Meteorology Exam 4 - Mizzou
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
what is weather forecasting?
predicting how the present state of the atmosphere will change over a period of time
what timescale is nowcasting?
present to 6 hours
what timescale is short range?
1 to 3 days
what timescale is medium range?
3 to 5 days
what timescale is long range?
5 to 10 days
what timescale is extended?
up to 90 days
why is weather forecasting important?
tells you how to dress, helps you plan your day, and helps with ag. info
what is folklore forecasting?
stories or anecdotes that predict weather
are all folklore forecasts accurate?
no!
what is climate forecasting?
using averages of weather conditions to predict the weather for a given day
what is one example of a time where weather forecasting won’t work?
if you are seeing record setting weather
what is the trend method of forecasting?
assumes that the speed and direction of weather systems will not change
what is the analogue method of forecasting?
also known as “pattern mapping” where you find a date in the past where the weather looked exactly like it does now and using that
when does the analogue method work the best?
with severe/winter weather events
what is the numerical method of forecasting?
using numerical equations to calculate the future state of certain variables (pressure, temp, winds, humidity, clouds, and precipitation)
what is the equations in the numerical method based on?
newton’s 2nd law of motion
what do the equations within the numerical method consist of?
pressure variations, gravity, friction, how heat and moisture are transferred, and how water vapor changes state
how is the data in the numerical method modeled?
plot or fed into the computer model
what does a good numerical method model depend on?
giving the computer program the right information at the beginning
what does garbage in = garbage out mean?
if you feed the computer inaccurate observations, the forecast won’t be accurate
what are spaghetti model plots?
looks like spaghetti on the plot, each model spits out its on idea of what the atmosphere will be like for a given time frame in the future (all at once)
what is an ensemble forecast?
different iterations of one model adjusted for different scenarios/eqations
what can a forecast 5 - 8 days out tell you?
very little. might give suggestions on upcoming pattern changes but can be very inaccurate
what can a forecast 3 - 5 days out tell you?
confidence increases on the potential storm area but the “when, where, type, and how much” are still very uncertain
what can a forecast 1 - 3 days out tell you?
forecast clears up, storm is now expected but the specifics can still be hard to pinpoint
what can a forecast 12 - 24 hours out tell you?
very detailed information and the forecasts need only minor adjustments
what is the forecasting process?
observations —> analysis —> predictions —> post-processing
what is post-processing?
seeing how well you did or didn’t do and why that happened
what are some ways weather data is collected around the world?
land observatories, ship observatories, weather balloons, and buoys
what is the analysis process of forecasting?
figure out what storm systems are out there and ask yourself questions
what is the predictions part of forecasting?
taking all the data you have collected and sharing it (or not lol)
what is one way you can be conservative with your forecasting?
start small and work your way up (be vague and then detailed closer to the day)
what percentage of accuracy is generally considered pretty good?
70% or higher
what is a station model plot?
a “cluster” of current weather data for one particular weather reporting site
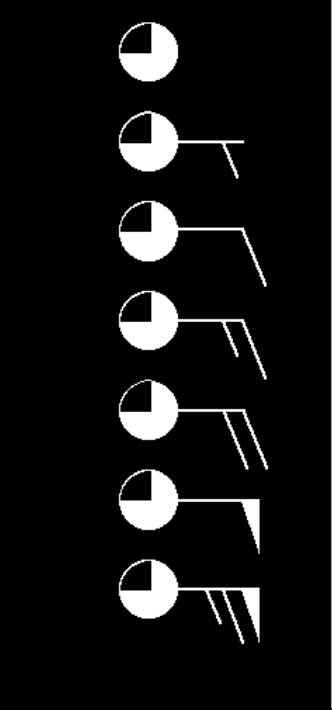
what does the first symbol in this image mean?
calm
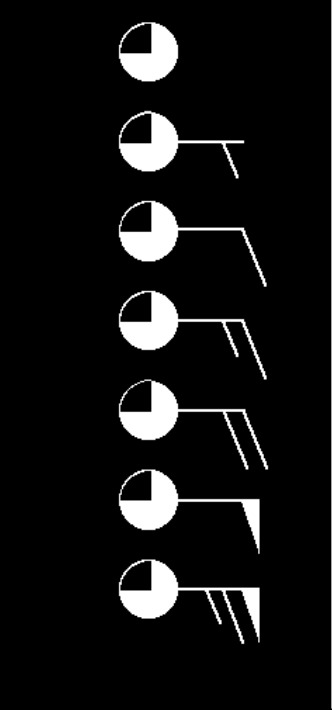
what does the second?
1 - 2 knots
what does the third mean?
10 knots
what does the fourth?
