KINESIOL 2F03: Quiz 1 Content
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
What is isometric growth?
- the growth of an organ within the organism grows at the SAME RATE as other parts of body: CONSTANT relative size
- adult proportions are similar to those of juvenile
- SIZE OF ORGAN INC. but EXTERNAL FEATURES REMAIN SAME
e.g. fish, grasshoppers, cockroaches
- adult proportions are similar to those of juvenile
- SIZE OF ORGAN INC. but EXTERNAL FEATURES REMAIN SAME
e.g. fish, grasshoppers, cockroaches
2
New cards
What is allometric growth?
- differential/unequal growth of body parts in relation to the whole organism
- diff. organs grow at diff. rates from e/o and overall growth
- involves change in size + external SHAPE of organism
- diff. organs grow at diff. rates from e/o and overall growth
- involves change in size + external SHAPE of organism
3
New cards
What are the relative/absolute sizes of the HEAD compared to the rest of the body for a 2 month fetus, a child at birth, and an adult?
2 month fetus: 50% of length
birth: 45% (0.8kg/1.8lb)
adult: 12.5% (6kg/13.2lb)
birth: 45% (0.8kg/1.8lb)
adult: 12.5% (6kg/13.2lb)
4
New cards
What are the relative/absolute sizes of the LEGS compared to the rest of the body for a 2 month fetus, a child at birth, and an adult?
2 month fetus: 15% of length
birth: 37% (15% weight)
adult: 50% (30% weight)
birth: 37% (15% weight)
adult: 50% (30% weight)
5
New cards
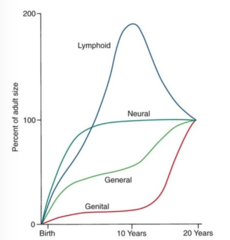
What is Scammon's curve? What are the IV and DV?
- made 4 basic curves to characterize body growth
- used tissues + organ weights at each age
IV: age (years)
DV: size attained as % of total postnatal growth
- used tissues + organ weights at each age
IV: age (years)
DV: size attained as % of total postnatal growth
6
New cards
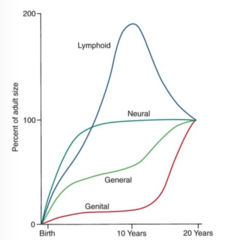
What were the 4 basic curves in Scammon's curve? Describe how each curve appears on the graph.
1. general curve (physical dimensions)
2. neural
3. genital
4. lymphoid (WBC, bone marrow)
2. neural
3. genital
4. lymphoid (WBC, bone marrow)
7
New cards
What are the 4 phases of growth (in regards to Scammon's curve)?
1. RAPID gain in infancy/early childhood
2. STEADY gain during mid-childhood
3. RAPID gain during adolescent spurt
4. SLOW INC. until a stop in growth = adult body (but not stop in mass)
2. STEADY gain during mid-childhood
3. RAPID gain during adolescent spurt
4. SLOW INC. until a stop in growth = adult body (but not stop in mass)
8
New cards
What are 5 examples of growth vs. maturation vs. development?
GROWTH:
1. physique
2. size
3. proportions
4. bodily composition
5. systemic
MATURATION:
1. skeletal
2. sexual
3. neuromuscular
4. dental
5. somatic
DEVELOPMENT:
1. emotional
2. social
3. cognitive
4. moral
5. motor
ALL TIES INTO SELF-ESTEEM + COMPETENCE
1. physique
2. size
3. proportions
4. bodily composition
5. systemic
MATURATION:
1. skeletal
2. sexual
3. neuromuscular
4. dental
5. somatic
DEVELOPMENT:
1. emotional
2. social
3. cognitive
4. moral
5. motor
ALL TIES INTO SELF-ESTEEM + COMPETENCE
9
New cards
Why do you think chronological age does not always reflect biological processes?
CHRONOLOGICAL: operates in a time framework (age)
BIOLOGICAL: not so linear or generalizable, diff. people w the same age can have diff. biological maturities
- postnatal growth: divided into 3/4 age groups instead
BIOLOGICAL: not so linear or generalizable, diff. people w the same age can have diff. biological maturities
- postnatal growth: divided into 3/4 age groups instead
10
New cards
What is the difference between actual and adjusted age (chronological age)? Give an example.
