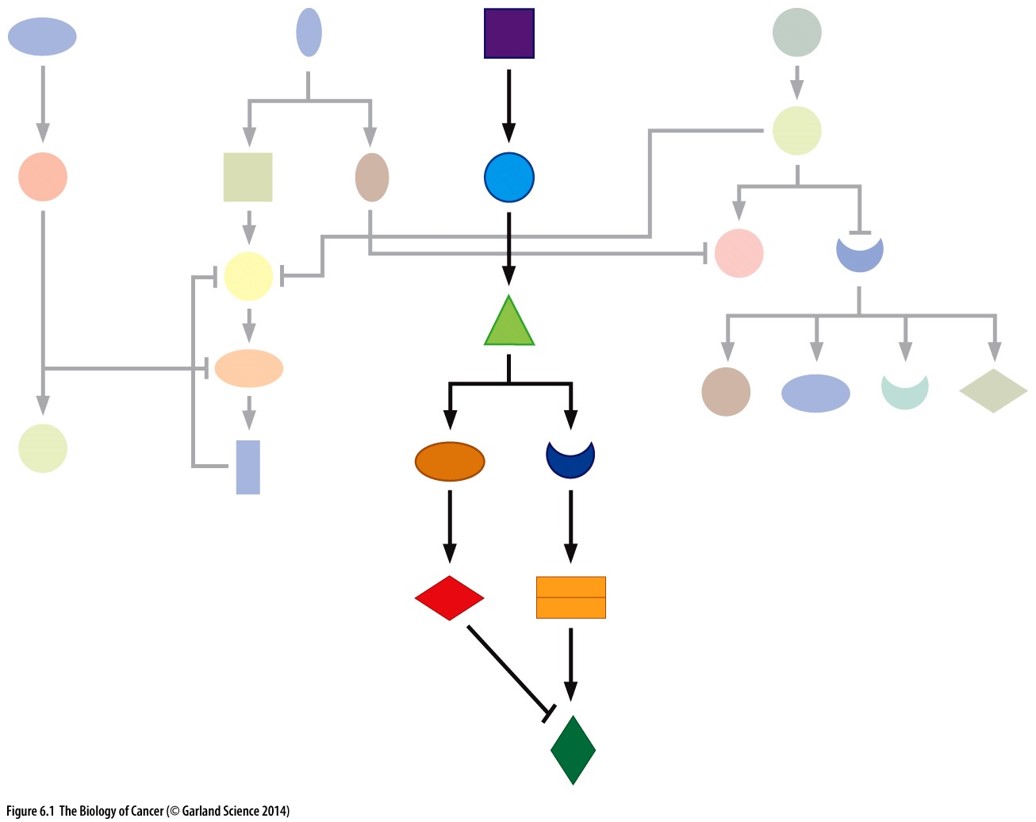
chapter 6
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:55 PM on 3/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
True or False: Cancer cells make relatively large modification to the control machinery inside cells
False
•Cancer cells make relatively __**minor modifications**__ to the control machinery inside cells; tweak existing controls
•Cancer cells make relatively __**minor modifications**__ to the control machinery inside cells; tweak existing controls
2
New cards
True of False: Single cell can express over 20,000 proteins
True
3
New cards
Are most of the proteins expressed in a cell involved for cell signaling?
