Physiology: Cardiorespiratory - Unit 3
1/193
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
Prognosis & ex
Expected impact of disease on life
ex: asthma for life, PCOS for life but can be managed through medication.
Diagnosis & ex
Identifying an illness based on symptoms a patient has.
ex: breathing trouble caused by asthma.
Treatment
Can reduce symptoms or delay progression of a disease.
Cure & ex
After medical care, individual no longer has the disease
ex: tumor removal, antibiotics after bacterial infection.
(Types of Diseases) Acute & ex
Short term illness or symptom that has sudden onset.
ex: heart attack comes suddenly.
(Types of Diseases) Chronic & ex
Long term illness with symptoms that last for months or more.
ex: asthma, diabetes.
(Respiratory Tissues) Simple Squamous & Pseudostratified Columnar group
E
(Respiratory Tissues) Simple Squamous function
In alveoli
Single layers allow for easier diffusion
AT ENDS OF LUNGS
(Respiratory Tissues) Simple Squamous specialized cells
none
(Respiratory Tissues) Pseudostratified Columnar function
Airway- nose through bronchiole.
Secretion of mucus, propels mucus with cilia.
(Respiratory Tissues) Pseudostratified columnar specialized cells
Goblet cells: make mucus
Respiratory System Function
Exchange Gases (O2 & CO2) & Produce Vocal Sounds
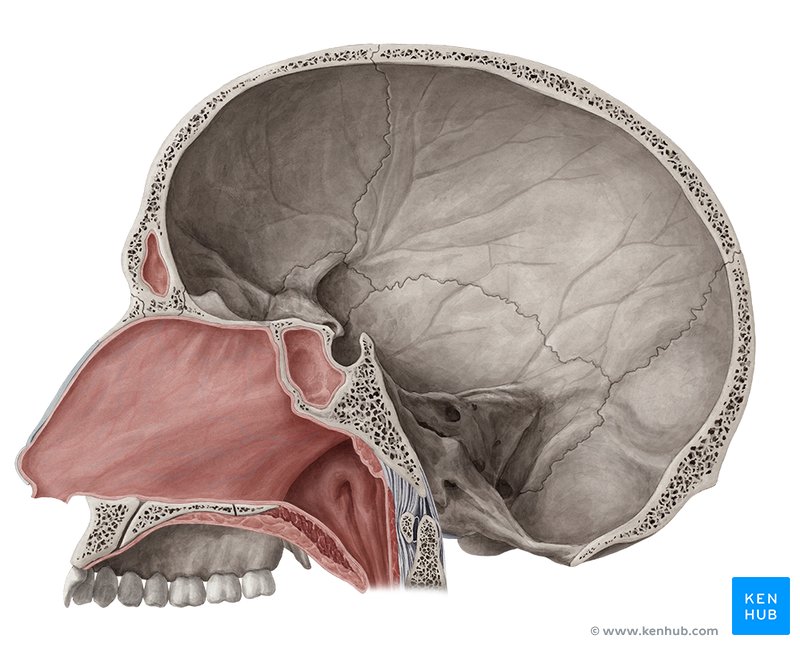
Nasal Cavity
Inhales Air
Oral Cavity
(Can also inhale air)
Pharynx
Back of Throat
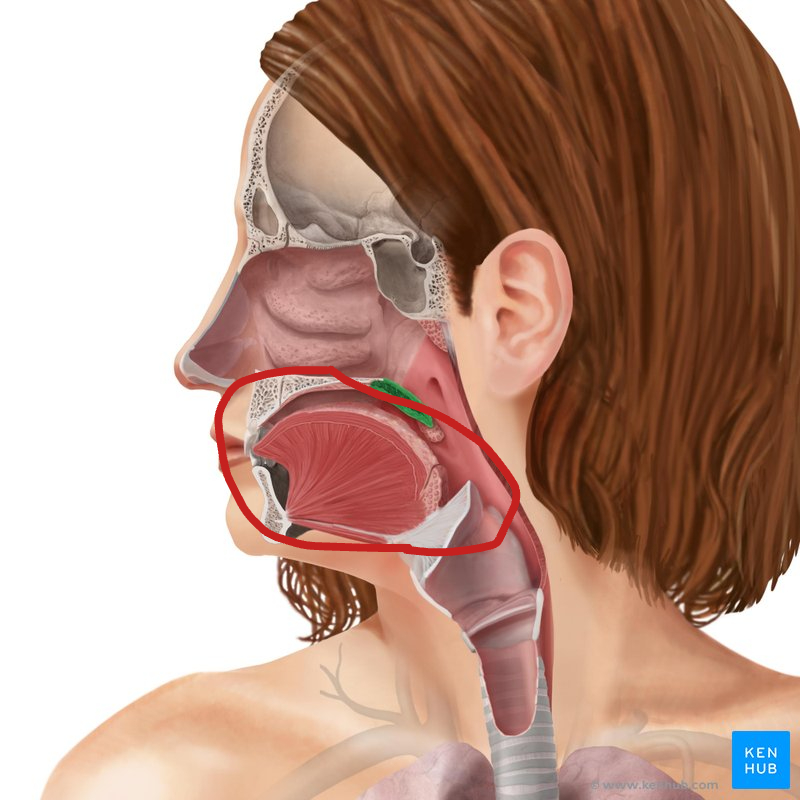
Larynx
Voice box: Has Vocal Cords
Trachea
(Windpipe)
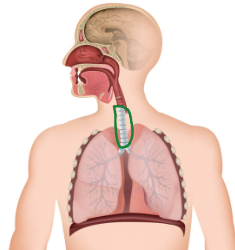
Bronchi
First branch of airways into lungs.
