Cell bio 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:56 AM on 4/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
least
Compounds that are the most oxidized have the _____ energy
2
New cards
catabolism
reactions which breakdown complex molecules into simpler ones, usually done to release energy for work (respiration)
3
New cards
anabolsim
reactions which use simpler molecules to build more complex ones, usually require an input of energy (photosythesis)
4
New cards
multiple steps
cells do not have an effective means of transforming and storing an explosive amount to energy, so metabolims is done in _____
5
New cards
most
Compounds that are reduced have the _____ energy
6
New cards
activation energy, we capture energy, step regulation
Animal cells do not combust because_____
7
New cards
cAMP
formed by ATP activation of epinephrine or glucagon, activates a PKA
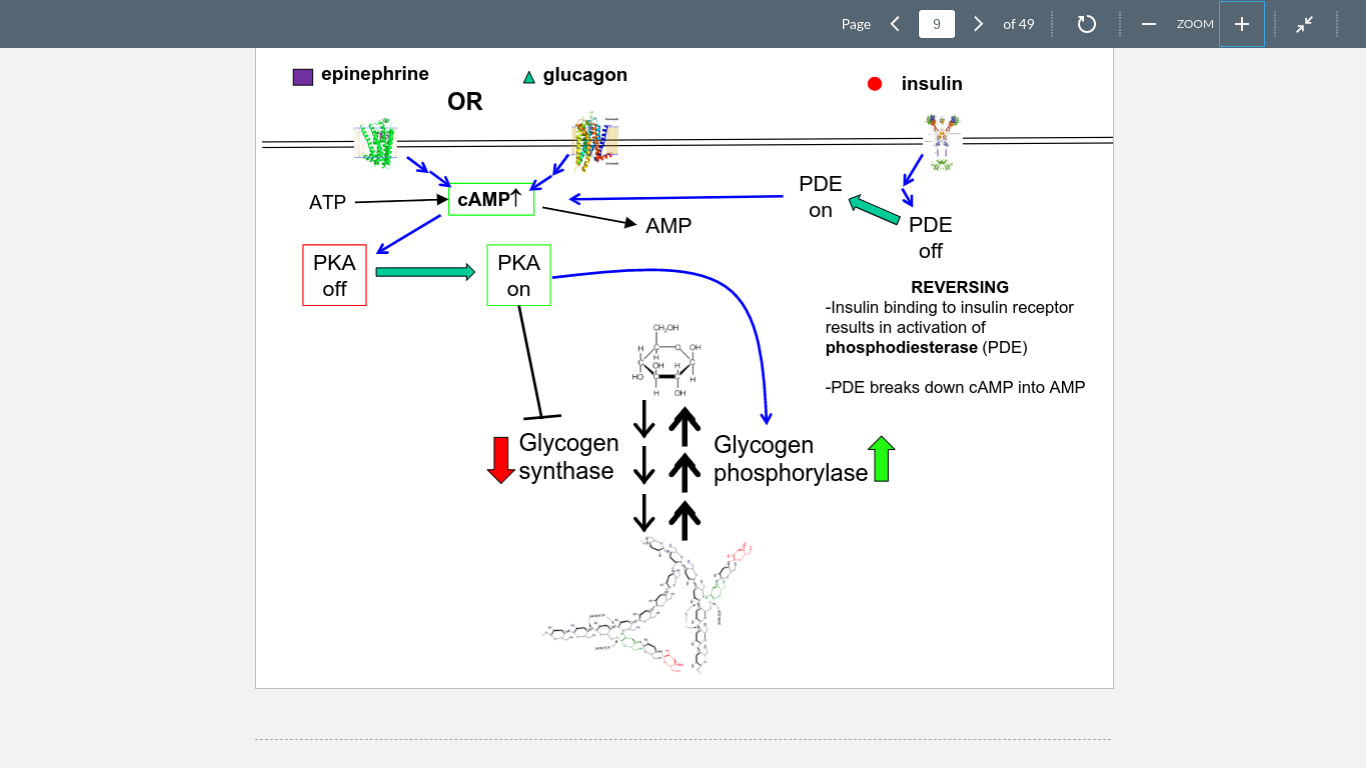
8
New cards
PKA
Turns glycogen synthase off and phosphorylase on
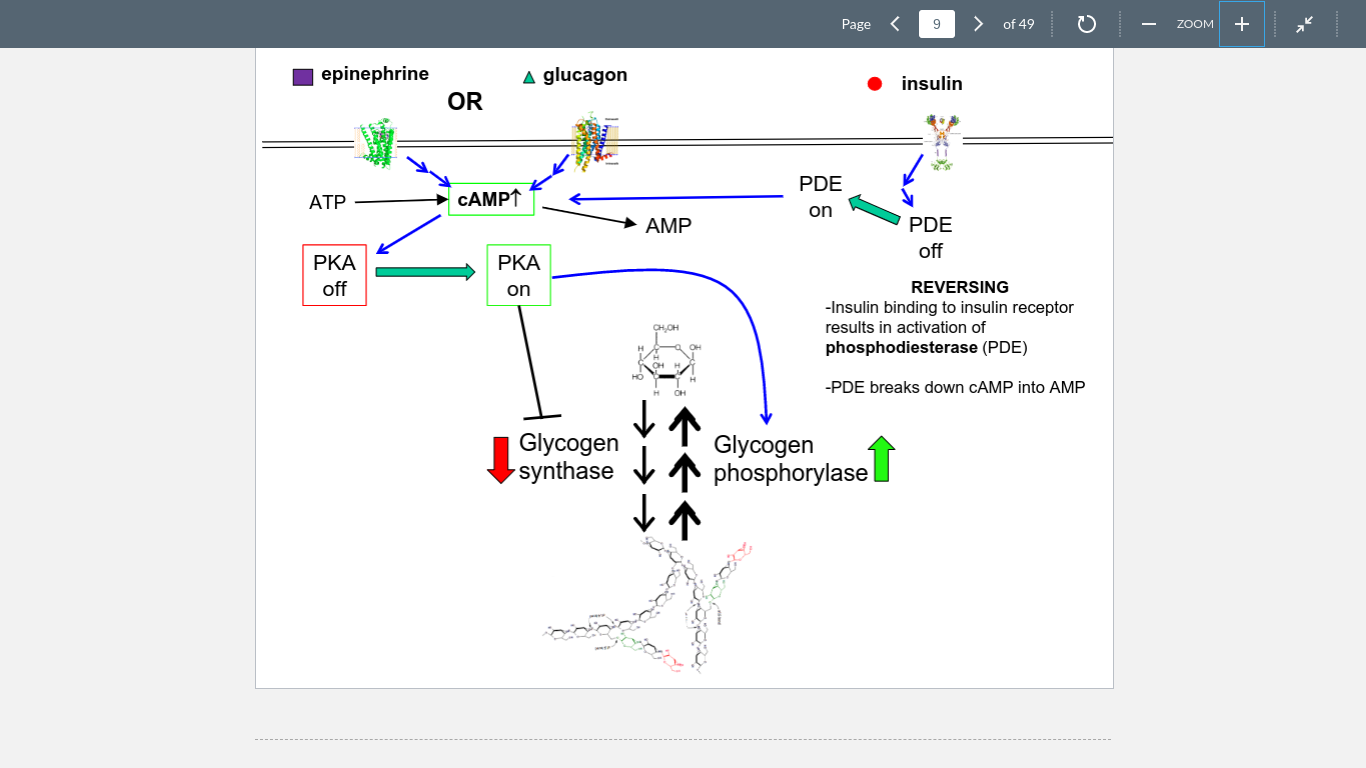
9
New cards
insulin
Bonds to its receptors to produce PDE, which deactivates cAMP
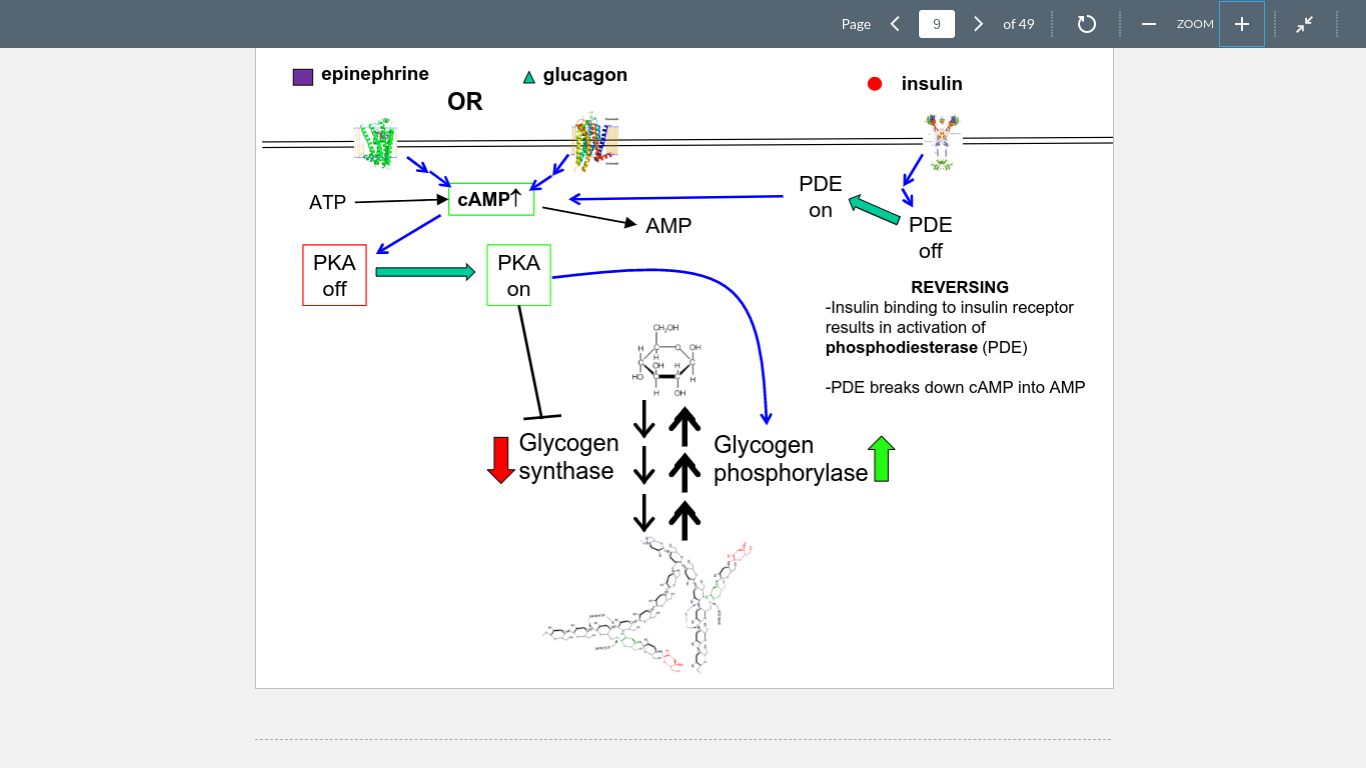
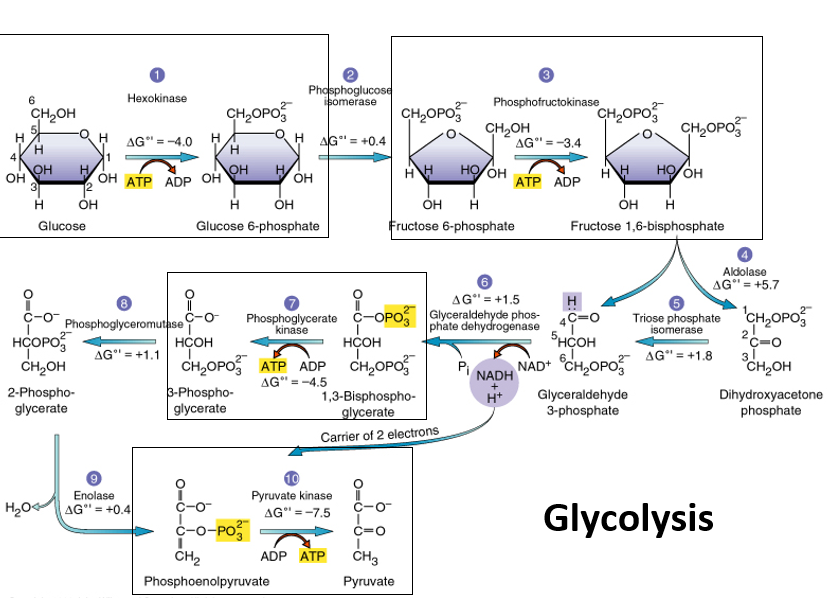
10
New cards
