OOP Polymorphism
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Polymorphism
the concept of entity providing multiple implementations or behaviors
ability of a variable to change behavior according to what object instance is holding.
This allows multiple objects of different subclasses to be treated as objects as a single parent class
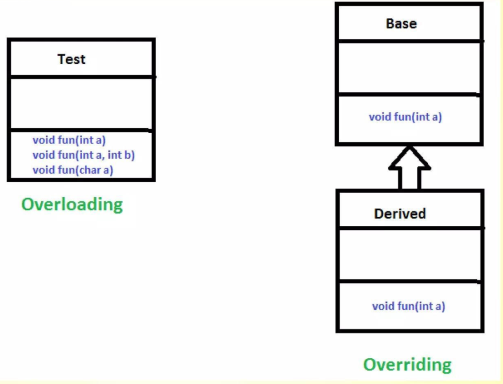
Compile-Time Or Static Polymorphism
refers to behaviour that is resolved when your Java
class is compiled.
Method overloading is using method of same name to do different things based on the parameters passed.

Illustration — Method Overloading
return
new
class MultiplyFun {
int multiply(int a, int b) {
r____ a * b;
}
int multiply(int a, int b, int c) {
return (a * b) + c;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiplyFun mf = __ MultiplyFun();
System.out.println(mf.multiply(2, 4));
System.out.println(mf.multiply(2, 7, 3));
}
}
Illustration — Method Overloading
void overloading
obj
class OperatorOVERDDN {
v__ o____(String str1, String str2) {
String s = str1 + str2;
System.out.println("Concatenated String = " + s);
}
void operator(int a, int b) {
int c = a + b;
System.out.println("Sum = " + c);
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OperatorOVERDDN __= new OperatorOVERDDN();
obj.operator(2, 3);
obj.operator("joe", "now");
}
}
Run-Time Or Dynamic Polymorphism
Definition: Resolved when your Java class is run by the JVM.
Key Mechanism: Method overriding by a subclass is an example of run-time polymorphism.
Method Overriding Explained
Child classes provide their own implementation of a method already defined in the parent class.
The JVM determines which version of the method to execute—parent or child—based on the object used to invoke the method.
class Parent {
void print() {
System.out.println("Parent");
}
}
class SubClass1 extends Parent {
void print() {
System.out.println("SubClass 1");
}
}
class SubClass2 extends Parent {
void print() {
System.out.println("SubClass 2");
}
}
public class TestPolymorphism3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent a;
a = new SubClass1();
a.print();
a = new SubClass2();
a.print();
}
}
Overriding vs Overloading
advantage of polymorphism