yes
4
New cards
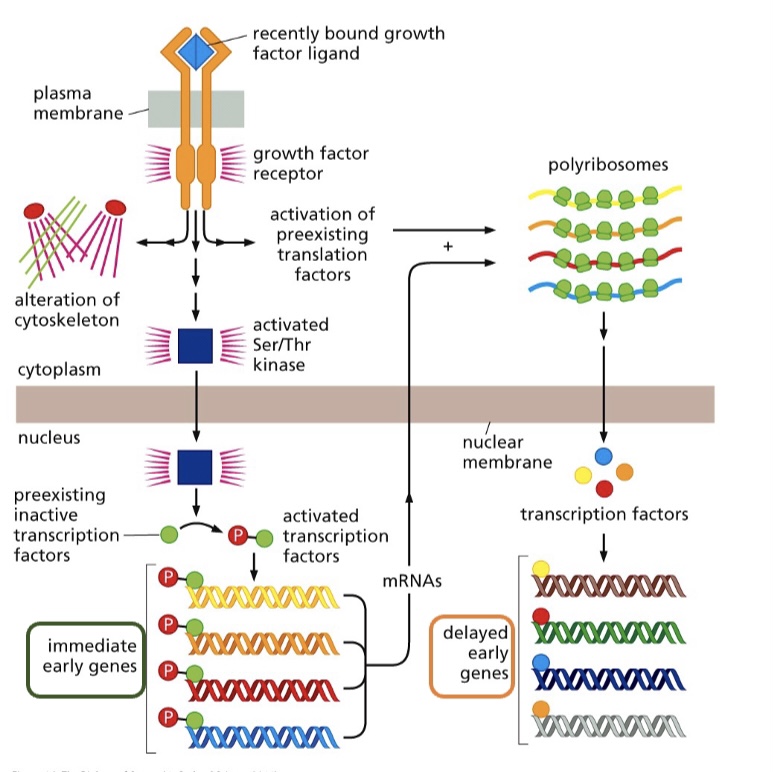
Immediate early genes
the genes that have increased expression have the proteins already in theme
5
New cards
When cells are exposed to growth factors after being deprived for a certain amount of time, they express certain genes right away called ______ ; this does not require new protein synthesis
\
* Immediate late genes
* Delayed early genes
* Protein dependent genes
* Immediate early genes
\
* Immediate late genes
* Delayed early genes
* Protein dependent genes
* Immediate early genes
Immediate early genes
6
New cards
True or False: Immediate early genes are dependent on the synthesis of new proteins
False
7
New cards
If **cycloheximide**, a drug that shuts down protein synthesis is added along with the fresh serum, induction of the immediate early genes proceeds normally – What does this tell us??
the genes that have increased expression, have the proteins in them already
8
New cards
**cycloheximide**
a drug that shuts down protein synthesis
9
New cards
\
What’s the difference between immediate and delayed early genes?
What’s the difference between immediate and delayed early genes?
\-**Immediate early genes** already have the transcription factors/proteins there and do NOT need to be synthesized
\
\-**Delayed early genes** need newly synthesized proteins/transcription factors in order to be activated
\
\-**Delayed early genes** need newly synthesized proteins/transcription factors in order to be activated
10
New cards
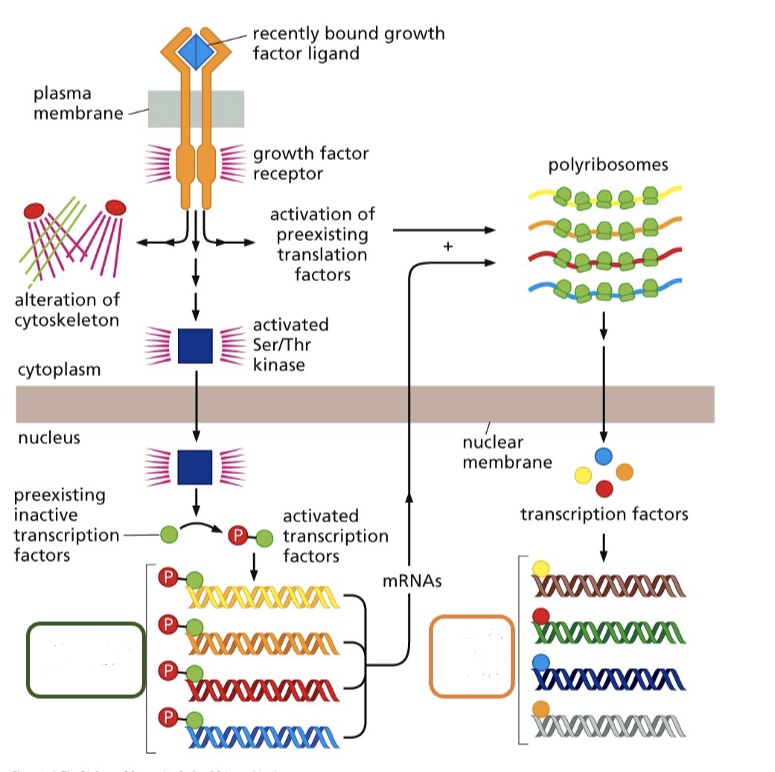
What type of early genes are seen in the orange box?
