eukaryote organisms exam 1
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
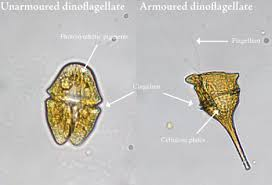
Dinoflagellates (algae)
Causes disease through release of toxins, including domoic acid, that are ingested from contaminated shellfish. Not an infection.
Disease characterized by nausea, diarrhea, cramps, memory loss.
Paralytic shellfish poisoning, characterized by general numbness, dizziness, muscle weakness, impaired breathing, death by respiratory failure.
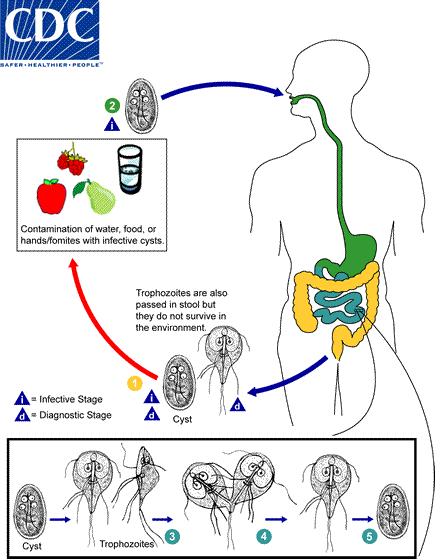
Giardia (protozoa)
Contracted from consumption of fecal contaminated water. Cyst form in environment.
Causes “campers” and “traveler’s diarrhea”.
Usually acute case of diarrhea, vomiting, and cramps lasting 1-4 weeks.
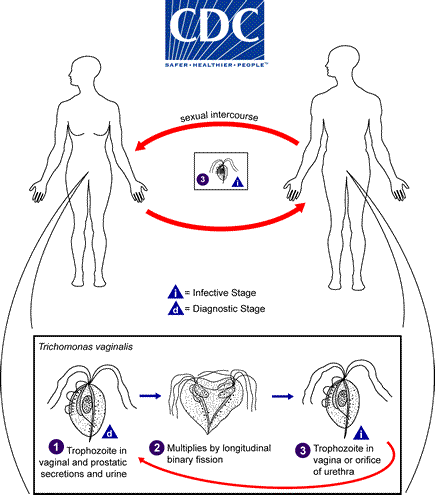
Trichomonas vaginalis (protozoa)
Flagellated organism that is transmitted through sexual contact.
Infected men are generally asymptomatic.
In women, disease characterized by itching vulva, inner thighs, and vagina, green-frothy discharge, burning with urination.
strawberry cervix
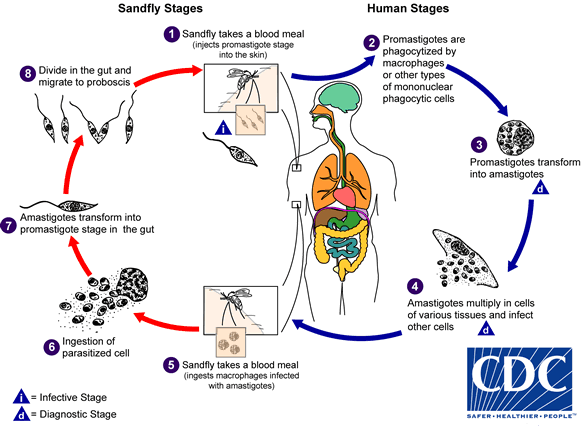
Leishmania (protozoa)
Organism transmitted through the bite of sandflies or other arthropods. Endemic in rodent populations.
Cutaneous infection produces circular sores.
The liver and spleen may be effected months to years after infection.
