AP Psych Final Review for AP Exam! [for the updated 2025 exam]
Section I: 75 MCQs [90 min] ~ 66.7%
Section II: 2 FRQs [70 min] ~ 33.3%
Unit 0: Science Practices
Psychology - The Scientific study of behavior and mental processes
The Scientific Attitude - a mindset that promotes the use of critical thinking
1) Curiosity; 2) Skepticism; 3) Humility
Structuralism - the first school of psychology
focused on introspection
Introspection - recognizing one’s own psychological processes, perceptions, and judgments
Functionalism - an early school of thought promoted by William James and influenced by Darwin
Explored how mental and behavioral processes function and how they enable the organism to adapt, survive, and flourish
Critical Thinking - thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions
examines assumptions, appraises the source, discerns hidden biases, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
Epirical Approach - the idea that knowledge comes from experience
Observation and experimentation enable scientific knowledge
Confirmation Bias - the tendency to interpret new evidence as confirmation of one’s existing beliefs or theories
interpreting info to support your existing beliefs
only remembering details that uphold your beliefs
Hindsight Bias - the belief, after learning an outcome, that you foresaw it
“I knew it all along.”
Overconfidence - we think we know more than we do
Cultural Norms - the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to another
Hypothesis - a potential solution to the question, usually an if/then statement
testifiable prediction
Null-Hypothesis - no connection between variables
Likelihood (the null-hypothesis that is correct) is called the P-value or Probability Value
Probability Value - calculated by the size of the sample (larger sample, lower p-value || vice versa) and standard deviation (lower standard deviation, lower p-value || vice versa)
Falsifiable - a hypothesis is falsifiable if a study can be proven wrong
Experiment - study that manipulates one variable under carefully controlled conditions and observes whether there are effects on the second variable
the purpose of an experiment is to show causation
Independent variable - the factor being manipulated
Dependent variable - the outcome
the variable that may change due to independent variable manipulation
Confounding Variable - may influence the dependent variable
Operational Definition - explains HOW variables are measured
important because it 1) defines variables used in a study, 2) allows others to accurately replicate a study to see the reliability, and 3) ensures that psychologists consider their biases
Replication - the process of reproducing a study to see if the same results can be attained
crucial part of the research process that helps to improve the understanding of human behavior, or can verify a previous study
Population - the group a study is trying to understand
Random Sampling - from the population / means everyone in the population has an equal chance of being selected for the study
lottery, flip coin, random number generator
Convenience Sampling - when people are chosen based on their availability and willingness to participate
Representative Sampling - a subset of a population that accurately reflects the characteristics of the entire population
truly representative of the same = generalizability
Generalizability - the results can be applied to the whole population
Beyond the specific context of the study
Sampling Bias - when the sample is not representative of the population
Experimental Group - receives special treatment in an experiment
Control Group - does NOT experience special treatment
Placebo Group - control group that receives special treatment, but no effect
substance identical to the experimental group
Random Assignment - likelihood that all participants in a group or a sample have an equal chance of getting assigned to different conditions within an experiment
exp vs control vs placebo group
necessary component
Placebo Effect - when participants’ expectations lead them to experience some changes when they receive an empty or fake treatment
Sugar pill vs antidepressant (very interesting, I recommend looking it up and reading about it!)
Social Desirability Bias - when participants act or answer in a way they believe will be viewed favorably by others
Experimenter Bias - when researchers’ expectations can influence the result of the study
Single-Blind Study - ensures the participants don’t know if they are in the experimental or control group can limit social desirability bias
Double-Blind Study - when both research participants and staff are ignorant about whether the participants have received treatment or a placebo
helps prevent Social Desirability Bias and Experimenter Bias
Quantitative Research - provides depth and context to understand human behavior
structured interviews
Qualitative Research - measurable, generalizable data that can test theories and hypotheses
bar graph
Case Study - examines one individual or group in depth in the hopes of revealing things true to us all
Suggest directions for future studies
can be misleading with typical individuals
can be challenging because of subjectivity
Naturalistic Observation - the descriptive technique of observing and recording behavior in natural situations without interference/manipulation
Survey - a descriptive technique for obtaining self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a certain group
correlational research
ADVANTAGE: Look at cases in depth
DISADVANTAGE: tricky to get good results because of the particular wording
Self-Report Bias - may not always provide accurate answers
memory errors, misunderstanding of questions, lack of introspection, or intentional deception
Meta-Analysis - a statistical technique that combines and synthesizes the results of multiple individual studies on a particular topic
identifies patters
study of studies
Directionality Problem - when it is unclear which variable is the cause and which is the effect
difficult to determine the direction of the causal relationship
Third Variable Problem - when an unmeasured 3rd variable influences both of the correlated variables
Statistics - Practice or science of collecting and analyzing numerical data in large quantities
Descriptive Statistics - numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups
