Control to memorise
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
3 Key properties of Linear time invariant systme
obey principle of superposition (x1+x2)→(y1+y2)
homogeneity (Ax→Ay)
time invariance( x (t-T)→y (t-T) )
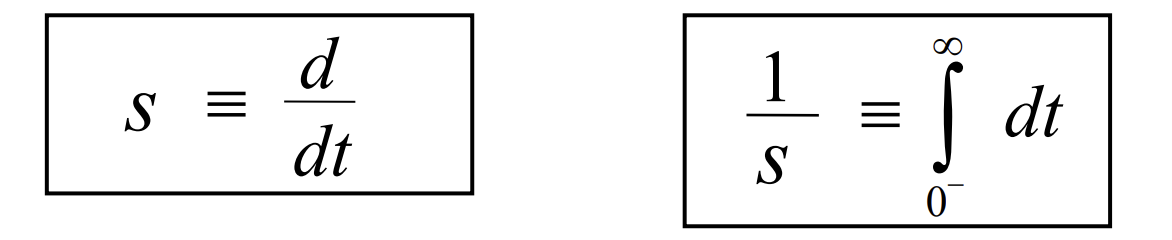
Laplace of derivative and integral
Basic transfer function system

Calcuating >1 resistor, inductor and capacitor relationship

Equation for damping force

Standard form transfer function of first order systems
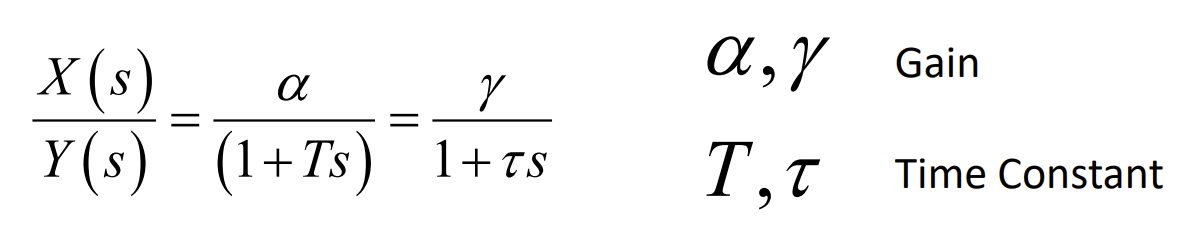