glycolysis
Occurs in cytoplasm, doesn’t require oxygen, starting pathway in all organisms, produces little ALP
11
New cards
glycolysis
Is very thermodynamically favorable due to large negative G and \[reactants\] >>> \[products\]
![Is very thermodynamically favorable due to large negative G and \[reactants\] >>> \[products\]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7031129c08af466badc9e377effde054.jpeg)
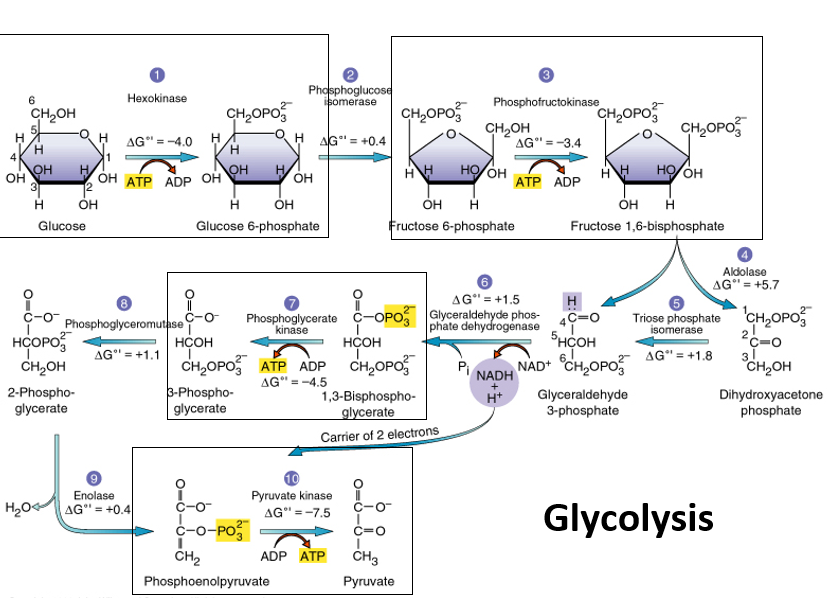
12
New cards
phosphofructokinase
uses ATP to catalyze the conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by adding a phosphate in step 3, ends energy investment phase