Mode - most frequently occurring scores
Mean - the average
Median - score in the middle
Standard Deviation - a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
Range - the difference between the highest and lowest scores
Percentile Rank - the percentage of scores that are lower than a given score
If you are in the 79th percentile, your score is higher than 79% of competitors
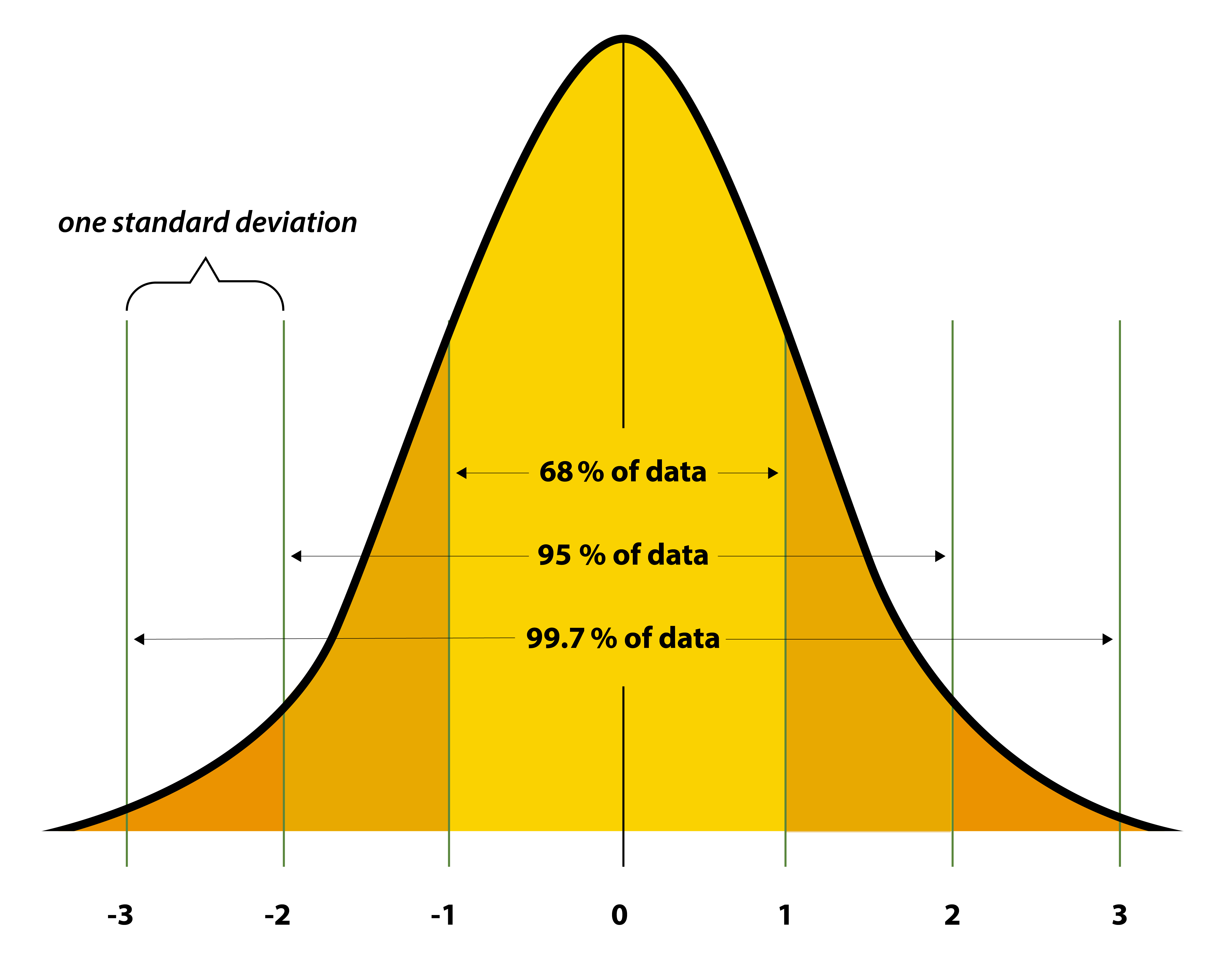
Normal Curve - shape of an important class of probabilities
68-95-99.7 Rule
[image best viewed in light mode]
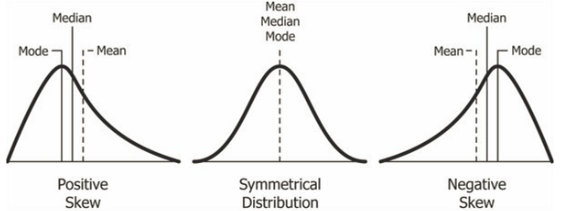
Skewed Distribution - a representation of scores that lack symmetry around their average value
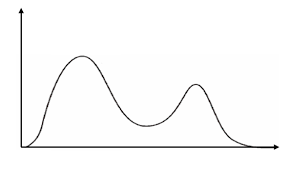
Bimodal Distribution - when there are two distinct peaks in a distribution
two different modes
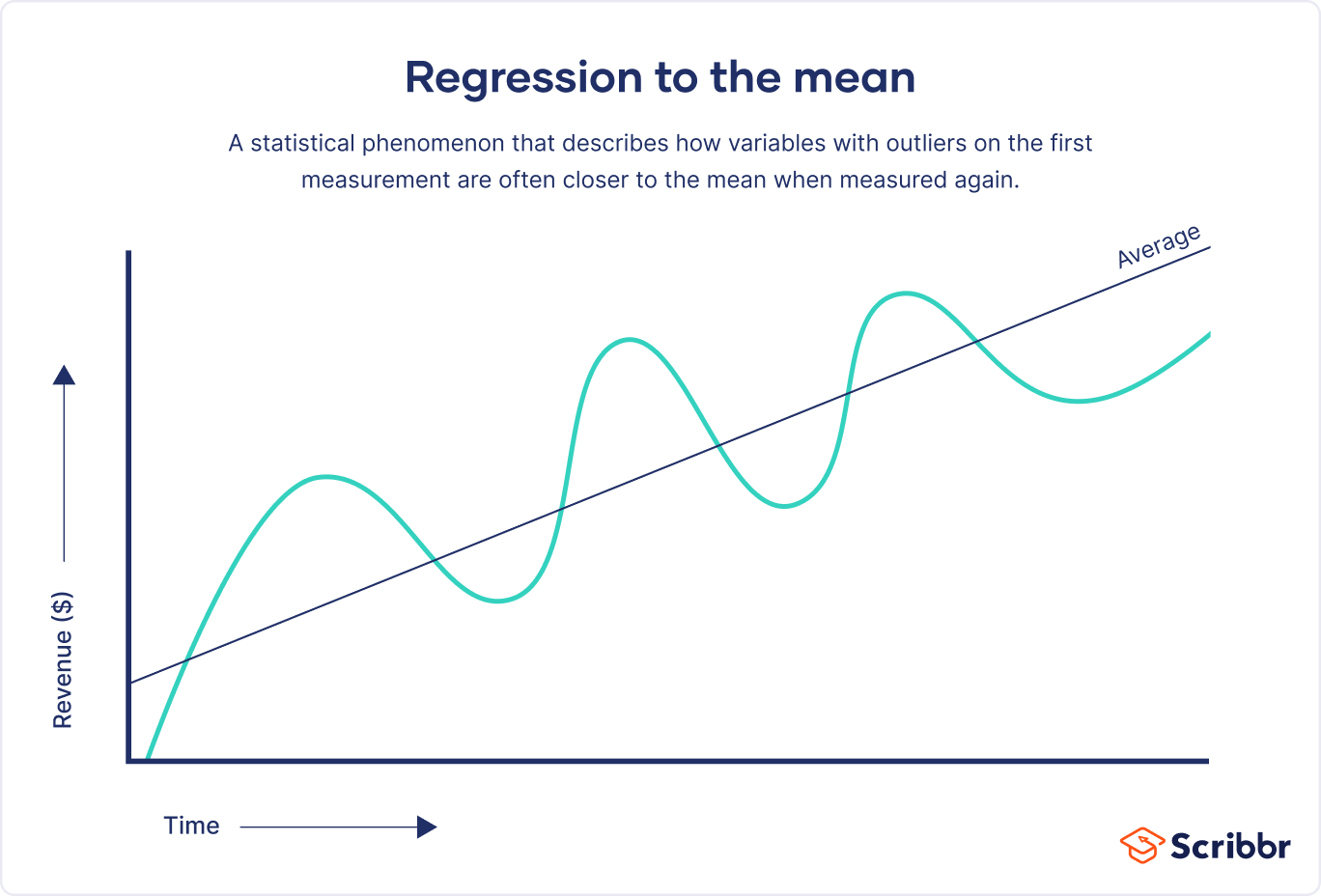
Regression Toward the Mean - a statistical phenomenon that refers to the tendency of extreme observations (outliers) on one measurement to be closer to the average on a subsequent measurement
Correlation - shows a connection and helps us predict
Correlation Coefficient - a statistical index of the relationship between two things
the closer it gets to -1 or +1, the stronger the correlation
the closer it gets to 0, the weaker the correlation
Scatterplot - a graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the value of two variables
Histogram - bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
Illusory Correlation - perceiving a relationship where none exists, or perceiving a stronger-than-actual relationship
We believe there is a relationship, we are likely to notice instances that confirm our beliefs
EX: chilly/wet weather gives you a cold
Inferential Statistics - numerical data that allows one to generalize
to infer from sample data
the probability of something being true for a population
Statistical Significance - a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
if the p-value is low enough, then the results are statistically significant
The Psychological Perspectives
Biological - How the body and brain enable emotions, memories, and sensory experiences
TLDR: behavior through the brain
Evolutionary - How the natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes
TLDR: genetic adaptation
Cognitive - How we mentally encode, process, store, and retrieve information
TLDR: How we think about our experiences
Humanistic - How we achieve personal growth and self-fulfillment
TLDR: Self-Fulfillment
Psychodynamic - How behavior springs from unconscious needs, desires, conflicts, and memories
TLDR: Unconscious needs and desires
Behavioral - How we learn; observable responses
TLDR: Learned rewards and punishments
Sociocultural- How behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures
TLDR: Cultural differences
Unit 1: Biological Bases of Behavior
Nature v. Nurture - a longstanding controversy over whether you are the way you are due to upbringing or genes
Evolutionary Perspective - study of the evolution of behavior and the mind
using principles of natural selection
Natural Selection - the driving force behind evolution
How the environment ‘selects’ the fittest organisms
Behavior Genetics - study out differences and weigh the effects and interplay of heredity and environment
can include how mutations may affect individuals
Mutation - random errors in gene replication that lead to a change
Heredity - genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring
Genes - the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes
Segments of DNA capable of synthesizing proteins
Genomes - the complete instructions for making an organism
consisting of all the genetic material in that organism’s chromosomes
Identical Twins - developed from a single fertilized egg that splits into two
Creating two genetically identical organisms
Fraternal Twins - develop from separate fertilized eggs
They are genetically no closer than ordinary siblings, but they share a prenatal environment
Gene-Environment Interaction - how genes and the environment influence one another
How malnutrition during childhood influences a person’s genes
permanently changed
Epigenetics - the study of how environmental changes like childhood experiences can affect the expression of genes
can be changed
Eugenics - promoting reproduction for the highly intelligent and potential sterilization for those with ‘less desirable traits’
Nervous System
The Nervous System - the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network
consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous system
Peripheral Nervous System - the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
TLDR: sensory and motor
Central Nervous System - brain and spinal cord
Somatic (Voluntary) - the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles
Also called the skeletal nervous system
EX: reading and getting the hand ready to turn the page, and then turning it
Autonomic (involuntary) - the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs
heart rate, digestion, respiration rate
Contains Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions
Sympathetic Division - the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body
mobilizing its energy
EX: thinking // fight or flight
TLDR: thinking and arousal
Parasympathetic Division - the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body
conserving its energy
EX: eating // undoes the work of the sympathetic division after a stressful situation
TLDR: Eating and Calming
Neurons
Neurons - a nerve cell
the basic building block of the nervous system
Gial Cells - cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
This plays a leading role in learning, thinking, and memory
TLDR: Glue cells
Cell Body (soma) - contains nucleus
cell’s life support center
Dendrites - receive and integrate messages
conducting impulses towards the cell body
Axon - neuron extension that passes messages through branches to other neurons or muscular glands
Terminal Buttons (Axon Terminal) - form junctions with other cells
Myelin Sheath - enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hop from one node to the next
it deteriorates
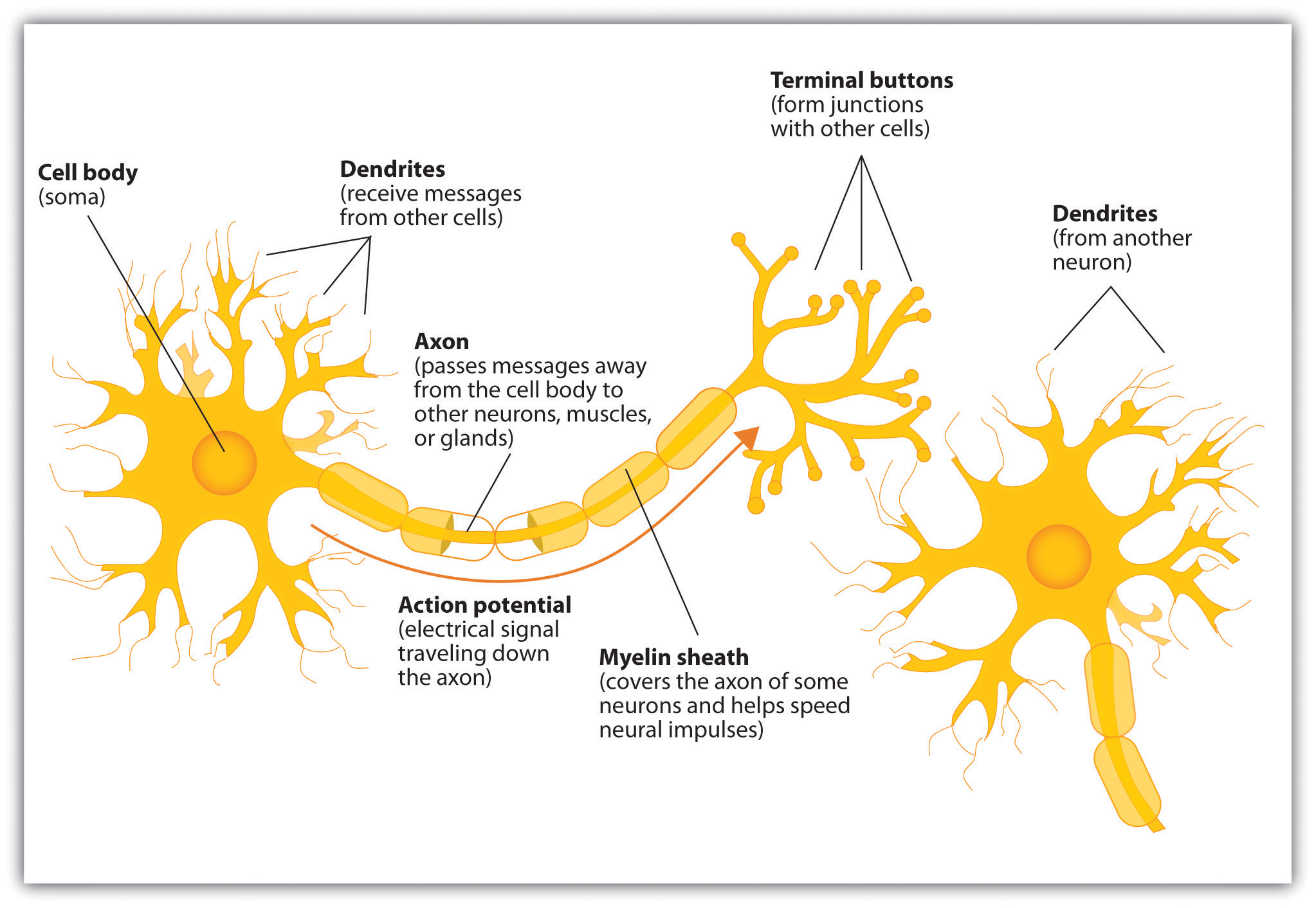
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons - messages from sense organs to the CNS system
EX: water is hot
Motor (Efferent) Neurons - carry messages from the CNS to muscles and glands.