Delayed or immediate?
Delayed or immediate?
Delayed early genes
* new proteins were synthesized in order to activate or express them
* new proteins were synthesized in order to activate or express them
11
New cards
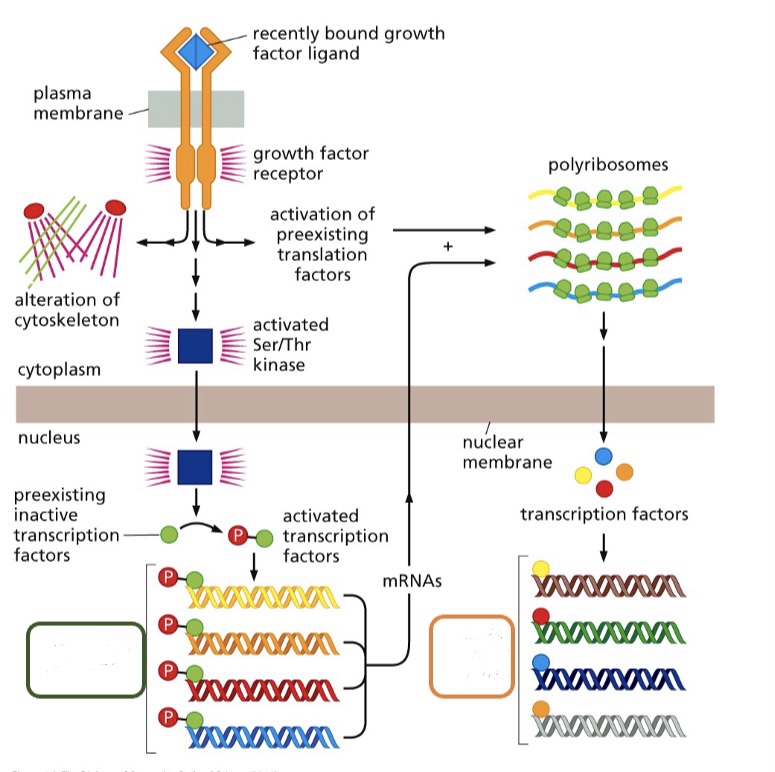
What type of early genes are seen in the green box?
Immediate early genes
* The cell already had preexisting transcription factors that needed to be activated in order to express the genes
* No synthesis of proteins required
\
* The cell already had preexisting transcription factors that needed to be activated in order to express the genes
* No synthesis of proteins required
\
12
New cards
T or F: Growth factors only cause cells to grow
False
Growth Factors can induce a variety of cellular changes
Growth Factors can induce a variety of cellular changes
13
New cards
What are ways growth factors can affect a cell?
**Growth Factors can…**
1. Increase the rate of protein synthesis
2. Induce motility of cells
3. Reorganization of the cytoskeleton
4. Protect cells from activation of apoptotic pathways
1. Increase the rate of protein synthesis
2. Induce motility of cells
3. Reorganization of the cytoskeleton
4. Protect cells from activation of apoptotic pathways
14
New cards
All of the following are potential effects of growth factors **except**
1. inhibition of apoptotic pathways
2. induction of cell motility
3. decrease in the rate of protein synthesis
4. reorganization of the cytoskeleton to promote changes in cell shape
1. inhibition of apoptotic pathways
2. induction of cell motility
3. decrease in the rate of protein synthesis
4. reorganization of the cytoskeleton to promote changes in cell shape
decrease in the rate of protein synthesis
15
New cards
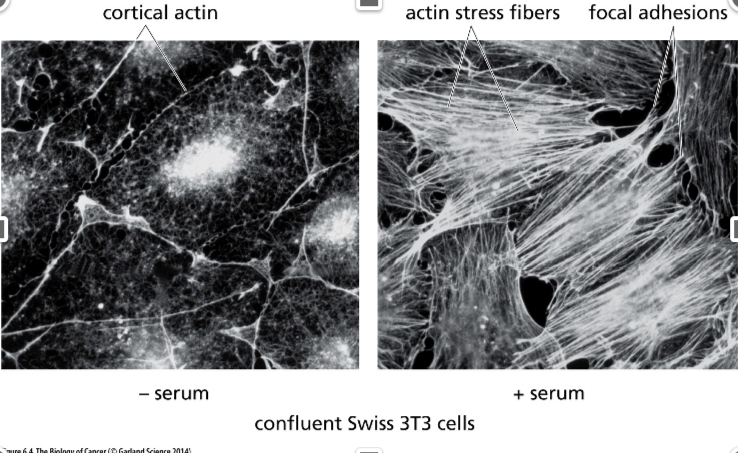
What cellular change is seen ?