ACTUAL: according to days/months AFTER birth
ADJUSTED: according to developmental age based on DUE date
e.g. for PREMATURE birth: normally, baby should be born after 34 weeks, but a baby is born at 29 weeks. what are its actual and adjusted ages after 6 months?
ACTUAL: 6 months
ADJUSTED: 1 month
ADJUSTED: according to developmental age based on DUE date
e.g. for PREMATURE birth: normally, baby should be born after 34 weeks, but a baby is born at 29 weeks. what are its actual and adjusted ages after 6 months?
ACTUAL: 6 months
ADJUSTED: 1 month
11
New cards
Why is chronological age used more widely? What are the 3 types of participant variations? Why are they important?
- easier/more accurate data for researchers to anchor to while conducting studies = helps define children's age group
participant variation
WITHIN: compare GMD of child over the years
BETWEEN: compare GMD of child by age/gender w/ other children
BETWEEN POPULATION: compare GMD between population
IMPORTANCE: use info of 'normal' patterns to research and understand why variations occur, their origins + biological significance
= modify conditions and OPTIMIZE outcome of potential = reach full potential
participant variation
WITHIN: compare GMD of child over the years
BETWEEN: compare GMD of child by age/gender w/ other children
BETWEEN POPULATION: compare GMD between population
IMPORTANCE: use info of 'normal' patterns to research and understand why variations occur, their origins + biological significance
= modify conditions and OPTIMIZE outcome of potential = reach full potential
12
New cards
What constitutes as infancy and childhood?
INFANCY:
- perinatal- 1st week
- neonatal- 1st month
- postnatal- rest of 1st year
CHILDHOOD:
- end of infancy to start of adolescence
- early childhood- preschool
- middle childhood- elementary to 5/6th grade
- perinatal- 1st week
- neonatal- 1st month
- postnatal- rest of 1st year
CHILDHOOD:
- end of infancy to start of adolescence
- early childhood- preschool
- middle childhood- elementary to 5/6th grade
13
New cards
What is adolescence? (normal variation for girls vs. boys)
- ages 10-18
NORMAL variation
girls: ages 8-19
boys: ages 10-22
NORMAL variation
girls: ages 8-19
boys: ages 10-22
14
New cards
By using info on participant variation, how can you predict the link between growth/maturity and adult health? (3)
1. LOW birthweight infant --> adult hypertension, diabetes
2. early sexual maturation --> assoc. w cancer in adulthood
3. overweight adolesc. --> overweight adults + health issues
2. early sexual maturation --> assoc. w cancer in adulthood
3. overweight adolesc. --> overweight adults + health issues
15
New cards
Other than comparing growth/maturation (e.g. height, weight, physical performance) to another population/the norm or track growth over time/predict future growth, what can you use GMD info for (using chronological age)?
SPORT PARTICIPATION (done by age)
- GMD factors like height/weight/physique impact performance
- GMD factors like height/weight/physique impact performance
16
New cards
What impacts the peak performance years in sport for individuals? (4)
- endurance
- strength
- flexibility
- power
- strength
- flexibility
- power
17
New cards
What are 2 ways to measure in research and studies? Describe them.
1. CROSS-SECTIONAL
- measures participants at a GIVEN AGE
- each one rep. ONCE (no growth in performance over time) = look into an AGE GROUP
--> use one cohort, take their data, don't go back to collect data on progress/growth
2. LONGITUDINAL
- REPEATED OBSERVATIONS over period of time = shows growth/change/development over time
- measures participants at a GIVEN AGE
- each one rep. ONCE (no growth in performance over time) = look into an AGE GROUP
--> use one cohort, take their data, don't go back to collect data on progress/growth
2. LONGITUDINAL
- REPEATED OBSERVATIONS over period of time = shows growth/change/development over time
18
New cards
What does 'growth' refer to? What are the 3 processes?