EX: Move your hand
Interneurons - carry messages between nerve cells, mainly in the brain and spinal cord
Synapse - the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
the tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap
Reuptake - Remaining neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap are absorbed back into the sending neuron
All-or-Nothing Principle - either the axon ‘fires’ or it doesn’t
Almost immediately, cells’ ion pumps flush out positively charged ions and restore neurons
Depolarization - term used to describe the loss of he inside or outside charge difference
Action Potential - The neural impulse created when a neuron ‘fires'.
the impulse travels from the dendrites down the axon to the axon terminals
Refractory Period - The brief instant when a new action potential cannot be generated because the neuron is ‘recharging’ after the previous action potential
Resting Potential - The state of a neuron when it is ‘charged’ but waiting for the next action potential to be generated
Fluid outside of an axon has mostly positively charged ions, while a resting axon’s fluid (intracellular fluid) is more negatively charged.
Threshold - the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Multiple Sclerosis - a chronic disease in which communication between muscles and brain regions slows, causing low muscle control and sometimes impaired cognition
Causes: Deterioration of the Myelin Sheath
Myasthenia gravis - a disease that causes symptoms such as muscle weakness, eyelid drooping, and difficulty swallowing or breathing
Reflex Arc - neural pathway that controls a reflex (invouluntary response to a stimulus)
evolutionary adaptation that allows for faster action by activating spinal motor neurons instead of waiting for signals to reach the brain
Neurotransmitters
Excitatory Neurotransmitters - arousing
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters - block / prevent the chemical message from being passed any further
Dopamine - influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion/reward
Oversupply: mental illness/schizophrenia
Undersupply: Parkinson’s, addictions
Serotonin - affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
Oversupply: anxiety, happiness
Undersupply: depression
Norepinephrine - helps control alertness and arousal
Contributes to the sympathetic nervous system in the ‘fight or flight’ response
Glutamate - a major excitatory neurotransmitter
involved in memory
Oversupply: migraine/seizures
Undersupply: tremors/seizures
GABA - major inhibitory neurotransmitter
helps control stress in the body
Undersupply: anxiety disorders
Oversupply: not enough brain activity
Endorphins - a neurotransmitter that influences the perception of pain or pleasure
Oversupply: feel no pain
Undersupply: aches/pains
Substance P - a neuropeptide that acts as a neurotransmitter
essential in pain perception and immune responses
Regulates metabolism and fracture healing
mediating pain, touch, and temperature
Acetylcholine (ACh) - enables muscle actions, learning, and memory
motor control
Myasthenia gravis
Endocrine System
Endocrine System - the body’s chemical communication system that helps regulate growth, reproduction, metabolism, and behavior
Pituitary Gland - The endocrine system’s most influential gland
Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
Oxytocin - often called the ‘love hormone’
associated with bonding, social interaction, and childbirth
Adrenaline - the adrenal gland’s active adrenaline
activated by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system in moments of danger
Leptin - signals that you are full and less interested in food
Ghrelin - hunger hormone
produced in the stomach and signals the brain to eat
Melatonin - signals sleepiness
Psychoactive Drugs
Psychoactive Drugs - chemicals that change perceptions
Agonists - a molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action
occupies receptors and activates them
TLDR: mimics
Antagonists - a molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter’s action
block receptor activation by agonists
TLDR: blocks
Reuptake Inhibitors - Stop/delay the body from reabsorbing serotonin
Stimulants - drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions
EX: caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine, ecstasy
increase in heart rate, breathing, and blood sugar, and a decrease in appetite/energy
Depressants - drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body function
EX: alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates
associated with many neurotransmitters, but mainly GABA
Hallucinogens - psychedelic drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
similar to opiates
THC blocks a receptor that blocks GABA, but nothing tells the brain to stop
Opioids - severely depress neural activity and temporarily lessen pain
can stop the brain from producing endorphins
EX: opium, morphine, and heroin
Tolerance - the diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose of a drug
requiring the user to take larger and larger doses before experiencing the drug’s effect
Withdrawal - the discomfort and distress that follow discontinuing an addictive drug or behavior
physical pain and cravings
Dependence - the feeling of need to use a drug
physical or biological
Addiction - compulsive drug craving and use despite adverse consequences
The Brain
Biological Psychology - the study of links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes
Biopsychosocial Approach - an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and socio-cultural levels of analysis
Neuroplasticity - the brain’s ability to change by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
Neural Measures
EEG (Electroencephalogram) - amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain’s surface
These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
PET (positron emission tomography) - a visual display of brain activity that detects where the radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
MEG (magnetoencephalography) - a brain imaging technique that measures magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity
CT (Computed tomography) - a series of X-ray photos taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) - a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissues
shows brain anatomy
fMRI (functional MRI) - a technique for revealing blood flow and therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans
brain function/structure
Hindbrain
Hindbrain - the most primitive part of the brain
consists of 3 structures:
the medulla
pons
cerebellum
Medulla - regulates breathing and heart rate
operates without our conscious awareness
Pons - helps coordinate movement and regulates the brain during the sleep cycle.
Cerebellum - controls balance and the complex movements we perform without consciously thinking about it.
Midbrain
Midbrain - the topmost most of the brainstem
the connection center between the brain and the spinal cord
Reticular Formation - a nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus
plays an important role in controlling arousal
Forebrain
Forebrain - the largest part of the brain, encompassing structures like the thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebellum
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Cortex - ultimate control and information processing center
thinking cap
Limbic System - neural system located mostly in the forebrain and is associated with emotions and drives
Includes:
thlamus
hypothalamus
pituitary gland
hippocampus
amygdala
Thalamus - relays messages between lower brain centers and the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus - controls maintenance functions such as eating
helps govern the endocrine system
linked to emotion and reward
Pituitary Gland - the master endocrine gland
Hippocampus - linked to conscious memory
processes explicit memory
EX: removal = inability to form new memories, facts, or events
Amygdala - linked to emotion
helps us remember emotionally charged events
EX: removal = loses any sense of fear
Brainstem - the central core of the brain, responsible for automatic survival functions
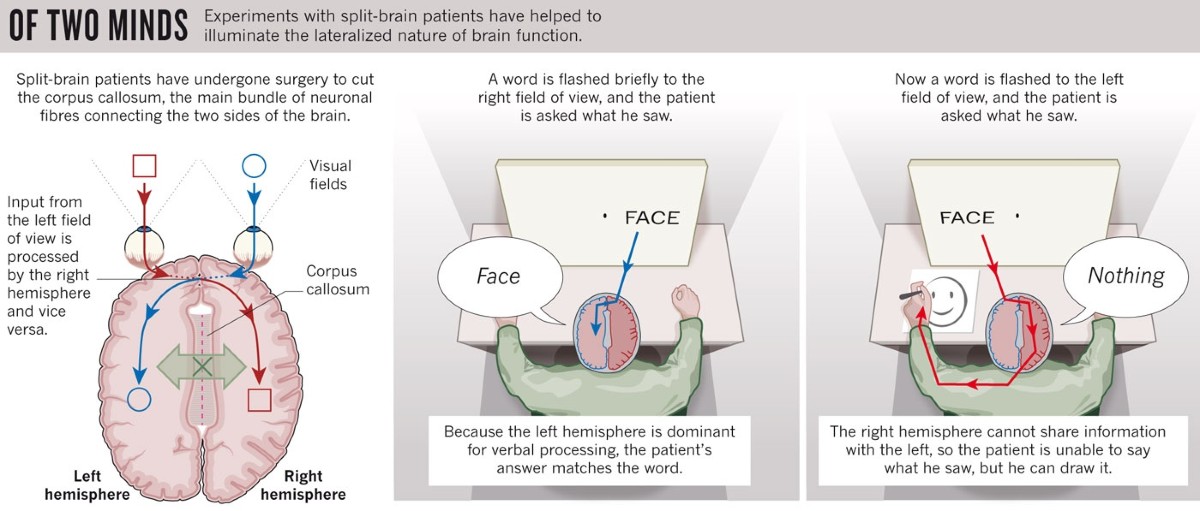
Corpus Callosum - axon fibers connecting the two cerebral hemispheres
Split Brain
type of condition where there is a severance between the corpus callosum, splitting the two hemispheres
Structure of the Cortex
Frontal Lobe - generally controls linguistic processing, higher-order thinking, and executive function.
Home to the motor cortex
Location: forehead area
Parietal Lobe - generally controls association areas (processes and organizes info) and the somatosensory cortex
processes touch sensitivity
Location: Back crown
Temporal Lobe - generally controls auditory and linguistic processing and stores long-term memories.
