the blood's ability to clot
medication reconciliation
The process when the physician assesses the current home medications with the newly prescribed drugs. It must be completed on client admission, transfer, or discharge from the hospital
hospital–associated infections (HAIs)
Nosocomial infections. Infections that occurred while the client was in the hospital.
Jean Watson 10 Caritas Processes
Ten caring processes that provide a common language to guide nurses
Embrace – Loving‑Kindness
Inspire – Faith‑Hope
Trust – Sensitivity to Self and Others
Nurture – Helping‑Trusting Relationship
Forgive – Expression of Positive and Negative Feelings
Deepen – Creative Problem‑Solving
Balance – Transpersonal Teaching‑Learning
Co‑create – Healing Environment
Minister – Basic Needs with Dignity
Open – Spiritual‑Existential Care
Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring
Theory of client care stemming from holistic mind-body-spirit healing perspective characterized by caring moments in which the nurse and the client have a human-to-human connection
Medically Futile
doing useless treatments that don’t do anything for the patient
palliative care
multidisciplinary care approach that focuses on the management of symptoms for a chronic or life threatening condition while maintaining the highest quality of life possible
4 questions to ask before administering medication
What Medications is the client currently taking?
Interaction with prescription?
Allergies?
Physical assessments needed?
Nursing Process
5 step sequential process that allows nurses in prioritizing care for clients
assessment
analysis
planning
implementation
evaluation
Controlled Substances
Medication with the potential for addiction, misuse, and physical or mental injury regulated Drug Enforcement Administration. (NOT FOUND IN CLIENTS CABNIET)
Troche
a flat, round tablet also called a lozenge that is designed to be dissolved in the mouth and not swallowed. No food 5 min before or after
Sublingual/Buccal Administration
Under the tongue/Inside of the cheek
DO NOT CHEW or eat until fully dissolved
Elixirs and Syrup
Elixir - contains water, alcohol, sweeter and medication
Syrup - contains water, concentrated sugar and medication
Suspension
A liquid medication prepared when the drug doesn't dissolve but is crushed into fine particles.. Shake or stir IMMEDIATELY before administration
First Step of Clinical Judgment Model
Assessment, recognize and analyze cues
General Survey, Lab/Assessment Results, Diagnostic material … ect
Recognize Cues
When you identify problems from the information you have gathered and you put them together to form a hypothesis or multiple
Analyze Cues
After your cues have been grouped together this is where you break down the reasoning behind the different hypothesis(s) you have formed
Time Management Matrix
A tool that divides activities into four quadrants: important, not important, urgent, not urgent.
EMRGENT - NOWWWWW
SMART Goals
S: Specific
M: Measurable
A: Attainable
R: Realistic
T: Timely
SBAR Tool
(situational, background, assessment and recommendation)
helps relay client information systemically and concisely making sure no critical details are missed
SOAP Note
S: Subjective
O: Objective
A: Assessment
P: Plan
A acronym used for how nurses should document things in the clinical setting
Acuity Level
How much the requirement of nursing services is needed and the amount of nursing time to meet those requirements. AKA the complexity of a client's condition.
Client Assignment Types
Direct: one nurse → specific client(s)
Area: one nurse → specific location/zone
Group: one nurse → group of clients
IDEAL Discharge Planning
I: Include the client and caregivers.
D: Discuss the five key areas—medications, home life, warning signs, test results, and follow-up.
E: Educate the client on the condition, the discharge process, and next steps.
A: Assess the effectiveness of the education.
L: Listen to the client’s goals and preferences.
Teach-Back Method
Nurse teaches → client explains it back
Confirms understanding
Used during education & discharge
5 Rights of Delegation
Right Task: within role; no critical thinking
Right Circumstance: client is stable
Right Person: competent to do task
Right Directions/Communication: clear instructions given
Right Supervision/Evaluation: nurse supervises & evaluates
OUD: Steps of Care
Prevention – education, safe opioid use, risk screening
Identification – recognize misuse, assess risk factors
Treatment (1-2 years) – MAT (buprenorphine, methadone, naltrexone) + counseling
Recovery – long-term support, relapse prevention
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
Physiological – food, water, oxygen, sleep
Safety – security, shelter, stability, protection
Love & Belonging – relationships, family, friends
Esteem – self-worth, confidence, respect
Self-Actualization – reaching full potential
ABCDE Priority of care Framework
A: Airway
B: Breathing
C: Circulation
D: Disability (neurological)
E: Exposure (environment safe? Expose patient to inspect)
Triage
To sort and rank clients based on their urgency of their need for care.
emergent (red) - needs treatment ASAP
urgent or delayed (yellow) - needs treatment in the next 30 min to 1hr
non-urgent or minimal (green) - can be okay without treatment for a few days
expectant (black) - probably going to die
Acuity Level
Used in the ED. Nurses focused client data when assigning an acuity level to each client. The acuity level helps with deciding which clients can wait to be seen and which clients should be seen immediately. (level 1 urgent - level 5 less urgent)
Increased fever can indicate
increased metabolism