APES Unit 4: Earth Systems and Resources
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Key terms to know for AP Environmental Science Unit 4: Earth Systems and Resources.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
core
dense mass of solid nickel, iron, and radioactive elements that release massive amounts of heat
mantle
liquid layer of magma surrounding core, kept liquified from core’s intense heat
asthenosphere
solid, flexible outer layer of mantle
lithosphere
thin, brittle layer of rock floating on top of mantle
crust
earth’s surface, very outer layer of lithosphere
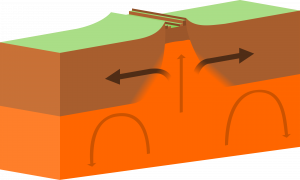
divergent boundary
plates move away from each other bc of magma rising
forms mid-oceanic ridges, volcanoes, seafloor spreading, rift valleys
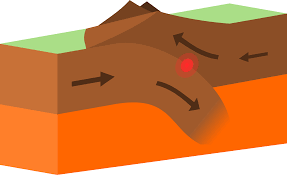
convergent boundary
plates move toward each other, leads to subduction
forms mountains, island arcs, earthquakes, volcanoes
transform boundary
plates slide past each other in opposite directions
forms earthquakes

oceanic-oceanic subduction zone
one oceanic plate subducts under another
forms mid-ocean volcanoes, island arcs, off-shore trenches
oceanic-continental subduction zone
oceanic plate subducts under continental plate, melts back into magma
forms coastal mountains, volcanoes on land, trenches, tsunamis
continental-continental subduction zone
one continental plate subducts under another, forces surface crust up
forms mountains
Ring of Fire
pattern of volcanoes all around Pacific plate

hotspots
areas of hot magma constantly rising up to lithosphere
soil
mix of geological and organic components
humus
main organic part of soil, broken down organic matter