13
New cards
TCA/Kreb’s/citric acid
Occurs in mitochondria, requires oxygen indirectly, ATP from GTP
14
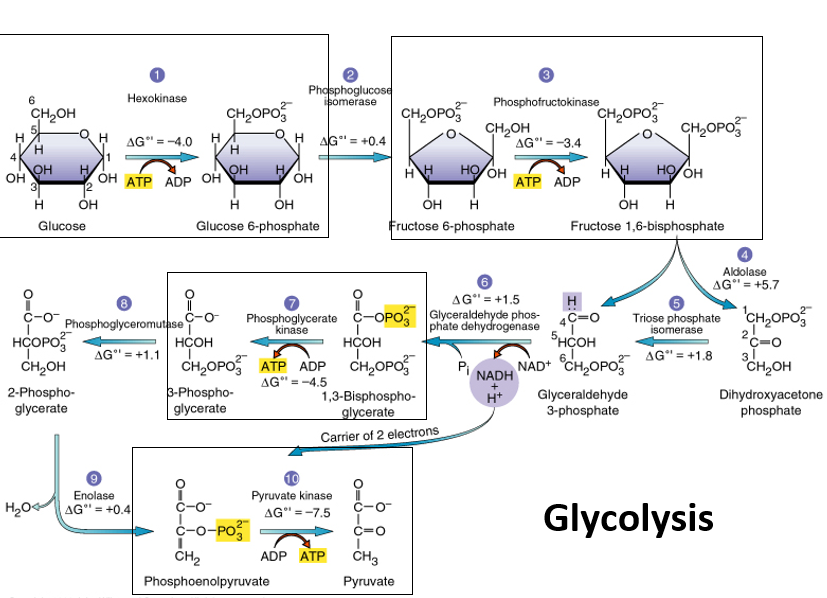
New cards
hexokinase
uses ATP convert glucose and remove it from the reactant pool in the 1st step of glycolysis
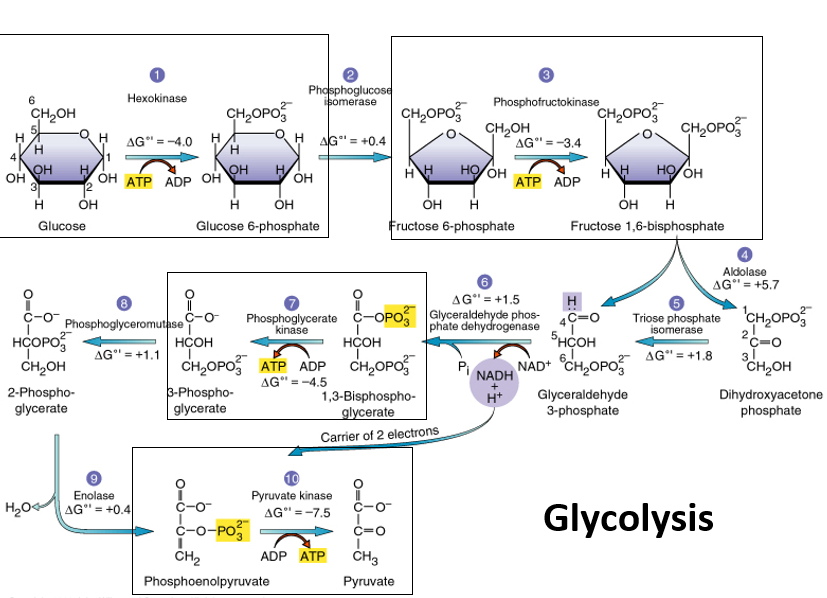
15
New cards
NAD+
Important cofactor/coenzyme that accepts electrons and becoms reduced, adds a 2nd phosphate in glycolysis
16
New cards
allosteric activator
binds to a site on an enzyme other than the active site, typically sensitive indicators of the cells needs.