Cytoskeletal changes
On the left, there’s no serum and it localized to the surface
On the right is the affected cell, you can see the adhesions, adhering to the substrate is seen
On the left, there’s no serum and it localized to the surface
On the right is the affected cell, you can see the adhesions, adhering to the substrate is seen
16
New cards
What happens after transphosphorylation ?
Following transphosphorylation, the growth factor receptor attracts cytoplasmic proteins to specific phosphotyrosines
17
New cards
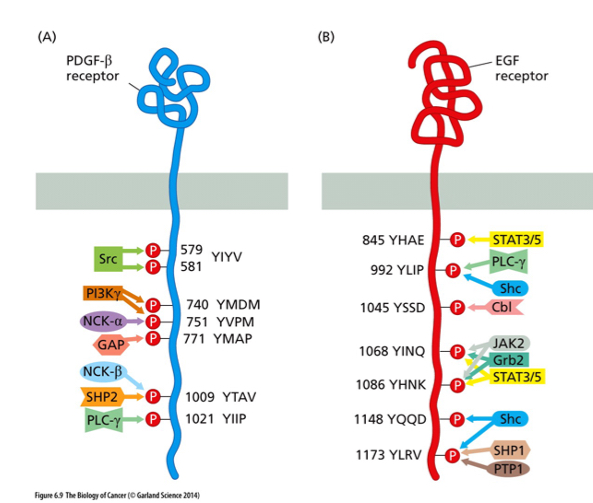
\
Why does each RTK attract its own set of downstream signaling parters?
Why does each RTK attract its own set of downstream signaling parters?
The proteins recognize the sequence of amino acids that are next to the tyrosine
18
New cards
The SH2 domains of proteins bind to_____
1. phosphorylated tyrosine residues
2. acetylated lysine
3. phosphorylated lysine residues
4. phosphoserine
1. phosphorylated tyrosine residues
2. acetylated lysine
3. phosphorylated lysine residues
4. phosphoserine
1. phosphorylated tyrosine residues
19
New cards
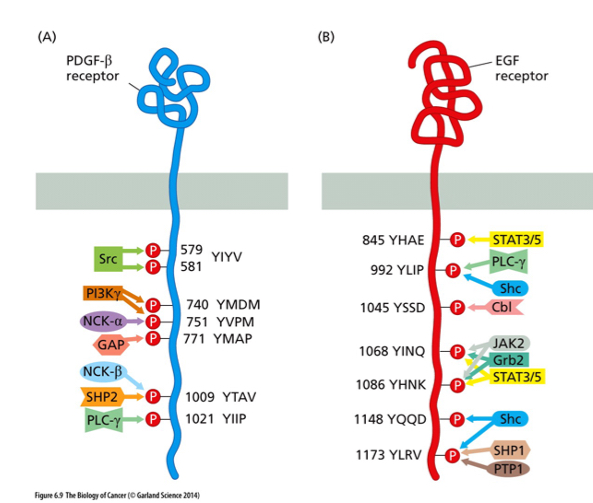
What do the numbers in the picture denote?
what do the letters indicate?
what do the letters indicate?