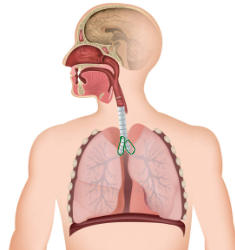
Lung
Right 3 Lobes, Left 2 Lobes (Heart takes up space)
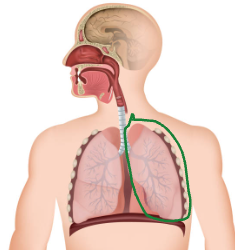
Bronchioles
Small Airways
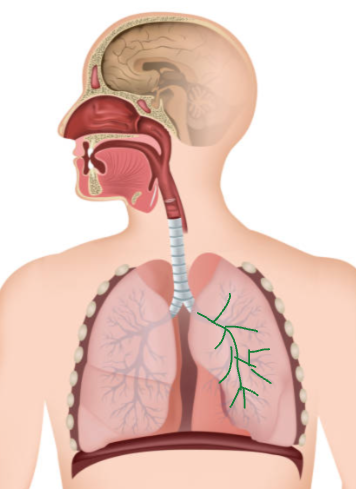
Alveoli Definition
Location where exchange of O2 for CO2 occur
Diaphragm
Muscle Aids in Breathing.
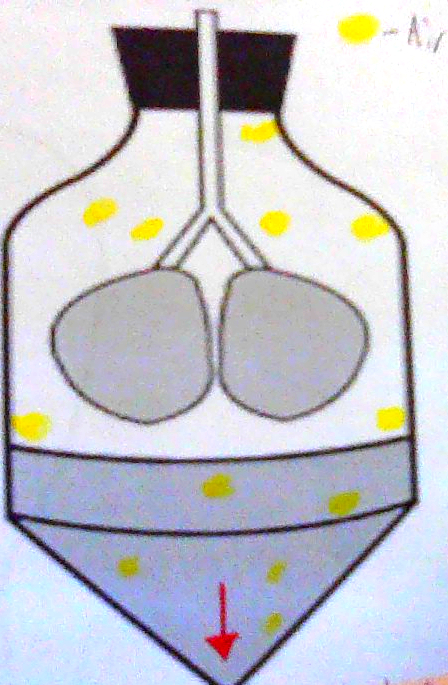
Diaphragm Changes Volume of
Chest Cavity
(Thoracic Mechanics) When it Contracts & Moves DOWN (4)
Chest Cavity gets larger
Pressure DECREASES
Air flows in
Lungs INFLATE
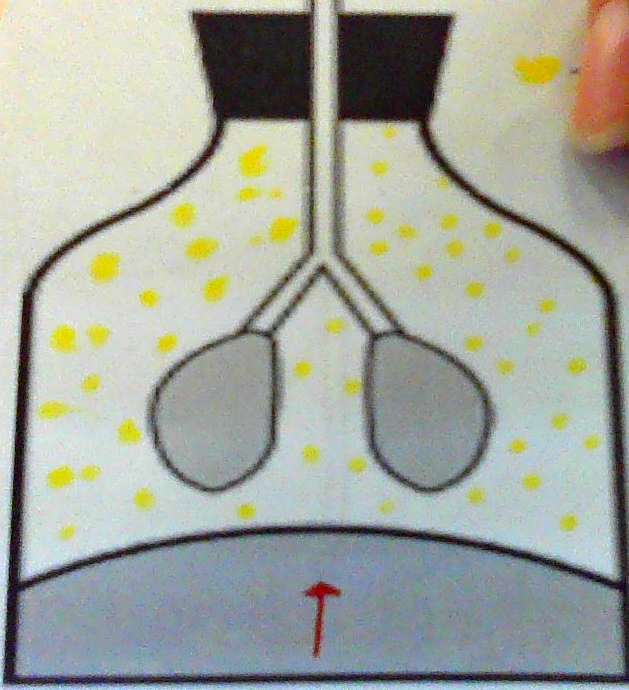
(Thoracic Mechanics) When Diaphragm Relaxes & MOVES UP (4)
Chest Cavity Gets Smaller
Pressure INCREASES
Air Flows Out
Lungs DEFLATE
Airway Overview (9)
Breathe in Oxygen (O2)
Trachea
a. Supportive Cartilage
Bronchi
a. Tubes lead into either left / right lung
Lungs
a. Right Lung: 3 Lobes
b. Left Lung: 2 Lobes
i. Heart Crowding
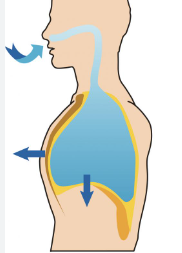
INHALATION (2)
Diaphragm moves DOWN
Air fills lungs
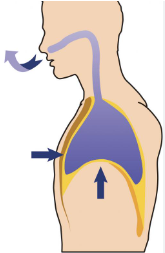
EXHALATION
Diaphragm moves UP
Air leaves lungs