Standard form transfer function of second order system
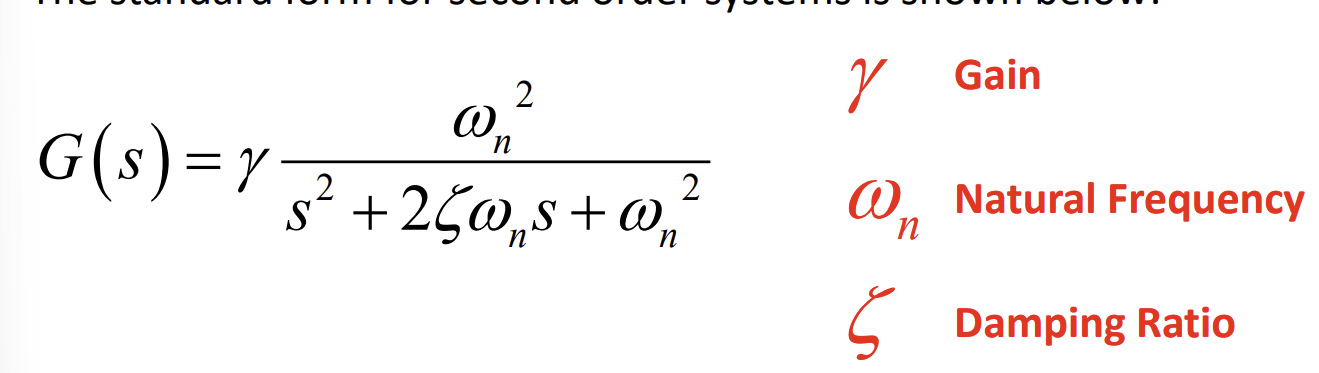
time domain of a second order transfer function
assuming its underdamped
Input functions

Characteristics of first order system step response
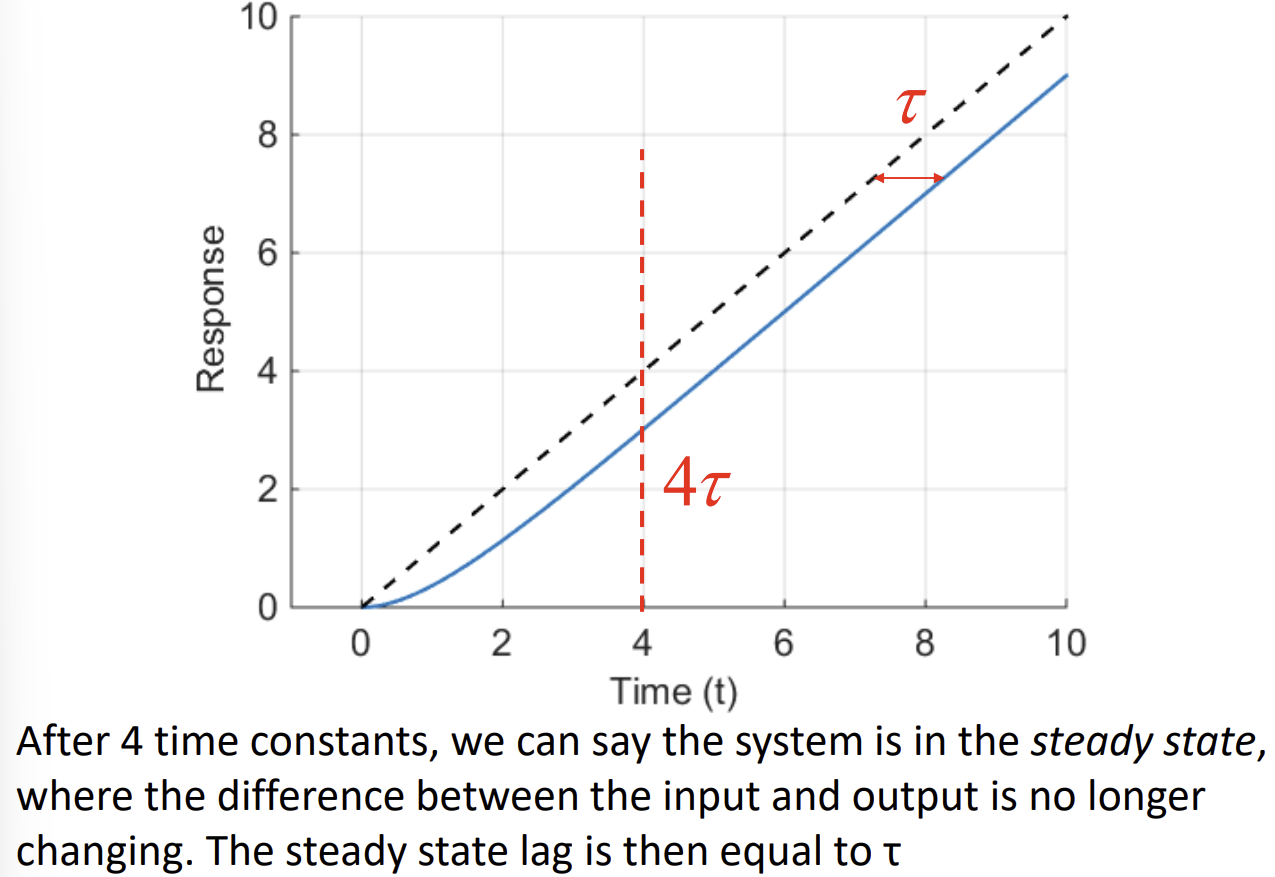
Characteristics of first order system ramp response
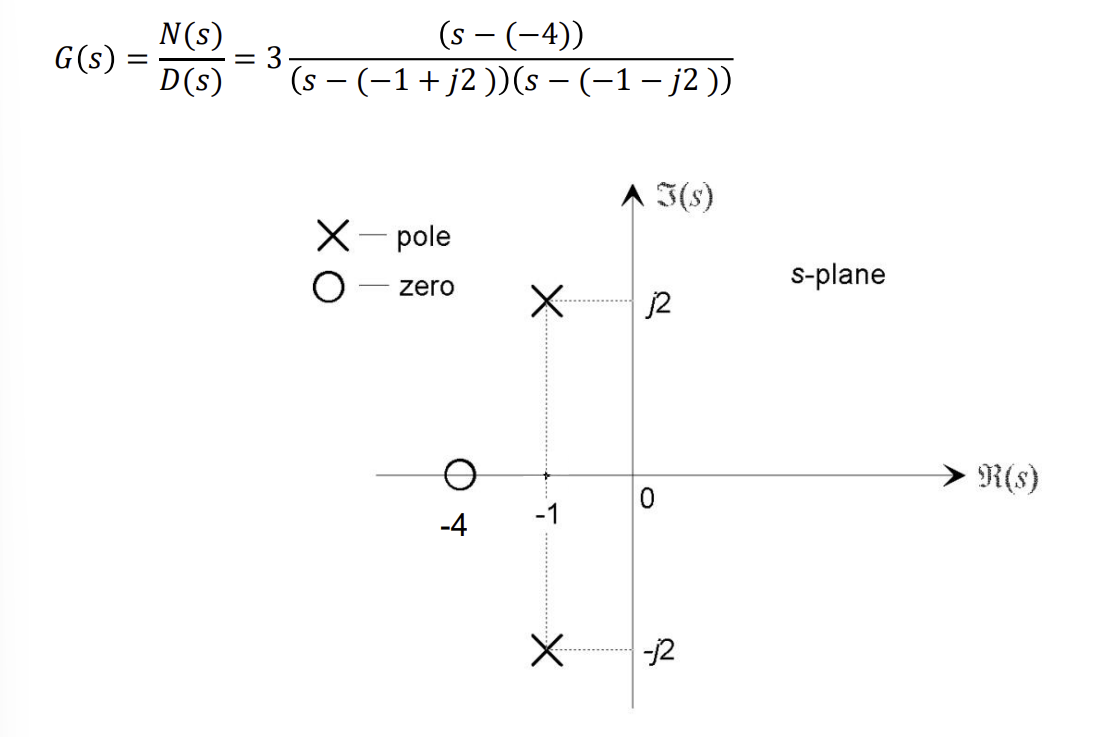
Definition of poles and zeros
roots of transfer function
numerator: zeros
denominator: poles
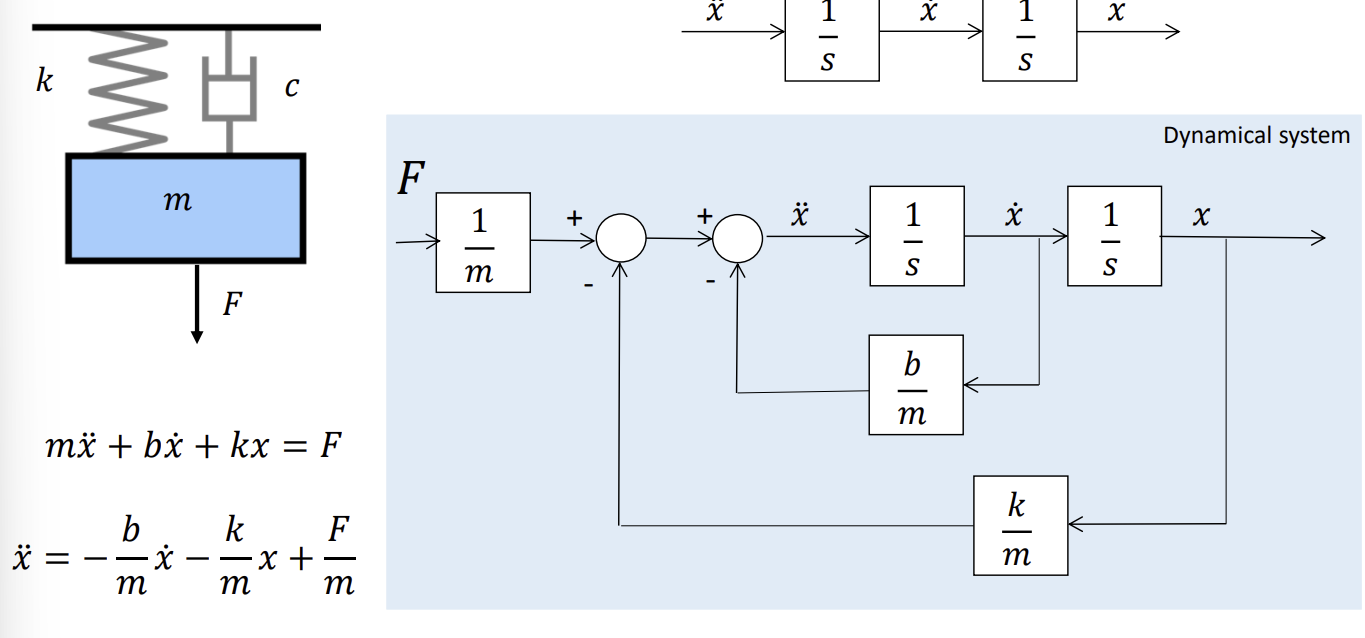