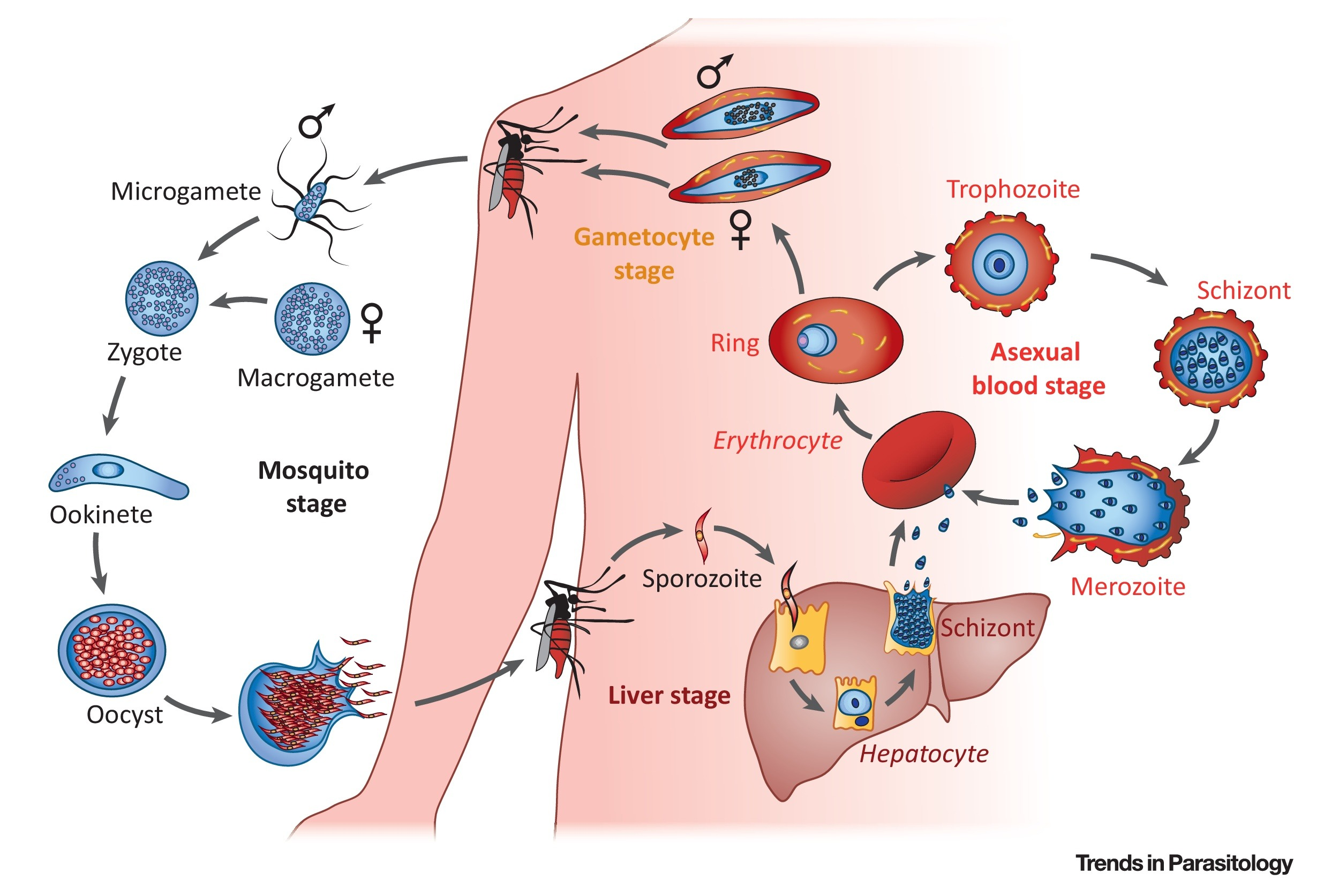
Plasmodium (protozoa)
Organism transmitted from person to person from the bite of infected mosquito.
Causes malaria, recurrent bouts of violent chills and fever.
Red blood cells are destroyed, causing spleen enlargement and oxygen deprivation.
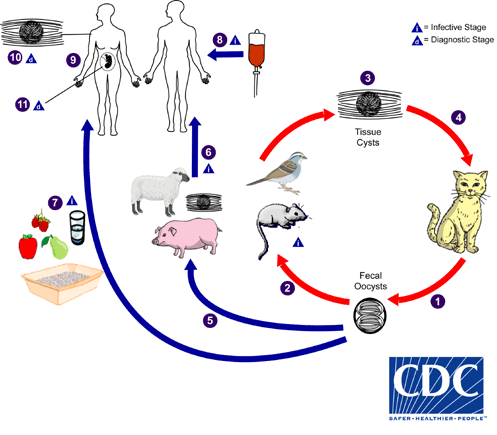
Toxoplasma gondii (protozo)
Organism infects most warm-blooded animals. Infection is acquired from exposure to cat feces or undercooked meat, turns into toxoplasmosis.
In healthy individuals, causes sore throat, fever, rash.
Fetal infections result in miscarriage, stillbirth, birth defects, epilepsy, mental retardation. (crosses placenta membrane)
Immunodeficient individuals may experience confusion, paralysis, seizures, and coma.