Location: on the sides, near the ears
Occipital Lobe - visual information processing
Location: rear of the brain
Somatosensory Cortex - an area at the front of the parietal lobe that registers and processes bodily touch and movement sensations
Motor Cortex - Controls skeletal muscle movements
Broca’s Area - production of speech
Left hemisphere
Wernicke’s Area - understanding speech and writing, control of the sequence of movements, memory for words/numbers, and positive emotions
Left hemisphere
Association Areas - regions of the cerebral cortex throughout the four lobes that are responsible for higher mental functions
seem to connect parts to allow it to perform “higher” functions
Neurogenesis - creation of neurons that happens mostly in prenatal stages and continues into childhood
Lateralization - look-alike hemispheres that serve different functions, the
right hemisphere controls the left side and vice versa
Both hemispheres work together to produce our thoughts/feelings
Sleep
Cognitive Neuroscience - the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition
including perception, thinking, memory, and language
Circadian Rhythm - regular body rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle
wakefulness, temperature, etc
Waking Beta Waves - High frequency
conscious thought and logical thinking
Waking Alpha Waves - relatively slow brain waves
relaxed, awake state
NREM1- irregular brain waves
light sleep
may experience hallucinations
hypnagogic sensations, like falling or kicking
NREM2 - Sleep spindles/burst of rapid, rhythmic brain wave activity
easy to wake up, but definitely asleep
NREM3 (Delta Waves) - slow delta waves of brain activity
deep sleep
bed-wetting, sleep walking, sleep talking
REM - similar to being awake, in terms of brain activity
Rapid eye movement
Dream sleep
electrical activity in the brain
1st episode is around 10 mins, but increases over time
Sleep Cycle
NREM1
NREM2
NREM3
NREM2
REM
NREM2
NREM3
NREM2REM
repeats every 90 mins
SCN (Suprachiasmatic Nucleus)
a pair of neuron clusters in the hypothalamus that regulates circadian rhythm
Brain’a master clock, controlling daily cycles
signals the pineal gland to decrease melatonin
Sleep Deprivation - lack of sleep
Insomnia - problems falling asleep or staying asleep
Often has a psychological cause
Narcolepsy - uncontrollable sleep attacks
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder - The Body is not paralyzed during REM sleep
Sleep Apnea - cessations of breathing during sleep
Somnambulism - Sleepwalking
Dream Theories
Activation-Synthesis - to make sense of neural static
neural activity has to make sense, but are random event in the brain
Information Processing/Consolidation - to file away memories
learning and rehearsing the day’s events
Physiological Function - to develop and preserve neural pathways
REM sleep keeps our neural networks strong
Cognitive Development - to reflect cognitive development
we are just maturing and differentiating dreams that reflect our age
REM Rebound - natural response to sleep deprivation, stress, or drug withdrawal
more REM, vivid dreams, nightmares, headaches, feeling disoriented
Processing
Dual Processing - the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks
Parallel Processing - processing many aspects of a problem simultaneously
generally used to process well-learned information or to solve easy problems
Sequential Processing - processing one aspect of a problem at a time
Generally used to process new information or to solve difficult problems
Blindsight - a condition in which a person can respond to a visual stimulus without consciously thinking about it
Sensation
Sensation - the reception of information from our sensory receptors
physical
Perception - the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information
giving meaning
more psychological
Psychophysics - the study of relationships between the physical characteristics of stimuli
such as intensity and our psychological experience of them
Sensory receptors - Nerve endings that detect environmental stimuli and send information to the brain
part of sensory neurons
Transduction - converting sensory information into electrical impulses the brain understands
Absolute Threshold - the smallest detectable level of a stimulus
the level at which a stimulus is first detected 50% of the time
Below the absolute threshold is less than 50%
Signal Detection Theory - detection depends on a person’s experience, expectations, motivations, and alertness
Theory tries to predict when we will detect weak signals
When might you best see, hear, smell, etc
Subliminal - below one’s absolute threshold for conscious awareness
meant to slip past your mental radar and embed itself deep into your subconscious mind
Priming - an invisible image or word can prime (unconsciously prepare) our responses to later questions
Difference Threshold (Just-Noticeable Difference) - the smallest recognizable and physical difference between two stimuli
Weber’s Law - the greater the magnitude of the stimulus, the larger the difference needed for it to be detected
Two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum %, not amount
Sensory Adaptation - Diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
occurs in the body, and the stimulus is continuous
Sensory Interaction - when one sense can influence another
occurs when the brain has to process conflicting information from various sensory systems
Synesthesia - a neurological condition that causes people to experience more than one sense at the same time
Gate Control Theory - we have a “gate” in our spinal cord that can sometimes block incoming signals
In some cases, pain messages are minimized or even prevented from reaching the brain at all
Gustation - sense of taste
the sense is based on chemicals
smell + taste = flavour
can detect sweet, sour, salty, and bitter tastes without olfaction, but not subtle flavours
Olfaction - sense of smell
1) orders airborne chemical molecules to interact with receptors associated with specialized hairs in the nose
2) Stimulated nerve cells associated with these hairs convey information to the brain’s olfactory bulbs
Kinesthesis - how we sense our body movements
Vestibular Sense - balance
Sensory Interaction - how the senses interact so we can respond to stimuli
Embodied Cognition - an approach to cognition that has roots in motor behavior
Proprioception - body awareness
involved the vestibular sense and kinesthesis (sense of one’s body movement)
Receptors in muscles and joints
directional awareness
Vision
Cornea - The Eye’s clear, protective outer layer bends light into focus
Pupil - Adjustable center of the eye through which light enters
Iris - colored proportion of the eye around the pupil,
controls the size of the pupil
Lens - Structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
Retina - the inner surface of the eye where transduction takes place
Fovea - the central focal point in the retina, in which visual acuity is the highest
allows us to drive, read, etc
sharpest vision
Optic Nerve - bipolar cells that send to the Ganglion cells
makes up the optic nerve
Blind spot
Blind spot - a point where the optic nerve leaves the eye
No receptor cells are located there
Color Processing
Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory - Humans perceive color because the eye can receive light of 3 different wavelengths and combine them into the entire visible spectrum
Opponent-Process Theory - the brain avoids extremes of emotional experience by countering the stimulation it receives with an opposite (opponent) reaction
Feature Detectors - the process by which the nervous system sorts or filters complex natural stimuli
occipital lobe
identification
Hearing
Frequency - physical phenomenon
frequency determines pitch
Pitch - perpetual phenomenon
Eardrum - vibrates when sounds reach it
Semicircular Canals - helps maintain balance
Hammer and Anvil - pass vibrations along
Middle Ear - hammil, anvil, and stirrup
passing along vibrations
Cochlea - creates an impulse
transduction
Inner Ear - semicircular conals
helps maintain balance and detects head motion
Sound Localization - Sound waves strike one ear sooner and more intensely than the others
Hearing Loss / Pitch
Sensorineural Hearing Loss - damage in auditory nerve or other higher processing centers
aging neurological
Conduction Hearing Loss - interference/interruption in which sound waves convert to nerve energy
allergies
Cochlear Implants - devices for converting sounds into electrical signals and stimulating the auditory nerve through electrodes in the cochlea
Place Theory - we hear different pitches because sound waves activate different places on the basilar membrane
where it lands
higher frequency
Frequency Theory - we hear different pitches because never impulses match frequency of a sound wave
lower frequency
Unit 2: Cognition
Perception and Processing
Perception - process or organizing and interpreting sensory information
giving meaning (psychological)
Bottom-Up Processing - Starts at sensory receptors and works up to higher levels of processing
Top-Down Processing - constructs perceptions from this sensory input by drawing on your experience and expectations
Attention and Perceptual Set
Selective Attention - focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
11,000,000 bits of info per second
We can only process about 40
Cocktail Party Effect - a type of selective attention, the ability to attend to one voice among other voices
Cognitive radar can bring an unattended voice to mind
EX: You hear your name being called
Inattentional Blindness - Failing to see visible objects when our attention is somewhere else
Change Blindness - failing to notice changes in the environment
Perceptual Set - your tendency to view things only in a certain way
can change what we see, feel, taste, and touch
This is determined by our schemas
concepts that organize information in our experience
Effect of Context on Perceptual Set - The environment or circumstances in which a stimulus occurs can significantly affect our interpretation of the stimulus
Effect of Motivation on Perceptual Set and Emotion - experience filters perception
Effect of Culture on Perceptual Set - Culture sets up the framework through which we interpret the sensory world
Binocular Depth Cues
Retinal Disparity - the slight difference in the images projected on the retinas of each eye due to their horizontal separation
Convergence - inward movement of eyes as they focus on a closer object
Monocular Depth Cues
Relative Clarity - objects that appear sharp, clear, and detailed are seen as closer than more hazy objects.
Texture Gradient - a gradual change from a coarse, distant texture to a fine, indistinct texture signals increasing distance
Relative Size - the depth cue in which we perceive distance based on the composition of sizes between objects
Linear Perspective - a type of depth prompt that the human eye perceives when viewing two parallel lines that meet at a distance
Interposition - one object that is covered up may seem farther away.
Gestalt Psychology
Figure-Ground - how people distinguish an object (its figure) from its surrounding area (the ground)

Closure - if parts of a picture are missing, our minds fill in the gaps
Proximity - we perceive objects that are close to each other as being in a group
Similarly, we perceive elements that are similar in appearance to be connected or part of a whole
Perceptual Constancy - perceiving objects as unchanging, even when illumination and retinal images change
Apparent Motion - involved the general perception of movement when nothing is happening
Phi Phenomenon - a specific type of apparent movement where the illusion of movement arises from light flashing in a sequence
creates a perception of movement
Thinking
Concepts - mental groupings of similar objects, events, ideas, and people
Natural Concepts: understanding through direct observation and experience
Formal Concepts: formed by definition
Prototypes - mental images or the best example of a category
ideal example of any given concept
the closer something matches our prototype of a concept, the more readily we will accept it
Schema - basic units of intellect
frameworks that organize and interpret information
Assimilation - fitting new information into an existing schema
Accommodation - creating a new schema
or drastically changing the schema
Algorithms - a methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem
Heuristics - a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgements and solve problems efficiently.