- changes in SIZE, outcome of 3 processes:
1. hyperplasia: inc. in cell NUMBER (e.g # of neurons mid-pregn. or # muscle fibres postnatally)
2. hypertrophy: inc. in cell SIZE (inc. in functional units within cell protein + substrate)
3. accretion: inc. in INTRACELLULAR SUBSTANCES (e.g. adipose tissue. material binding/aggregating cells in networks)
1. hyperplasia: inc. in cell NUMBER (e.g # of neurons mid-pregn. or # muscle fibres postnatally)
2. hypertrophy: inc. in cell SIZE (inc. in functional units within cell protein + substrate)
3. accretion: inc. in INTRACELLULAR SUBSTANCES (e.g. adipose tissue. material binding/aggregating cells in networks)
19
New cards
Which of the 3 processes of growth are intracellular? Intercellular?
INTRA: hyperplasia/trophy
INTER: accretion
INTER: accretion
20
New cards
What are the 2 diff. types of hypertrophy?
1. neuron hypertrophy: 2nd half of pregn. into postnatal
2. muscle hypertrophy: during early growth + resistance training during post puberty
2. muscle hypertrophy: during early growth + resistance training during post puberty
21
New cards
Do cellular hyperplasia and hypertrophy in muscle tissue grow in the same pattern?
NO
hyperplasia: very constant (not moving) growth after initial inc.
hypertrophy: slow, gradual increase into adolescence
hyperplasia: very constant (not moving) growth after initial inc.
hypertrophy: slow, gradual increase into adolescence
22
New cards
What is the difference between growth, maturation and maturity?
Growth: size + number, usually intercellular/intracellular processes (hypertrophy/plasia, accretion)
Maturation: a process that cells/tissues/organs go through. refers to TIMING + TEMPO of progress
Maturity: a state that varies acc. to the system considered (e.g. skeletal maturity = ossified skeleton, BUT sexual maturity = fully functional reproductive system)
Maturation: a process that cells/tissues/organs go through. refers to TIMING + TEMPO of progress
Maturity: a state that varies acc. to the system considered (e.g. skeletal maturity = ossified skeleton, BUT sexual maturity = fully functional reproductive system)
23
New cards
What does the maturation of the neuroendocrine systems have an effect on?
- skeletal, sexual, somatic maturation during later childhood/early adolescence
24
New cards
What are the 2 main factors of maturation?
Timing: WHEN it happens
Tempo: RATE at which it happens
Tempo: RATE at which it happens
25
New cards
What is 1 common underlying process between growth and maturation?
- underlying processes are cellular
26
New cards
What are the 2 concepts of development?
1. BIOLOGICAL:
- differentiation + specialization of stem cells (into cell types, tissues, organs, functional units) --> prenatal (MAIN), but continues postnatally
2. BEHAVIOURAL:
- acquisition/REFINEMENT of behaviors accepted by society
- differentiation + specialization of stem cells (into cell types, tissues, organs, functional units) --> prenatal (MAIN), but continues postnatally
2. BEHAVIOURAL:
- acquisition/REFINEMENT of behaviors accepted by society
27
New cards
What factors impact motor competence and physical performance in development?
- learning + practice = REFINEMENT
- development of basic movement patterns depend on: RATE of maturation, growth, maturity status
- environment + opportunity
- development of basic movement patterns depend on: RATE of maturation, growth, maturity status
- environment + opportunity
28
New cards
What did Karl Newell suggest?
- movements arise from the interaction 3 things:
1. the individual (constraints) (structural + functional)
2. the environment (constraints) they're in
3. the task (constraints) in hand
= AFFECTS motor development
1. the individual (constraints) (structural + functional)
2. the environment (constraints) they're in
3. the task (constraints) in hand
= AFFECTS motor development
29
New cards
What is the difference between physical activity, training for sport, and physical fitness?
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: any form of movement that increases energy expenditure
TRAINING FOR SPORT: systemic, specialized/organized practice for a certain sport/discipline
PHYSICAL FITNESS: and ADAPTIVE state (varies w/ growth, maturity, function) exercise with the goal of improving health, much easier to measure (aerobic/anaerobic, endurance, strength)
- planned, structured, repetitive (e.g. going to the gym w/ a motive)
TRAINING FOR SPORT: systemic, specialized/organized practice for a certain sport/discipline
PHYSICAL FITNESS: and ADAPTIVE state (varies w/ growth, maturity, function) exercise with the goal of improving health, much easier to measure (aerobic/anaerobic, endurance, strength)
- planned, structured, repetitive (e.g. going to the gym w/ a motive)