weathering
breakdown of rocks in 3 ways (physical, biological, chemical), forms soil
erosion
transport of weathered rock carried by wind and rain
parent material
sometimes called bedrock, rock that underlies soil
O-horizon
layer of organic matter on top of soil
provides nutrients and limits H2O loss to evaporation
A-horizon
topsoil, layer of humus from parent material
has most biological activity, breaking down organic matter
B-horizon
subsoil, lighter layer below topsoil
contains some nutrients, little to no organic matter
C-horizon
least weathered soil closest to parent material
most intact rock
soil degradation
loss of ability of soil to support plant growth
compaction
compression of soil by machines, grazing livestock, and humans
nutrient depletion
repeatedly growing crops on same soil, removing key nutrients over time
soil texture
% of sand, silt, and clay in soil, always adds up to 100%
porosity
amount of pore space a soil has
permeability
water’s ability to drain through soil
H2O holding capacity
how well water is retained/held by soil
troposphere
0-16 km, change in weather occurs here, most dense, temp decreases
stratosphere
16-60 km, thickest layer of O3 here, absorbs UV rays, temp increases
mesosphere
60-80 km, even less dense, coldest place on Earth, temp decreases
thermosphere
80-800 km, hottest place on Earth, absorbs x-rays, temp increases
Coriolis effect
makes objects traveling long distances around Earth appear to move at a curve rather than straight line due Earth’s spin
watershed
body of land that drains into a body of water
Chesapeake Bay Watershed
6 state region that drains into a series of streams/rivers and eventually into Chesapeake Bay
