Midterm - World Studies
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:53 AM on 1/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Chapter 7
The Middle Ages
2
New cards
Charlemagne
* Charles the Great
* King of Franks, the Lombards, and emperor of the Romans
* Strove to unite and govern diverse conquered people
* conducted a long series of successful military campaigns
* made efforts to spread Christianity and implement religious reform
* sought to make more effective inherited political institutions and procedures
* supported cultural renewal through a revival of learning
* King of Franks, the Lombards, and emperor of the Romans
* Strove to unite and govern diverse conquered people
* conducted a long series of successful military campaigns
* made efforts to spread Christianity and implement religious reform
* sought to make more effective inherited political institutions and procedures
* supported cultural renewal through a revival of learning
3
New cards
Feudalism
* A decentralized political and economic structure.
* was a loosely organized system of rule in which powerful local lords divided their landholdings among lesser lords
* was a loosely organized system of rule in which powerful local lords divided their landholdings among lesser lords
4
New cards
Fief (fief-holding)
Estates
5
New cards
Knights
mounted warrior
6
New cards
Lords
Noble who held land
7
New cards
Serfs
peasants who were bound to the land
8
New cards
Chivalry
A code of conduct that was adopted by knights
9
New cards
Manor System
The lord of the manor exercised legal and economic power over the peasants who lived on the estate
10
New cards
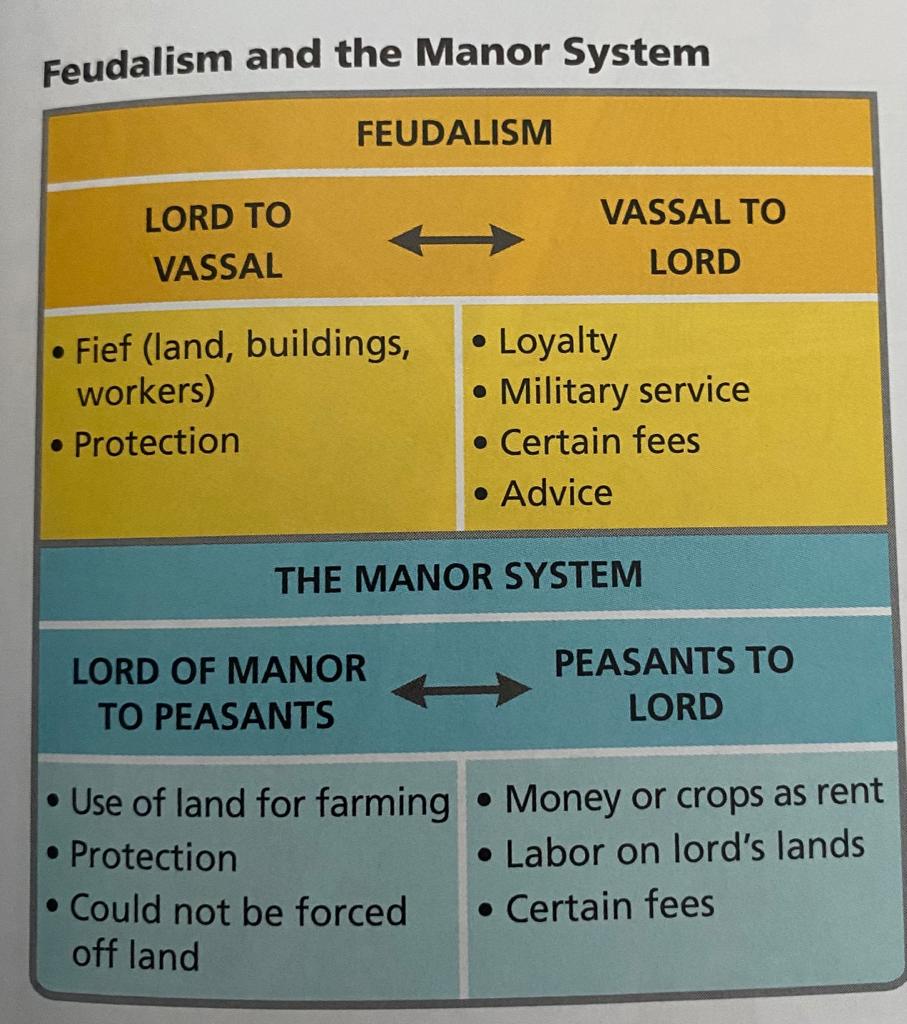
Describe and understand feudalism and manorialism.
