AP Psychology - Full Brain Unit Review
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that cover the cerebral hemispheres
The body’s ultimate control and information processing center
Contains 20 to 23 billion nerve cells
If flattened, it would cover four full pages of our textbook
Frontal Lobe
Contain the motor cortex which controls voluntary movement
Controls:
Intellect
Moral compass
Reasoning
Planning
Contains the motor strip/cortex
Helps with working memory
Motor Cortex
Located in the frontal lobe:
Controls voluntary movements
Left motor cortex controls the right side of the body, the right motor cortex controls the left side of the body
Parietal Lobe
Located at the top of the head towards the rear:
Contains the sensory cortex
Spatial relations
Kinesthetic Sense
Recognizing your own body
Sensory Cortex
Located at the front of the parietal lobe, and behind the motor cortex:
Registers and processes body sensations:
Touch
Pain
Pressure
Temperature
Left side of this brain part processes sensations from the right side of the body and the right side of this brain part processes sensations from the left side of the body.
Temporal Lobe
Located above the ears:
Contains the auditory cortex - processes everything you are hearing
Memory
Emotion
Face Recognition (Right side of this brain part)
Occipital Lobe
Located in the back of the head:
Includes the visual cortex, which receives information from the opposite visual field
Primary function is VISION
Association Areas
Areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions
Instead, they are involved in higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking
They are responsible for integrating and acting on information received and processed by sensory areas
Combine sensory and motor information; coordinate interaction among different brain areas
Areas of the cortex not involved in sensory or motor functions. They are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, planning, and language.
Brainstem
The Brain’s “basement” - oldest and innermost region.
At the top of the spinal cord
Responsible for automatic survival functions
Oldest area of the brain. Also called the reptilian brain.
Medulla
Located where the spinal cord enters the base of the brain at the brain stem:
Controls involuntary functions
Breathing
Heart rate
Digestion
Vomit Reflex
Keeps us alive!
Reticular Formation
Network of neurons in the brain stem:
In charge of arousal and attention
If damaged, can cause a coma
A neural network within the brainstem; important in arousal including sleep.
Pons
Located in front of the medulla
Helps coordinate movements on left and right side of the body - reflexive movements
Helps with sleep
Regulates sleep and balances movement for left and right sides of the body for reflexes
Cerebellum
Controls voluntary movements
eg. Kicking a ball, playing the piano
Helps assist with coordination and balance
Place where procedural memories are kept:
eg. How to ride a bike, how to tie your shoes
Word means “little brain”
Thalamus
Located at the top of the brainstem
Relay station in the brain
Takes all sensory information and sends it to the appropriate lobe in the brain
EXCEPT smell
The post office of the brain - taking messages and delivering them where they need to go
Limbic System
System of neural structures at the border of the brain stem and cerebral hemisphere:
Donut shaped
Associated with emotions and drives
Contains four major components:
Hypothalamus
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Pituitary Gland
Hypothalamus, Amygdala, Hippocampus, Pituitary Gland
4 main components of the Limbic System
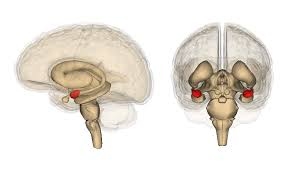
Amygdala
Emotional center of the brain
Deals primarily with fear and aggression
Identifies emotion from facial expressions
Involved in rage and fear as well as emotional memories.