17
New cards
allosteric inhibitor
binds to a site on an enzyme other than the active site, typically downstream products
18
New cards
pyruvate kinase
makes the product 2 ATP and 2 pyruvate in the 10th step of glycolysis
19
New cards
anarobic metabolism
another word for fermentation, occurs in the cytosol, returns NADH to NAD+ which is recycled in the glycolysis pathway
20
New cards
High NAD+
_____ = low energy
21
New cards
Low NAD+
____ = high energy
22
New cards
electron transport chain
23
New cards
glucose, pyruvate
Glycolysis starts with _____ and ends with ………
24
New cards
outer
the _____ membrane of the mitochondria is more permeable, a 1:1 protein:lipid ratio, and is homologous to bacterial membranes
25
New cards
inner
the _____ membrane of the mitochondria is less permeable, 3:1 protein:lipid ratio, and required special transport proteins
26
New cards
water
a pH gradient inside of the mitochondria is maintained by _____ and used to bring H+ ions inside to produce ATP
27
New cards
ubiquinone
small, mobile, carbon ring, e- transporter, lipid-soluble, travels by lateral diffusion in the lipid bilayer, accepts/donates 2 H+ and 2 e- from complex I or II
28
New cards
oxygen
terminal electron acceptor (highest affinity) in aerobic respiration
29
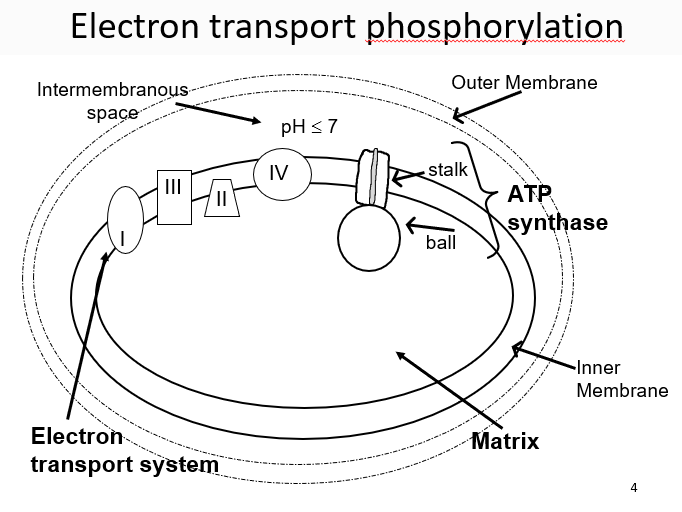
New cards
cytochrome c
mobile carrier that is small and soluble, transport electrons to complex IV
30
New cards
complex II
can shuttle electrons between complexes, gather electrons from FADH2 or NADH
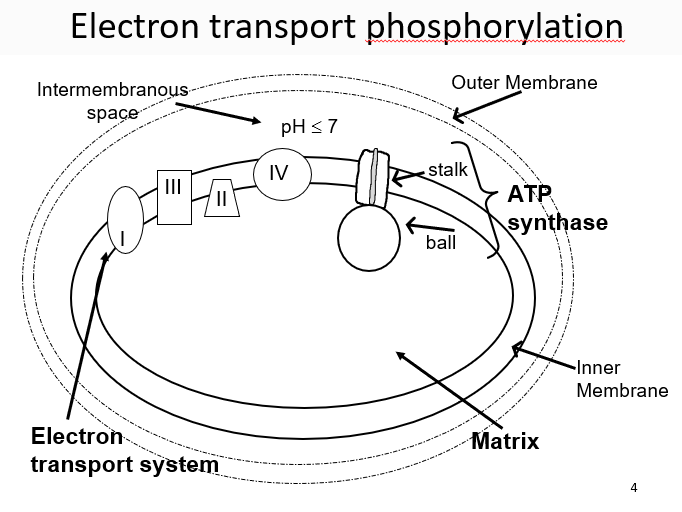
31
New cards
complex IV
collects 4 e- and then uses them to reduce oxygen and produce water
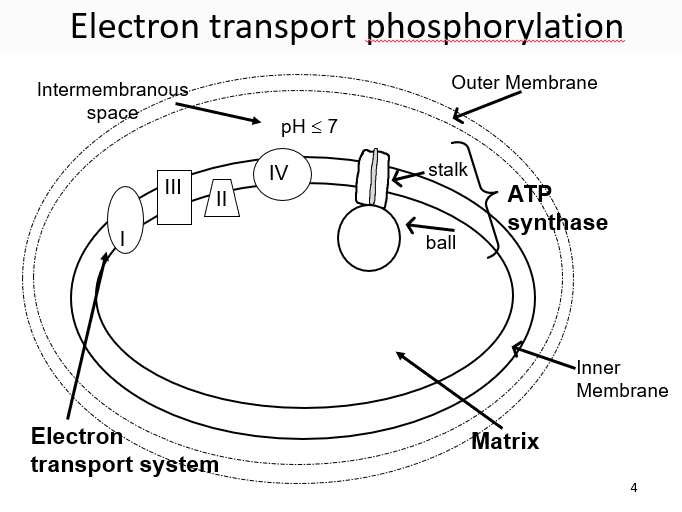
32
New cards
3 ways to contribute to gradient
electron pumps (complexes 1, 3, 4), ubiquinone, Oxygen removing H+ from the solution
33
New cards
ATP synthases
enzyme consisting of F1 and F0, the F1 (orange has alpha/beta subunits) (bannana is stalk)
34
New cards
ADP
most important factor controlling respiration rate
35
New cards
beta
catalytic domains that cause ADP to turn into ATP
36
New cards
gamma
as _____ subunit turns, it interacts with the beta subunits differently
37
New cards
open, loose, tight