cover crops
a buffer plant to hold soil in place, prevents runoff
topographic map
2D representation of 3D space, each line represents elevation
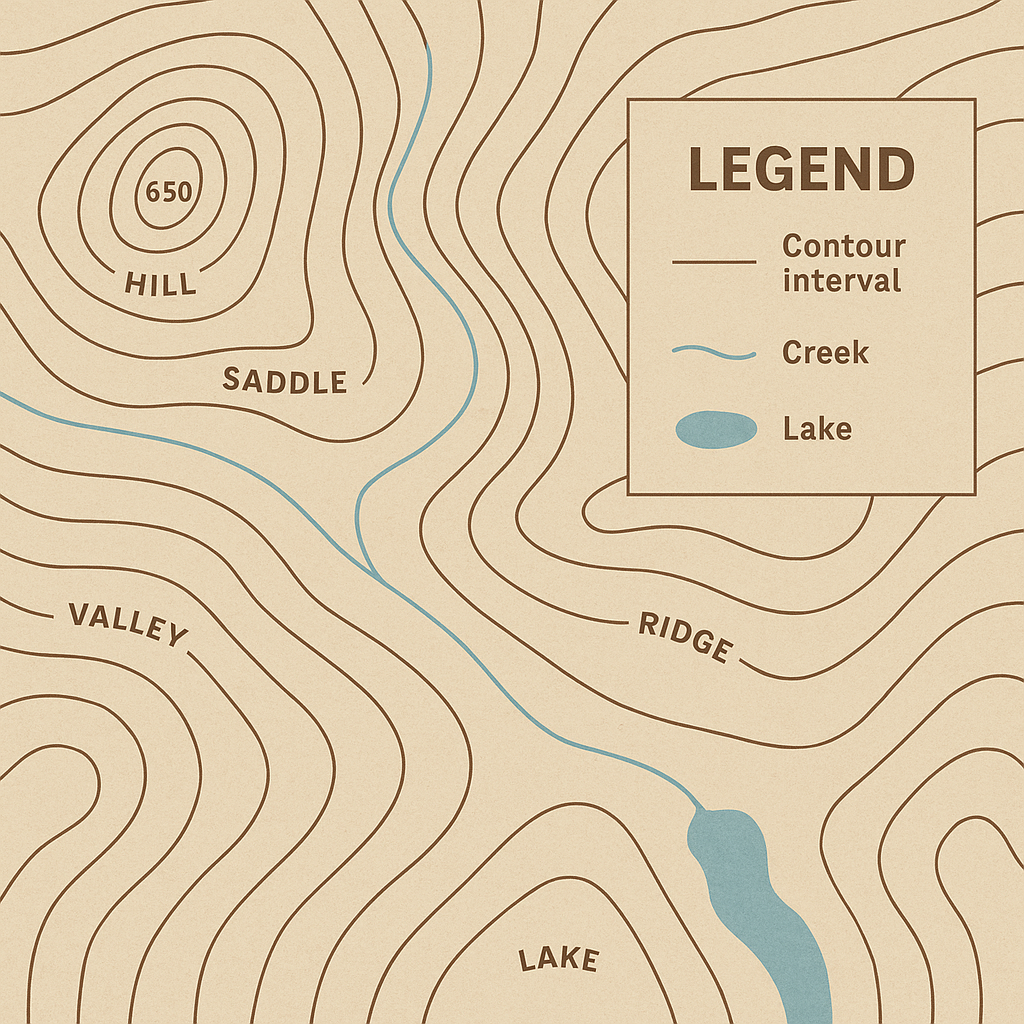
elevation
distance above sea level
relief
distance between point A and point B
insolation
amount of solar radiation reaching an area, measured in Watts/m²
latitude
distance from equator
solstice
North or South hemispheres maximally tilted toward sun (Summer/Winter)
equinox
North and South hemispheres equally face sun
albedo
proportion of light that’s reflected by surface
urban heat island
urban areas are hotter than surrounding rural area
rain shadow effect
warm, moist air from ocean hits windward side of mountain, dry air descends down leeward side of mountain
gyres
large ocean circulation patterns due to global wind (clockwise North, counter South)
upwelling zones
areas of ocean where winds blow warm surface water away from land, drawing up colder, deeper water to replace
thermohaline circulation
connects all world’s oceans, mixing salt, nutrients, and temp
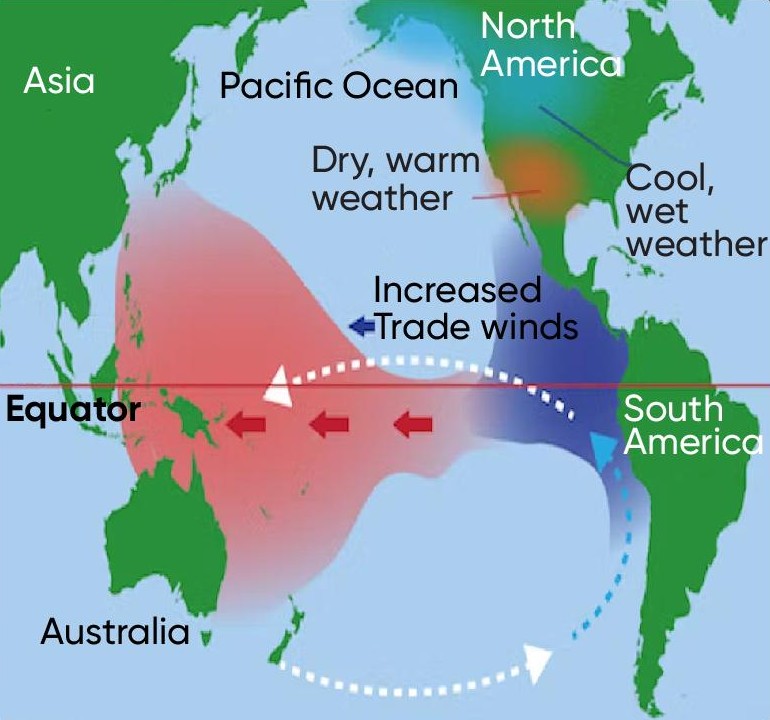
El Nino Southern Oscillation
pattern of shifting atmospheric pressure and oceancurrents in Pacific between South Amer and Australia/Southeast Asia
normal year
trade winds blow hot equator water W ← E, productive fisheries
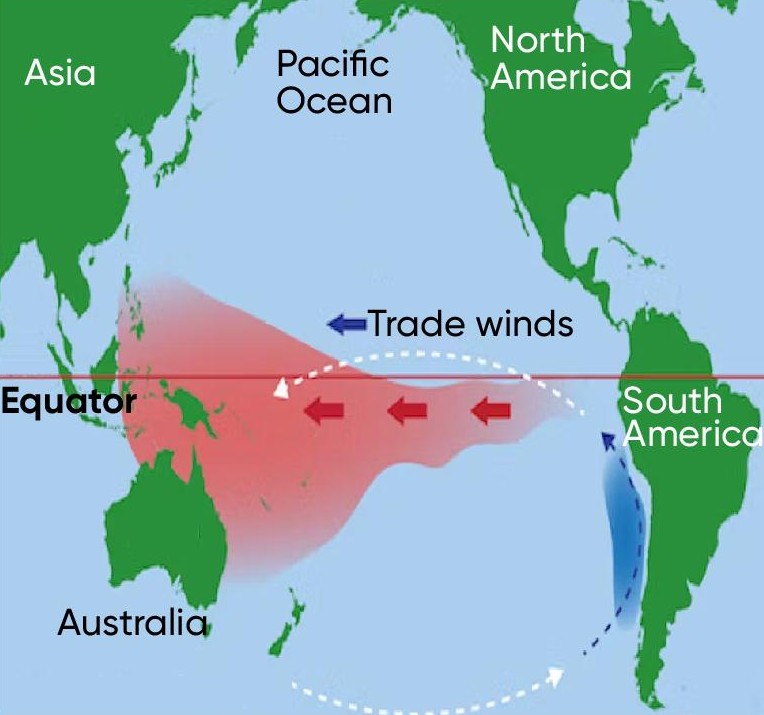
El Niño year
trade winds weaken and reverse W → E, suppressed upwelling off South Amer coast, damaged fisheries
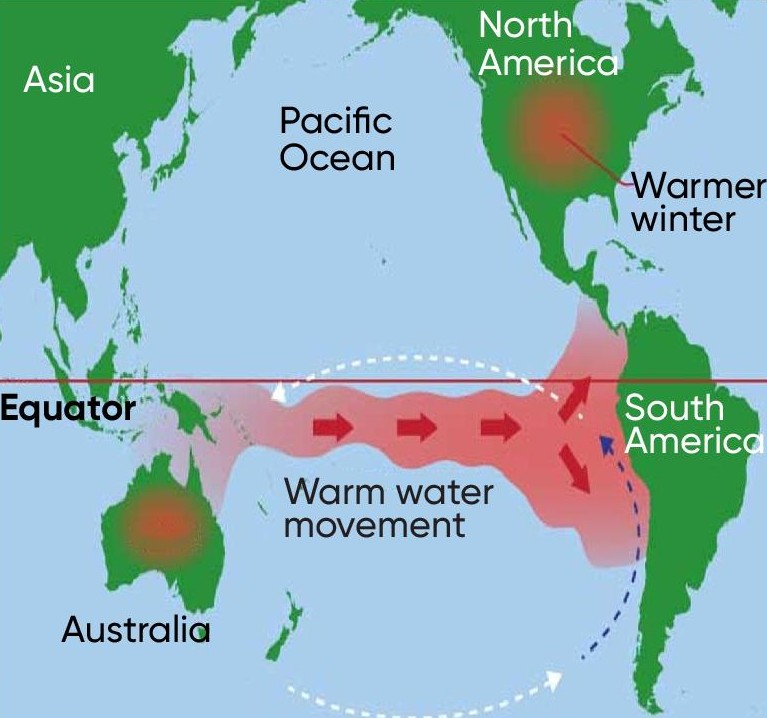
La Niña year
stronger than normal trade winds W ← E, increased upwelling off South Amer coast, productive fisheries