Numbers denote the position of the tyrosine residues in the polypeptide chain
Letters indicate the amino acids next to tyrosine (Y) that are recognized by the proteins listed via the SH2 domain
Letters indicate the amino acids next to tyrosine (Y) that are recognized by the proteins listed via the SH2 domain
20
New cards
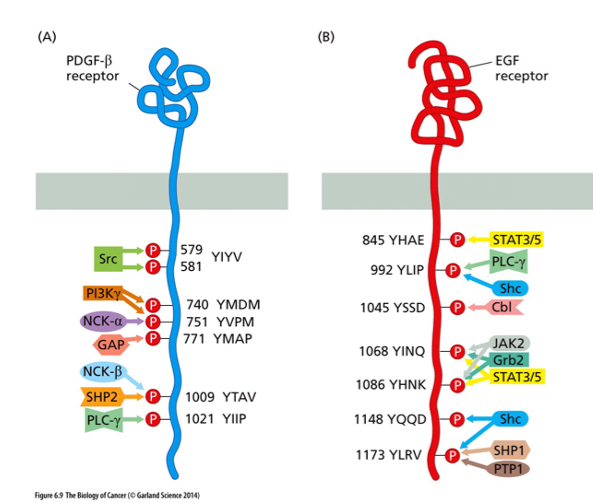
How do proteins recognize the amino acid sequence next to the tyrosine?
The SH2 Domain
Can also recognize phosphorylation tyrosine
Can also recognize phosphorylation tyrosine
21
New cards
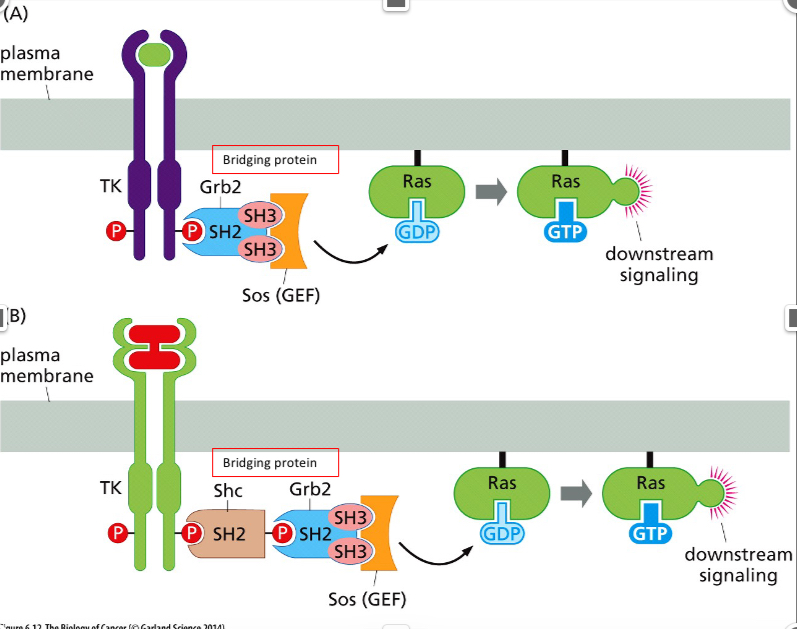
What does SOS do in the pic?
It coverts GDP to GTP which activates Ras
22
New cards
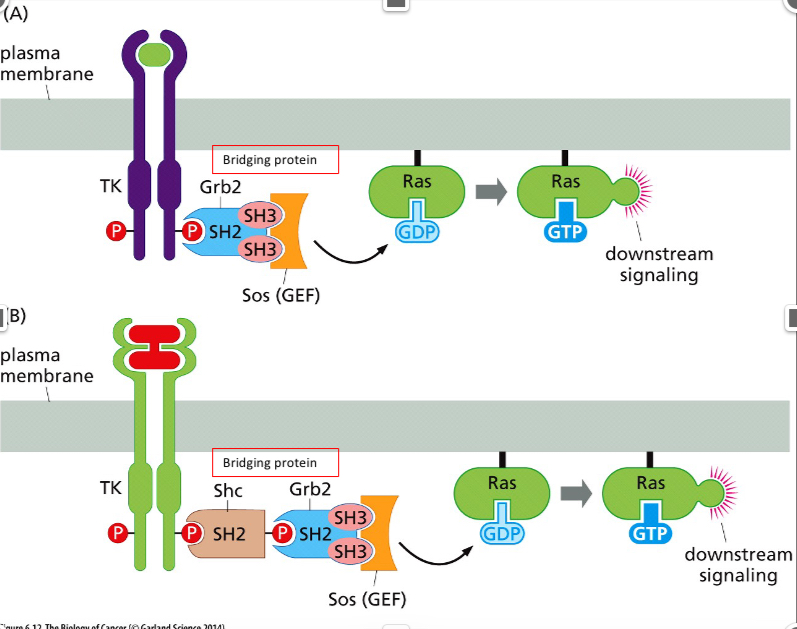
What sequences are seen within the intermolecular links between RTK and Ras?