the three positions of the beta subunits which are caused by the gamma subunit
38
New cards
c
intermembrane subunit that acts as a water wheel for the H+ gradients
39
New cards
proton-motive force
energy provided by the H+ gradient, can:
1\.Make ATP via ATP synthase
2\.Exchange ADP for ATP (antiport).
3\.Bring in Pi with H+ (symport)
4\.Bring in pyruvic acid with H+ (symport)
1\.Make ATP via ATP synthase
2\.Exchange ADP for ATP (antiport).
3\.Bring in Pi with H+ (symport)
4\.Bring in pyruvic acid with H+ (symport)
40
New cards
rotenone
poison that blocks e- flow at complex 1
41
New cards
antimycin
poison that blocks e- flow at complex 3
42
New cards
cyanide
poison that blocks e- flow at complex 4
43
New cards
CO
poison that blocks e- flow at complex 4
44
New cards
uncouplers
allow H+ ions to diffuse through membrane and never reach high concentrations of ATP
45
New cards
chloroplast
large organelle with 3 membranes (2 outer 1 inner) containing stacks (granum) of thylakoids (pennies)
46
New cards
light dependent
reactions that occur in thylakoid membranes, uses sunlight and water to make NADPH and ATP
47
New cards
calvin cycle
reaction that turns CO2 into a carbohydrate using energy from the light reactions, recycles ADP and NADP+ to begining of cycle
48
New cards
NADP+
terminal electron acceptor (highest affinity) in photosynthesis
49
New cards
chlorophyll
pigment within the membrane of thylakoid that is excited by light and releases energy by (a.) fluorescence (b.) resonance energy transfer (c.) e- transfer
50
New cards
photosystem II
system where light is absorbed by reaction center and starts e- transport through the plastoquinone
51
New cards
photosystem I
system that makes NADPH from the e- transport
52
New cards
rubisco
ribose biphosphate carboxylase (RuBP), fixes CO2 in the Calvin cycle to make carboxylkase intermediates, start with 6 of them
53
New cards
stroma
where light independent rxn/Calvin cycle occurs
54
New cards
thylakoid membrane
where light dependent rxn occurs
55
New cards
regulated secretion
Type of secretion where proteins are stored in secretory granules and released upon a specific signal. Examples include insulin and digestive enzymes.