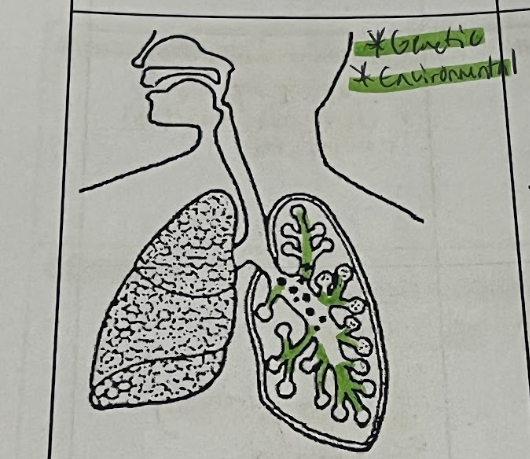
Asthma (Organ Affected)
Bronchioles
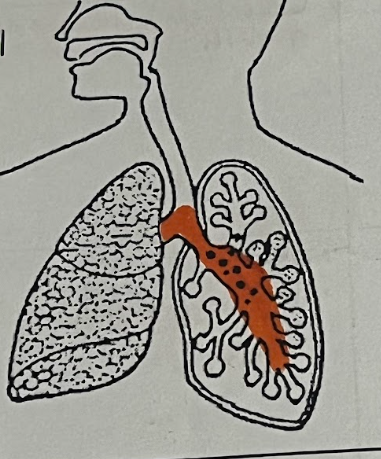
Bronchitis (Organ Affected)
Bronchi
COPD (Organs Affected) (3)
Bronchi, Bronchioles & Alveoli
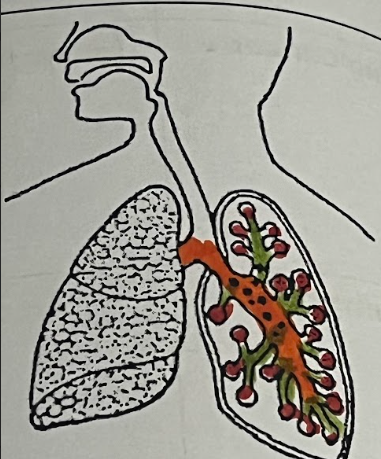
COVID (Organs Affected) (2)
Alveoli & Blood Vessels
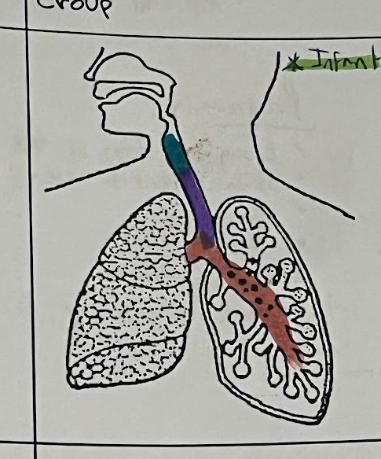
Croup (Organs Affected) (3)
Larynx, Trachea & Bronchi
Cystic Fibrosis (Organs Affected) (2)
Lungs (Bronchioles & Alveoli)
Emphysema (Organ Affected)
The Alveoli
Lung Cancer (Organ Affected)
Lung Tissue
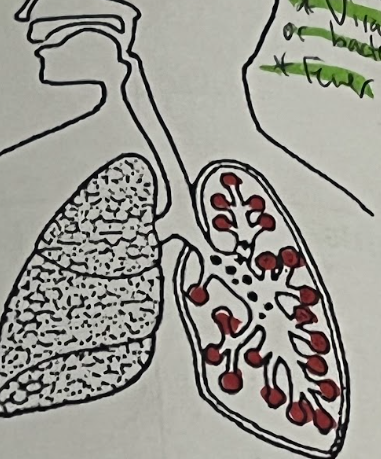
Pneumonia (Organ Affected)
(alveoli)
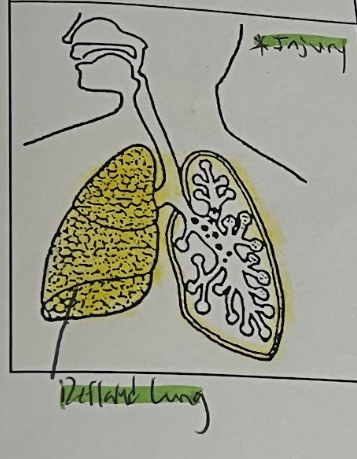
Pneumothorax (Organs Affected) (2)
Pleural (chest) Cavity & lungs
Rhinitis (Organ Affected)
Nasal Cavity
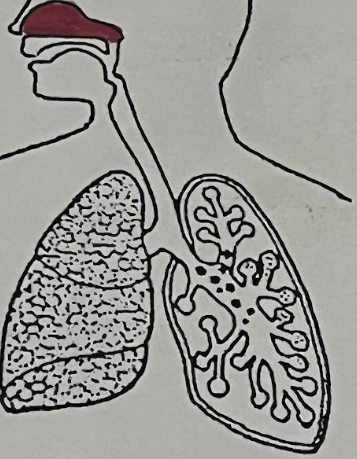
Asthma Organ Tissue
Swell & Produce extra mucus
Asthma Symptoms (3)
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness or pain
Wheezing / Coughing attacks
Bronchitis Organ Tissue
Inflamation of Bronchi
Bronchitis Symptoms (2)
Coughing up mucus
Chest discomfort
