Lecture 11 - Coordination of Cell Processes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Describe the levels by which the concentration of a protein can be regulated.
Transcriptional Level
mRNA Level
Translation Level
Post-translational Level
Examples of Transcriptional Level Regulation
Frequency of RNAP recruitment to a promoter
leve lf DNA supercoiling affects accessibility
Examples of mRNA Level Regulation
Frequency of transcription termination
mRNA stability (short lived in microbes)
Examples of Translational Level Regulation
Frequency of ribosome assembly onto mRNA
Examples of Post-translational Level Regulation
Protein Localization
Degradation or stabilization of proteins
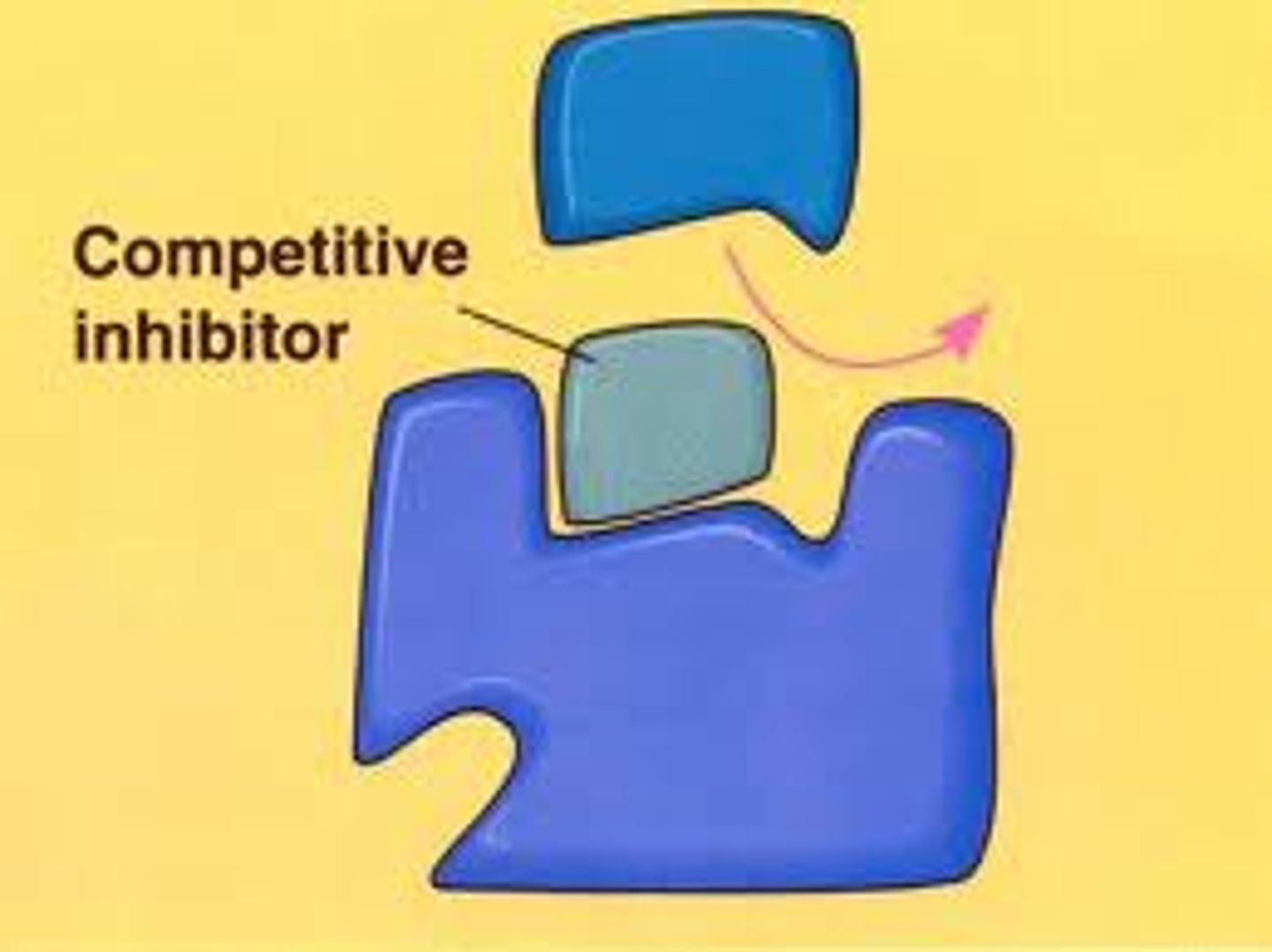
Competitive Inhibition
inhibitor molecules resemble the substrate and compete for the enzyme's active site., preventing the real substrate from binding.