56
New cards
constitutive secretion
Type of secretion by cells where secretory products are continuously released into the extracellular space without any specific stimulus.
57
New cards
pathway of secreted proteins and IMPs
what is the picture?
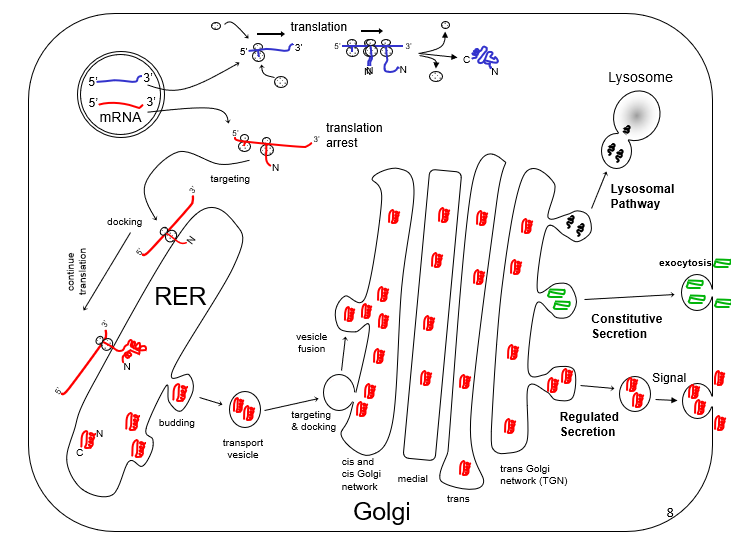
58
New cards
rough ER
functions: production, folding, quality control and secretion of some proteins
59
New cards
smooth ER
functions: synthesis of steroid hormones, detoxification, and sequestration of calcium ions
60
New cards
cytosolic ribosome
all translation starts in the ______
61
New cards
cytosolic
cytoplasmic proteins imported mitochondrial proteins , and nuclear proteins are made by _____ ribosomes
62
New cards
exocytosis
vesicle fusion for secretion outside the cells (e.g. RER to cis Golgi at PM)
63
New cards
endocytosis
vesicle formation for intake of molecules at the plasma membrane (also called budding at organelles)
64
New cards
cisternae
part of the ribosome where proteins are synthesized
65
New cards
golgi complex
stack of flattened cisternae divided into functional groups, including a cis and trans face
functions: process proteins from the RER for secretion or the lysosome
functions: process proteins from the RER for secretion or the lysosome
66
New cards
signal hypothesis
signal codons in the mRNA cause a signal peptide, which causes insertion into the RER, where it is cleaved off. allows for certain proteins to be secreted
67
New cards
pellet 1
contains: nuclei, mitochondria, and other big stuff
68
New cards
pellet 2
contains: microsomes (ER and Golgi)
69
New cards
lysate
in vitro translation: the supernatant containing soluble proteins, ribosomes, tRNA, initiation & elongation factors (all the good stuff for protein synthesis)
70
New cards
gel autoradiograph
using a SDS page, is labeled with a radiocactive ion
71
New cards
sufficient
adding a 28 aa signal pathway is _____ to turning a regular protein into a secretory one
72
New cards
signal recognition particle (SRP)
G protein that (regulated by GTP or GDP) binds to the signal peptide, binds ribosome (stopping translation) and binds SRP receptor (docking station)
73
New cards
SRP-receptor
an IMP resident in RER membrane. cytoplasmic domain binds to SRP-GTP
74
New cards
stop transfer sequence
stretch of 20 hydrophobic AAS after a signal sequence, causes a cytosolic C terminus and a luminal N terminus
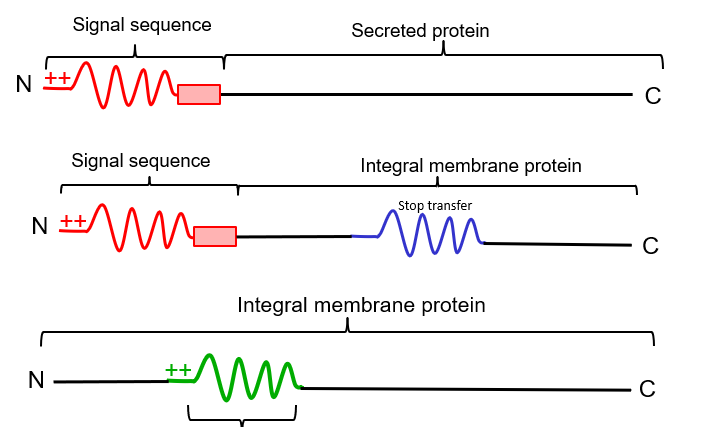
75
New cards
start transfer sequence
stretch of \~20 hydrophobic AAs not at N terminus, causes a cytosolic N terminus and luminal C terminus
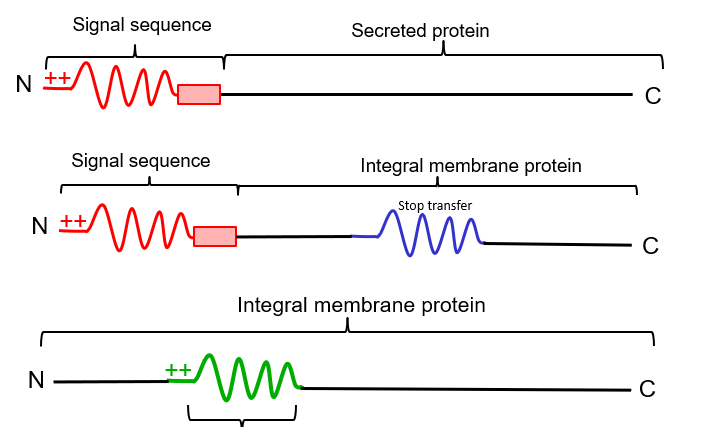
76
New cards
translocon
protein complex that forms pore for passage of nascent polypeptide. Sec61 = main protein compenent
77
New cards
binding protein
\
an RER lumenal protein that helps seal the translocon and functions as a chaperone.