Block diagram for this system
Characteristic of an underdamped 2nd order system
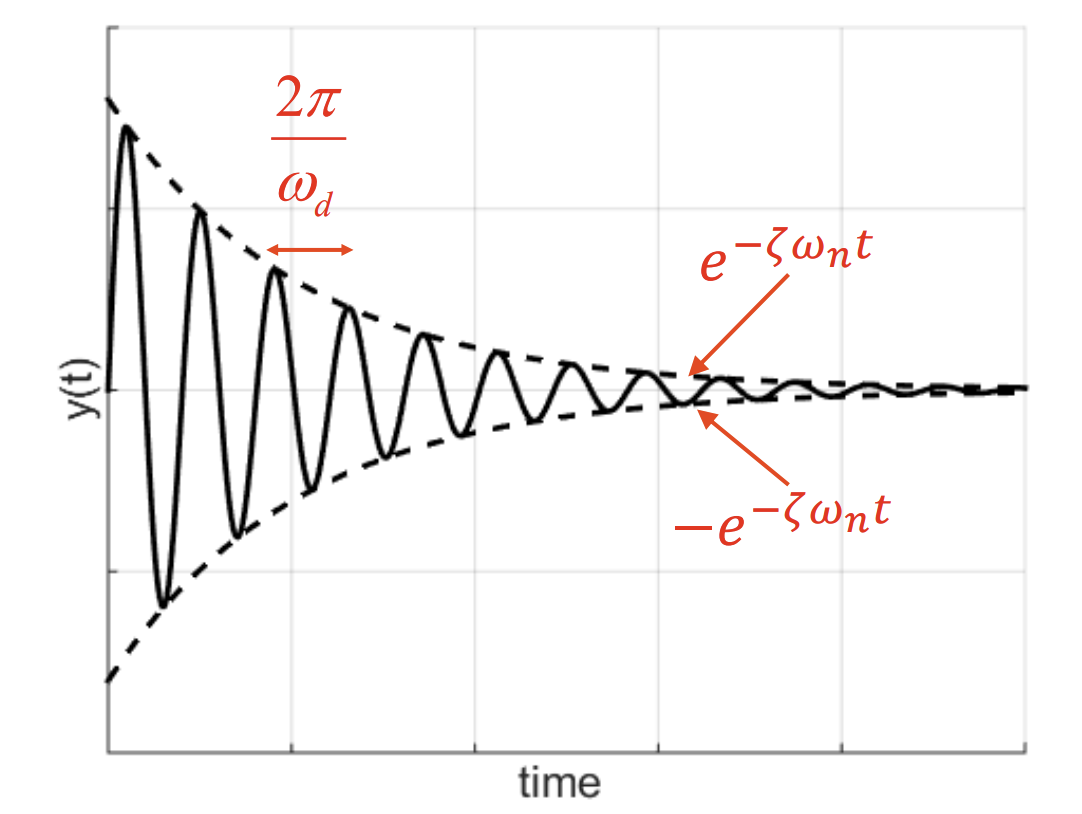
Relationship between damping ratio and characteristic equation of s

Characteristics of critically damped 2nd order system
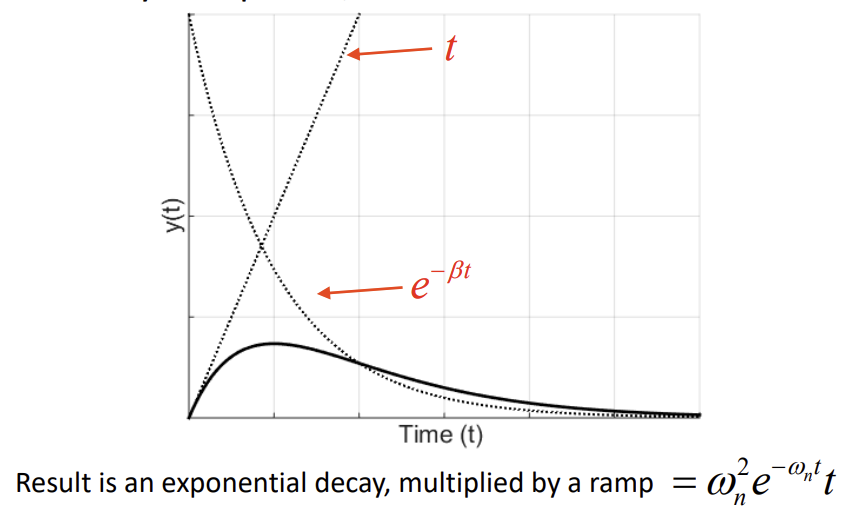
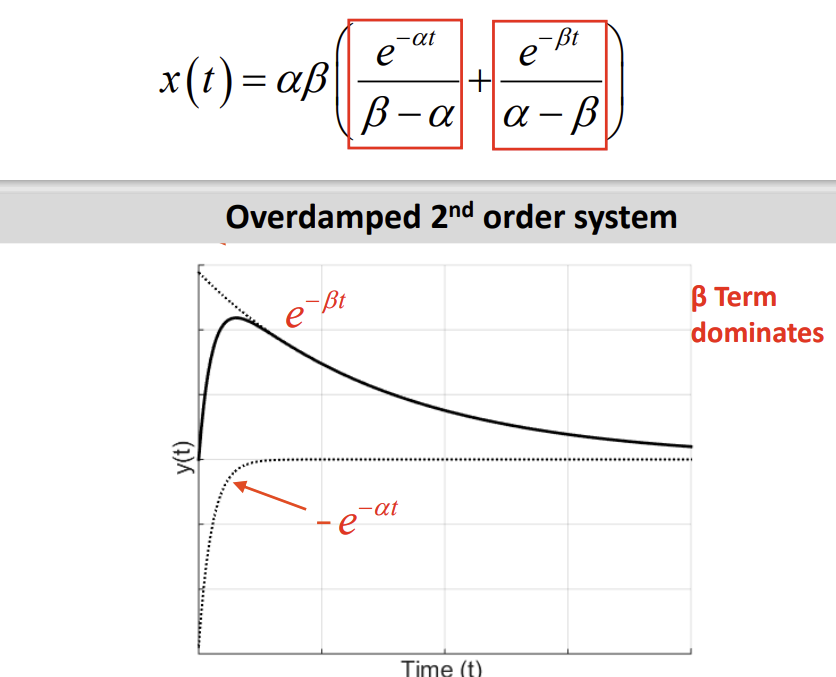
Characteristic of a overdamped 2nd order system
right most pole dominates response
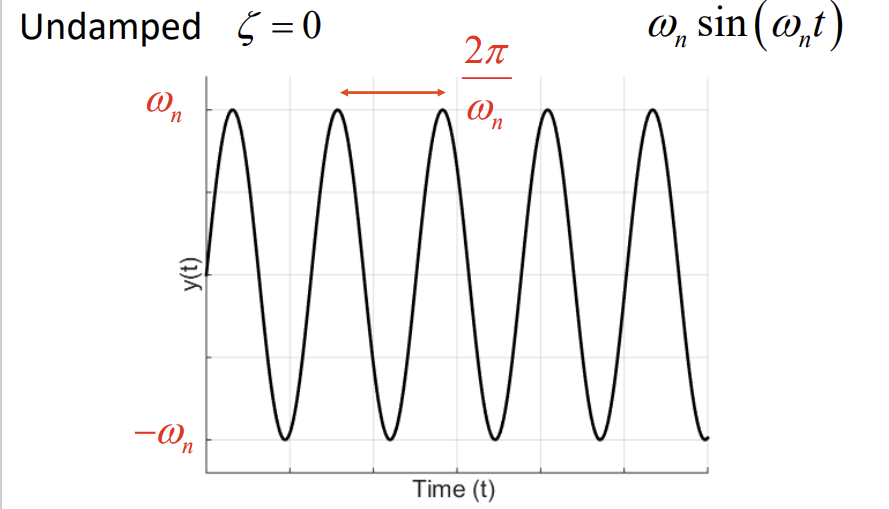
Characteristic of an undamped 2nd order system
Definition and formula of rise time