Manorialism was an economic structure.
Feudalism was a social structure.
Feudalism was a social structure.
11
New cards
Great Schism
The permanent split between eastern and western Christianity
12
New cards
Monastery
A building occupied by a community of monks living under religious vows.
13
New cards
Crusades
A series of wars in which Christians battled Muslims for control of land in the middle east
14
New cards
What are the causes and results of the Crusades?
Causes: western European Christians (pope Urban 11) wanted to
* stop the expansion of Muslim states
* reclaim Christianity in the Holy Land in the Middle East
* recapture territories that had formerly been Christian. Religious idealism.
Effects
* bitter legacy of religious hatred
* increased trade in Europe and development of towns
* stop the expansion of Muslim states
* reclaim Christianity in the Holy Land in the Middle East
* recapture territories that had formerly been Christian. Religious idealism.
Effects
* bitter legacy of religious hatred
* increased trade in Europe and development of towns
15
New cards
William the Conqueror
* became duke on Normandy at 7
* was knighted at 15
* Pressured King Edward of England to name him heir to the throne
* Invaded England and won the throne after the battle of Hastings in 1066
* was knighted at 15
* Pressured King Edward of England to name him heir to the throne
* Invaded England and won the throne after the battle of Hastings in 1066
16
New cards
Magna Carta
The Great Charter was approved by King John of England in 1215; it limited royal power and established certain rights for English freemen
17
New cards
Scholasticism
used reason to support Christian beliefs
18
New cards
Flying Buttresses
Stone supports that stood outside the church
19
New cards
Black Death
an epidemic of the bubonic plague that ravaged Europe in the 1300s
20
New cards
Hundred Years War
* lasted from 1337 - 1453
* was a series of wars
* Causes
* long standing rivalry between England and France over lands in France
* Edward III of England claims the French throne
* Edward III’s armies invade france
* Effects
* English monarchy is weakened; french monarchy is strengthened
* Knights displaced as main fighting force; replaced with soldiers for hire
* Weapons become more technologically advanced
* was a series of wars
* Causes
* long standing rivalry between England and France over lands in France
* Edward III of England claims the French throne
* Edward III’s armies invade france
* Effects
* English monarchy is weakened; french monarchy is strengthened
* Knights displaced as main fighting force; replaced with soldiers for hire
* Weapons become more technologically advanced