Receptor→ Grb2 → Sos→Ras Or
Receptor →Shc → Grb2 → Sos → Ras
Receptor →Shc → Grb2 → Sos → Ras
23
New cards
MAPK
mitogen-activated protein kinase
24
New cards
Erk
extracellular signal-related kinase
25
New cards
Ets transcription factor
**Ets transcription factor** – stimulates expression of important growth-regulating genes, i.e. Fos, Cyclin D1, p21
26
New cards
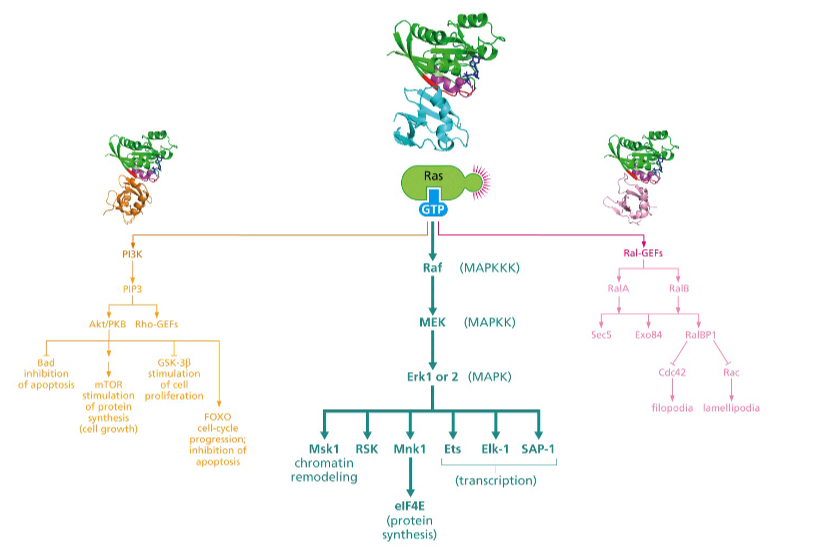
What is the middle pathway?
The Ras → Raf → MAP kinase pathway
27
New cards
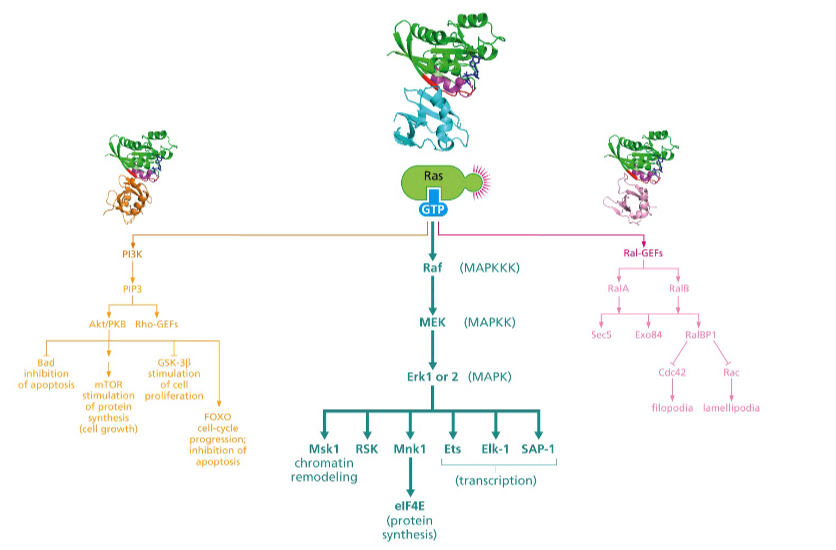
What does the Ras → Raf → MAP kinase pathway do?