Time to reach steady state value (for first time)
can be read from graph
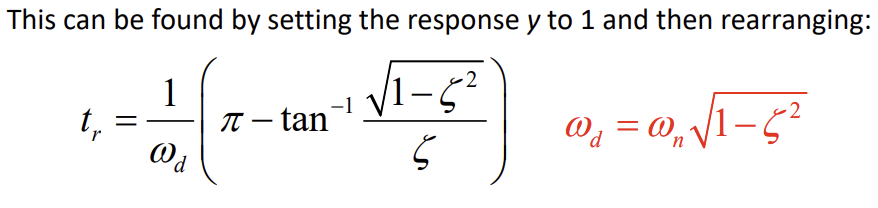
Definition and formula of peak time
Time where y value is maximum
occur at T/2
or dydt=0 for the first maximum value
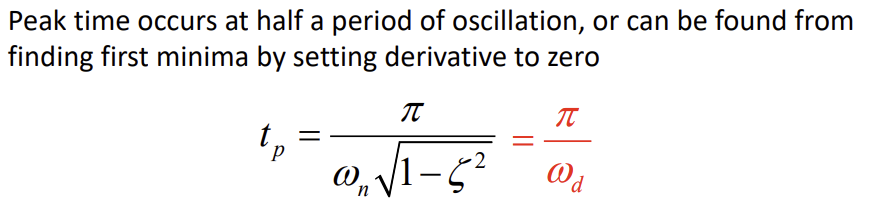
Definition and formula of overshoot
y(t_p)-t(t_ss)
can be rearranged to find damping ratio required for overshoot
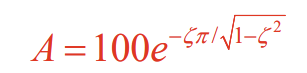
Definition and formula of settling time