Non-competitive Inhibition (allosteric)
inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site (an allosteric site), changing the enzyme's shape, preventing the substrate from binding onto the enzyme
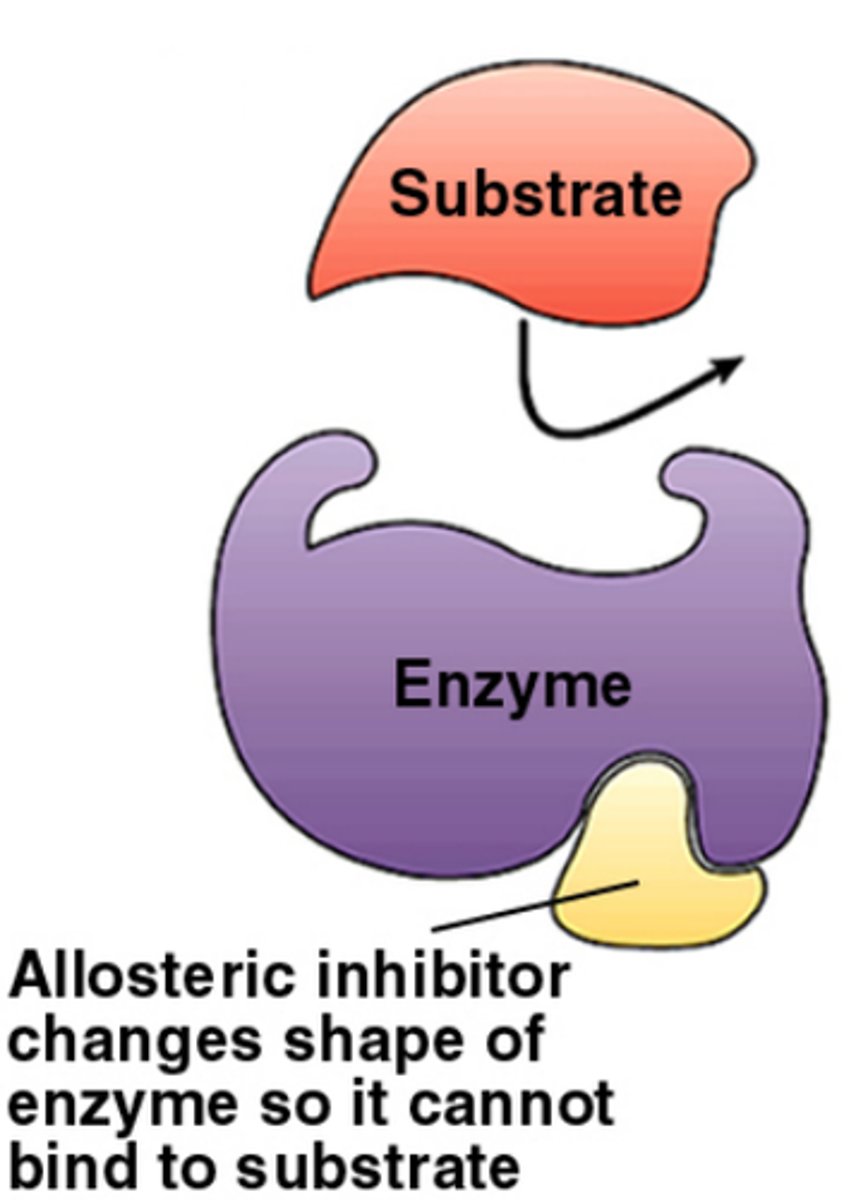
Covalent Modification
enzyme activity can be altered by chemical modifications, causing reversible changes that "switch" activity on or off.