21
New cards
Chapter 8
The Muslim Empires
22
New cards
Akbar
* 1542-1605
* extended the Mughal empire over most of europe
* maintained an efficient centralized government through policies that won the loyalty of non-muslim subjects
* extended the Mughal empire over most of europe
* maintained an efficient centralized government through policies that won the loyalty of non-muslim subjects
23
New cards
Suleiman the Magnificent
* Ruled from 1520-1566
* Extended the Ottoman rule eastward into the Middle East
* advanced deeper into Europe through a diplomacy and warfare
* brought bureaucracy and stability to the empire
* advanced the arts, law, and architecture
* Extended the Ottoman rule eastward into the Middle East
* advanced deeper into Europe through a diplomacy and warfare
* brought bureaucracy and stability to the empire
* advanced the arts, law, and architecture
24
New cards
Janissaries
The elite force of the ottoman empire
25
New cards
Shah Abbas the Great
* was Shah of the Safavid dynasty from 1588-1629
* drove ottoman and Uzbek troops from persia
* sponsored the golden age of persian arts and achievements
* drove ottoman and Uzbek troops from persia
* sponsored the golden age of persian arts and achievements
26
New cards
Isfahan
Capital of safavid empire during the 1600s
27
New cards
5 Pillars of Islam

28
New cards
Chapter 9
East Asia (Isolationism in China and Japan)
29
New cards
Taj Mahal
The building of the magnificent tomb
30
New cards
Daimyo
A great warrior lord
31
New cards
Tokugawa Shogunate
* was centralized feudalism
* was a unified, orderly, controlling society
* controlled daimyos
* alternate attendance system
* was a unified, orderly, controlling society
* controlled daimyos
* alternate attendance system
32
New cards
Zheng He
* was an admiral in the Ming Chinese navy and a diplomat
* Between 1405 and 1433, he made 7 expeditions, exploring and trading goods
* Between 1405 and 1433, he made 7 expeditions, exploring and trading goods
33
New cards
Chapter 10
Renaissance, Reformation, and the Scientific Revolution
34
New cards
Renaissance
The transition between medieval and early modern times
35
New cards
Humanism
an intellectual movement at the heart of the renaissance that focused on education and the classics
36
New cards
Francesco Petrarch
* was an early renaissance humanist, poet, and scholar
* assembled a library of Greek and Roman manuscripts gathered from monasteries and churches
* preserved these classic works for future generations
* assembled a library of Greek and Roman manuscripts gathered from monasteries and churches
* preserved these classic works for future generations
37
New cards
Perspective