time where y begins to settle around 2 or 5% of its SS value

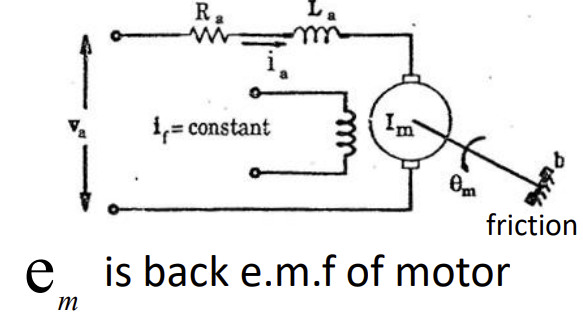
Calculation of voltage in a circuit in laplace
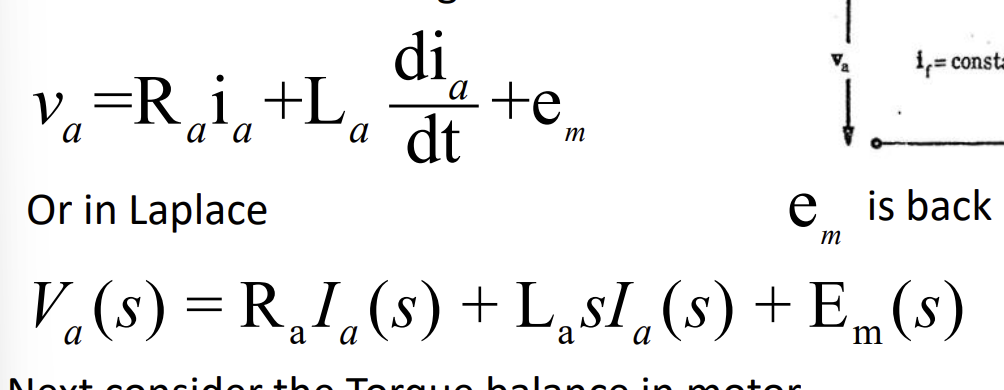
Calculation of torque in a motor, with friction b and inertia I
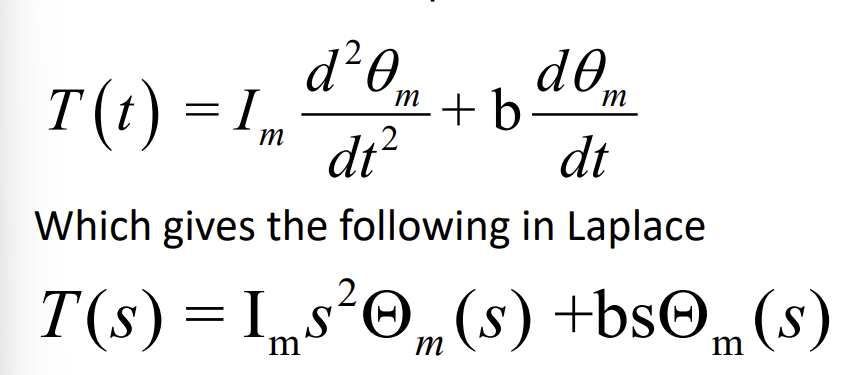
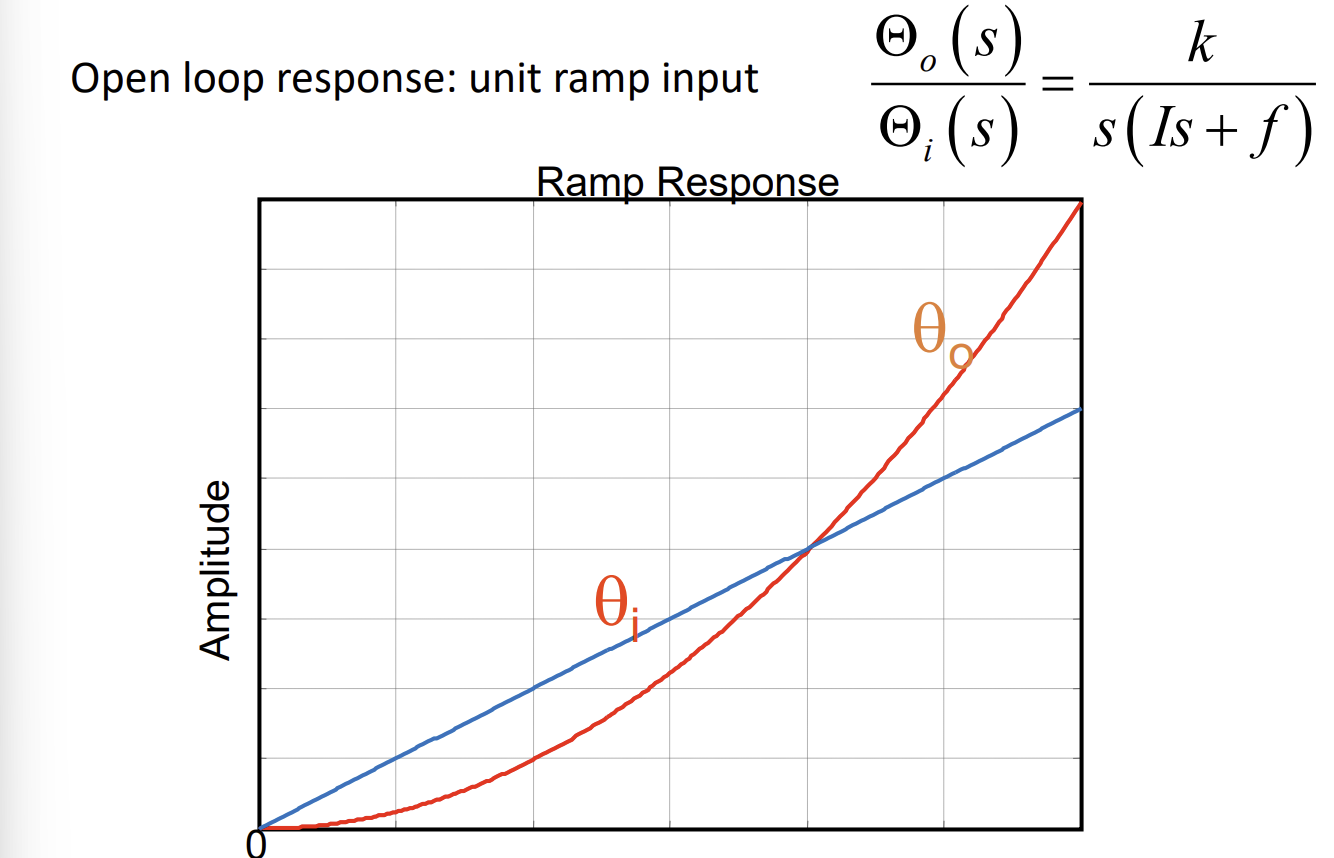
Ramp input for a first order system*s
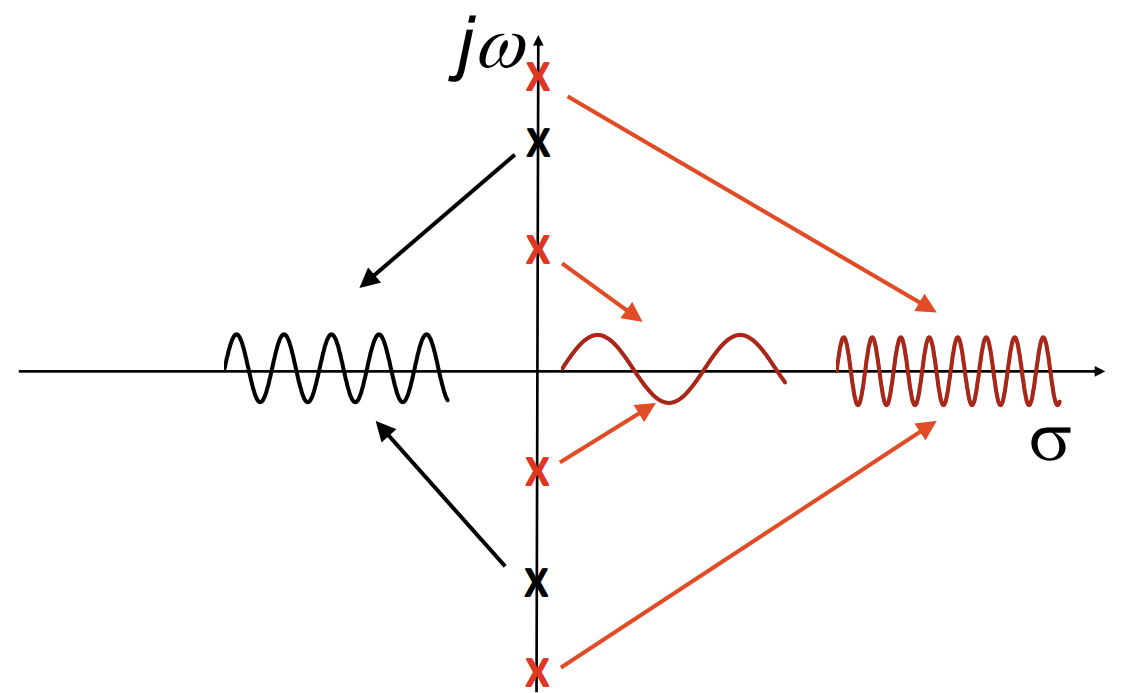
changes in graph in s plane, through the real axis
larger magnitude→ faster increase or decay
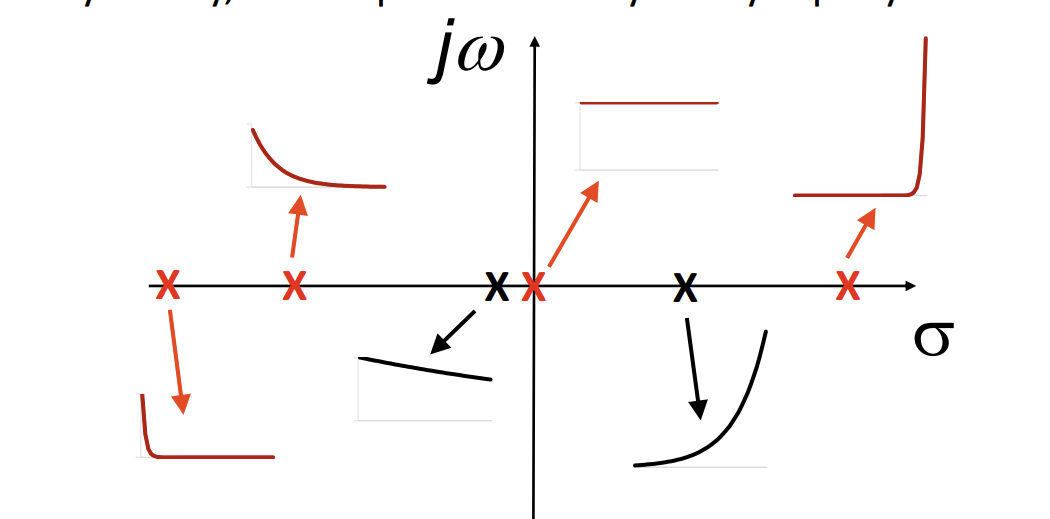