Representative Heuristic - estimating the likelihood of events in terms of how well the seem to represent or match particular prototypes
Availability Heuristic - estimating the likelihood of events based on their available memory
Decision-Making and Judgments
Insight - a sudden realization of a problem’s solution
Intuition - an effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted with explicit, conscious reasoning
Fixation - inability to view problems from a new angle
Mental Set - a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way
Often, a way that has been successful in the past
Belief Perserverance - ignoring evidence that proves our beliefs are wrong
Priming and Framing - the way an issue is posed/worded can significantly change/affect ur decisions and judgements
Gambler’s Fallacy - the belief that the chances of something happening with a fixed probability become higher or lower as the process is repeated
Sunk-Cost Fallacy - our tendency to continue with an endeavor we have invested money, effort, or time into
Even if current costs outweigh the benefits
Executive Functions - management of cognitive processes, including working memory, reasoning, flexibility, and problem solving, as well as planning and execution
Creativity - the ability to innovate valuable ideas
Expertise: well-developed knowledge
Imaginative Thinking Skills: see things in a new way
Venturesome Personality - Tolerance for ambiguity or risks
Intrinsic Motivation: internal motivation
Creative Environment: helps foster creativity
Convergent Thinking - narrowing the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
EX: how a little kid would react
Divergent Thinking - expanding the number of possible problem solutions
creative thinking that diverges in different directions
Functional Fixedness - A tendency to only think of an object’s most common use when presented with a problem
Encoding
Encoding - get information into our brain by selecting, identifying, and labeling memories to fit the preferred format for memory
Storage - retain the information
Retrieval - later get the information back from our brain
the recovery of information
Mnemonic Devices - a technique used to enhance memory and recall
Method of Loci - a mnemonic technique that works by placing an image of each item to be remembered at particular points along an imaginary journey through a location
Chunking - organizing items into familiar, manageable units
often occurs automatically
Categories - organizing information into meaningful groups
Hierarchies - systems where individuals or concepts are ranked one above another based on specific criteria
Spacing Effect - The tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term memory
Massed Practice - can produce short-term learning and a feeling of confidence
cramming
Those who learn quickly forget quickly
Distributed Practice - produces better long-term memory
Serial Position Effect - the tendency of a person to recall the first and last items in a series best and the middle worst
Maintenance rehearsal - Repetition of a piece of information to keep it within your active, short-term memory
mnemonic, speech
Elaborative Rehearsal - A Technique used to help the short-term memory store thoughts or ideas and pass them into long-term memory
relating new concepts to old concepts that are already in long-term memory
Autobiographical Memory - the process of remembering personal experiences or events from our own lives
ability to retrieve specific details such as time, place, emotions, and sensory information associated with those memories
Retrograde Amnesia - the inability to recall memories from before the onset of the amnesia
Anterograde Amnesia - the inability to retain or learn new information
Infantile Amnesia - the inability of adults to recollect early episodic memories
associated with the rapid forgetting that occurs in childhood
Alzheimer’s Disease - a chronic brain disease that gradually erodes an individual’s memory, intellectual abilities, and personality
the most obvious symptom is the inability to learn and remember information
Retrieving Memories
Retrieval Cues - stimuli that assist in memory retrieval
EX: A test question may fail to cue memory because of its wording or context
Recall - you can access information without cues
Recognition - a type of memory retrieval in which one must identify present information as having been previously presented
Context-Dependent Memory - theory that suggests that information is optimally remembered when it is recalled in the same place in which it was initially learned
EX: taking an exam in the place where you learned the content
Mood-Congruent Memory - The tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one’s good or bad mood
EX: if someone is upset, they might recall more negative events
State-Dependent Memory - A state in which the retrieval of recently obtained information may be possible if the subject exists in a similar physiological situation as during the period of the encoding stage
EX: Scuba divers recalling information underwater
Testing Effect - an enhancement in the long-term retention of information as a result of taking a memory test
repeatedly self-test
Metacognition - the ability to control and be aware of your thoughts
EX: realizing you know the answer to a test, but cannot think of the answer at that moment
monitoring and evaluating your learning
Ebbinghaus’ Forgetting Curve - a graph that represents how memory decreases over time when there is no attempt to retain or retrieve the information
As rehearsal time increases, relearning time decreases
Encoding Failure - a breakdown in the process of getting information into the cognitive system
can occur because of inattention to the target information or interface when the target information is presented
Proactive Interference - occurs when old information or knowledge interferes with the learning of new information
EX: writing the date wrong during the first few months of the year,// confusion when using foreign currency
Retroactive Interference - when newly acquired information inhibits your ability to recall previously acquired information
EX: forgetting the address of your previous location because you moved,// forgetting the names of previous co-workers
Tip-of-the-Tongue Phenomenon - Occurs when someone cannot recall a specific word or term, but feels certain that they know it
the information is just out of reach
Repression - when unacceptable ideas, impulses, and memories are kept out the consciousness
Addressed more in later units
Misinformation Effect - occurs when a memory has been corrupted by misleading information
asking leading questions
Source Amnesia - faulty memory for how, when, and where information was learned for images
Deja Vu
Memory Consolidation - memories become less susceptible to interference with time
Consolidation is based on rearrangements of the neural circuitry involved in memory
Imagination Inflation - people increase their confidence that an event happened after imagining the details of the event
First birthday recollection, actually just household photos
Intelligence and Achievement
G (general intelligence) - underlies all mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test
According to Spearman and others
Multiple Intelligence - our abilities are classified into eight or nine independent intelligences
Includes a broad range of skills beyond traditional school smarts
Mental Age - the level of performance typically associated with children of a certain chronological age
Devised by Alfred Binet
Chronological Age - the actual amount of time a person has been alive
measured in years from birth to present
IQ (Intelligence Quotient) - ratio of mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca) multiplied by 100
IQ = (ma/ca)/100
Flynn Effect - the finding that IQ scores have been steadily surpassing previous generations
Psychological Assessments
Standardized - defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group
Validity - the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to do
Construct - the extent to which a test samples the behavior that is of interest
Predictive - the success with which a test predicts the behavior it is trying to predict
Reliability - the extent to which a test yields consistent results
Test-Retest - a property exhibited by a test on which people get about the same scores when they take the test more than once
Split-Half - data collected is split randomly in half and then compared
to see if results taken from each part of a measure are similar
Achievement Tests - a test designed to assess what a person has learned
Aptitude Tests - a test designed to predict a person’s future performance
Aptitude is someone’s capacity to learn
Stereotype Threat - a self-fulfilling prophecy that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
Stereotype Lift - occurs when non-targets perform better than the stereotype
Heritability - The proportion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes
Fixed Mindset - asserts that the brain and intelligence cannot change
Growth Mindset - belief that one’s ability and intellect can be developed through effort, learning, and perseverance
Memory
Explicit Memory - information that you have to work to remember consciously
Episodic Memory - explicit memory of personally experienced events
½ of our conscious memory system
Semantic Memory - explicit memory of facts and general knowledge
½ of our conscious memory system
Procedural Memory -the type of memory that we use to do everyday tasks
tying shoes or riding a bike
Conditioned Memory - if you were classically conditioned to do something, you do not need to remember it consciously
being scared of dogs for life if one bit you when you were a kid
Prospective Memory - remembering to act at a certain time
Remembering to take medicine after breakfast
Long-Term Potentiation - a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity
This is thought to be a key mechanism behind learning and memory
Central Executive - coordinates your focus processing as you integrate new information with your existing long-term memory
Phonological Loop - briefly holds auditory information
EX: Repeating a phone number as you enter it
Visuospatial Sketchpad - briefly holding information about an object’s appearance or location in space
EX: Where did you park your car?
Sensory Memory - the immediate and brief recording of sensory information to the memory system
Sensory Memory (Iconic) - photographic picture-image memory
lasting no more than a few seconds
Sensory Memory (Echoic) - mementary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
If attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can only be recalled for 3-4 seconds
Short-Term Memory - briefly activated memory of a new item that is later stored or forgotten
EX: digits of a phone number while calling it
Long-Term Memory - a relatively permanent and limitless archive of the memory system
includes knowledge, skills, and experiences
Automatic Processing - unconscious encoding of incidental information (space, time, and frequency) and well learned information (word meanings)
Effortful Processing - encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Working Memory - a newer understanding of short-term memory
conscious and active processing of 1) incoming sensory information and 2) information retrieved from a long time ago
Levels of Processing (shallowest to deepest)
Structural - focusing on the appearance of words
Phonemic - focuses on the sound of words
Semantic - focuses on the meaning of words
visual
Unit 3: Development and Learning
Themes and Methods in Developmental Psychology
Developmental Psychology - the study of how we change over our lifespan physically, cognitively, socially, and morally
lifelong
multidimensional and multidirectional
Physical Development - Changes in the physical body
Muscle development
coordination
sexual development
Cognitive Development - how a person thinks
Social Development - Relationships and how we think, feel, and behave in them
Moral Development - our understanding of how our choices affect others
Gender Development - An Individual’s anatomical sex
sexual assignment
cultural and social aspects
Stability vs. Change
Stability: characteristics we develop in childhood are permanent and fixed
Change: occurs in predictable and unpredictable ways in our lives
Nature vs. Nurture
Naturists: development is due to genetic determination
Nurturists: At birth, our minds are a blank slate
Continuous vs. Discontinuous Stages of Development - Is developmental gradual or a sequence of separate stages?
Continuous Theorists: Development is continuous and focuses on quantitative change
Stage Theorists: development occurs in a series of distinct stages
Cross-sectional - many individuals at a single point in time
Logitudinal - Same group of participants over a long period of time
Kohlberg’s Moral Development
Level 1 - Preconventional Morality
Stage 1: Obedience and punishment orientation
The individual is good at avoiding punishment
Stage 2: individualism and exchange
Children realize there is not one right view that is handed down by authorities
Level 2: Conventional Morality
Stage 3: Good interpersonal relationships
the individual is good to be seen as being good
approval of others
Stage 4: Maintaining Social Order
aware of wider rules in society
Judgements concern obeying the rules to avoid guilt
Level 3: Postconventional Morality
Stage 5: social contact and individual rights
become aware of which rules/laws exist for the good of the greater number
Stage 6: universal principles
People at this stage have developed their set of moral guidelines, which may or may not fit the law
Physical Dev. Across the Lifespan
Maturation - refers to biological growth processes that occur naturally and are largely determined by genetics
Critical Period - a time interval during which specific stimuli have major effects on development
high brain plasticity
the brain is receptive to learning, and the environment influences
development of language acquisition from early childhood