COPD Organ Tissue
Blocked / “obstructed”
COPD Symptoms (4)
Breathing difficulty
Coughing up mucus
Wheezing
Lack of energy
COVID Organ Tissue
Mucus build up in alveoli
COVID Symptoms (4)
Fever & tiredness
Continuous cough
Loss of taste or smell
Breathing difficulties
Croup Organ Tissue
Swelling
Croup Symptoms (3)
Barking cough
Whistle sound when inhaling
Fever
Cystic Fibrosis Organ Tissue
Blocked by sticky mucus
Cystic Fibrosis Symptoms (4)
Overproduction of sticky mucus
Exhaustion
Wheezing / coughing
Lung infections
Emphysema Organ Tissue
Walls of alveoli are damaged / broken
Emphysema Symptom
Shortness of breath
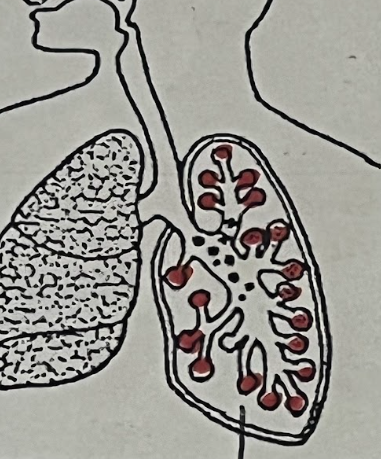
Lung Cancer Organ Tissue
Uncontrolled lung cell growth = tumor
Lung Cancer Symptoms (3)
Chronic coughing
Coughing up blood
Chest pain, shortness of breath.
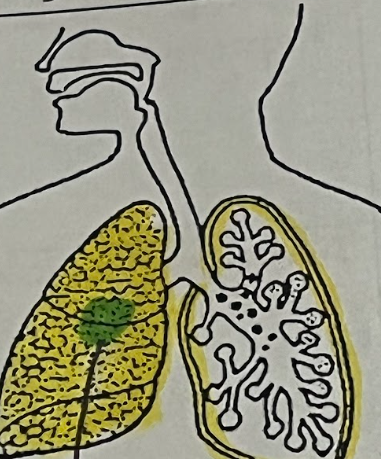
Pneumonia Organ Tissue
Inflamed & filled with mucus
Pneumonia Symptoms (5)
Cough
Fever
Chest Pain
Difficulty Breathing
Exhaustion
Pneumothorax Organ Tissue
Air leaks in between lung & space around it.