changes in graph in s plane, through the imaginary axis
larger magnitude-smaller period
Final Value Theorem
final value reached when t→ infinity
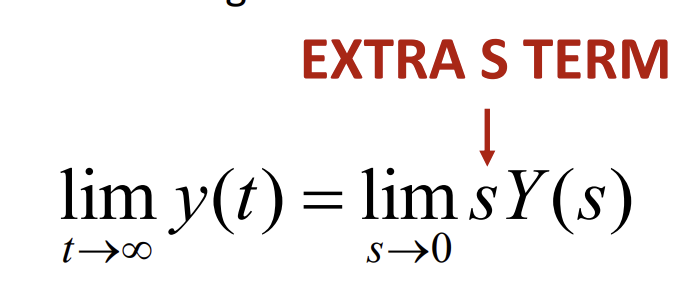
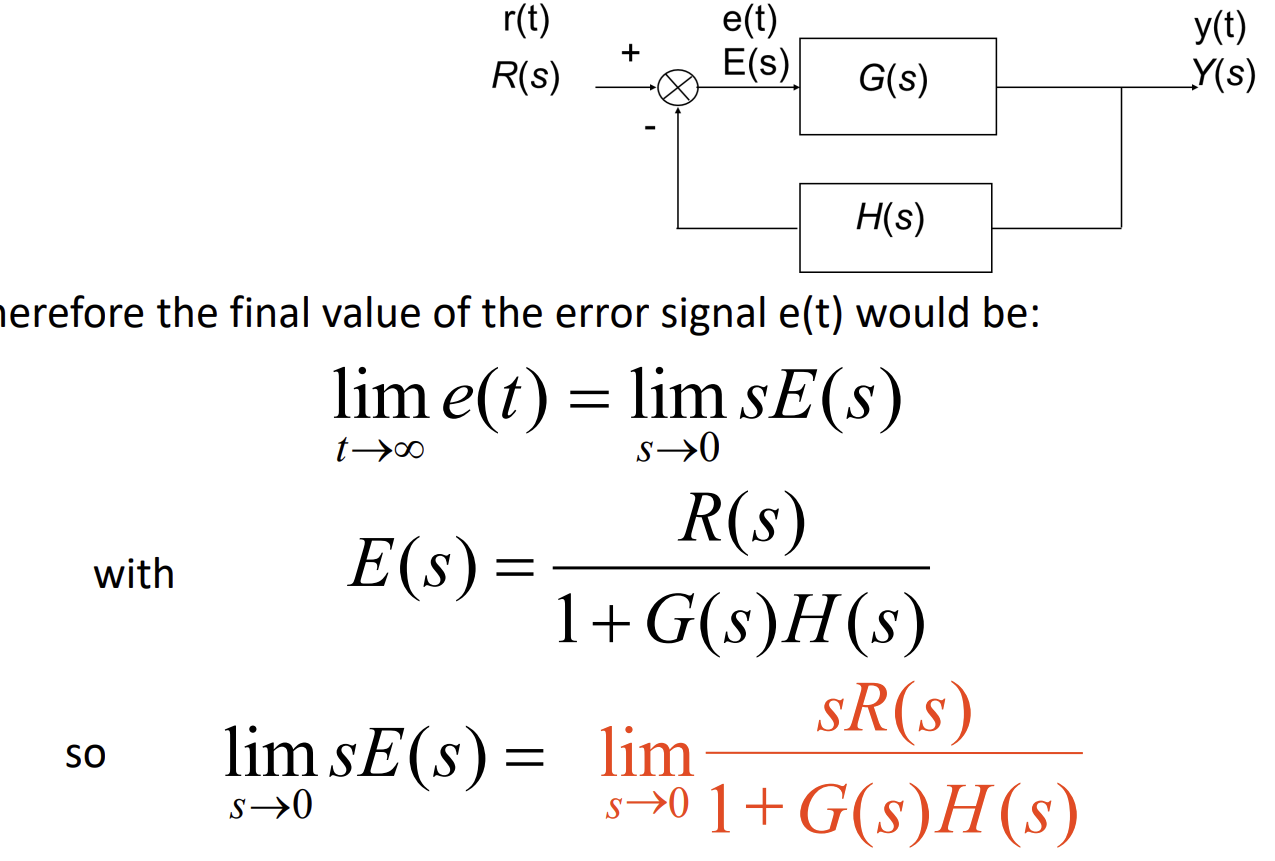
Equation to find final value of steady state error
Steady state position error formula
SSE for step input
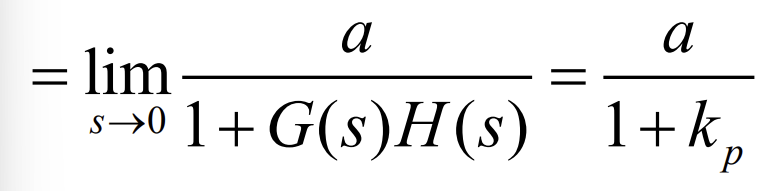
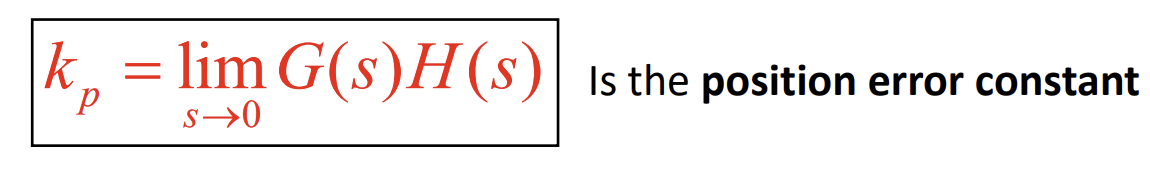
Formula of position error constant
amount of steady state error of the system when stimulated by a unit input