an RER lumenal protein that helps seal the translocon and functions as a chaperone.
78
New cards
signal peptidase
will cut peptide bind connecting signal sequence to the remainder of the protein
79
New cards
NLS
sequence marking a protein for insertion into the nucleus
80
New cards
motif of ML
K (K/L) X (K/L)
81
New cards
initial or core glycosylation of glycoproteins
addition of oligosaccharides onto asp, 3 of which are cut off to help with folding
82
New cards
inside
proteins stay _____ the RER during folding in order to esure proper function
83
New cards
UGGT
functions as a folding sensor in the RER, if improperly folded, UGGT adds a glucose onto a protein
84
New cards
Calnexin
in the RER, modifies folding proteins by removing a glucose molecule
85
New cards
ubiquination
in the RER, addition of ubiquinone to a protein that fails to fold, marks for destruction in the cytoplasm
86
New cards
co-immunoprecipitation
determins if and how proteins interact by observint the pellet in an SDS page and immunoblotting the protein of interest (not the target of the antibody)
87
New cards
transmembrane proteins
have cytoplasmic sorting signals that bind to adapter proteins
88
New cards
coat proteins
assemble onto adapters, forming a sphere and making a pinch-off bud
89
New cards
adapter proteins
binds to transmembrane proteins with sorting signals and allows for binding of coat proteins
90
New cards
COPII-coated vesicles
coat protein that move materials friom the RER to Golgi
91
New cards
COPI-coated vesicles
coat protein that recycle materials back to precious Golgi
92
New cards
Clathrin coated vesicles
coat protein that uses AP2 for plasma membrane and AP1 for golgi
93
New cards
SNARE
(1) Tethering: Rab G-proteins on the vesicle and target surface each bind to tethering proteins that \n mediate the first connection between vesicle and target. \n (2) Docking: v-SNARES on the vesicle and t-SNARES on the target surface interact in a specific \n manner to allow docking of the vesicle at the target surface. \n (3) Fusion: the v- and t-SNARES are helical and they coil around one another and twist which \n physically pulls on the vesicle and target membranes and allows them to become one
94
New cards
CIS & CGN
modification in the Golgi: __Sorting for RER retrieval__, __PO4 addition on mannose,__ mannose removal
95
New cards
medial
modification in the Golgi: further mannose removal, N-acetylglucosamine addition,
96
New cards
trans
modification in the Golgi: Fucose, glucose and galactose addition
97
New cards
TGN
modification in the Golgi: sialic acid addition, __sorting__
98
New cards
asp-x-x-leu-leu
used for transport from the TGN to the lysosome via clathrin
99
New cards
lys-lys-X-X (kkxx)
used for transport back to the RER through Arf 1by COP I
100
New cards
DXE, or FF, FY, or YY
used for transport from RER to the golgi by COP II through Sar 1