Examples of Covalent Modification
Phosphorylation
Methylation
Acetylation
Sigma Factors
proteins in prokaryotic cells that bind to RNA polymerase and direct it to specific classes of promoters
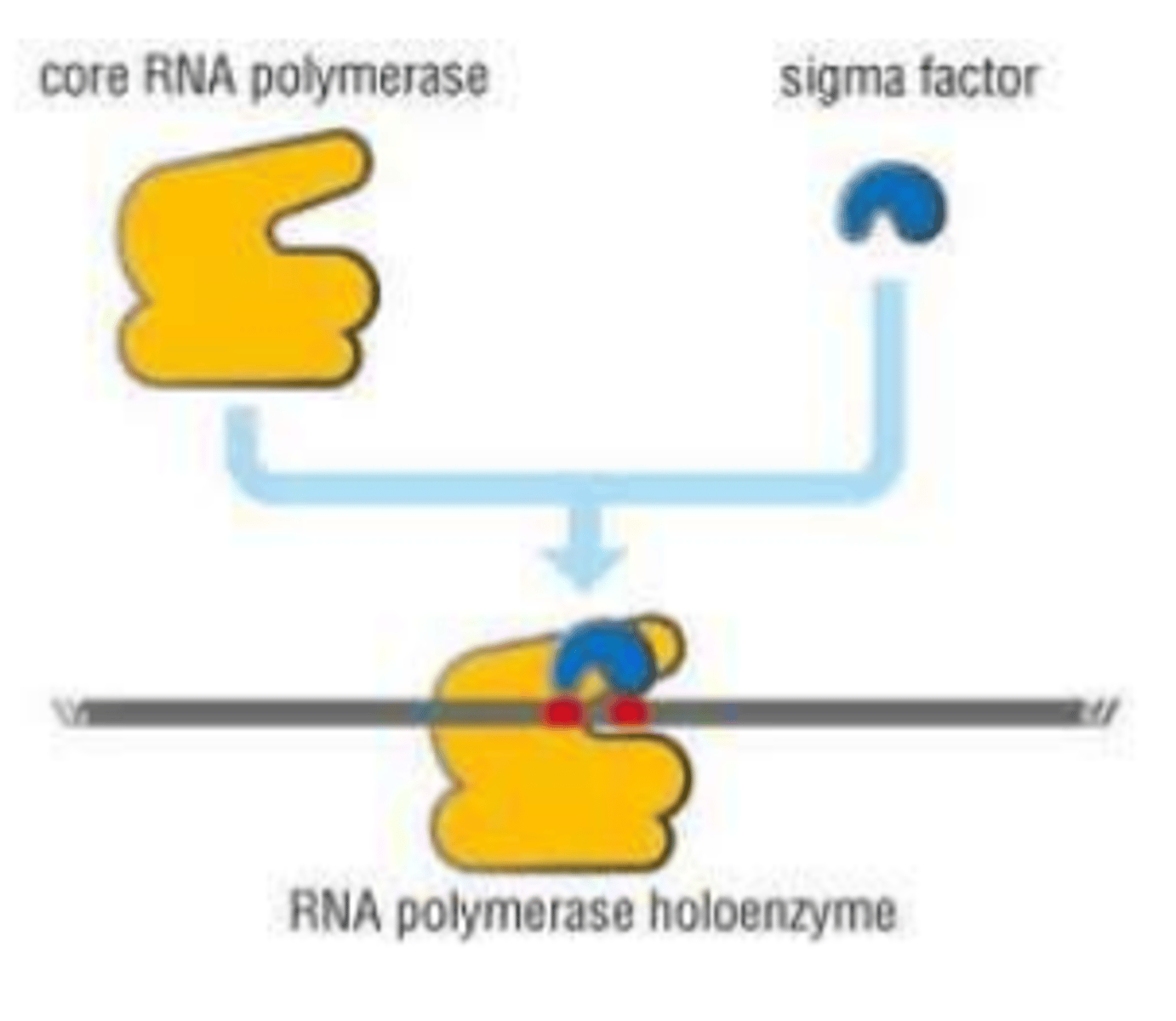
Explain differences between various sigma factors.
different sigma factors recognize different sequences, controlling transciption of the genes and allowing bacteria to switch transcriptional programs depending on conditions (e.g., stress, starvation, heat shock)
Lac Operon
a gene system whose operator gene and three structural genes control lactose metabolism in E. coli
Cis-acting elements
DNA sites that do not move
Examples of Cis-acting Elements
Promoter
Operator
CRP-cAMP binding site
Promoter
the site where RNA polymerase binds, activating transcription
Operator
a site on the lac operon for LacI (and inhibitor) to bind onto, blocking RNA polymerase from transcription
CRP-cAMP binding site
a site on the lac operon where CRP-cAMP binds to enhance transciption
Trans-acting Factors
a regulatory protein that binds to a regulatory element in the DNA and exerts a trans effect
Examples of Trans-acting factors
LacI repressor protein
Allolactose (an inducer)
CRP-cAMP
LacI repressor protein
binds operator and blocks transcription when lactose is absent
Allolactose (an inducer)
binds to LacI and prevents it from repressing, allowing transcription
CRP-cAMP
bind the promoter region to increase RNAP binding when glucose is low
Is the lac operon ever off?
No, the lac operon is always on to produce β-galactosidase, converting lactose into allollactose to be used.
Feedback Inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
Example of a feedback inhibition mechanism
Histidine biosynthetic pathway
Histidine Biosynthesis Pathway
excess histidine inhibits the first enzyme in the pathway, preventing unnecessary synthesis.