artistic technique used to give paintings and drawings a three- dimensional effect
38
New cards
Sir Thomas More
* was a lawyer, scholar, writer, and member of British parliament during the reign of Henry VIII
* wrote *Utopia*
* described an ideal society
* wrote *Utopia*
* described an ideal society
39
New cards
Johannes Gutenberg
* was a goldsmith, printer, and publisher
* around 1455, he printed the first compete edition of the Christian bible using his press
* around 1455, he printed the first compete edition of the Christian bible using his press
40
New cards
Martin Luther
A German monk and professor of theology.
41
New cards
Secularism
Having nothing to do with worldly, rather than religious, matters; nonreligious
42
New cards
Catholic Reformation
Reform movement that took hold within the Catholic church, because of corruption within the church.
43
New cards
Society of Jesus (Jesuits)
Religious order found by Ignatius of Loyola, dedicated to combating heresy and spreading the Catholic Faith.
44
New cards
95 Thesis
Created by Martin Luther, Challenges the church
45
New cards
Witchcraft hysteria
In times of trouble people looked for the source and accused them of witchcraft.
46
New cards
John Calvin
Challenges the church, razor sharp mind, his ideas had a profound effect on the direction of the Protestant Revoulution.
47
New cards
Henry VIII
Second Tudor king of England, Constantly involved in wars and desire for a male heir was the catalyst for his break with the Roman Catholic Church and formation of the Church of England
48
New cards
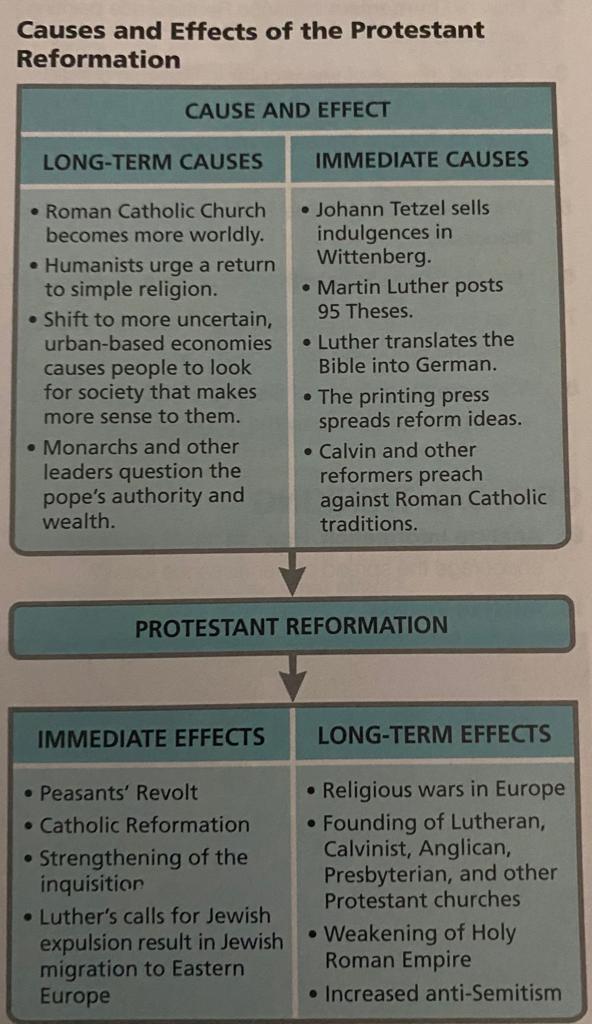
Causes and effects of the Protestant Reformation
49
New cards
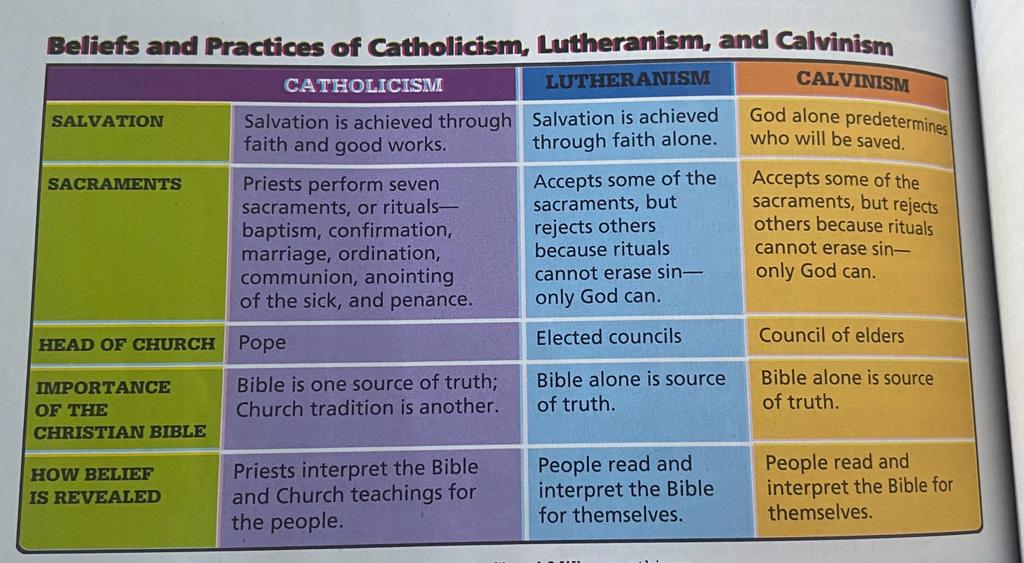
Catholicism, Lutheranism, and Calvinism
Catholicism
* the faith, practice, and church order of the Roman Catholic Church.
Lutheranism
* branch of Christianity that traces its interpretation of the Christian religion to the teachings of Martin Luther and the 16th-century movements that issued from his reforms.
Calvinism
* the Protestant theological system of John Calvin and his successors, which develops Luther's doctrine of justification by faith alone and emphasizes the grace of God and the doctrine of predestination.
* the faith, practice, and church order of the Roman Catholic Church.
Lutheranism
* branch of Christianity that traces its interpretation of the Christian religion to the teachings of Martin Luther and the 16th-century movements that issued from his reforms.
Calvinism
* the Protestant theological system of John Calvin and his successors, which develops Luther's doctrine of justification by faith alone and emphasizes the grace of God and the doctrine of predestination.