Definition and formula of steady state velocity lag
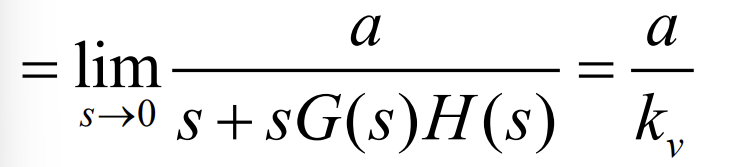
Formula and definition of velocity error constant
amount of steady state error when the system is stimulated with a ramp input

Determining system type
depends on number of poles at origin
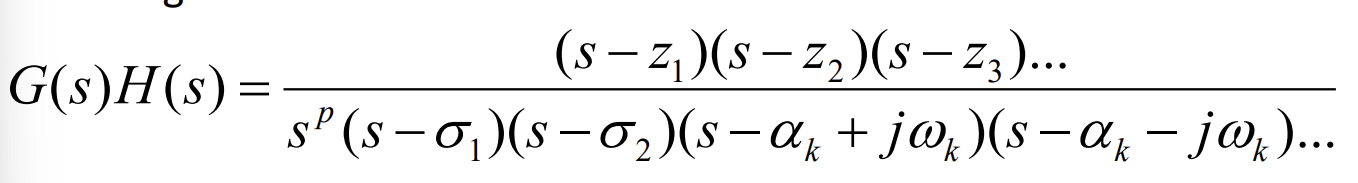
Relationship of pole with SSE

Relationship of proportional gain to behaviour of system
adjust system to reach steady state as soon as possible
inertia leads to large overshoot