Pneumothorax Symptoms (2)
Sudden chest pain
Shortness of breath
Rhinitis Organ Tissue
Inflammation, swelling & mucus in tissue
Rhinitis symptoms (3)
Sneezing
Runny nose
Itchy
Whooping Cough Organ Tissue
Bacteria stick to lung lining & make toxins.
Whooping Cough Symptoms (3)
Hacking Cough
Runny nose & fever
Extreme fatigue, vomiting.
Whooping Cough Organ Affected
Lung
Asthma is (2)
Genetic
Environmental
Emphysema is (2)
Smoker
Alveoli are damaged
Pneumonia is (2)
Viral (or) bacterial
Fever
Covid is (2)
Viral
Fever
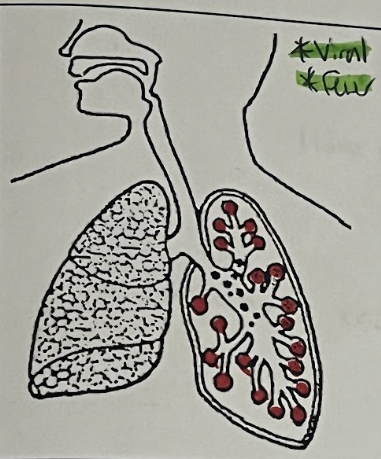
Croup is (1)
Infants
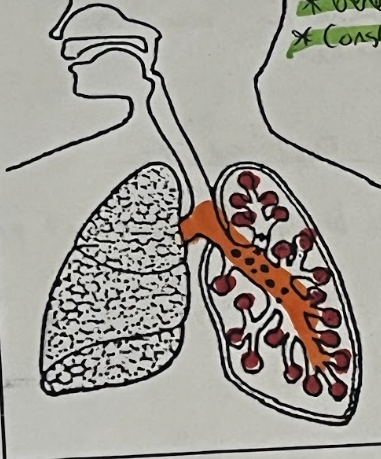
Cystic Fibrosis is (2)
Genetic
Constantly sick
Pneumothorax (2)
Injury
Deflated lung
Whooping Cough is (2)
Bacterial
Lung Lining infected
Blue Blood Cells Represent
Deoxygenated RBC (CO2>O2)
Deoxygenated RBC comes
FROM the Heart
Red Blood Cells Represent
Oxygenated RBC (O2>CO2)
Oxygenated RBC go
BACK to the Heart
the tissue that lines the Alveoli and capillaries are
Lined by Simple Squamous Tissue
Tissues that are Pseudo Stratified Tissue are (6)
Nasal Cavity
Larynx
Pharynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Lungs are both
Pseudo & Simple tissue
Diaphragm is _____ tissue
Muscle tissue
Cilia in Nasal Cavity (3)
Traps dirt, moves mucus and warms the air.
Blood Group
C for connective
Blood Function (2)
Found in blood vessels.
Transports nutrients and waste & maintains homeostasis in the body.
Blood Specialized Cells (3)
RBC: Carry oxygen
WBC: Immune
Platlets: Clot
(Blood Components) Plasma
Liquid, carries nutrients, Co2, O2 (More than half of blood)
(Blood Components) Red Blood Cells name
Erythocytes
(Blood Components) RBC functions (2)
Carry out towards tissue
Carry CO2 away from tissue
(Blood Components) WBC name
Leukocytes
(Blood Components) WBC function
Fight infection (immune)
(Blood Components) Platelets name
Thrombocytes
(Blood Components) Platelets function
Blood Clotting
Characteristics of RBC (3)
Biconcave discs (thin in center)
Lacks a NUCLEUS
Allows for greater oxygen capacity inside
(Circulatory Tissues) Smooth Muscle Group
M
(Circulatory Tissues) Simple Squamous
Epithelial
Smooth Muscle Functions (2)
Around arteries / veins
Aid in involuntary blood vessel contraction
Simple Squamous Functions (2)
Surrounds blood vessels
Single layer allows for diffusion
Neither Smooth Muscle nor Simple Squamous have
Specialized cells.
Capillaries Diameter
Single Cell
Capillaries Surrounding Tissue
is the Simple Squamous Tissue
Capillaries Function
Diffusion of gas molecules (O2 & CO2)