Prenatal Development and Birth Defects
Prenatal Period - begins with fertilization and ends at birth
critical period for eyes, ears, arms, legs, and heart
In the first 3 months
Defects - generic, hormonal, or environmental stimuli
malnutrition over time and over-the-counter drugs cause birth defects
Negatively Affect Prenatal Developments - maternal illness
Infections during pregnancy can affect both
Genetic Mutations: schizophrenia, autism, Down syndrome, and cystic fibrosis are all due to genetic mutations
Physical Development of Early Childhood
Pruning Process - unused neurons eliminated
Primary Sex Characteristics - innate and include sex organs and genitals
Secondary Sex Characteristics - develop during puberty
facial hair, enlarged breasts, pubic hair, deeper voices
Cognitive Development Across the Lifespan
Jean Piaget - a developmental psychologist who studied how our minds grow
studied children’s cognition
Piaget’s Stages of Development
Sensorimotor Stage (0-2 years)
Infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities
Object permanence - objects exist even when out of sight
separation anxiety disorder develops (8-10 months)
~8 months: stranger anxiety
Preoperational Stage (2-7 years)
stage where a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete language
ability to pretend
egocentric: being unable to think about something from someone else’s perspective
Trial and error
answers questions instinctively rather than logically
Concrete Operational Stage (7-11 years)
Children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events
mastery of conservation
mass, volume, and # remain the same despite changes in the form of objects
Recognizes reversability
1+2=2+1
Formal Operational Stage (12+ years)
People begin to think critically about abstract concepts
reason like adults
think hypothetically
make inferences
deeper concepts of existence
mature moral reasoning
Lev Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development - the space between what a learner can do without help and what a learner can do with help or in collaboration with peers
scaffolding
guided learning
Fluid Intelligence - the ability to think abstractly, reason quickly, and solve any problem due to previous knowledge
Crystalized Intelligence - intelligence involves learning, knowledge, and skills that are acquired over a lifetime
Cognitive Disorders - when a person experiences a loss or interruption of normal thought processes
dementia and alzhiemers
Communication and Language
Language - a flexible system of communication using sounds, rules, gestures, or symbols to convey emotion
Skinner's Language Theory - Children learn language through interactions with their environment
parents
Chomsky's Language Theory - children possess the inherent ability to learn language
Innate universal grammar
Phonology - study of sound patterns and rules that govern language
Phonemes - the smallest meaningful unit of sound that is recognizable as human speech and makes words distinct
Morphology - the study of word structure and how words are formed
Morphemes -the smallest recognizable units of sounds
Syntax - the system of rules for combining words and phrases to form grammatically correct sentences
Semantics - the rules for determining the meaning of words and sentences
using the right words
Pragmatics - the study of how language is used in real-world contexts and how the meaning influences situations
Grammar - a set of rules governing how symbols in a given language are used to form meaningful expressions
Linguistic Determinism/Relativism - The concept that language and its structures limit and determine human knowledge and thought
Nonverbal Communication - signals we send and receive through body language, facial expressions, gestures, and other forms of nonverbal communication
often convey emotions, attitudes, and intentions without the use of words
Development of Formal Language - the process by which individuals acquire and improve their ability to understand and use language
Overgeneralization - occurs when the use of grammar is applied too broadly beyond exceptions
Children often make these mistakes when learning the language
Telegraphic Speech - context words only
no functions, tenses, or plural endings
Social-Emotional Development Across the Lifespan
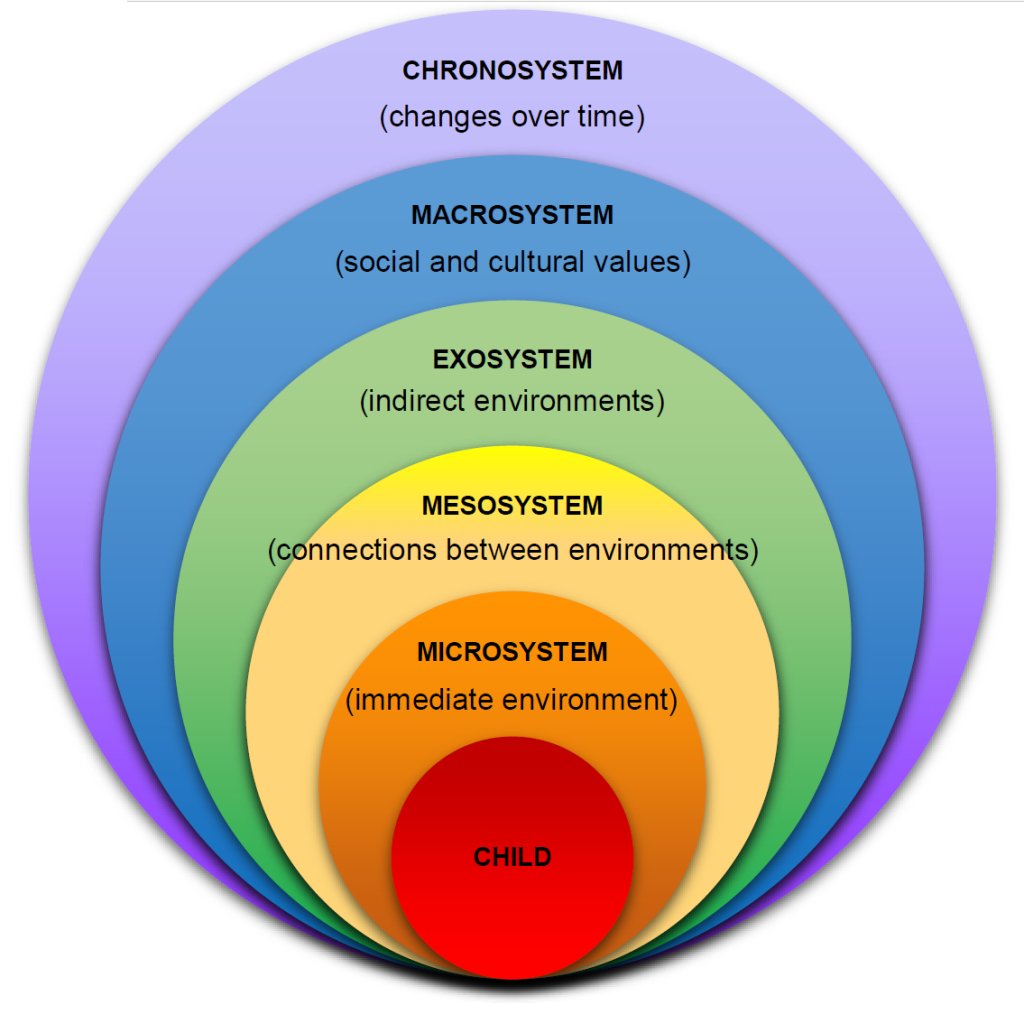
Chronosystem - the individual’s current stage of life
tech advancements, family restructure over time
Macrosystem - cultural events that affect the individuals and others around them
societal values, cultural norms
Exosystem - indirect factors in individual life
parents’ jobs // stress could affect the family dynamic
Mesosystem - relationships between groups in school
Academics affect the family
extra curricular could influence peer relationships
Microsystem - groups that have direct contact with the individual
family, friends, classmates, and extra curriculars
Authoritarian Parenting - focuses on obedience
punishment over discipline
Authoritative Parenting - create positive relationships with their child
enforce rules
high expectations for a child’s maturity
Permissive Parenting - Don’t enforce rules
“Kids will be kids.”
low expectations of a child’s maturity
Neglectful Parenting - Provide little to no guidance, nurturing, attention, and expectations
Secure Attachment Style
As a child, able to separate from my parents
Seek comfort from parents when frightened
Return of parents is met with emotions
prefers parents to strangers
As an adult, having a trusting, lasting relationship
tend to have good self-esteem
comfortable sharing feelings with friends
seek out social support
Insecure Attachment Style
As a child, may avoid parents
does not seek much comfort or contact from parents
shows little or no preference between a parent and a stranger
As an adult, one may have problems with intimacy
Invest little emotion in social and romantic relationships
unable or unwilling to share thoughts and feelings with others
Temperament - a person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
more on the nature, but nature matters too
Separation Anxiety - a child’s generalized fear of being separated from a primary caregiver or other familiar adult
Harlow’s Money Study and Contact Comfort
2 “mothers,’ (cloth mother and robot mother)
found that the monkey was more attached to the cloth mother
proving the importance of contact comfort
Erikson’s Theory of Psychosocial Development

Peer Relationships - peers exert increasing influence over us while simultaneously parental influence decreases
Imaginary Audience - belief that you are constantly being watched or judged
Personal Fable - belief that you are so unique that nobody can understand you
Adolescent Identity Development Theory - Erikson’s 5th stage
EX: Are you seeking out an identity for yourself, and do you eventually commit to identity?
Sex - biological status, defined by your chromosomes and anatomy
Gender - socially influenced characteristics by which people define boy, girl, man, or woman
the body defines sex, the mind defines gender
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) - potentially traumatic events that occur during childhood
attachment issues
emotional dysregulation
interpersonal challenges
Adulthood Social Development
Primarily shaped by life events rather than age/physical development
Classical Conditioning
Habituation - diminishing response to a repeated stimulus
Repeated fire alarm → starting to ignore it
Mere Exposure Effect - learned preference for things we are familiar with
Behavioral Learning - a branch of psychology that focuses on how people learn through their interactions with the environment
Focuses on observable behavior, not mental processes
Classical Conditioning - associating 2 stimuli together to create a response
Unconditioned Stimulus - something that causes an unlearned (natural) response
Unconditional Response - an automatic reaction given to a stimulus without training
Neutral Stimulus - an unlearned stimulus not associated with anything
Conditioned Stimulus - a neutral stimulus prior to training
Same as an unconditioned response
Conditioned Response - an automatic reaction given to a stimulus
Acquisition - the first point when you learn or understand something
Generalization - associating one experience with all similar experiences
stimulus similar to a Conditioned Stimulus and a Conditioned Response
Discrimination - to be able to tell the difference between 2 similar stimuli
When a stimulus identical to a conditioned stimulus does not elicit a conditioned response
Extinction - when you no longer react to something
Spontaneous Recovery - When a conditioned response reappears after being extinguished, even when there has been no additional conditioning
Higher-Order Conditioning - a form of learning in which a stimulus is first made meaningful for an organism through an initial step of learning
Stimulus is used as a basis for learning
Counterconditioning - a therapy technique that tries to evoke a new response to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors
Taste Aversions - associating illness with something you ate or drank, even if it didn’t make you sick
One-Trial Conditioning - when association is acquired after one pairing of stimulus and response
especially powered with taste
differs from Classical Conditioning because it is quickly acquired
considerably
Biological Preparedness - Biological predisposition to learn certain pairings more quickly than others
People have an innate ability to identify life-threatening objects
Operant Conditioning
Law of Effect - rewarded behavior is likely to occur
Behaviors followed by negative consequences are weakened
Operant Conditioning - A Learning process through which behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment
We learn how to operate in the environment to elicit a particular stimulus
Shaping - reward successive approximations of a target behavior
Boo-Yah game
Relies on positive reinforcement
Instinctive Drift - the tendency to revert to your innate, instinctive behaviors after being conditioned to perform a learned behavior
Revert to an accent despite learning the language proficiently
Learned Helplessness - occurs when an individual continuously faces a negative, uncontrollable situation and stops trying to change their circumstances
even while they can do so
Primary Reinforcers - a stimulus that is innately satisfying and requires no learning
food, water, sex
Secondary Reinforcer (Conditioned)
coupons, money, grades, and praise have their value learned or acquired through experience
Skinner’s Box - operant conditioning chamber
used to study animal behavior in a controlled environment where they can learn to perform a specific task
Positive Reinforcement - something is being added to increase the likelihood of a behavior
The child gets praised for getting good grades
Negative Reinforcement - Every occurrence of a behavior is reinforced
Not helpful if trying to establish long-term motivation
Positive Punishment - something is being added to decrease the likelihood of a behavior
A parent scolding a child for fighting with their siblings
Negative Punishment - something is being removed to decrease the likelihood of a behavior
Child loses iPad after refusing to eat veggies
Continuous Reinforcement - Every occurrence of a behavior is reinforced
Not helpful if trying to establish long-term motivation
Partial Reinforcement - behaviors are reinforced only some of the time
Fixed Interval - Reinforcement is delivered at predictable time intervals
EX: Weekly paycheck for your job as a Starbucks employee
Result: Moderate response rate with significant pauses after reinforcement
Variable Interval - reinforcement is delivered at unpredictable time intervals
EX: Pop quiz in a class
Result: Moderate yet steady response rate
Fixed Ratio - Reinforcement is delivered after a predictable number of examples
EX: $10 for every 4 customers you help at the store
Result: High response rate with pauses after reinforcement
Variable Ratio - reinforcement is delivered after an unpredictable number of responses
EX: Slot machines
Result: High and steady response rate
Factors in Learning
Social Learning Theory - proposed that learning occurs through observation, imitation, and modeling
influenced by factors
attention
motivation
attitudes
emotions
Observational Learning - the process of learning by watching the behavior of others
Modeling - the process through which children learn a large number of behaviors, skills, and ways of thinking without direct experience
Mirror Neurons - facilitate our learning by enabling us to imitate and understand the actions and behaviors of those we observe
Vicarious Conditioning - learning through observing other people’s responses to an environmental stimulus that is most noticeable to the observer
reading a book
listening to a story
Insight Learning - Cognitive form of learning involves the mental rearrangement or restructuring of the elements in a problem to achieve a sudden understanding of the problem and arrive at a solution
Latent Learning - a form of learning that is not immediately expressed in an overt response
trying to compute a 20% discount at the market
Cognitive Maps - a mental picture or image of the layout of the physical environment
EX: being able to navigate your room in the dark
Unit 4: Social Psychology
Attribution Theory and Personal Perception
Dispositional Attributions - relates to internal qualities of others
such as intelligence or personality
Situational Attributions
Relate to external circumstances that are experienced
Explanatory Style - people explain the events in their lives and the lives of others in predictable ways
Optimistic Explanatory Style: temporary controllable causes
Pessimistic Explanatory Style: focuses on permanent, uncontrollable causes
Actor/Observer Bias - the tendency to attribute the behavior of others to internal causes, while attributing our behavior to external causes
EX: Bob believes he cannot stop gambling because his friends gamble and are a bad influence. Tim cannot stop gambling because he is an addict.