15 knots
for the sake of simplicity, what does a knot equal?
mph
what does “,” mean in weather symbols?
drizzle
what does “.” mean in weather symbols?
rain
what does “*” mean in weather symbols?
snow
what does this symbol mean?
thunderstorm
what does “)(“ mean in weather symbols?
funnel cloud
can you mix and match weather symbols to depict the weather?
yes!
what are some signs of thunderstorms?
thunder and lightening, strong & gusty winds, hail (all sizes), precipitation (rain/snow), and may contain tornados
what are the 3 types of thunderstorms? (from least to most harmful)
ordinary, multicell, supercell
what are ordinary thunderstorms?
the most common type of thunderstorm
what areas do ordinary thunderstorms usually form in?
areas with weak wind shear
what is the timeframe for an ordinary thunderstorm?
usually last under an hour
what are the 3 stages of an ordinary thunderstorm?
growth stage, mature stage, and decaying stage
what is the beginning of the mature stage of a thunderstorm?
the downdraft
what weakens the storm during the decaying stage?
updrafts
what are multicell thunderstorms?
clusters of storms that form in different growth stages in one area
what are the main differences between ordinary and multicell thunderstorms?
winds (ordinary = weak, multicell = strong), and severe weather (multicell can last hours, ordinary usually don’t)
what are squall-line thunderstorms?
an organized line of thunderstorms
what is a bow echo?
a portion of the leading line edge that jumps out ahead of the rest of the line, likely to produce damaging winds
what is a supercell thunderstorm?
a thunderstorm with a rotating updraft
what is another word for a rotating updraft?
a mesocyclone
what is a typical lifetime for a supercell thunderstorm?
2 hours or longer
what does HP and LP mean?
high precipitation, low precipitation
why is a HP supercell thunderstorm more dangerous?
you can’t see what is in them (could be a tornado!)
what classifies severe weather?
1 of 3 (or all): winds (greater than 58 mph), hail (larger than 1”), and a tornado or possible rotation within the thunderstorm
true or false: all supercell thunderstorms are severe.
true!
what is the flanking line (on a thunderstorm)?
updraft/food supply for the mesocyclone (warm, moist air)
what is the rear-flanking downdraft?
rear portion of the mesocyclone’s downdraft (cold, dry air)
what is the inflow of a thunderstorm?
“suck zone” - influx of moisture rich air into a mesocyclone
what does MCS stand for?
mesoscale convection system
what is an MCS? (what is it not what does it stand for)
large grouping of multiple storms that move together and last for hours
what are the 2 types/shapes of MCS’s?
circular and linear
what does a circular MCS do?
covers many states, can produce severe weather, and generally produces heavy rain
what does a linear MCS do?
produces very strong winds and is generally isolated and can cause quick tornados
what is a gust front?
leading edge of cold air from a large, severe thunderstorm (aka “exhaling” air)
what is a microburst?
a very localized column of sinking air, producing damaging, and straight-line winds at the surface
where are microbursts usually located?
strong downdraft areas
what is a derechos?
a widespread and long-lived, violent windstorm that is associated with a fast-moving band of severe t-storms usually taking the form of a bow echo
when and where do derechos usually occur?
the summer, associated with buoyant, warm airmasses
what is lightening?
a discharge of electricity in a mature thunderstorm
what can lightening heat the air to?
over 50,000 F
what is thunder?
heating and expansion of the air creating a shock wave
how can you tell how far away the lightening is?
count the seconds between the flash and thunder (5 seconds = 1 mile)
what does the thunder sound like if the lightening is close-by?
a crack then a loud boom/bang
why does thunder “rumble” when it is far away?
because the sound bounces off various surfaces before reaching the
where are the negative charges found in the cloud?
near the cloud base
where are the positive charges found in the cloud?
up in the cloud and at the ground
what is the “stepped leader”?
initial spark of lightening that leaves the cloud base
what is the return stroke?
the upward flow of current that we see (as lightening)
what is the most common type of lightening?
cloud to ground
what is cloud to cloud lightening?
stays inside the cloud
what is sheet lightening?
lightening that is diffused by the reflection within the cloud
what is heat lightening?
distant lightening the illuminates the sky but is too far away for thunder to be heard, has nothing to do with “summer-time heat”
what is a tornado?
a rapidly rotating column of air whose rotation reached the ground
what are characteristics of a tornado?
diameter of 50-100+ yards, path length of 2-4 miles, lifespan of 5-10 minutes, wind speeds of 80-300 mph, and forward speed of about 30 mph
where was the largest tornado in the world located?
El Reno, OK in 2013
where is the “tornado capital of the world”?
the US
where was the strongest tornado located?
Greenfield, IA in 2024
what was the deadliest tornado in the world and how many people died?
the “tri-state tornado” (MO, IL, and IN) and it killed 695 people in 1925
when was the largest tornado outbreak in a single day?
April 27, 2011 (across 7 states)
what is the average amount of tornados per month?
~ 30
what is the average amount of people killed by tornados annually?
~ 60 (usually from debris)