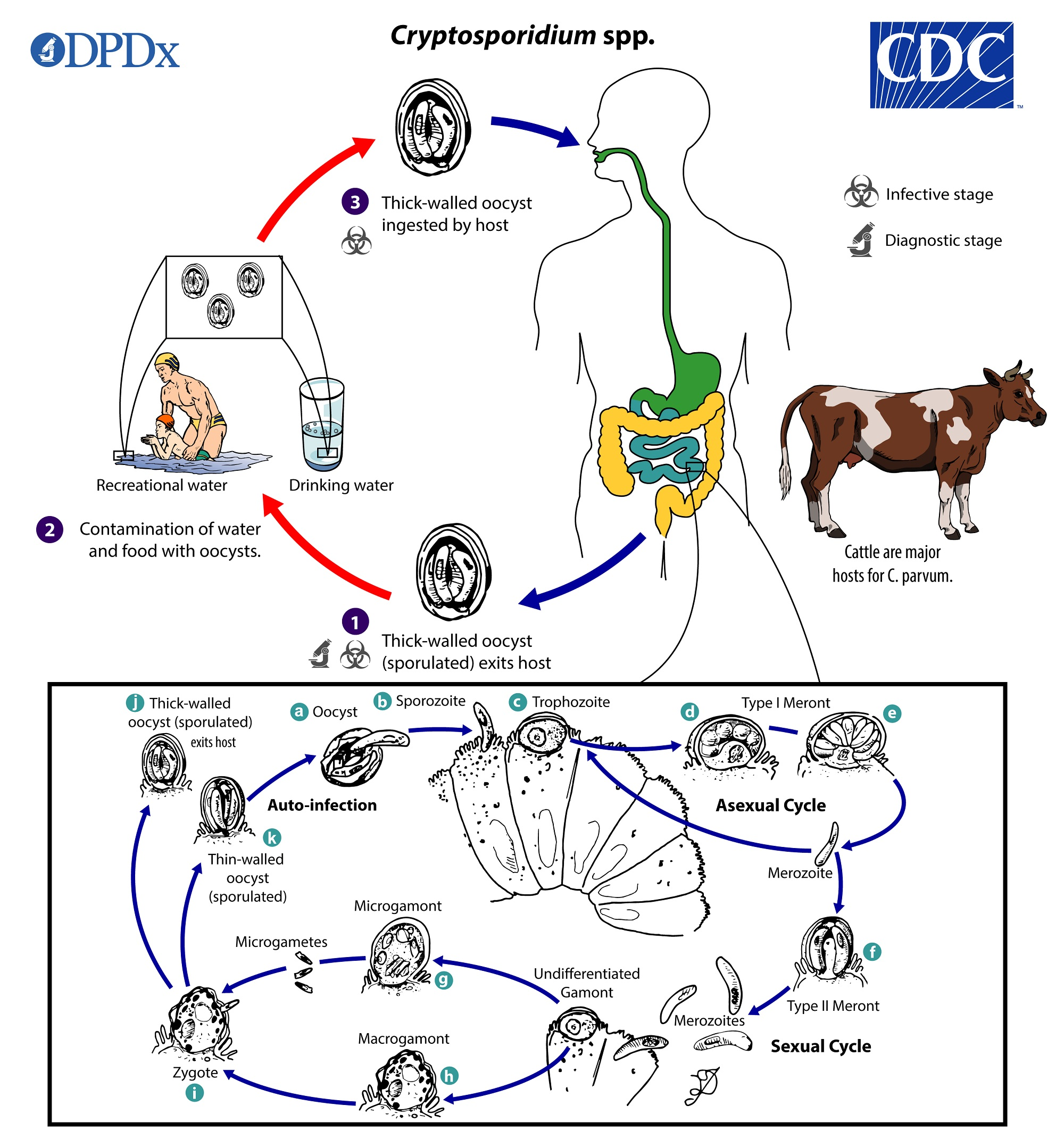
Cryptosporidium (protozoa)
Contracted from consumption of fecal contaminated water. Cyst form in environment.
Causes fever, nausea, cramps, and watery diarrhea for 1-2 weeks.
In immunodeficient individuals it may be life-threatening.
Candida albicans (fungi)
Yeast that forms pseudohyphae
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (“yeast-infection) occurs following disruption of normal microbiota. Symptoms are itching and burning with a whitish, curdlike discharge.
Causes thrush, an infection of the mucus membranes of the mouth and throat, in immunodeficient individuals.
Coccidioides immitis (fungi)
A dimorphic fungus found in soil in American southwest. Infection acquired through inhalation of spores.
Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever) produces fever, cough, chest pain, weight loss.
Sometimes pain in joints and nodules produced from immune response.
Cryptococcus neoformans (fungi)
An encapsulated yeast. Infection acquired by inhalation of spores (sometimes found in pigeon droppings)
Causes meningoencephalitis (inflammation of the brain and meninges) resulting in headache, vomiting, confusion, seizures, paralysis, coma, and death.
Histoplasma capsultum (fungi)
A dimorphic fungus found in soils contaminated by bat or bird droppings in central United States. Infection acquired through inhalation of spores.
Most infections are asymptomatic. Lung infection can cause fever, cough, and chest pain.
Granulomas form in lungs, mimicking Tuberculosis.
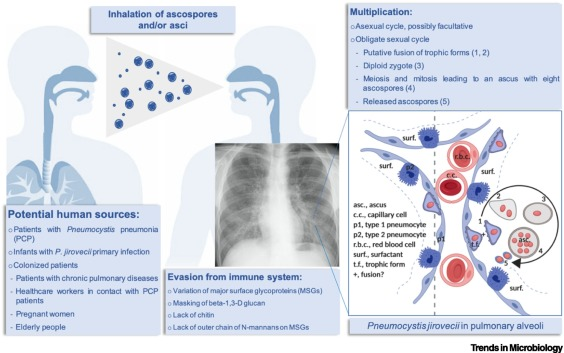
Pneumocystis jirovecii (fungi)
A tiny fungus. Cell wall differs chemically from most other fungi, making it resistant to common anti-fungal medications. Most likely transmitted through inhalation of spore.
Lung infection characterized by gradual increasing shortness of breath and rapid breathing, only mild fever, infrequent non-productive cough.
The leading opportunistic infection in AIDS patients.