50
New cards
Scientific revolution
profound changes that led to new understandings about the physical world
51
New cards
Nicolaus Copernicus
* polish scholar
* published *On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres* in 1543
* He proposed a heliocentric model of the universe
* heliocentric = Sun-centered
* published *On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres* in 1543
* He proposed a heliocentric model of the universe
* heliocentric = Sun-centered
52
New cards
Tycho Brahe
* Danish Astronomer
* provided evidence to support Nicolaus Copernicus’s theory
* provided evidence to support Nicolaus Copernicus’s theory
53
New cards
Johannes Kepler
* German astronomer and mathematician
* used Brahe’s data to calculate the orbits of the planets revolving around the sun
* his data supported Copernicus’s heliocentric view but it also showed that each planet moves in an oval shape orbit
* oval shape orbit = ellipse
* used Brahe’s data to calculate the orbits of the planets revolving around the sun
* his data supported Copernicus’s heliocentric view but it also showed that each planet moves in an oval shape orbit
* oval shape orbit = ellipse
54
New cards
Galileo Galilei
* Used technology to assemble an astronomical telescope
* he observed that the 4 moons of Jupiter move slowly around that planet
* he observed that the 4 moons of Jupiter move slowly around that planet
55
New cards
Scientific method
a careful, step by step process used to confirm findings and to prove or disprove a hypothesis
56
New cards
Francis Bacon
* Englishman
* devoted himself to understanding how the truth was determined
* rejected Aristotle’s scientific assumptions
* argued that the truth is not known at the beginning of the inquiry but at the end, after a long process of investigation
* stressed experimentation and observation
* wanted science to make life better for people by leading to practical technologies
* devoted himself to understanding how the truth was determined
* rejected Aristotle’s scientific assumptions
* argued that the truth is not known at the beginning of the inquiry but at the end, after a long process of investigation
* stressed experimentation and observation
* wanted science to make life better for people by leading to practical technologies
57
New cards
René Descartes
* Frenchman
* devoted himself to understanding how the truth was determined
* rejected Aristotle’s scientific assumptions
* argued that the truth is not known at the beginning of the inquiry but at the end, after a long process of investigation
* wrote *Discourse on Method*
* explains how he decided to discard all traditional authorities and search for provable knowledge
* concluded that doubt was the only thing he could not question
* Famous statement - “I think, therefore I am”
* devoted himself to understanding how the truth was determined
* rejected Aristotle’s scientific assumptions
* argued that the truth is not known at the beginning of the inquiry but at the end, after a long process of investigation
* wrote *Discourse on Method*
* explains how he decided to discard all traditional authorities and search for provable knowledge
* concluded that doubt was the only thing he could not question
* Famous statement - “I think, therefore I am”
58
New cards
Andreas Vesalius
* published *On the Structure of the Human Body* in 1543
* was the first accurate and detailed study of human anatomy
* was the first accurate and detailed study of human anatomy
59
New cards
Robert Boyle
* English Chemist
* explained that all matter was composed of tiny particles that behave in knowable ways
* distinguished between individual elements and chemical compounds
* explained that all matter was composed of tiny particles that behave in knowable ways
* distinguished between individual elements and chemical compounds
60
New cards
Issac Newton
* developed the basis for calculus
* using mathematics, he showed that a single force keeps the planets in their orbits around the sun
* Force = gravity
* published *Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy* in 1687
* explained the law of gravity
* argued nature follows uniform laws
* said all motion in the universe can be measured and described mathematically
* using mathematics, he showed that a single force keeps the planets in their orbits around the sun
* Force = gravity
* published *Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy* in 1687
* explained the law of gravity
* argued nature follows uniform laws
* said all motion in the universe can be measured and described mathematically
61
New cards
Chapter 11
Age of Exploration
62
New cards
Columbian Exchange
Columbus brought 1,200 settlers and a collection of European animals and plants to the Americas, sparking the exchange.
63
New cards
Treaty of Tordesillas
Dividing the non-European world into two zones. Between Spain and Portugal.
64
New cards
Atlantic Slave Trade
Buying enslaved Africans for labor and trading them overseas.
65
New cards
Mercantilism
Economic policy, aimed at strengthening their national economies.
66
New cards
Bartolome de Las Casas
Bold priest, condemned the evils of the encomienda system.
67
New cards
Conquistador
Spanish Conquerors, who soon arrived in the Americas continued Columbus ruthless pattern.
68
New cards
Prince Henry
Henry the Navigator, The seizing of the North African coast sparked the imagination of him.
69
New cards
Francisco Pizarro
an adventurer, and explorer that beat the Incas.