\
\
\*\*\*__***Raf pathway is responsible for most of the transforming powers of Ras oncoproteins******__
**This pathway induces the gene expression of Fos and Jun transcription factors** – associate with one another to form AP-1 – AP-1 acts as a transcription factor and is often hyperactivated in cancer cells
this pathway **also confers anchorage independence and loss of contact inhibition**;
also **contributes to changes in cell shape associated with transformation by the** ***ras*** **oncogene**
**This pathway induces the gene expression of Fos and Jun transcription factors** – associate with one another to form AP-1 – AP-1 acts as a transcription factor and is often hyperactivated in cancer cells
this pathway **also confers anchorage independence and loss of contact inhibition**;
also **contributes to changes in cell shape associated with transformation by the** ***ras*** **oncogene**
28
New cards
What happens when raf protein kinase is introduced into cells in a mutant oncogenes form?
\*\*When Raf protein kinase is introduced into cells in a mutant, oncogenic form, it can **evoke most of the transformation phenotypes induced by the ras oncoprotein**; Raf pathway is responsible for most of the transforming powers of Ras oncoproteins.
29
New cards
What’s erk 1/2
transcription factors because they can translocate into the nucleus
30
New cards
Are ras proteins always anchored to membrane?
Yes
31
New cards
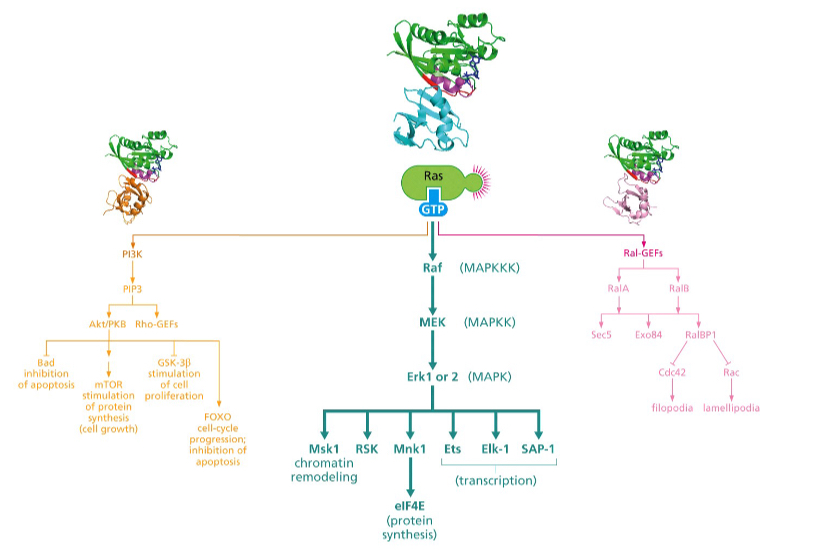
Which pathway is involved mostly in suppression of apoptosis?
\
\
The PI3 kinase pathway
First one
First one
32
New cards
PTEN
****PTEN** = phosphatase that removes the phosphate that was added by PI3K from PIP3 to deactivate this pathway
33
New cards
True or false: PI3K attached phosphates to proteins
False
\*\*PI3K attached phosphates to a lipid not a protein
\*\*PI3K attached phosphates to a lipid not a protein
34
New cards
What happens when activated Ras bonds to PI3K
\*\*When activated Ras binds to PI3K it causes it to be closely associated with the plasma membrane
35
New cards
What happens when AKT/PKB is activated
Akt/PKB activation also influences **angiogenesis** (The production of new blood vessels) – this is poorly understood
36
New cards
What does the Ral pathway control?
The cytoskeleton
37
New cards
Which pathway controls the cytoskeleton?
Ral pathway
Third one
Third one
38
New cards
Filopodia
**Filopodia** – small fingerlike extensions that the cell uses to explore its environment and form adhesions with the extracellular matrix
39
New cards
Lamellipodia
**Lamellipodia** – broad ruffles extending from the plasma membrane found on the leading edges of motile cells
40
New cards
What do sec5 and exo84 contribute to in the Ral pathway?
Sec5 and Exo84 contribute to **Ras-mediated anchorage independent growth**
41
New cards
What type of proteins are cdc42 and rac
Cdc42 and Rac are **Rho proteins**; GTPases (GTP-GDP bound)
42
New cards
What are rho proteins involved in?