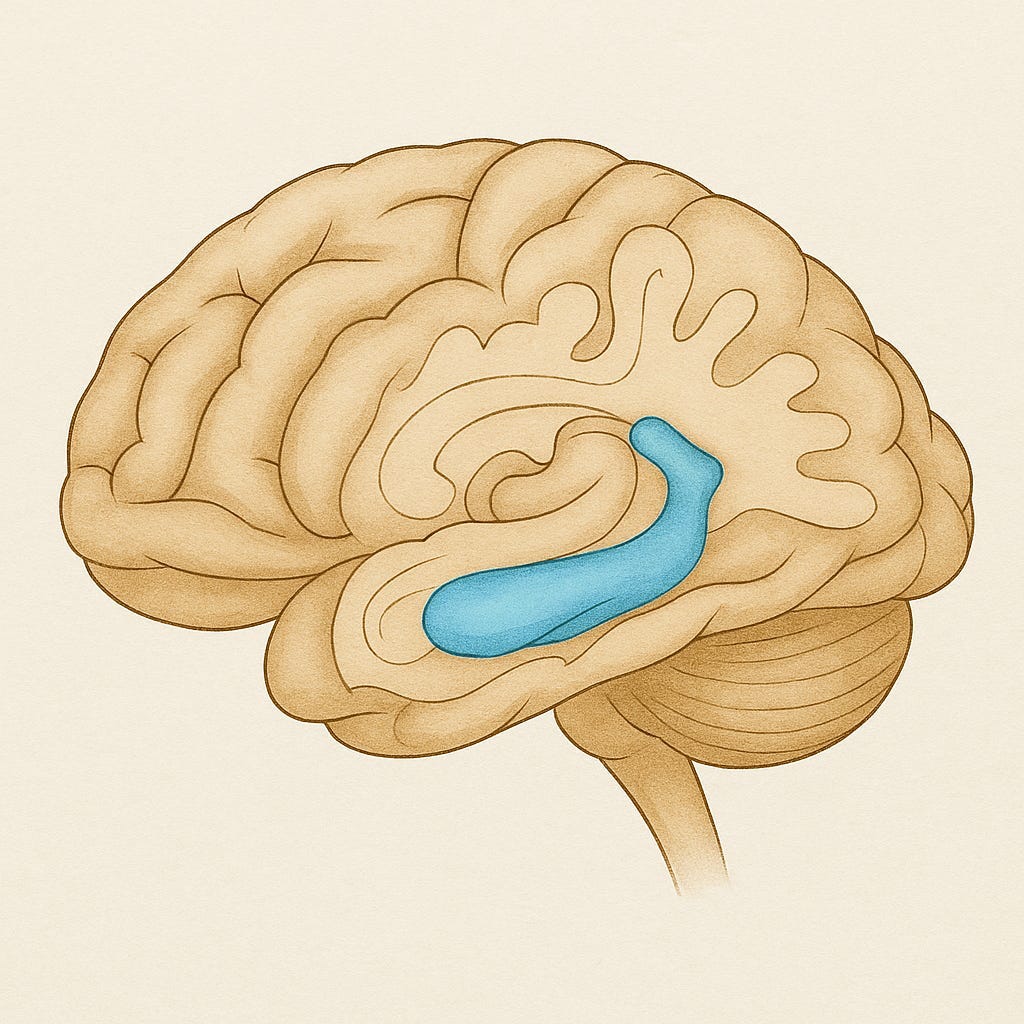
Hippocampus
Wishbone-shaped structure:
Helps us form new memories
Transfers short-term memories to long-term memories
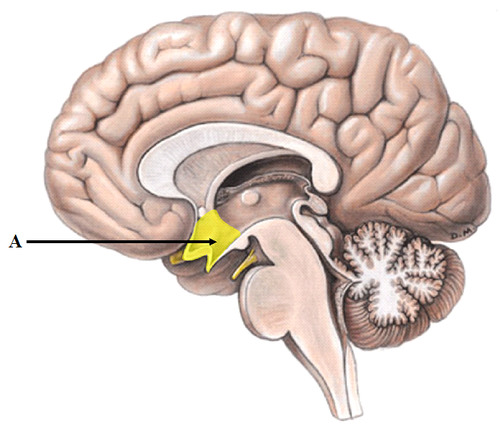
Hypothalamus
The “pleasure center” of the brain that also controls the endocrine (hormonal system) via the pituitary gland.
Helps maintain homeostasis
Temperature regulation
Water and salt balance
Links endocrine system to brain
Is in charge of drives:
Hunger
Thirst
Sex
Sleep
Contains the “pleasure center”
provides us with pleasurable when we fulfill one of our drives
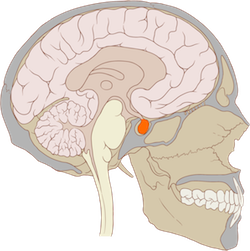
Pituitary Gland
Master gland in charge of the other endocrine glands.
Regulates growth
Phrenology
Thought up by Franz Gall:
Belief that the bumps in the skull determines your personality
Lesions
Destruction of the brain tissue
Lobotomy
Removal of part of the brain
Plasticity
The brain’s ability to reorganize itself should it get damaged - explains phantom limb sensation
EEG
Amplified recordings of brain wave activity
CT Scan
X-ray photos of slices of the brain. This type of scan shows the structures within the brain, but not its functions.
PET Scan
Visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose is being used while the brain performs certain tasks.
MRI
Technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to see structures within the brain
fMRI
Allows us to see where oxygen is being used in the brain while various tasks are being performed
Brainstem
Oldest area of the brain. Also called the reptilian brain.
