26 - Health Insurance
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the greatest benefit of health insurance?
Financial protection for catastrophic health events
What is a deductible?
The amount you pay for covered health insurance before the insurance starts paying.
What is Coinsurance?
The percentage of costs of a covered health insurance service someone pays after a deductible is met
What is Copay?
A fixed amount a person pays for a covered health insurance service, typically collected at time of service
What is premium?
A fixed amount a person pays for health insurance coverage every month.
What is out of pocket maximum?
The maximum amount a person must pay for covered services in a plan year
Calculate the out of pocket costs:
Procedure cost: $10,000
Plan: $2,000 deductible, 20% coinsurance, $50 copay, $6,500 OOP max
Pay deductible: $2,000
Remaining amount: $10,000 – $2,000 = $8,000
Pay 20% coinsurance on remaining: 0.20 × $8,000 = $1,600
Add copay: $50
Total Out-of-Pocket Cost = $2,000 + $1,600 + $50 = $3,650
What were the main goals of the ACA?
Lower the number of uninsured Americans
Give people options for healthcare coverage
Prior to ACA:
People could be denied insurance for pre-existing conditions
Dependents were only covered under parents’ insurance if:
under 18, or
under 24 and in secondary school
(ACA changed this to under 26 regardless of circumstance)
Women were charged higher premiums than men (“gender gap”) due to pregnancy-related cost assumptions
What are Managed Care Organizations (MCOs)?
Managed Care Organizations:
The most dominant healthcare delivery system in the U.S.
Seek to achieve efficiency by integrating basic functions of healthcare delivery
Determine the price at which the services are purchased, and, in turn, how much providers get paid
Offers select plan(s) to employees
Negotiates rates and contracts with providers
Discount rates to be “in network” to MCO patients
2 major categories: HMO and PPO
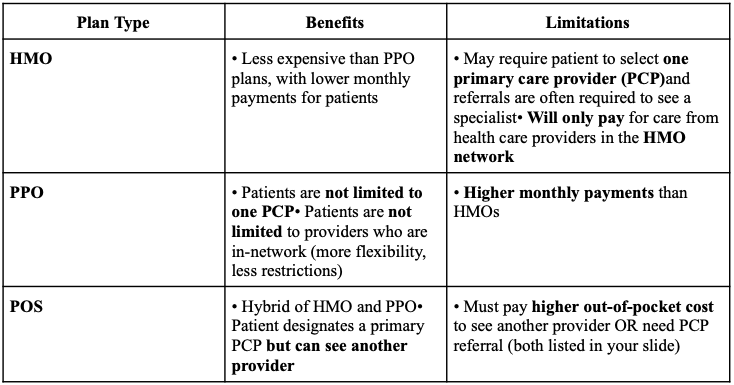
What is an HMO?
Health Maintenance Organization: A network of providers who agree to offer care at set rates.
Usually requires choosing one primary care provider (PCP)
Referrals often needed to see specialists
Only covers care within the HMO network
Lower monthly premiums than PPOs
What is a PPO?
Preferred Provider Organization: A network of providers offering discounted rates.
No PCP requirement
Specialists can be seen without a referral
Covers in- and out-of-network (higher cost out-of-network)
Higher monthly premiums than HMOs (more flexibility)
What is a Point-of-Service (POS)?
A hybrid of HMO and PPO, where a patient designates a primary PCP but can see another provider for a higher out-of-pocket cost or with a referral from their primary PCP.
What are some benefits and limitations of HMOs, PPOs, and POS?
What is HDHP?
HDHP: High Deductible Health Plan
Low monthly premium, very high deductible (must pay full deductible before insurance pays)
Minimum deductible: $1,400 individual / $2,800 family
Total yearly out-of-pocket max: $6,900 individual / $13,800 family
Good for people who rarely use healthcare and can afford higher out-of-pocket costs
Often paired with HSA, HRA, or FSA
What is HSA?
A health savings account that is employee-owned and used to pay for qualified medical expenses.
Contributions are pretax and unused money rolls over.
What is HRA?
A health reimbursement arrangement that is employer-owned and used to help employees pay for medical expenses not covered by the health plan.
What is FSA?
A flexible spending account used by employees to pay for qualified expenses.
Contributions are pretax.
What is catastrophic health insurance?
An individual plan option available only to adults under 30 or with hardship exemption.
Very low premium, VERY high deductible.
Free preventive care services - 3 primary care visits per year are paid for
What is a benefit of catastrophic health insurance?
Good for young adults who do not regularly need healthcare services or monthly prescriptions and can afford the higher deductible
What are some reasons for the increase in healthcare costs?
High prices of healthcare services, chronic disease burden, administrative costs, and increasing cost of technology and medications.
How are the majority of Americans covered for healthcare?
Through private insurance, most of that is employment based