Fundamental Attribution Error - We observe another’s behavior and underestimate the impact of the situation, and overestimate the impact of personal disposition
This is like a bias
Self-Serving Bias - attributing our successes to our efforts and qualities, while attributing our failures to external factors and other people
EX: I did well on a test → I am smart
EX: I did poorly on a test → The teacher did not teach us well
Internal Locus of Control - belief that outcomes of someone’s abilities
believing they are in control and take responsibility for their actions
better academic achievement, greater efforts to learn, positive attitudes to exercise
External Locus of Control - The belief that one blames external forces for their circumstances
more resigned to conditions “as they are,” lower efforts to deal with health, lower level of adjustments
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy - Behave in ways that elicit behaviors from others that confirm their beliefs or perceptions about themselves or others
Social Comparison - when people evaluate themselves based on comparisons to other members of a society or social circles
can be upward and downward
Relative Deprivation - the feeling of being deprived or lacking in something compared to others in a relevant social group
based on the idea that people perceive their situation relative to others, not just in absolute terms
Projective Tests - a personality test in which subjects are shown ambiguous images or given situations and asked to interpret them
Attitude Formation and Change
Prejudice - an unjustifiable and negative attitude toward a group
Racial stereotypes
Stereotypes - generalized beliefs and categories about a group of people
can help reduce cognitive load when making decisions and judgments
can be caused
result of biased perceptions
experienced
Implicit Attitudes - evaluations that occur without conscious awareness towards an attitude object or the self
Just-World Phenomenon - the tendency to believe that the world is just and that people get what they deserve
Out-Group Homogeneity Bias - tendency to perceive members of an outgroup as more similar to each other than they are
while seeing greater diversity within their ingroup
In-Group Bias - favors beliefs and members of the ingroup
Ethnocentrism - the belief that your culture is natural and “correct” while other people’s cultures are incorrect, unnatural, or inferior
Cognitive Dissonance - when we are aware that our attitudes and actions don’t coincide
EX: Student values honesty, but cheats on a test to maintain a high GPA
Social Situations
Conformity - adjusting behavior to coincide with a group standard
Obedience - behavior in response to an order from someone in a position of power
Social Norms - Shared separation or rule within a group about how an individual is supposed to behave in a specific situation
What is typically expected
Social Influence Theory (Normative) - we follow norms to gain approval
EX: using slang to fit in
Social Influence Theory (Informative) - we follow norms because we believe others have accurate information
following someone during fire drill
Central Route to Persuasion - the content of the message does the persuading
more thoughtful and more likely to cause lasting change
Periferal Route to Persuasion - indirect or unrelated content does the persuading
Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon - Tendency for people to comply with a larger request after they agreed to a smaller one
Door-in-the-Face Phenomenon - ask for more that what you want, then back off
negotiation
Cultural Phenomena
Individualism - the ways in which people identify themselves and focus their goals
Collectivism - a worldview in which social behavior is guided largely by goals that are shared by a collective
Multiculturalism - the systematic study of behavior, cognitions, and affect in settings where people if different backgrounds interact
Effect of Group on Mental Precoesses
Group Polarization - the idea that groups tend to make decisions that are more extreme compared to the original thoughts of individual group members
Groupthink - opting to conform with the consensus view rather than engage in critical thinking
Diffusion of Responsibility - phenomenon such that when there are multiple people present, each individual feels less of a responsibility of the situation
EX: college student who has a seizure but no one helps him
Social Loafing - tendency to exert less effort in a group task
EX: if athletes know they are being filmed individually, they will perform better
Deindividualation - the loss of self-awareness and individual identity that can occur in a group setting
Social Facilitation - stronger response or performance in the presence of others
Does not work on complex or difficult tasks
When you do well, you will likely do better in front of a group
False Consensus Effect - a tendency to overestimate how many people share their beliefs and behaviors
Superordinate Goals - opponents working together towards a common goal
Social Traps - when individuals do NOT unite and act in their own self-interest to the detriment group
Industrial Organizational Psychologists - the behavior of employees in the workplace
Altruism - unselfish behavior intended to help others
individual performs an action that benefits someone else without expecting personal gain or reward
Prioritizing the welfare
Social Reciprocity Norm - people will help those who have helped them
Social Responsibility Norm - people will help those who are dependent on us
no expectation of future payback
EX: blood donation or helping a lost kid
Bystander Effect - tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to help if there are other people present
EX: Murder of Kitty Genovese
Theories of Personality
Personality - the collection of characteristics that make up a person’s unique way of thinking, feeling, and behaving
Unconscious - mental activities and processes occurring outside of conscious awareness
influencing behavior and emotions without our realization
Psychodynamic Theory of Personality - a perspective that asserts our behaviors are largely influenced by unconscious drives and experiences from our past
Humanistic Theory of Personality - Personality focuses on unconditional regard and the self-actualizing tendency as primary motivating factors
Unconditional Positive Regard - accepting and respecting others as they are without judgment or evaluation
Self-Actualization - the Process of realizing and fulfilling one’s potential and capability
Ego Defense Mechanisms
Denial - when someone acts as if the negative feelings or events that cause negative emotions do not exist
Displacement - when someone takes their negative emotions and focuses them on a different, safer target
Projection - defense mechanism where individuals attribute characteristics they find unacceptable in themselves to another person
Rationalization - when someone decides or some up with a seemingly logical explanation to justify an event to avoid the true explanation
Reaction Formation - expressing the opposite of how one truly feels
act contrary to true feelings in order to keep feelings hidden
Regression - returning to an earlier, comforting form of behavior
Repression - pushing anxiety-causing thoughts out of conscious awareness
Sublimation - channeling one’s frustration toward socially acceptable behavior
EX: Sports
Social Cognitive and Trait Theories of Personality
Self-Concept - the view someone has of themselves after evaluating their own beliefs, physical and mental attributes, likes and dislikes, and strengths and weaknesses
Self-Esteem - being able to have confidence in your abilities and sense of self
Self-Efficacy - the belief you can achieve your goals and succeed at tasks
Social-Cognitive Theory of Personality - reciprocal determinism shapes personality
Reciprocal Determinism - a person’s behavior both influences and is influenced by personal factors and the social environment
Trait Theory of Personality - describes people based on their characteristic patterns of behavior, thoughts, and feelings
Big Five Theory - OCEAN
O: Openness
prefers routine, practical vs. imaginative, spontaneous
C: Conscientious
impulsive, disorganized vs. disciplined, careful
E: Extraversion
Reserved, thoughtful vs. sociable, fun-loving
A: Agreeable
Suspicious, uncooperative vs. trusting, helpful
N: Neutricism
Calm, confident vs. anxious, pessimistic
Factor Analysis - a technique used to identify traits by condensing a large amount of factors into traits that represent the underlying characteristics of a person
Motivation
Drive-Reduction Theory - when a physiological need increases, there is a psychological drive to reduce it
we seek to maintain homeostasis
we form habits by doing things to over again to feel comfortable
EX: I am hungry. I will eat
Arousal Theory - curiosity and uncertainty can bring excitement → increase motivation
Yerkes-Dodson Law - Psych yourself up for easy opponents, but stay calm for touch opponents
Strengths: explains non-psychological needs for knowledge, success
Weaknesses: Not comprehensive; seems subjective in some cases
Self-Determination Theory - proposes that people are motivated by intrinsic or extrinsic motivations
Intrinsic Motivations: desire to do an activity for its own sake
Extrinsic Motivations: desire to do an activity to achieve a reward or an external consequence
Incentive Theory - we are motivated by incentives in the form of rewards and punishments
personally undesirable outcomes or avoid behaviors that lead to personally undesirable outcomes
once a task gets too hard, it hinders motivation
Instincts - unlearned fixed behaviors throughout a theory
cannot be readily observed or scientifically tested and don’t explain all behaviors
Lewin’s Motivational Conflict Theory - proposes that choices create conflicts one must resolve on the basis of motivation
Approach-Approach Conflict - two good options
Approach-Avoidance Conflict - good and bad aspects of a choice
Avoidance-Avoidance Conflict - two bad options
Sensation-Seeking Theory - one’s level of need for varied or novel experiences is the basis of motivation
Experience-Seeking - a desire for novel sensory or mental experiences
Thrill/Adventure Seeking - an attraction to risky or fear-inspiring activities
Motivation and Eating - eating is a complex, motivated behavior that demonstrates the interaction of mental and physical processes
Miligram’s Agentic State - can act autonomously and choose their behavior
enter angetic state where they receive orders from an authority figure but does not feel responsible
Institutional Authority - the power and influence held by organizations and institutions (like governments, corporations, or educational institutions) to shape behavior and maintain norms
Proximity of Authority Figure - obedience increases when close
Victims Distance - when the victim is far away, obedience is more likely
Emotion
Emotion - a complex psychological state that involves a subjective experience, a physiological response, and a behavioral or expressive response
James-Lange Theory - stimulus → arousal → emotion
Witnessing an external stimulus leads to a response
EX: snarling → ANS arousal → fear
Cannon-Bard Theory - arousal and emotion occur simultaneously
thalamus sends messages to the cortex and the hypothalamus at the same time
snarling dog → brain activity → arousal and fear
Schachter-Singer Two-Factor Theory - stimulus → physiological arousal → cognitive appraisal = emotion
Ledoux - highlights how some emotional responses can occur instantly and unconsciously
Facial Feedback Hypothesis - our facial expressions can directly influence out emotional experience
Broaden-and-Build Theory - positive emotional experiences tend to broader awareness and encourage new actions and thoughts
builds emotional resilience
Negative emotions tend to reduce awareness
Universal Emotions - research has explored whether the expression of emotions is universally common → mixed emotions
refers to the six basic emotions
happiness
sadness
fear
disgust
anger
surprise
Display Rules - permissible ways of emotions in a society
Display Elicitors - stimuli that trigger an emotional response
Unit 5: Mental and Physical Health
Health Psychology
Stress - how we perceive and respond to certain events that we appraise as threatening or challenging
catastrophes, anxiety, significant life changes, daily hassles
Stressors - any event, situation, or external stimulus that is perceived as a threat or challenge, and that triggers a stress response in the body
Tend-and-Befriend Theory - taking care of your own needs and/or the needs of others and seeking connection with others
thought to release certain hormones like oxytocin and estrogen
Problem-Focused Coping - Managing or fixing the situation
EX: you are failing a class, so you form a study group to improve your performance
Unhealthy: avoidance, aggression, substance use, overworking
Emotion-Focused Coping - controlling or replacing the negative emotional responses to the stressor