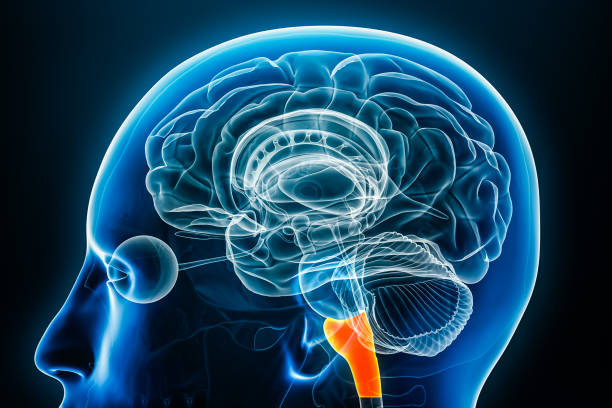
Medulla
The base of the brain stem; controls heartbeat and breathing
Reticular Formation
A neural networks within the brain stem; important in arousal including sleep
Pons
Regulates sleep and balances movement for left and right sides of the body for reflexes
Pons
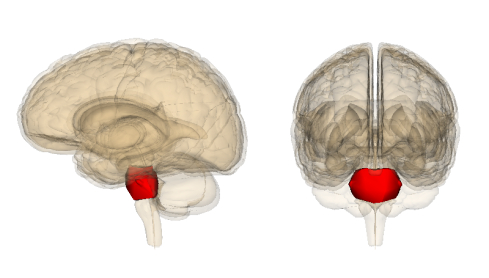
Thalamus
Sits on top of the brain stem; receives all incoming sensory information (except smell) and sends it to the appropriate part of the brain for further processing
Thalamus
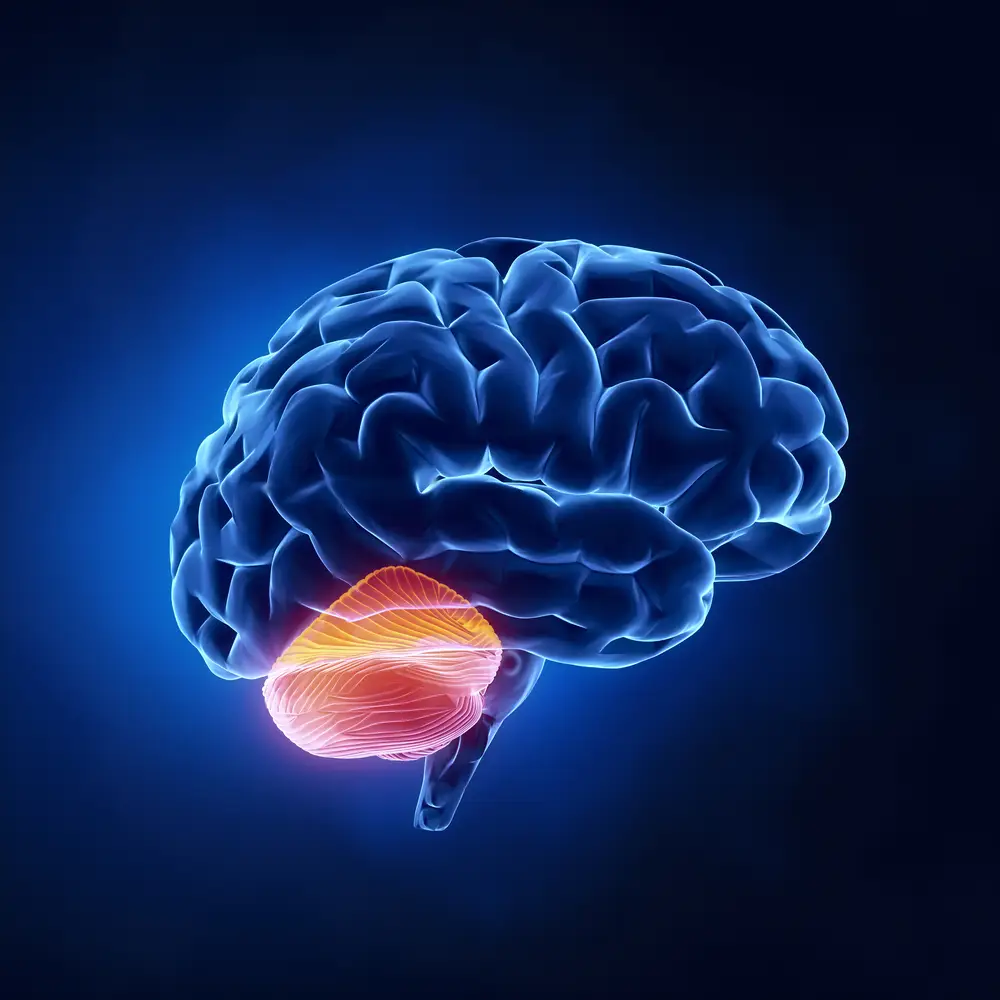
Cerebellum
The “little brain” attached to the back of the brainstem; it helps coordinate voluntary movement and balance
Cerebellum
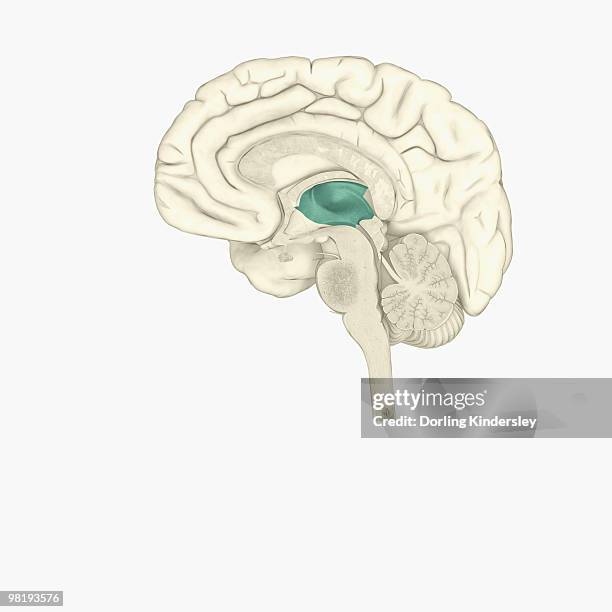
Limbic System
A doughnut-shaped structure between the brainstem and the cerebral hemispheres. It is considered the “seat of emotion” and is also involved in motivated behavior like eating, drinking, and sex
Amygdala
Involved in rage and fear as well as emotional memories
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Involved in memory
Hippocampus
Hypothalamus
Involved in drives (eating, drinking, and sexual behavior). It also controls the endocrine (hormonal system) via the pituitary gland. It is sometimes referred to as “the pleasure center” of the brain.
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Master gland in charge of the other endocrine glands. Regulates growth
Pituitary Gland
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres. The ultimate information-processing center of the brain
Cerebral Cortex
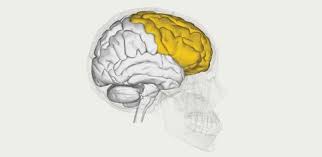
Frontal Lobe
Contains the motor cortex which controls voluntary movement. This part of the brain contains Broca’s Area which controls our ability to speak
Frontal Lobe
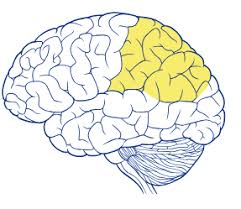
Parietal Lobes
Contain the somatosensory cortex which registers bodily sensations (touch)
Parietal Lobes
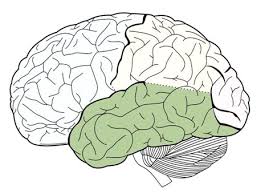
Temporal Lobes
Contain the primary auditory cortex (audition) and areas for the senses of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT side of this lobe contains the Wernicke’s Area which controls language comprehension and expression