70
New cards
Christopher Columbus
Italian Navigator from the Port of Genoa, wanted to reach the East Indies
71
New cards
Chapter 12
Absolutism and Revolution
72
New cards
Absolutism
The political theory that one ruler should hold all power within the boundaries of a country~~,~~ free from any constitutional restraint or limitation
73
New cards
Divine Right
The idea that God created the monarch and that the monarch acted as God's representative on earth
74
New cards
Causes of Absolutism
1. Religious and territorial conflicts created fear and uncertainty
2. Due to warfare, governments built large armies and placed high taxes on the peasant population
3. Poor economic conditions (taxes) and food shortages (little ice age) resulted in peasant revolts
75
New cards
Edict of Nantes
Granted Huguenots religious toleration and other freedoms.
76
New cards
Louis XIV
* Believed it was his divine right to rule
* Strengthened the state
* Appointed wealthy middle-class men to gov. jobs
* limited the influence of nobles
* expanded the bureaucracy
* Appointed Intendants
* Under him, the French Army became the strongest in Europe
* Versailles
* Strengthened the state
* Appointed wealthy middle-class men to gov. jobs
* limited the influence of nobles
* expanded the bureaucracy
* Appointed Intendants
* Under him, the French Army became the strongest in Europe
* Versailles
77
New cards
Philip II of Spain
* Expanded Spanish influence
* Strengthened the catholic church through wars
* Made his own power absolute
* Escorial A Spanish monastery and palace built by Philip II)
* Strengthened the catholic church through wars
* Made his own power absolute
* Escorial A Spanish monastery and palace built by Philip II)
78
New cards
Versailles
* A palace built by Louis XIV outside of Paris
79
New cards
Peter the Great
* Tsar of Russia
* Was one of Russia's greatest statesmen, organizers, and reformers
* The Grand Embassy
* Embarked on a policy of Westernization
* Became the most autocratic of Europe's absolute monarchs
* Was one of Russia's greatest statesmen, organizers, and reformers
* The Grand Embassy
* Embarked on a policy of Westernization
* Became the most autocratic of Europe's absolute monarchs
80
New cards
The Grand Embassy
was a Russian diplomatic mission to Western Europe to learn about western technology in 1697-1698
81
New cards
The Glorious Revolution
The bloodless overthrow of king James II by his protestant daughter Mary and her Dutch protestant husband William III of Orange.
82
New cards
English Bill of Rights
Ensured the superiority of Parliament over the Monarchy
83
New cards
Enlightenment
A new intellectual movement that stressed reason and thought and the power of individuals to solve problems. Also known as the Age of Reason.
84
New cards
Age of Reason
Philosophers sought new ideas on government, economics, religion, education, and society. They also fought against religion, the hereditary aristocracy (nobility), and absolutism. They believed human reason could be used to fight ignorance, superstition, and tyranny
85
New cards
5 Core concepts of the Enlightenment
1. Reason
1. Believed truth could be discovered through logical thinking
2. Nature
1. what was natural was also good and reasonable
3. Happiness
1. Rejected medieval notion that people should find joy in the hereafter and urged people to seek well-being on earth
4. Progress
1. Stressed that society and human kind could improve
5. Liberty
1. Called for liberties that the English people had won in the Glorious Revolution and the English Bill of Rights
86
New cards
Natural Laws
unchanging principle, discovered through reason, that governs human conduct
87
New cards
Thomas Hobbes
* English thinker who wrote Leviathan in 1651.
* argued people were naturally cruel, greedy, and selfish
* To escape it, people entered into a social contract (people gave up their freedom for an organized lifestyle)
* He believed that only a powerful government, such as an absolute monarchy, could ensure an orderly society.
* argued people were naturally cruel, greedy, and selfish
* To escape it, people entered into a social contract (people gave up their freedom for an organized lifestyle)
* He believed that only a powerful government, such as an absolute monarchy, could ensure an orderly society.
88
New cards
Baron de Montesquieu
* he published *The Spirit of the Laws* in 1748,
* discussed governments throughout history.