EX: this is upsetting but I can stay calm and not lose my temper
Positive Psychology
Positive Psychology - focuses on the study of human strengths, well-being, and the factors that contribute to a fulfilling and meaningful life
Subjective Well-Being - self-perceived happiness or satisfaction with life
6 Categories of Virtues
Wisdom: cognitive strengths that involve the acquisition and use of knowledge
Courage: emotional strengths that involve the exercise of will to accomplish goals
Humaity: caring for others
Justice: fairness, leadership, and teamwork
Temperance: forgiveness, modesty, and self-regulation
Transcendence: Appreciation of beauty and excellence, gratitude, hope, humor, and spirituality
Posttraumatic Growth - the positive psychological change that some individuals experience after a life crisis or traumatic event
therapy and learning about trauma and community service
Psychological Disorders
Three D’s of Psychological Disorders
Deviance: This refers to behaviors, thoughts, and emotions that deviate significantly from what is considered normal within a given culture or society
Dysfunction: This describes a breakdown in a person’s ability to function normally in daily life
Distress: indicates significant emotional pain or suffering experienced by the individual
Eclectic Approach - a therapeutic method that combines techniques and insights from various psychological theories and perspectives
Biopsychosocial Model - a comprehensive model used to understand why and how an illness occurs
combination of genetic vulnerability, negative thought patterns, and lack of social support

Diathesis Stress Model - suggests that the development of psychological disorders is influenced by both a genetic predisposition and environmental stressors
Genetic factors place the individual at risk, while environmental stress factors transform this potential into an actual disorder
Neurodevelopmental Disorders - a condition involving early disruptions in brain development, often resulting in impairments in cognition, communication, behavior, or motor skills
Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) - inability to pay attention, complete tasks, or keep things in place, combined with fidgeting, interrupting, and excessive talking
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) - characterized by deficits in two core domains:
1) social communication and interaction
2) restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, and activities
Schizophrenic Spectrum Disorder
Causes:
Susceptibility seems genetic
dopamine hypothesis
Brain abnormality from exposure to prenatal viruses
hyperactivity
diathesis stress model
Actute:
short-term period with severe symptom flare-up
sudden
Chronic:
long-term persistent condition
Positive Symptoms:
hallucinations/delusions and additional abnormal behaviors
Negative Symptoms:
Inability to read social cues and to respond appropriately
Characteristic - Delusions:
false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur
scare someone is out for you, or that something bad is going to happen
Characteristic - Hallucination:
false sensory experiences
EX: seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
Characteristic - Disorganized Thinking/Speech
Disorganized Speech - a jumble of incoherent speech
Disorganized Thinking - inability to create understandable and coherent thoughts
Characteristic - Disorganized Motor Behavior or Catatonia
Movements that are not purposeful or goal-directed and can include a variety of unusual or inappropriate behaviors
Characteristic - Flat Affect
a lack of emotional response
monotonous tone/facial expression
Depressive Disorders
Symtoms
difficulty concentrating, remembering, and making decisions
thoughts of suicide
Causes
death/loss
genes
susceptibility
gender (women are more likely to get diagnosed)
substance abuse
Major Depressive Disorder
2+ weeks of significantly depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and inability to do daily tasks
change in appetite and weight, sleep disturbances, fatigue
Persistent Depressive Disorder
a chronic form of depression where individuals have less severe but long-term symptoms that last for at least 2 years
Bipolar Disorders
Symptoms
over talkative, overactive, elated, little need for sleep, fewer inhibitions, poor judgement, and promiscuity
Causes
Lifestyle issues and the environment affect its severity
norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine
Bipolar I
Involves full manic episodes with periods of depression
more manic (abnormal)
Bipolar II
involves hypomanic (less severe period) episodes that are less intense, with periods of depression
Anxiety Disorders
Symptoms
worry, anxiety, or fear that is strong enough to interfere with one’s daily abilities
Causes
brain chemistry, genes, differences in the way threats are perceived, development, and personality
Specific Phobia
a strong, specific, persistent fear of something extreme enough to interfere with normal living
Agoraphobia
an excessive fear of open or public places
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
a disorder in which people are almost constantly plagued by exaggerated worries
Panic Disorder
frequent bouts of moderate anxiety and occasional attacks of sudden increased heart rate, chest pain, difficulty breathing, sweating, faintness, trembling
Social Anxiety Disorder
persistent, intense, and chronic fear of being watched and judged by others, leading to avoidance of social situations
fear of being judged or watched
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
Symptoms
characteristics by the presence of obsessions and/or compulsions
experience obsessive thoughts
compulsive behavior
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
recurrent, unwanted thoughts, feelings, or sensations, and repetitive behaviors of compulsions aimed at reducing anxiety associated with those compulsions
Hoarding Disorder
difficulty discarding possessions, regardless of value, leading to excess accumulation and clutter that impairs daily functioning or causes distress
Dissociative Disorders
Symptoms
loss of memory
impaired sense of self
Causes
risk factors
abuse, trauma
Dissociative Amnesia
Inability to recall important personal information
usually following a traumatic event that is beyond ordinary forgetting
Dissociative Identity Disorder
presence of 2 or more distinct personality states
Dissociative Dugue
very rare
Amnesia couples with sudden travel
usually forgets all of the memories
Depersonalization Disorder
periods of feeling disconnected or detached from one’s body and thoughts
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Symptoms
high anxiety, flashbacks
detachment, sleep issues, irritability, hypervigilance, recurring memory
Causes
difficulty recovering after experiencing/witnessing a terrifying or traumatic event
Eating Disorders - a biologically based mental illness that can have serious consequences on one’s health, productivity, and relationships
Causes
other disorders, sexual abuse
Genetics: people with first-degree relatives, siblings, or parents are most at risk
Anorexia Nervosa
a disorder characterized by a strong desire to lose weight, a low BMI, and habitually restrictive eating
Bulimia Nervosa
episodes of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors such as vomiting, fasting, or binge eating
Personality Disorders
Personality Disorders - long-term, inflexible patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving that deviate from societal norms and cause distress
Causes:
genetics, early childhood experiences, and environmental influences
Cluster A (Odd and Eccentric)
Paranoid
extreme distrust/suspicion of others
belief that others have harmful intentions without proof
difficulty trusting close friends, family, or coworkers
Schizotypal
unusual thinking patterns, beliefs, or behaviors
Social anxiety and discomfort in close relationships
odd speech, appearance, or belief in the supernatural
Schizoid
strong preference for being alone and avoiding social relationships
limited emotional expression and indifference to praise or criticism
lack of interest in forming close connections
Cluster B (Dramatic and Erratic)
Borderline
Intense fear of abandonment and unstable relationships
Rapid mood swings and impulsive behaviors
self-harm tendencies and chronic feelings of emptiness
Histrionic
excessive attention seeking and emotional overreaction
Strong emotions shift quickly
constant need for approval and dramatic behavior
Narcissitic
inflated sense of self-importance and entitlement
Lack of empathy for others
need for excessive admiration
sensitivity to criticism despite appearing confident
Antisocial
disregard for rules, laws, and the rights of others
manipulative or deceitful
lack of empathy
impulsivity and frequent aggression
Cluster C (Anxious and Fearful)
Avoidant
fear of rejection and a strong feeling of inadequacy
avoidance of social situations despite wanting relationships
extreme sensitivity to criticism
Dependent
strong need for reassurance and support from others
difficulty making decisions without guidance
Fear of being alone
Submissive behaviors in relationships
Obsessive-Compulsive (OCPD)
preoccupation with order
perfection and rigid control
difficulty delegating tasks
extreme focus on work over relationships
strong need for structure and resistance to change
Treatment
Psychotropic Medication Therapy
Drugs that are prescribed to treat mental health disorders
Ethical Principles
Beneficence and Monlmalefience
benefit those you work with and don’t harm them
Fidelity and Responsibility
establish relationships of trust and follow professional responsibilities to clients and the profession
Integrity
promote accuracy and honesty in the science and practice of psychology
Justice
All people should have access to and benefit from psychology
Respect for people’s rights and dignity
Regarding privacy and confidentiality
Free Association - the practice of allowing the patient to discuss thoughts, dreams, memories, or words, regardless of coherency
Dream Interpretation - the process of assigning meaning to dreams, often focusing on the underlying symbolic or unconscious content
Cognitive Restructuring - a therapeutic process where individuals learn to identify and challenge negative or irrational thoughts and replace them with more balanced and realistic ones
ultimately improving emotional well-being
Fear Hierarchies - a graded list of feared situations or stimuli
ranked from least to most anxiety
used in systematic desensitization to help individuals gradually overcome their fears
Cognitive Triad - refers to the 3 negative thought patterns that are believed to contribute to depression
regarding the (1) self, (2) world, and (3) future
Exposure Therapies - a form of evidence-based treatment that involves gradually exposing individuals to feared objects, activities, or situations in a safe and controlled environment
Aversion Therapies - a form of behavioral therapy used to reduce or eliminate undesirable behaviors by pairing them with unpleasant stimuli
Token Economies - an operant conditioning procedure where individuals earn tokens for exhibiting desired behavior, which they can later exchange for various privileges or treats
Biofeedback - a process where individuals learn to control physiological responses like heart rate or muscle tension by monitoring their body’s signals with instruments, aiming to improve health or performance
Dialectical Behavior Therapy - A Type of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
Teaches skills to improve emotional regulation
distress tolerance
interpersonal effectiveness and mindfulness
Rational-Emotive Behavior Therapy - a type of behavior therapy that focuses on correcting negative thought patterns and cognition in order to correct destructive moods or behaviors
Active Listen - therapist listens attentively, asks clarifying questions, and reflects on the client’s words and emotions
Unconditional Positive Regard - accepting and supporting a person, regardless of their thoughts, feelings, or behaviors, without judgment
Group Therapy - a form of psycho therapy where 1 or more therapists treat a small group of clients together as a group
Hypnosis - the mental state of highly focused concentration, diminished peripheral awareness, and heightened suggestibility
Lithium - mood stabilizing meds primarily used to treat bipolar disorders
Antipsychotic Medications - a class of psychoactive drugs used to treat and manage symptoms of psychosis
Tardive Dyskinesia - involuntary movements of the facial muscles, tongue, and limbs
Psychosurgery - surgical procedures in the brain to treat mental disorders
Lesioning - destruction of brain tissue
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) - a procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain
Electroconvulsive Therapy - Biomedical treatment for severe mental disorders
Lobotomy - severing the nerve in the prefrontal cortex of the brain