Biology term 1 y9
1/48
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
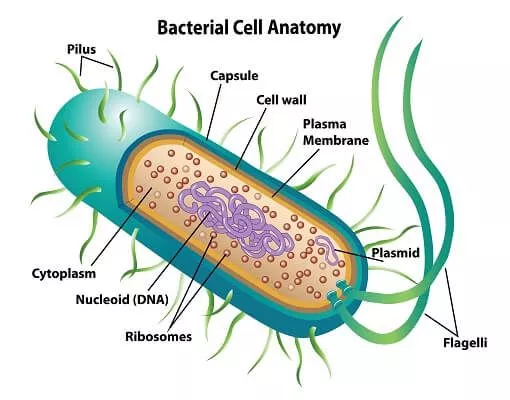
stage 1 (transcription)
the process of when the mrna is created and transported out of the nucleus into the ribosomes. This is carried out by an enzyme which unzips the dna and makes a copy of the relevant strand. This copy is the mrna. The mrna is the transported out of the nucleic pores and into the ribosome.
stage 2 (translating)
The mrna is is used as a guide to sort the trna into the correct order by reading the mrna 3 nucleotides (triplets) at a time and attaching a trna complementary set of nucleotides (anticodons).In this process, the amino acids that the trna carry are also ordered which makes them join together with hydrogen bonds, making them form a polypeptide. The polypeptide will go on to make a protein.
Scanning electron microscope
A type of electron microscope that uses a beam of electron across the surface of a specimen where reflected electrons are collected to produce an image
.images created are in black and white and specimen need to be dead as electrons pass through a vacuum
.expensive and not portable
.difficult preparation (thin slices especially tem)
.it can view image in natural colours
.it is cheap and portable
.easy to prepare ( slide w specimen and specific stain)
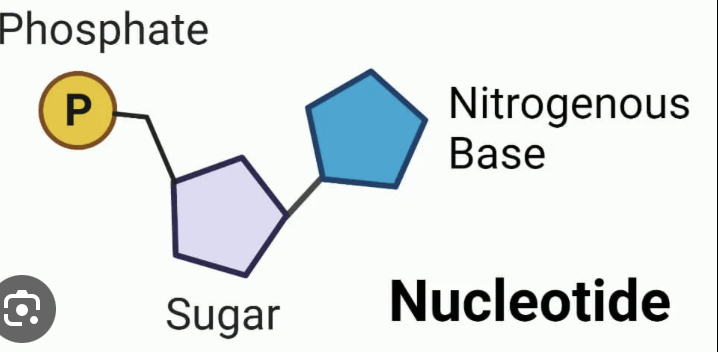
Cytosine, guanine