* He felt that the best way to protect liberty was to divide the various functions and powers of government into 3 branches: Legislative, Executive, and Judicial.
* discussed governments throughout history.
* He felt that the best way to protect liberty was to divide the various functions and powers of government into 3 branches: Legislative, Executive, and Judicial.
89
New cards
Marie Arouet - Voltaire
* defended the principle of freedom of speech
* used biting wit as a weapon to expose the abuses of his day
* targeted officials and aristocrats, battled inequality, injustice, and superstition
* detested the slave trade, and deplored religious prejudice
* He was later imprisoned and forced into exile.
* used biting wit as a weapon to expose the abuses of his day
* targeted officials and aristocrats, battled inequality, injustice, and superstition
* detested the slave trade, and deplored religious prejudice
* He was later imprisoned and forced into exile.
90
New cards
Denis Diderot
* produced a 28-volume set of books called the Encyclopedia.
* His purpose was "to change the general way of thinking".
* The Encyclopedia:
* denounced slavery
* praised freedom of expression
* urged education for all.
* His purpose was "to change the general way of thinking".
* The Encyclopedia:
* denounced slavery
* praised freedom of expression
* urged education for all.
91
New cards
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
* believed people in their natural state were basically good
* natural innocence was corrupted by the evils of society
* Wrote his ideas in a book titled *The Social Contract*
* wrote about how society placed too many limitations on people's behavior
* believed some controls were necessary but should be minimal
* Believed that the good of the community as a whole should be placed above individual interests.
* natural innocence was corrupted by the evils of society
* Wrote his ideas in a book titled *The Social Contract*
* wrote about how society placed too many limitations on people's behavior
* believed some controls were necessary but should be minimal
* Believed that the good of the community as a whole should be placed above individual interests.
92
New cards
John Locke
* was an English thinker
* thought people were basically reasonable and moral
* believed people had natural rights
* wrote the *Two Treatises of Government*
* he argued that people formed governments to protect their natural rights
* Rejected absolute monarchy.
* Believed people were born with a blank slate
* “tabula rasa”
* thought people were basically reasonable and moral
* believed people had natural rights
* wrote the *Two Treatises of Government*
* he argued that people formed governments to protect their natural rights
* Rejected absolute monarchy.
* Believed people were born with a blank slate
* “tabula rasa”
93
New cards
Cesar Beccana
* believed laws exist to preserve social order not to avenge crimes and that an accused person should receive a speedy trial (no torture).
* criticized common abuses of justice such as torture and the death penalty.
* believed that the degree of punishment should be based on the seriousness of the crime (not their social status).
* Abolish capital punishment
* criticized common abuses of justice such as torture and the death penalty.
* believed that the degree of punishment should be based on the seriousness of the crime (not their social status).
* Abolish capital punishment
94
New cards
Laissez Faire
a policy or attitude of letting things take their own course, without interfering
95
New cards
Know the enlightened absolute monarchs and their ideas and actions
Joseph ll - abolishing serfdom, ending press censorship, and limiting the power of the catholic church
Catherine the Great - separating church from state
Frederick the Great - modernized Prussian bureaucracy and civil service, and pursued religious policies.
Catherine the Great - separating church from state
Frederick the Great - modernized Prussian bureaucracy and civil service, and pursued religious policies.
96
New cards
Louis XVI
King of Pre-Revolutionary France, failed to support his ministries, agreed in 1789 to summon Estates-General although he resisted demands for reform by the National assembly. Later branded a traitor and executed.
97
New cards
Estates-General
The legislative body consisting of representatives of the three estates
98
New cards
Cahiers
notebooks with lists of grievances
99
New cards
Tennis Court Oath
famous oath made by the third estate on a tennis court in pre-revolutionary France
100
New cards
Marie Antoinette
* was the daughter of Maria Theresa of Austria
* was known for being frivolous and extravagant
* told her husband, Louis XIV to resist reform demands by the National Assembly
* was branded a traitor and executed
* was known for being frivolous and extravagant
* told her husband, Louis XIV to resist reform demands by the National Assembly
* was branded a traitor and executed