Rho proteins are involved in **reconfiguring the structure of the cytoskeleton** and the attachment the cell makes with its physical surroundings; __***control cell shape and motility; in cancer cells -- invasiveness***__
43
New cards
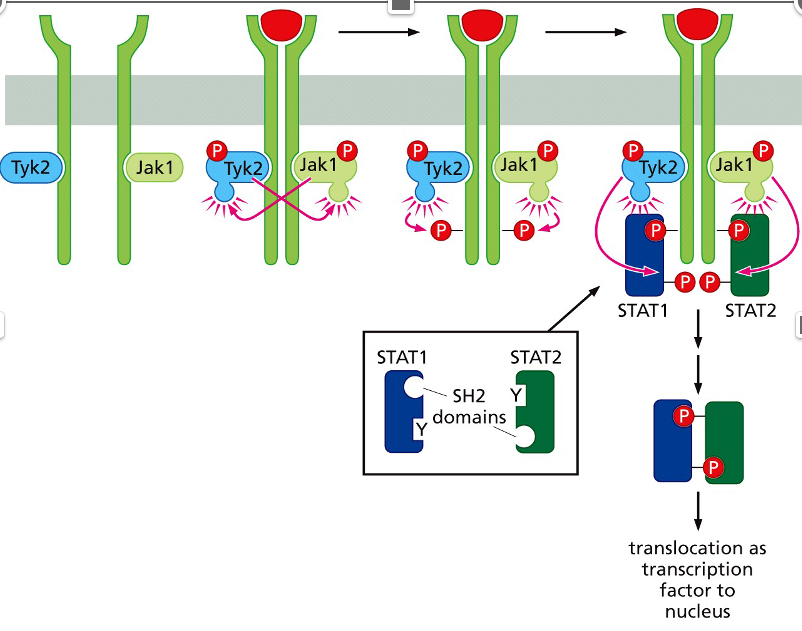
What pathway is shown?
Jak-STAT pathway
44
New cards
Cytokines
**Cytokines =** growth factors that stimulate components of the hematopoietic system
45
New cards
What do STATs do
\*\*STATs activate target genes that are important for cell proliferation and cell survival; *myc,* Cyclin D1 and D3
46
New cards
What’s STAT 3 know for?
STAT3 known to be constitutively active in a number of human cancers including melanomas and breast cancers
47
New cards
Which mutant proteins can transform normal cells into cancer cells?
Mutant STAT 3
Mutant STAT 2
Mutant STAT 1
Jak 1
Tyk 2
Mutant STAT 3
Mutant STAT 2
Mutant STAT 1
Jak 1
Tyk 2
**mutant STAT3** protein can transform normal cells into cancer cells
48
New cards
\
Ras is active when it is bound to _______
GDP
GTP
ATP
ADP
Ras is active when it is bound to _______
GDP
GTP
ATP
ADP
GTP
49
New cards
What is the role of mTOR in the PI3K pathway?
Stimulate protein synthesis (cell growth)
50
New cards
All of the following are molecules that bind to receptors that activate Jak-STAT signaling pathways except
* EGF
* interleukins
* interferon
* EGF
* interleukins
* interferon
egf
51
New cards
Which signaling pathway is most involved in inhibiting apoptosis?
PI3K
Ral-GEFs
Raf
Jak/STAT
PI3K
Ral-GEFs
Raf
Jak/STAT
PI3K
52
New cards
In the ras-raf pathway, Ets, Elk-1, and SAP-1 represent
* transcription factors that are inhibited by Erk1/2
* transcription factors that are activated by Erk1/2
* translation initiation factors that are activated by Erk1/2
* kinases that phosphorylate other proteins in the cell
* transcription factors that are inhibited by Erk1/2
* transcription factors that are activated by Erk1/2
* translation initiation factors that are activated by Erk1/2
* kinases that phosphorylate other proteins in the cell
* transcription factors that are activated by Erk1/2
53
New cards
The expression of delayed early genes
* does not require the binding of transcription factors
* does not require new protein synthesis
* is dependent on the translation of new transcription factors
* is dependent on the presence of transcription factors being present inside the cell before it is exposed to growth factors
* does not require the binding of transcription factors
* does not require new protein synthesis
* is dependent on the translation of new transcription factors
* is dependent on the presence of transcription factors being present inside the cell before it is exposed to growth factors
* is dependent on the translation of new transcription factors