Relationship of derivative gain to behaviour of system
Improve transient response by resisting overshoot
SSVL remain unchanged
Relationship of integral gain to behaviour of system
decrease or remove SSE
increase type (P+1)

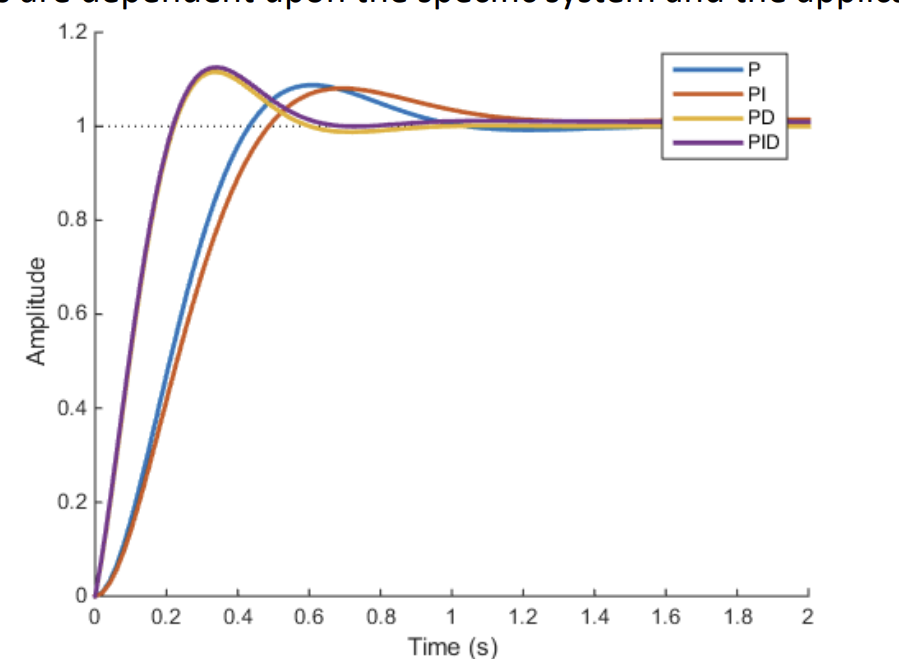
Observation of each gain
PI
little effect on transient response
as it is a type one system with step input, already has no steady state
PD
improve transient response
allow greater proportional gain to be used while still minimising overshoot