Temporal Lobe
Occipital Lobes
Contain the Primary Visual Cortex
Occipital Lobes
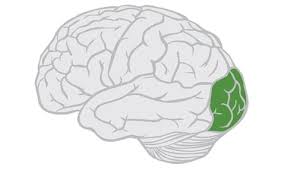
Association Areas
Areas of the cortex not involved I n sensory or motor functions. They are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, planning, and language. About 75-80% of the brain is composed of these types of areas.
Left Hemisphere
This hemisphere receives sensory information from the right side of the body and controls movement of the right side of the body. It is also involved in language, science, math, etc.
Right Hemisphere
This hemisphere receives sensory information from the left side of the body and controls movement of the left side of the body. It is involved in music, artistic ability, and spatial skills.
Corpus Callosum
Connection between the Right and Left Hemispheres.
If this is cut due to epileptic seizures, the patient would become split-brained.
Broca’s Area
Controls speech production:
Located in the left frontal lobe
Directs the muscle movements involved in speech
Wernicke’s Area
Controls speech reception:
Located in the left temporal lobe
Involved in language comprehension and expression
Angular Gyrus
Located near the back of the temporal lobe:
Takes letters/words and makes them sounds
Receives the visual information from the visual cortex and transforms it into the auditory form, which it then sends to the Wernicke’s Area
Aphasia
Partial or complete inability to articulate ideas or understand language because of brain injury or damage
Broca’s Aphasia
Type of Aphasia:
A person has trouble formulating words but can still understand speech
Wernicke's Aphasia
Type of Aphasia
Person has a hard time speaking in meaningful ways and understanding speech
Brain Plasticity
The brain’s ability to reorganize itself
Structural Plasticity
Actual changing of the neuron or actual growing new neurons:
Only can occur in the hippocampus
Functional Plasticity
When an area of the brain takes up a new function to replace a damaged area of the brain
Phantom Limb
If a body part is amputated, the surrounding neurons in the sensory cortex rewire themselves to other areas of the body